Amelioration of Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis in a Rat Model via Consumption of Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid-Enriched Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Using Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermentation Conditions
2.2. PγG and Free Glutamic Acid Analyses
2.3. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.4. Biological Properties
2.5. Antithrombotic Activity
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Cellular Neutral Lipid Accumulation
2.8. Animals, Experimental Design, and Diet
2.9. Dissection and the Analytical Procedure
2.10. Analysis of Alcohol-Metabolizing Enzymes
2.11. Serum Alcohol Concentration
2.12. Liver Histopathological Study
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PγG Content of FPBs at Different Fermentation Times
3.2. Effect of Fermentation on the DPPH Radical Scavenging and Antithrombotic Activities of PbsLs
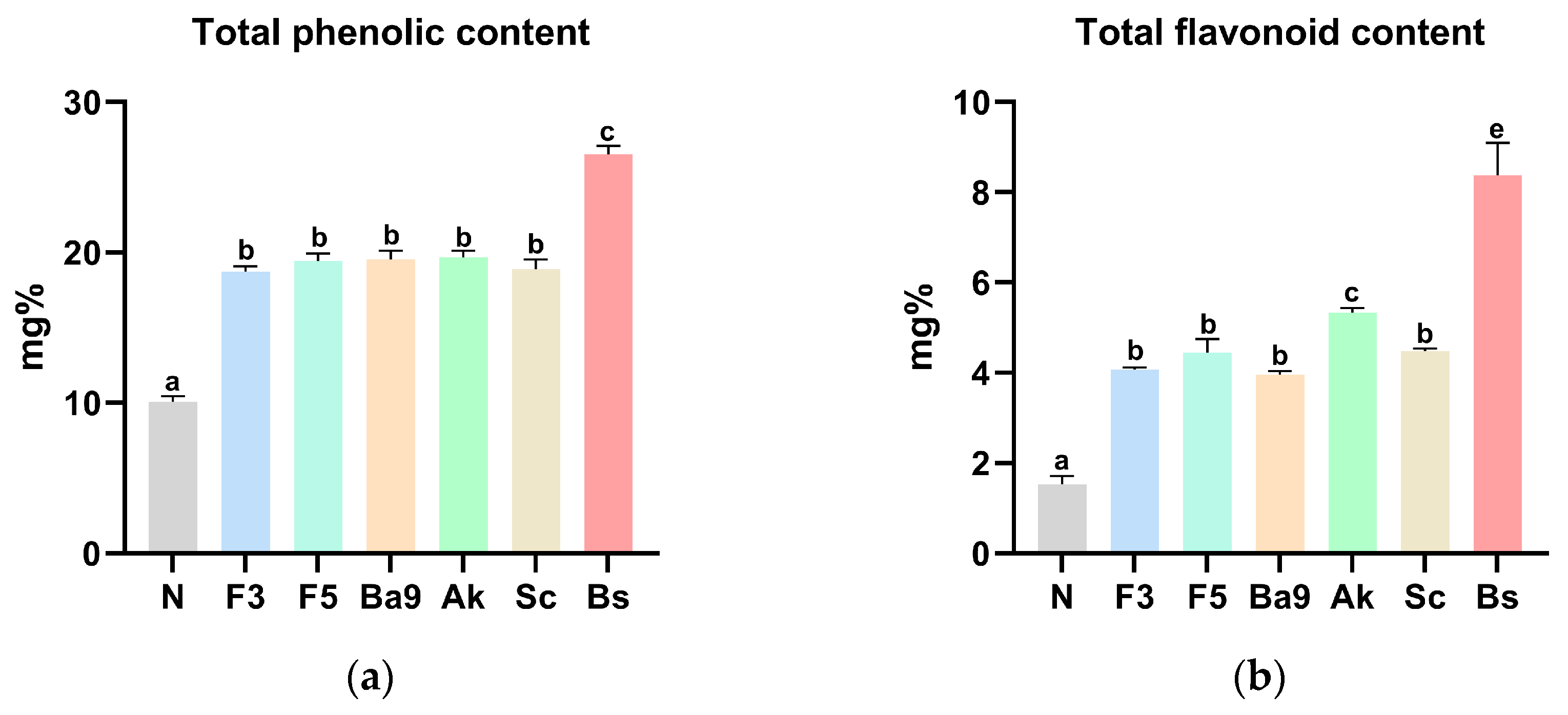
3.3. Biological Properties of FPBs
3.4. Effect of FPBs on the Inhibition of Neutral Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells
3.5. Body Weight Gain, Relative Liver Weight, and Water Consumption of the Experimental Rats
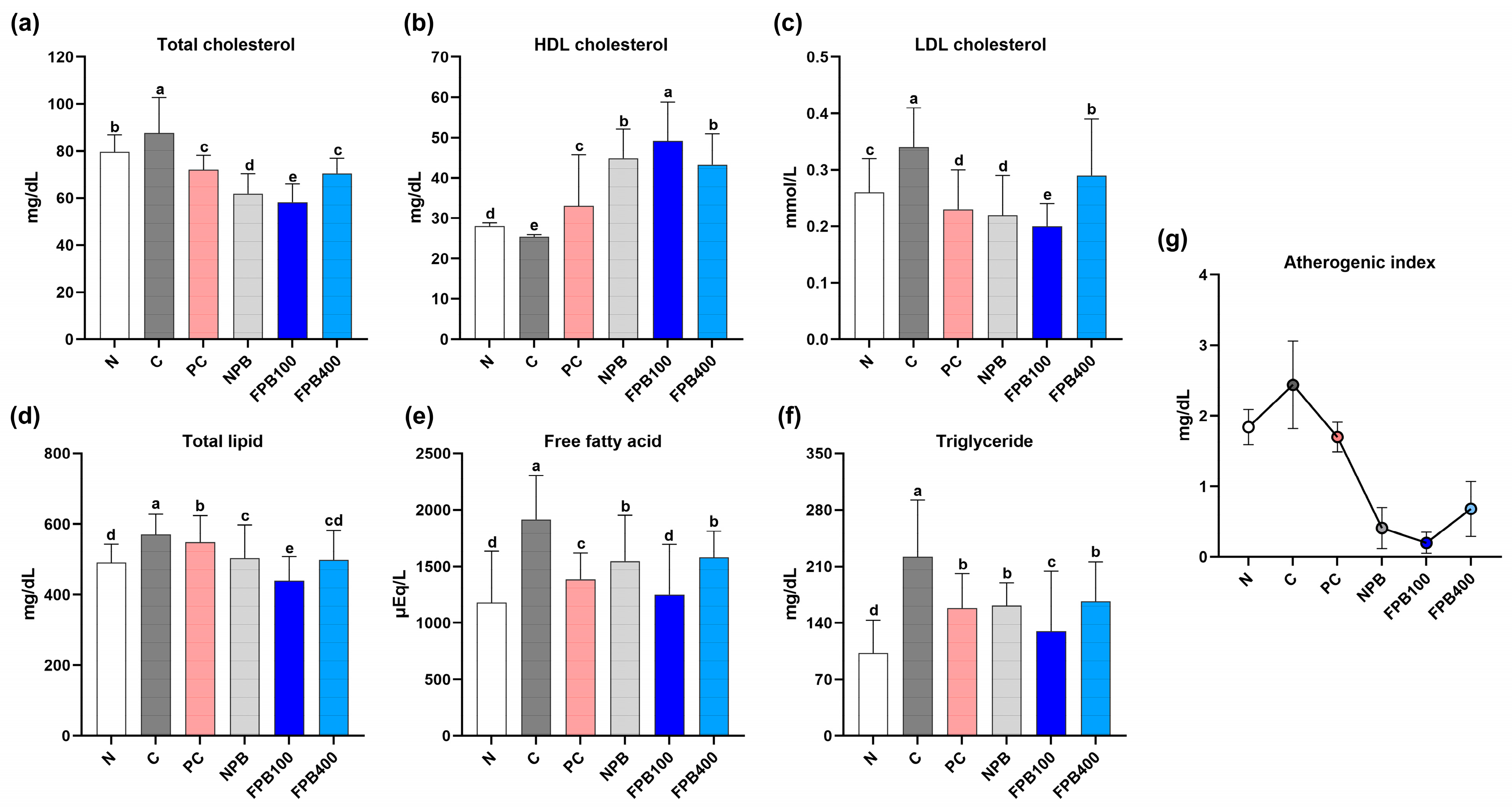
3.6. Effect of FPBs on Serum Lipid Profiles
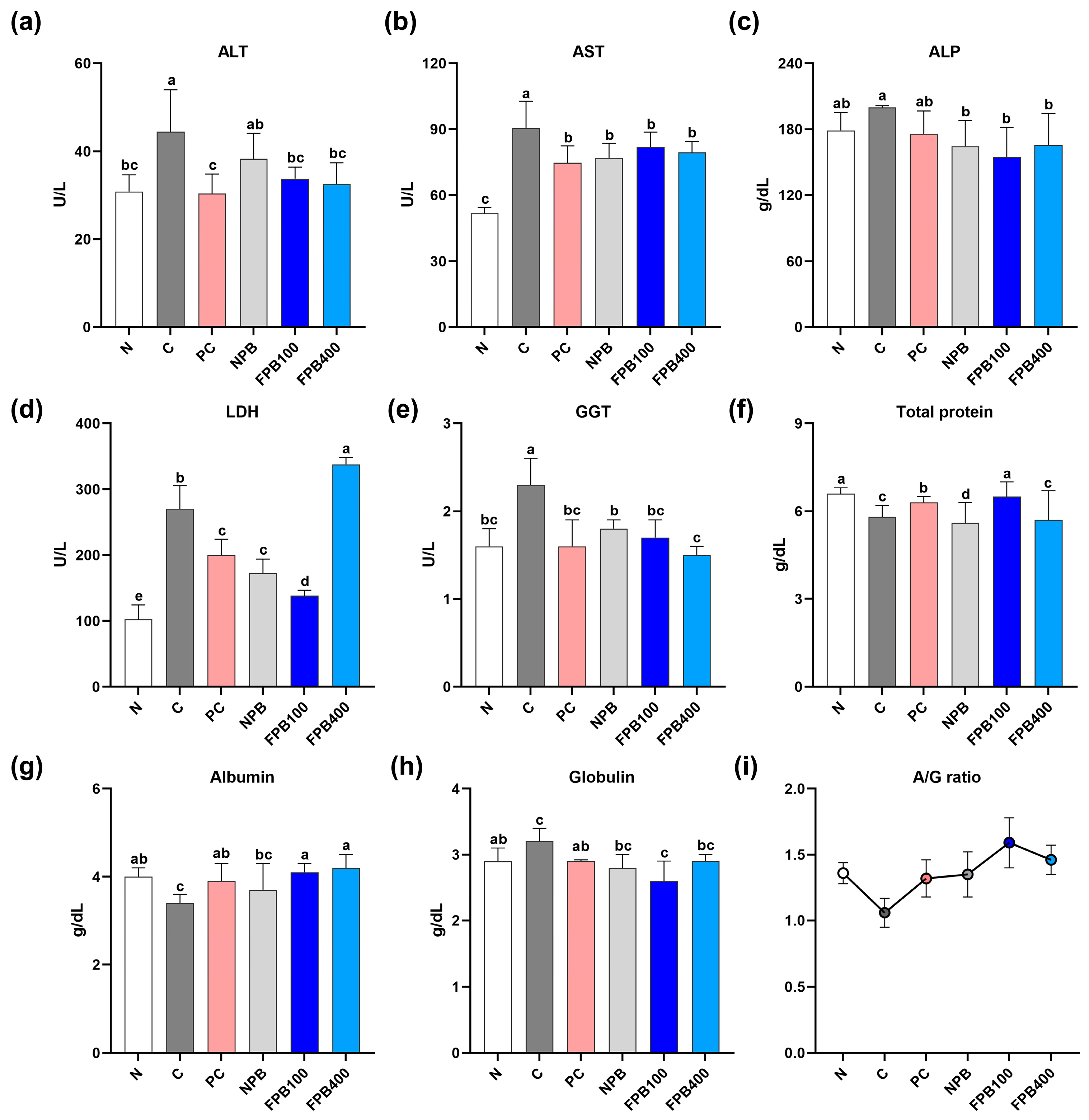
3.7. Effect of FPBs on Liver Function Test Results
3.8. Effect of FPBs on Components of the Alcohol Metabolism Pathway
3.9. Effect of FPBs on the Liver and Serum Glutathione Content
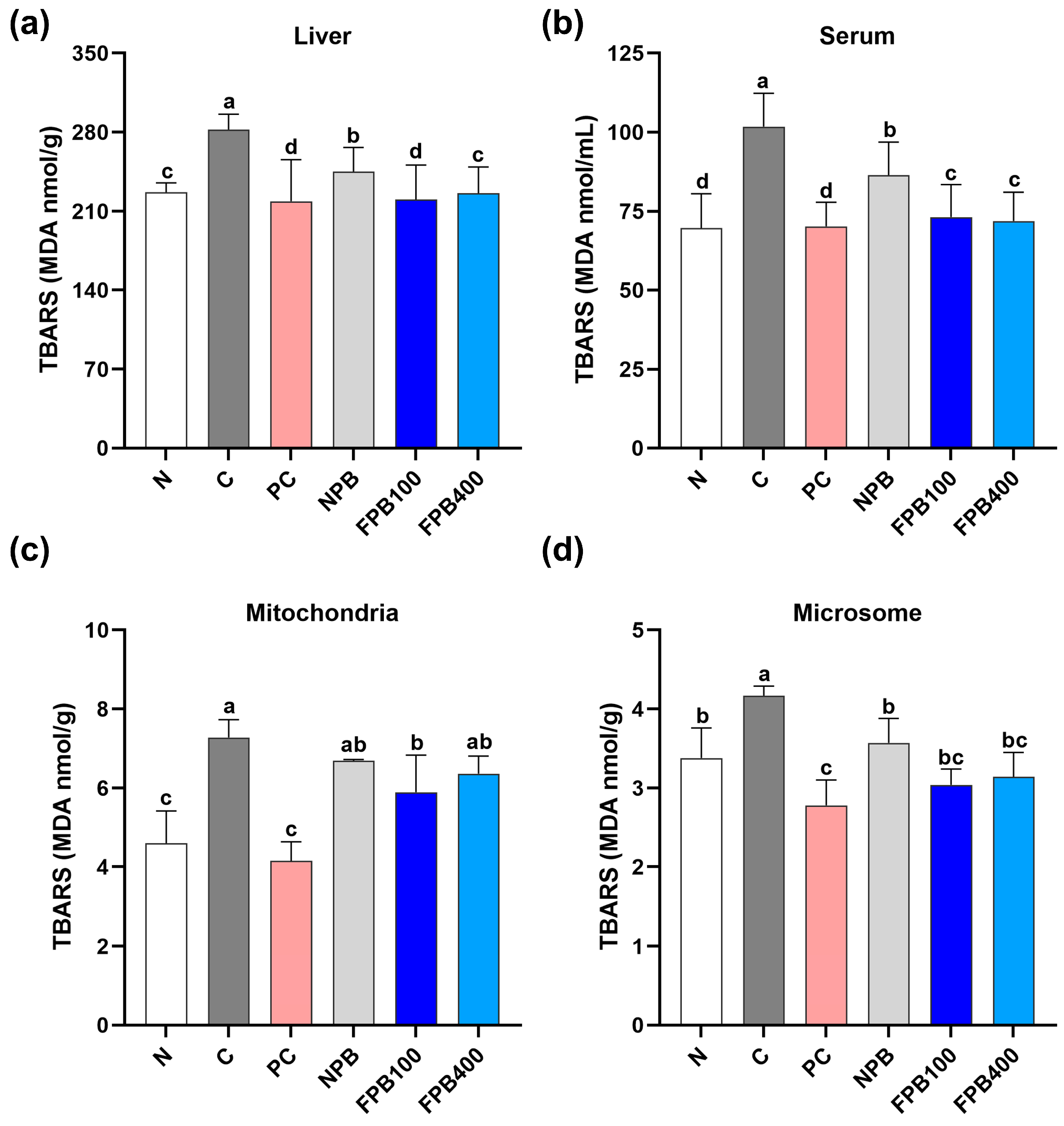
3.10. Effect of FPBs on Hepatic and Serum Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels
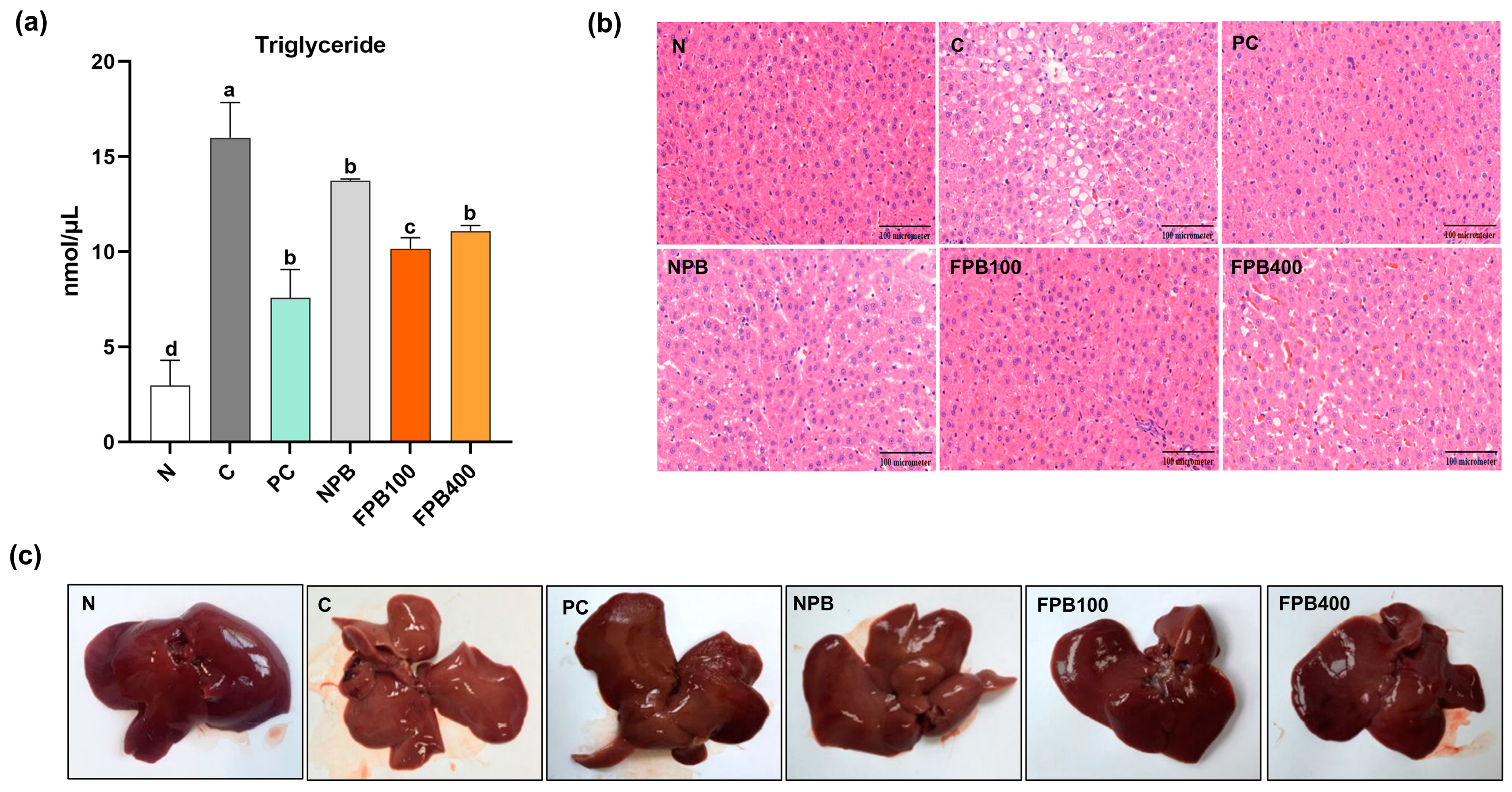
3.11. Effect of FPBs on Triglyceride Accumulation and Histopathological Alterations in Hepatic Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehman, A.; Mehta, K.J. Betaine in ameliorating alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoz-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osna, N.A.; Rasineni, K.; Ganesan, M.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Kharbanda, K.K. Pathogenesis of Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1492–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Song, L.; Qian, B.; Xu, W.; Ren, J.; Jing, P.; Oey, I. Understanding the effect of anthocyanins extracted from purple sweet potatoes on alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.Y.; Ahn, H.Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Je, J.Y. Protective effect of cordycepin-enriched Cordyceps militaris on alcoholic hepatotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. Edible insects: An overview on nutritional characteristics, safety, farming, production technologies, regulatory framework, and socio-economic and ethical implications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.C.; Miller, A.C.; Miller, M.E.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X. Potential health benefits of edible insects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3499–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.Y.; Ahn, H.Y.; Seo, K.I.; Cho, Y.S. Physicochemical Properties and Biological Activities of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis Larvae Fermented by Several Kinds of Micro-organisms. J. Life Sci. 2018, 28, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Kang, H.S.; Hyun, W.B.; Kim, K.P. High prevalence of Bacillus subtilis-infecting bacteriophages in soybean-based fermented foods and its detrimental effects on the process and quality of Cheonggukjang. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Garcia, C.V.; Lee, S.P. Fortification of Poly-gamma-Glutamic Acid and gamma-Aminobutyric Acid in Homogenized Hydroponic Ginseng Co-Fermented by Bacillus subtilis HA and Lactobacillus plantarum EJ2014. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, J.C.; Sung, M.H.; Kang, J.H.; Chang, M.J. High molecular weight poly-gamma-glutamic acid regulates lipid metabolism in rats fed a high-fat diet and humans. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.S.; Kim, S. Effect of In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion on Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Activities in Cherry Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum var. cerasiforme). Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 28, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherbal, A.; Bouabdallah, M.; Benhalla, M.; Hireche, S.; Desdous, R. Phytochemical Screening, Phenolic Content, and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Foeniculum vulgare Seed Extract. