Effects of Irradiation Combined with Partial Freezing Treatment on Texture, Flavor Compounds, and Storage Quality of Fermented Stinky Sea Bass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. FSSB Sample Preparation
2.3. Irradiation Dose Selection Criteria and Experimental Design
2.4. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Analysis
2.5. Histamine Content Analysis
2.6. Peroxide Value Content Analysis
2.7. Determination of Aerobic Plate Count
2.8. Coliform Determination
2.9. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.10. pH Analysis
2.11. Color Analysis
2.12. Cooking Loss Analysis
2.13. Free Amino Acid (FAA) Analysis
2.14. GC-IMS Analysis of FSSB
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
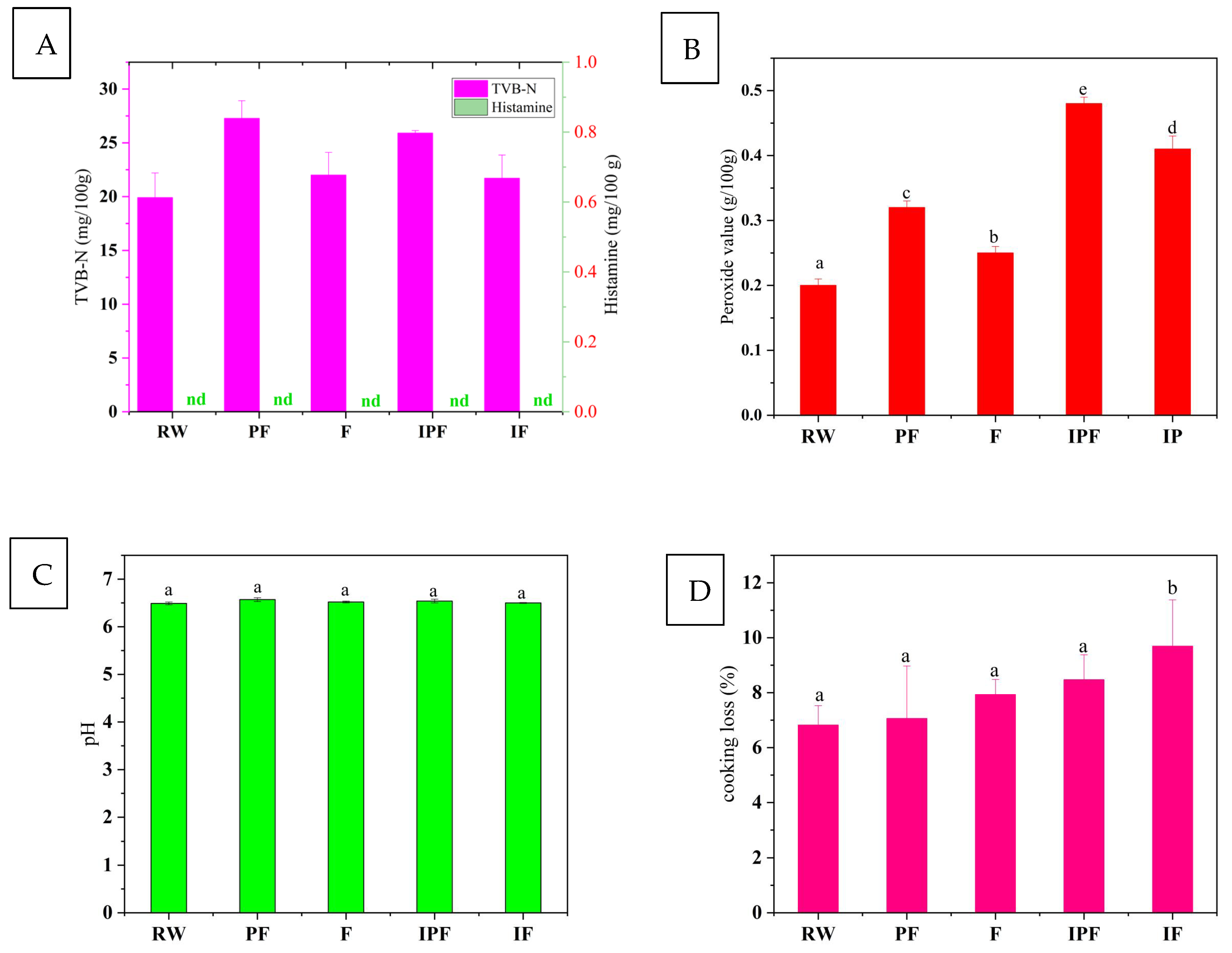
3.1. TVB-N Analysis of FSSB
3.2. Histamine Content Analysis
3.3. Peroxide Value Content Analysis
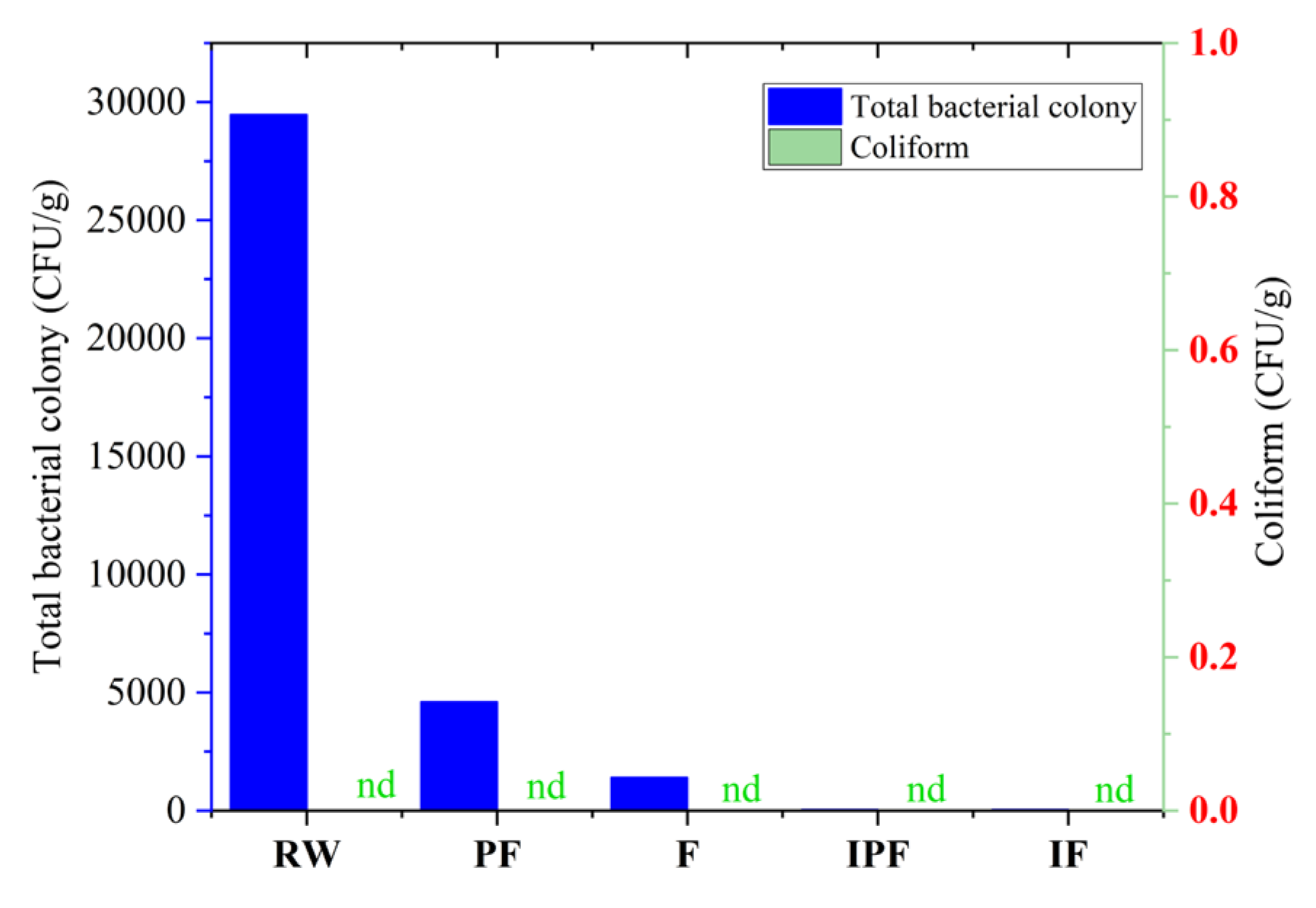
3.4. Determination of Total Bacterial Colony
3.5. Coliform Determination
3.6. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
3.7. pH Analysis
3.8. Color Analysis
3.9. Cooking Loss Analysis
3.10. Free Amino Acid (FAA) Analysis
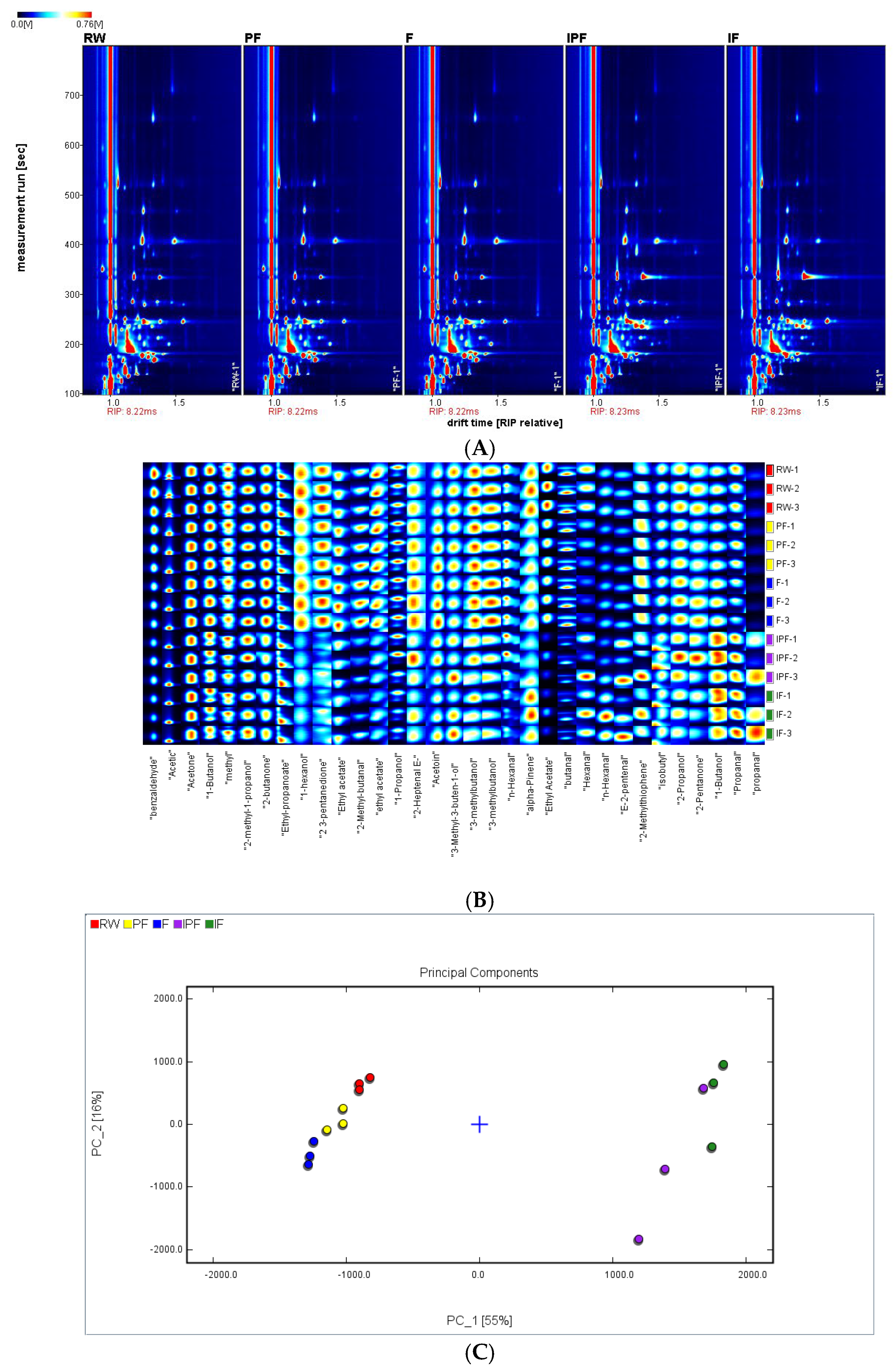
3.11. GC-IMS Analysis of FSSB
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.Y.; Zhou, W.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhu, J.S.; Sun, T.; Li, J.R.; Cheng, L. Synergistic effects of ε-polylysine hydrochloride and gallic acid on Shewanella putrefaciens and quality of refrigerated sea bass fillets. Food Control 2022, 139, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center, China Society of Fishery. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, A.; Barat, J.M.; Fernandez-Segovia, I.; Serra, J.A. Study of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) salting process: Kinetic and thermodynamic control. Food Control 2008, 19, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, F.; Kotan, G. Effects of different cooking methods and fat levels on the formation of heterocyclic aromatic amines in various fishes. Food Control 2016, 67, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Fernandez-Segovia, I.; Serra, J.A.; Barat, J.M. Development of a smoked sea bass product with partial sodium replacement. LWT 2010, 43, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Lipolysis and Lipid Oxidation in Perch during Curing and Air Drying Ripening. Food Sci. 2012, 33, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Yu, J.; Hu, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Yuan, Z.Z.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C.H. Development of novel fermented stinky sea bass and analysis of its taste active compounds, flavor compounds, and quality. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Feng, T.Y.; Yu, J.; Hu, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Jiang, X.M.; Zhang, T.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C.H. Development of room-temperature fermented stinky sea bass and novel insights into its physicochemical and flavor formation and microbial diversity. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.R.; Wu, Y.X.; Chen, J.W.; Xia, W.S.; Liao, E.; Wang, H.B. Effects of superchilling on quality of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): Water migration, biogenic amines accumulation, and nucleotides catabolism. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Maheswarappa, N.B. Superchilling of muscle foods: Potential alternative for chilling and freezing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2019, 59, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaale, L.D.; Eikevik, T.M. The development of ice crystals in food products during the superchilling process and following storage, a review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2014, 39, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaale, L.D.; Eikevik, T.M.; Rustad, T.; Kolsaker, K. Superchilling of food, a review. J. Food Eng. 2011, 107, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsson, H. Deep Chilling (Superchilling, Partial Freezing)—A Literature Survey; SIKs Service Series (30) Goteborg; SIK-The Swedish Food Institute; Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Magnussen, O.M.; Haugland, A.; Torstveit Hemmingsen, A.K.; Johansen, S.; Nordtvedt, T.S. Advances in superchilling of food-process characteristics and product quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; An, K.A.; Arshad, M.S.; Kwon, J.H. Effects of e-beam irradiation on amino acids, fatty acids, and volatiles of smoked duck meat during storage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2018, 47, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.S. Irradiation effects on meat flavor: A review. Meat Sci. 2009, 81, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.F.; Zhu, Y.K.; Xu, D.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W.G. Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation with Different Doses on Flavor of Lateolabrax japonicus Meat. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.J.; Huang, J.J.; Chen, Y.N.; Cai, J.; Li, H.L.; Zu, X.Y. Storage Quality of Electron Beam Irradiated Cooked Silver Carp. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Javanmard, M.; Rokni, N.; Bokaie, S.; Shahhosseini, G. Effects of gamma irradiation and frozen storage on microbial, chemical and sensory quality of chicken meat in Iran. Food Control 2006, 17, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 1256-2006; Frozen Aquatic Product Irradiation Sterilization Process Standards. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Wu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, D.X.; Zhang, J.X.; Chu, L.M.; Wang, T.T.; Jiang, W.; Sun, H.J.; Jin, S.L. Effect of Ultra High Pressure on the Bacterial Community Structure and Quality of Stinky Mandarin Fish. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- GB5009.228-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Volatile Salt Nitrogen in Food. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.208-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Biogenic Amines in Food. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.227-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Peroxide Value in Food. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB4789.2-2022; Food Microbiology Test-Determination of Aerobic Plate Count. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2022.
