Sex-Specific Biochemical and Histopathological Effects of Chronic Meat-Based vs. Plant-Based Burger Consumption in a Rodent Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
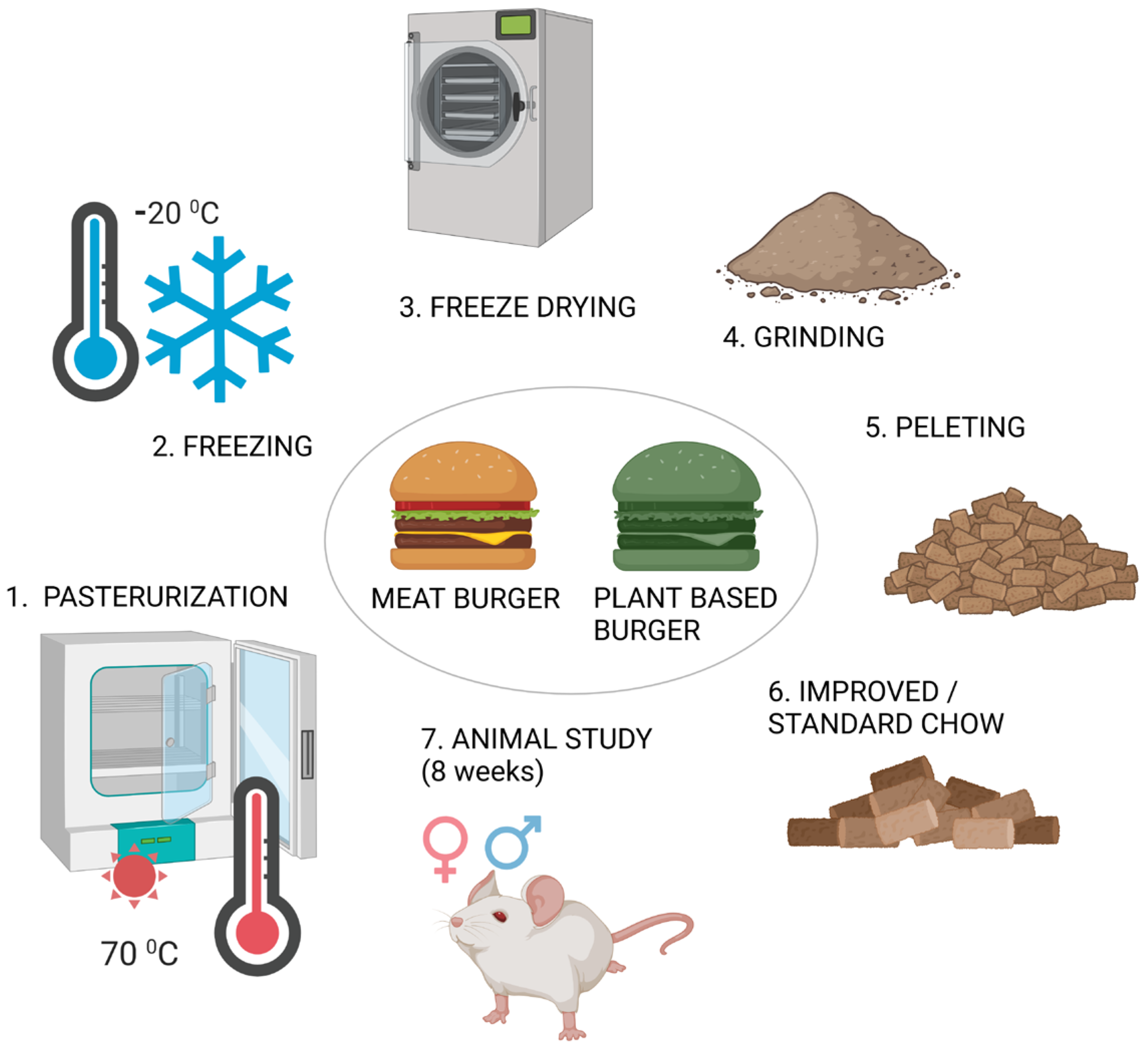
2.1. Sample Selection
2.2. Preparation of Improved Chow
2.3. Animals Included in This Study
2.4. Animal Procedures
2.5. Determination of Biochemical Parameters
2.6. Analysis of Biological Tissue Samples
2.7. Statistical Analysis of the Results
3. Results
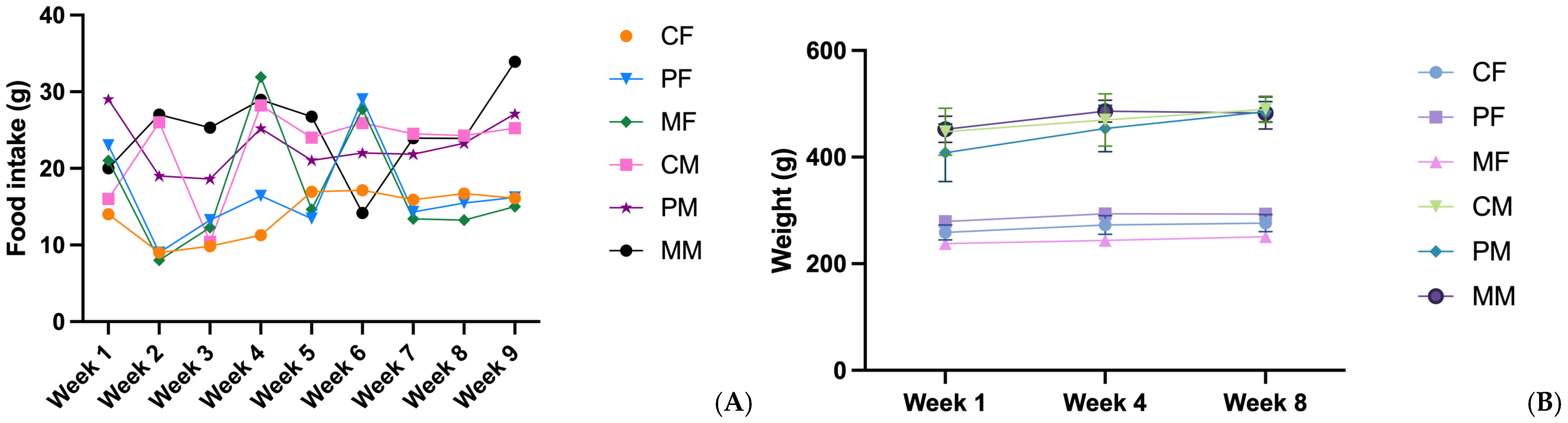
3.1. Food Intake and Weight Gain
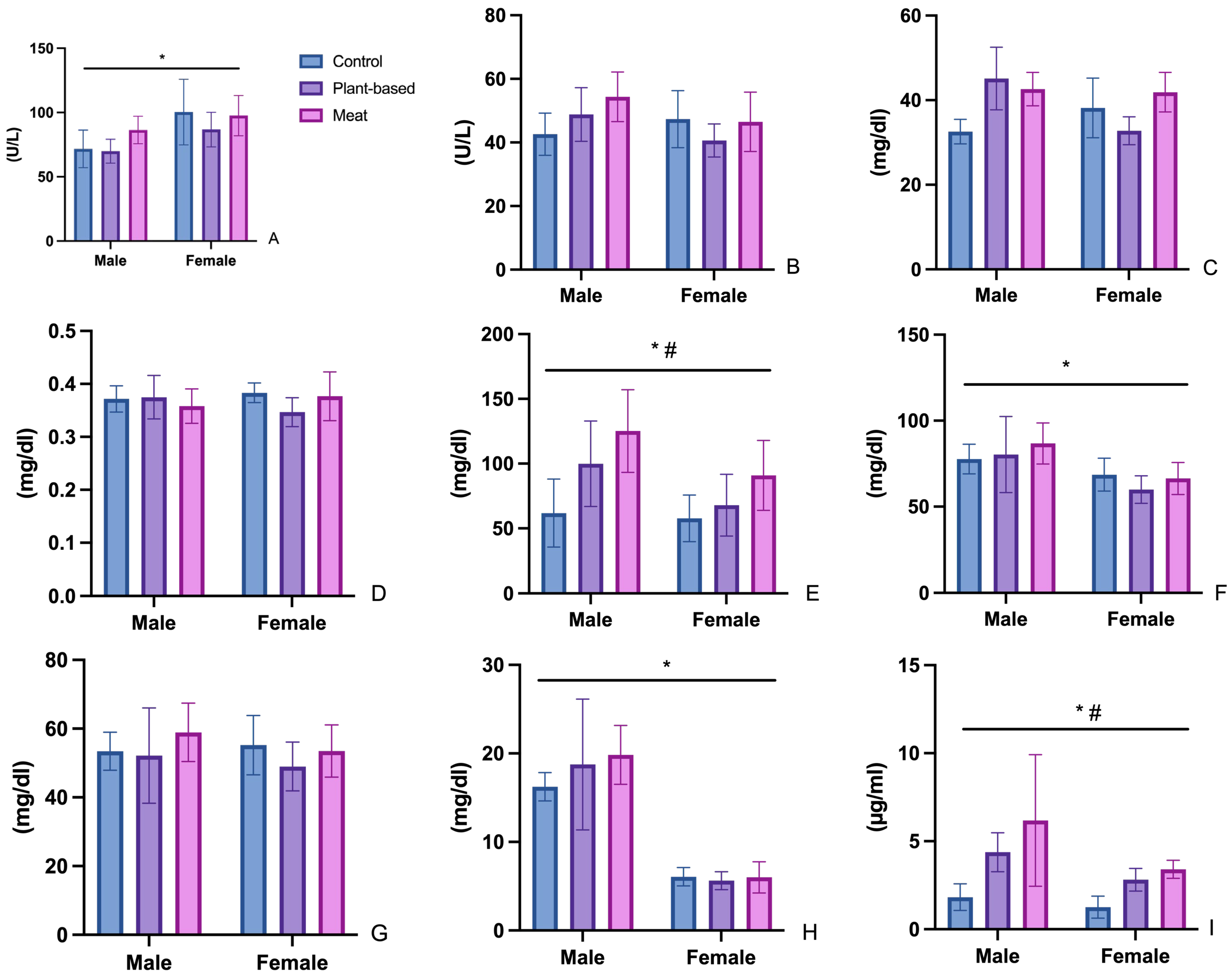
3.2. Biochemical Parameters
3.2.1. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) and Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
3.2.2. Urea (UR)
3.2.3. Creatinine (CR)
3.2.4. Triglycerides (TG), Total Cholesterol (CHOL), HDL Cholesterol (HDL), and LDL Cholesterol (LDL)
3.3. Leptin
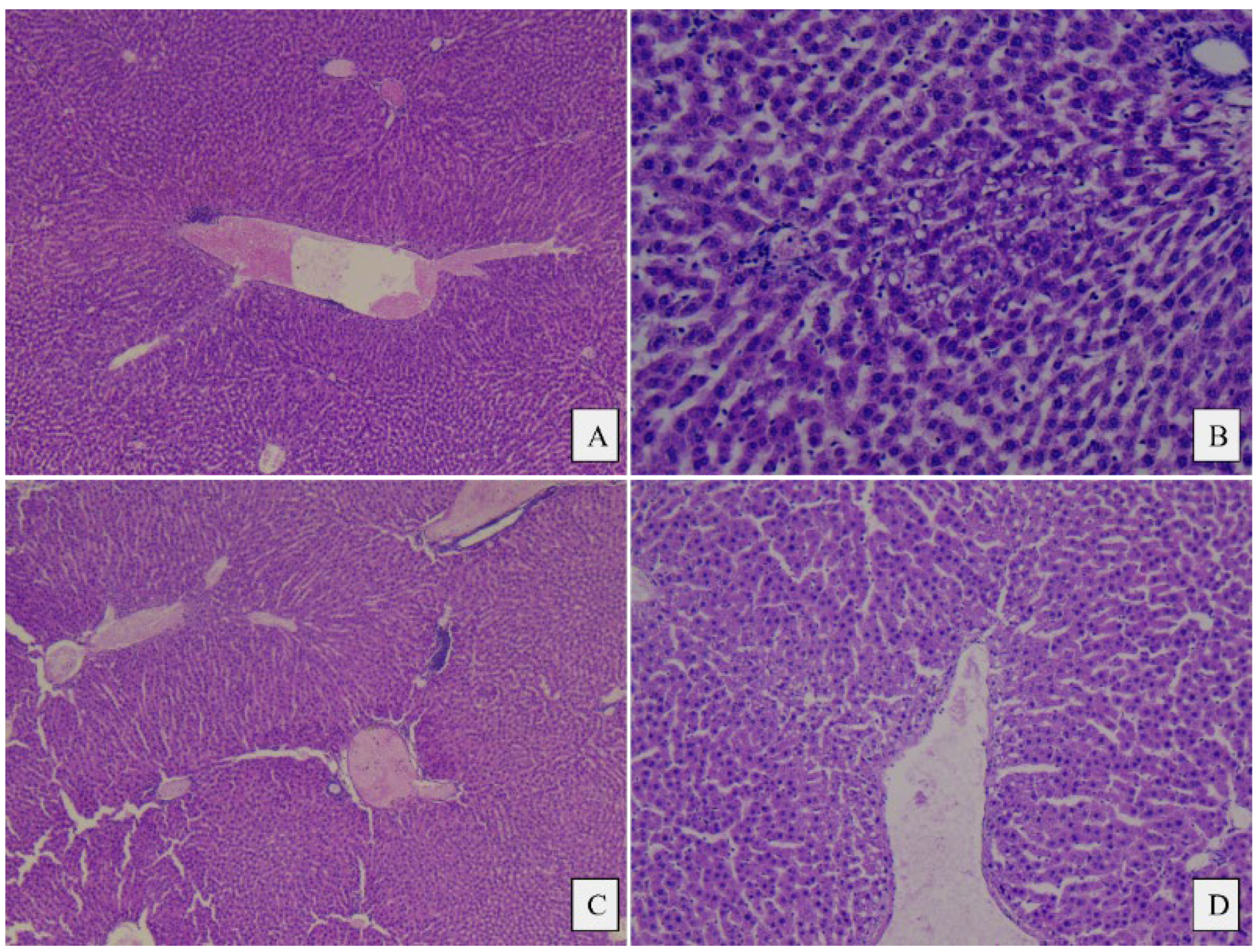
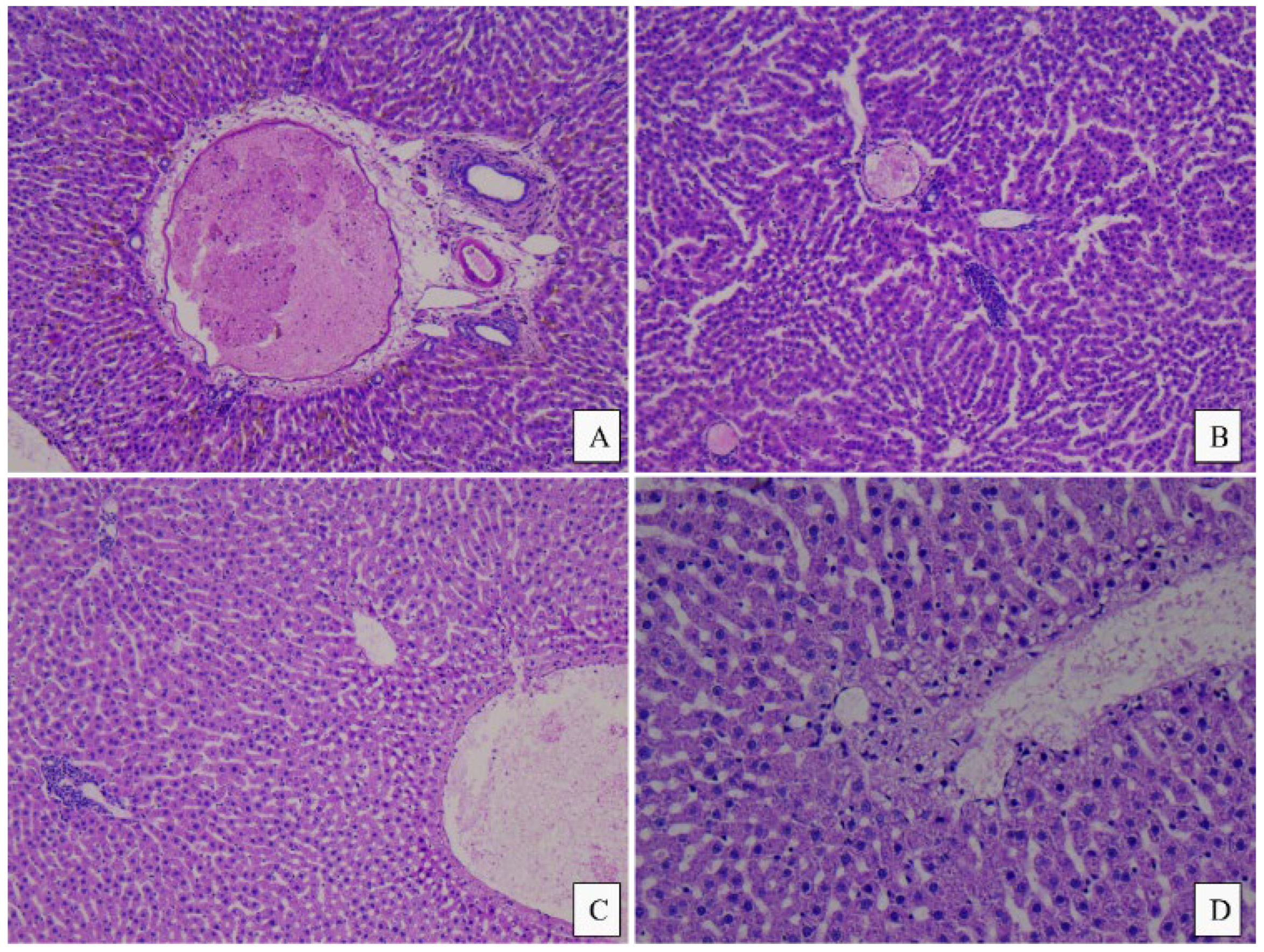
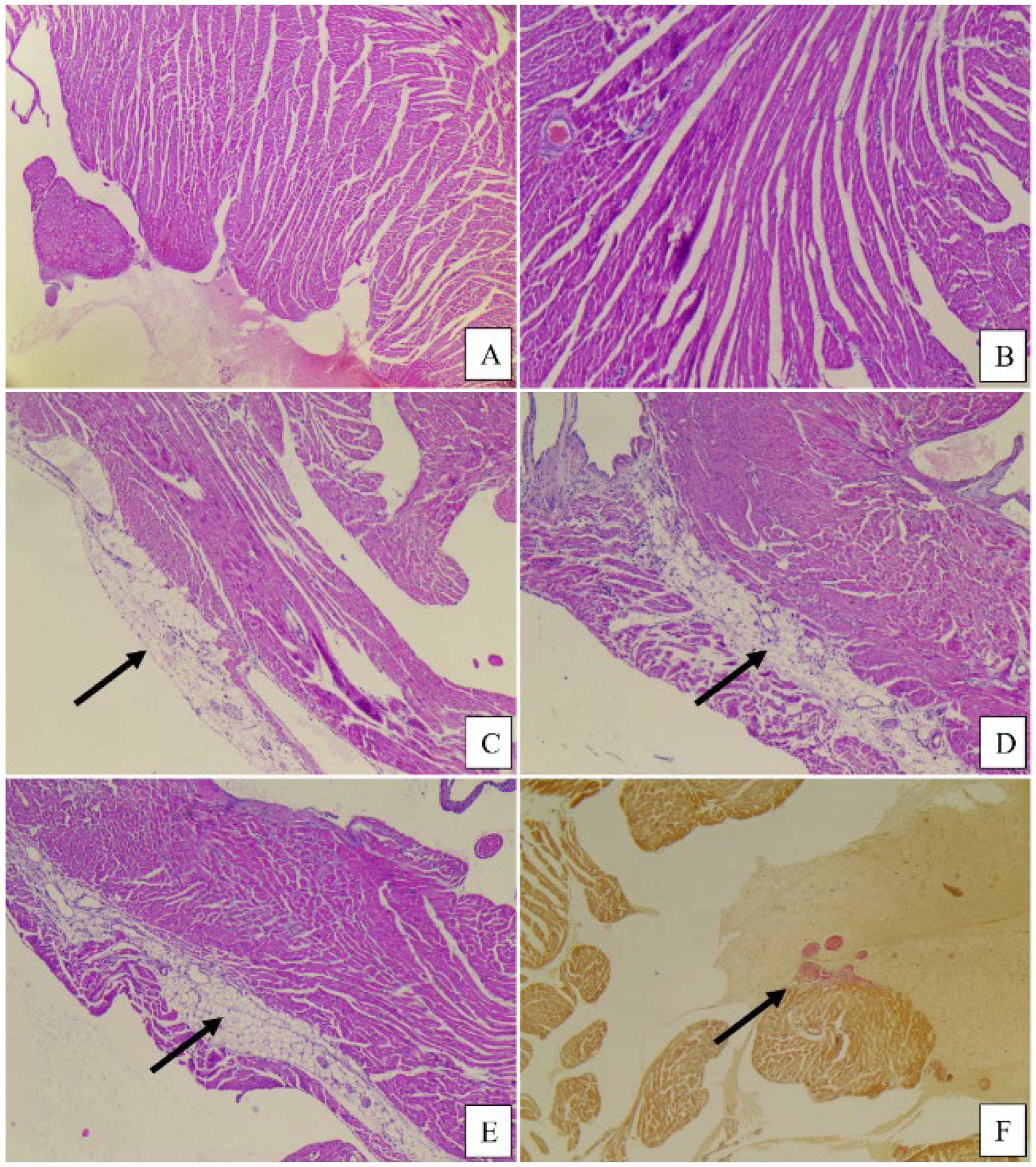
3.4. Histopathological Analysis
4. Discussions
4.1. Food Intake and Weight Gain
4.2. Analysis of Changes in Biochemical Parameters
4.2.1. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) and Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) Changes
4.2.2. Urea (UR) and Creatinine (CR)
4.2.3. Triglycerides (TG), Total Cholesterol (CHOL), HDL Cholesterol (HDL), and LDL Cholesterol (LDL)
4.3. Leptin and Appetite Regulation
4.4. Histopathological Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; McClements, D.J. Digestibility and Gastrointestinal Fate of Meat versus Plant-Based Meat Analogs: An in Vitro Comparison. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szenderák, J.; Fróna, D.; Rákos, M. Consumer Acceptance of Plant-Based Meat Substitutes: A Narrative Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begho, T.; Zhu, Y. Determinants of Consumer Acceptance of Meat Analogues: Exploring Measures of Risk Preferences in Predicting Consumption. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 11, 100509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Alvi, T.; Sameen, A.; Khan, S.; Blinov, A.V.; Nagdalian, A.A.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Adli, D.N.; Onwezen, M. Consumer Acceptance of Alternative Proteins: A Systematic Review of Current Alternative Protein Sources and Interventions Adapted to Increase Their Acceptability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, S.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Provenza, F.D.; Kronberg, S.L.; Pieper, C.F.; Huffman, K.M. A Metabolomics Comparison of Plant-Based Meat and Grass-Fed Meat Indicates Large Nutritional Differences despite Comparable Nutrition Facts Panels. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Catala, J.; Toro-Funes, N.; Comas-Basté, O.; Hernández-Macias, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, S.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.L.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Castell-Garralda, V.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Comparative Assessment of the Nutritional Profile of Meat Products and Their Plant-Based Analogues. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutroneo, S.; Prandi, B.; Faccini, A.; Pellegrini, N.; Sforza, S.; Tedeschi, T. Comparison of Protein Quality and Digestibility between Plant-Based and Meat-Based Burgers. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcorta, A.; Porta, A.; Tárrega, A.; Alvarez, M.D.; Vaquero, M.P. Foods for Plant-Based Diets: Challenges and Innovations. Foods 2021, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cai, L.; Huang, Z.; Shan, K.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Plant-Based Meat Analogues Aggravated Lipid Accumulation by Regulating Lipid Metabolism Homeostasis in Mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimarco, A.; Landry, M.J.; Carter, M.M.; Gardner, C.D. Assessing the Effects of Alternative Plant-Based Meats v. Animal Meats on Biomarkers of Inflammation: A Secondary Analysis of the SWAP-MEAT Randomized Crossover Trial. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.A.; Cannon, G.; Levy, R.B.; Moubarac, J.-C.; Louzada, M.L.; Rauber, F.; Khandpur, N.; Cediel, G.; Neri, D.; Martinez-Steele, E.; et al. Ultra-Processed Foods: What They Are and How to Identify Them. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryngelsson, S.; Moshtaghian, H.; Bianchi, M.; Hallström, E. Nutritional Assessment of Plant-Based Meat Analogues on the Swedish Market. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzolo-Brime, L.; Orta-Ramirez, A.; Puyol Martin, Y.; Jakszyn, P. Nutritional Assessment of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: A Comparison of Nutritional Information of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives in Spanish Supermarkets. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauber, F.; Da Costa Louzada, M.L.; Steele, E.; Millett, C.; Monteiro, C.A.; Levy, R.B. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases-Related Dietary Nutrient Profile in the UK (2008–2014). Nutrients 2018, 10, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanparast, H.; Islam, N.; Shafiee, M.; Ramdath, D.D. Increasing Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Decreasing Red and Processed Meat in the Diet Differentially Affect the Diet Quality and Nutrient Intakes of Canadians. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, R.; Brown, M.K.; Pombo-Rodrigues, S.; Bhageerutty, S.; He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Nutritional Quality of Plant-Based Meat Products Available in the UK: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwezen, M.C.; Verain, M.C.D.; Dagevos, H. Social Norms Support the Protein Transition: The Relevance of Social Norms to Explain Increased Acceptance of Alternative Protein Burgers over 5 Years. Foods 2022, 11, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, G. Advantages and Limitations of the Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) as a Method for Evaluating Protein Quality in Human Diets. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S333–S336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzler, S.R.; Lieblein-Boff, J.C.; Weiler, M.; Allgeier, C. Plant Proteins: Assessing Their Nutritional Quality and Effects on Health and Physical Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Real Meat and Plant-Based Meat Analogues Have Different in Vitro Protein Digestibility Properties. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.; Reedy, J.; Cudhea, F.; Zhang, J.; Shi, P.; Erndt-Marino, J.; Coates, J.; Micha, R.; Webb, P.; Mozaffarian, D.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Consumption of Animal-Source Foods between 1990 and 2018: Findings from the Global Dietary Database. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e243–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G. Dietary Protein Intake and Human Health. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Raghavan, V. Effects of Different Processing Degrees of Plant-Based Meat on the Blood Biochemical Level, Inflammation and Intestinal Microorganisms in Mice. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Guidance Documents Redbook 2000: IV.C.3.a. Short-Term Toxicity Studies with Rodents; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific purposesText with EEA Relevance. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 53, 276.
- Keenan, C.M.; Baker, J.F.; Bradley, A.E.; Goodman, D.G.; Harada, T.; Herbert, R.; Kaufmann, W.; Kellner, R.; Mahler, B.; Meseck, E.; et al. International Harmonization of Nomenclature and Diagnostic Criteria (INHAND) Progress to Date and Future Plans. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 28, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Keppler, J.K.; Van Der Goot, A.J. Functionality of Ingredients and Additives in Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and Developing a Literature-Derived, Population-Based Dietary Inflammatory Index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Xiao, X.; Yang, J.; Lei, M. Sex Differences in the Association of Dietary Inflammatory Index with Chronic Kidney Disease in US Adults. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iluz-Freundlich, D.; Zhang, M.; Uhanova, J.; Minuk, G.Y. The Relative Expression of Hepatocellular and Cholestatic Liver Enzymes in Adult Patients with Liver Disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, S.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, W. Dietary Fiber Intake and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Mediating Role of Obesity. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1038435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Caulfield, L.E.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Steffen, L.M.; Coresh, J.; Rebholz, C.M. Plant-Based Diets Are Associated with a Lower Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Disease, Cardiovascular Disease Mortality, and All-Cause Mortality in a General Population of Middle-Aged Adults. JAHA 2019, 8, e012865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oaks, B.M.; Jorgensen, J.M.; Baldiviez, L.M.; Adu-Afarwuah, S.; Maleta, K.; Okronipa, H.; Sadalaki, J.; Lartey, A.; Ashorn, P.; Ashorn, U.; et al. Prenatal Iron Deficiency and Replete Iron Status Are Associated with Adverse Birth Outcomes, but Associations Differ in Ghana and Malawi. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan, W.J.; Yang, R.-Z.; Park, S.; Goldstein, R.; Brees, D.; Gong, D.-W. Metabolic Adaptive ALT Isoenzyme Response in Livers of C57/BL6 Mice Treated with Dexamethasone. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, C.; Krishnasamy, R.; Stanton, T.; Savill, E.; Snelson, M.; Mihala, G.; Morrison, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Campbell, K.L. Diet Quality and Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins: Investigation of Novel Risk Factors and the Role of Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022, 32, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Cui, X.; Wang, B.; Tang, Q.; Cai, J.; Shen, X. Healthy Adult Vegetarians Have Better Renal Function than Matched Omnivores: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesen, E.I.; Wang-France, J.; Rahman, S.S. Sex Differences in Systemic and Renal Tissue Urea Concentrations. FASEB J. 2019, 33, lb532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X.; Lv, Y. Age- and Sex-Specific Reference Intervals for Blood Urea Nitrogen in Chinese General Population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.; Colombini, B.; Pagliai, G.; Giangrandi, I.; Cesari, F.; Gori, A.; Giusti, B.; Marcucci, R.; Sofi, F. Effects of Vegetarian versus Mediterranean Diet on Kidney Function: Findings from the CARDIVEG Study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukovic, V.; Hantikainen, E.; Raftopoulou, A.; Gögele, M.; Rainer, J.; Domingues, F.S.; Pramstaller, P.P.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Pattaro, C. Association of Dietary Proteins with Serum Creatinine and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in a General Population Sample: The CHRIS Study. J. Nephrol. 