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 28, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y. The Antioxidant and Anti-Complementary Activities of Crude Polysaccharides from Trifoliate Orange (Poncirus trifoliate) Seeds. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 28, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.-Y.; Ahn, H.-Y.; Cho, Y.-S. Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis larvae fermented by Bacillus subtilis on serum lipid contents and liver morphology in orotic acid-induced fatty-liver model Sprague-Dawley rats. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2019, 26, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmeyer, H.U.; Bent, E. UV-Assay with Pyruvate and NADH. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Koivula, T.; Koivusalo, M. Different forms of rat liver aldehyde dehydrogenase and their subcellular distribution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1975, 397, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Gabriela Medina-Meza, I. Impact of Fermentation on the Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Whole Cereal Grains: A Mini Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Chen, S.-C.; Wang, Q.-L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Xiao, J.-H.; Huang, D.-W. Nutritional value of Protaetia brevitarsis powder and its effect on the flavor and antioxidant capacity of dough. LWT 2024, 195, 115849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Teotia, P. Isolation, characterization and strain improvement of soil bacteria Bacillus subtilis for invertase production. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2021, 42, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.H.; Son, W.C.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, B.H. Anti-obesity effects of poly-gamma-glutamic acid with or without isoflavones on high-fat diet induced obese mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, M.; Watanabe, J.; Hori, S.; Inose, A.; Kubo, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Ikezawa, M.; Araki, R.; Kobori, M. Effects of a high-gamma-polyglutamic acid-containing natto diet on liver lipids and cecal microbiota of adult female mice. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2021, 40, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisi, T.; Addolorato, G. Effect of Alcohol Combined with High Fat Diet: Two Wrongs Don’t Make a Right but They Could Make a Good Excuse. Alcohol Alcohol. 2021, 56, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidurrahman, M.; Mujahid, M.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Alsuwayt, B.; Rahman, M.A. Evaluation of hepatoprotective activity of ethanolic extract of Pterocarpus marsupium Roxb. leaves against paracetamol-induced liver damage via reduction of oxidative stress. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Badimon, L. Benefits and Risks of Moderate Alcohol Consumption on Cardiovascular Disease: Current Findings and Controversies. Nutrients 2019, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, B.G.; Kim, J.H.; Woo, M.; Song, Y.O.; Choi, Y.H.; Noh, J.S.; Cho, E.J. Skate cartilage extracts containing chondroitin sulfate ameliorates hyperlipidemia-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in high cholesterol diet-fed LDL receptor knockout mice in comparison with shark chondroitin sulfate. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2020, 14, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.-Y.; Li, H.-W.; Liu, F.-G.; Li, Y.-C.; Tian, S.; Cao, L.-H.; Hu, K.; Wu, X.-X.; Miao, M.-S. Effects of Portulaca Oleracea Extract on Acute Alcoholic Liver Injury of Rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.M.; Myung, N.Y.; Jung, H.A.; Kim, S.J. The ameliorative effect of Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae in HFD-induced obese mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeepipalli, S.P.K.; Du, B.; Sabitaliyevich, U.Y.; Xu, B. New insights into potential nutritional effects of dietary saponins in protecting against the development of obesity. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.S.; Shin, K.S.; Jung, H.W.; Lee, Y.; Sathesh-Prabu, C.; Lee, S.K. Combinatorial Metabolic Engineering Strategies for the Enhanced Production of Free Fatty Acids in Escherichia coli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13913–13921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Y.; Fu, X.; Luo, R.; Xue, J.; Yang, S.; Ling, L.; et al. Nanoparticles loaded with pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: Biomedical applications and toxicity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 225, 113214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhangyuan, G.