- GB4789.3-2016; Food Microbiology Test-Determination of Coliforms. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Xiao, H.; Li, N.N.; Yan, L.T.; Xue, Y. The Hydration Characteristics, Structural Properties and Volatile Profile of Squid (Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis) Mantle Muscle: Impacts of Steaming, Boiling and Sous-vide Cooking. Foods 2021, 10, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathare, P.B.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Said, F.A. Colour measurement and analysis in fresh and processed foods: A review. Food Boiprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.J.; Xue, C.H.; Sun, C.; Chen, L.P.; Sun, Z.K.; Wen, Y.Q.; Li, Z.J.; Chen, G.D.; Wei, Z.H.; Liu, H.Y. Impact of transportation and rehydration strategies on the physiological responses of clams (Ruditapes philippinarum). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 100976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB10136-2015; National Food Safety Standards Animal Aquatic Products. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Oyelese, O.A.; Sao, O.M.; Adeuya, M.A. Acidity/rancidity levels, chemical studies, bacterial count/flora of fermented and unfermented silver catfish (Chrysichthys nigrodigitatus). Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 4, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, I.D.; Mitch, W.E.; Sands, J.M. Urea and ammonia metabolism and the control of renal nitrogen excretion. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1444–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.N. Research on Keep Fresh Tedmology of Tilapia Fillets by Partial Freezing Combined with Modified Atmosphere; Hainan University: Haikou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.G.; Xu, D.L.; Lou, Q.M.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, C.; Shi, X.Y.; Shi, H.G. Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation on Sterilization and Preservation of Fresh Ostrea Plicatula. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.G.; Lin, C.X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Meng, J.; He, L.P.; Deng, L.; Zeng, X.F. Exploring the bacterial community for starters in traditional high-salt fermented Chinese fish (Suanyu). Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lv, M.C.; Mei, K.L.; Lu, J.F.; Yang, W.G. Effects of Electron Beam Irradiation on the Preservation and Quality of Sea Bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) Meat. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, X.Y.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, J.M.; Chen, Y.X.; Liao, T.; Xiong, G.Q. Effects of Different Doses of Electron Beam Irradiation on Sterilization and Quality of Semi-finished Products of Micropterus salmoides. Storage Process 2018, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.G.; Fjaera, S.O.; Skjervold, P.O. Salmon fillet texture is determined by myofiber-myofiber and myofiber-myocommata attachment. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, T.T.; Zheng, J.W.; Chen, S.G.; Jiang, Q.Q.; Liu, W.J.; Ye, X.Q.; Hu, Y.Q. Effect of Super-chilling and Frozen on the Meat Quality of Snakehead. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, P.L.; Hunecke, M.E. Correlations of sensory and instrumental evalutions of rosat beeef texture. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, L.; Purslow, P.P. The effect of ageing on the water-holding capacity of pork: Role of cytoskeletal proteins. Meat Sci. 2001, 58, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, J.H.; Xu, Y.S.; Xia, W.S.; Regenstein, J.M. Quality, functionality, and microbiology of fermented fish: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2020, 60, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.F.; Zhang, J.B.; Lin, X.P.; Han, J.; Dong, X.P.; Yang, S.; Yan, X.M.; Zhu, B.W. Metaproteomic analysis of microbiota in the fermented fish, Siniperca chuatsi. LWT 2017, 80, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Zhang, M. Non-volatile taste active compounds in the meat of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Casla, V.; León-González, M.E.; Pérez-Arribas, L.V.; Polo-Díez, L.M. Direct chiral determination of free amino acid enantiomers by two-dimensional liquid chromatography: Application to control transformations in E-beam irradiated foodstuffs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belitz, H.D.; Grosch, W.; Schieberle, P. Amino acids, peptides, proteins. In Food Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 8–91. [Google Scholar]
- Josephson, D.B.; Lindsay, R.C.; Stuiber, D.A. Enzyrnichydroperoxide initiated effects in fresh fish. J. Food Sci. 1987, 52, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB10781.2-2006; Mild Flavor Chinese Spirits. Chinese Standard Publisher: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Xu, Y.X.; Bai, X.T.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.L.; Li, X.P.; Li, J.R.; Yi, S.M.; Xie, J.; Guo, X.H. Changes of Flavor Compounds in Sea Bass during Steaming Process as Analyzed by Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
| Samples | Hardness (N) | Cohesiveness | Springiness (mm) | Gumminess (N) | Chewiness (mJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RW | 39.92 ± 3.32 b | 0.36 ± 0.01 a | 3.34 ± 0.85 b | 14.20 ± 1.58 b | 47.60 ± 14.03 b |
| PF | 35.45 ± 1.73 b | 0.38 ± 0.04 a | 2.35 ± 0.07 a | 13.59 ± 1.77 b | 31.99 ± 4.98 a |
| F | 36.44 ± 4.05 b | 0.38 ± 0.00 a | 2.40 ± 0.18 a | 13.90 ± 1.63 b | 33.60 ± 6.41 a |
| IPF | 31.79 ± 0.85 a | 0.45 ± 0.01 b | 3.17 ± 0.28 b | 14.38 ± 0.66 b | 45.78 ± 5.93 b |
| IF | 26.74 ± 1.70 a | 0.43 ± 0.04 b | 3.22 ± 0.70 b | 11.39 ± 0.57 a | 37.03 ± 10.06 a |
| Samples | L* | a* | b* | Whiteness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RW | 65.90 ± 2.13 b | −1.53 ± 0.78 a | 11.28 ± 0.87 b | 64.02 ± 1.93 b |
| PF | 65.86 ± 1.94 b | −1.30 ± 0.75 a | 11.68 ± 0.69 b | 63.87 ± 1.82 b |
| F | 65.51 ± 2.15 b | −1.26 ± 0.65 b | 11.51 ± 1.46 b | 63.57 ± 1.73 b |
| IPF | 63.74 ± 2.84 ab | −0.65 ± 1.26 a | 9.80 ± 1.40 a | 62.37 ± 2.64 b |
| IF | 63.47 ± 2.63 a | −1.37 ± 0.81 a | 11.52 ± 1.16 b | 61.62 ± 2.27 a |
| Items | Mouthfeel | RW | PF | F | IPF | IF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glu | umami | 25.47 ± 1.10 b | 19.00 ± 1.43 a | 20.15 ± 0.62 a | 14.71 ± 3.31 a | 15.66 ± 1.73 a |
