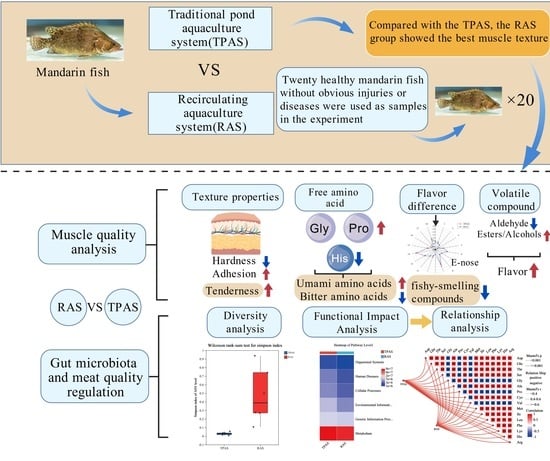
Comparative Study on the Nutritional, Textural and Flavor Profiles of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) in Industrialized Recirculating and Traditional Pond Aquaculture Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Determination of Physical Properties
2.3. Determination of Nutrient Content
2.4. Free Amino Acid Content
2.5. Determination of Volatile Metabolites
2.6. Determination of Electronic Nose
2.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Texture Analysis
3.2. Proximate Composition Analysis
3.3. Free Amino Acids Analysis
3.4. Electronic Nose Analysis
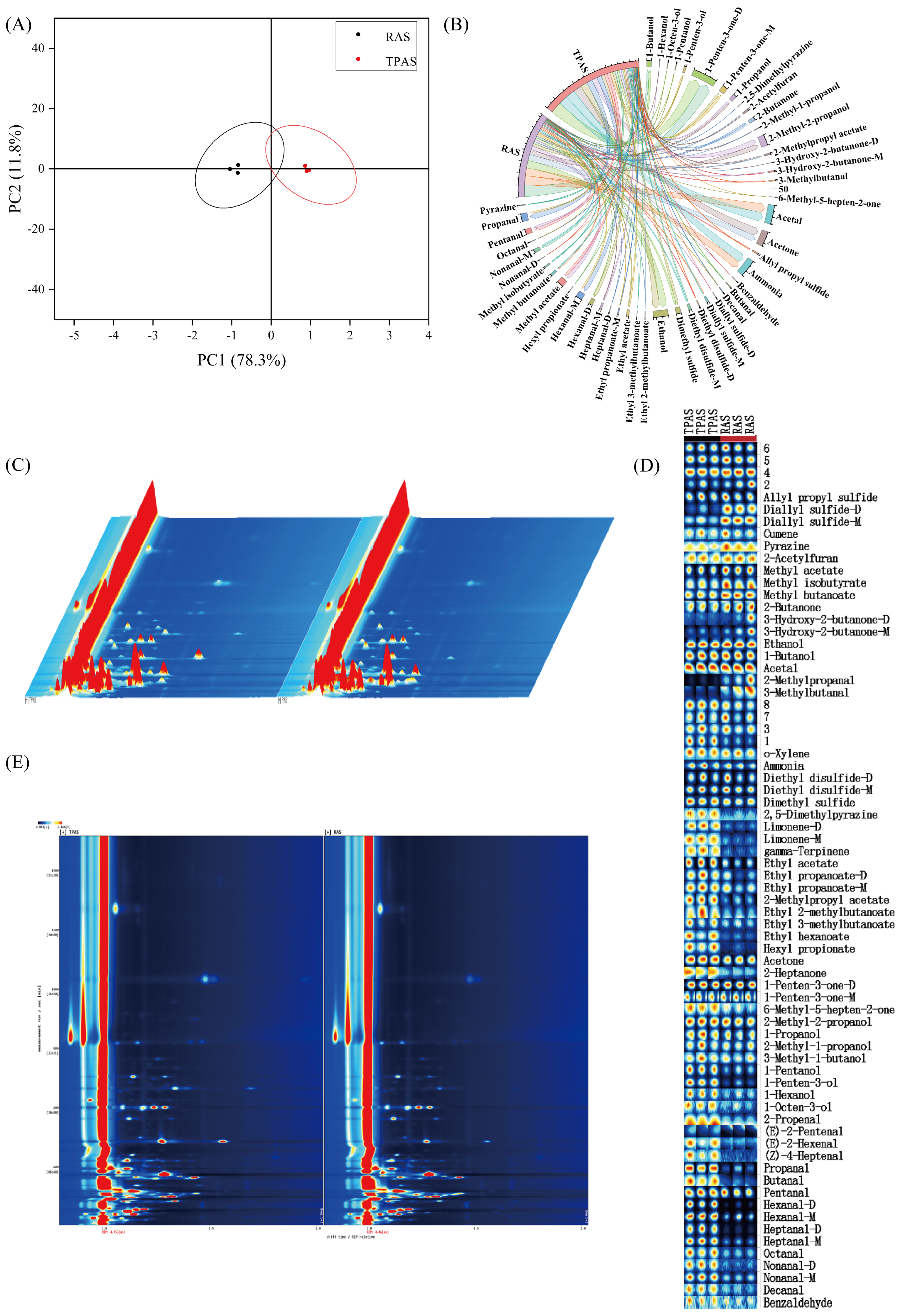
3.5. GC-iMS Analysis
3.6. Gut Microbiome Analysis
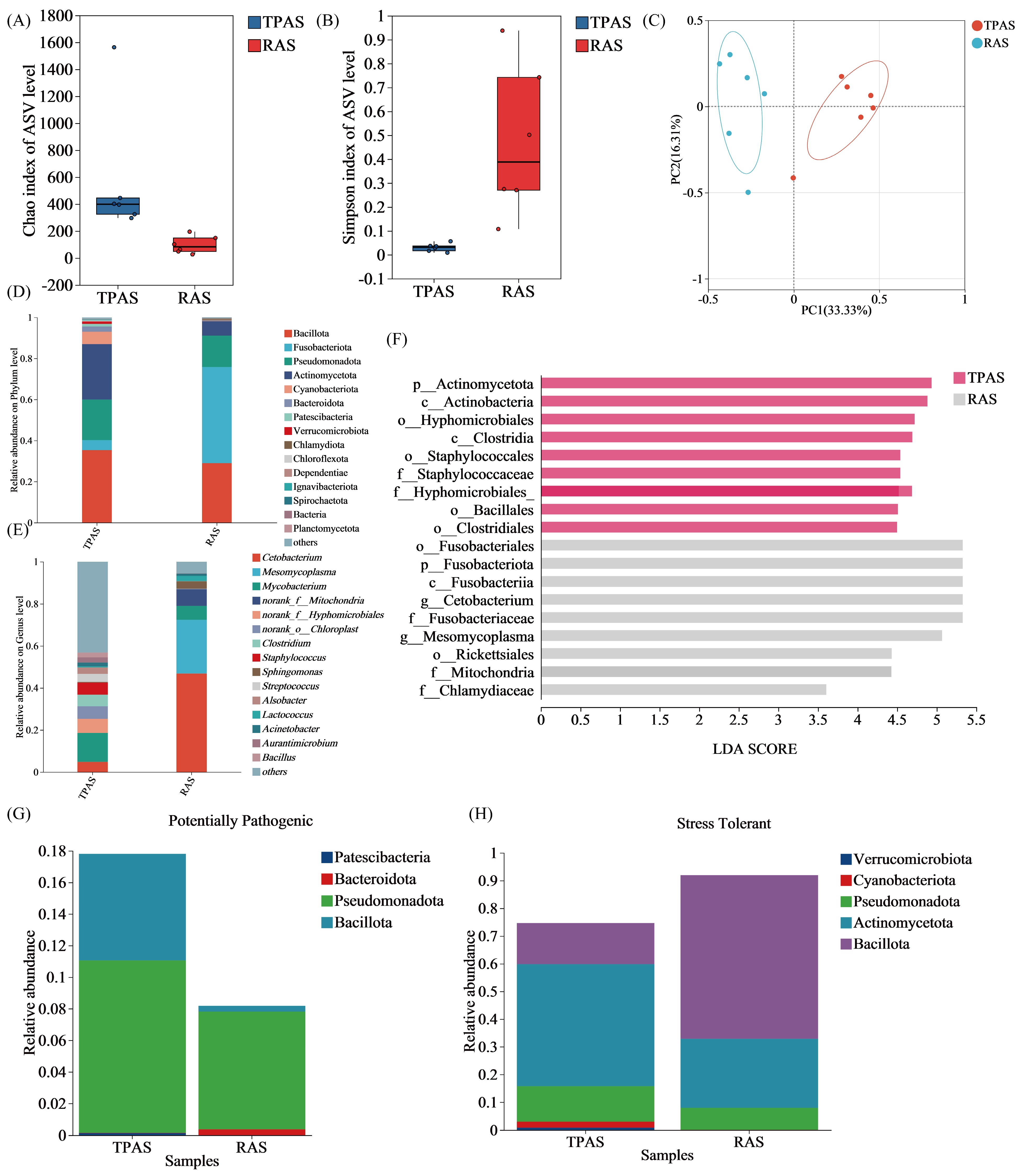
3.6.1. Gut Microbiota Diversity Analysis
3.6.2. Gut Microbiota Taxonomic Composition Analysis
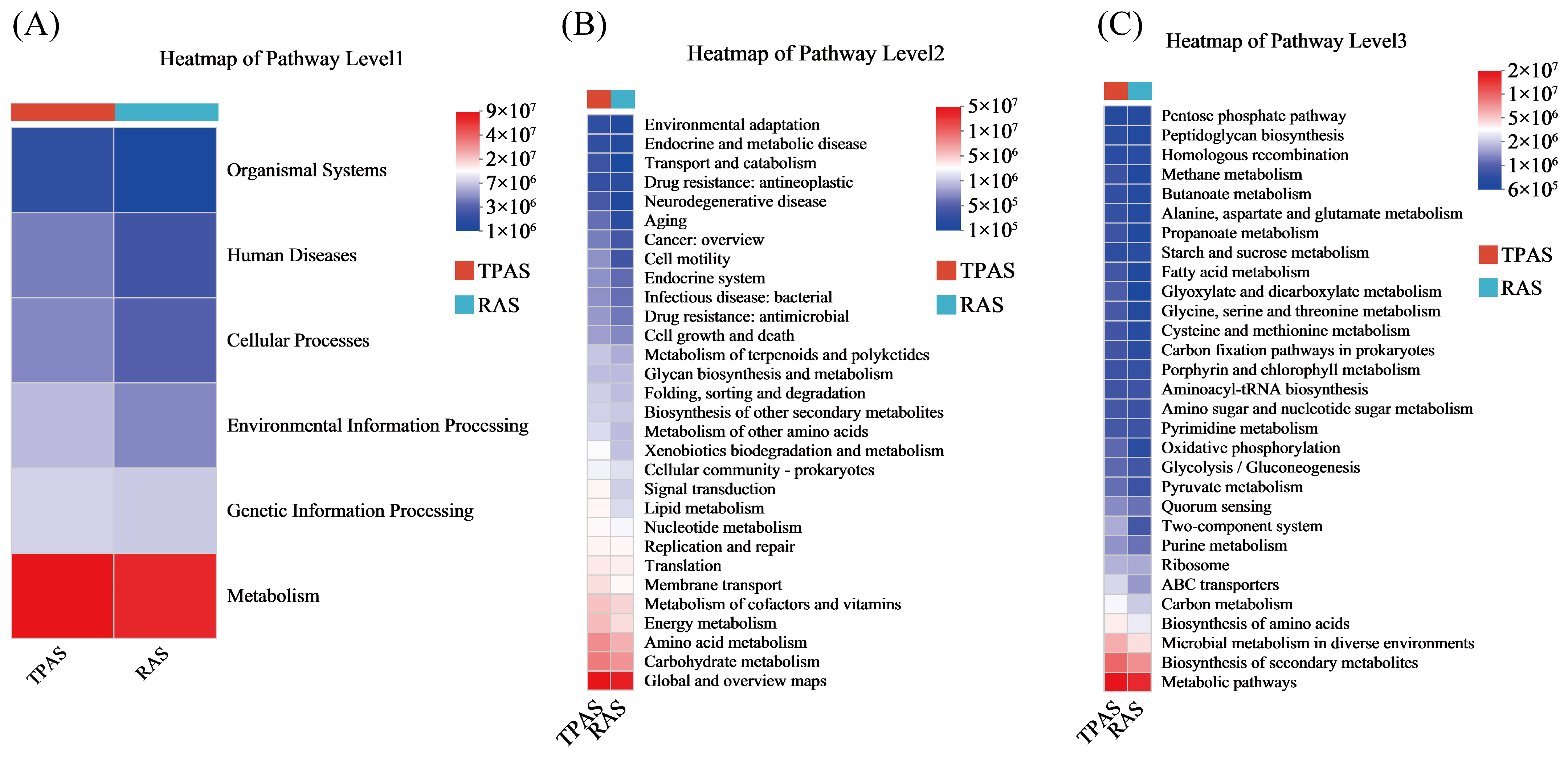
3.6.3. Gut Microbiota Function Analysis
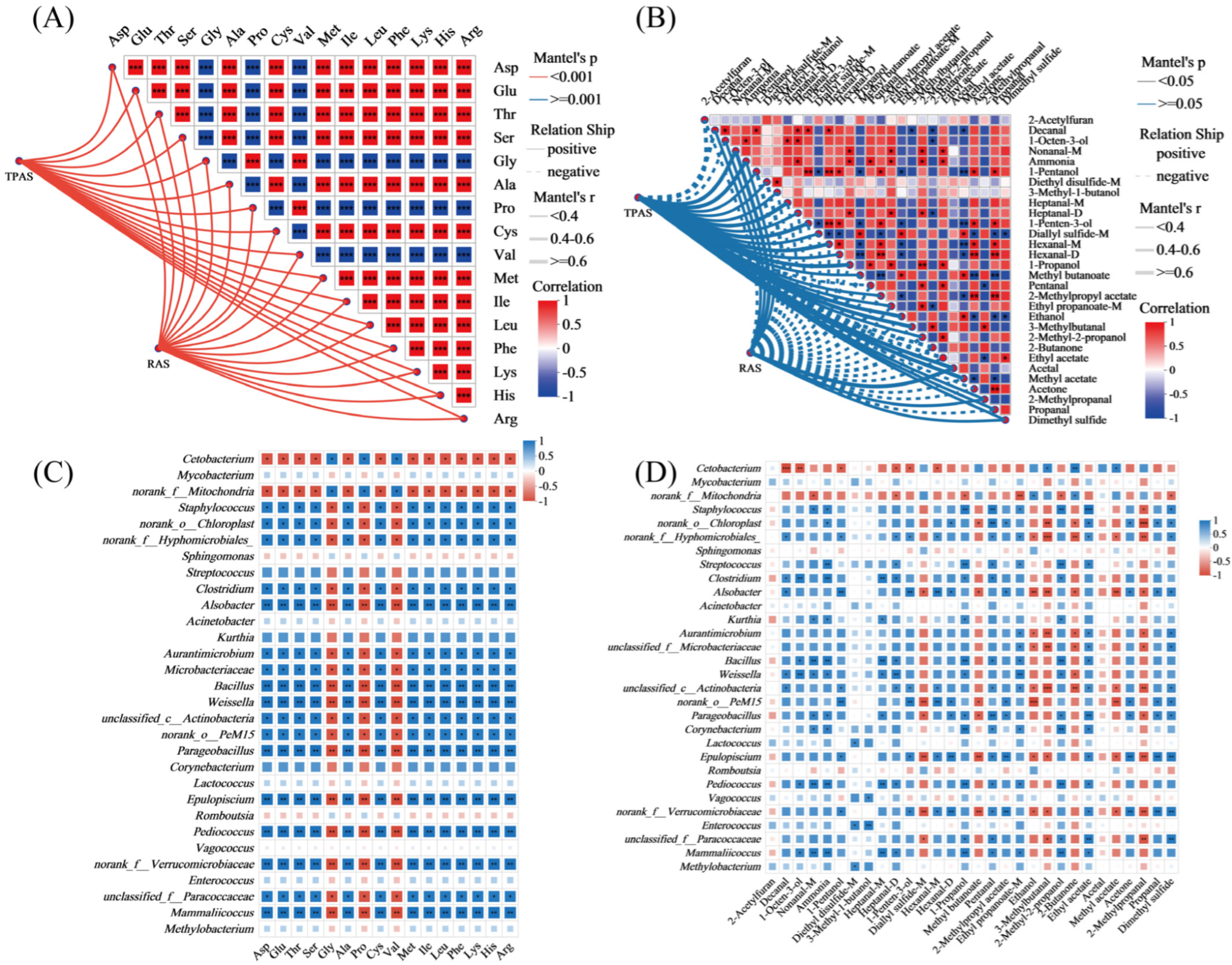
3.7. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, W.; Leng, X.; Yun, B.; Wang, L.; Qian, X. A comparative study of natural or artificial feed on physiological health and gut microbiota in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Qi, M.; Liang, Q.R.; Yao, G.H.; Ma, C.; Ding, X.Y.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Q. Integrated Transcriptome and Microbiome Analyses Reveal Growth- and Stress-Response-Related Genes and Microbes in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Fishes 2025, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.H.; Li, S.X.; Shen, X.J.; Liang, Q.Q.; Xu, T.; Shi, W.Z. Effects of different fermenters on the quality and flavour of fermented mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2024, 59, 4992–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bich, T.T.N.; Tri, D.Q.; Yi-Ching, C.; Khoa, H.D. Productivity and economic viability of snakehead Channa striata culture using an aquaponics approach. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 89, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Ju, D.; Xu, H.; Gong, B. The Intestinal Microbial Community of the Farmed Mandarin Fish Siniperca chuatsi in Recirculating Ponds Aquaculture System (RAS) Compared to a Pond System. Microbiology 2024, 93, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.W.