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Jin, K.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B. High preoperative serum globulin in hepatocellular carcinoma is a risk factor for poor survival. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3494–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinella, R.; Sawhney, R.; Jalan, R. Albumin in chronic liver disease: Structure, functions and therapeutic implications. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheinenzon, A.; Shehadeh, M.; Michelis, R.; Shaoul, E.; Ronen, O. Serum albumin levels and inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.H.; Chun, S.Y.; Yoon, B.; Han, M.H.; Chung, J.W.; Ha, Y.S.; Lee, J.N.; Kim, H.T.; Kim, D.H.; Beik, G.Y.; et al. Antiobesity and Hepatoprotective Effects of Protein Hydrolysates Derived from Protaetia brevitarsis in an Obese Mouse Model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 4492132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.L.; Yang, H.T.; Lee, H.L.; Yin, M.C. Protective effects of maslinic acid against alcohol-induced acute liver injury in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Yang, M. Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 Invasion into the Liver and Hepatic Injury in Patients with COVID-19. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 14, e2022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. Co-expression of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis for alcohol detoxification. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Qin, P.; Ren, G. Effect of anthocyanin-rich extract from black rice (Oryza sativa L. Japonica) on chronically alcohol-induced liver damage in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Zheng, K.; Xue, S.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Q. Serum AFU, GGT and TK1 levels in PHC patients and their correlation with clinicopathology and diagnostic value. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 2020, 66, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Tang, W.; Fu, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Hu, G.; Hu, G.; Sun, W. Pre-treatment Serum Lactate Dehydrogenase Predicts Distant Metastasis and Poor Survival in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3657–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Current Mechanistic Aspects with Focus on Their Clinical Relevance. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapan Kumar, M.; Vishwakarma, S. Present scenario of policies & hazards related to alcohol in India. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2021, 3, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tian, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H. Nicotinamide riboside ameliorates high-fructose-induced lipid metabolism disorder in mice via improving FGF21 resistance in the liver and white adipose tissue. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12400–12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, E.K.; Park, S.D.; Shim, J.J.; Lee, J.L.; Yoo, H.H. Effects of Plant-Based Extract Mixture on Alcohol Metabolism and Hangover Improvement in Humans: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Paralleled, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Ahn, H.Y.; Kim, Y.W.; Sim, S.Y.; Seo, K.I.; Cho, Y.S. Hepatoprotective Effect of Bacillus subtilis-fermented Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) Extract on an Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Rats. J. Life Sci. 2018, 28, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, N.; Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Fan, M. Multivariate analysis reveals effect of glutathione-enriched inactive dry yeast on amino acids and volatile components of kiwi wine. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.Y.; Ham, J.R.; Ryu, H.S.; Lee, S.S.; Miguel, M.A.; Paik, M.J.; Ji, M.; Park, K.W.; Kang, K.Y.; Lee, H.I.; et al. Defatted Tenebrio molitor Larva Fermentation Extract Modifies Steatosis, Inflammation and Intestinal Microflora in Chronic Alcohol-Fed Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ciaula, A.; Calamita, G.; Shanmugam, H.; Khalil, M.; Bonfrate, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Baffy, G.; Portincasa, P. Mitochondria Matter: Systemic Aspects of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Diagnostic Assessment of Liver Function by Stable Isotope Dynamic Breath Tests. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.C.; Bailey, S.M. Ethanol consumption and liver mitochondria function. Biol. Signals Recept. 2001, 10, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Carr, R. Alcohol effects on hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.P.; Mao, X.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Yan, L.L.; Ye, L.P.; Li, S.W. Reactive Oxygen Species Induce Fatty Liver and Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Inflammation and Cell Death. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 870239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Tan, W.Y.; Li, Y.; Bowden, J.A.; Ahmadireskety, A.; Patt, A.C.; Orlicky, D.J.; Mathe, E.; Kroeger, N.M.; Thompson, D.C.; et al. Lipidomics and Redox Lipidomics Indicate Early Stage Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.L.; Kim, J.M.; Go, M.J.; Joo, S.G.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Son, J.S.; Heo, H.J. Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Ameliorates Chronic Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice via AMPK and TLR-4/TGF-beta1 Pathways. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredients (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casein | Corn Starch | Corn Oil | Cellulose | Mineral (1) | Vitamin (2) | L-Methionine | Sucrose | Choline | Total |
| 20.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 44.5 | 0.2 | 100 |
| Group | Composition |
|---|---|
| N | normal diet |
| C | normal diet + Alcohol |
| PC | normal diet + Alcohol + Silymarin |
| NPB | normal diet + Alcohol + NPB 400 mg/kg b.w./day |
| FPB100 | normal diet + Alcohol + FPB 100 mg/kg b.w./day |
| FPB400 | normal diet + Alcohol + FPB 400 mg/kg b.w./day |
| PγG Content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | NPB | FPB/D1 | FPB/D2 | FPB/D3 |
| mg/g | 47.17 ± 0.02 c | 50.31 ± 0.01 b | 64.74 ± 0.01 a | 65.50 ± 0.01 a |
| Group | DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activity | Antithrombotic Activity |
|---|---|---|
| (%) | (Unit) | |
| BHT | 87.90 ± 1.36 a | - |
| N | 14.05 ± 0.52 b | 2.88 ± 0.17 a |
| F3 | 55.69 ± 1.94 ce | 39.20 ± 0.55 b |
| F5 | 56.98 ± 0.25 c | 39.20 ± 0.60 b |
| Ba9 | 57.81 ± 1.49 c | 42.00 ± 0.58 b |
| Ak | 46.33 ± 0.48 d | 33.80 ± 0.44 c |
| Sc | 53.89 ± 2.81 a | 33.80 ± 0.62 d |
