Physicochemical Characteristics, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Stingless Bee Honey from Malaysia: Heterotrigona itama, Lophotrigona canifrons, and Tetrigona binghami
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stingless Bee Honey (SBH) Samples
2.2. Chemical Reagents
2.3. Analytical Methods to Determine Physicochemical Characteristics of SBH
2.3.1. Sugar Content
2.3.2. Moisture Content, Color Analysis, and Acidity
2.3.3. Electrical Conductivity (EC)
2.3.4. pH
2.3.5. Diastase Activity
2.3.6. Content of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF)
2.4. Analytical Methods to Determine Antioxidant Activity of Stingless Bee Honey
2.4.1. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.4.2. 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Assay
2.4.3. 2,2′-Azino-Bis (3-Ethylbenzothiazoline-6-Sulfonic Acid) (ABTS) Assay
2.4.4. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
2.5. Analytical Methods to Determine Antibacterial Activity of Stingless Bee Honey
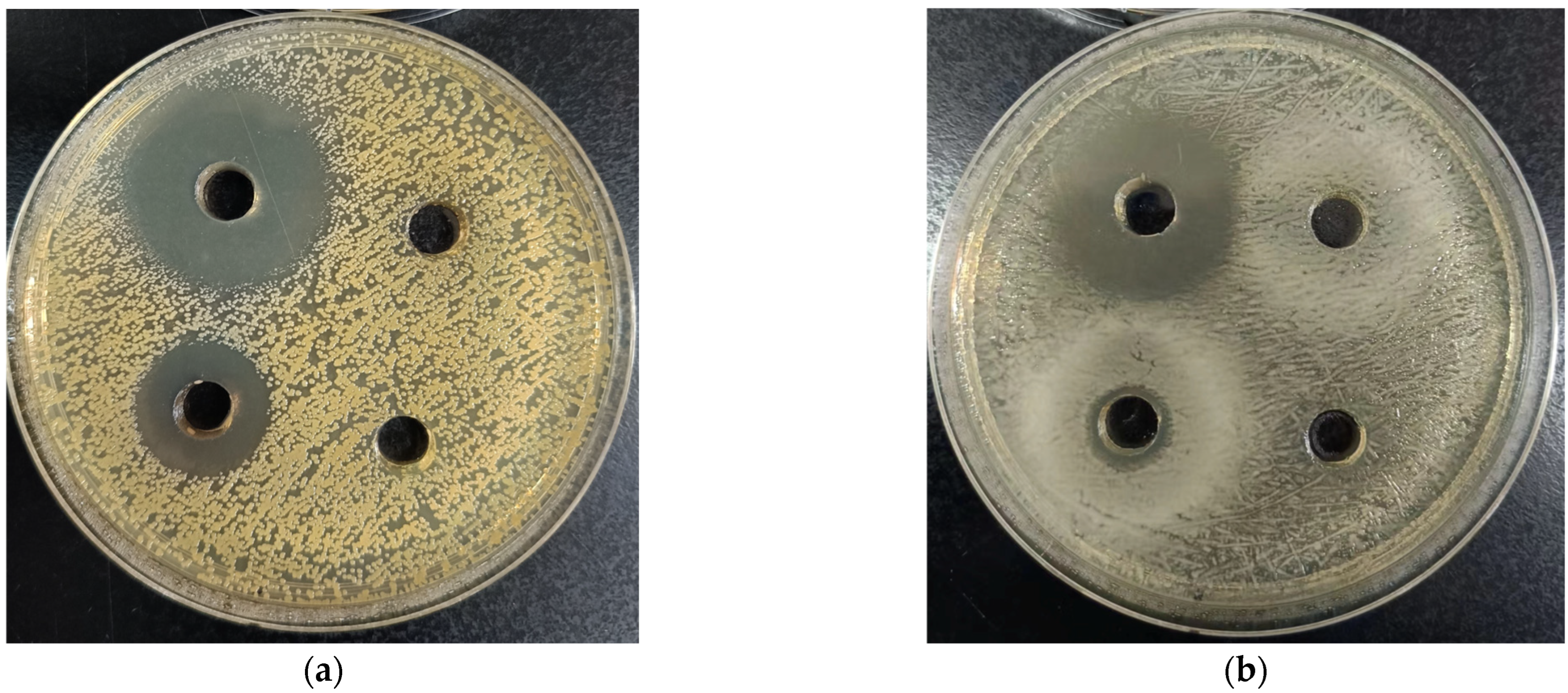
2.5.1. Agar Diffusion Assay
2.5.2. Broth Microdilution Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of SBH
Correlation Coefficients Between Physicochemical Parameters
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
Correlation Coefficients Between Antioxidant Assays
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity
3.3.1. Agar Diffusion Assay
3.3.2. Broth Microdilution Assay
3.3.3. Correlation Coefficients Between Antimicrobial Activities and Antioxidant Activities
3.3.4. Correlation Between Bioactivities and Physicochemical Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basari, N.; Ramli, S.N.; Khairi, N. Food Reward and Distance Influence the Foraging Pattern of Stingless Bee, Heterotrigona itama. Insects 2018, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, L.P.W.; Jawan, R.; Faik, A.A.M.; Gansau, J.A. A Review of Stingless Bees’ Bioactivity in Different Parts of the World. J. Med. Life 2023, 16, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hatamleh, M.A.; Boer, J.C.; Wilson, K.L.; Plebanski, M.; Mohamud, R.; Mustafa, M.Z. Antioxidant-Based Medicinal Properties of Stingless Bee Products: Recent Progress and Future Directions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esa, N.E.F.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Abd Razak, S.I.; Ismail, N.I.; Jusoh, N.; Zawawi, N.A.; Jamaludin, M.I.; Sagadevan, S.; Nayan, N.H.M. A Review on Recent Progress of Stingless Bee Honey and Its Hydrogel-Based Compound for Wound Care Management. Molecules 2022, 27, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chettri, U.; Kumari, S. A Review on Prebiotic Importance of Stingless Bee Honey and Its Ethnomedicinal and Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2020, 63, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, E.C.A.; Menezes, C.; Flach, A. Stingless Bee Honey (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini): A Review of Quality Control, Chemical Profile, and Biological Potential. Apidologie 2021, 52, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.; Zhang, J.; Hungerford, N.L.; Yates, H.S.A.; Webber, D.C.; Farrell, M.; Tinggi, U.; Bhandari, B.; Fletcher, M.T. Unique Physicochemical Properties and Rare Reducing Sugar Trehalulose Mandate New International Regulation for Stingless Bee Honey. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkhairi Amin, F.A.; Sabri, S.; Mohammad, S.M.; Ismail, M.; Chan, K.W.; Ismail, N.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Zawawi, N. Therapeutic Properties of Stingless Bee Honey in Comparison with European Bee Honey. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 2018, 6179596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello dos Santos, M.; Khan, N.; Lim, L.Y.; Locher, C. Antioxidant Activity, Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Stingless Bee Honey from Australia. Foods 2024, 13, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, S.; Selamat, J.; Sanny, M.; Bahari, S.A.R.; Jambari, N.N.; Khatib, A. A Comparative Characterization of Physicochemical and Antioxidants Properties of Processed Heterotrigona itama Honey from Different Origins and Classification by Chemometrics Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenório, E.G.; de Jesus, N.R.; Nascimento, A.R.; Teles, A.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Honey of Stingless Bees, Tiúba (Melipona fasciculata) and Jandaira (Melipona subnitida) Compared to the Strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1702. [Google Scholar]
- Cabezas-Mera, F.; Cedeño-Pinargote, A.C.; Tejera, E.; Álvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Machado, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Stingless Bee Honey (Tribe: Meliponini) on Clinical and Foodborne Pathogens: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Front. 2024, 5, 964–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaldivar-Ortega, A.K.; de Cenobio-Galindo, A.J.; Morfin, N.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Esturau-Escofet, N.; Garduño-García, A.; Angeles-Hernandez, J.C. The Physicochemical Parameters, Phenolic Content, and Antioxidant Activity of Honey from Stingless Bees and Apis mellifera: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mduda, C.A.; Muruke, M.H.; Joseph, C.O.; Hussein, J.M. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Stingless Bee (Meliponula spp.) Honey from the Northern Highlands of Tanzania, in Comparison with Apis mellifera Honey. Food Humanit. 2024, 2, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, O.; Muleta, D.; Desalegn, A. In Vitro Antimicrobial Properties of Apis mellifera L. and Meliponulla beccarii L. Honeys from Kellem and West Wollega Zones, Western Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.L.R.; Gouveia-Nhanca, M.; da Veiga Dutra, M.L.; Batista, K.S.; de Araújo, A.N.V.; dos Santos Lima, M.; Ribeiro, M.D.; Silva, A.S.; Alves, A.F.; Pimentel, T.C.; et al. Malícia Honey (Mimosa quadrivalvis L.) Produced by the Jandaíra Bee (Melipona subnitida D.) Shows Antioxidant Activity via Phenolic Compound Action in Obese Rats. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1524642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biluca, F.C.; da Silva, B.; Caon, T.; Mohr, E.T.B.; Vieira, G.N.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Vitali, L.; Micke, G.; Fett, R.; Dalmarco, E.M.; et al. Investigation of Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities in Stingless Bee Honey (Meliponinae). Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Seerangan, P.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Osman, Z.F.; Abdullah, J.M.; Idris, Z. Anti-Cancer Properties of Heterotrigona itama sp. Honey Via Induction of Apoptosis in Malignant Glioma Cells. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 26, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.A.; Mohamed, M.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Zainuddin, A. In Vitro Modulation of Extracellular Matrix Genes by Stingless Bee Honey in Cellular Aging of Human Dermal Fibroblast Cells. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N.; Jaafar, N.M.; Mohamad, A.Z. Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anti-Diabetic Activities of Stingless Bee Honey from Selected Areas in Peninsular Malaysia. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 596, p. 012093. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, I.R.; Acevedo-Fernández, J.; Negrete-Leon, E.; Betancur-Ancona, D.A.; Moguel-Ordoñez, Y.B. In Vivo Wound-Healing and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Honey Produced by Melipona beecheii Bees. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2024, 19, e143682. [Google Scholar]
