Optimizing GC-IMS for Pork Volatile Fingerprinting: Effects of Incubation Conditions and Medium on Aroma Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
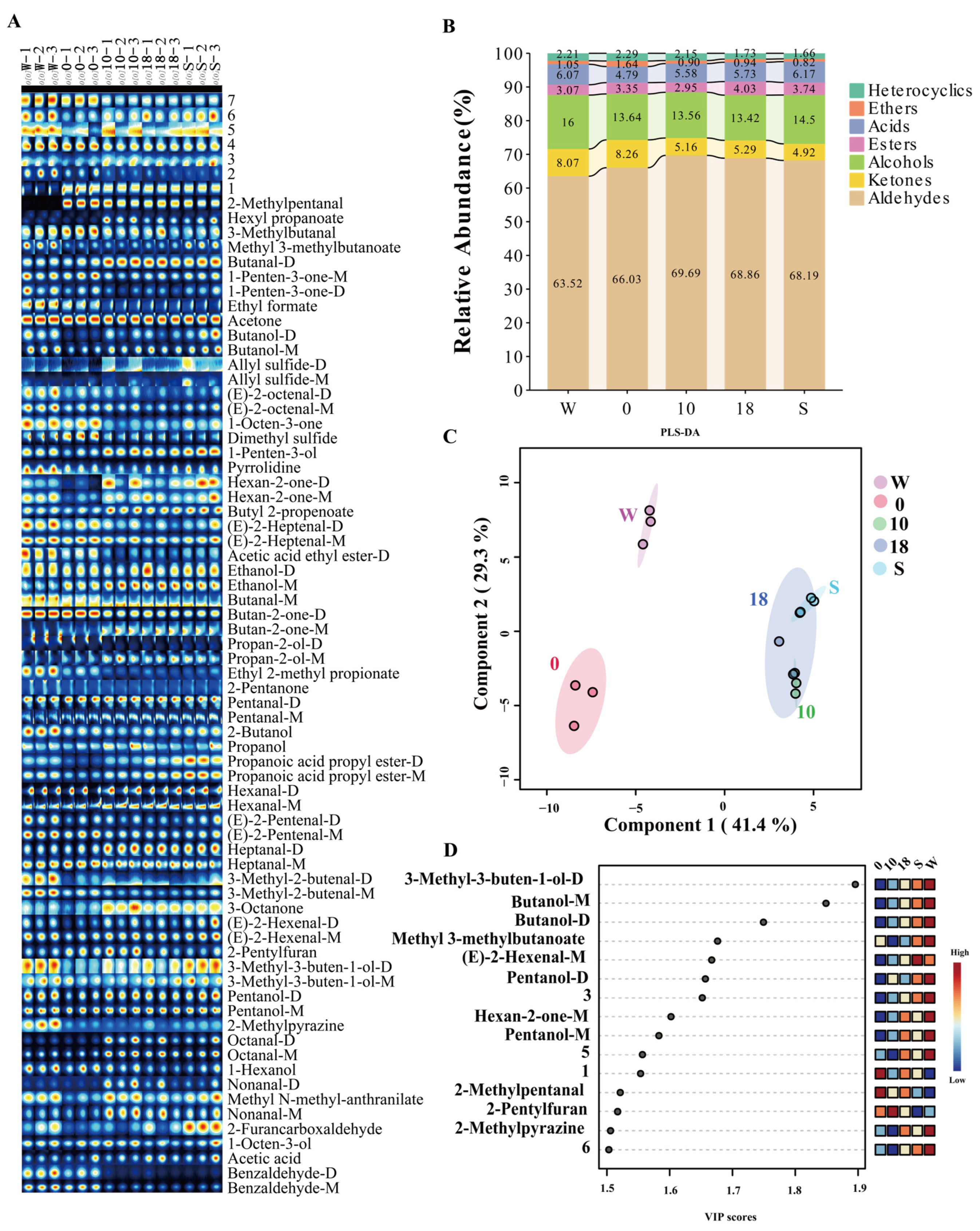
3.1. Effect of Incubation Conditions on Vocs
3.2. Effect of Media on VOCs
3.3. Gc-Ims Analysis of VOCs in Pork
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, R. Drivers of Consumer Liking for Beef, Pork, and Lamb: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosowska, M.; Majcher, M.A.; Fortuna, T. Volatile Compounds in Meat and Meat Products. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, J.; Rohn, S.; Weller, P. Gc-Ims-Tools—A New Python Package for Chemometric Analysis of GC–IMS Data. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Gao, L.L.; Zhang, C.; Feng, T.; Zhuang, H.N. Analysis of Volatile Flavor Compounds of Corn under Different Treatments by GC-MS and GC-IMS. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 725208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Ren, F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.X.; Dai, X.; Song, J.B. Application of GC-IMS in Detection of Food Flavor Substances. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 545, 12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitain, C.; Weller, P. Non-Targeted Screening Approaches for Profiling of Volatile Organic Compounds Based on Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectroscopy (GC-IMS) and Machine Learning. Molecules 2021, 26, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Sun, C.; Bai, T.; Yan, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.M. Recent Advances and Challenges in the Interaction between Myofibrillar Proteins and Flavor Substances. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1378884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šikuten, I.; Štambuk, P.; Karoglan, J.K.; Maletić, E.; Tomaz, I.; Preiner, D. Optimization of SPME-Arrow-GC/MS Method for Determination of Free and Bound Volatile Organic Compounds from Grape Skins. Molecules 2021, 26, 7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.L.; Chen, R.; Lan, F.; Yang, H.; Gao, R.C.; Jin, W.G. Analysis of VOCs in Lueyang Black Chicken Breast Meat during the Steaming Process with GC-IMS and Stoichiometry. J. Food Qual. 2024, 2024, 6663167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Woerner, D.R.; Franco, T.M.; Miller, M.F.; Legako, J.F. Development of Beef Volatile Flavor Compounds in Response to Varied Oven Temperature and Degree of Doneness. Meat Muscle Biol. 2021, 5, 12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yang, F.; Zhu, B.Q.; Yin, S.S.; Fu, Y.