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, J.L.; Tang, S.J.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, Y.H.; Chen, X.W. The digestive system of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) can adapt to domestication by feeding with artificial diet. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Pu, D.; Li, P.; Wei, X.; Li, D.; Gao, L.; Zhai, X.; Zhao, C.; Du, Y. Comparative evaluation of nutritional quality and flavor characteristics for Micropterus salmoides muscle in different aquaculture systems. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmody, R.N.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Gut Microbes Make for Fattier Fish. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese National Standard GB5009.3-2016; National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Moisture in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- Chinese National Standard GB5009.5-2016; National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Protein in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- Chinese National Standard GB5009.4-2016; National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Ash Content in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- Chinese National Standard GB5009.6-2016; National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Lipid in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- Xu, J.-X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, B.-F.; Qiao, X.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.-B.; Cheng, S.-Z.; Du, M. Impact of Cooking Processes on Volatile Flavor Compounds and Free Amino Acids in Fish Sauce. Foods 2025, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, W.; Choi, S.Y.; Upatissa, S.; Mitchell, R.J. Predatory bacteria as potential biofilm control and eradication agents in the food industry. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Liu, Q.; Bao, H.; Wang, X.; Miao, S. Effects of different freshness on the quality of cooked tuna steak. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Wang, X.; Bu, W.; Fan, H.