2022, 36, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, T.S.; Schompoopong, M.; Wu, S.-Y.; Kosch, C.; Bains, G.; Berk, L.; Zamora, F.; Ji, L. An Acute Comparison of the Change of Serum Lipids, Glucose, and Hs-CRP Levels After Consumption of a Beef Burger Versus a Vegetarian Burger in Healthy Adults. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, nzaa042_001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Amer, H.; Sultani, A.; Nasr, P.; Wang, Y.; Corradini, M.G.; Douglas Goff, H.; LaPointe, G.; Rogers, M.A. The Digestive Fate of Beef versus Plant-Based Burgers from Bolus to Stool. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Tian, K.; Lim, K.S.; et al. The Functional Role of Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis: Novel Directions for Diagnosis and Targeting Therapy. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnier, J.; Giovachini, L.; Ducrocq, G.; Ferrari, R.; Ford, I.; Tendera, M.; Fox, K.M.; Steg, P.G. Sex Differences in Management of LDL-Cholesterol in Patients with Chronic Coronary Syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, ehae666.1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.; Clemmensen, C. Physiological Protection against Weight Gain: Evidence from Overfeeding Studies and Future Directions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2023, 378, 20220229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bo’, C.; Chehade, L.; Tucci, M.; Canclini, F.; Riso, P.; Martini, D. Impact of Substituting Meats with Plant-Based Analogues on Health-Related Markers: A Systematic Review of Human Intervention Studies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Herrera, K.; Florio, A.A.; Moore, M.; Marrero, A.; Tamez, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Mattei, J. The Leptin System and Diet: A Mini Review of the Current Evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 749050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdeva, O.; Borodkina, D.; Uchasova, E.; Dyleva, Y.; Barbarash, O. Leptin Resistance: Underlying Mechanisms and Diagnosis. DMSO 2019, 12, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, A.M.; Asadi, A.; Johnson, J.D.; Covey, S.D.; Kieffer, T.J. Leptin Deficiency in Rats Results in Hyperinsulinemia and Impaired Glucose Homeostasis. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hemat Jouy, S.; Mohan, S.; Scichilone, G.; Mostafa, A.; Mahmoud, A.M. Adipokines in the Crosstalk between Adipose Tissues and Other Organs: Implications in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haschimi, K.; Pierroz, D.D.; Hileman, S.M.; Bjørbæk, C.; Flier, J.S. Two Defects Contribute to Hypothalamic Leptin Resistance in Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zusi, C.; Csermely, A.; Rinaldi, E.; Bertoldo, K.; Bonetti, S.; Boselli, M.L.; Travia, D.; Bonora, E.