Synergistic Bactericidal Efficiency of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water–High-Pressure Parallel Processing on Escherichia coli in Freshly Cut Gastrodia elata Slices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation and Inoculation Method of Freshly Cut G. elata Slices
2.3. Preparation of SAEW
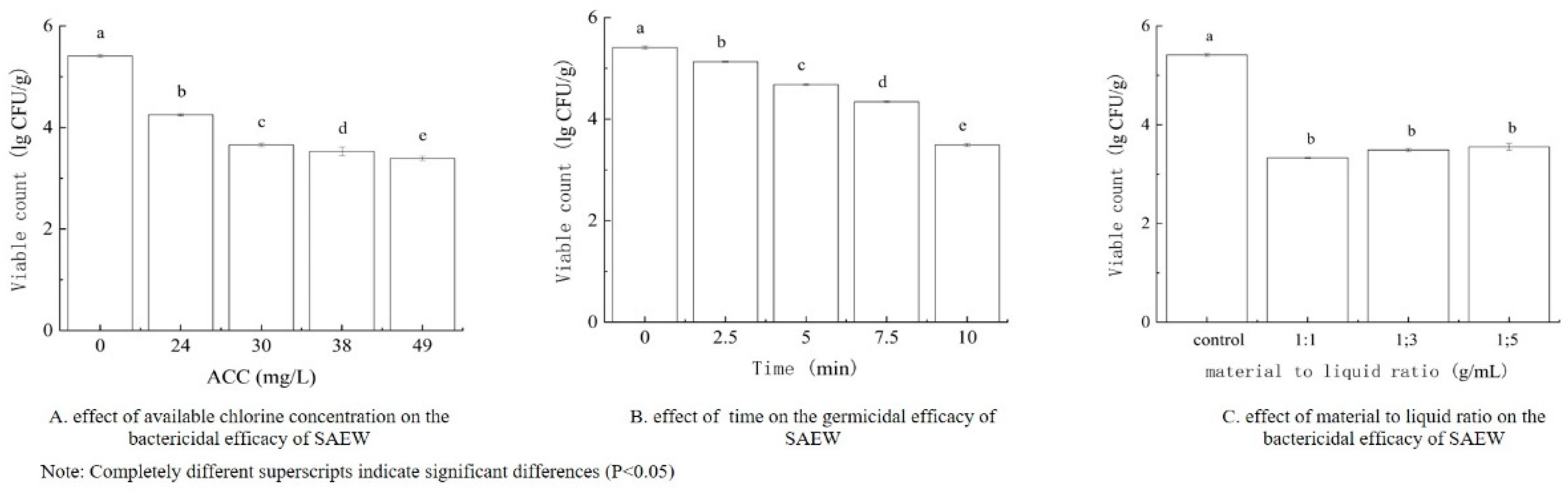
2.4. Single-Factor Experiment
2.4.1. SAEW Bactericidal Treatment
Determination of ACC of SAEW
Determination of Treatment Time of SAEW
Determination of Material-to-Liquid Ratio of SAEW
2.4.2. HP Bactericidal Treatment
Determination of HP
Determination of HP Treatment Time
Determination of HP Material-to-Liquid Ratio
2.4.3. Response Surface Design
2.4.4. Measurement of Total Number of Colonies
2.5. Construction Method for the Bactericidal Synergy Term Model
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Different Treatment Methods on the Bactericidal Efficiency Against E. coli on the Surfaces of Freshly Cut G. elata Slices
3.2. Establishment of the Synergistic Bactericidal Prediction Model
3.2.1. Analysis of the Response Surface Results for the Bactericidal Efficiency of SAEW on Freshly Cut G. elata Slices
3.2.2. Analysis of the Response Surface Results for the Bactericidal Efficiency of HP on Freshly Cut G. elata Slices
3.2.3. Response Surface Analysis of the Bactericidal Efficiency of SAEW–HP Parallel Treatment on Freshly Cut G. elata Slices
3.2.4. Analysis of the Synergistic Enhancement Effect of SAEW–HP Parallel Bactericidal Treatment
3.3. Validation Experiment for the Optimized Conditions of Freshly Cut G. elata Slices
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, W. Study on microbial growth in fresh cut Citrullus lanatus under normal and refrigerated conditions. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2025, 16, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, W.; Yuan, X. Research progress on the browning mechanisms and preservative technologies of fresh-cut fruit and vegetables. Food Sci. 2025, 1–37. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.20241105.1332.028.html (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Du, Y.; Tian, Q.; Li, G.; Yi, J.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Y. Advanced application of slightly acidic electrolyzed water for fresh-cut fruits and vegetables preservation. Food Res. Int. 2024, 195, 114996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Medicinal Materials. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/s7892/202311/f0d6ef3033b54333a882e3d009ff49bf.shtml (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Du, J.; Jin, L. Effect of methyl jasmonate on storage quality of fresh-cut Cistanche deserticola. Food Ferment. Ind. 2024, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G. Analysis of the Effect of Different Processing Conditions on the Quality and Flavor of Tianma. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.B.; Poonam, S.; Kumar, S.S. A comprehensive review on impact of non-thermal processing on the structural changes of food components. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110647. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F. Development of non-thermal processing technology for food at home and abroad. Food Saf. Guide 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabiscol, E.; Tamarit, J.; Ros, J. Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by teactive oxygen species. Int. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Lan, L.S.; Shi, H. Sublethal injury and recovery of E. coli O157:H7 after freezing and thawing. Food Control 2021, 120, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa-Zacharia, A. Application of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water as a Potential Sanitizer in the Food Industry. J. Food Qual. 2024, 2024, 5559753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midori, K.; Takaaki, I.; Angelica, N. Spatial disinfection potential of slightly acidic electrolyzed water. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253595. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, M.; Luo, Z.-S.; Wang, L.; Yang, M.; Li, D.; Liang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, L. Application of slightly acidic electrolyzed water in food preservation and disinfection. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 3795–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Ha, J.H. Bactericidal efficiencies of diluted slightly acidic electrolyzed water in quantitative suspension and cabbage tests. LWT 2021, 152, 112291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xue, S.J.; Tang, J. Characterization of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on effective disinfection against microbial safety and retention of phenolic compound in SAEW treated fresh-cut romaine lettuce. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyae029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, P.; Ran, R. Bactericidal Efficiency of combined slightly acidic electrolyzed water and ultrasonic treatment against E. coli on Fresh-Cut lettuce. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Li, L.; Tan, L.; Yan, X.; Fan, J.; Ye, Z.; He, J. Effect of slightly acidic electrolytic water on storage quality of Fresh-cut Yunnan red pear. J. Food Saf. Qual. Insp. 2017, 8, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Gao, W.; Tan, L.; Fan, J.; Ye, Z.; He, J. Study on bactericidal efficiency of slightly acidic electrolytic water on Xuanwei ham slices. J. Food Saf. Qual. Insp. 2016, 7, 4059–4065. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.-Y.; He, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, Q. Optimization of the Sterilization Process of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water and Its Effect on the Storage Quality of Yunnan Fresh-cut Rice Noodles. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Bi, B.; He, J. Effects of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water on the Quality of Fresh-Cut Apple. Foods 2022, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yue, H.; Xu, S.; Tian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J. The effect of electrolyzed water on fresh-cut eggplant in storage period. LWT 2020, 123, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palotás, P.; Palotas, P., Jr.; Jónás, G.; Lehel, J.; Friedrich, L. Preservative Effect of Novel Combined Treatment with Electrolyzed Active Water and Lysozyme Enzyme to Increase the Storage Life of Vacuum-Packaged Carp. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 4861471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Xiang, Q.; Cullen, P.J.; Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Liu, D.; Ding, T. Plasma-activated water (PAW) and slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) as beef thawing media for enhancing microbiological safety. LWT 2020, 117, 108649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Ye, Z.; He, J. Effect of slightly acidic electrolytic water treatment on storage quality of wild fungi. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Donda Zbinden, M.; Schmidt, M.; Vignatti, C.I.; Pirovani, M.É.; Böhm, V. High-Pressure Processing of Fruit Smoothies Enriched with Dietary Fiber from Carrot Discards: Effects on the Contents and Bioaccessibilities of Carotenoids and Vitamin E. Molecules 2024, 29, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houška, M.; Silva, F.V.M.; Evelyn; Buckow, R.; Terefe, N.S.; Tonello, C. High pressure processing applications in plant foods. Foods 2022, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nema, P.K.; Sehrawat, R.; Ravichandran, C.; Kaur, B.P.; Kumar, A.; Tarafdar, A. Inactivating food microbes by high-pressure processing and combined nonthermal and thermal treatment: A review. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 5797843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I. Evaluation of pulsed electric field and high-pressure processing on the overall quality of refrigerated Concord grape juice. LWT 2024, 198, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Yang, J.-L.; Hao, B.; Lu, Y.-C.; Qian, Z.-L.; Li, Y.; Ye, S.; Tang, J.-R.; Chen, M.; Long, G.-Q.; et al. Comparative transcriptome and metabolome ana-lyses provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying taproot thickening in Panax notoginseng. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, S.; Pokhrel, P.R.; Unluturk, S.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Identification of equivalent processing conditions for pasteurization of strawberry juice by high pressure, ultrasound, and pulsed electric fields processing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 57, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, R.M.; Zeng, X.