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Zhang, S.; Weng, X.; Zheng, B.; Xiang, X. Recirculating aquaculture-fasting strategy (RASF) to modulate gut microbiota and enhance the fish meat quality of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis). Food Chem. 2025, 481, 143946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Liu, L.; Monto, A.R.; Su, K.; Zhang, H.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, G.; Luo, Y.; Bao, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profile of muscles from tilapia cultured in recirculating aquaculture systems and traditional aquaculture in ponds and protein stability during freeze-thaw cycles. Food Chem. 2024, 451, 139325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, R.; He, X.; Li, L.; Takagi, Y.; Li, D. Improvement of Muscle Quality of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) with a Bio-Floating Bed in Culture Ponds. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jia, S.-p.; Zhang, L.; Ma, F.-R.; Zhang, M.; Yu, M.; Jiang, H.-X.; Qiao, Z.-G.; Li, X.-J. Comparative study on nutritional quality and volatile flavor compounds of muscle in Cyprinus carpio haematopterus under wild, traditional pond and in-pond raceway system culture. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Correia, T.; Teixeira, B.; Mendes, R.; Valente, L.M.P.; Pessoa, M.F.; Nunes, M.L.; Gonçalves, A. Nucleotides and free amino acids in sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus gonads: Contributions for freshness and overall taste. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.-P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.-M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, F.-R.; Huang, M.-L.; Liu, S.-S.; Gong, J.-H.; Zhang, M.; Yu, M.; et al. Comparative study on the morphological characteristics and nutritional quality of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) cultured in an aquaculture system using land-based container with recycling water and a traditional pond system. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Qi, Y.; Shen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yu, D. Fine segmentation-driven quality enhancement of unrinsed surimi: Decoupling component differentials for surimi performance. Food Chem. 2025, 491, 145216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Yi, S.; Zhu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. Prediction of the freshness of horse mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) using E-nose, E-tongue, and colorimeter based on biochemical indexes analyzed during frozen storage of whole fish. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chong, Y.; Ding, Y.; Gu, S.; Liu, L. Determination of the effects of different washing processes on aroma characteristics in silver carp mince by MMSE–GC–MS, e-nose and sensory evaluation. Food Chem. 2016, 207, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, W.; Bai, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Gao, R.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y. Influence of thermal processing on flavor and sensory profile of sturgeon meat. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, D.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Liang, F.; Ma, W.; et al. Identification of odor-causing compounds in six species of odor-producing microalgae separated from drinking water source with distinct fishy odor: Insight into microalgae growth and odor characteristics. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Li, Q.; Hong, H.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Xiong, S.; Liu, R. Exploring the quality changes of carp roes: Perspective from flavor characteristics and microstructure. Food Res. Int. 2025, 218, 116765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, S.J.; Lindholm-Lehto, P.C.; Pulkkinen, J.T.; Kiuru, T.; Vielma, J. Effect of ozone and hydrogen peroxide on off-flavor compounds and water quality in a recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Eng. 2022, 98, 102277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Qin, L.; Geng, Y.; Kong, Q.; Wang, S.; Lin, S. The Aroma Fingerprints and Discrimination Analysis of Shiitake Mushrooms from Three Different Drying Conditions by GC-IMS, GC-MS and DSA. Foods 2021, 10, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Hou, Z.; Xiang, D.; Yan, Y.; Ye, K.; Li, R.; Lai, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y. Tracing odors of key tobacco processing stages using a multitechnology collaboration of GC–MS, GC–IMS and sensory evaluation. Microchem. J. 2025, 216, 114784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yu, J.; Yan, S.; Bai, J.; Xu, H.; Li, M. Volatile flavor behavior characterization of Hericium erinaceus during postharvest storage using E-nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC–MS after treated with electron-beam generated X-ray irradiation. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Cui, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Liu, L.; Wen, J.; Zhao, G. Fatty acid metabolism-related genes are associated with flavor-presenting aldehydes in Chinese local chicken. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 902180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, C.; Knight, A.; May, T.; Davidson, J.; Good, C. Performance, processing yields, and fillet composition of specific United States diploid and triploid rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) lines reared in a semi-commercial scale freshwater recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lv, X.; Xie, R.; Chen, B.-H.; Lai, Y.-W.; Chen, L.; Teng, H.; Cao, H. A systematic study on the chemical model of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons formation from nutrients (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids) in food. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ling, F.; Xue, X.; He, X.; Zhai, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, G.; et al. Rice flowering improves the muscle nutrient, intestinal microbiota diversity, and liver metabolism profiles of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in rice-fish symbiosis. Microbiome 2022, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Guryn, K.; Leone, V.; Chang, E.B. Regional Diversity of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Zhi, L.; Junaid, M.; Chen, G.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, J.; Chong, Y. Polystyrene nanoplastics sequester the toxicity mitigating potential of probiotics by altering gut microbiota in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbauer, E.; Aguanno, D.; Mindermann, N.; Omer, H.; Metwaly, A.; Krammel, T.; Faro, T.; Remke, M.; Reitmeier, S.; Bärthel, S.; et al. Mitochondrial perturbation in the intestine causes microbiota-dependent injury and gene signatures discriminative of inflammatory disease. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1347–1364.e1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Lessing, D.J.; Chu, W. The attenuating effects of synbiotic containing Cetobacterium somerae and Astragalus polysaccharide against trichlorfon-induced hepatotoxicity in crucian carp (Carassius carassius). J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hoedt, E.C.; Liu, Q.; Berendsen, E.; Teh, J.J.; Hamilton, A.; O’ Brien, A.W.; Ching, J.Y.L.; Wei, H.; Yang, K.; et al. Elucidation of Proteus mirabilis as a Key Bacterium in Crohn’s Disease Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 317–330.e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lin, T.; Jiang, W.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, L.; Tian, Y.; Ma, K.; Zhang, C.; Ji, F.; Mahsa, G.C.; et al. Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5 Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Wen, H.; Zheng, B.; Xiang, X.; Zhu, C. Dietary Carbohydrates and the Intestinal Barrier: Emerging Insights into NF-κB Modulation and Health Outcomes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 21264–21282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Physical Characteristics | TPAS | RAS |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | 3044.14 ± 321.15 a | 2428.54 ± 125.61 b |
| Adhesion | −24.55 ± 0.63 b | −37.94 ± 1.56 a |
| Elasticity | 0.44 ± 0.06 a | 0.42 ± 0.08 a |
| Mastication | 612.61 ± 42.98 a | 514.37 ± 21.33 b |
| Resilience | 0.319 ± 0.05 a | 0.29 ± 0.06 a |
| Chemical Compositions | TPAS | RAS |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 79.13 ± 0.31 a | 78.49 ± 0.75 a |
| Crude fat (%) | 1.96 ± 0.01 a | 1.41 ± 0.01 b |
| Crude ash (%) | 1.20 ± 0.05 a | 1.17 ± 0.01 a |
| Crude protein (%) | 17.26 ± 0.26 b | 18.92 ± 0.15 a |
| Amino Acid (mg/g) | TPAS | RAS |
|---|---|---|
| Asp | 6.07 ± 0.97 a | 4.09 ± 0.76 b |
| Glu | 35.75 ± 1.09 a | 30.30 ± 2.44 b |
| Thr * | 38.06 ± 1.10 a | 31.53 ± 2.80 b |
| Ser | 83.34 ± 1.41 a | 43.89 ± 3.44 b |
| Gly | 69.84 ± 1.05 a | 108.39 ± 8.67 b |
| Ala | 58.18 ± 1.03 a | 36.67 ± 3.05 b |
| Pro | 59.43 ± 3.10 a | 107.75 ± 6.14 b |
| Cys | 1.43 ± 0.16 a | 0.89 ± 0.57 a |
| Val * | 12.85 ± 0.44 a | 13.85 ± 1.13 a |
| Met * | 3.14 ± 0.38 a | 2.63 ± 0.31 a |
| Ile * | 3.90 ± 0.27 a | 2.16 ± 0.51 b |
| Leu * | 5.47 ± 0.46 a | 3.80 ± 0.41 b |
