Screening, Characterization and Mutagenesis Breeding of Monascus Isolates with High Esterification Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preliminary Screening of Monascus Strains from Red Koji Samples
2.3. Identification and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis of Monascus Strains
2.4. Solid-State Fermentation and Esterase Activity Determination
2.5. Ethanol Tolerance Test
2.6. Emulsified Screening Medium for Esterification Activity
2.7. Mutation Breeding by Atmospheric and Room Temperature Plasma Mutagenesis (ARTP) Technology
3. Results
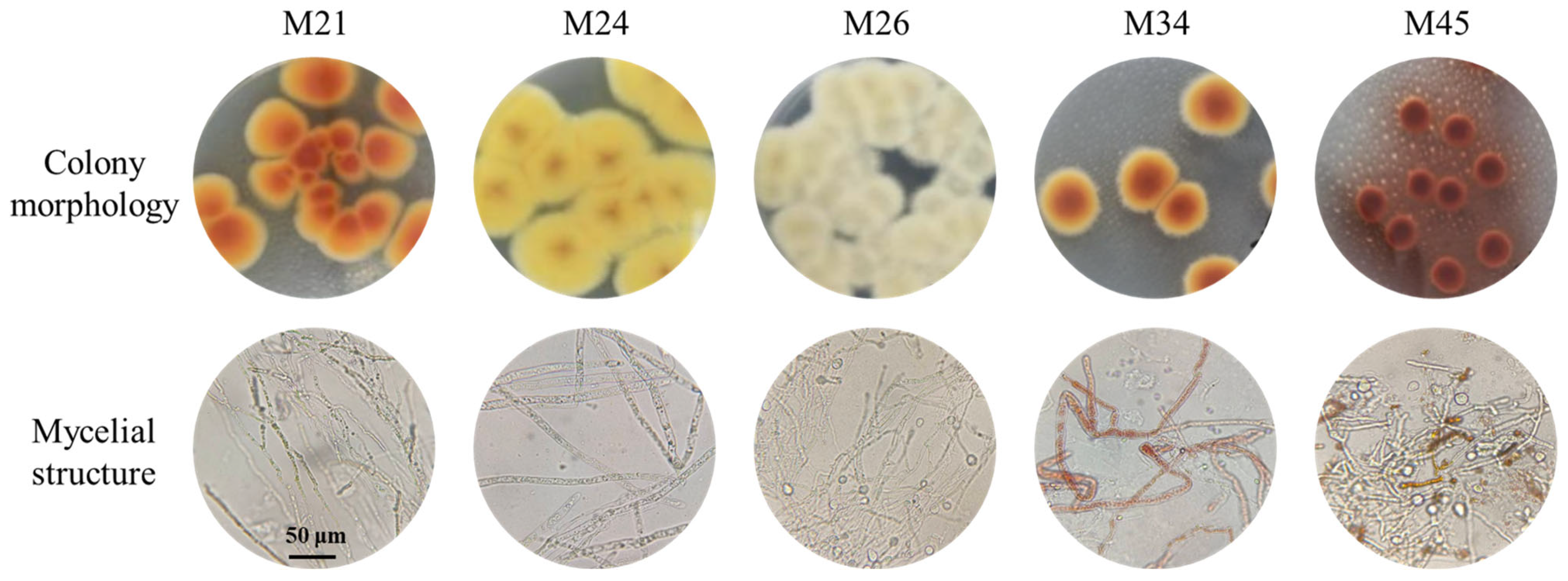
3.1. Screening of Monascus Strains
3.2. Species Identification of Monascus Strains
3.3. Solid-State Fermentation and Esterase Activity
3.4. Ethanol Tolerance
3.5. Mutational Breeding of M. purpureus M21
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srianta, I.; Ristiarini, S.; Nugerahani, I.; Sen, S.K.; Zhang, B.B.; Xu, G.R.; Blanc, P.J. Recent research and development of Monascus fermentation products. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, X. Optimization of Monascus purpureus culture conditions in rice bran for enhanced Monascus pigment biosynthesis. Fermentation 2025, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Shi, R.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, W. Recent advances in Monascus pigments produced by Monascus purpureus: Biosynthesis, fermentation, function, and application. LWT 2023, 185, 115162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husakova, M.; Patakova, P. Purified Monascus pigments: Biological activities and mechanisms of action. J. Nat. Prod. 2025, 88, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Cai, Y.; Huang, S.; Xiao, L.; Ye, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z. Enhancing Monacolin K and GABA biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus via GAD Overexpression: Multi-omics elucidation of regulatory mechanisms. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, A.; Monacolin, K. A new hypocholesterolemic agent produced by a Monascus species. J. Antibiot. 1979, 32, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Yang, J.-C.; Uang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-J. Improved dissolution rate and oral bioavailability of lovastatin in red yeast rice products. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 444, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Qi, Z.; Wen, A.; Qin, L.; Zeng, H. Mechanism of the secondary metabolites and key enzymes of Monascus spp. to promote tocopherol enrichment. Food Chem. 2025, 488, 144860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Hammad, S.F.; Abdel-Mawgood, A.L. Optimization, characterization, and molecular modelling of an acid and organic solvent-tolerant lipase isolated from Monascus pilosus as a potential detergent additive. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 317, 144883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, P.N.; Toyokawa, Y.; Toyama, H.; Taira, T.; Yasuda, M. Purification and characterisation of two extracellular acid proteinases from Monascus pilosus. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hou, S.; Lu, Z.; Kang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Dynamic changes and transformation mechanisms of alkylpyrazines and α-dicarbonyl compounds during Monascus vinegar brewing. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 148, 108166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Flavor quality and lipid-lowering function of mixed fermented pu-erh tea with various Monascus species. Foods 2025, 14, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.B.; Stevely, A.K.; Kersbergen, I.; McGrane, E.; Moore, E.C.; Pryce, R.E.; Brown, J.; Holmes, J. Current and future trends in the consumption, sale and purchasing of alcohol-free and low-alcohol products in Great Britain, 2014 to 2023. Addiction 2025, 120, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, T.; Jiang, J.; Sun, D.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Epidemiology characteristics of the drinking patterns and alcohol consumption among adults in Hainan Province, China. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1490439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, Y.; Yin, R.; Guo, L.; Song, Y.; Zhong, B.; Zhao, D. Analysis of the relationship between personal characteristics and alcohol consumption behavior of Chinese consumers. Foods 2025, 14, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K. Mid, Low- and No- Is All Go: Moving Toward Lower-Alcohol Beers in Australia. 2022. Available online: https://economics.adelaide.edu.au/wine-economics/ua/media/146/wine-brief-36.