Combined Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation and Physical Milling on Physicochemical Properties of Glutinous Rice Flour and Texture of Glutinous Dumplings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemical Composition
2.3. Properties of GRF
2.3.1. Determination of Color of GRF
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.3. Determination of Water Hydration Properties
2.3.4. Rapid Visco Analysis
2.3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. Preparation of Glutinous Dumpling
2.5. Evaluation of Glutinous Dumpling Quality
2.5.1. Transparency of the Glutinous Dumpling Soups After Boiling
2.5.2. Textural Properties of Cooked Glutinous Dumpling
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of Different GRF
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Different GRFs
3.2.1. Color Evaluation
3.2.2. Microstructure
3.2.3. Water Hydration Properties
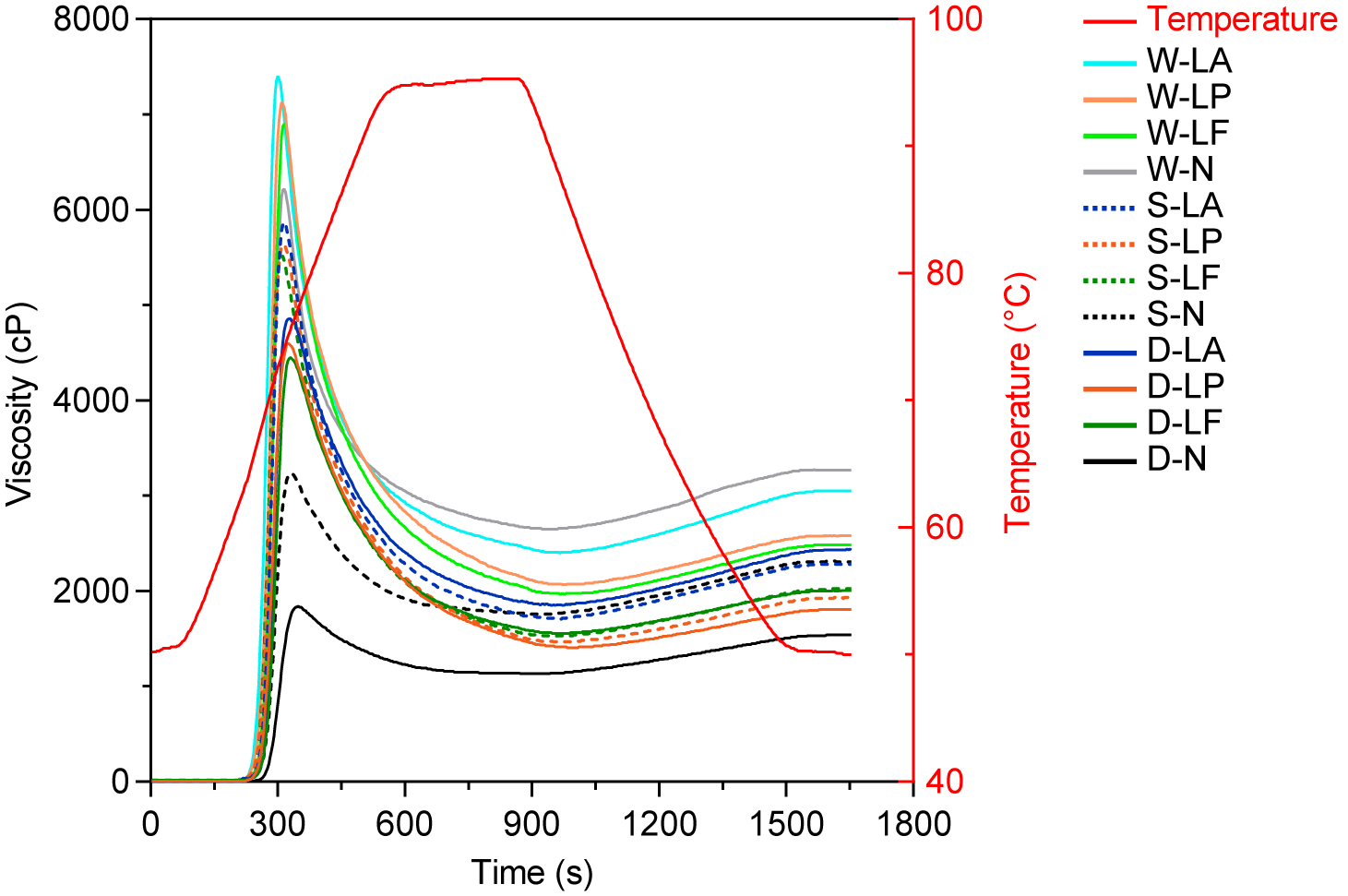
3.2.4. Pasting Properties
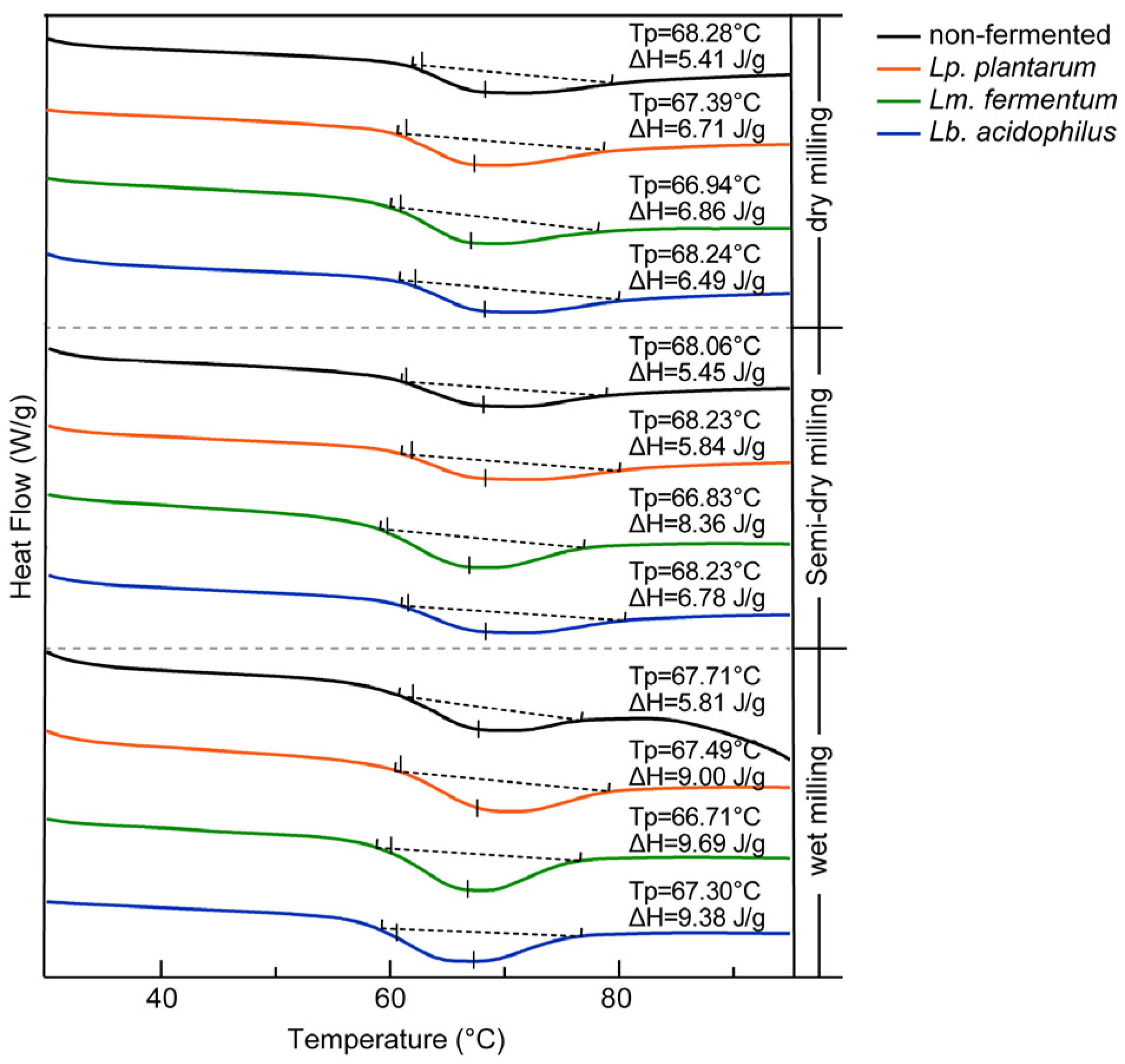
3.2.5. Thermodynamic Properties
3.3. Effects of Different GRF on the Cooking Quality of Prepared Glutinous Dumplings
3.3.1. Transmittance of the Soup
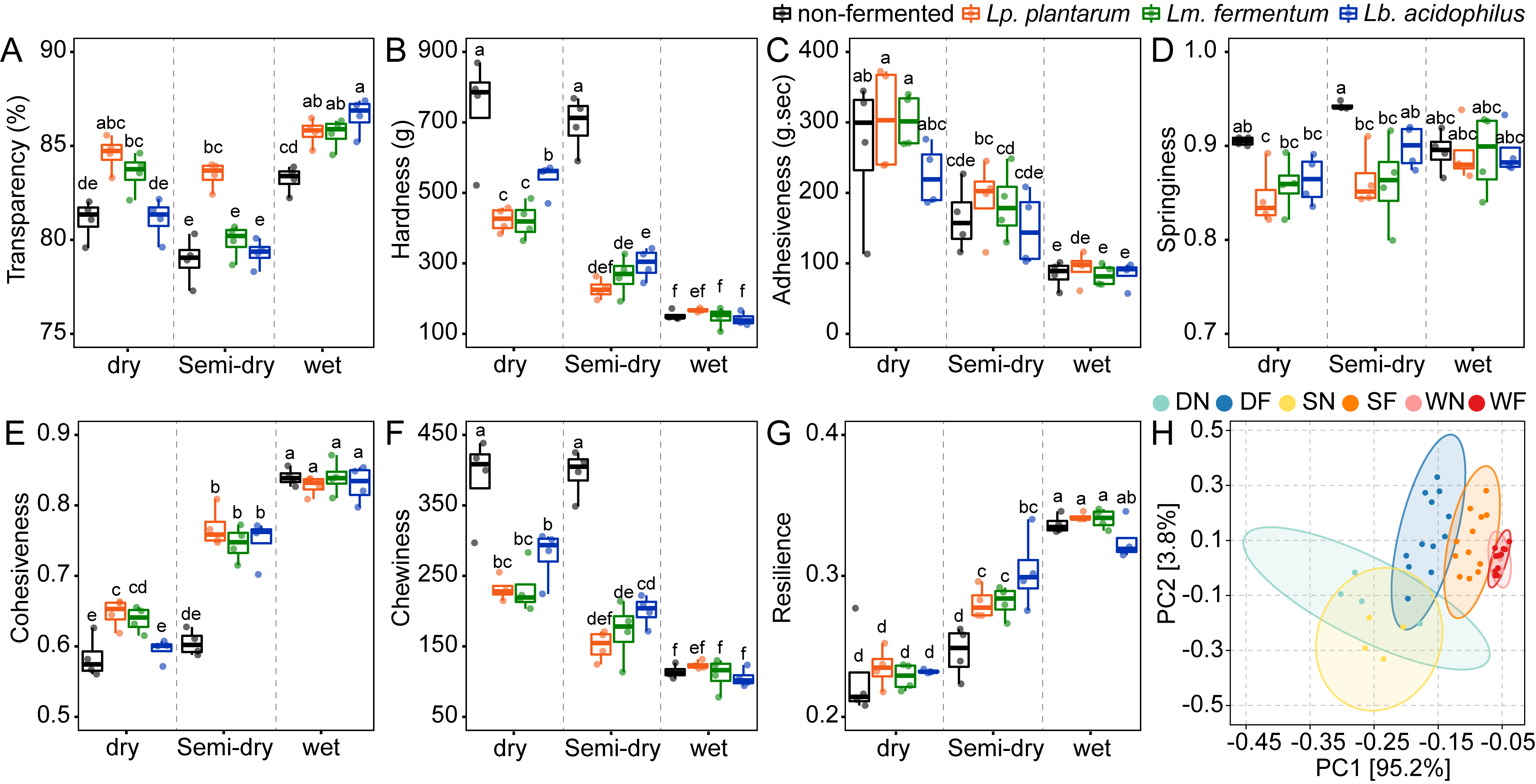
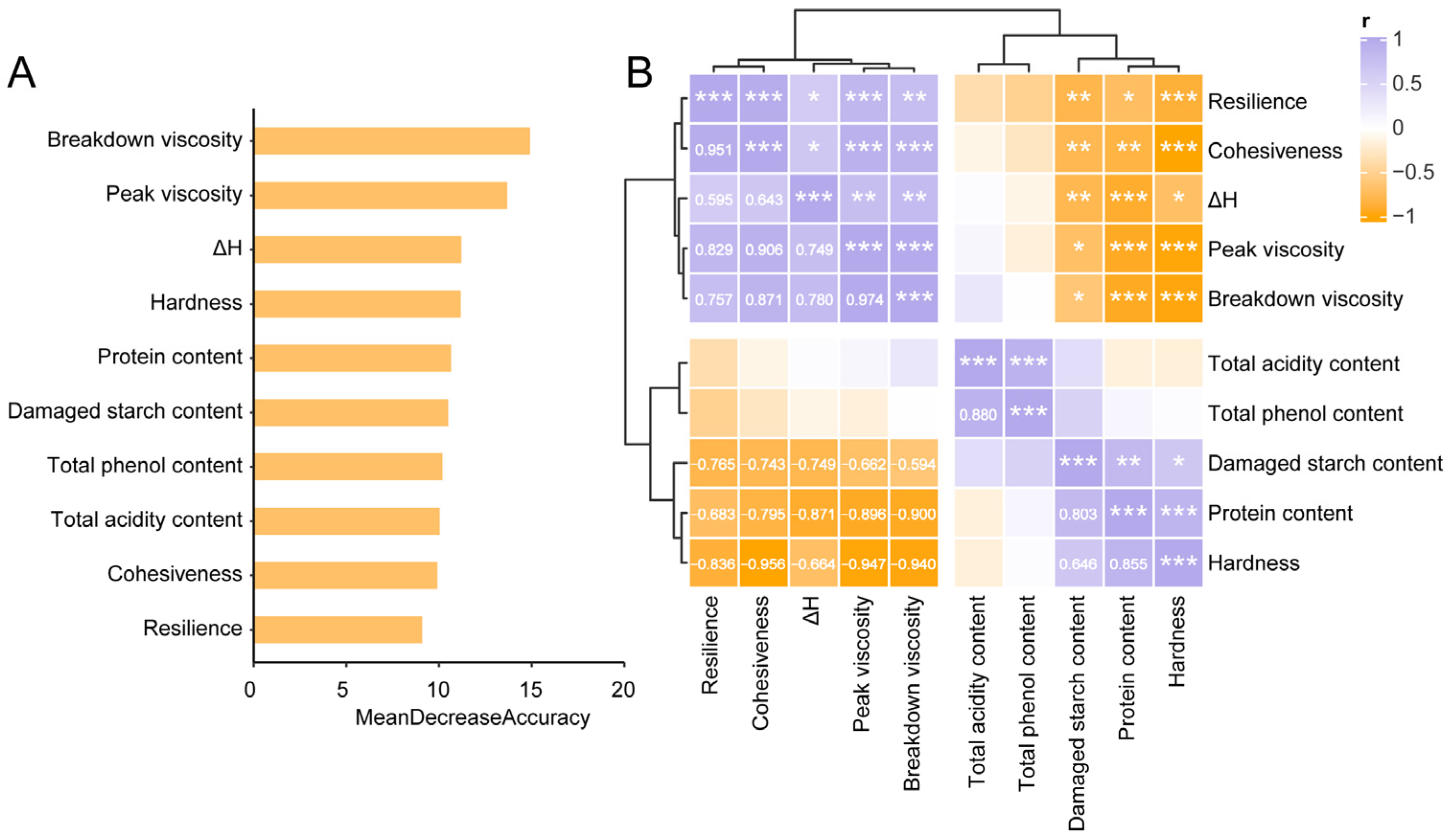
3.3.2. Textural Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Xu, D.; Xu, X. Endogenous alpha-amylase explains the different pasting and rheological properties of wet and dry milled glutinous rice flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Cao, J.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Differences in physicochemical, morphological, and structural properties between rice starch and rice flour modified by dry heat treatment. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Xu, D.; Xu, X. Effects of milling methods on the properties of glutinous rice flour and sweet dumplings. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Cereal Grains for the Food and Beverage Industries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ngamnikom, P.; Songsermpong, S. The effects of freeze, dry, and wet grinding processes on rice flour properties and their energy consumption. J. Food Eng. 2011, 104, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Ouyang, D.; Sang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xing, J.; Luo, X. Effect of water content in semidry grinding on the quality of glutinous rice flour. Foods 2024, 13, 3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, H. Improving quality attributes of sweet dumplings by germination: Effect of glutinous rice flour microstructure and physicochemical properties. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Wu, S.; Lai, S.; Ye, F. Effects of Stir-Frying and Heat–Moisture Treatment on the Physicochemical Quality of Glutinous Rice Flour for Making Taopian, a Traditional Chinese Pastry. Foods 2024, 13, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I. Changes in the glutinous rice grain and physicochemical properties of its starch upon moderate treatment with pulsed electric field. Foods 2021, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W.; Fan, H.; Fan, S.; Ai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Suo, B. Bactericidal effect of ultrasound on glutinous rice during soaking and its influence on physicochemical properties of starch and quality characteristics of sweet dumplings. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 110, 107034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, Y.; Yamagata, E.; Takahama, N.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yanagida, R.; Mitsutake, S. Liberation of eicosapentaenoic acid and degradation of the major cell wall polysaccharide porphyran by fermentation of nori, the dried thalli of Pyropia yezoensis, with koji. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 4105–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedorowicz, G.K.M. Comparison of molecular structure and selected physicochemical properties of spelt wheat and common wheat starches. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 53, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; He, Y. Role of Lactic acid bacteria in the eating qualities of fermented rice noodles. Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.I.; Ransom-Jones, E.; Sadiq, S.; Vitlic, A.; McLay, N.; Rojas, M.F.; Ale, E.C.; Binetti, A.G.; Collett, A.; Humphreys, P.N. Structural characterisation of two medium molecular mass exopolysaccharides produced by the bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum Lf2. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 488, 107909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İspirli, H.; Özmen, D.; Yılmaz, M.T.; Sağdıç, O.; Dertli, E. Impact of glucan type exopolysaccharide (EPS) production on technological characteristics of sourdough bread. Food Control 2020, 107, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Guo, Y.; Tang, X.