Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Six Commercially Important Bivalves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Genomic DNA Isolation
2.2. Design of Species-Specific Primers for Six Bivalve Species
2.3. Species-Specific Multiplex PCR Primer Set Amplification
2.4. Determining the Efficient Annealing Temperature of a Multiplex PCR Primer Set
2.5. Assessment of Multiplex PCR Performance at Varying DNA Concentrations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design of Species-Specific Primers for the Mitochondrial COX1 Region
3.2. Multiplex PCR Set Amplification
3.3. Multiplex PCR Amplification Efficiency Across Annealing Temperatures
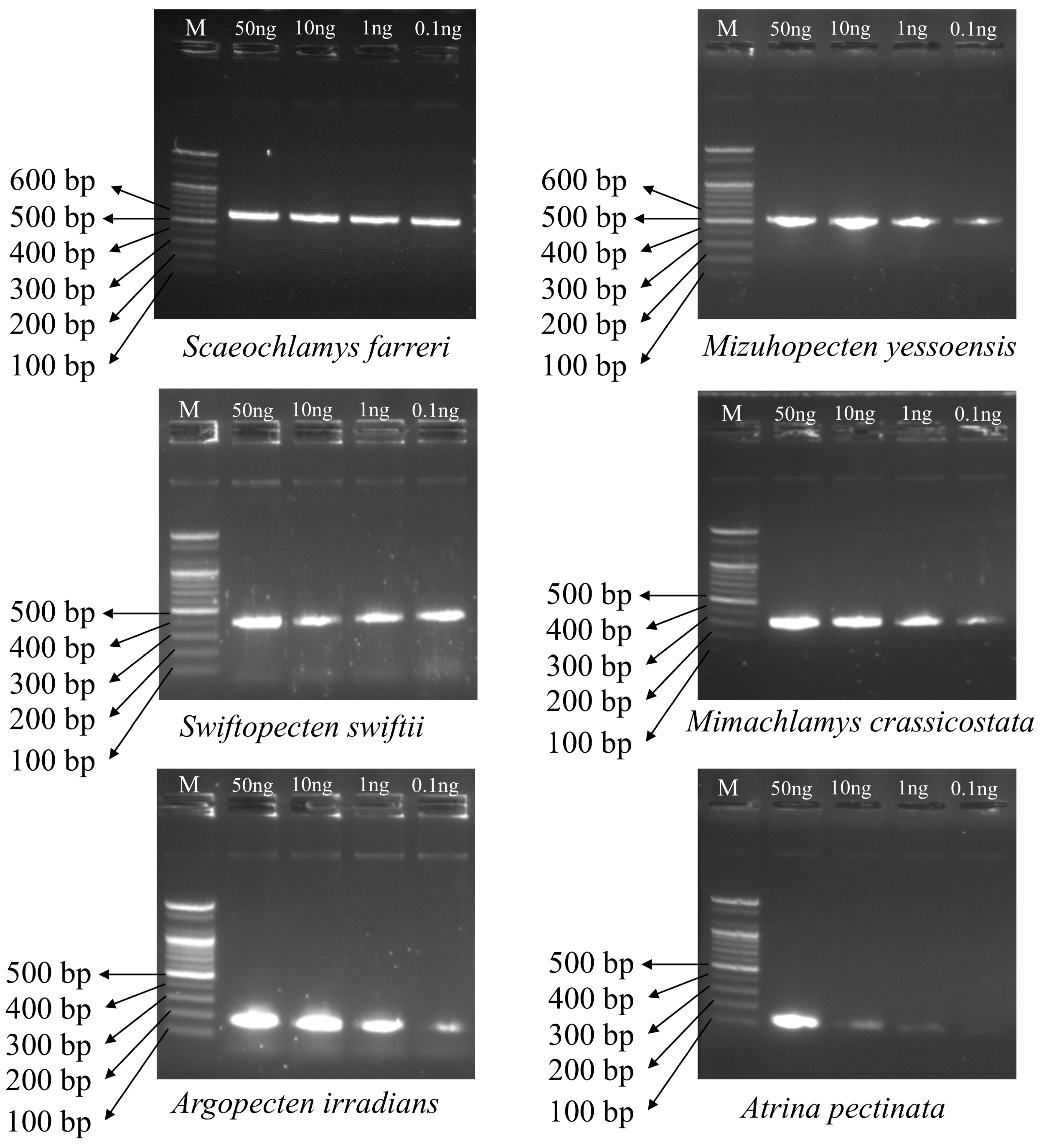
3.4. Sensitivity of Multiplex PCR Amplification Across DNA Concentrations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Peng, C.; Hou, X.; Lu, W.; Xing, Q.; Hu, J.; et al. Metabonomic Analysis Provides New Insights into the Response of Zhikong Scallop (Chlamys farreri) to Heat Stress by Improving Energy Metabolism and Antioxidant Capacity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Kawamata, K.; Zaslavskaya, N.; Nakamura, A.; Ohta, T.; Nishikiori, T.; Brykov, V.; Nagashima, K. Development of microsatellite markers for Japanese scallop (Mizuhopecten yessoensis) and their application to a population genetic study. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Han, D.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Geographical origin traceability and species identification of three scallops (Patinopecten yessoensis, Chlamys farreri, and Argopecten irradians) using stable isotope analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, Y. Scallop fisheries and aquaculture in Japan. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 40, pp. 891–936. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Zhang, H.; Lim, L.; Zheng, H. Selection breeding program of Nan’ao Golden Scallop Chlamys nobilis with higher nutritional values and less susceptible to stress. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; YanWu, Y.G.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Qiao, H.; Cheng, L.; Tong, J.; Li, M. Isolation and characterization of 15 polymorphic microsatellite markers for comb pen shell. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, e703–e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, W.-C.; Kim, H.C.; Kang, C.-K. Gross biochemical and isotopic analyses of nutrition-allocation strategies for somatic growth and reproduction in the bay scallop Argopecten irradians newly introduced into Korean waters. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.-C.; Kim, J.H.; Park, Y.J.; Kang, H.W.; Chung, J.S.; Chung, E.-Y. Morphology and Taxonomic Values of the Sperm in Male Chlamys (Swiftopecten) swiftii (Pteriomorphia: Pectinidae) in Western Korea. Korean J. Malacol. 