Recent Advances in Physicochemical Control and Potential Green Ecologic Strategies Related to the Management of Mold in Stored Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Common Molds and Their Hazards During Grain Storage
2.1. Types of Molds That Contaminate Cereal Crops
2.2. Environmental Requirements for Mold Growth
2.3. The Detrimental Effects of Mold Infection and the Imperative for Prevention and Management
2.4. Techniques for Preventing and Controlling Mold
3. Physical Prevention and Control Technologies
3.1. Mechanical Ventilation Technology
3.2. Low-Temperature Plasma (LTP) Technology
3.3. Electron Beam Irradiation Technology
4. Chemical Prevention and Control Technologies
4.1. Solid Inhibitors for the Prevention and Control of Molds
4.2. Liquid Inhibitors for the Prevention and Control of Molds
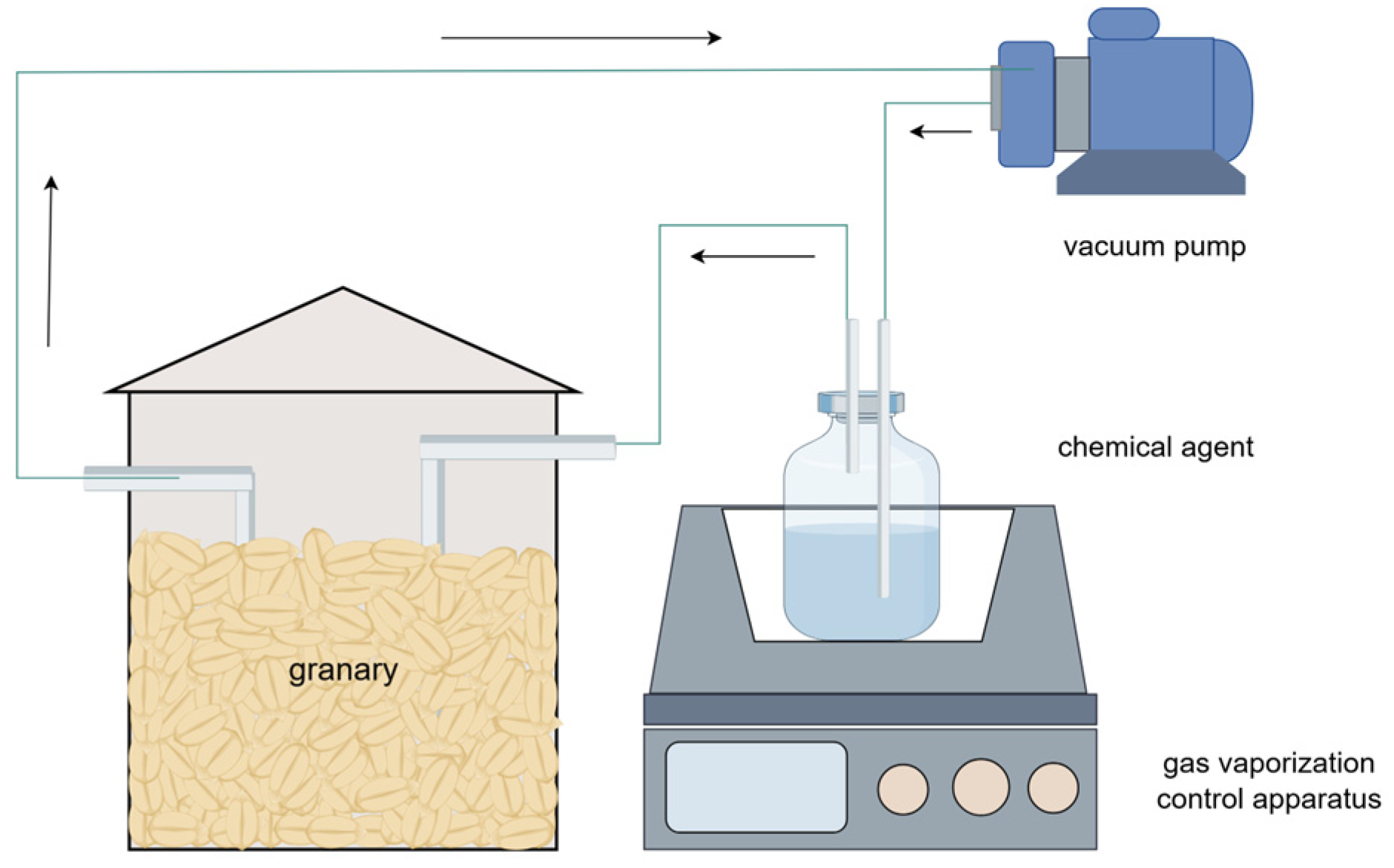
4.3. Chemical Gas Conditioning
5. Innovative Mold Inhibitors for Grain Storage
5.1. Microbial-Derived Mold Inhibitors
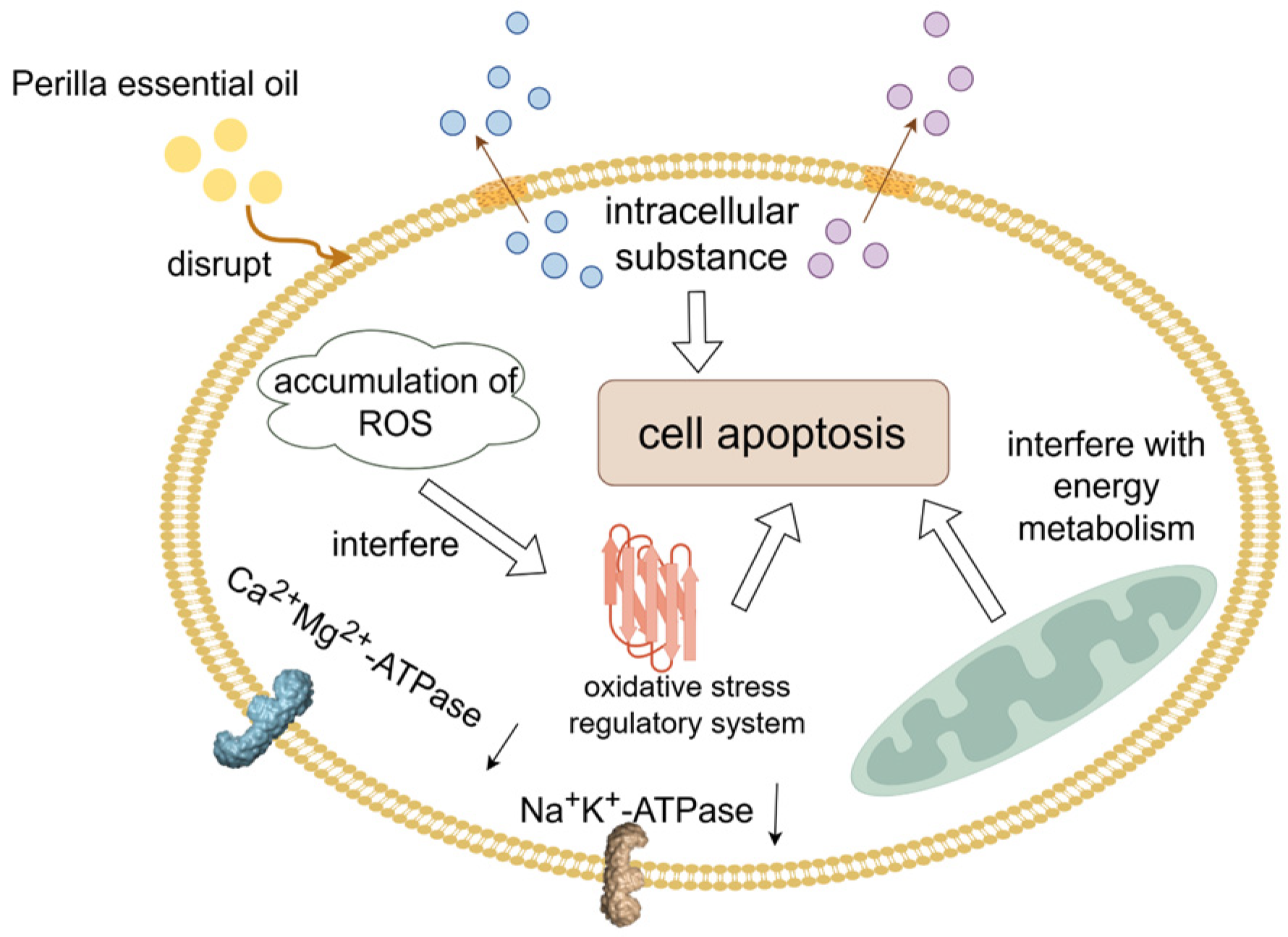
5.2. Plant-Derived Mold Inhibitors
6. Micro–Nano Prevention and Control Technology
7. Economic Costs of Prevention and Control Technologies
8. Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mannaa, M.; Kim, K.D. Influence of Temperature and Water Activity on Deleterious Fungi and Mycotoxin Production during Grain Storage. Mycobiology 2017, 45, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, M.; Jin, R.; Liu, Y.; Guan, E.; Mohamed, S.R.; Bian, K. Interactions among the composition changes in fungal communities and the main mycotoxins in simulated stored wheat grains. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Wu, F.; Hu, H.; Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, P.; Ling, J.; Cui, Y.; Ye, J.; Fang, G.; et al. Deciphering the Microbiological Mechanisms Underlying the Impact of Different Storage Conditions on Rice Grain Quality. Foods 2024, 13, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Lin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, G. Nutritional Changes and Early Warning of Moldy Rice under Different Relative Humidity and Storage Temperature. Foods 2022, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R. Mycotoxins in food: Occurrence, health implications, and control strategies-A comprehensive review. Toxicon 2024, 248, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sufar, E.K.; Bernhoft, A.; Seal, C.; Rempelos, L.; Hasanaliyeva, G.; Zhao, B.; Iversen, P.O.; Baranski, M.; Volakakis, N.; et al. Mycotoxin contamination in organic and conventional cereal grain and products: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleurat-Lessard, F. Integrated management of the risks of stored grain spoilage by seedborne fungi and contamination by storage mould mycotoxins—An update. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2017, 71, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, M.; Jin, R.; Liu, Y.; Guan, E.; Mohamed, S.R.; Bian, K. Analysis of wheat fungal community succession in traditional storage structures using Illumina MiSeq sequencing technology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 425, 110876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Z. Element tests and simulation of effects of vertical pressure on compression and mildew of wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Patriarca, A.; Magan, N. Alternaria in Food: Ecophysiology, Mycotoxin Production and Toxicology. Mycobiology 2015, 43, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwayemi, E.F.; Yu, J.; Rehrah, D.; Davis, S.S.; Williams, L.L. Inhibitory effects of essential oils on the growth of grain storage molds and the formation of aflatoxin in stored organic corn grains. JSFA Rep. 2024, 4, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrot–Rhodes, L.; Campo, E.; Poujaud, P. Review of monitoring systems for stored grains in a modified atmosphere. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almiman, B. Identifying the optimal temperature and water activity conditions of phytopathogenic fungi recovered from Al-Baha province. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 2024, 10, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuchi, C.G.; Ondari, E.N.; Eseoghene, I.J.; Twinomuhwezi, H.; Amagwula, I.O.; Morya, S. Fungal Growth and Mycotoxins Production: Types, Toxicities, Control Strategies, and Detoxification. In Fungal Reproduction and Growth; Sultan, S., Singh, G.K.S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zingales, V.; Taroncher, M.; Martino, P.A.; Ruiz, M.-J.; Caloni, F. Climate Change and Effects on Molds and Mycotoxins. Toxins 2022, 14, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, S.; Sanchis, V.; Sáenz, R.; Ramos, A.J.; Magan, N. Ecological determinants for germination and growth of some Aspergillus and Penicillium spp. from maize grain. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, S.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J.; Vinas, I.; Magan, N. Environmental factors, in vitro interactions, and niche overlap between Fusarium moniliforme, F. proliferatum, and F. graminearum, Aspergillus and Penicillium species from maize grain. Mycol. Res. 1998, 102, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, R. Ecology ang Control of Fusarium Species and Mycotoxins in Wheat Grain. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Bedfordshire, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Stuper-Szablewska, K.; Busko, M.; Goral, T.; Perkowski, J. The fatty acid profile in different wheat cultivars depending on the level of contamination with microscopic fungi. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Weng, X.; Shi, J.; Feng, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, G. A Monitoring Device and Grade Prediction System for Grain Mildew. Sensors 2024, 24, 6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.M.; Coradi, P.C.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; Teodoro, P.E.; Moraes, R.d.S.; Leal, M.M. Monitoring and predicting corn grain quality on the transport and post-harvest operations in storage units using sensors and machine learning models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.L.; Fernandes, J.O.; Cunha, S.C. Mycotoxins in cereals and related foodstuffs: A review on occurrence and recent methods of analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 96–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, X.; Yao, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, X. Numerical simulation and energy consumption analysis of ventilation patterns in grain silo. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 109, 102469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chu, F.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, J.; Mao, Y. Study on the Modified Ventilation Network on the Ventilation Effect and Ozone Migration Characteristics in Grain Pile. Buildings 2024, 14, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.B.; Jayas, D.S. 6-Grain storage and management. In Unit Operations in Food Grain Processing; Sunil, C.K., Athmaselvi, K.A., Venkatachalapathy, N., Anandharamakrishnan, C., Balasubramaniam, V.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M. Study on the Controlling Effectiveness of Mold in Stored Grain by Different Treatment Modes. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ekezie, F.-G.C.; Sun, D.-W.; Cheng, J.