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Trombetta, M. Crosstalk between Genetic Variability of Adiponectin and Leptin, Glucose-Insulin System and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. The Verona Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Study 14. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Choi, D.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Koo, S.-H. Fast Food Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Exerts Early Protective Effect against Acetaminophen Intoxication in Mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greibe, E.; Nymark, O.; Fedosov, S.N.; Heegaard, C.W.; Nexo, E. Dietary Intake of Vitamin B12 is Better for Restoring a Low B12 Status Than a Daily High-Dose Vitamin Pill: An Experimental Study in Rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujianti, I.; Sianipar, I.R.; Prijanti, A.R.; Hasan, I.; Arozal, W.; Jusuf, A.A.; Wibowo, H.; Prihartono, J.; Amani, P.; Santoso, D.I.S. Effect of Roselle Flower Extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn.) on Reducing Steatosis and Steatohepatitis in Vitamin B12 Deficiency Rat Model. Medicina 2023, 59, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.C.; Blusztajn, J.K.; Caudill, M.A.; Klatt, K.C.; Natker, E.; Zeisel, S.H.; Zelman, K.M. Choline: The Underconsumed and Underappreciated Essential Nutrient. Nutr. Today 2018, 53, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchi, M.; Costa, A.; Pozza, M.; Goi, A.; Manuelian, C.L. Detailed Characterization of Plant-Based Burgers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Ahmed, Y.; Lafdil, F. Novel Insights into the Impact of Liver Inflammatory Responses on Primary Liver Cancer Development. Liver Res. 2023, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, G.; Datz, C.; Trauner, M. Eating, Diet, and Nutrition for the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S244–S260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelnuovo, G.; Perez-Diaz-del-Campo, N.; Rosso, C.; Armandi, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Bugianesi, E. A Healthful Plant-Based Diet as an Alternative Dietary Approach in the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Energetic Value kcal/100 g | Protein g/100 g | Fat g/100 g | Salt g/100 g | Carbohydrates g/100 g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat burger * | 238 | 19 | 18 | 1 | 0.1 |
| PBM burger * | 231 | 16 | 16 | 1.7 | 5.8 |
| Standard chow | 87.45 | 18 | 1.5 | - | - |
| Components | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energetic Value kcal/100 g | Protein g/100 g | Fat g/100 g | Salt g/100 g | Carbohydrates g/100 g | |