2012, 28, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Tian, Y.; Chang, Y.; Hao, Z. Behavioral characteristics and related physiological and ecological indexes of cultured scallops (Mizuhopecten yessoensis) in response to predation by the crab Charybdis japonica. Fishes 2024, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo, M.; López, S.; Aparicio-Valencia, A.; Fueyo, A.; Quintanilla-García, P.; Arias, A.; Borrell, Y. Almost never you get what you pay for: Widespread mislabeling of commercial “zamburiñas” in northern Spain. Food Control 2021, 120, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahles, S.; DeWitt, C.A.M.; Hellberg, R.S. A meta-analysis of seafood species mislabeling in the United States. Food Control 2025, 171, 111110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Yang, Q.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, H. The price difference and trend analysis of Yesso scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) in Changhai county, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espineira, M.; Gonzalez-Lavin, N.; Vieites, J.M.; Santaclara, F.J. Development of a method for the genetic identification of commercial bivalve species based on mitochondrial 18S rRNA sequences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, A.; Fujimoto, T.; Arai, K. Rapid species identification of fresh and processed scallops by multiplex PCR. Food Control 2013, 32, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, A.; Villegas-Llerena, C.; Fujimoto, T.; Arai, K. Novel decaplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of scallop species with species-specific primers targeting highly variable 5′ end of the 16S rRNA gene. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gense, K.; Peterseil, V.; Licina, A.; Wagner, M.; Cichna-Markl, M.; Dobrovolny, S.; Hochegger, R. Development of a DNA metabarcoding method for the identification of bivalve species in seafood products. Foods 2021, 10, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, W.; Cai, H.; Cao, G.; Li, Z. Current Progress and Future Trends of Genomics-Based Techniques for Food Adulteration Identification. Foods 2025, 14, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhong, G.; Zhou, S.; Guo, Y.; Pan, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Xia, Q.; Cai, Z. Detection and characterization of meat adulteration in various types of meat products by using a high-efficiency multiplex polymerase chain reaction technique. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 979977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.R.; Kim, H.J.; Bang, I.C. Development of a Rapid and Cost-Effective Multiplex PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Identification of Three Commercially Important Sea Squirt Species (Halocynthia spp.). Foods 2025, 14, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitpipit, T.; Sittichan, K.; Thanakiatkrai, P. Direct-multiplex PCR assay for meat species identification in food products. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.Y.; Suh, S.M.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, H.Y. Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Five Types of Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis, Thunnus alalonga, T. albacares, T. obesus and T. thynnus). Foods 2022, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.Y. A Multiplex PCR Assay Combined with Capillary Electrophoresis for the Simultaneous Identification of Atlantic Cod, Pacific Cod, Blue Whiting, Haddock, and Alaska Pollock. Foods 2021, 10, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, S.F.; Krug, M.J.; Nielsen, M.E.; Santos, Y.; Call, D.R. Simultaneous detection of marine fish pathogens by using multiplex PCR and a DNA microarray. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen Hellberg, R.S.; Morrissey, M.T.; Hanner, R.H. A multiplex PCR method for the identification of commercially important salmon and trout species (Oncorhynchus and Salmo) in North America. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C595–C606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Stoeckle, M.Y.; Zemlak, T.S.; Francis, C.M. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.-S.; Suh, S.-J.; Oh, H.-W.; Hebert, P.D. Recovery of the mitochondrial COI barcode region in diverse Hexapoda through tRNA-based primers. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layton, K.K.; Martel, A.L.; Hebert, P.D. Patterns of DNA barcode variation in Canadian marine molluscs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, A.; De Mattia, F.; Losa, A.; Bruni, I.; Federici, S.; Casiraghi, M.; Martellos, S.; Labra, M. DNA barcoding as a new tool for food traceability. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Young, R.G.; Hellberg, R.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Corradini, M.G.; Farber, J.M. Twenty-three years of PCR-based seafood authentication assay development: What have we learned? Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Kumar, Y. Recent advances in multiplex molecular techniques for meat species identification. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Establishment of a multiplex-PCR detection method and development of a detection kit for five animal-derived components in edible meat. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, D.C.; Arnold, W.S. Shell morphologies of bay scallops, Argopecten irradians, from extant and prehistoric populations from the Florida Gulf Coast: Implications for the biology of past and present metapopulations. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2001, 28, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Liu, B.; Zhu, C. Morphological trends in three different populations of the noble scallop Mimachlamys crassicostata (G.B. Sowerby II, 1842) along the South China Sea Coast and their relationship to environmental factors. Indian J. Fish. 2023, 70, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravdukhina, O.Y.; Kodolova, O.P. Temporal dynamics of genetic diversity of Japanese scallop Mizuhopecten yessoensis (Jay, 1856). Biol. Bull. 2010, 37, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutaenko, K.A.; Noseworthy, R.G. Contribution to the knowledge of the marine bivalve mollusk fauna of Gangwon Province, Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2019, 12, 14–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, T. Phylogeography and taxonomic revision of the pen shell Atrina pectinata species complex in the South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 753553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Shirai, K.; Murakami-Sugihara, N.; Sakai, S.; Sasaki, T. Sexual dimorphism in shell growth