-H. A review on recent advances in cold plasma technology for the food industry: Current applications and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shao, L.; Jia, L.; Zou, B.; Dai, R.; Li, X.; Jia, F. Inactivation effects, kinetics and mechanisms of air- and nitrogen-based cold atmospheric plasma on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 79, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Nasiru, M.M.; Yan, W.; Zhuang, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, J. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma treatment on the structure and binding capacity of aroma compounds of myofibrillar proteins from dry-cured bacon. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezest, M.; Bulteau, A.-L.; Quinton, D.; Chavatte, L.; Le Bechec, M.; Cambus, J.P.; Arbault, S.; Negre-Salvayre, A.; Clement, F.; Cousty, S. Oxidative modification and electrochemical inactivation of Escherichia coli upon cold atmospheric pressure plasma exposure. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selcuk, M.; Oksuz, L.; Basaran, P. Decontamination of grains and legumes infected with Aspergillus spp. and Penicillum spp. by cold plasma treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5104–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zou, H.; Niu, M.; Zeng, Y.; Song, J. Modeling of low-temperature plasma inhibition and mechanism of Aspergillus flavus on corn kernels surface. CyTA-J. Food 2024, 22, 2338276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaneghah, A.M.; Moosavi, M.H.; Oliveira, C.A.F.; Vanin, F.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Electron beam irradiation to reduce the mycotoxin and microbial contaminations of cereal-based products: An overview. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Karim, A.A. Impact of Radiation Processing on Starch. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009, 8, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L. Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation on Storage Quality and Starch Properties of Rice with High Moisture Content. Master’s Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Federighi, M. Ionizing radiation as a food preservation method: State of the art. Rev. Med. Veterinaire 2019, 170, 58–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S.-E. Antifungal and antiaflatoxigenic properties of naphthoquinones toward Aspergillus flavus and their mode of inhibitory action on aflatoxin biosynthesis. Food Control 2021, 119, 107506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocloo, F.C.K.; Odai, B.T.; Darfour, B.; Mahami, T.; Armah, J.O.; Ayeh, E.A.; Adjei, I.; Basugilo, J.; Asomaniwaa, S.; Gryczka, U.; et al. Microbial quality and Aflatoxin levels of sorghum grains (Sorghum bicolor) irradiated with gamma rays, low energy electron beam (LEEB) and high energy electron beam (HEEB). Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2024, 216, 111474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, X.; Matinfar, G.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Singh, A.; Pratap-Singh, A. Emergence of cold plasma and electron beam irradiation as novel technologies to counter mycotoxins in food products. World Mycotoxin J. 2021, 14, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Li, L.; Shang, F.; Xie, Y.; Duan, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Study on antibacterial mechanism of electron beam radiation on Aspergillus flavus. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipley, J.R. Sodium Benzoate and Benzoic Acid. In Antimicrobials in Food, 4th ed.; Davidson, P.M., Taylor, T.M., David, J.R.D., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Activity and safety evaluation of natural preservatives. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Dong, Z.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. An evaluation of the effectiveness of four chemical additives on the fermentation characteristics, in vitro digestibility and aerobic stability of total mixed ration silage based on soy sauce residue. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 109, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; He, L.; Liu, C. Control of grey mould by sodium diacetate treatments and its effects on postharvest quality of ‘Red Globe’ grapes. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 125, 102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Malo, A.; Barreto-Valdivieso, J.; Palou, E.; Martin, F.S. Aspergillus flavus growth response to cinnamon extract and sodium benzoate mixtures. Food Control 2007, 18, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijksterhuis, J.; Kleinhoven, P.; van Kuijk, S.; Wolters, A.H.G.; Bruinenberg, P.G. Synergistic antifungal effects of the preservative ammonium propionate and medium chain fatty acids against dormant and germinating conidia, germ tubes and hyphae of Aspergillus chevalieri, a feed spoilage fungus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 422, 110802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, B.A.; Jooyandeh, H.; Vasiee, A.; Zeraatpisheh, F. Evaluation of anti-yeast metabolites produced by Lactobacillus strains and their potential application as bio-preservatives in traditional yogurt drink. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 188, 115428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaei, V.; Pilevar, Z.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Hosseini, H. Propionic Acid: Method of Production, Current State and Perspectives. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 58, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Shi, T.; Qi, C.; Huang, Z. Application of phosphine transverse circumfluent fumigation in paddy warehouse. Sci. Technol. Cereals Oils Foods (Chin. Ed.) 2015, 23, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Hu, J.; Hu, Y.; Pang, X.; Hu, W. Antimicrobial effect of different liquid mold inhibitors and their application in pellet feed. Cereal Feed. Ind. (Chin. Ed.) 2017, 12, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, E.; Gürakan, G.C.; Bayindirli, A. Effect of controlled atmosphere storage, modified atmosphere packaging and gaseous ozone treatment on the survival of Salmonella Enteritidis on cherry tomatoes. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.D.; Murphy, P.T.; Leandro, L.F.; Bern, C.J.; Beattie, S.E.; van Leeuwen, J. Mycoflora of high-moisture maize treated with ozone. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2013, 55, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hui, S.; Huang, H.; Liu, R.; Wang, S.; Huang, C. Antimicrobial mechanism of chlorine dioxide and its impacts on postharvest management in horticultural produce: A review. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 213, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, X. Effects of Ozone Treatment on Color of Wheat Flour. Cereal Feed. Ind. (Chin. Ed.) 2008, 5, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.; Zaritzky, N.; Graiver, N. Ozone treatment of meat and meat products: A review. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 1351801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H. Effects of Ozone Treatment on Microorganisms and Mycotoxins in Stored Corn. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Ning, H.; Xu, R.; Gao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Ke, Y.; Sun, Q. Inhibitory effect on the growth and aflatoxin-production of Aspergillus flavus by ClO2 and its application in corn of high water content. China Meas. Test (Chin. Ed.) 2017, 43, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves-Lopez, C.; Serio, A.; Gianotti, A.; Sacchetti, G.; Ndagijimana, M.; Ciccarone, C.; Stellarini, A.; Corsetti, A.; Paparella, A. Diversity of food-borne Bacillus volatile compounds and influence on fungal growth. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C. Study on the Prevention and Control of Bacillus sp. Volatile Substances on Paddy Rice Mildew. Master’s Thesis, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, L.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Li, W.; Wang, A.; Song, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. Effects of Volatile Organic Compounds from Streptomyces alboflavus TD-1 against Aspergillus flavus Growth and Aflatoxin Production. Food Sci. (Chin. Ed.) 2021, 42, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, A.; Li, C.; Tian, P.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Hu, Y. Expression and purification of recombinant puroindoline A protein in Escherichia coli and its antifungal effect against Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 9515–9527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W. The Study of Antifungal Activity of Recombinant Protein Puroindoline A on Grain Molds and Its Stability. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, A.; Song, M.; Zhang, J. Current Strategies in Controlling Aspergillus flavus and Aflatoxins in Grains during Storage: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E. Biocontrol of Aflatoxin-Producing Aspergillus flavus ATCC 22546 by a Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus ATCC 9643. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S. Research on the Biological Diversity of Aspergillus flavus Isolated from Stored Paddy in Southern China and Aflatoxin Biocontrol Technology. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, Nanjing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Liu, F. Perilla frutescens essential oil as a potential fumigant against quality deterioration of post-harvested rice caused by Aspergillus flavus. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Netala, V.R.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Perilla frutescens: A Rich Source of Pharmacological Active Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z. Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Perilla Frutescens Essential Oil on Aspergillus flavus. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, A.; Wu, H.; Ma, F.; Tan, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, W. The antifungal activity of cinnamaldehyde in vapor phase against Aspergillus niger isolated from spoiled paddy. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 159, 113181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, A.; Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Tan, S.; Wu, Y.; Yin, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, G.; Qiu, W. New insights into the persistent effect of transient cinnamaldehyde vapor treatment on the growth and aflatoxin synthesis of Aspergillus flavus. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, A.; Tan, L.; Tan, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, W. The Temporal Dynamics of Sensitivity, Aflatoxin Production, and Oxidative Stress of Aspergillus flavus in Response to Cinnamaldehyde Vapor. Foods 2023, 12, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, M.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y. Comparative investigation of key aroma terpenoids of Litsea cubeba essential oil by sensory, chromatographic, spectral and molecular studies. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 176, 114519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwell, I. Backhousia citriodora F. Muell. (Lemon Myrtle), an Unrivalled Source of Citral. Foods 2021, 10, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Ye, S.; Qu, G.; Ba, L. Inhibitory effect and action mechanism of citral against black rot in pitaya fruit. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 131, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Study on Regulation of Citral on the Growth of Fusarium graminearum and Mildew Control in Wheat. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Zhai, H.; Cai, J.; Hu, Y. Linalool, the main volatile constituent from Zanthoxylum schinifolium pericarp, prevents growth of Aspergillus flavus in post-harvest grains. Food Control 2022, 137, 108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Zhai, H.; Cai, J.; Hu, Y. Mechanisms underlying the inhibitory effects of linalool on Aspergillus flavus spore germination. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6625–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. Study on the Inhibitory Effects of Aspergillus flavus Growth by 1-octanol and 1-nonanol. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Study on the Growth Inhibition of Aspergillus flavus by Hexanal and Heptanal. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liang, Z.; Wang, L.; Qi, M.; Luo, Z.; Li, L. Microencapsulation Delivery System in Food Industry-Challenge and the Way Forward. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 7531810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.S.; Veloso, C.M. Microencapsulation of natural dyes with biopolymers for application in food: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.; Oliveira, M.C.; Marques, A.C.; dos Santos, R.G.; Serrano, C. Microencapsulation of Essential Oils and Oleoresins: Applications in Food Products. Foods 2024, 13, 3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarone, A.G.; Betim Cazarin, C.B.; Marostica Junior, M.R. Anthocyanins: New techniques and challenges in microencapsulation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.; Meghwal, M.; Das, K. Microencapsulation: An overview on concepts, methods, properties and applications in foods. Food Front. 2021, 2, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C. Preparation and Antifungal Activity of Essential Oil-Loaded Nanoparticle. Master’s Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]



| Technology | Consumable Costs (Euro/kg) | Instrument Costs (Euro/Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Microencapsulation | chitosan: 1.31–6.54; carvacrol: 39.22–78.43 | - |
| Mechanical ventilation | - | ventilator: 261.44–1307.19 |
| Solid mold inhibitors | benzoic acid: 1.05–1.91; sorbic acid: 2.61–3.92; sodium diacetate: 1.31–1.96; | - |
| Liquid mold inhibitors | propionic acid: 1.31–1.96; hexanal: 3.92–6.54; n-hexanol: 2.61–4.58 | - |
| Chemical gas conditioning | - | medium-sized ozone generator: 6535.95–26,143.79; medium-sized chlorine dioxide generator: 2614.38–13,071.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sha, T.; Lu, Y.; He, P.; Hassan, M.M.; Tong, Y. Recent Advances in Physicochemical Control and Potential Green Ecologic Strategies Related to the Management of Mold in Stored Grains. Foods 2025, 14, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060961
Sha T, Lu Y, He P, Hassan MM, Tong Y. Recent Advances in Physicochemical Control and Potential Green Ecologic Strategies Related to the Management of Mold in Stored Grains. Foods. 2025; 14(6):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060961
Chicago/Turabian StyleSha, Tianyu, Yujie Lu, Peihuan He, Md Mehedi Hassan, and Yehan Tong. 2025. "Recent Advances in Physicochemical Control and Potential Green Ecologic Strategies Related to the Management of Mold in Stored Grains" Foods 14, no. 6: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060961
APA StyleSha, T., Lu, Y., He, P., Hassan, M. M., & Tong, Y. (2025). Recent Advances in Physicochemical Control and Potential Green Ecologic Strategies Related to the Management of Mold in Stored Grains. Foods, 14(6), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060961