| Phe * | 11.14 ± 0.29 a | 10.95 ± 0.37 a |
| Lys * | 38.77 ± 2.62 a | 31.99 ± 2.50 b |
| His | 51.11 ± 1.10 a | 31.85 ± 0.80 b |
| Arg | 2.72 ± 0.15 a | 2.48 ± 0.32 a |
| Umami amino acids | 41.82 ± 1.91 a | 34.39 ± 3.10 b |
| Sweet amino acids | 308.85 ± 2.49 a | 328.23 ± 2.39 a |
| Bitter amino acids | 130.54 ± 3.66 a | 100.61 ± 4.46 b |
| EAA | 113.34 ± 2.92 a | 96.92 ± 6.93 b |
| NEAA | 367.87 ± 3.33 a | 366.31 ± 2.48 a |
| Total amino acid | 481.21 ± 5.49 a | 463.23 ± 3.12 a |
| EAA/TAA% | 0.24 ± 0.00 a | 0.21 ± 0.00 b |
| EAA/NEAA% | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, W.; Wu, R.; Fan, H.; Yao, G.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhu, N.; Liang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zheng, B.; et al. Comparative Study on the Nutritional, Textural and Flavor Profiles of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) in Industrialized Recirculating and Traditional Pond Aquaculture Systems. Foods 2025, 14, 4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234028
Su W, Wu R, Fan H, Yao G, Liu W, Li S, Zhu N, Liang Q, Ding X, Zheng B, et al. Comparative Study on the Nutritional, Textural and Flavor Profiles of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) in Industrialized Recirculating and Traditional Pond Aquaculture Systems. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234028
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Weifa, Rongfeng Wu, Hongjie Fan, Gaohua Yao, Wei Liu, Shimi Li, Ningyu Zhu, Qianrong Liang, Xueyan Ding, Bin Zheng, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Study on the Nutritional, Textural and Flavor Profiles of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) in Industrialized Recirculating and Traditional Pond Aquaculture Systems" Foods 14, no. 23: 4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234028
APA StyleSu, W., Wu, R., Fan, H., Yao, G., Liu, W., Li, S., Zhu, N., Liang, Q., Ding, X., Zheng, B., Xiang, X., & Zhou, F. (2025). Comparative Study on the Nutritional, Textural and Flavor Profiles of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) in Industrialized Recirculating and Traditional Pond Aquaculture Systems. Foods, 14(23), 4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234028