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Removal of cadmium from rice by Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation. Food Control 2019, 96, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Ren, X.; Zheng, Q.; He, Y.; Lv, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, P.; Hao, Y.; Chen, F.; Tang, X. Effects of Lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the physicochemical properties of rice flour and rice starch and on the anti-staling of rice bread. Foods 2023, 12, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotni, D.; Čukelj, N.; Smerdel, B.; Bituh, M.; Dujmić, F.; Ćurić, D. Glycemic index and firming kinetics of partially baked frozen gluten-free bread with sourdough. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 55, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ding, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Dang, B.; Li, L.; Gou, G.; Wu, G. The effect of different milling methods on the physicochemical and in vitro digestibility of rice flour. Foods 2023, 12, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Luo, S.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Gong, E.; Miao, J. Phenolic retention of brown rice after extrusion with mesophilic α-amylase. Food Biosci. 2018, 21, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhang, S.; Hong, B.; Shan, S.; Zhang, J.; Sha, D.; Gao, S.; Liu, Q.; Lu, S.; Ren, C. Dual Bioconversion Strategy: Synergistic Germination and Lactobacillus Fermentation Engineering for a γ-Aminobutyric Acid-Enriched Beverage from Brown Rice. Foods 2025, 14, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbica, A.; Hadnađev, M.; Hadnađev, T.D. Rice and buckwheat flour characterisation and its relation to cookie quality. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Lee, S.M.; Shim, J.-H.; Yoo, S.-H.; Lee, S. Effect of dry-and wet-milled rice flours on the quality attributes of gluten-free dough and noodles. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yan, X.; Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Chen, X.; Ding, W. Effects of milling methods on the properties of rice flour and steamed rice cakes. Lwt 2022, 167, 113848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, L.; Huang, J.; Zou, P.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, C.; Wu, J. Pre-fermentation of rice flour for improving the cooking quality of extruded instant rice. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of pregelatinized starch on the characteristics, microstructures, and quality attributes of glutinous rice flour and dumplings. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, H.; Yuan, Y.; Ju, Q.; Teng, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, W.; Fujita, K. Effects of different milling methods on physicochemical properties of common buckwheat flour. Lwt 2018, 92, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Feng, J.; Shen, X.; Li, H.; Chang, S.; Zhao, C. Characterization and the cholesterol-lowering effect of dietary fiber from fermented black rice (Oryza sativa L.). Food Funct. 2023, 14, 6128–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lei, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Qian, H.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, W. Study on the removal of cadmium in rice using microbial fermentation method. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Yuan, M.L.; Sasaki, T.; Li, L.T.; Kohyama, K. Rheological properties of fermented rice flour gel. Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, C.; Ji, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Qi, B. Improvement of nutritional value, bioactivity and volatile constituents of quinoa seeds by fermentation with Lactobacillus casei. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 84, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Rheu, K.-M.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-I.; Lee, B.-J.; Byun, K.; Ryu, B. Rice GABA®: Valorization of Rice Germ through Lactic acid bacterial Precision Fermentation for Enhanced GABA Production and Functional Properties. LWT 2025, 229, 118221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Miao, K.; Niyaphorn, S.; Qu, X. Production of gamma-aminobutyric acid from Lactic acid bacteria: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarno, M.; Cichońska, P. Lactic acid bacteria-fermentable cereal-and pseudocereal-based beverages. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.-P.; Zhou, H.-M.; Zhu, K.-R.; Li, Q. Effect of thermal treatment on the physicochemical, ultrastructural and nutritional characteristics of whole grain highland barley. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, A.; Sheng, Q.; Liu, J. Effects of dry and wet ball milling on physicochemical properties of foxtail millet. Food Chem. 2025, 483, 143916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Q.; Feng, W. Impact of protein content on processing and texture properties of waxy rice flour and glutinous dumpling. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leewatchararongjaroen, J.; Anuntagool, J. Effects of dry-milling and wet-milling on chemical, physical and gelatinization properties of rice flour. Rice Sci. 2016, 23, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Han, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, D.; Jiang, C.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xiang, X. The high molecular weight and large particle size and high crystallinity of starch increase gelatinization temperature and retrogradation in glutinous rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Huang, J.; Qin, W.; Geng, D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, S.; Tong, L.-T. Effects of moisture changes on physicochemical properties of rice flour during semidry grinding. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 100, 103254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Qin, L.; Wu, N.; Ge, P.; Hu, C.; Hu, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, Y. Intensification of rice flour gel structure by fermenting corresponding rice with Lactobacillus plantarum. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hong, S.; Zhang, J.-R.; Liu, P.-H.; Li, S.; Wen, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, G.; Habimana, O.; Shah, N.P. The effect of Lactic acid bacteria fermentation on physicochemical properties of starch from fermented proso millet flour. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Luo, S.; Li, C.; Ye, J.; Liu, C.; Gilbert, R.G. Physicochemical and structural properties of pregelatinized starch prepared by improved extrusion cooking technology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Saleh, A.S.; Yang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, S.; Xiao, Z. Influence of fluidized bed jet milling on structural and functional properties of normal maize starch. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 1700290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, J.; Yang, N.; Chen, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X. The roles of starch structures in the pasting properties of wheat starch with different degrees of damage. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 1700190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanipour, A.; Samaei, Y.; Böök, O.; Granfeldt, Y.; Lazarte, C.E. Impact of dehulling, germination and fermentation on the bioactive and functional properties of grey pea flour. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1478399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, J.-D.; Sung, J.M. Effects of fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum on rice flour: The role of granular characteristics. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.; Cheng, J.; Lei, T.; Lai, P.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, D.; Pan, Y. Solid-state fermentation with Ganoderma lucidum improves nutritional quality and processing characteristics of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). LWT 2025, 217, 117437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Nature of thermal transitions of native and acid-hydrolysed pea starch: Does gelatinization really happen? Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, S.; Niakousari, M. Microstructure, pasting and textural properties of wheat starch-corn starch citrate composites. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Xie, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, N.; Fan, H. Preparation of Lactic acid bacteria compound starter cultures based on pasting properties and its improvement of glutinous rice flour and dough. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, L.; Tong, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Effect of milling methods on the properties of rice flour and gluten-free rice bread. Lwt 2019, 108, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, H. Effects of Fermentation Modification and Combined Modification with Heat-Moisture Treatment on the Multiscale Structure, Physical and Chemical Properties of Corn Flour and the Quality of Traditional Fermented Corn Noodles. Foods 2024, 13, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Ma, C.M.; Xing, W.J.; Yang, Y.; Fan, J.; Yang, C.H.; Zhang, N. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus fermentation on the quality of glutinous rice products. Starch-Stärke 2023, 75, 2200193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Fang, X.-H.; Cai, W.-H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.-L. Retrogradation behaviors of damaged wheat starch with different water contents. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Dou, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Hao, Y. Enhancement of Anti-Staling Properties of Rice Bread Through Fermentation Rice Flour with Three Lactic acid bacteria. Foods 2025, 14, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Xu, L.; Tong, L.-T. Effects of alkali purification and fermentation on the structure and properties of rice starch gel. Food Struct. 2025, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavent-Gil, Y.; Román, L.; Gómez, M.; Rosell, C.M. Physicochemical Properties of Gels Obtained from Corn Porous Starches with Different Levels of Porosity. Starch-Stärke 2019, 71, 1800171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Bella, E.; Riolo, M.; Luz, C.; Baglieri, A.; Puglisi, I.; Meca, G.; Cacciola, S.O. Fermentates of consortia of Lactic acid bacteria and a Cyanobacterium are effective against toxigenic fungi contaminating agricultural produces. Biol. Control 2024, 191, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Hong, B.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, D.; Shan, S.; Wu, Q.; Lu, S.; Ren, C. Combined Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation and Physical Milling on Physicochemical Properties of Glutinous Rice Flour and Texture of Glutinous Dumplings. Foods 2025, 14, 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223882
Zhang J, Hong B, Zhang S, Yuan D, Shan S, Wu Q, Lu S, Ren C. Combined Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation and Physical Milling on Physicochemical Properties of Glutinous Rice Flour and Texture of Glutinous Dumplings. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223882
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingyi, Bin Hong, Shan Zhang, Di Yuan, Shan Shan, Qi Wu, Shuwen Lu, and Chuanying Ren. 2025. "Combined Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation and Physical Milling on Physicochemical Properties of Glutinous Rice Flour and Texture of Glutinous Dumplings" Foods 14, no. 22: 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223882
APA StyleZhang, J., Hong, B., Zhang, S., Yuan, D., Shan, S., Wu, Q., Lu, S., & Ren, C. (2025). Combined Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation and Physical Milling on Physicochemical Properties of Glutinous Rice Flour and Texture of Glutinous Dumplings. Foods, 14(22), 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223882