- Yaacob, M.; Rajab, N.; Shahar, S.; Sharif, R. Stingless Bee Honey and Its Potential Value: A Systematic Review. Food Res. 2018, 2, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.Z.; Yaacob, N.S.; Sulaiman, S.A. Reinventing the Honey Industry: Opportunities of the Stingless Bee. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif Zaidi, J.; Zawawi, N.; Ramlan, N.; Nor Fadhilah, S. Analysis of Trehalulose in Kelulut Honey Samples via HPLC-MS. Food Res. 2023, 6, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, S.; Beux, M.R.; Ribani, R.H.; Zambiazi, R.C. Stingless Bee Honey: Quality Parameters, Bioactive Compounds, Health Promotion Properties and Modification Detection Strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Revised Codex Standard for Honey; CODEX STAN 12-1981; Codex Alimentarius Commission: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, M.T.; Hungerford, N.L.; Webber, D.; Carpinelli de Jesus, M.; Zhang, J.; Stone, I.S.; Blanchfield, J.T.; Zawawi, N. Stingless Bee Honey, a Novel Source of Trehalulose: A Biologically Active Disaccharide with Health Benefits. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DMS 2683:2024; Malaysian Bureau of Standards (MBS). DMS 2683 Kelulut (Stingless Bee) Honey—Specification (First Revision). Department of Standards Malaysia: Selangor, Malaysia, 2024.
- A1257; Australian Native Bee Honey. Australia New Zealand Food Standards: Kingston, Australia, 2024.
- Zheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Granato, D.; de Oliveira, F.F.; Vit, P.; Luo, S.; Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Dan, Z.; et al. A Focus on the Chinese Stingless Bee Honey (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini): Exploring Physicochemical Parameters for Establishing Quality Standards. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 137, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatnaya, H.; Kahono, S.; Suhri, A.G.M.I.; Ismanto, A.; Anggraeni, I.; Fara, S.B.; Hasan, P.A.; Hashifah, F.N. Diversity, Distribution, Nesting, and Foraging Behavior of Stingless Bees and Recent Meliponiculture in Indonesia. In Melittology-New Advances; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jaapar, M.F.; Halim, M.; Mispan, M.R.; Jajuli, R.; Saranum, M.M.; Zainuddin, M.Y.; Ghazi, R.; Abd Ghani, I. The Diversity and Abundance of Stingless Bee (Hymenoptera: Meliponini) in Peninsular Malaysia. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sharin, S.N.; Sani, M.S.A.; Jaafar, M.A.; Yuswan, M.H.; Kassim, N.K.; Manaf, Y.N.; Wasoh, H.; Zaki, N.N.M.; Hashim, A.M. Discrimination of Malaysian Stingless Bee Honey from Different Entomological Origins Based on Physicochemical Properties and Volatile Compound Profiles Using Chemometrics and Machine Learning. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.; Ling, H.S.; Chung, K.C.; Yau, T.M.S.; Gindi, S.R.A. Chemical Analysis on the Honey of Heterotrigona itama and Tetrigona binghami from Sarawak, Malaysia. Sains Malays. 2019, 48, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Method 977.20; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2006.
- Zheng, X.; Wang, K.; Xue, X.; Wang, Z.; Pan, P.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, W. Determination of Trehalulose in Stingless Bee Honey by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Refractive Index Detector. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SN/T 0852-2012; Rules for the Inspection of Honey for Import and Export. Industry Standard for Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the PRC: Hangzhou, China, 2012.
- GB/T 18932.15-2003; Method for the Determination of Electrical Conductivity in Honey. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2003.
- GB 5009.237-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of pH in Food. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 18932.16-2003; Method for the Determination of Diastase Number in Honey- Spectrophotometric Method. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2003.
