Explore the Contamination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (ARB) of the Processing Lines at Typical Broiler Slaughterhouse in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction of Samples
2.3. Qualitative and Quantitative PCR of ARGs and intI 1
2.4. Microbial Community Analysis
2.5. Screening and Antibiotic Resistance Test of Foodborne Pathogens
2.6. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
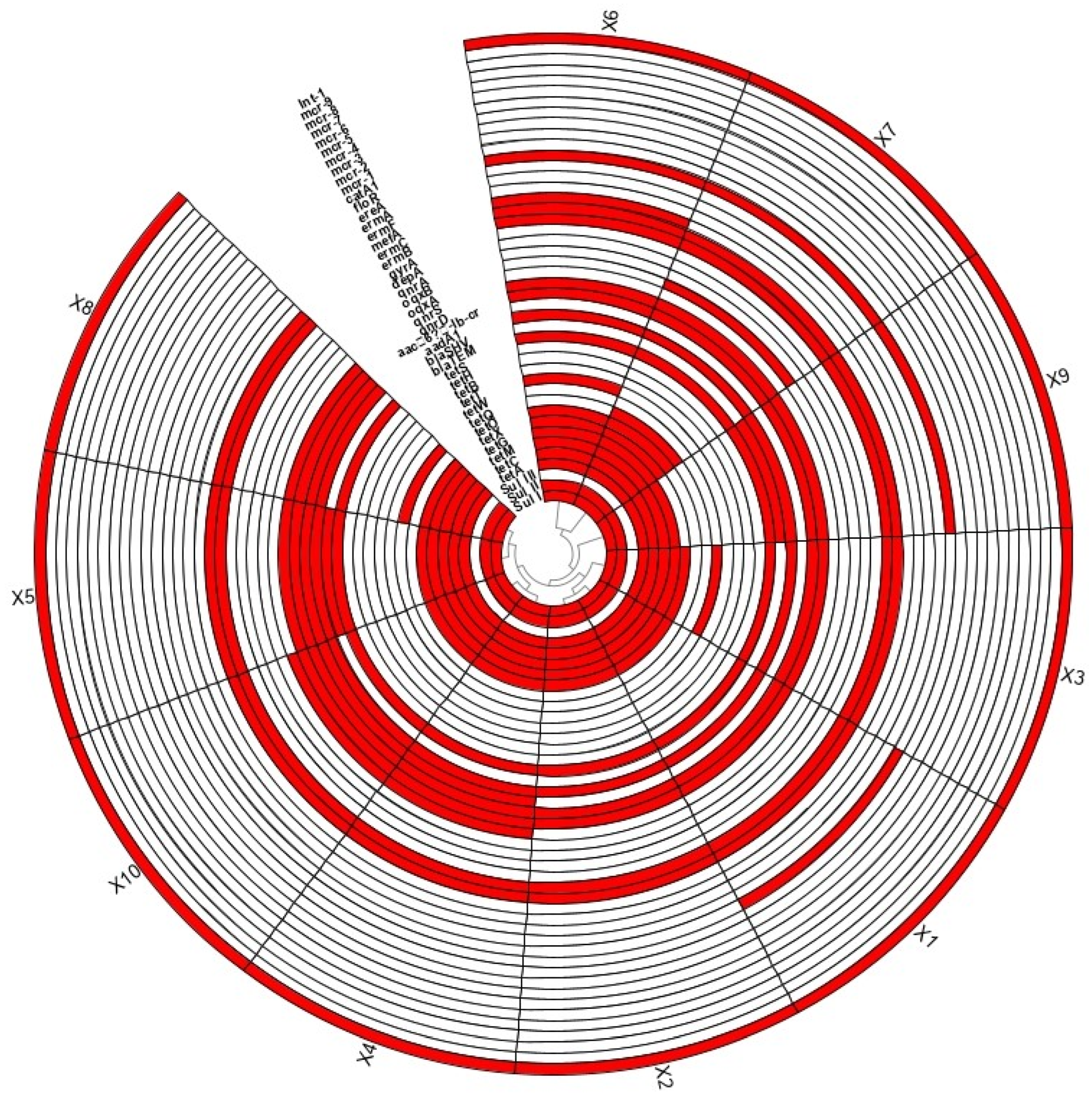
3.1. Pollution of ARGs
3.2. Transmission Patterns of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Production Chain of Broiler Slaughtering and Processing
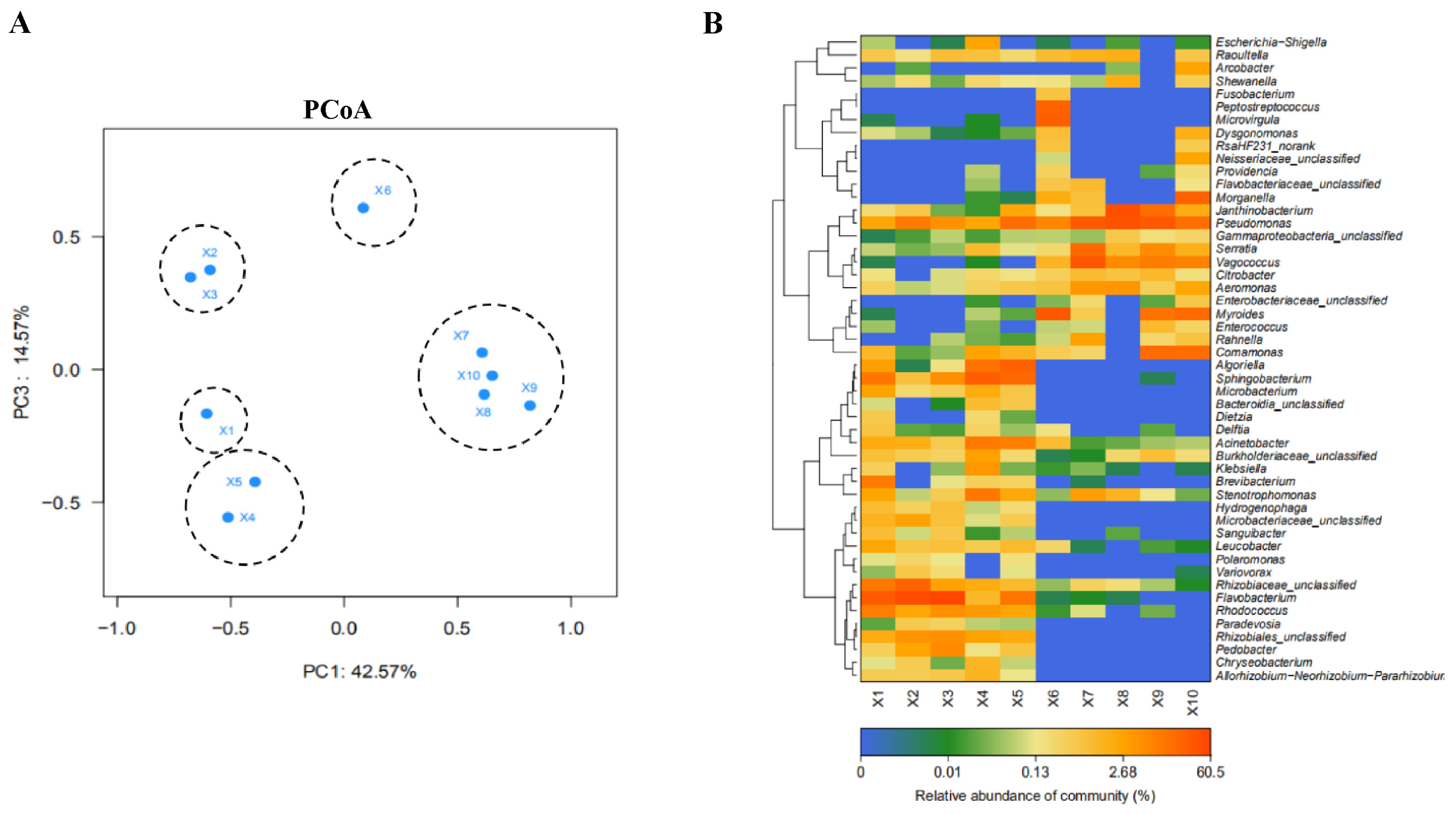
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Microbial Community at Different Slaughtering Links
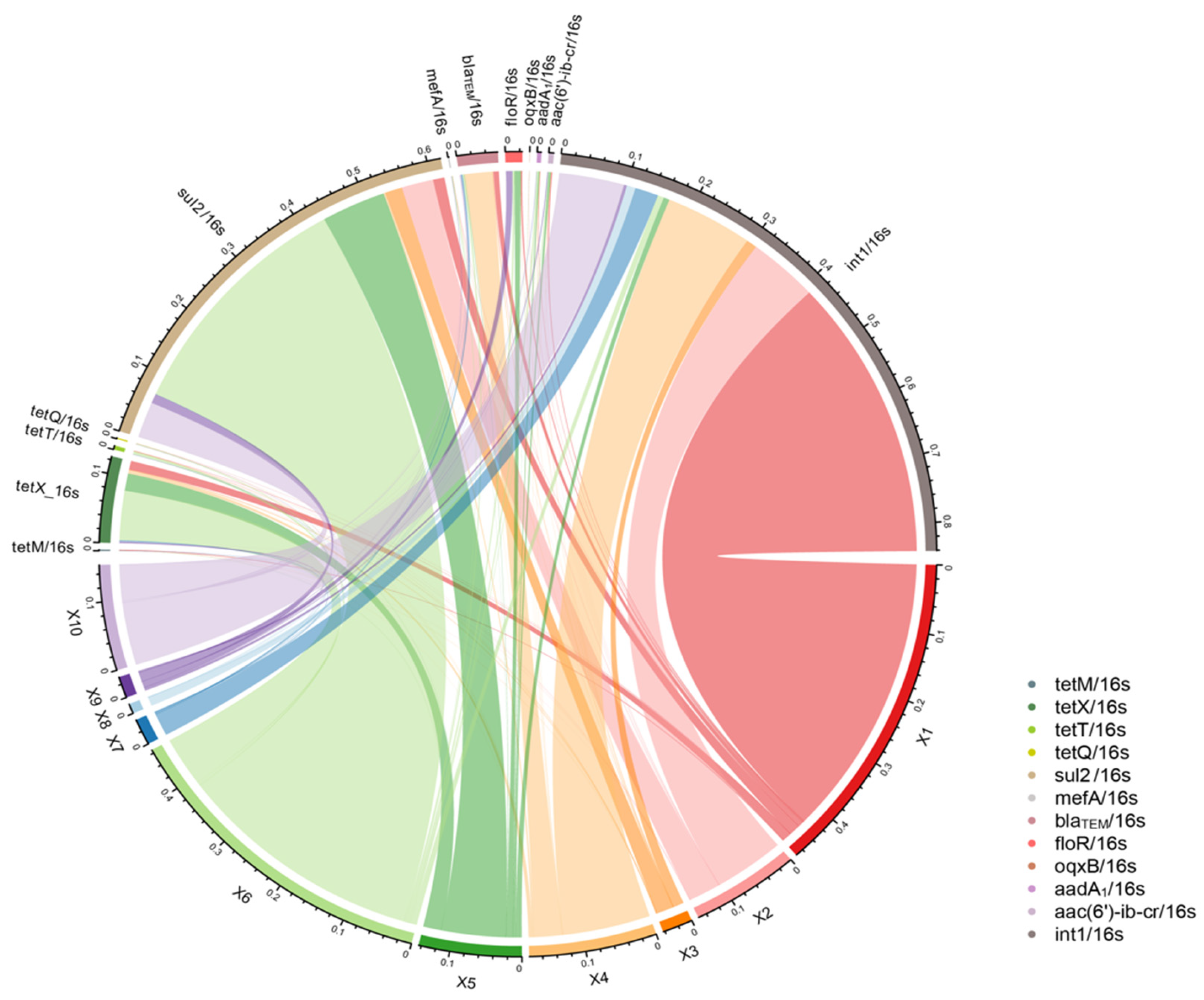
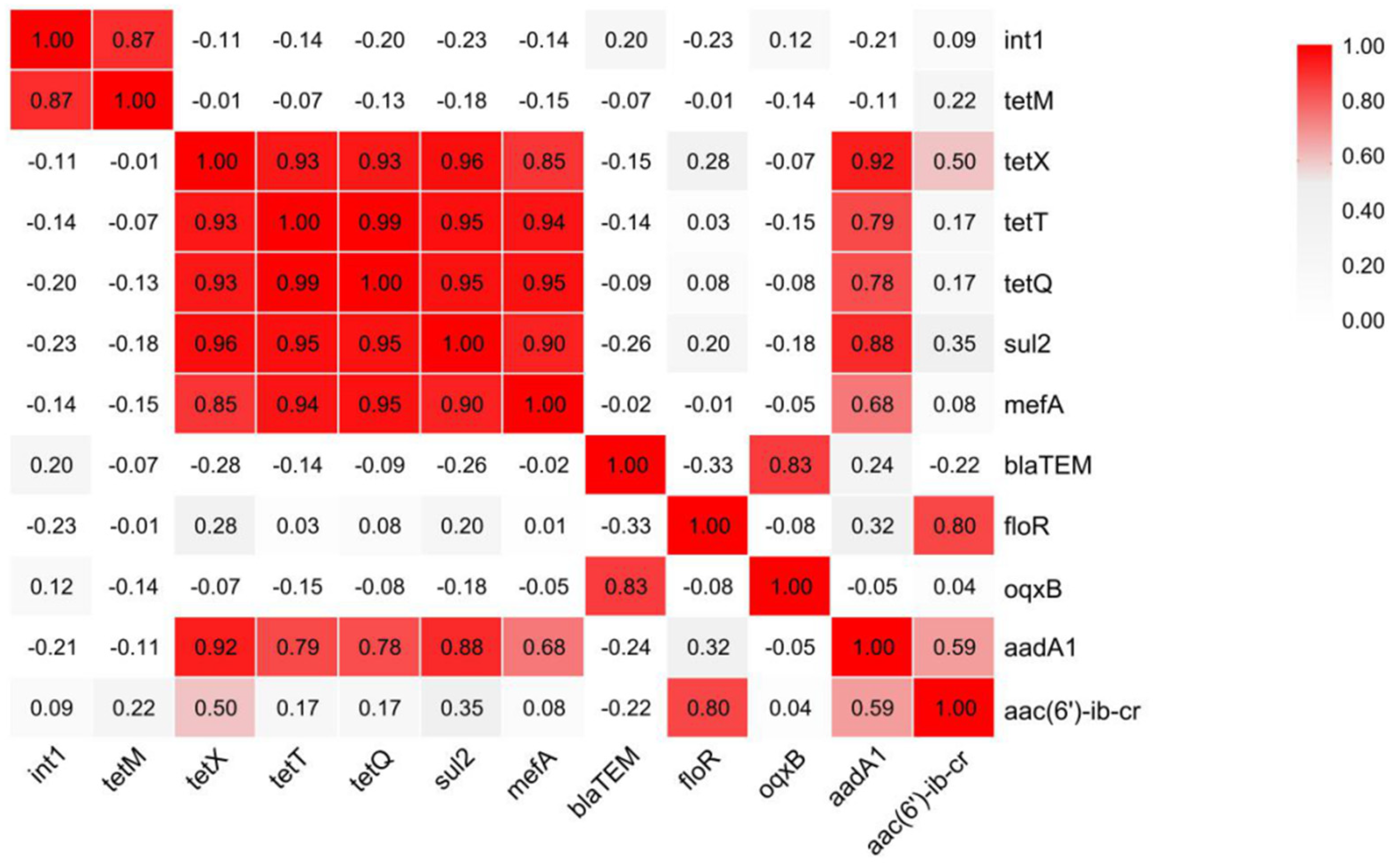
3.4. Analysis of Potential Hosts of ARGs and intI 1
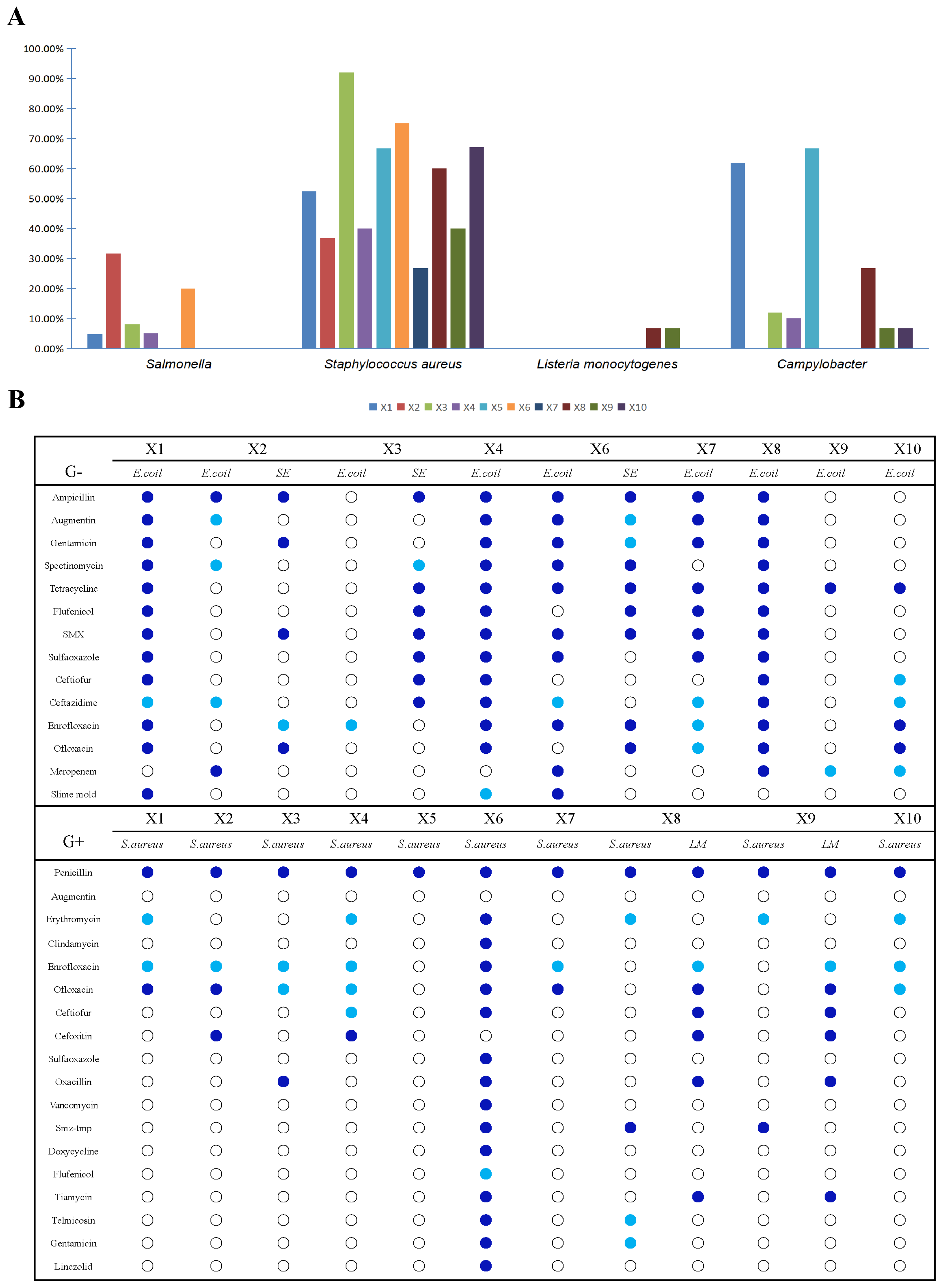
3.5. Contamination with Food-Borne Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in the Production Chain of Broiler Slaughtering and Processing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241564748 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance in the 21st Century. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2014, 6, S14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Jang, K.-M.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, L.-W.; Lee, S.H. Transmission of antibiotic resistance genes through mobile genetic elements in Acinetobacter baumannii and gene-transfer prevention. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.-N.; Gaston, J.M.; Dai, C.L.; Zhao, S.; Poyet, M.; Groussin, M.; Yin, X.; Li, L.-G.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Topp, E.; et al. An omics-based framework for assessing the health risk of antimicrobial resistance genes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhong, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, T.; Gu, Y.; Li, M.; Miao, X.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Xu, W.; et al. Metagenomic profiling uncovers microbiota and antibiotic resistance patterns across human, chicken, pig fecal, and soil environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.-L.; Shao, M.-F.; Luo, Y.; Dong, Y.-F.; Ouyang, F.; Dong, W.-Y.; Li, J. Airborne bacterial contaminations in typical Chinese wet market with live poultry trade. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theophilus, R.J.; Taft, D.H. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes (ARGs), the Gut Microbiome, and Infant Nutrition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebmeyer, S.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. A framework for identifying the recent origins of mobile antibiotic resistance genes. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.; Kaur, P. Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria: Relationships Between Resistance Determinants of Antibiotic Producers, Environmental Bacteria, and Clinical Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Han, L.; Zhang, H.; Long, Z.; Cai, L.; Yu, Y. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and human pathogenic bacteria from a pig feedlot to the surrounding stream and agricultural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinroth, M.D.; Thomas, K.M.; Doster, E.; Vikram, A.; Schmidt, J.W.; Arthur, T.M.; Wheeler, T.L.; Parker, J.K.; Hanes, A.S.; Alekoza, N.; et al. Resistomes and microbiome of meat trimmings and colon content from culled cows raised in conventional and organic production systems. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Klümper, U.; Shi, L.; Ye, L.; Li, M. From Pig Breeding Environment to Subsequently Produced Pork: Comparative Analysis of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Bacterial Community Composition. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, W.; Wang, J.; Pan, X.; Qiang, Z. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and their potential removal by on-farm treatment processes in nine swine feedlots in Shandong Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Kong, L.; Gao, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X. A Review of Current Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics in Food Animals. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 822689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-C.; Feng, W.-Q.; Han, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chen, T.; Wei, Y.-Y.; Gillings, M.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Chen, H. Prevalence and transmission of antibiotic resistance and microbiota between humans and water environments. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Pang, L.; Lai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Gan, Y.; et al. The hidden threat: Comprehensive assessment of antibiotic and disinfectant resistance in commercial pig slaughterhouses. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlet, J. The gut is the epicentre of antibiotic resistance. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2012, 1, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lai, H.; Zou, L.; Yin, S.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Xia, X.; Hu, K.; He, L.; Zhou, K.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance and resistance genes in Salmonella strains isolated from broiler chickens along the slaughtering process in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 259, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, X.-X.; Miao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, T. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes and their associations with bacterial community in livestock breeding wastewater and its receiving river water. Water Res. 2017, 124, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Yu, Y.; Diao, J.; Gong, X.; Li, J.; Sun, Y. Exploring the persistence and spreading of antibiotic resistance from manure to biocompost, soils and vegetables. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. Antibiotic resistance in the environment: A link to the clinic? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Avillan, J.J.; Call, D.R.; Davis, M.; Sischo, W.M.; Zhang, A. Dairy farm soil presents distinct microbiota and varied prevalence of antibiotic resistance across housing areas. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaire, T.N.; Odland, C.; Zhang, B.; Slizovskiy, I.; Jorgenson, B.; Wehri, T.; Meneguzzi, M.; Wass, B.; Schuld, J.; Hanson, D.; et al. Slaughtering processes impact microbial communities and antimicrobial resistance genes of pig carcasses. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, E.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Thissen, J.; van Asselt, E.D. Farm and slaughterhouse characteristics affecting the occurrence of Salmonella and Campylobacter in the broiler supply chain. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Production of Poultry Meat Worldwide from 1990 to 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/237637/production-of-poultry-meat-worldwide-since-1990/ (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. China—Poultry and Products Annual. Available online: https://fas.usda.gov/data/china-poultry-and-products-annual-7 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Pan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Hao, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, Y. The fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in Large-Scale chicken farm Environments: Preliminary view of