-A.; Han, Z.; Sahar, A.; Khalil, A.A.; Rahman, U.U.; Khan, M.; Mehmood, T. Combined effects of pulsed electric field and ultrasound on bioactive compounds and microbial quality of grapefruit juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadias, M.; Usall, J.; Oliveira, M.; Alegre, I.; Viñas, I. Efficacy of neutral electrolyzed water (NEW) for reducing microbial contamination on minimally-processed vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 123, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa-Zacharia, A.; Kamitani, Y.; Muhimbula, H. Antimicrobial effect of slightly acidic electrolyzed water for inactivation of Salmonella spp. and E.coli on fresh-cut straw berries (Fragaria L.). Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 2174–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.-R. Determination of available chlorine in sodium calcium hypochlorite by iodimetry. Inorg. Salt Ind. 2002, 1, 42–44+2. [Google Scholar]
- GB 4789.2-2016; National Standard for Food Safety Food Microbiological Test Determination of Total Number of Colonies. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC: Beijing, China; State Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Silva, F.V. Use of power ultrasound to enhance the thermal inactivation of Clostridium perfringens spores in beef slurry. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 206, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Barba, F.J.; Roselló-Soto, E.; Marszałek, K.; Kovačević, D.B.; Jambrak, A.R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Chemat, F.; Putnik, P. Green food processing: Concepts, strategies, and tools. In Green Food Processing Techniques; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Meullemiestre, A.; Turk, M.; Perino, S.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Abert-Vian, M. Review of Green Food Processing techniques. Preservation, transformation, and extraction. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunag, L.; Wu, H. Research and application of green processing technology in fruit and vegetable industry. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2015, 6, 2056–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Coding | ACC (mg/L) | Soaking Time (min) | Material-to-Liquid Ratio (g/mL) | Pressure (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 30 | 5 | 1:1 | 0.1 |
| 0 | 38 | 7.5 | 1:3 | |
| 1 | 49 | 10 | 1:5 |
| Coding | Pressure (MPa) | Pressurization Time (min) | Material-to-Liquid Ratio (g/mL) | ACC (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 100 | 5 | 1:1 | 0 |
| 0 | 150 | 7.5 | 1:3 | |
| 1 | 200 | 10 | 1:5 |
| Coding | ACC (mg/L) | Pressure (MPa) | Pressurization Time (min) | Material-to-Liquid Ratio (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 30 | 100 | 5 | 1:1 |
| 0 | 38 | 150 | 7.5 | 1:3 |
| 1 | 49 | 200 | 10 | 1:5 |
| Experiment No. | Pressure (MPa) | ACC (mg/mL) | Treatment Time (min) | Material-to-Liquid Ratio (g/mL) | ΔI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 39.5 | 7.5 | 1:3 | 12.03 |
| 2 | 150 | 39.5 | 7.5 | 1:5 | 10.05 |
| 3 | 200 | 30 | 5 | 1:3 | 10.67 |
| 4 | 150 | 39.5 | 5 | 1:5 | 12.38 |
| 5 | 200 | 30 | 5 | 1:5 | 10.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Q.; Nong, X.; Lang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; He, J. Synergistic Bactericidal Efficiency of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water–High-Pressure Parallel Processing on Escherichia coli in Freshly Cut Gastrodia elata Slices. Foods 2025, 14, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050790
Gao Q, Nong X, Lang T, Liu Y, Ye S, He J. Synergistic Bactericidal Efficiency of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water–High-Pressure Parallel Processing on Escherichia coli in Freshly Cut Gastrodia elata Slices. Foods. 2025; 14(5):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050790
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Qing, Xin Nong, Tuanjian Lang, Yajin Liu, Shuxin Ye, and Jinsong He. 2025. "Synergistic Bactericidal Efficiency of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water–High-Pressure Parallel Processing on Escherichia coli in Freshly Cut Gastrodia elata Slices" Foods 14, no. 5: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050790
APA StyleGao, Q., Nong, X., Lang, T., Liu, Y., Ye, S., & He, J. (2025). Synergistic Bactericidal Efficiency of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water–High-Pressure Parallel Processing on Escherichia coli in Freshly Cut Gastrodia elata Slices. Foods, 14(5), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050790