| Improved chow (with 23% lyophilized meat burger) | 164.21 | 21.45 | 8.47 | 0.03 | 0.4 |
| Improved chow (with 23% lyophilized PBM burger) | 120 | 17.54 | 4.83 | 0.39 | 4.83 |
| Standard feed | 87.45 | 18 | 1.5 | - | - |
| Biochemical Parameter | Analytical Method | Reagent | CAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| AST | International Federation for Clinical Chemistry (IFCC) standardized kinetics using the pyridoxal phosphate method | Aspartate aminotransferase, Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (ASTL) | 20764949322 |
| ALT | International Federation for Clinical Chemistry (IFCC) standardized kinetics using the pyridoxal phosphate method | Alanine aminotransferase, Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (ALTL) | 20764957322 |
| CHOL | Spectrophotometric (enzymatic colorimetric) method | Cholesterol Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (CHOL2) | 03039773190 |
| HDL | Spectrophotometric (enzymatic colorimetric) method | HDL Cholesterol Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (HDLC4) | 07528566190 |
| LDL | Spectrophotometric (enzymatic colorimetric) method | LDL Cholesterol Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (LDL-C Gen.3) | 07005717190 |
| TG | Spectrophotometric (enzymatic colorimetric) method | Triglycerides Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (TRIGL) | 20767107322 |
| CR | Kinetic (enzymatic colorimetric) Jaffé method | Creatinine Jaffé, 2nd generation, Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (CREJ2) | 04810716190 |
| UR | Spectrophotometric (kinetic) method | Urea, Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany (Ureal) | 04460715190 |
| Parameters Mean (SD) | CF | MF | PF | CM | MM | PM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial weight (g) | 258.83 (13.90) | 237.50 (8.29) | 279.33 (6.53) | 447.83 (44.31) | 452.33 (24.57) | 433.50 (11.14) |
| Final weight (g) | 276.01 (16.04) | 250.66 (5.12) | 293.04 (3.84) | 489.83 (24.57) | 482.67 (30.17) | 485.17 (18.91) |
| Weight gain (g) | 17.17 (18.77) | 13.17 (10.81) | 13.67 (11.79) | 42.00 (30.98) | 30.33 (28.31) | 51.66 (24.83) |
| Mean food intake (g/day) | 14.10 (3.23) | 17.58 (7.75) | 16.68 (5.91) | 24.62 (5.71) | 24.87 (5.55) | 23.69 (3.52) |
| FER | 1.21 (0.34) | 0.74 (0.51) | 0.81 (0.45) | 1.70 (1.34) | 1.21 (0.98) | 2.18 (1.89) |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | CF | MF | PF | CM | MM | PM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 0.64 | 2.72 | 2.13 | 0.92 | 2.84 | 3.19 |
| Maximum | 2.34 | 4.01 | 3.62 | 3.02 | 7.25 | 5.85 |
| Mean (SD) | 1.25 (0.62) | 3.40 (0.51) | 2.81 (0.64) | 1.82 (0.75) | 4.86 (2.07) | 4.37 (1.10) |
| Leptin index (ng/mL/g) | 0.0045 | 0.0135 | 0.0096 | 0.0037 | 0.0100 | 0.0090 |