the performance of National veterinary Antimicrobial use reduction Action in Guangdong, China. Environ. Int. 2024, 191, 108974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Mo, C.; Huang, F.; Liao, X.; Yang, Y. Microbial metabolism affects the antibiotic resistome in the intestine of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, R.; Ghanbari, M.; Antonissen, G.; Schatzmayr, G.; Duchateau, L.; Haesebrouck, F.; Garmyn, A.; Devreese, M. Dose-dependent impact of enrofloxacin on broiler chicken gut resistome is mitigated by synbiotic application. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 869538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpomasse, C.C.; Oke, O.E.; Houndonougbo, F.M.; Tona, K. Broiler production challenges in the tropics: A review. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Fegan, N.; Kocharunchitt, C.; Bowman, J.P.; Duffy, L.L. Changes of the bacterial community diversity on chicken carcasses through an Australian poultry processing line. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Vu, H.P.; Nguyen, L.N.; Wang, Q.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Donner, E.; Yin, H.; Nghiem, L.D. Monitoring antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment: Current strategies and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, M.; Shintani, M. Microbial evolution through horizontal gene transfer by mobile genetic elements. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wei, M.; Li, F.; Wu, C.; Yi, S.; Tian, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H. Diffusion and enrichment of high-risk antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) via the transmission chain (mulberry leave, guts and feces of silkworm, and soil) in an ecological restoration area of manganese mining, China: Role of heavy metals. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Yuan, T.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, S.; Qu, X.; Lu, P.; Feng, Q. Impact factors of the accumulation, migration and spread of antibiotic resistance in the environment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 43, 1741–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos Calero, G.; Caballero Gómez, N.; Benomar, N.; Pérez Montoro, B.; Knapp, C.W.; Gálvez, A.; Abriouel, H. Deciphering Resistome and Virulome Diversity in a Porcine Slaughterhouse and Pork Products Through Its Production Chain. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 4789.17-2003; Microbiology Inspection of Food Hygiene Inspection of Meat and Meat Products. Ministry of Health of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Scott, G.; Ryder, D.; Buckley, M.; Hill, R.; Treagus, S.; Stapleton, T.; Walker, D.I.; Lowther, J.; Batista, F.M. Long Amplicon Nanopore Sequencing for Dual-Typing RdRp and VP1 Genes of Norovirus Genogroups I and II in Wastewater. Food Environ. Virol. 2024, 16, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 4789.30-2016; Food Safety National Standard Food Microbiology Test Listeria monocytogenes Test. State Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 4789.4-2016; National Standard for Food Safety Microbiology Inspection of Food Salmonella Inspection. State Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 4789.10-2016; National Standard for Food Safety Food Microbiological Test Staphylococcus aureus Test. State Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jia, M.; Sun, S.; Cao, J.; Xiong, W. Evolutions of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), class 1 integron-integrase (intI1) and potential hosts of ARGs during sludge anaerobic digestion with the iron nanoparticles addition. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Sun, C.; Zheng, J.; Wen, C.; Ji, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Z.; Yang, N. Efficacy of Fecal Sampling as a Gut Proxy in the Study of Chicken Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto Jimenez, C.E.; Keestra, S.; Tandon, P.; Cumming, O.; Pickering, A.J.; Moodley, A.; Chandler, C.I.R. Biosecurity and water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) interventions in animal agricultural settings for reducing infection burden, antibiotic use, and antibiotic resistance: A One Health systematic review. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e418–e434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dagan, T. The evolution of antibiotic resistance islands occurs within the framework of plasmid lineages. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Peng, F.; Gao, X.; Xiao, P.; Yang, J. Decoupling the Dynamics of Bacterial Taxonomy and Antibiotic Resistance Function in a Subtropical Urban Reservoir as Revealed by High-Frequency Sampling. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xu, T.; Sun, S.; Yan, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jia, J.; Dou, T. Antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria: Occurrence, spread, and control. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, S.; Queiroga, M.C.; Laranjo, M. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Meat and Meat Products: A One Health Perspective. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, R.; ShangGuan, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, H. Analysis of Antibiotic Resistance Genes, Environmental Factors, and Microbial Community From Aquaculture Farms in Five Provinces, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 679805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thames, H.T.; Fancher, C.A.; Colvin, M.G.; McAnally, M.; Tucker, E.; Zhang, L.; Kiess, A.S.; Dinh, T.T.N.; Sukumaran, A.T. The Prevalence of Salmonella and Campylobacter on Broiler Meat at Different Stages of Commercial Poultry Processing. Animals 2022, 12, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boubendir, S.; Arsenault, J.; Quessy, S.; Thibodeau, A.; Fravalo, P.; Thériault, W.P.; Fournaise, S.; Gaucher, M.-L. Salmonella Contamination of Broiler Chicken Carcasses at Critical Steps of the Slaughter Process and in the Environment of Two Slaughter Plants: Prevalence, Genetic Profiles, and Association with the Final Carcass Status. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture. Announcement No. 2513, Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: https://www.moa.gov.cn/xw/bmdt/201704/t20170414_5560977.htm (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Warmate, D.; Onarinde, B.A. Food safety incidents in the red meat industry: A review of foodborne disease outbreaks linked to the consumption of red meat and its products, 1991 to 2021. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 398, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, F.; Klaharn, K.; Pichpol, D.; Meeyam, T.; Harintharanon, T.; Lohaanukul, P.; Punyapornwithaya, V. Bacterial contamination of chicken meat in slaughterhouses and the associated risk factors: A nationwide study in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
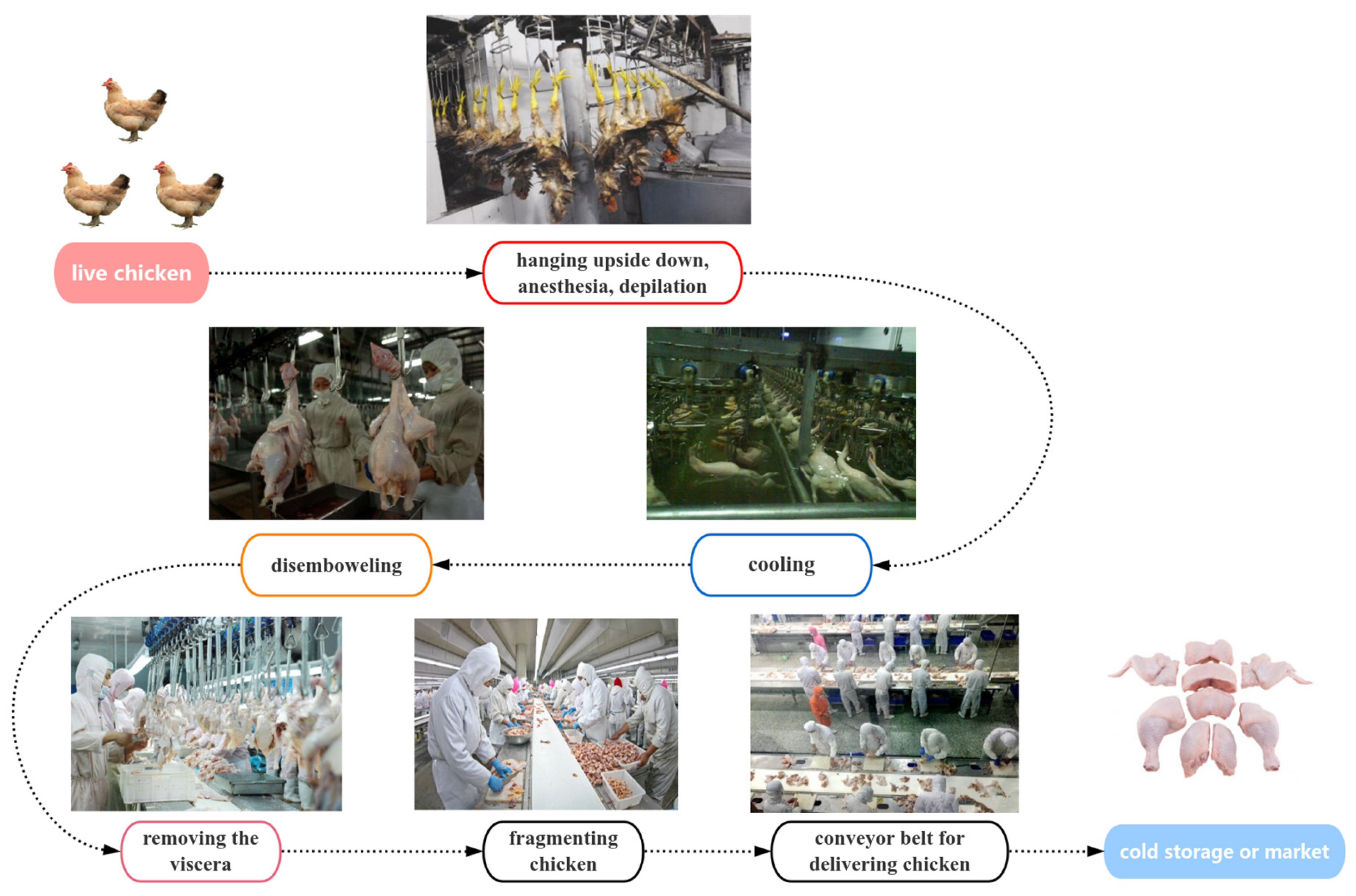
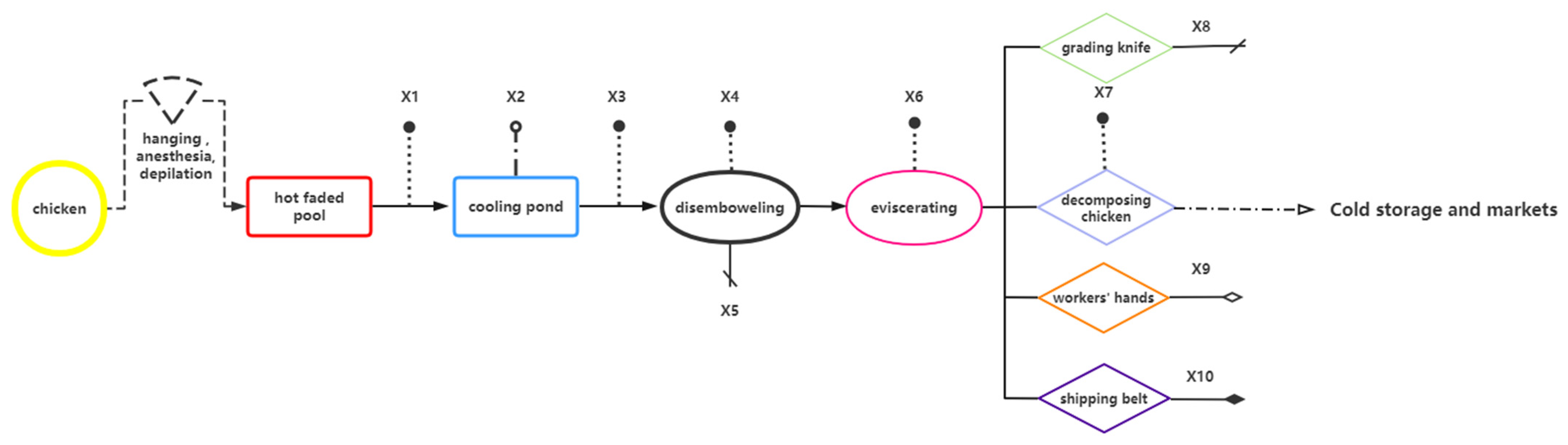

| Sample Name | Sampling Stage | Sampling Point | Number of Samples Collected |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | scalding | carcasses surface | 25 |
| X2 | cooling pool water | 25 | |
| X3 | carcasses surface after washing with cooling water | 25 | |
| X4 | disemboweling | carcasses surface | 25 |
| X5 | knife surface | 25 | |
| X6 | eviscerating | entrails surface | 25 |
| X7 | fragmenting | carcasses surface | 25 |
| X8 | knife surface | 25 | |
| X9 | hand surface | 25 | |
| X10 | conveyor surface | 25 | |
| total | / | 250 |