of the oviparous boreal scallop Swiftopecten swiftii (Bivalvia: Pectinidae). J. Molluscan Stud. 2019, 85, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Qiu, H.; Wei, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. Exploring the Impact of Primer-Template Mismatches on PCR Performance of DNA Polymerases Varying in Proofreading Activity. Genes 2024, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, F.; Uematsu, C.; Sakaki, Y.; Ito, T. A novel strategy to design highly specific PCR primers based on the stability and uniqueness of 3′-end subsequences. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokamani, M.; Figgou, E.; Papamichail, L.; Sakka, E.; Toros, A.; Bouchorikou, A.; Giannakakis, A.; Matthaiou, E.I.; Sandaltzopoulos, R. A Multiplex PCR Melting-Curve-Analysis-Based Detection Method for the Discrimination of Five Aspergillus Species. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, A.V.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Haydon, S.R.; Gasser, R.B. Multiplex PCRs for the specific identification of marsupial and deer species from faecal samples as a basis for non-invasive epidemiological studies of parasites. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Naquiah, N.N.A.; Ali, M.E. Novel multiplex PCR-RFLP assay discriminates bovine, porcine and fish gelatin substitution in Asian pharmaceuticals capsule shells. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2018, 35, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

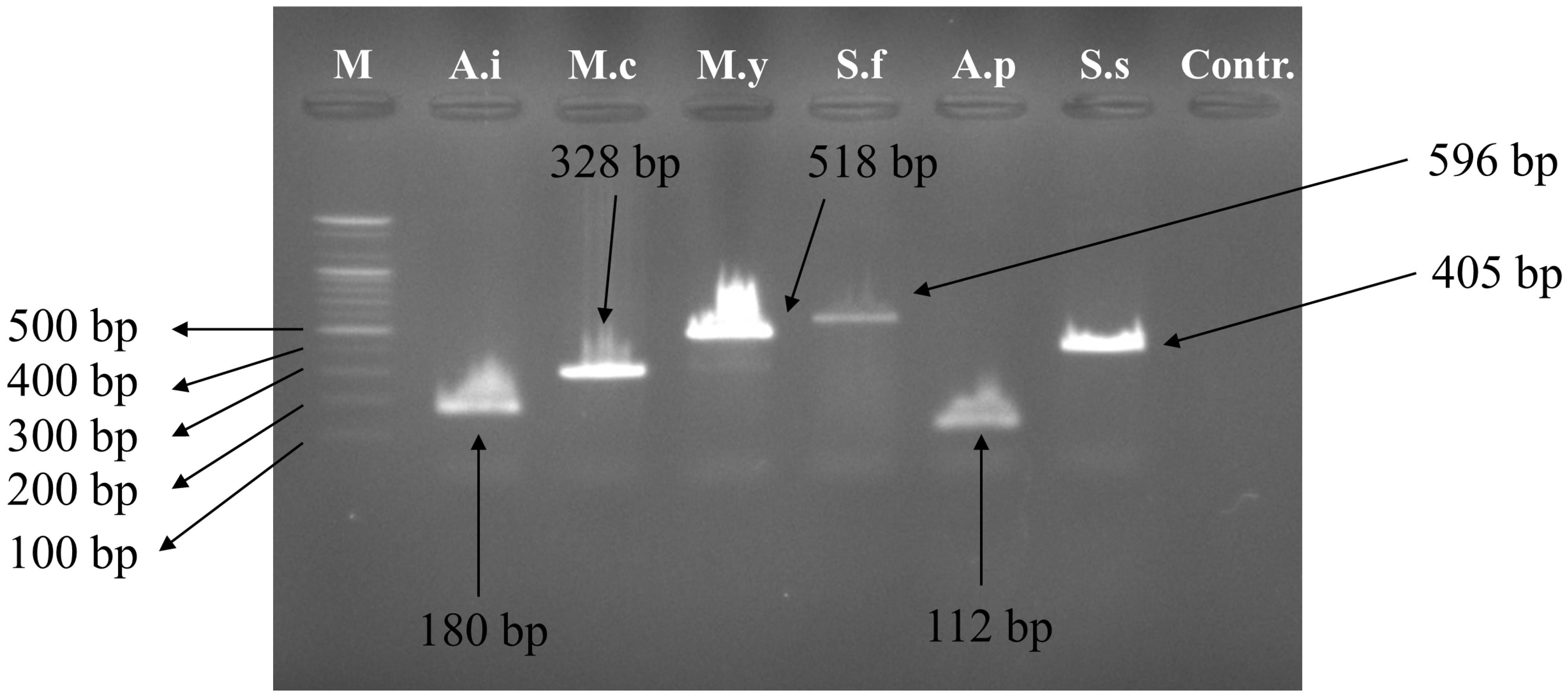

| Primer Name | Scientific Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Primer Direction | Expected Amplification Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. farreri COI F4 | Scaeochlamys farreri | CCTGGGATGTGGCTTCCTAGA | Forward | 596 |
| M. yessoensis CO1 F2 | Mizuhopecten yessoensis | GTTATGCCGGTTCTTATTGGA | Forward | 518 |
| S. swiftii COI F1 | Swiftopecten swiftii | TGCGCTATACATAGTGGTGAC | Forward | 405 |
| M. crassicostata CO1 F | Mimachlamys crassicostata | TCCAGAACTCCTTACCAGAGT | Forward | 328 |
| A. irradians CO1 F | Argopecten irradians | CCCTTTCGTTTGGGCGCTT | Forward | 180 |
| A. pectinata CO1 F | Atrina pectinata | GTGGGATTACTATGCTCCTAAC | Forward | 112 |
| Pectinidae_R | - | TCDGGRTGVCCAAARAAYCAA | Reverse | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-R.; Kim, H.-J.; Bang, I.-C. Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Six Commercially Important Bivalves. Foods 2025, 14, 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223881
Kim K-R, Kim H-J, Bang I-C. Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Six Commercially Important Bivalves. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223881
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kang-Rae, Hye-Jin Kim, and In-Chul Bang. 2025. "Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Six Commercially Important Bivalves" Foods 14, no. 22: 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223881
APA StyleKim, K.-R., Kim, H.-J., & Bang, I.-C. (2025). Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Six Commercially Important Bivalves. Foods, 14(22), 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223881







