A Snapshot of Microbial Succession and Volatile Component Dynamics of Marselan Wine in Xinjiang During Spontaneous Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spontaneous Fermentation and Sample Collection
2.2. Physicochemical Properties Determined During the Fermentation Process
2.3. Volatile Compound Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Microbial Diversity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamics of Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Substances During Fermentation
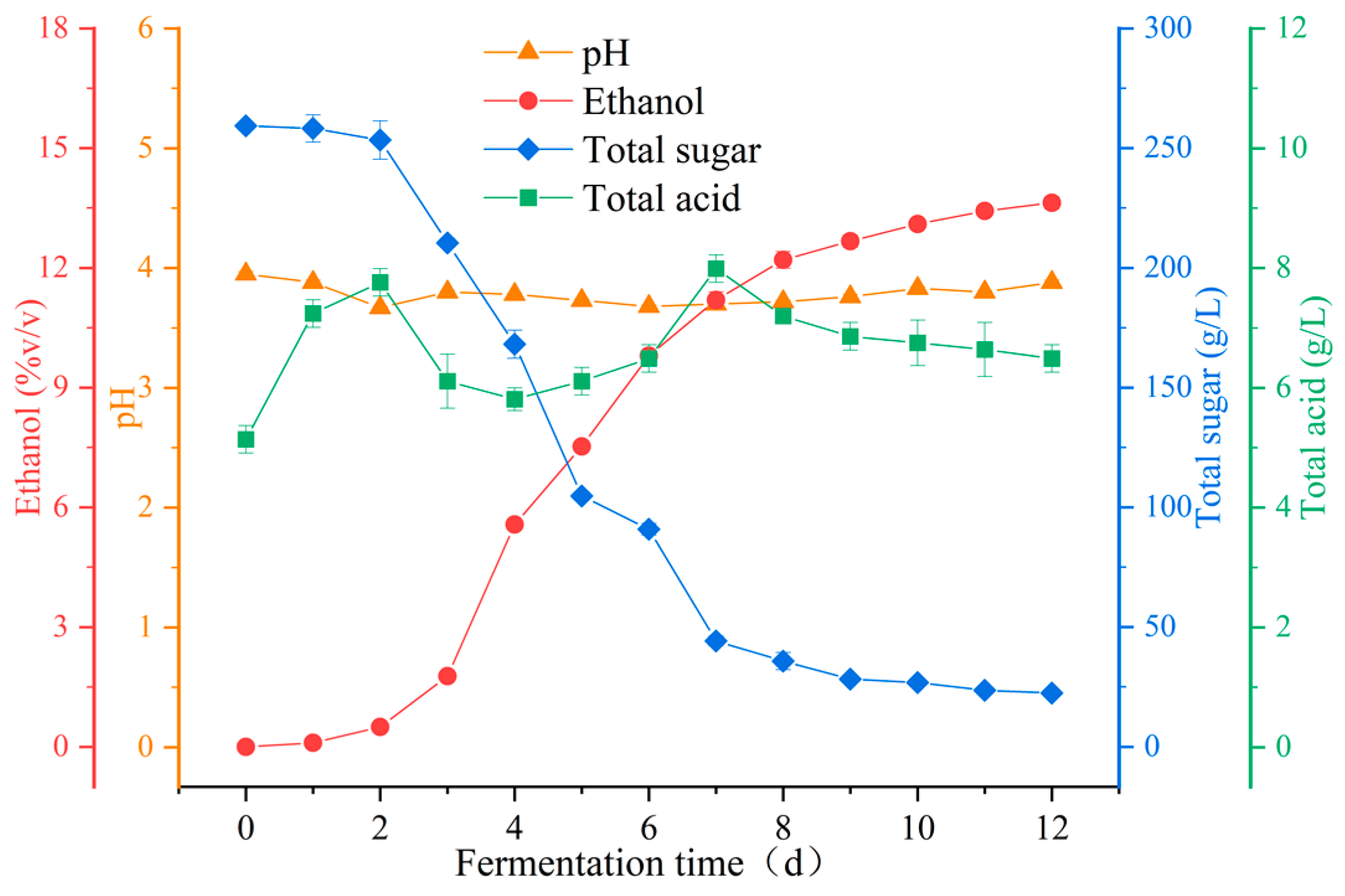
3.1.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics
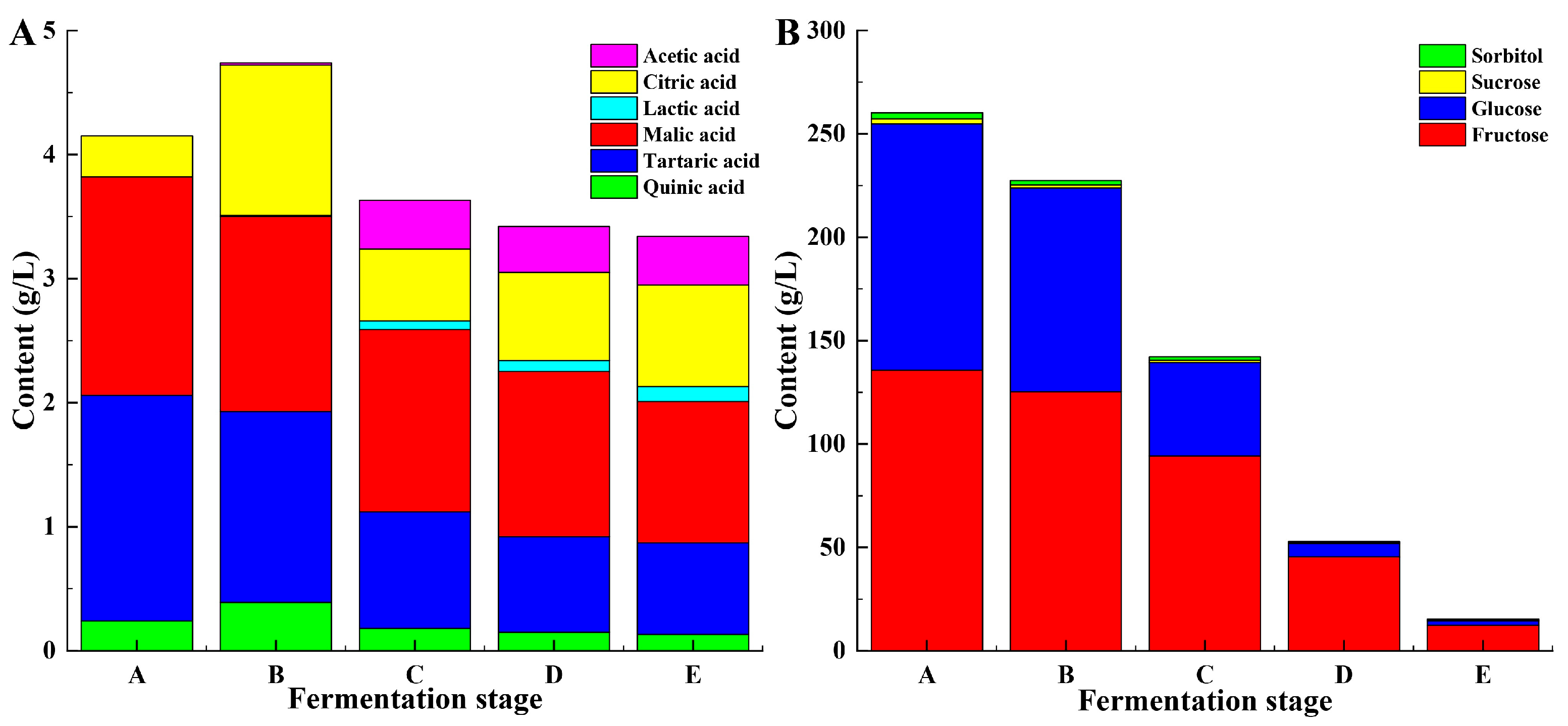
3.1.2. Organic Acid Composition
3.1.3. Sugar Composition
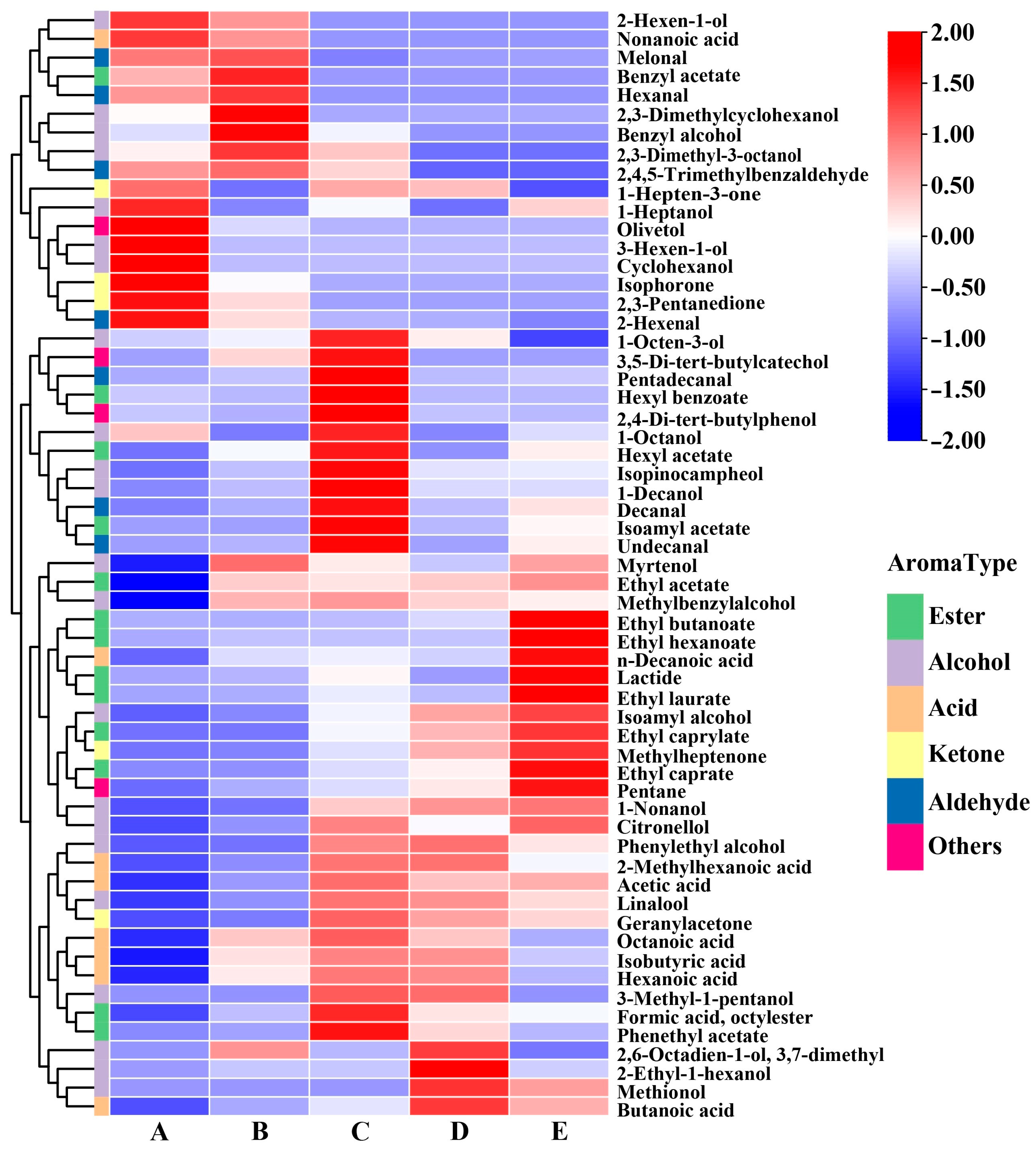
3.1.4. Volatile Compounds
3.2. Microbial Community During Fermentation Process
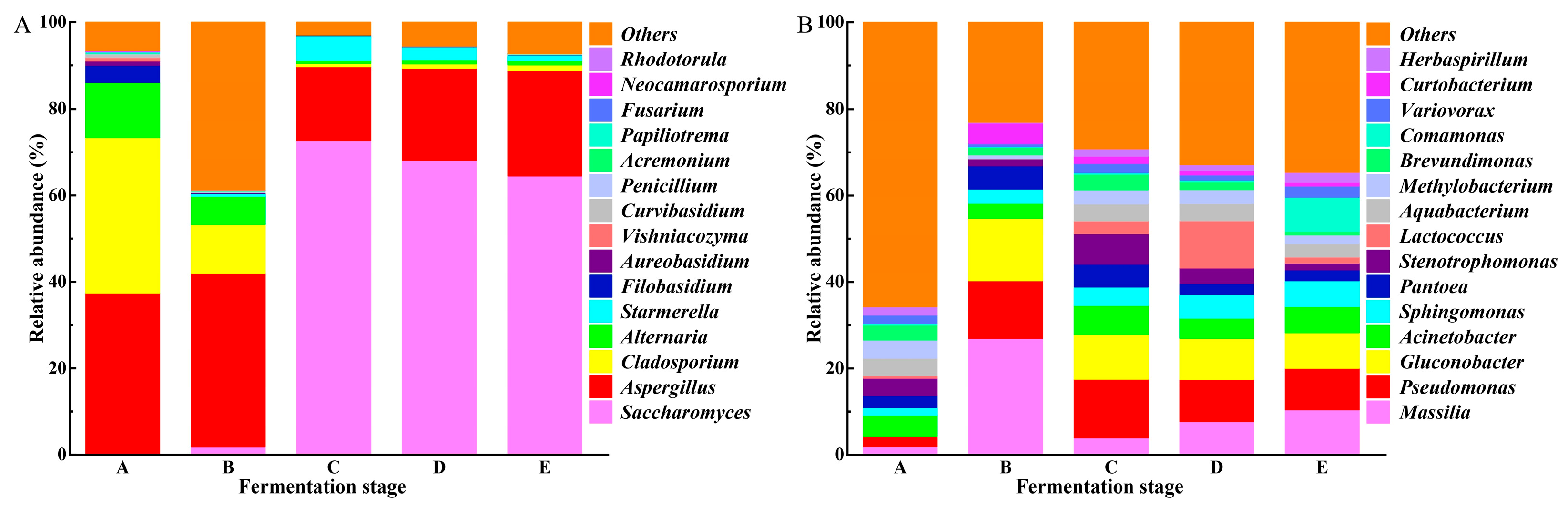
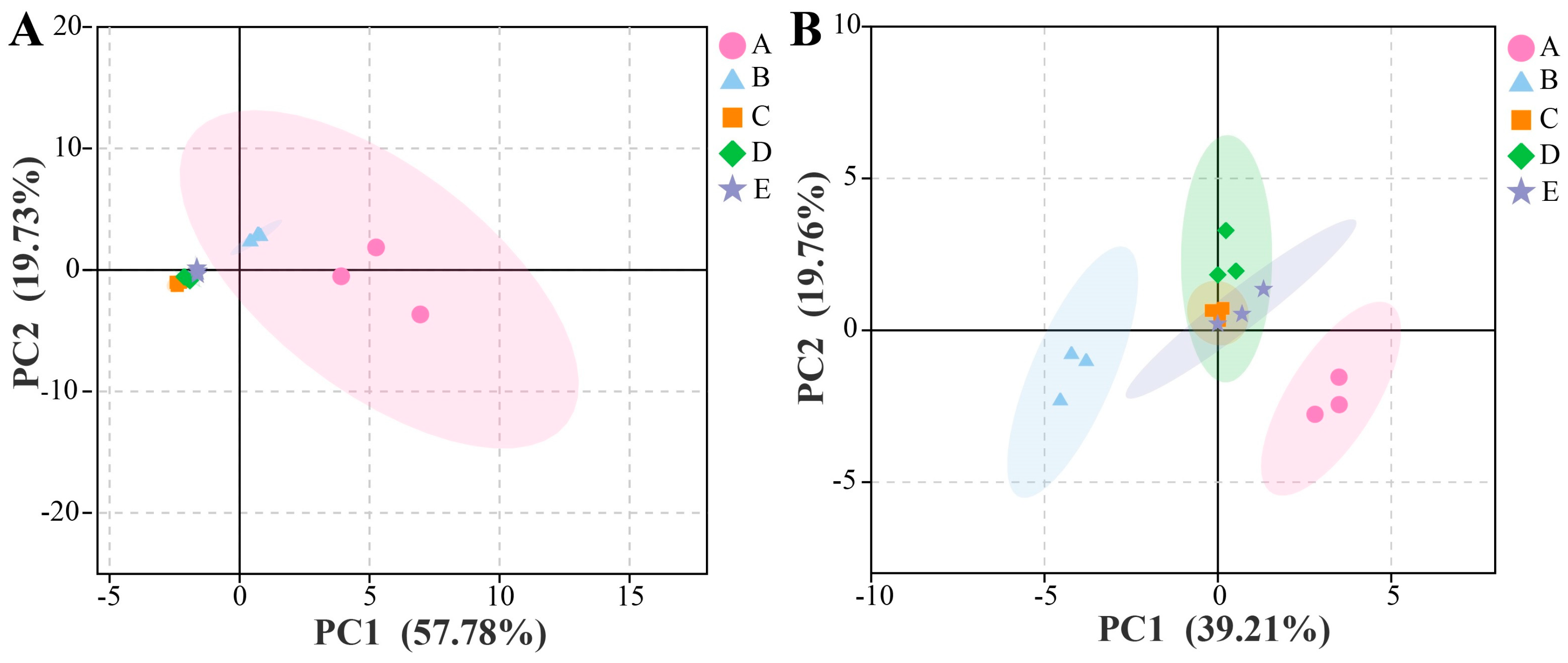
3.2.1. Microbial Diversity
3.2.2. Co-Occurrence and Exclusion Analyses Among Different Microorganisms
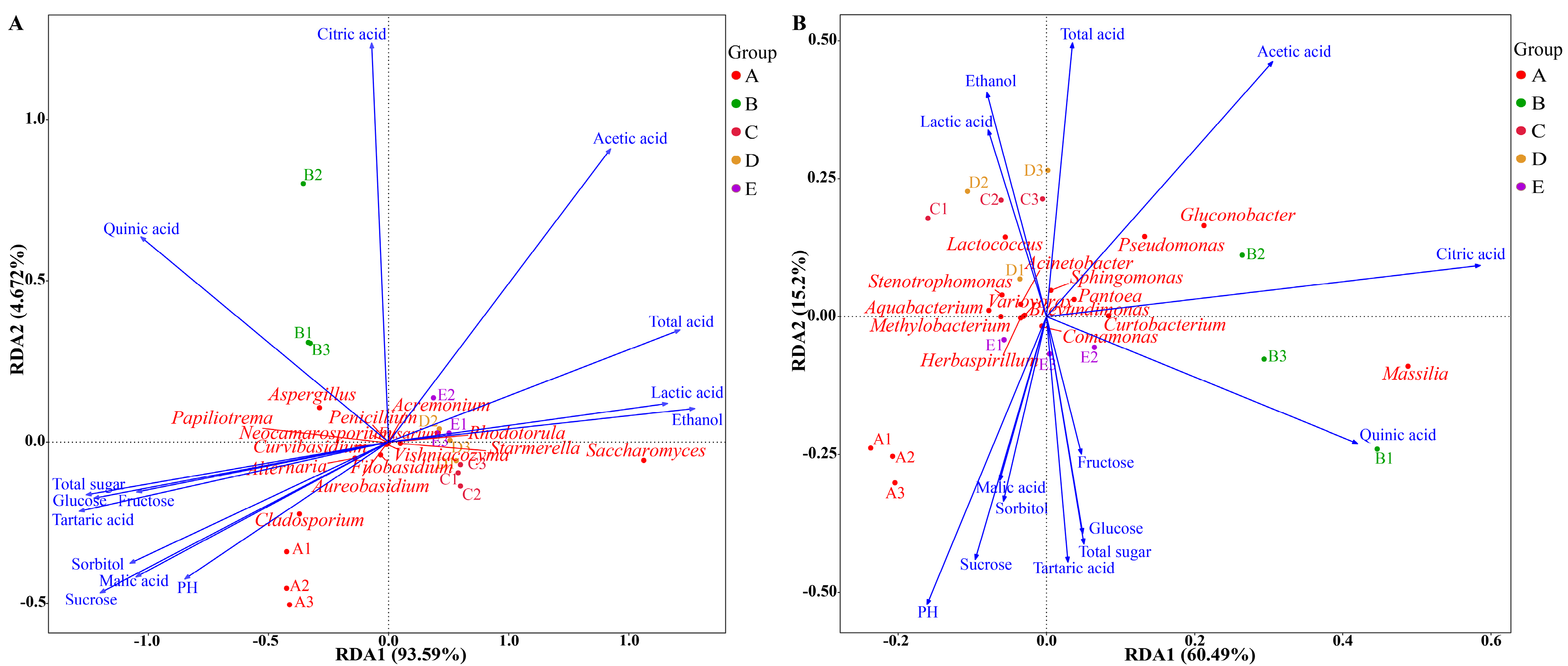
3.3. Microbial Community Succession Driven by Physicochemical Factors
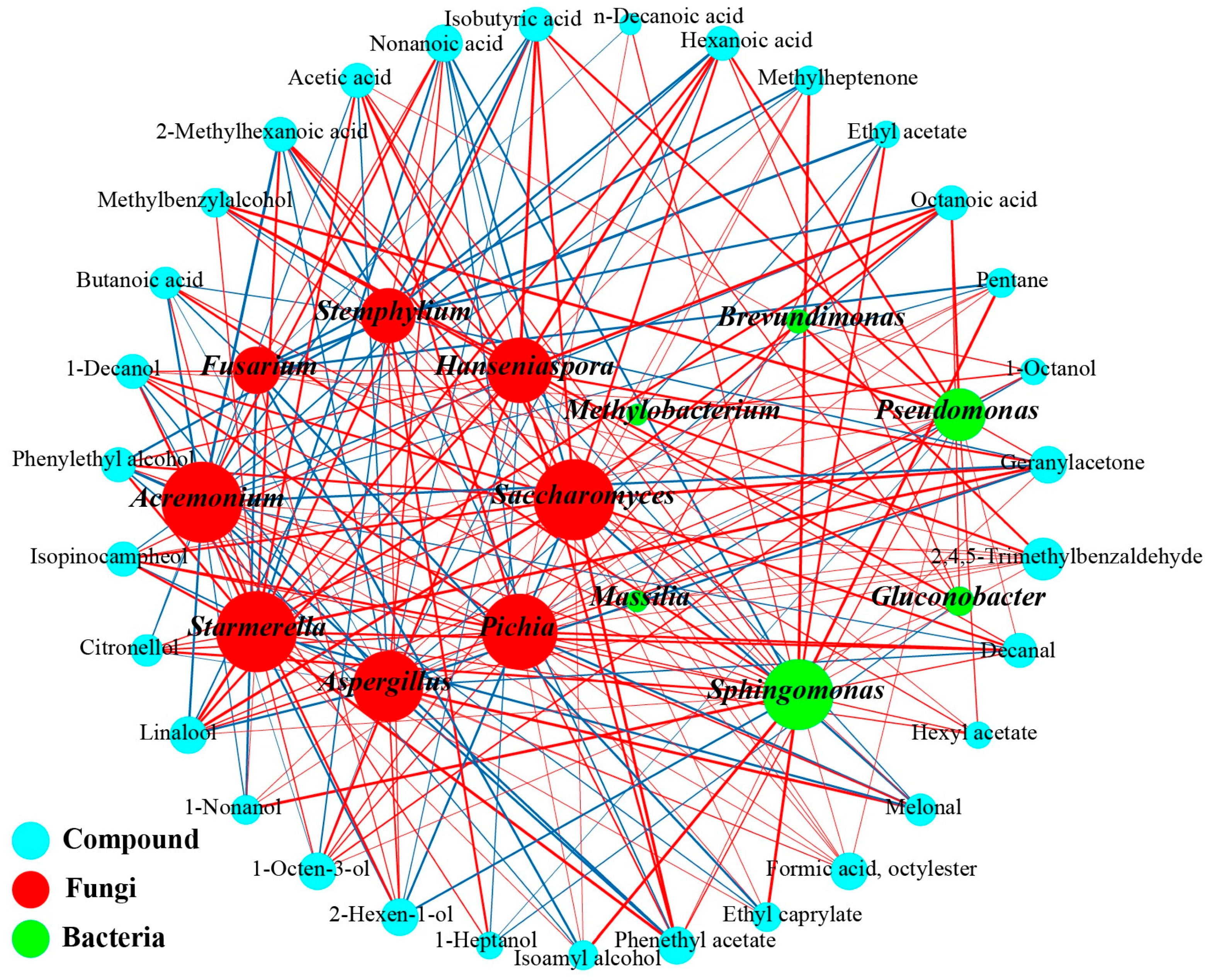
3.4. Analysis Between Key Microorganisms and Volatile Compounds
3.4.1. Identification of Key Microorganisms and Volatile Compounds
3.4.2. Correlation Analysis Microbes and Flavor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saranraj, P.; Sivasakthivelan, P.; Naveen, M.J. Fermentation of fruit wine and its quality analysis: A review. Aust. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 1, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Ye, P.; Wu, H.; Zhao, R.; Shi, X.; Cai, F. Chemical and Sensory Characteristics of Different Red Grapes Grown in Xinjiang, China: Insights into Wines Composition. Fermentation 2022, 8, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, X.-A.; Fang, Z. The art of flavored wine: Tradition and future. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejudo-Bastante, M.J.; del Barrio-Galán, R.; Heredia, F.J.; Medel-Marabolí, M.; Peña-Neira, Á. Location effects on the polyphenolic and polysaccharidic profiles and colour of Carignan grape variety wines from the Chilean Maule region. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Miao, Y.; Xu, X.; Ye, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, B.; Shi, X. Effects of Blending on Phenolic, Colour, Antioxidant and Aroma Components of Cabernet Sauvignon Wine from Xinjiang (China). Foods 2022, 11, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, I.S. Tailoring wine yeast for the new millennium: Novel approaches to the ancient art of winemaking. Yeast 2000, 16, 675–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wei, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Exploring the ecological characteristics of natural microbial communities along the continuum from grape berries to winemaking. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanzone, M.; Zamora, F.; Jofré, V.; Assof, M.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Peña-Neira, Á.J. Phenolic characterisation of red wines from different grape varieties cultivated in Mendoza province (Argentina). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Shi, Y.; Duan, C. Regional Variation of Chemical Characteristics in Young Marselan (Vitis vinifera L.) Red Wines from Five Regions of China. Foods 2022, 11, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, M.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M.J. Historical and heritage sustainability for the revival of ancient wine-making techniques and wine styles. Beverages 2022, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Moore, H.R.; Jelley, R.E.; Marangon, M.; Fedrizzi, B.J. The interactions of wine polysaccharides with aroma compounds, tannins, and proteins, and their importance to winemaking. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordão, A.; Vilela, A.; Cosme, F. From Sugar of Grape to Alcohol of Wine: Sensorial Impact of Alcohol in Wine. Beverages 2015, 1, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagatić Korenika, A.-M.; Tomaz, I.; Preiner, D.; Plichta, V.; Jeromel, A. Impact of Commercial Yeasts on Phenolic Profile of Plavac Mali Wines from Croatia. Fermentation 2021, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, C.; Eeg-Olofsson, M.J. Describing sensory experience: The genre of wine reviews. Metaphor. Symb. 2013, 28, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiegers, J.; Bartowsky, E.; Henschke, P.; Pretorius, I.J. Yeast and bacterial modulation of wine aroma and flavour. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2005, 11, 139–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Kiene, F.; Belda, I.; Fracassetti, D.; Marquina, D.; Navascués, E.; Calderón, F.; Benito, A.; Rauhut, D.; Santos, A.J. Effects on varietal aromas during wine making: A review of the impact of varietal aromas on the flavor of wine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7425–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, A.A.; Das, D.K. Grapes, wines, resveratrol, and heart health. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 54, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappa, I.K.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Pateraki, C.; Koulougliotis, D.; Eriotou, E.; Kopsahelis, N. Indigenous yeasts: Emerging trends and challenges in winemaking. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Ding, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, L.; Gao, F.; Zhang, L.; Song, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities during spontaneous fermentation of Cabernet Sauvignon (Vitis vinifera L.) from different regions of China and their relationship with the volatile components in the wine. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, C.; Sumby, K.; Bartowsky, E.; Jiranek, V. Lactic Acid Bacteria in Wine: Technological Advances and Evaluation of Their Functional Role. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 612118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borren, E.; Tian, B. The Important Contribution of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts to the Aroma Complexity of Wine: A Review. Foods 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Miao, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, X.; Wang, B. Analysis of Microbial Community Diversity on the Epidermis of Wine Grapes in Manasi’s Vineyard, Xinjiang. Foods 2022, 11, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Sam, F.E.; Peng, S.; Li, M.; Wang, J. Dynamic analysis of microbial communities and flavor properties in Merlot wines produced from inoculation and spontaneous fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Tian, H. Influence of 4 lactic acid bacteria on the flavor profile of fermented apple juice. Food Biosci. 