Different Varieties of Water Caltrop (Trapa bispinosa) Starch: Physicochemical Properties and Digestibility Modulated by Its Multi-Scale Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Isolation of Water Caltrop Starch
2.3. Amylose Content
2.4. Structural Characteristics
2.4.1. Normal Light Microscopy and Polarized Light Microscopy
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.3. Particle Size
2.4.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.4.6. Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS)
2.4.7. 13C CP/MAS Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
2.4.8. Amylopectin Chain Length Distributions
2.5. Physicochemical Properties
2.5.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.2. Pasting Properties
2.5.3. Swelling Power and Solubility
2.6. In Vitro Digestibility
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Amylose Content
3.2. Structural Characteristics
3.2.1. Granule Morphology
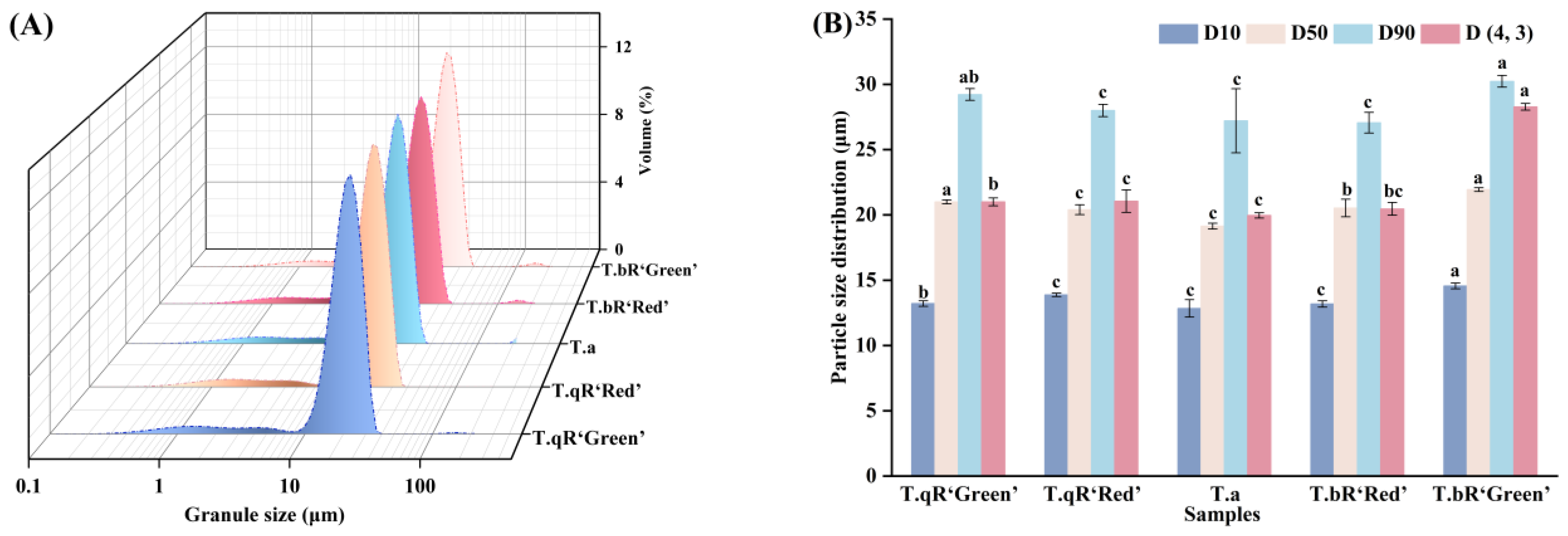
3.2.2. Particle Size
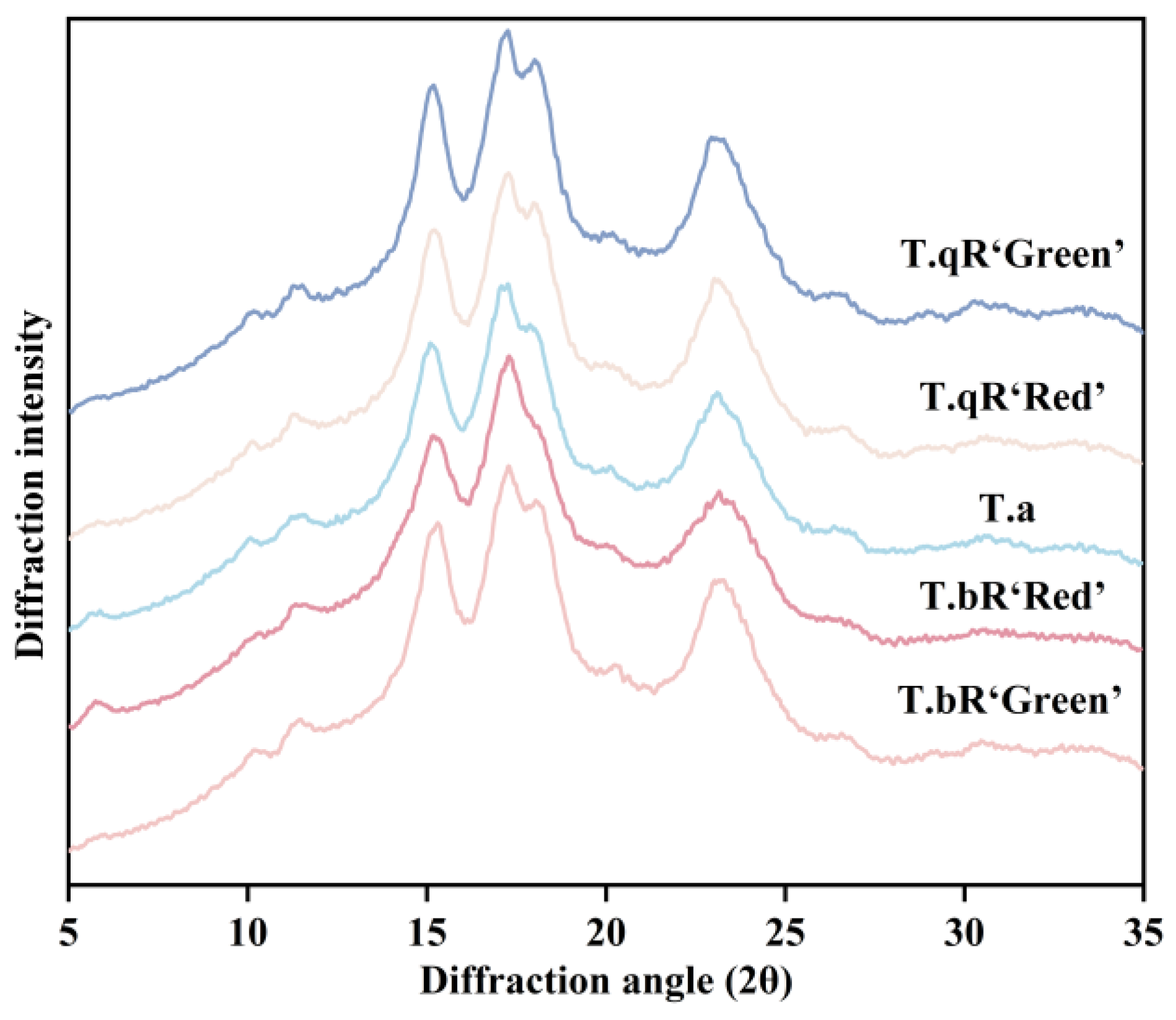
3.2.3. Crystalline Structure
3.2.4. Short-Range Ordered Structure
3.2.5. Lamellar Structure
3.2.6. Helical Structure
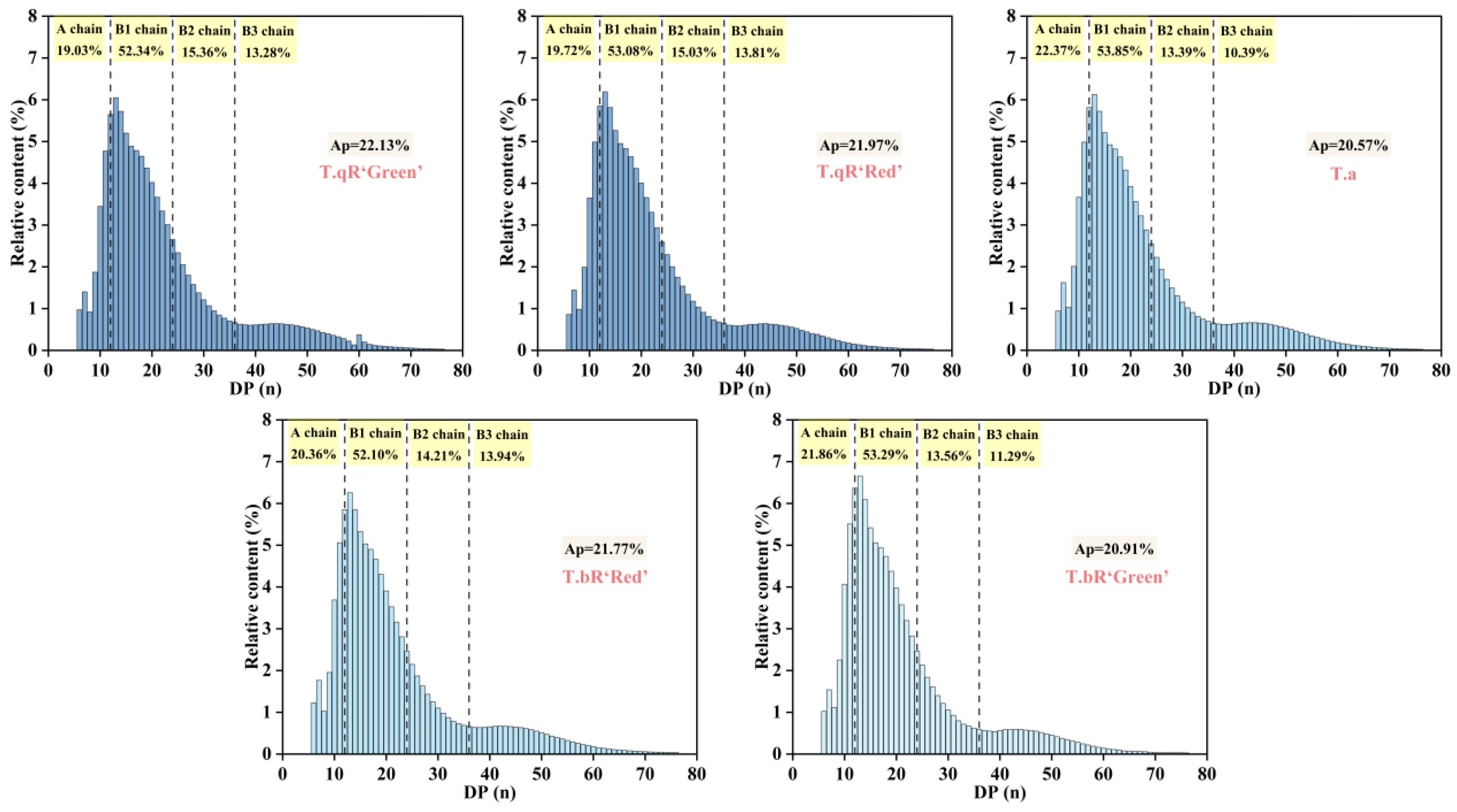
3.2.7. Fine Structure of Amylopectin
3.3. Physicochemical Properties
3.3.1. Thermal Properties
3.3.2. Pasting Properties
3.3.3. Swelling Power and Solubility
3.4. In Vitro Digestibility
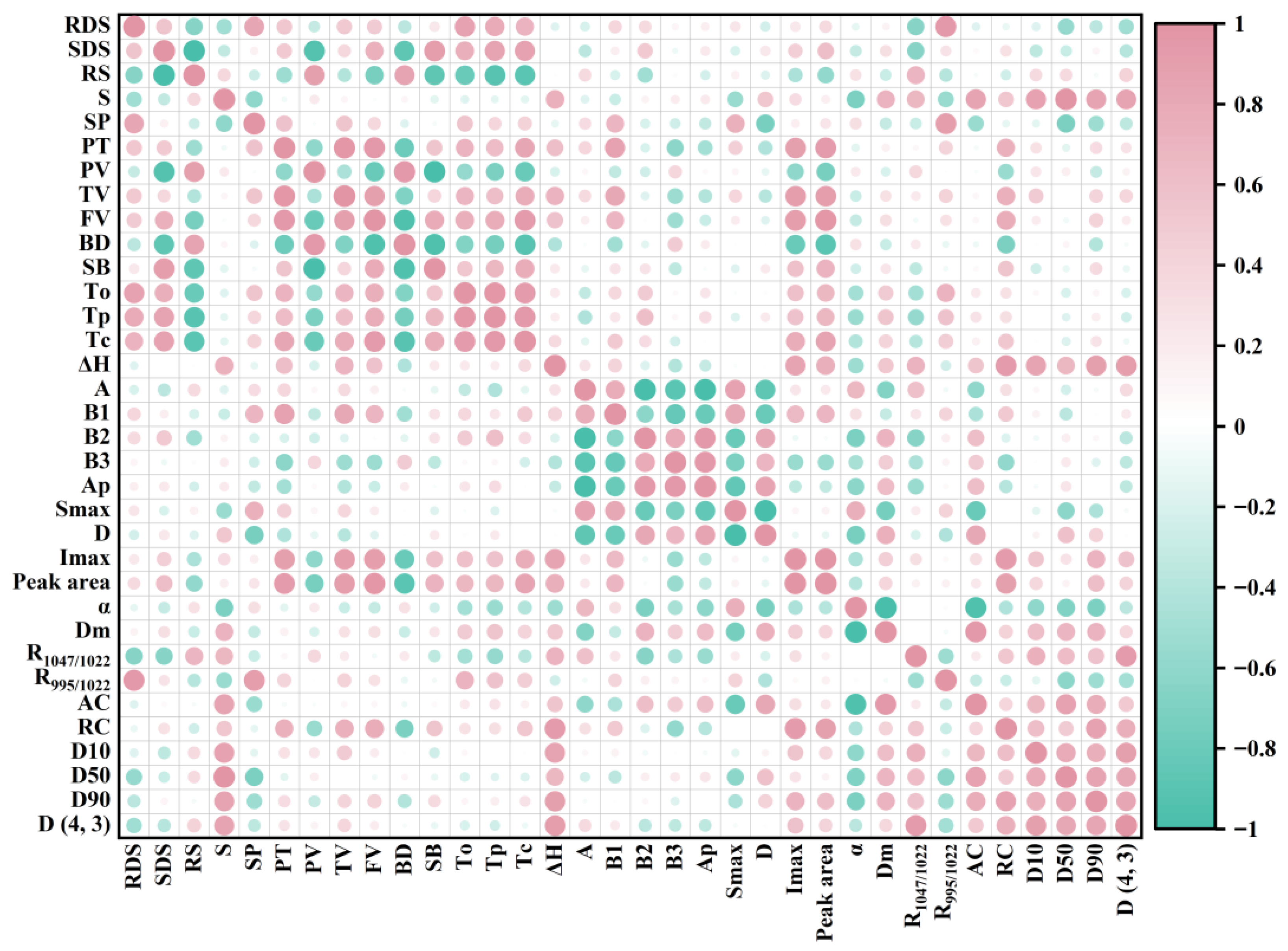
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, F. Chemical Composition, Health Effects, and Uses of Water Caltrop. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Shukla, S.S.; Dubey, A.D.; Gautam, S.; Tripathi, J. Control of Post-Harvest Storage Losses in Water Chestnut (Trapa Bispinosa Roxburg) Fruits by Natural Functional Herbal Coating and Gamma Radiation Processing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 2842–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Kaur, G.; Singh, A. Water Chestnut Starch: Extraction, Chemical Composition, Properties, Modifications, and Application Concerns. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023, 1, 228–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, L.; Ali, T.M.; Hasnain, A. Effect of Chemical Modifications on Morphological and Functional Characteristics of Water-chestnut Starches and Their Utilization as a Fat-replacer in Low-fat Mayonnaise. Starch Starke 2017, 69, 1600041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-F.; Wong, W.