| Bs | 50.58 ± 2.61 c | 64.80 ± 0.74 e |
| Oil Red O Absorbance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | N | C | NPB | FPB/D1 | FPB/D2 | FPB/D3 |
| % of control | 100.00 ± 6.46 d | 305.50 ± 11.68 a | 257.80 ± 6.49 b | 235.78 ± 11.68 b | 234.86 ± 7.78 b | 179.82 ± 28.54 c |
| Group | Body Weight (g) | Relative Liver Weight (% of Terminal Body Weight) | Water Consumption (mL/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 166.33 ± 7.37 a | 3.33 ± 0.24 bc | 35.88 ± 6.77 a |
| C | 124.33 ± 10.41 e | 3.76 ± 0.41 a | 25.43 ± 3.41 b |
| PC | 156.33 ± 10.79 c | 3.33 ± 0.29 bc | 23.75 ± 2.36 b |
| NPB | 144.67 ± 14.19 d | 3.51 ± 0.23 ab | 26.83 ± 4.62 b |
| FPB100 | 161.67 ± 27.68 b | 3.08 ± 0.26 d | 29.50 ± 7.92 b |
| FPN400 | 125.67 ± 13.05 e | 3.33 ± 0.21 bc | 22.50 ± 2.95 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sim, S.-Y.; Cho, H.-D.; Lee, S.-B. Amelioration of Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis in a Rat Model via Consumption of Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid-Enriched Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Using Bacillus subtilis. Foods 2025, 14, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050861
Sim S-Y, Cho H-D, Lee S-B. Amelioration of Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis in a Rat Model via Consumption of Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid-Enriched Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Using Bacillus subtilis. Foods. 2025; 14(5):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050861
Chicago/Turabian StyleSim, So-Yeon, Hyun-Dong Cho, and Sae-Byuk Lee. 2025. "Amelioration of Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis in a Rat Model via Consumption of Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid-Enriched Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Using Bacillus subtilis" Foods 14, no. 5: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050861
APA StyleSim, S.-Y., Cho, H.-D., & Lee, S.-B. (2025). Amelioration of Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis in a Rat Model via Consumption of Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid-Enriched Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Using Bacillus subtilis. Foods, 14(5), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050861