2019, 27, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, B.; Bauer, F.F.; Setati, M.E. The Impact of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on a Wine Yeast Consortium in Natural and Inoculated Fermentations. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, G. Yeast fermentation management for improved wine quality. In Managing Wine Quality; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisson, L.; Walker, G. The microbial dynamics of wine fermentation. In Advances in Fermented Foods and Beverages; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 435–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, K.; Boido, E.; Fariña, L.; Gioia, O.; Gomez, M.; Barquet, M.; Gaggero, C.; Dellacassa, E.; Carrau, F.J. Increased flavour diversity of Chardonnay wines by spontaneous fermentation and co-fermentation with Hanseniaspora vineae. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, S.; Lin, M.; Guo, S.; Han, X.; Ren, M.; Du, L.; Song, Y.; You, Y.; Zhan, J.; et al. The Biogeography of Fungal Communities Across Different Chinese Wine-Producing Regions Associated With Environmental Factors and Spontaneous Fermentation Performance. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 636639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Mu, J.; Gao, Z.J. Effects of spontaneous fermentation on the microorganisms diversity and volatile compounds during ‘Marselan’ from grape to wine. LWT 2020, 134, 110193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Huang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Jing, X. An effervescence tablet-assisted microextraction based on the solidification of deep eutectic solvents for the determination of strobilurin fungicides in water, juice, wine, and vinegar samples by HPLC. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Miao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, P.