-T. Edible Clusteroluminogenic Films Obtained from Starch of Different Botanical Origins for Food Packaging and Quality Management of Frozen Foods. Membranes 2022, 12, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Singh, A.; Nath, L.K.; Pani, N.R. Evaluation of Trapa Bispinosa Roxb. Starch as Pharmaceutical Binder in Solid Dosage Form. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, S86–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, K.; Nawab, A.; Alam, F.; Hadi, A.; Raza, M. Development of Novel Biodegradable Water Chestnut Starch/PVA Composite Film. Evaluation of Plasticizer Effect over Physical, Barrier, and Mechanical Properties. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Shibata, T.; Shibata, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Kubo, E. Lutein plus Water Chestnut (Trapa Bispinosa Roxb.) Extract Inhibits the Development of Cataracts and Induces Antioxidant Gene Expression in Lens Epithelial Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9204620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaoka, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Kato, N.; Hayakawa, C.; Kawabe, S.; Ganeko, N.; Uemura, T.; Ito, H. Characterization and Identification of Bioactive Polyphenols in the Trapabispinosa Roxb. Pericarp Extract. Molecules 2021, 26, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinno, M.; Nagai, R.; Takeuchi, M.; Watanabe, A.; Teruya, K.; Sugawa, H.; Hatakeyama, N.; Jinno, Y. Trapa Bispinosa Roxb. Extract Lowers Advanced Glycation End-Products and Increases Live Births in Older Patients with Assisted Reproductive Technology: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2021, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Tian, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, M.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X. The Multi-Scale Structure, Thermal and Digestion Properties of Mung Bean Starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K. Variations in the Multilevel Structure, Gelatinization and Digestibility of Litchi Seed Starches from Different Varieties. Foods 2022, 11, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovač, M.; Ravnjak, B.; Šubarić, D.; Vinković, T.; Babić, J.; Ačkar, Đ.; Lončarić, A.; Šarić, A.; Bulatović, V.O.; Jozinović, A. Isolation and Characterization of Starch from Different Potato Cultivars Grown in Croatia. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Wang, W.; Lei, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, X. Changes in Crystal Structure of Chickpea Starch Samples during Processing Treatments: An X-Ray Diffraction and Starch Moisture Analysis Study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuryev, V.P.; Krivandin, A.V.; Kiseleva, V.I.; Wasserman, L.A.; Genkina, N.K.; Fornal, J.; Blaszczak, W.; Schiraldi, A. Structural Parameters of Amylopectin Clusters and Semi-Crystalline Growth Rings in Wheat Starches with Different Amylose Content. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Gao, L.; Wu, D.; Gao, C.; Meng, L.; Feng, X.; Tang, X. Effect of Improved Extrusion Cooking Technology on Structure, Physiochemical and Nutritional Characteristics of Physically Modified Buckwheat Flour: Its Potential Use as Food Ingredients. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 109872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, K.; Goux, A.; Meynier, A.; Quigley, M.; Englyst, H.; Brack, O.; Vinoy, S. Inter-Laboratory Validation of the Starch Digestibility Method for Determination of Rapidly Digestible and Slowly Digestible Starch. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, F.; Liu, K.; Wang, H. Understanding the Multi-Scale Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Millet Starch with Varied Amylose Content. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, A.; Kadono, Y. Allozyme Variations and Classification of Trapa (Trapaceae) in Japan. Aquat. Bot. 2005, 83, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effect of Ultrasonic Pretreatment on Physicochemical, Thermal, and Rheological Properties of Chemically Modified Corn Starch. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Shui, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhuang, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ye, R. Hericium Erinaceus β-Glucan Modulates in Vitro Wheat Starch Digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E.; Hernandez-Landaverde, M.A.; Delgado, J.M.; Ramirez-Gutierrez, C.F.; Ramirez-Cardona, M.; Millan-Malo, B.M.; Londoño-Restrepo, S.M. Crystalline Structures of the Main Components of Starch. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Cai, J.; Han, W.; Huai, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, C. Comparison of Starches Isolated from Three Different Trapa Species. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 37, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xue, W.; Li, T.; Wang, L. Understanding the Relationship between the Molecular Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soft Rice Starch. Foods 2023, 12, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Morales, A.; Jiménez-Estrada, M.; Mora-Escobedo, R. Determination of the Structural Changes by FT-IR, Raman, and CP/MAS 13C NMR Spectroscopy on Retrograded Starch of Maize Tortillas. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Gao, L.; Gong, X.; Qu, Y.; Feng, B. Functional and Physicochemical Properties of Flours and Starches from Different Tuber Crops. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, X.; Pan, Q.; Huang, Z.; et al. The Influence of Temperature Changes on the Rice Starch Structure and Digestive Characteristics: One and Two-Step Annealing. Foods 2022, 11, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, G.; Hemar, Y.; Corke, H.; Zhu, F. Granular Architecture of Lotus Seed Starch and Its Impact on Physicochemical Properties. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X. Heat-Moisture Modified Blue Wheat Starch: Physicochemical Properties Modulated by Its Multi-Scale Structure. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, L.; Qu, J.; Blennow, A.; Hansen, A.R.; Wu, Y.; Guo, D.; Liu, X. Amylose Content and Specific Fine Structures Affect Lamellar Structure and Digestibility of Maize Starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Tu, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Li, N.; Nishinari, K.; Riffat, S.; Jiang, F. Understanding the Multi-Scale Structure and Digestion Rate of Water Chestnut Starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, D.; Fan, T.; Wang, M.; Zhu, M.; Ding, J.; Zhu, X.; Guo, W.; Shi, Y.-C. Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Two Waxy Wheat Starches. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Xu, B.; Qin, F.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Meng, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. C-Type Starch from High-Amylose Rice Resistant Starch Granules Modified by Antisense RNA Inhibition of Starch Branching Enzyme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7383–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Cai, C.; Man, J.; Zhou, W.; Wei, C. Structural and Functional Properties of C-Type Starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Abe, J.; Hizukuri, S. A Periodic Distribution of the Chain Length of Amylopectin as Revealed by High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 283, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, B.A.