| Histopathological Findings/Group | CM | MM | PM | CF | MF | PF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | ||||||
| Periportal inflammatory infiltrate/Multifocal lymphocytic infiltrates, mainly peri-portal (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Intraparenchymal inflammatory infiltrate/Multifocal lymphocytic infiltrates, diffuse in the liver parenchyma (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Microvacuolar dystrophy/Hepatic micro-vesicular steatosis, mainly centrilobular (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 0/1 | 1 | 0 | 0/1 | 0 | 0/1 |
| Portal fibrosis/portal fibrosis (0 = absent, 1 = reduced, 2 = moderate, 3 = well expressed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Heart | ||||||
| Mean right ventricular cord/thickness (mm) | 1.16 | 0.83 | 1.16 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.83 |
| Mean left ventricular cord/thickness (mm) | 3.00 | 2.66 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 2.16 |
| Subepicardial adipose tissue (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Intramyocardial adipose tissue (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Interstitial, subendocardial, perivascular fibrosis (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Ischemic lesions (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Kidney | ||||||
| Kidney Interstitial inflammatory infiltrate (0 = absent, 1 = present) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filip, C.; Ștefănescu, R.; Ősz, B.-E.; Pușcaș, A.; Tanase, C.; Nechifor-Boilă, A.; Tero-Vescan, A. Sex-Specific Biochemical and Histopathological Effects of Chronic Meat-Based vs. Plant-Based Burger Consumption in a Rodent Model. Foods 2025, 14, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050888
Filip C, Ștefănescu R, Ősz B-E, Pușcaș A, Tanase C, Nechifor-Boilă A, Tero-Vescan A. Sex-Specific Biochemical and Histopathological Effects of Chronic Meat-Based vs. Plant-Based Burger Consumption in a Rodent Model. Foods. 2025; 14(5):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050888
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilip, Cristina, Ruxandra Ștefănescu, Bianca-Eugenia Ősz, Amalia Pușcaș, Corneliu Tanase, Adela Nechifor-Boilă, and Amelia Tero-Vescan. 2025. "Sex-Specific Biochemical and Histopathological Effects of Chronic Meat-Based vs. Plant-Based Burger Consumption in a Rodent Model" Foods 14, no. 5: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050888
APA StyleFilip, C., Ștefănescu, R., Ősz, B.-E., Pușcaș, A., Tanase, C., Nechifor-Boilă, A., & Tero-Vescan, A. (2025). Sex-Specific Biochemical and Histopathological Effects of Chronic Meat-Based vs. Plant-Based Burger Consumption in a Rodent Model. Foods, 14(5), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050888