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Zhao, R.; Wang, B.; Shi, X. A Snapshot of Microbial Succession and Volatile Compound Dynamics in Flat Peach Wine During Spontaneous Fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 919047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Ge, X.; Fu, X.; Dang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Sequential fermentation with indigenous non-Saccharomyces yeasts and Saccharomyces cerevisiae for flavor and quality enhancement of Longyan dry white wine. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufariello, M.; Pati, S.; D’Amico, L.; Bleve, G.; Losito, I.; Grieco, F. Quantitative issues related to the headspace-SPME-GC/MS analysis of volatile compounds in wines: The case of Maresco sparkling wine. LWT 2019, 108, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Fu, Q.; Xu, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Du, J.; Wang, B.; Shi, X. Investigation of microbial succession and volatile compounds dynamics during the fermentation of traditional cereal vinegar in Xinjiang. LWT 2023, 186, 115258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacosa, S.; Parpinello, G.P.; Río Segade, S.; Ricci, A.; Paissoni, M.A.; Curioni, A.; Marangon, M.; Mattivi, F.; Arapitsas, P.; Moio, L.; et al. Diversity of Italian red wines: A study by enological parameters, color, and phenolic indices. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zou, M.; Tang, C.; Ao, H.; He, L.; Qiu, S.; Li, C. The insights into sour flavor and organic acids in alcoholic beverages. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Escobar, R.; Aliaño-González, M.J.; Cantos-Villar, E. Wine Polyphenol Content and Its Influence on Wine Quality and Properties: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyten, K.; Riou, C.; Blondin, B. The hexose transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae play different roles during enological fermentation. Yeast 2002, 19, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Moore, H.R.; Jelley, R.E.; Marangon, M.; Fedrizzi, B. The polysaccharides of winemaking: From grape to wine. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigou, P.; Mekoue, J.; Sieczkowski, N.; Doco, T.; Vernhet, A. Impact of industrial yeast derivative products on the modification of wine aroma compounds and sensorial profile. A review. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, P.; Braschi, G.; Siesto, G.; Patrignani, F.; Lanciotti, R. Role of Yeasts on the Sensory Component of Wines. Foods 2022, 11, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.-Q.; Fu, X.-M.; Dong, S.-S.; Xiao, D.-g.; Dong, J. Modulating acetate ester and higher alcohol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through the cofactor engineering. J. Industr. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.M.; Basso, T.O. Mitigating stress in industrial yeasts. Fungal Biol. 2020, 124, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, P.; Chen, D.; Howell, K. From the Vineyard to the Winery: How Microbial Ecology Drives Regional Distinctiveness of Wine. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Dang, X.-J.; Wang, Y.-B.; Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, W.-S. Diversity and composition of microbiota during fermentation of traditional Nuodeng ham. J. Microbiol. 2020, 59, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radecka, D.; Mukherjee, V.; Mateo, R.Q.; Stojiljkovic, M.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M.; Nielsen, J. Looking beyond Saccharomyces: The potential of non-conventional yeast species for desirable traits in bioethanol fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-R.; Ma, E.-B.; Yan, L.-Z.; Meng, H.; Du, X.-W.; Zhang, S.-W.; Quan, Z.-X. Bacterial and fungal diversity in the traditional Chinese liquor fermentation process. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 146, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, H.; Hawley, E.; Kopf, S.; DeScenzo, R.; Sealock, S.; Henick-Kling, T.; Hess, M. Insights into the bacterial community and its temporal succession during the fermentation of wine grapes. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.P.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Meng, X.Y.; Ji, Z.W.; Zhou, Z.L.; Ai-Lati, A. Bacterial succession and the dynamics of volatile compounds during the fermentation of Chinese rice wine from Shaoxing region. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, L. Environmental Factors Affecting Microbiota Dynamics during Traditional Solid-state Fermentation of Chinese Daqu Starter. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-R.; Hong, J.-L.; Xu, J.-X.; Li, L.; Guo, W.-L.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Bai, W.-D.; Rao, P.-F.; Ni, L.; et al. Exploring core functional microbiota responsible for the production of volatile flavour during the traditional brewing of Wuyi Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, N.; Zhao, X. Response mechanisms of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to the stress factors present in lignocellulose hydrolysate and strategies for constructing robust strains. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2022, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englezos, V.; Giacosa, S.; Rantsiou, K.; Rolle, L.; Cocolin, L. Starmerella bacillaris in winemaking: Opportunities and risks. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 17, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eardley, J.; Timson, D.J. Yeast cellular stress: Impacts on bioethanol production. Fermentation 2020, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conacher, C.; Luyt, N.; Naidoo-Blassoples, R.; Rossouw, D.; Setati, M.; Bauer, F.J. The ecology of wine fermentation: A model for the study of complex microbial ecosystems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 3027–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaud, N.; Giniés, C.; Navarro, D.; Fabre, N.; Crapart, S.; Gimbert, I.H.; Levasseur, A.; Raouche, S.; Sigoillot, J.-C. Exploring fungal biodiversity: Organic acid production by 66 strains of filamentous fungi. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2014, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Ren, Q. The changes of microbial diversity and flavor compounds during the fermentation of millet Huangjiu, a traditional Chinese beverage. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.; Tian, Y. Analysis of the formation mechanism of volatile and non-volatile flavor substances in corn wine fermentation based on high-throughput sequencing and metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, N.A.; Russo, N.; Foti, P.; Pino, A.; Caggia, C.; Randazzo, C.L. Inside Current Winemaking Challenges: Exploiting the Potential of Conventional and Unconventional Yeasts. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yi, H.; Wang, B.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, X.; Jiankun, X.; Jiang, L.; Shi, X. Microbial community composition and its role in volatile compound formation during the spontaneous fermentation of ice wine made from Vidal grapes. Proc. Biochem. 2020, 92, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styger, G.; Prior, B.; Bauer, F.F. Wine flavor and aroma. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Jiang, J.; Su, Y.; Yu, H.; Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Song, Y. Microbial community succession and volatile compounds changes during spontaneous fermentation of Cabernet Sauvignon (Vitis vinifera L.) under rain-shelter cultivation. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Q.; Wang, F.; Tang, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, B. A Snapshot of Microbial Succession and Volatile Component Dynamics of Marselan Wine in Xinjiang During Spontaneous Fermentation. Foods 2025, 14, 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060994
Fu Q, Wang F, Tang T, Liu Z, Wang L, Wang Q, Shi X, Wang B. A Snapshot of Microbial Succession and Volatile Component Dynamics of Marselan Wine in Xinjiang During Spontaneous Fermentation. Foods. 2025; 14(6):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060994
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Qingquan, Fangfang Wang, Tiantian Tang, Zimen Liu, Lilin Wang, Qingling Wang, Xuewei Shi, and Bin Wang. 2025. "A Snapshot of Microbial Succession and Volatile Component Dynamics of Marselan Wine in Xinjiang During Spontaneous Fermentation" Foods 14, no. 6: 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060994
APA StyleFu, Q., Wang, F., Tang, T., Liu, Z., Wang, L., Wang, Q., Shi, X., & Wang, B. (2025). A Snapshot of Microbial Succession and Volatile Component Dynamics of Marselan Wine in Xinjiang During Spontaneous Fermentation. Foods, 14(6), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060994