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Impact of Starch Chain Length Distributions on Physicochemical Properties and Digestibility of Starches. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cao, S.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, W. Modification in Physicochemical, Structural and Digestive Properties of Pea Starch during Heat-Moisture Process Assisted by Pre- and Post-Treatment of Ultrasound. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, S.W.; Wang, A.; Li, Z.; Qiu, J. Influence of Superheated Steam Treatment with Tempering on Lipid Oxidation and Hydrolysis of Highland Barley during Storage. Food Control 2021, 127, 108133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Jia, M.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, B.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, G.; Qin, P.; et al. Amylopectin Chain Length Distributions and Amylose Content Are Determinants of Viscoelasticity and Digestibility Differences in Mung Bean Starch and Proso Millet Starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, A.; Yu, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, E.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q. Parameterizing Starch Chain-Length Distributions for Structure-Property Relations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, C.; Li, E.; Gilbert, R.G.; Xu, B. A Molecular Explanation of Wheat Starch Physicochemical Properties Related to Noodle Eating Quality. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, F.; Ji, X.; Feng, B.; Liang, J.; Yu, X.; Du, S. Structure, Physicochemical, Functional and in Vitro Digestibility Properties of Non-Waxy and Waxy Proso Millet Starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, B.; Yang, X.; Zou, L.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N.; Ren, G.; Zhang, L.; et al. Starch Chain-Length Distributions Determine Cooked Foxtail Millet Texture and Starch Physicochemical Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, B.; Liang, Y.; Jia, M.; Yun, J.; Niu, J.; Li, H.; Ren, G.; Qin, P.; et al. Starch Chain-Length Distributions Affect the Processing and Digestion Characteristics of Proso Millet Starch. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.I. Protein-Starch Matrix Microstructure during Rice Flour Pastes Formation. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 74, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Bian, X.; Guo, K.; Zhou, L.; Wei, C. Characterization and Comparative Study of Starches from Seven Purple Sweet Potatoes. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liang, B.; Chai, Y.; Xue, L.; Wang, X.; Yin, X. Effect of Different Heat Treatments on Physicochemical Properties and Structural and Digestibility of Water Caltrop Starch. Starch Starke 2020, 72, 1900275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, D.; Sang, S.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X.; Cui, B. Effect of Superheated Steam Treatment on the Structural and Digestible Properties of Wheat Flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Lan, T.; Lei, Y.; Suo, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lei, J.; Sun, X.; Ma, T. Modification in Structural, Physicochemical, Functional, and in Vitro Digestive Properties of Kiwi Starch by High-Power Ultrasound Treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 86, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Qi, W.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, J. Clarifying the Structure and Characteristics of Different Varieties Potatoes Starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Gong, X.; Feng, B. Physicochemical Properties of Starches in Proso (Non-Waxy and Waxy) and Foxtail Millets (Non-Waxy and Waxy). Molecules 2019, 24, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, F. Amylopectin Molecular Structure in Relation to Physicochemical Properties of Quinoa Starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wu, X.; Gao, T.; Chen, L.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effects of Ultrasonic and Chemical Dual Modification Treatments on the Structural, and Properties of Cornstarch. Food Chem. 2024, 451, 139221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | Amylose Content (%) | Relative Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| T.qR‘Green’ | 30.93 ± 1.73 a | 27.60 ± 0.44 b |
| T.qR‘Red’ | 30.10 ± 0.48 ab | 26.76 ± 0.61 b |
| T.a | 25.37 ± 0.42 b | 27.14 ± 0.16 b |
| T.bR‘Red’ | 28.22 ± 0.63 ab | 24.94 ± 0.61 c |
| T.bR‘Green’ | 30.71 ± 0.21 ab | 29.04 ± 0.42 a |
| Samples | Smax (nm−1) | D (nm) | Peak Area | Imax (a.u.) | α | Dm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T.qR‘Green’ | 0.612 ± 0.001 d | 10.27 ± 0.02 a | 34.66 ± 0.55 b | 145.03 ± 0.79 c | −2.88 ± 0.04 a | 2.88 ± 0.04 a |
| T.qR‘Red’ | 0.626 ± 0.001 bc | 10.04 ± 0.01 bc | 33.86 ± 0.57 bc | 147.64 ± 0.87 b | −2.87 ± 0.09 a | 2.87 ± 0.09 a |