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Liao, Y.C.; Kang, M.; Zhang, Y.B.; He, J.; et al. Optimization of HS-SPME-GC-MS for the Determination of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Ningxiang Pork. Foods 2023, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Liu, L.; Yuan, X.Y.; Jin, Y.X.; Zhao, G.P.; Wen, J.; Cui, H.X. A Comparison of Different Tissues Identifies the Main Precursors of Volatile Substances in Chicken Meat. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 927618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.L.; Ai, M.Y.; Lu, S.F.; Xu, H.L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, S.B.; Hu, Y. Effect of Raw Material Frozen Storage on Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Compounds of Fermented Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 101027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrubini, G.; Dugheri, S.; Cappelli, G.; Arcangeli, G.; Mucci, N.; Appelblad, P.; Melzi, C.; Speltini, A. Experimental Designs for Solid-Phase Microextraction Method Development in Bioanalysis: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1119, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrega, A.; Yven, C.; Semon, E.; Mielle, P.; Salles, C. Effect of Oral Physiology Parameters on In-Mouth Aroma Compound Release Using Lipoprotein Matrices: An In Vitro Approach. Foods 2019, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.L.; Jia, Z.F.; An, J.; Ding, Y.C.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhou, X.X. Rapid and Visual Favor Analysis Using Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry (GC-IMS) in Meat Products: Research Progress and Future Trends. J. Food Biochem. 2024, 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Nicolás, M.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Arce, L.; Hernández-Córdoba, M.; Viñas, P. Headspace Gas Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry and Ion Mobility Spectrometry: Classification of Virgin Olive Oils as a Study Case. Foods 2020, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhu, L.T.; Han, Y.X.; Xu, L.P.; Jin, J.H.; Cai, Y.M.; Wang, H.M. Analysis of Volatile Compounds between Raw and Cooked Beef by HS-SPME–GC–MS. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.H.; Tong, L.J.; Chi, X.L.; Ai, N.S.; Cao, Y.G.; Sun, B.G. Comparison of Sensory and Electronic Tongue Analysis Combined with HS-SPME-GC-MS in the Evaluation of Skim Milk Processed with Different Preheating Treatments. Molecules 2019, 24, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Qin, K.K.; Qi, K.; Zhang, R.N.; Xu, Z.W.; Men, X.M. Construction of a Molecular Regulatory Network for Lipids and Volatile Flavor in Chinese Indigenous and Hybrid Pig Pork through Integrating Multi-Omics Analysis. LWT 2024, 199, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17236-2019; Operating Procedures of Livestock and Poultry Slaughtering——Pig. State Administration for Market Regulation-Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Li, H.Q.; Xi, B.; Lin, S.Q.; Tang, D.F.; Gao, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.M.; Liang, J.; Yang, W.Y.; Li, J.L. Volatile