Evaluation of the Oxidative Process of Chia Seed Oil by Means of ESR Combined with LF-NMR and SAXS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fatty Acid Composition Analysis of Chia Seed Oil
2.3. ESR Measurements
2.4. LF-NMR Analysis of Chia Seed Oil
2.5. SAXS Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fatty Acids Composition
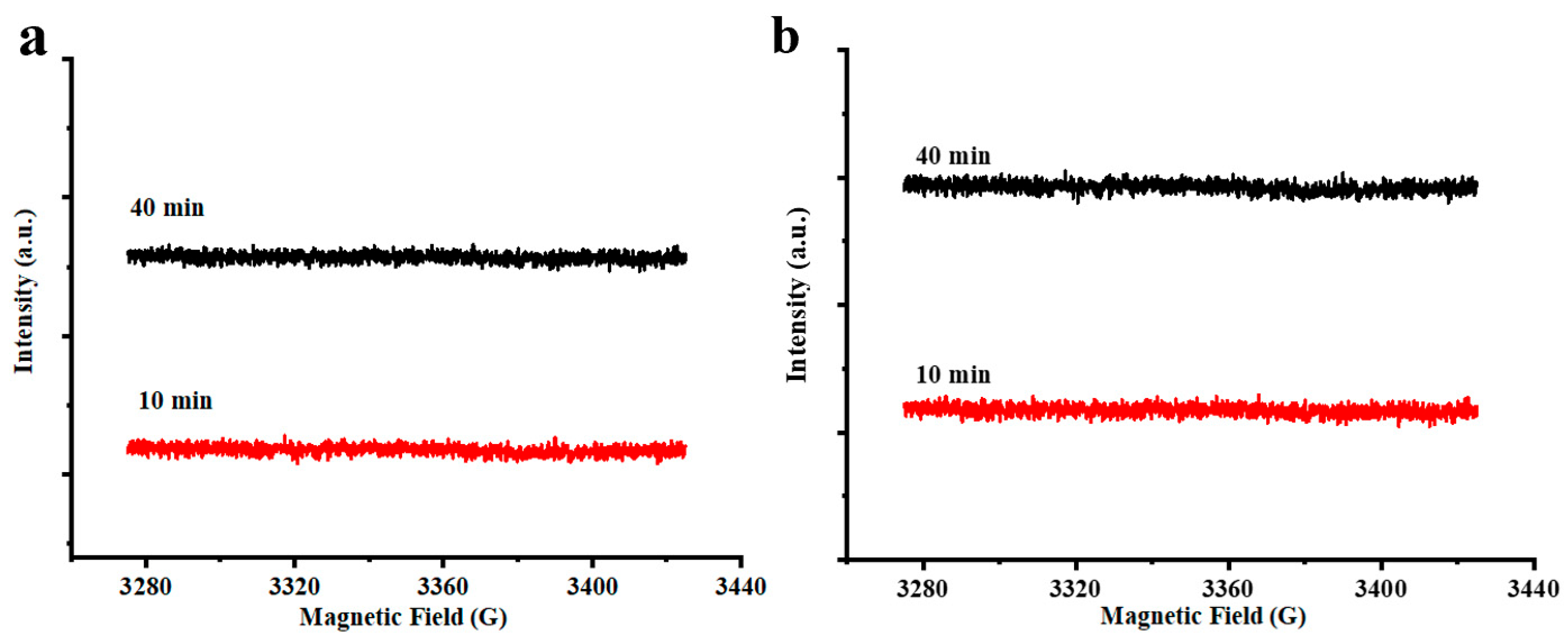
3.2. Study on Free Radicals of Chia Seed Oil by ESR
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature
3.2.2. Radicals Analysis of the Main Fatty Acids
3.2.3. Analysis of the Radicals in Chia Seed Oil
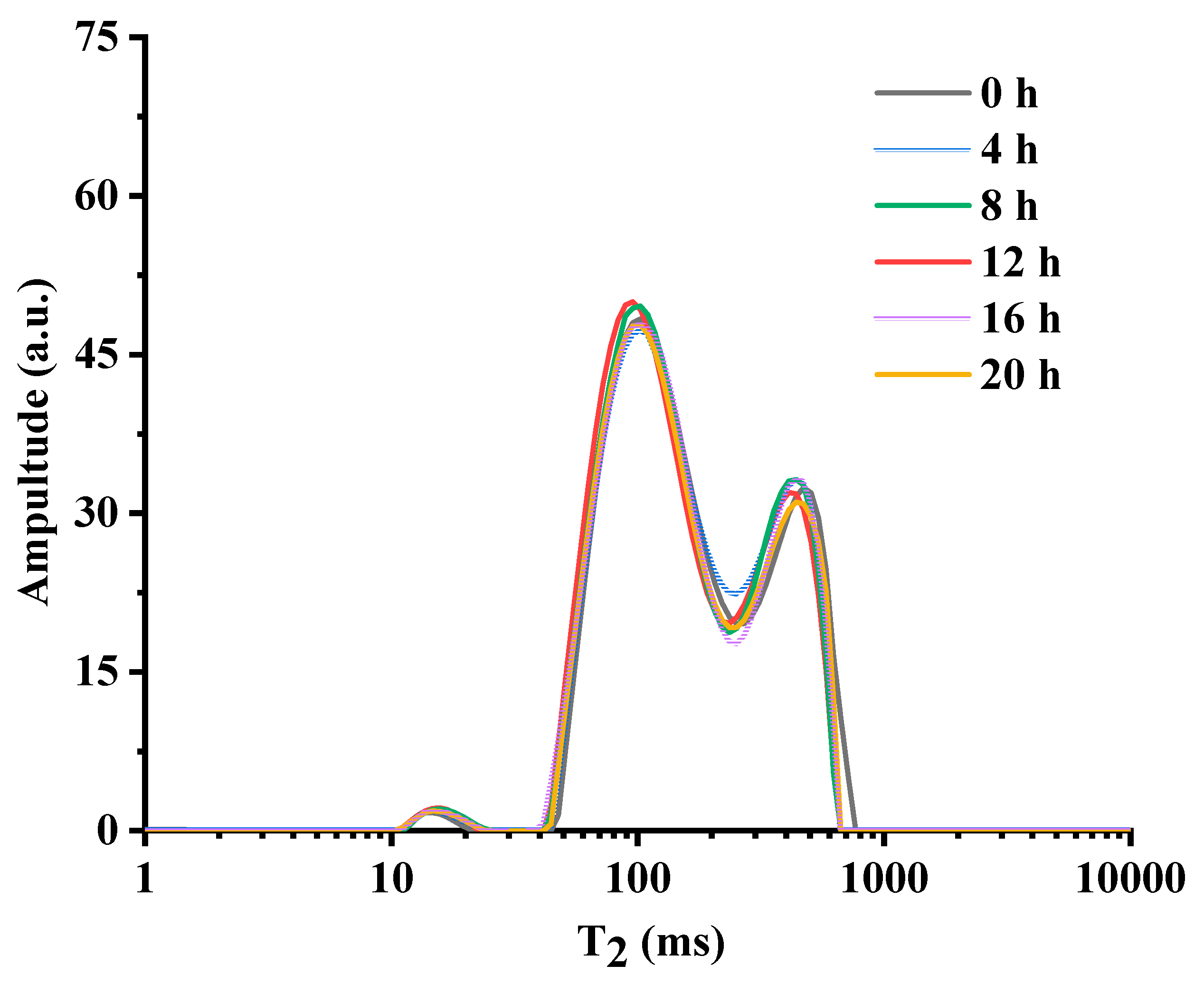
3.3. LF-NMR Study of Chia Seed Oil
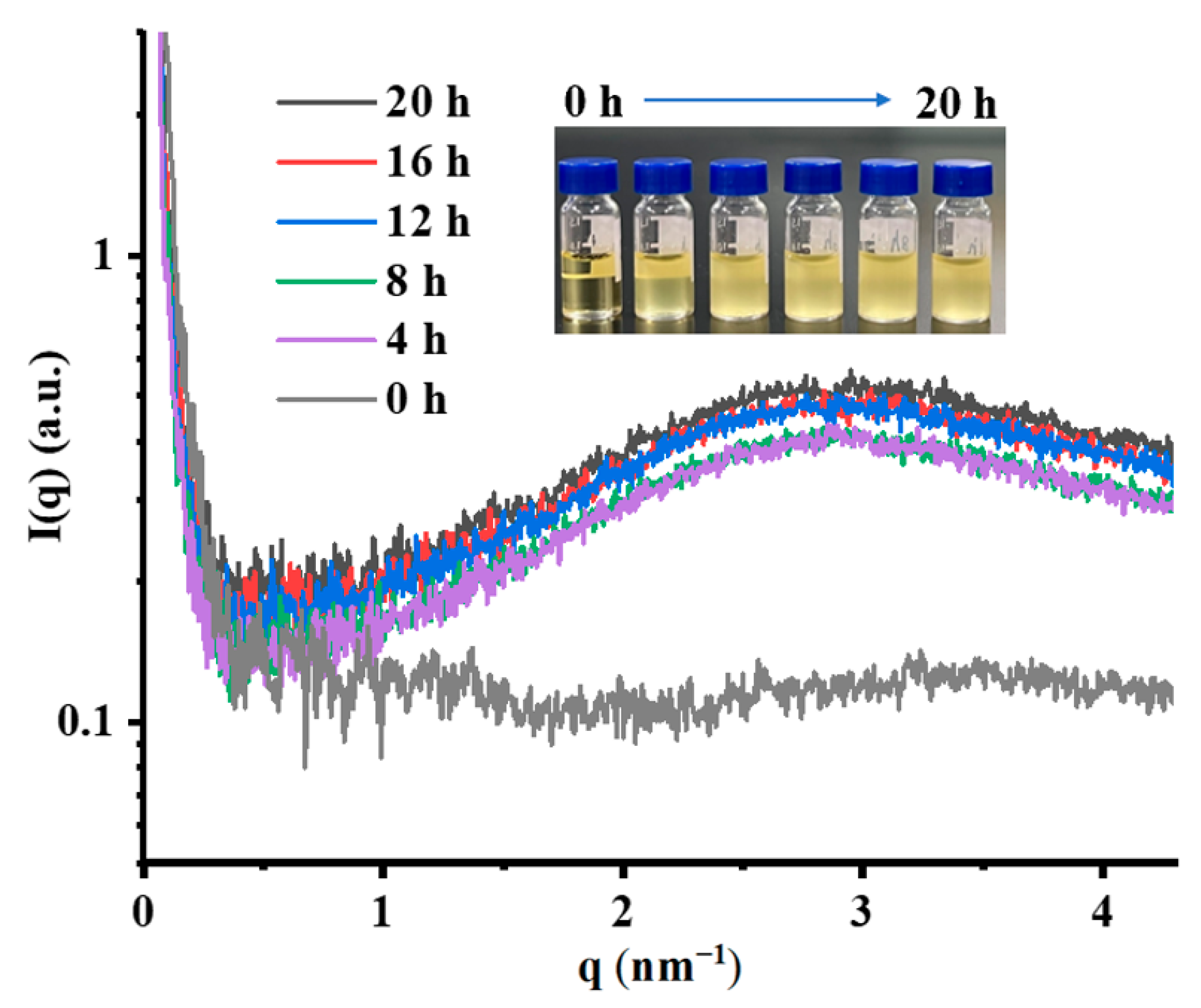
3.4. SAXS Analysis of Chia Seed Oil
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LF-NMR | Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance |
| SAXS | Small-angle X-ray scattering |
| ESR | Electron spin resonance |
References
- Wang, S.H.; Lai, G.Y.; Lin, J.Z.; Xia, F.; Ding, Z.N.; Feng, J.H.; Xu, J.J.; Shen, G.P. Rapid Detection of Adulteration in Extra Virgin Olive Oil by Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Combined with Pattern Recognition. Food Anal. Method. 2021, 14, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.N.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhou, M.; Wei, C.Q.; Liu, W.Y.; Ma, Y.E.; Luo, P. Comparison of co-pressing and separate pressing on the oxidative stability and lipidomic signature of ω-6/ω-3 balanced flaxseed-peanut blended oils. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 148, 108356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente-Cebrian, S.; Costa, A.G.V.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Zabala, M.; Martinez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. Role of omega3 fatty acids in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular diseases: A review of the evidence. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 69, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Barrow, C.J.; Adhikari, B. Digestion behaviour of chia seed oil encapsulated in chia seed protein-gum complex coacervates. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. An increase in the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio increases the risk for Obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinfenwa, A.O.; Cheikhyoussef, A.; Cheikhyoussef, N.; Hussein, A.A. Cold pressed chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seed oil. In Cold Pressed Oils; Ramadan, M.F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Jindal, N.; Riar, C.S. Effect of seed-to-solvent ratio and ultrasound-assisted two-stage coldsolvent extraction on the characteristics of oil from chia seed. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 373, 133579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic, N.; Pondaven, S.; Vezin, H. EPR Spin-Trapping Study of Free Radical Intermediates in Polyalphaolefin Base Oil Autoxidation. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2021, 192, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velascoa, J.; Andersena, M.L.; Skibsted, L.H. ESR spin trapping for in situ detection of radicals involved in the early stages of lipid oxidation of dried microencapsulated oils. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Chen, Y.S.; McClements, D.J.; Meng, C.; Zhang, M.K.; Chen, H.J.; Deng, Q.C. Recent advances in understanding the interfacial activity of antioxidants in association colloids in bulk oil. Adv. Colloid. Interfac. 2024, 325, 103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J. Detection and characterisation of radicals using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin trapping and related methods. Methods 2016, 109, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerekamp, D.M.W.; Andersen, M.L.; Jacobsen, C.; Chronakis, I.S.; Garcia-Moreno, P.J. Oxygen permeability and oxidative stability of fish oil-loaded electrosprayed capsules measured by Electron Spin Resonance: Effect of dextran and glucose syrup as main encapsulating materials. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.B.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.G.; Yu, D.Y.; Wang, L.Q. Effect of deodorization conditions on fatty acid profile, oxidation products, and lipid-derived free radicals of soybean oil. Food Chem. 2024, 453, 139656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Cao, P.R.; Li, B.; Sun, D.W.; Li, J.W.; Liu, Y.F. High sensitive and efficient detection of edible oils adulterated with used frying oil by electron spin resonance. Food Control 2017, 73, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Qu, L.H.; Su, X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Gao, Y.; Yu, X.Z. Utilizing low-field NMR for comprehensive quality evaluation of edible oil and oil product. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2025, 8, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolze, J.; Kogan, V.; Beckers, D.; Fransen, M. High-performance small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS/WAXS) experiments on a multi-functional laboratory goniometer platform with easily exchangeable X-ray modules. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 085115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkal, R.; Cohaut, N.; Khodja, M.; Ahmed-Zaida, T.; Bergaya, F. Rheo-SAXS investigation of organoclay water in oil emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibasa, E.; Vicent, V.; Rweyemamu, L. Moringa-enriched sunflower oil: A novel approach to enhancing nutritional quality and oxidative stability. Food Chem. Adv. 2025, 9, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momchilova, S.; Kazakova, A.; Taneva, S.; Aleksieva, K.; Mladenova, R.; Karakirova, Y.; Petkova, Z.; Kamenova-Nacheva, M.; Teneva, D.; Denev, P. Effect of Gamma Irradiation on Fat Content, Fatty Acids, Antioxidants and Oxidative Stability of Almonds, and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Study of Treated Nuts. Molecules 2023, 28, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzi, R.; Bartucci, R. Electron spin resonance of spin-labeled lipid assemblies and proteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 580, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punis, R.; Zoleo, A. Exploring the early stages of verdigris-linseed oil mixture curing by EPR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2026, 1350, 144016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Rao, J.J.; Chen, B.C. Effects of antioxidants on the oxidative stability of expeller-pressed higholeic soybean oil (EPHOSO) oleogel and cookie. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, S.; Saealle, N. Oxidative stability and fatty acid profile of vegetable oils from the Estonian market. Meas. Food 2025, 20, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Manglano, N.E.; Andersen, M.L.; Guadix, E.M.; GarciaMoreno, P.J. Oxidative stability and oxygen permeability of oil-loaded capsules produced by spray-drying or electrospraying measured by electron spin resonance. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 136894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Zhou, Q.; Su, M.; Zheng, S.S.; Xie, S.L.; Li, J. Quantitative determination of the carbonyl value in frying oils based on LF-NMR combined with chemometrics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 198, 116067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.K.; Zhang, D.Y.; Geng, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, Y.N.; Wang, J.H. Chemometrics analysis of camellia oil authenticity using LF NMR and fatty acid GC fingerprints. J. Food. Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Lv, B.W.; Zhang, K.X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Li, C.B. Rapid Detection of Avocado Oil Adulteration Using Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Foods 2022, 11, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Sun, D. Study on Relationship between Polar Compounds and LF-NMR Properties in Fried Camellia Seed Oil. J. Food. Nutr. Res. 2018, 6, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, L.L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.X.; Mujumdar, A.S. Monitoring of free fatty acid content in mixed frying oils by means ofLF-NMR and NIR combined with BP-ANN. Food Control 2022, 133, 108599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.N.; Zhang, M.; Fan, D.C. Effect of ultrasonic on deterioration of oil in microwave vacuum frying and prediction of frying oil quality based on low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Vijay, A.; Kaur, J.; Vaidya, S. Investigating the interplay of Catanionic surfactant and co-surfactants with Wo on the structural parameters of Hexylammonium Hexanoate-based water-in-oil microemulsions using SAXS. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 434, 128001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, L.; Ducouret, G.; Gobeaux, F.; Lesaine, A.; Hotton, C.; Bizien, T.; Michot, L.; Viguerie, L. Rheo-SAXS characterization of lead-treated oils: Understanding the influence of lead driers on artistic oil paint’s flow properties. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2023, 63, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Ruiz, K.; Castera, A.R.; Bauduin, P.; Diat, O.; Chemat, F. Comprehension of direct extraction of hydrophilic antioxidants using vegetable oils by polar paradox theory and small angle X-ray scattering analysis. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xing, C.M.; Wang, Z.S.; Sun, W.X.; Wu, C.F.; Xu, G.F.; Wang, X.G. LF-NMR intelligent evaluation for lipid oxidation indices of polar compound distribution, fatty acid unsaturation, and dynamic viscosity: Preference and mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fatty Acids | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Myristic acid (14:0) | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| palmitic acid (16:0) | 6.18 ± 0.02 |
| stearic acid (18:0) | 3.37 ± 0.08 |
| Arachidic (20:0) | 0.26 ± 0.00 |
| Behenic acid (22:0) | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| Palmitoleic acid (16:1) | 0.07 ± 0.03 |
| Oleic acid (18:1) | 7.88 ± 0.05 |
| Eicosenoic acid (20:1) | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
| Linoleic acid (18:2) | 18.98 ± 0.09 |
| Linolenic acid (18:3) | 63.03 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Wu, N.; Yang, C.; Liu, F. Evaluation of the Oxidative Process of Chia Seed Oil by Means of ESR Combined with LF-NMR and SAXS. Foods 2025, 14, 4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244280
Ma Y, Wu N, Yang C, Liu F. Evaluation of the Oxidative Process of Chia Seed Oil by Means of ESR Combined with LF-NMR and SAXS. Foods. 2025; 14(24):4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244280
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yun, Nan Wu, Cheng Yang, and Fei Liu. 2025. "Evaluation of the Oxidative Process of Chia Seed Oil by Means of ESR Combined with LF-NMR and SAXS" Foods 14, no. 24: 4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244280
APA StyleMa, Y., Wu, N., Yang, C., & Liu, F. (2025). Evaluation of the Oxidative Process of Chia Seed Oil by Means of ESR Combined with LF-NMR and SAXS. Foods, 14(24), 4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244280