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Anderson, K. The emergence of lower-alcohol beverages: The case of beer. J. Wine Econ. 2023, 18, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinhuanet. The Liquor Industry Is Quietly Undergoing a Transformation to Reduce Alcohol Content and Seek Breakthroughs. Available online: http://www.xinhuanet.com/food/20250714/39ab57192a0a4a549fd42a1687e85a08/c.html (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Piornos, J.A.; Koussissi, E.; Balagiannis, D.P.; Brouwer, E.; Parker, J.K. Alcohol-free and low-alcohol beers: Aroma chemistry and sensory characteristics. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Dai, M.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Sun, B. Simulated fermentation of strong-flavor baijiu through functional microbial combination to realize the stable synthesis of important flavor chemicals. Foods 2023, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Shaffer, C.E.H.; Bennett, G.N. Microbial formation of esters. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, X.-A.; Fang, Z. The art of flavored wine: Tradition and future. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Lin, M.; Liang, X.; Ding, Z.; Dong, W.; Yang, M. Molecular mechanism of LIP05 derived from Monascus purpureus YJX-8 for synthesizing fatty acid ethyl esters under aqueous phase. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1107104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Liang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Cai, Q.; Weng, Q.; Guo, W.; Ni, L.; Lv, X. Metagenomics reveals the differences in flavor quality of rice wines with Hongqu and Maiqu as the fermentation starters. Food Microbiol. 2025, 125, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liang, Z.; Huo, Y.; Wu, Q.; Ni, L.; Lv, X. A comparative study of microbial communities, biogenic amines, and volatile profiles in the brewing process of rice wines with Hongqu and Xiaoqu as fermentation starters. Foods 2024, 13, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Yang, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, L. Microbial communities and flavor compounds during the fermentation of traditional Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Foods 2022, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.; Deng, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Wu, Z.; Tang, L.; Suyama, T.; Zhang, W. Investigating the main contributors to esterification activity and identifying the aqueous-phase ester synthases in Daqu. Food Biosci. 2025, 66, 106227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Gao, X. Impact of Monascus purpureus fermentation on antioxidant activity, free amino acid profiles and flavor properties of kelp (Saccharina japonica). Food Chem. 2023, 400, 133990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QB/T 5188-2017; Brewing Red Kojic Rice. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Wang, K.; Tang, N.; Bian, X.; Geng, D.; Chen, H.; Cheng, Y. Structural characteristics, chemical compositions and antioxidant activity of melanoidins during the traditional brewing of Monascus vinegar. Lwt 2024, 209, 116760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Jia, M.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Ren, J.; Luo, F.; Bai, J.; Liu, J. Toward improvements for enhancement the productivity and color value of Monascus pigments: A critical review with recent updates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7139–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wan, J.; Wang, D.; Shao, Y. Effective enhancement of the ability of Monascus pilosus to produce lipid-lowering compound monacolin K via perturbation of metabolic flux and histone acetylation modification. Food Res. Int. 2024, 195, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lai, Y.; Gou, Y.; Guo, J.; Lian, X. Screening of Monascus to produce high-yield monacolin K by solid-state fermentation on medium of coix seed and gluten fractions. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, H.; Zhen, D.; Fang, S. Research on the esterification property of esterase produced by Monascus sp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 5166–5172. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, B. Changes in key aroma compounds and esterase activity of Monascus-fermented cheese across a 30-day ripening period. Foods 2022, 11, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.T. Isolation, Identification and Application of High-Production Esterase Monascus hm Based on Flavorand Enzyme-Producing Properties; Shanxi Agricultural University: Jinzhong, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.P.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.X. Isolation of Monascus strains from the production environment of qingxiang xiaoqu baijiu and study on their fermentation characteristics. Liquor.