Flavor Analysis in Yak Meat: Effects of Different Breeds, Feeding Methods, and Parts Using GC-IMS and Multivariate Analyses. Foods 2024, 13, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Cai, W.Q.; Jiang, C.Y.; Hang, J.B.; Miao, X.Q.; Sun, N. Feasibility of Circular Fermentation as a New Strategy to Accelerate Fermentation and Enhance Flavor of Antarctic Krill Paste. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 9, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gemert, L.J. Flavour Thresholds: Compilations of Flavour Threshold Values in Water and Other Media, 2. enlarged and rev. ed.; Olieman: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 978-90-810894-3-2. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.Q.; Tang, Q.; Fan, L.; Xu, X.D.; Song, Z.; Hayat, K.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.F. Identification of Pork Flavour Precursors from Enzyme-Treated Lard Using Maillard Model System Assessed by GC–MS and Partial Least Squares Regression. Meat Sci. 2017, 124, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitain, C.C.; Nejati, F.; Zischka, M.; Berzak, M.; Junne, S.; Neubauer, P.; Weller, P. Volatilomics-Based Microbiome Evaluation of Fermented Dairy by Prototypic Headspace-Gas Chromatography–High-Temperature Ion Mobility Spectrometry (HS-GC-HTIMS) and Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (NNMF). Metabolites 2022, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Simon, C.; Mumm, R.; Hall, R.D. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Volatiles as a New Tool for Understanding Aroma and Flavour Chemistry in Processed Food Products. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.L.; Zhu, C.L.; Wu, B.Z.; Wang, T.Y.; Yang, L.; Guan, J.; Yi, Y.W.; Deng, J.; Wu, H.C. Effect of Different Salt Additions on the Flavor Profile of Fermented Ciba Pepper. Fermentation 2024, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.T.; Ding, S.H.; Pan, Z.P.; Li, X.; Fu, F.H. Characteristic Volatile Fingerprints and Odor Activity Values in Different Citrus-Tea by HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.G.; Li, X.A.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, Q. Flavour Profile of Traditional Dry Sausage Prepared with Partial Substitution of NaCl with KCl. Foods 2023, 12, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, H.; Alizadeh, M.; Hassanzadeh, R.; Ghanbarzadeh, B. Garlic Essential Oil-based Nanoemulsion Carrier: Release and Stability Kinetics of Volatile Components. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 1613–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyjakon, A.; Noszczyk, T.; Sobol, Ł.; Misiakiewicz, D. Influence of Torrefaction Temperature and Climatic Chamber Operation Time on Hydrophobic Properties of Agri-Food Biomass Investigated Using the EMC Method. Energies 2021, 14, 5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, C.; Ansorena, D.; Bello, J.; Cid, C. Optimizing Headspace Temperature and Time Sampling for Identification of Volatile Compounds in Ground Roasted Arabica Coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.S.; Zhu, J.Y. Determination of the Solubility of Inorganic Salts by Headspacegas Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 996, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleicher, J.; Ebner, E.E.; Bak, K.H. Formation and Analysis of Volatile and Odor Compounds in Meat—A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajo, J.P. Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Bread and Related Products. Improvement of Gluten-Free Breads Aroma. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Fu, C.C.; Chen, M.F.; Jin, C.H. The Effect of Sodium Chloride on the Physicochemical and Textural Properties and Flavor Characteristics of Sous Vide Cooked Duck Meat. Foods 2023, 12, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, W.G.; Zhu, K.Y.; Miao, X.Q.; Dong, X.P.; Jiang, P.F. Effects of Curing Concentration and Drying Time on Flavor and Microorganisms in Dry Salted Spanish Mackerel. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Yin, X.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Liao, G.Z.; Gu, D.H.; Pu, Y.H.; Wang, G.Y. Effect of Different Salt Additions on the Taste and Flavor-Related Compounds in Chicken Soup. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1368789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.C.; Li, M.Y.; Bai, F.F.; Yao, W.S.; You, L.T.; Liu, D.Y. Effect of Fat to Lean Meat Ratios on the Formation of Volatile Compounds in Mutton Shashliks. Foods 2023, 12, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.Z.; Wang, S.L.; Luo, R.M.; Wang, Y.R.; Chen, F.; Sun, Y. Effect of NaCl on Volatile Flavor Compounds and Water Distribution in Pig Skin Jelly. Food Sci. Anim. Prod. 2023, 1, 9240020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.K.; Ge, K.L.; Zhang, R.N.; Wang, B.B.; Tao, X.; Qin, K.P.; Men, X.M.; Xu, Z.W. Unveiling the Impact of Muscle Fiber Composition on Taste and Aroma Compounds in Jinhua Pig Skeletal Muscles. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliáš, Z.; Hluchý, S.; Mlynek, J. Histological Structure of the Musculus Longissimus Lumborum et Thoracis in Pigs with the Same Ryanodine Receptor Genotype (CC) in Relation to Carcass Indicators. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 52, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.J.; Du, Z.Q. Advances in the Discovery of Genetic Elements Underlying Longissimus dorsi Muscle Growth and Development in the Pig. Anim. Genet. 2023, 54, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, S.