- GB/T 18932.18-2003; Method for the Determination of Hydroxymethylfurfural in Honey-HPLC-UV Detection Method. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Wilczyńska, A. Effect of Filtration on Colour, Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolics of Honey. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-Costa, F.M.; Zambiazi, R.C.; Bohmer, B.W.; Chaves, F.C.; da Silva, W.P.; Zanusso, J.T.; Dutra, I. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity of Honeys from the State of Rio Grande Do Sul, Brazil. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, R.; Lu, Q.; Hao, P.; Xu, A.; Zhang, J.; Tan, J. Biochemical Properties, Antibacterial and Cellular Antioxidant Activities of Buckwheat Honey in Comparison to Manuka Honey. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majkut, M.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Wszelaczyńska, E.; Pobereżny, J.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E.; Wojtacki, K.; Barczak, T. Antimicrobial Activity of Heat-Treated Polish Honeys. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlan, N.A.F.M.; Mohamad Azman, E.; Muhammad, K.; Jusoh, A.Z.; Johari, N.A.; Yusof, Y.A.; Zawawi, N. Physicochemical Homogeneity of Stingless Bee Honey (Heterotrigona itama) Produced in the West Coast, East Coast and Inland Area of Peninsular Malaysia. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 1756–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melia, S.; Juliyarsi, I.; Kurnia, Y.F.; Aritonang, S.N.; Rusdimansyah, R.; Sukma, A.; Setiawan, R.D.; Pratama, Y.E.; Supandil, D. Profile of Stingless Bee Honey and Microbiota Produced in West Sumatra, Indonesia, by Several Species (Apidae, Meliponinae). Vet. World 2024, 17, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita-Calvo, C.; Vázquez, M. Differences between Honeydew and Blossom Honeys: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello dos Santos, M.; Jacobs, C.; Islam, M.K.; Lim, L.Y.; Locher, C. Validation of a High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Method for the Quantitative Determination of Trehalulose. JPC–J. Planar Chromatogr.–Mod. TLC 2023, 36, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seevanathan, Y.; Zawawi, N.; Salleh, A.B.; Oslan, S.N.; Ashaari, N.S.; Hamzah, A.S.A.; Sabri, S. Trehalulose: Exploring Its Benefits, Biosynthesis, and Enhanced Production Techniques. Carbohydr. Res. 2024, 545, 109293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, M.F.; Sivakumar, M.; Maulidiani, M.; Ismail, W.I.W. Bibliometric Approach to Trehalulose Research Trends for Its Potential Health Benefits. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hungerford, N.L.; Yates, H.S.; Smith, T.J.; Fletcher, M.T. How Is Trehalulose Formed by Australian Stingless Bees?—An Intermolecular Displacement of Nectar Sucrose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6530–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuttong, B.; Chanbang, Y.; Sringarm, K.; Burgett, M. Effects of Long Term Storage on Stingless Bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Meliponini) Honey. J. Apic. Res. 2015, 54, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, M.W.; Wanjau, T.W.; Omwenga, E.O. Stingless Bee Honey: Nutritional, Physicochemical, Phytochemical and Antibacterial Validation Properties against Wound Bacterial Isolates. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoko, M.L.K.; Mduda, C.A. Harvesting Location Influences the Physicochemical Properties, Microbiological Quality and Sensory Attributes of Honey Produced by an Afrotropical Stingless Bee, Axestotrigona ferruginea. Food Humanit. 2024, 3, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Ngaini, Z. The Enzymatic Role in Honey from Honey Bees and Stingless Bees. Curr. Org. Chem. 2023, 27, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuttong, B.; Chanbang, Y.; Sringarm, K.; Burgett, M. Physicochemical Profiles of Stingless Bee (Apidae: Meliponini) Honey from South East Asia (Thailand). Food Chem. 2016, 192, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biluca, F.C.; Braghini, F.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Physicochemical Profiles, Minerals and Bioactive Compounds of Stingless Bee Honey (Meliponinae). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 50, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, Y.; Torres, A.; Hoffmann, W. Colombian Stingless Bee Honeys Characterized by Multivariate Analysis of Physicochemical Properties. Apidologie 2019, 50, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S.; Ruoff, K.; Oddo, L.P. Physico-Chemical Methods for the Characterisation of Unifloral Honeys: A Review. Apidologie 2004, 35, S4–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasias, I.N.; Kiriakou, I.K.; Proestos, C. HMF and Diastase Activity in Honeys: A Fully Validated Approach and a Chemometric Analysis for Identification of Honey Freshness and Adulteration. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraglio, S.K.T.; Silva, B.; Bergamo, G.; Brugnerotto, P.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; Costa, A.C.O. An Overview of Physicochemical Characteristics and Health-Promoting Properties of Honeydew Honey. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.S.; Nanda, V.; Bhat, M.; Khan, A. Kinetic Studies of HMF Formation and Diastase Activity in Two Different Honeys of Kashmir. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Han, B.; Chen, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, S. Quantification of Bioactive Components and Evaluation of Microbial Community and Antibacterial Activity from Heterotrigona itama and Tetrigona binghami Honeys. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May-Canché, I.; Moguel-Ordoñez, Y.; Valle-Mora, J.; González-Cadenas, R.; Toledo-Núñez, B.; Arroyo-Rodríguez, L.; Piana, L.; Vandame, R. Sensory and Physicochemical Analysis of Honeys of Nine Stingless Bee Species of Mexico and Guatemala. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4772–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MS 2683:2017; Kelulut (Stingless Bee) Honey-Specification. Department of Standard Malaysia: Selangor, Malaysia, 2017.