| Target Genes | Antibiotic | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| tetA | tetracyclines | GCGCGATCTGGTTCACTCG | 164 |
| AGTCGACAGYRGCGCCGGC | |||
| tetC | tetracyclines | CTTGAGAGCCTTCAACCCAG | 418 |
| ATGGTCGTCATCTACCTGCC | |||
| tetG | tetracyclines | GTCGATTACACGATTATGGC | 432 |
| CACTTGGCCGATCAGTTGA | |||
| tetM | tetracyclines | ACAGAAAGCTTATTATATAAC | 171 |
| GGCGTGTCTATGATGTTCAC | |||
| tetO | tetracyclines | ACGGARAGTTTATTGTATACC | 171 |
| TGGCGTATCTATAATGTTGAC | |||
| tetQ | tetracyclines | AGAATCTGCTGTTTGCCAGTG | 169 |
| CGGAGTGTCAATGATATTGCA | |||
| tetT | tetracyclines | AAGGTTTATTATATAAAAGTG | 169 |
| AGGTGTATCTATGATATTTAC | |||
| tetW | tetracyclines | AGGTGTATCTATGATATTTAC | 168 |
| GGGCGTATCCACAATGTTAAC | |||
| tetX | tetracyclines | GACCCGTTGGACTGACTATGG | 168 |
| CTTCCTGACCTGAACCTTTGTG | |||
| sul1 | sulfonamides | CGCACCGGAAACATCGCTGCAC | 163 |
| TGAAGTTCCGCCGCAAGGCTCG | |||
| sul2 | sulfonamides | TCCGGTGGAGGCCGGTATCTGG | 191 |
| CGGGAATGCCATCTGCCTTGAG | |||
| Sul III | sulfonamides | TCCGTTCAGCGAATTGGTGCAG | 128 |
| TTCGTTCACGCCTTACACCAGC | |||
| ermB | macrolides | CCGATACCGTTTACGAAATTGG | 190 |
| TAGCAAACCCGTATTCCACG | |||
| mefA | macrolides | AGTATCATTAATCACTAGTGC | 186 |
| TTCTTCTGGTACTAAAAGTGG | |||
| blaTEM | β-lactams | GCATCTTACGGATGGCATGA | 99 |
| CCTCCGATCGTTGTCAGAAGT | |||
| blaSHV | β-lactams | GGTTATGCGTTATATTCGCCTGTG | 861 |
| TTAGCGTTGCCAGTGCTCGATCA | |||
| oqxA | 4-quinolones | GATCAGTCAGTGGGATAGTTT | 627 |
| TACTCGGCGTTAACTGATTA | |||
| oqxB | 4-quinolones | TCCTGATCTCCATTAACGCCCA | 131 |
| ACCGGAACCCATCTCGATGC | |||
| qnrD | 4-quinolones | ACGACAGGAATAGCTTGGAAGG | 465 |
| TCAGCCAAAGACCAATCAAACG | |||
| floR | Florfenicol | CGGTCGGTATTGTCTTCACG | 171 |
| TCACGGGCCACGCTGTAT | |||
| aadA1 | aminoglycosides | AGCTAAGCGCGAACTGCAAT | 195 |
| TGGCTCGAAGATACCTGCAA | |||
| aac(6′)-ib-cr | aminoglycosides | GCTCTATGAGTGGCTAAATCGATC | 182 |
| GCAATGTATGGAGTGACGGAC | |||
| intI1 | class I integrons | CCTCCCGCACGATGATC | 280 |
| TCCACGCATCGTCAGGC | |||
| mcr-1 | polymyxins | ATGATGCAGCATACTTCTGTG | 1626 |
| TCAGCGGATGAATGCGGTG | |||
| mcr-2 | polymyxins | GATGGCGGTCTATCCTGTAT | 715 |
| AAGGCTGACACCCCATGTCAT | |||
| mcr-3 | polymyxins | ACCAGTAAATCTGGTGGCGT | 929 |
| AGGACAACCTCGTCATAGCA | |||
| mcr-4 | polymyxins | TTGCAGACGCCCATGGAATA | 1116 |
| GCCGCATGAGCTAGTATCGT | |||
| mcr-5 | polymyxins | GGACGCGACTCCCTAACTTC | 1644 |
| ACAACCAGTACGAGAGCACG | |||
| mcr-6 | polymyxins | GTCCGGTCAATCCCTATCTGT | 556 |
| ATCACGGGATTGACATAGCTAC | |||