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.A.; Panea, B.; Latorre, M.A. Physicochemical and Sensorial Characteristics of Four Muscles from Commercial Crossbred Pigs Slaughtered at 130 Kg Body Weight. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 10, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetzer, A.J.; Tucker, E.; McKeith, F.K.; Brewer, M.S. Quality Changes in Beef Complexus, Serratus Ventralis, Vastus Lateralis, Vastus Medialis, and Longissimus Dorsi Muscles Enhanced Prior to Aging. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, S6–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, T.; Saito, K.; Nade, T.; Misumi, S.; Masuda, Y.; Sakuma, H.; Nakayama, S.; Fujita, K.; Kawamura, T. Effects of Intramuscular Fat on the Sensory Characteristics of M. Longissimus Dorsi in Japanese Black Steers as Judged by a Trained Analytical Panel. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 20, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Xie, J.C.; Zhao, M.Y.; Hou, L.; Liang, J.J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J. Volatile Flavor Constituents in the Pork Broth of Black-Pig. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.C.; Liu, M.Y.; Yan, X.; Bao, R.Q.; Liu, A.X.; Wang, W.Q.; Zhang, Z.L.; Liang, H.P.; Ji, C.F.; Zhang, S.F.; et al. Lipase Addition Promoted the Growth of Proteus and the Formation of Volatile Compounds in Suanzhayu, a Traditional Fermented Fish Product. Foods 2021, 10, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, D.V. Sensory Characterisation Studies on Warmed-over Flavour in Meat. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Todeschini, S.; Perreault, V.; Goulet, C.; Bouchard, M.; Dubé, P.; Boutin, Y.; Bazinet, L. Assessment of the Performance of Electrodialysis in the Removal of the Most Potent Odor-Active Compounds of Herring Milt Hydrolysate: Focus on Ion-Exchange Membrane Fouling and Water Dissociation as Limiting Process Conditions. Membranes 2020, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xing, S.H.; Fu, C.C.; Fang, F.; Liu, J.; Kan, J.; Qian, C.L.; Chai, Q.Q.; Jin, C.H. Effects of Drying Methods on Taste Components and Flavor Characterization of Cordyceps Militaris. Foods 2022, 11, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhong, F.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, T. Effect of Microbial Fermentation on the Fishy-Odor Compounds in Kelp (Laminaria japonica). Foods 2021, 10, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiyaborworntham, N.; Oz, F.; Richards, M.P.; Wu, H. Paradoxical Effects of Lipolysis on the Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

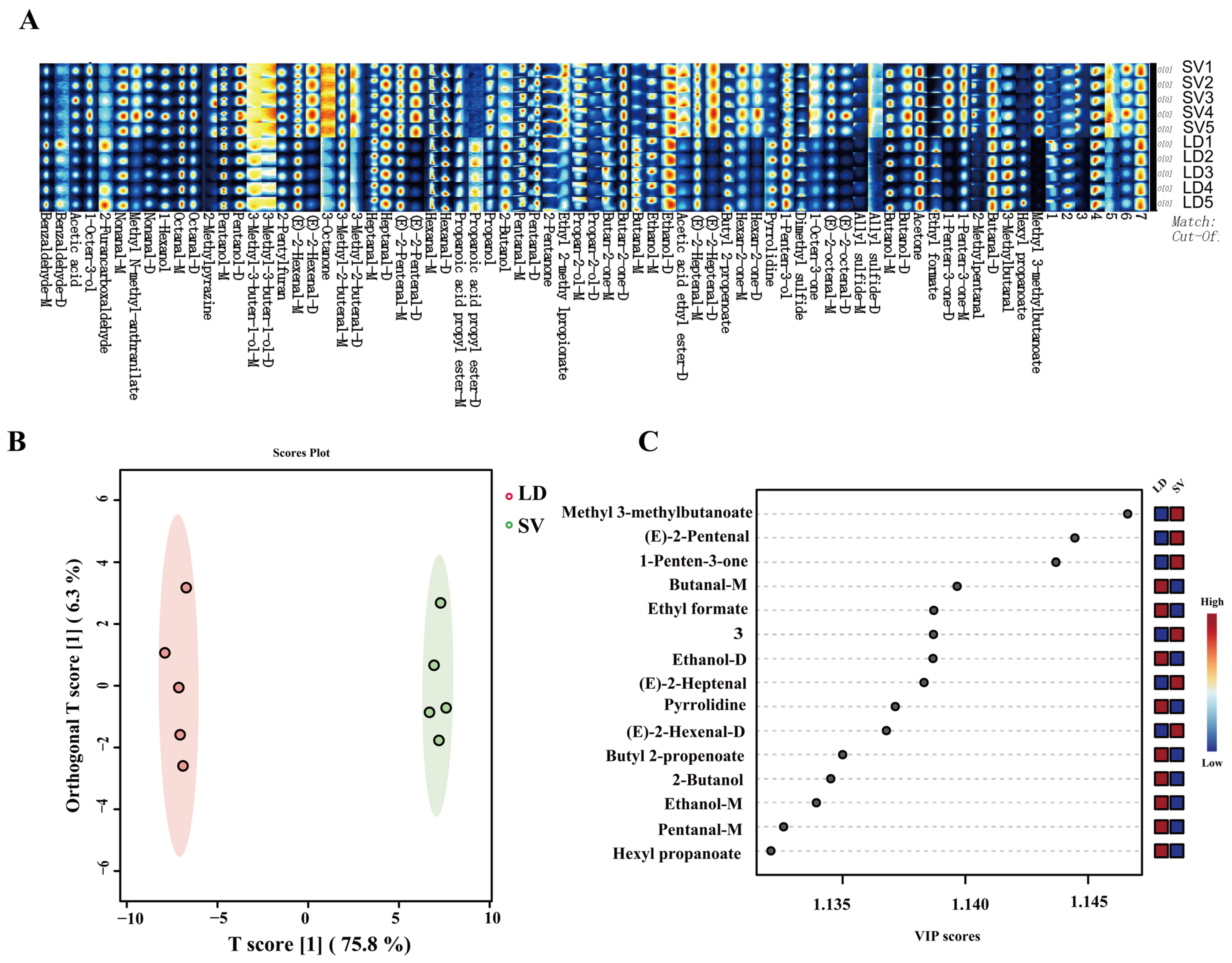
| Label | CAS# | VIP Value | p Value | Serratus ventralis | Longissimus dorsi | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SV1 | SV 2 | SV3 | SV4 | SV5 | LD1 | LD2 | LD3 | LD4 | LD5 | ||||