- Bong, Z.R. A Comparative Study of Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties Between Stingless Bee Honey from Sarawak and Honey from Other Origins. Ph.D. Thesis, Swinburne University of Technology, Sarawak, Malaysia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa, J.M.B.; de Souza, E.L.; Marques, G.; de Toledo Benassi, M.; Gullón, B.; Pintado, M.M.; Magnani, M. Sugar Profile, Physicochemical and Sensory Aspects of Monofloral Honeys Produced by Different Stingless Bee Species in Brazilian Semi-Arid Region. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Ali, F.; Zarei, M.; Akim, A.M.; Abd Hamid, H.; Khazaai, H. Malaysian Stingless Bee and Tualang Honeys: A Comparative Characterization of Total Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Profile Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. LWT 2018, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, S.; Selamat, J.; Sanny, M.; Abd Razak, S.B.; Jambari, N.N.; Mian, Z.; Khatib, A. Influence of Origins and Bee Species on Physicochemical, Antioxidant Properties and Botanical Discrimination of Stingless Bee Honey. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 238–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.-J.; Sit, N.-W.; Ooi, P.A.-C.; Ee, K.-Y.; Lim, T.-M. Botanical Origin Differentiation of Malaysian Stingless Bee Honey Produced by Heterotrigona itama and Geniotrigona thoracica Using Chemometrics. Molecules 2021, 26, 7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, Z.; Yildiz, O.; Sahin, H.; Akyuz Turumtay, E.; Silici, S.; Kolayli, S. An Investigation of Turkish Honeys: Their Physico-Chemical Properties, Antioxidant Capacities and Phenolic Profiles. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuredo, O.; Míguez, M.; Fernández-González, M.; Carmen Seijo, M. Nutritional Value and Antioxidant Activity of Honeys Produced in a European Atlantic Area. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kato, A.; Kuroda, K.; Abe, H. Extrafloral Nectaries in Acacia mangium. Trop. Plant Biol. 2012, 5, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Kumar, A. Morphology, Anatomy, Ultrastructure and Ant-Patrolling of Extrafloral Nectaries (Efns) in Three Species of Mimosaceae. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2015, 7, 15505–15508. [Google Scholar]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Amrah Sulaiman, S.; Gan, S.H. Phenolic Acid and Flavonoid Composition of Malaysian Honeys. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Jia, Z.; Zheng, X.; Cui, S.; Chen, W. A Recent Review of Citrus Flavanone Naringenin on Metabolic Diseases and Its Potential Sources for High Yield-Production. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanwar, A.A.; Badole, S.L.; Shende, P.S.; Hegde, M.V.; Bodhankar, S.L. Chapter 21—Antioxidant Role of Catechin in Health and Disease. In Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 267–271. ISBN 978-0-12-398456-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-O.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.Y. Vitamin C Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (VCEAC) of Phenolic Phytochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floegel, A.; Kim, D.-O.; Chung, S.-J.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K. Comparison of ABTS/DPPH Assays to Measure Antioxidant Capacity in Popular Antioxidant-Rich US Foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, P.; Jin, Y.; Hu, H.; Xue, X.; Zhang, J. Comparison of the Antioxidant and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activities of Different Types of Honey. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilo, K. Stingless Bee (Meliponulla baccaerii) Honey Antibacterial Activities against Salmonella typhi, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2024, 15, 506. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.E.A.; Mansour, E.-T.I. Three Species of Stingless Bee (Meliponini) Honey from Sudan: A Contribution to the Nest Components, Proximate Composition, and Antimicrobial Properties. In Bee World; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkasovska, J.; Bugarova, V.; Godocikova, J.; Majtan, V.; Majtan, J. The Role of Hydrogen Peroxide in the Antibacterial Activity of Different Floral Honeys. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2739–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godocikova, J.; Bugarova, V.; Kast, C.; Majtan, V.; Majtan, J. Antibacterial Potential of Swiss Honeys and Characterisation of Their Bee-Derived Bioactive Compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, F.I.; Hilmi, A.B.M.; Aliyu, S. Effect of Non-Hydrogen Peroxide on Antibacterial Activity of Malaysian Meliponini Honey against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2020, 12, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, S.H.; Saragih, B.; Kusuma, I.W.; Arung, E.T. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Screening of Honey of Hiterotrogona Itama Collected from Differents Meliponiculture Areas in East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Nusant. Biosci. 2021, 13, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Han, L.; Li, S.; Zheng, H.; Hu, F. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Three Monofloral Kinds of Honey from Medicinal Plants. Food Ferment. Ind. 2024, 50, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. A Review of Commonly Used Methodologies for Assessing the Antibacterial Activity of Honey and Honey Products. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuksitha, L.; Chen, Y.-L.S.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wong, K.-Y.; Peng, C.-C. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Capacity of Stingless Bee Honey from Borneo (Sarawak). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloi de Sousa Guimarães, N.; Larissa Salles Oliveira, M.; Nathan Fernandes dos Santos, D.; Gonçalves de Araújo, R.; Vieira da Cunha, A.C.; de Oliveira da Silva, J.; Fernandes, F.H.A. Chemical Characterisation, Thermal Analysis, and Antibacterial Activity of Honeys from Caatinga Stingless Bees of Melipona Spp. In Natural Product Research; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X. Research on the Diversity and Carbohydrate Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Bee Intestines. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, S.K.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A.; Chong, K.Y. Quality Characteristics of Dehydrated Raw Kelulut Honey. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; O’Brien, M.; Georges, K.; Suepaul, S. Physical Characteristics and Antimicrobial Properties of Apis mellifera, Frieseomelitta nigra and Melipona favosa Bee Honeys from Apiaries in Trinidad and Tobago. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Honey | Sample | Harvest Time | Location of Bee Farm | Botanical Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. itama | HI 1-HI 3 | 2023.8 | Labuan | Fruit trees, forest |
| HI 4 | 2023.8 | Labuan | Acacia mangium, star fruit, rambutan, wild vegetation | |
| HI 5 | 2023.8 | Skudai, Johor | Fruit trees, forest | |
| HI 6 | 2023.8 | Temiang, Negeri Sembilan | A. mangium, banana, wild vegetation | |
| HI 7 | 2022.12 | Temiang, Negeri Sembilan | A. mangium, banana, wild vegetation | |
| HI 8-HI 9 | 2023.6 | 16 miles, Sarawak | A. mangium, wild vegetation | |
| HI 10 | 2022.11 | 16 miles, Sarawak | A. mangium, wild vegetation | |