| Asp | umami | 2.47 ± 0.58 a | 2.36 ± 0.05 a | 2.26 ± 0.65 a | 1.44 ± 0.04 a | 1.73 ± 0.34 a |
| Gly | sweet | 71.21 ± 1.45 a | 77.18 ± 9.80 a | 87.46 ± 11.18 a | 93.65 ± 5.69 a | 73.33 ± 9.35 a |
| Ser | sweet | 9.89 ± 0.23 a | 12.77 ± 0.73 b | 11.62 ± 1.30 ab | 13.78 ± 1.21 b | 10.91 ± 0.16 ab |
| Ala | sweet | 17.72 ± 0.62 a | 19.32 ± 0.85 a | 18.75 ± 1.14 a | 21.60 ± 6.29 a | 15.53 ± 1.25 a |
| Thr | sweet | 5.15 ± 0.69 a | 7.50 ± 1.00 a | 6.37 ± 0.35 a | 6.09 ± 0.41 a | 7.01 ± 1.15 a |
| Pro | sweet | 15.01 ± 0.35 a | 15.43 ± 3.66 ab | 15.67 ± 1.69 ab | 9.20 ± 0.11 a | 14.05 ± 0.76 a |
| Arg | sweet | 4.45 ± 1.41 ab | 5.24 ± 0.02 ab | 6.11 ± 0.64 b | 2.79 ± 0.40 a | 4.33 ± 0.87 ab |
| Tyr | bitter | 3.94 ± 1.03 a | 3.25 ± 0.18 a | 3.90 ± 1.25 a | 3.11 ± 0.35 a | 3.30 ± 0.25 a |
| Lys | bitter | 10.00 ± 3.27 a | 9.47 ± 1.36 a | 10.86 ± 0.41 a | 9.11 ± 1.54 a | 14.39 ± 2.14 a |
| Met | bitter | 2.99 ± 0.78 a | 3.74 ± 0.10 a | 3.60 ± 0.82 a | 4.06 ± 0.53 a | 3.64 ± 0.02 a |
| Phe | bitter | 9.80 ± 0.51 a | 9.71 ± 0.17 a | 9.97 ± 0.93 a | 6.81 ± 3.30 a | 4.93 ± 1.55 a |
| Val | bitter | 13.69 ± 4.06 a | 11.75 ± 0.51 a | 11.79 ± 0.70 a | 14.13 ± 2.33 a | 7.15 ± 1.61 a |
| His | bitter | 17.08 ± 0.21 a | 17.50 ± 0.89 a | 17.10 ± 2.54 a | 21.34 ± 3.41 a | 19.11 ± 0.35 a |
| Ile | bitter | 9.62 ± 0.36 a | 11.28 ± 0.49 a | 11.27 ± 0.85 a | 8.08 ± 3.69 a | 6.17 ± 1.68 a |
| Leu | bitter | 14.09 ± 0.70 a | 16.68 ± 0.72 a | 16.71 ± 1.58 a | 11.68 ± 5.53 a | 9.04 ± 2.72 a |
| Cys | sour | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.89 ± 0.05 b | 0.81 ± 0.03 b |
| Total umami amino acid | / | 27.95 ± 1.69 b | 21.35 ± 1.48 a | 22.41 ± 1.27 ab | 16.15 ± 3.35 a | 17.39 ± 2.07 a |
| Total pleasant tasting amino acid | / | 151.38 ± 6.43 a | 158.81 ± 17.53 a | 168.37 ± 17.58 a | 163.26 ± 17.46 a | 142.56 ± 15.61 a |
| Total FAA | / | 233.14 ± 3.06 a | 242.19 ± 21.96 a | 254.24 ± 27.43 a | 242.47 ± 38.21 a | 211.08 ± 25.94 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, H.; Feng, T.; Liu, H.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C. Effects of Irradiation Combined with Partial Freezing Treatment on Texture, Flavor Compounds, and Storage Quality of Fermented Stinky Sea Bass. Foods 2025, 14, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061035
Xiao H, Feng T, Liu H, Xue Y, Xue C. Effects of Irradiation Combined with Partial Freezing Treatment on Texture, Flavor Compounds, and Storage Quality of Fermented Stinky Sea Bass. Foods. 2025; 14(6):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061035
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Hong, Tingyu Feng, Hongying Liu, Yong Xue, and Changhu Xue. 2025. "Effects of Irradiation Combined with Partial Freezing Treatment on Texture, Flavor Compounds, and Storage Quality of Fermented Stinky Sea Bass" Foods 14, no. 6: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061035
APA StyleXiao, H., Feng, T., Liu, H., Xue, Y., & Xue, C. (2025). Effects of Irradiation Combined with Partial Freezing Treatment on Texture, Flavor Compounds, and Storage Quality of Fermented Stinky Sea Bass. Foods, 14(6), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061035