| T.a | 0.641 ± 0.000 a | 9.81 ± 0.00 d | 33.69 ± 0.45 c | 144.88 ± 0.54 c | −2.50 ± 0.05 b | 2.50 ± 0.05 b |
| T.bR‘Red’ | 0.624 ± 0.002 c | 10.07 ± 0.03 b | 21.25 ± 0.24 d | 93.43 ± 0.33 d | −2.61 ± 0.04 b | 2.61 ± 0.04 b |
| T.bR‘Green’ | 0.627 ± 0.001 b | 10.02 ± 0.02 c | 38.16 ± 0.43 a | 165.37 ± 0.42 a | −2.81 ± 0.11 a | 2.81 ± 0.11 a |
| Samples | PT (°C) | PV (cP) | TV (cP) | FV (cP) | BD (cP) | SB (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T.qR‘Green’ | 83.70 ± 0.36 b | 2850.33 ± 69.78 d | 2088.66 ± 12.05 c | 3873.33 ± 37.85 b | 747.00 ± 9.84 d | 1757.33 ± 6.65 a |
| T.qR‘Red’ | 85.88 ± 0.59 a | 3456.67 ± 35.11 b | 2286.67 ± 14.64 a | 3868.00 ± 7.54 b | 1193.00 ± 6.08 b | 1589.33 ± 9.01 c |
| T.a | 86.55 ± 0.60 a | 3081.00 ± 26.88 c | 2233.33 ± 10.69 b | 3927.00 ± 30.44 a | 874.00 ± 5.29 c | 1681.33 ± 6.65 b |
| T.bR‘Red’ | 79.40 ± 0.52 c | 3963.33 ± 56.86 a | 1867.00 ± 30.01 d | 3316.67 ± 6.42 c | 2062.67 ± 6.65 a | 1479.33 ± 9.07 d |
| T.bR‘Green’ | 85.63 ± 0.40 a | 3476.67 ± 20.81 b | 2270.33 ± 19.00 a | 3844.67 ± 19.55 b | 1182.00 ± 6.08 b | 1596.00 ± 5.29 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, T.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, Q.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Han, W. Different Varieties of Water Caltrop (Trapa bispinosa) Starch: Physicochemical Properties and Digestibility Modulated by Its Multi-Scale Structure. Foods 2025, 14, 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244304
Ma T, Wu Q, Yuan Y, Chen X, Lin Q, Xiao H, Li J, Han W. Different Varieties of Water Caltrop (Trapa bispinosa) Starch: Physicochemical Properties and Digestibility Modulated by Its Multi-Scale Structure. Foods. 2025; 14(24):4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244304
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Tengfei, Qiong Wu, Yuyang Yuan, Xiaoxin Chen, Qinlu Lin, Huaxi Xiao, Jiangtao Li, and Wenfang Han. 2025. "Different Varieties of Water Caltrop (Trapa bispinosa) Starch: Physicochemical Properties and Digestibility Modulated by Its Multi-Scale Structure" Foods 14, no. 24: 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244304
APA StyleMa, T., Wu, Q., Yuan, Y., Chen, X., Lin, Q., Xiao, H., Li, J., & Han, W. (2025). Different Varieties of Water Caltrop (Trapa bispinosa) Starch: Physicochemical Properties and Digestibility Modulated by Its Multi-Scale Structure. Foods, 14(24), 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244304