| HI 11 | 2023.6 | Panasu, Sarawak | fruit trees, forest | |
| L. canifrons | LC 1-LC 3 | 2023.8 | Temiang, Negeri Sembilan | A. mangium, banana, wild vegetation |
| LC 4-LC 6 | 2023.7 | Gambang, Pahang | A. mangium, fruit trees | |
| LC 7-LC 9 | 2023.8 | Bangi, Selangor | Coconut trees, plants | |
| T. binghami | TB 1-TB 3 | 2023.8 | Ng. Dap, Sarawak | A. mangium, wild vegetation |
| TB 4-TB 8 | 2023.7 | Ng. Dap, Sarawak | A. mangium, wild vegetation | |
| TB 9 | 2022.8 | Jelebu, Negeri Sembilan | fruit trees, forest | |
| TB 10 | 2022.12 | Jelebu, Negeri Sembilan | fruit trees, forest |
| Parameters | Stingless Bee Species | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| H. itama (n = 11) | L. canifrons (n = 9) | T. binghami (n = 10) | |
| Moisture (%) | 29.05 ± 1.02 a | 27.61 ± 2.59 a | 34.67 ± 2.29 b |
| (27.12–30.48) | (25.44–33.45) | (32.78–40.36) | |
| Color (mm) | 105.09 ± 32.17 a | 77.22 ± 36.07 ab | 62.60 ± 38.85 b |
| (64.00–150.00) | (31.00–140.00) | (31.00–150.00) | |
| Fructose (g/100 g) | 11.28 ± 3.59 a | 7.60 ± 1.20 b | 9.80 ± 3.93 ab |
| (6.17–16.91) | (5.66–9.31) | (5.45–15.74) | |
| Glucose (g/100 g) | 11.50 ± 5.00 a | 5.49 ± 1.40 b | 17.09 ± 3.54 c |
| (5.61–19.45) | (3.85–7.76) | (7.31–19.64) | |
| Sucrose (g/100 g) | 0.70 ± 0.72 a | 0.73 ± 0.82 a | 1.37 ± 0.36 a |
| (ND-1.89) | (ND-2.47) | (0.68–1.90) | |
| Trehalulose (g/100 g) | 33.59 ± 7.12 a | 38.13 ± 7.38 a | 20.81 ± 3.52 b |
| (22.71–41.77) | (22.64–43.75) | (15.42–24.75) | |
| 5-HMF (mg/kg) | 1.33 ± 0.72 a | 2.03 ± 1.80 a | 1.69 ± 0.68 a |
| (0.53–2.63) | (ND-5.40) | (0.53–2.44) | |
| Diastase activity (DN) | ND | ND | ND |
| pH | 3.17 ± 0.12 a | 3.21 ± 0.16 a | 2.83 ± 0.17 b |
| (2.99–3.36) | (2.93–3.39) | (2.62–3.09) | |
| Electricity Conductivity (μs/cm) | 810.73 ± 134.33 a | 608.17 ± 141.48 a | 1005.28 ± 285.88 ab |
| (578.25–1066) | (478.40–889.40) | (788.70–1573.00) | |
| Acidity (meq/kg) | 238.57 ± 47.61 a | 305.69 ± 70.66 a | 515.72 ± 146.48 b |
| (140.99–312.78) | (240.85–446.17) | (395.90–787.89) | |
| Moisture | Color | Trehalulose | pH | EC | Acidity | 5-HMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 1 | −0.155 | −0.668 ** | −0.570 ** | 0.622 ** | 0.708 ** | −0.141 |
| Color | −0.119 | 1 | 0.158 | 0.132 | 0.467 ** | 0.117 | −0.078 |
| Trehalulose | −0.668 ** | 0.205 | 1 | 0.738 ** | −0.569 ** | −0.562 ** | 0.011 |
| pH | −0.570 ** | 0.187 | 0.738 ** | 1 | −0.501 ** | −0.616 ** | −0.177 |
| EC | 0.622 ** | 0.435 * | −0.569 ** | −0.501 ** | 1 | 0.797 ** | 0.084 |
| Acidity | 0.708 ** | 0.096 | −0.562 ** | −0.616 ** | 0.797 ** | 1 | 0.232 |
| 5-HMF | −0.141 | 0.063 | 0.011 | −0.177 | 0.084 | 0.232 | 1 |
| Moisture | 1 | −0.155 | −0.668 ** | −0.570 ** | 0.622 ** | 0.708 ** | −0.141 |
| Stingless Bee Species | Total Phenolic Content (µg GAE/g) | DPPH (mg TE/100 g) | ABTS (mmol TE/kg) | FRAP (mmol FeSO4/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. itama (n = 11) | 601.02 ± 143.43 a | 21.23 ± 10.25 a | 3.67 ± 0.46 a | 2.33 ± 0.70 a |
| (424.43–880.23) | (10.63–42.48) | (3.09–4.70) | (1.39–3.67) | |
| L. canifrons (n = 9) | 626.32 ± 70.91 a | 17.84 ± 5.14 ab | 3.53 ± 0.19 a | 1.46 ± 0.64 b |
| (531.89–730.97) | (7.93–23.26) | (3.16–3.74) | (0.42–2.31) | |
| T. binghami (n = 10) | 434.82 ± 102.00 b | 10.80 ± 6.87 b | 2.69 ± 0.27 b | 1.44 ± 0.68 b |
| (320.34–623.38) | (6.06–28.32) | (2.24–2.92) | (0.82–2.99) |
| Samples | Inhibition Zones (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| 10% phenol solution | 27.09 ± 0.99 | 23.81 ± 0.88 |
| Sterile water | - | - |
| HI 1 | 9.31 ± 0.37 | - |
| HI 2 | 8.73 ± 0.06 | - |
| HI 3 | 8.26 ± 0.41 | - |
| HI 4 | 18.62 ± 0.89 | - |
| HI 5 | 8.29 ± 0.20 | - |
| HI 6 | 10.12 ± 1.43 | - |
| HI 7 | 8.05 ± 0.21 | - |