| mcr-7 | polymyxins | AGGGGATAAACCGACCCTGA | 335 |
| TGATCTCGATGTTGGGCACC | |||
| mcr-8 | polymyxins | AACCGCCAGAGCACAGAATT | 667 |
| TTCCCCCAGCGATTCTCCAT | |||
| mcr-9 | polymyxins | GGTAGTTATTCCGCTGG | 1572 |
| TCGCGGTCAGGATTAAC | |||
| tetS | tetracyclines | GGTCAACGGCTTGTCTATGTA | 667 |
| CCAGGCTCTCATACTGAATGC | |||
| tetB | tetracyclines | AAAACTTATTATATTATAGTG | 169 |
| TGGAGTATCAATAATATTCAC | |||
| tetH | tetracyclines | CAGTGAAAATTCACTGGCAAC | 185 |
| ATCCAAAGTGTGGTTGAGAAT | |||
| qnrS | 4-quinolones | GCAAGTTCATTGAACAGGGT | 428 |
| TCTAAACCGTCGAGTTCGGCG | |||
| qnrA | 4-quinolones | AGGATTTCTCACGCCAGGATT | 124 |
| CCGCTTTCAATGAAACTGCAA | |||
| depA | 4-quinolones | CCAGCTCGGCAACTTGATAC | 570 |
| ATGCTCGCCTTCCAGAAAA | |||
| gyrA | 4-quinolones | CAAGAATCGTGGGTGATG | 351 |
| GTGGAATATTTGTCGCCA | |||
| ermC | macrolides | GAAATCGGCTCAGGAAAAGG | 293 |
| TAGCAAACCCGTATTCCACG | |||
| ermF | macrolides | TCTAGCAATGAGAATGAAGGT | 309 |
| ACTATAACGTGATGGTTGGGAGGGA | |||
| ermA | macrolides | AAGCGGTAAACCCCTCTGA | 190 |
| TTCGCAAATCCCTTCTCAAC | |||
| ereA | macrolides | CCTTCACATCCGGATTCGCTCGA | 420 |
| CTTCACATCCGGATTCGCTCGA | |||
| CatA1 | chloram phenicols | GGGTGAGTTTCACCAGTTTTGATT | 101 |
| CACCTTGTCGCCTTGCGTATA | |||
| 16S rDNA | - | TGTGTAGCGGTGAAATGCG | 140 |
| CATCGTTTACGGCGTGGAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Lu, F.; Zhao, H. Explore the Contamination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (ARB) of the Processing Lines at Typical Broiler Slaughterhouse in China. Foods 2025, 14, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061047
Ren L, Li Y, Ye Z, Wang X, Luo X, Lu F, Zhao H. Explore the Contamination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (ARB) of the Processing Lines at Typical Broiler Slaughterhouse in China. Foods. 2025; 14(6):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061047
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Lu, Ying Li, Ziyu Ye, Xixi Wang, Xuegang Luo, Fuping Lu, and Huabing Zhao. 2025. "Explore the Contamination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (ARB) of the Processing Lines at Typical Broiler Slaughterhouse in China" Foods 14, no. 6: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061047
APA StyleRen, L., Li, Y., Ye, Z., Wang, X., Luo, X., Lu, F., & Zhao, H. (2025). Explore the Contamination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (ARB) of the Processing Lines at Typical Broiler Slaughterhouse in China. Foods, 14(6), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061047