-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Hu, W.; He, M.; Hu, G. Novel mutagenesis and screening technologies for food microorganisms: Advances and prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabín, M.; Jelínek, L.; Kotrba, P.; Cejnar, R.; Dostálek, P. Enhancing the performance of brewing yeasts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Rao, J.W.; Meng, F.B.; Wang, Z.W.; Liu, D.Y.; Yu, H. Combination of mutagenesis and adaptive evolution to engineer salt—Tolerant and aroma—Producing yeast for soy sauce fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4288–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Q.-Q.; Zhang, X.-F.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chang, H.-B.; Li, H.-P.; Oda, Y.; Xing, X.-H. Quantitative evaluation of DNA damage and mutation rate by atmospheric and room-temperature plasma (ARTP) and conventional mutagenesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5639–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketkaeo, S.; Nagano, Y.; Baba, S.; Kimura, K.; Futagami, T.; Sanpamongkolchai, W.; Kobayashi, G.; Goto, M. Development of Monascus purpureus monacolin K-hyperproducing mutant strains by synchrotron light irradiation and their comparative genome analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 133, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Gong, Z.; Shu, M.; Zhao, H.; Ye, F.; Tang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, B.; Lu, D.; Zhou, X. Increased water-soluble yellow Monascus pigment productivity via dual mutagenesis and submerged repeated-batch fermentation of Monascus purpureus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 914828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, R.; Tallapragada, P. Development and screening of mutants from Monascus sanguineus for secondary metabolites production. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, T.; Lu, D.; Zhou, X. Optimization of medium compositions and X-ray irradiation to enhance monacolin K production by Monascus purpureus in submerged fermentation. Process Biochem. 2024, 141, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Pan, Q.; Xue, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zheng, Y. Synthetic biology for Monascus: From strain breeding to industrial production. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, 2400180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.-Y.; Zhao, Q.; He, Q.-L. Application of CRISPR in filamentous fungi and macrofungi: From component function to development potentiality. ACS Synth. Biol. 2023, 12, 1908–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.B.; Fraga, L.P.; Fleuri, L.F.; Macedo, G.A. Lipase and esterase: To what extent can this classification be applied accurately? Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 31, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Huang, L.; Lian, J. Alcohol acyltransferases for the biosynthesis of esters. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruis, A.J.; Bohnenkamp, A.C.; Patinios, C.; van Nuland, Y.M.; Levisson, M.; Mars, A.E.; van den Berg, C.; Kengen, S.W.; Weusthuis, R.A. Microbial production of short and medium chain esters: Enzymes, pathways, and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoleva, T.; Vesenmaier, F.; Koch, L.; Schunke, J.E.; Novak, K.D.; Grobe, S.; Dörr, M.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Bayer, T. Biosensor—Guided engineering of a baeyer—Villiger monooxygenase for aliphatic ester production. ChemBioChem 2025, 26, e202400712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| 0% | 3% | 6% | 9% | 12% | 15% | 18% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M21 | + + + + | + + + | + | − | − | − | − |
| M24 | + + + + | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| M26 | + + + + | + + + | + | − | − | − | − |
| M34 | + + + + | + + + + | + + + | + + | − | − | − |
| M45 | + + + + | + + + | + | − | − | − | − |
| M21-2 | + + + + | + + + | + | − | − | − | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Yang, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Lu, Z. Screening, Characterization and Mutagenesis Breeding of Monascus Isolates with High Esterification Activity. Foods 2025, 14, 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223949
Zhou C, Yang S, Zhu X, Li X, Li J, Lu Z. Screening, Characterization and Mutagenesis Breeding of Monascus Isolates with High Esterification Activity. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223949
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Chen, Shuran Yang, Xingche Zhu, Xiaoxi Li, Jing Li, and Zhenghui Lu. 2025. "Screening, Characterization and Mutagenesis Breeding of Monascus Isolates with High Esterification Activity" Foods 14, no. 22: 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223949
APA StyleZhou, C., Yang, S., Zhu, X., Li, X., Li, J., & Lu, Z. (2025). Screening, Characterization and Mutagenesis Breeding of Monascus Isolates with High Esterification Activity. Foods, 14(22), 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223949