| HI 8 | 17.34 ± 2.32 | - |
| HI 9 | 18.58 ± 0.89 | - |
| HI 10 | 14.94 ± 1.77 | - |
| HI 11 | 8.97 ± 0.88 | - |
| LC 1 | 13.82 ± 0.26 | - |
| LC 2 | 18.56 ± 1.78 | - |
| LC 3 | 8.92 ± 0.20 | - |
| LC 4 | 9.31 ± 0.48 | - |
| LC 5 | 9.44 ± 0.65 | - |
| LC 6 | 19.59 ± 0.67 | - |
| LC 7 | 8.14 ± 0.21 | - |
| LC 8 | 8.32 ± 0.22 | - |
| LC 9 | 8.24 ± 0.30 | - |
| TB 1 | 22.58 ± 1.10 | 8.34 ± 0.31 |
| TB 2 | 22.71 ± 1.52 | 8.75 ± 1.04 |
| TB 3 | 23.72 ± 0.24 | 8.28 ± 0.48 |
| TB 4 | 23.53 ± 0.37 | 9.28 ± 0.22 |
| TB 5 | 22.64 ± 0.48 | 9.51 ± 0.51 |
| TB 6 | 22.76 ± 0.21 | 10.09 ± 1.33 |
| TB 7 | 17.28 ± 0.93 | - |
| TB 8 | 18.14 ± 0.63 | - |
| TB 9 | 14.06 ± 0.95 | - |
| TB 10 | 14.39 ± 0.80 | - |
| Mean for HI | 11.92 ± 4.45 a | - |
| Mean for LC | 11.59 ± 4.69 a | - |
| Mean for TB | 20.18 ± 3.83 b | - |
| Honey | MBC/% (w/v) | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| HI 1 | 10 | 20 |
| HI 2 | 10 | 12.5 |
| HI 3 | 12.5 | 20 |
| HI 4 | 5 | 12.5 |
| HI 5 | 12.5 | 20 |
| HI 6 | 12.5 | 20 |
| HI 7 | 12.5 | 25 |
| HI 8 | 10 | 12.5 |
| HI 9 | 10 | 20 |
| HI 10 | 10 | 12.5 |
| HI 11 | 10 | 12.5 |
| LC 1 | 20 | 20 |
| LC 2 | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| LC 3 | 10 | 20 |
| LC 4 | 10 | 20 |
| LC 5 | 10 | 12.5 |
| LC 6 | 10 | 12.5 |
| LC 7 | 12.5 | 20 |
| LC 8 | 12.5 | 20 |
| LC 9 | 10 | 20 |
| TB 1 | 5 | 10 |
| TB 2 | 3.125 | 10 |
| TB 3 | 5 | 10 |
| TB 4 | 5 | 10 |
| TB 5 | 3.125 | 10 |
| TB 6 | 3.125 | 6.25 |
| TB 7 | 6.25 | 10 |
| TB 8 | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| TB 9 | 5 | 10 |
| TB 10 | 5 | 10 |
| MBC (S. aureus) | MBC (E. coli) | |
|---|---|---|
| TPC | 0.306 | 0.360 |
| DPPH | 0.332 | 0.445 * |
| ABTS | 0.558 ** | 0.550 ** |
| FRAP | 0.137 | 0.255 |
| MBC (S. aureus) | 1 | 0.790 ** |
| MBC (E. coli) | 0.790 ** | 1 |
| Moisture | Color | Trehalulose | pH | EC | Acidity | 5-HMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | −0.467 ** | 0.716 ** | 0.498 ** | 0.410 * | −0.057 | −0.234 | 0.029 |
| DPPH | −0.327 | 0.704 ** | 0.351 | 0.322 | 0.079 | −0.188 | −0.108 |
| ABTS | −0.734 ** | 0.459 * | 0.578 ** | 0.656 ** | −0.430 * | −0.727 ** | −0.101 |
| FRAP | −0.142 | 0.731 ** | 0.069 | 0.059 | 0.382 * | −0.011 | −0.087 |
| MBC (S. aureus) | −0.707 ** | 0.134 | 0.663 ** | 0.671 ** | −0.467 ** | −0.601 ** | −0.09 |
| MBC (E. coli) | −0.619 ** | 0.052 | 0.607 ** | 0.641 ** | −0.543 ** | −0.635 ** | 0.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiang, E.R.; Han, L.; Hu, F. Physicochemical Characteristics, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Stingless Bee Honey from Malaysia: Heterotrigona itama, Lophotrigona canifrons, and Tetrigona binghami. Foods 2025, 14, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060995
Tiang ER, Han L, Hu F. Physicochemical Characteristics, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Stingless Bee Honey from Malaysia: Heterotrigona itama, Lophotrigona canifrons, and Tetrigona binghami. Foods. 2025; 14(6):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060995
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiang, En Ruth, Lingyun Han, and Fuliang Hu. 2025. "Physicochemical Characteristics, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Stingless Bee Honey from Malaysia: Heterotrigona itama, Lophotrigona canifrons, and Tetrigona binghami" Foods 14, no. 6: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060995
APA StyleTiang, E. R., Han, L., & Hu, F. (2025). Physicochemical Characteristics, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Stingless Bee Honey from Malaysia: Heterotrigona itama, Lophotrigona canifrons, and Tetrigona binghami. Foods, 14(6), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060995