| (E)-2-octenal-D | C2548870 | 1.09 | <0.01 | 5.34 | 5.59 | 5.17 | 8.47 | 6.08 | 1.52 | 1.29 | 1.62 | 1.59 | 1.82 |
| 1-Octen-3-one | C4312996 | 1.04 | <0.01 | 151.06 | 152.40 | 164.96 | 164.51 | 161.07 | 91.72 | 77.59 | 80.47 | 88.87 | 76.05 |
| 3-Methylbutanal | C590863 | 1.12 | <0.01 | 27.81 | 27.43 | 27.87 | 29.14 | 29.34 | 36.78 | 33.93 | 30.48 | 31.97 | 32.05 |
| Butanal-D | C123728 | 1.08 | <0.01 | 30.11 | 30.96 | 32.26 | 29.56 | 32.90 | 29.92 | 27.87 | 27.14 | 27.35 | 27.31 |
| Butanal-M | C123728 | 1.14 | <0.01 | 2.10 | 2.24 | 2.55 | 1.60 | 2.31 | 10.03 | 9.87 | 8.34 | 8.26 | 7.83 |
| Butyl 2-propenoate | C141322 | 1.14 | <0.01 | 1.38 | 1.42 | 1.57 | 1.35 | 1.52 | 2.13 | 1.92 | 1.76 | 1.75 | 1.78 |
| Dimethyl sulfide | C75183 | 1.12 | <0.01 | 16.18 | 15.02 | 14.33 | 13.72 | 14.00 | 24.69 | 21.35 | 18.82 | 20.55 | 19.57 |
| Ethanol-D | C64175 | 1.14 | <0.01 | 6.31 | 6.73 | 6.97 | 6.09 | 6.86 | 8.46 | 8.43 | 7.58 | 8.05 | 7.65 |
| Heptanal-D | C111717 | 1.10 | <0.01 | 41.79 | 43.23 | 45.23 | 41.24 | 44.08 | 40.77 | 40.77 | 40.24 | 40.38 | 39.29 |
| Heptanal-M | C111717 | 1.12 | <0.01 | 12.03 | 12.03 | 13.36 | 10.25 | 12.52 | 18.36 | 17.91 | 15.62 | 16.00 | 14.83 |
| Hexanal-M | C66251 | 1.13 | <0.01 | 47.71 | 47.74 | 51.45 | 46.19 | 50.13 | 53.99 | 51.09 | 49.46 | 49.55 | 49.69 |
| Hexyl propanoate | C2445763 | 1.13 | <0.01 | 1.35 | 1.40 | 1.36 | 1.45 | 1.44 | 3.03 | 2.52 | 2.76 | 2.86 | 3.52 |
| Octanal-M | C124130 | 1.11 | <0.01 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Pentanal-D | C110623 | 1.12 | <0.01 | 13.87 | 14.19 | 14.70 | 13.75 | 14.70 | 15.48 | 14.42 | 13.49 | 13.52 | 13.47 |
| Pentanal-M | C110623 | 1.13 | <0.01 | 7.80 | 8.02 | 8.39 | 6.96 | 8.08 | 9.84 | 9.32 | 8.79 | 8.81 | 8.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Wang, B.; Xu, Z.; Ge, K.; Yuan, Y.; Ding, X.; Men, X.; Qi, K. Optimizing GC-IMS for Pork Volatile Fingerprinting: Effects of Incubation Conditions and Medium on Aroma Profiles. Foods 2025, 14, 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234164
Yu L, Wang B, Xu Z, Ge K, Yuan Y, Ding X, Men X, Qi K. Optimizing GC-IMS for Pork Volatile Fingerprinting: Effects of Incubation Conditions and Medium on Aroma Profiles. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234164
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Lei, Binbin Wang, Ziwei Xu, Kaili Ge, Yihan Yuan, Xiangbin Ding, Xiaoming Men, and Keke Qi. 2025. "Optimizing GC-IMS for Pork Volatile Fingerprinting: Effects of Incubation Conditions and Medium on Aroma Profiles" Foods 14, no. 23: 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234164
APA StyleYu, L., Wang, B., Xu, Z., Ge, K., Yuan, Y., Ding, X., Men, X., & Qi, K. (2025). Optimizing GC-IMS for Pork Volatile Fingerprinting: Effects of Incubation Conditions and Medium on Aroma Profiles. Foods, 14(23), 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234164





