Integrative Analysis of Flavoromics, Lipidomics, and Transcriptomics Reveals the Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Unique Meat Flavor of Jianli Pigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Information
2.2. Fat Deposition Performance Measurement
2.3. Research Conditions for Flavoromics
2.4. Research Conditions for Lipidomics
2.5. Research Conditions for Transcriptomics
2.6. Correlation Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
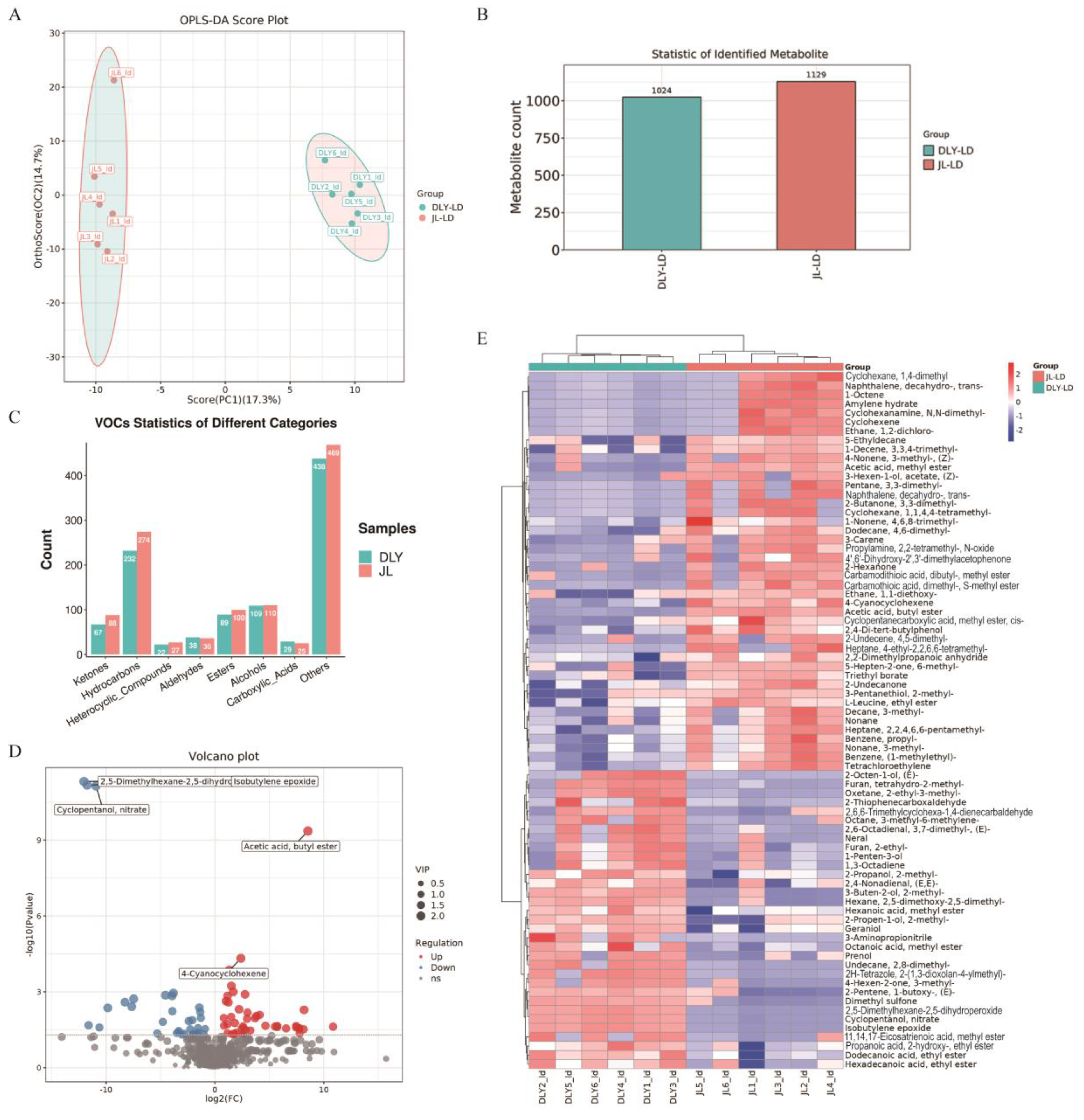
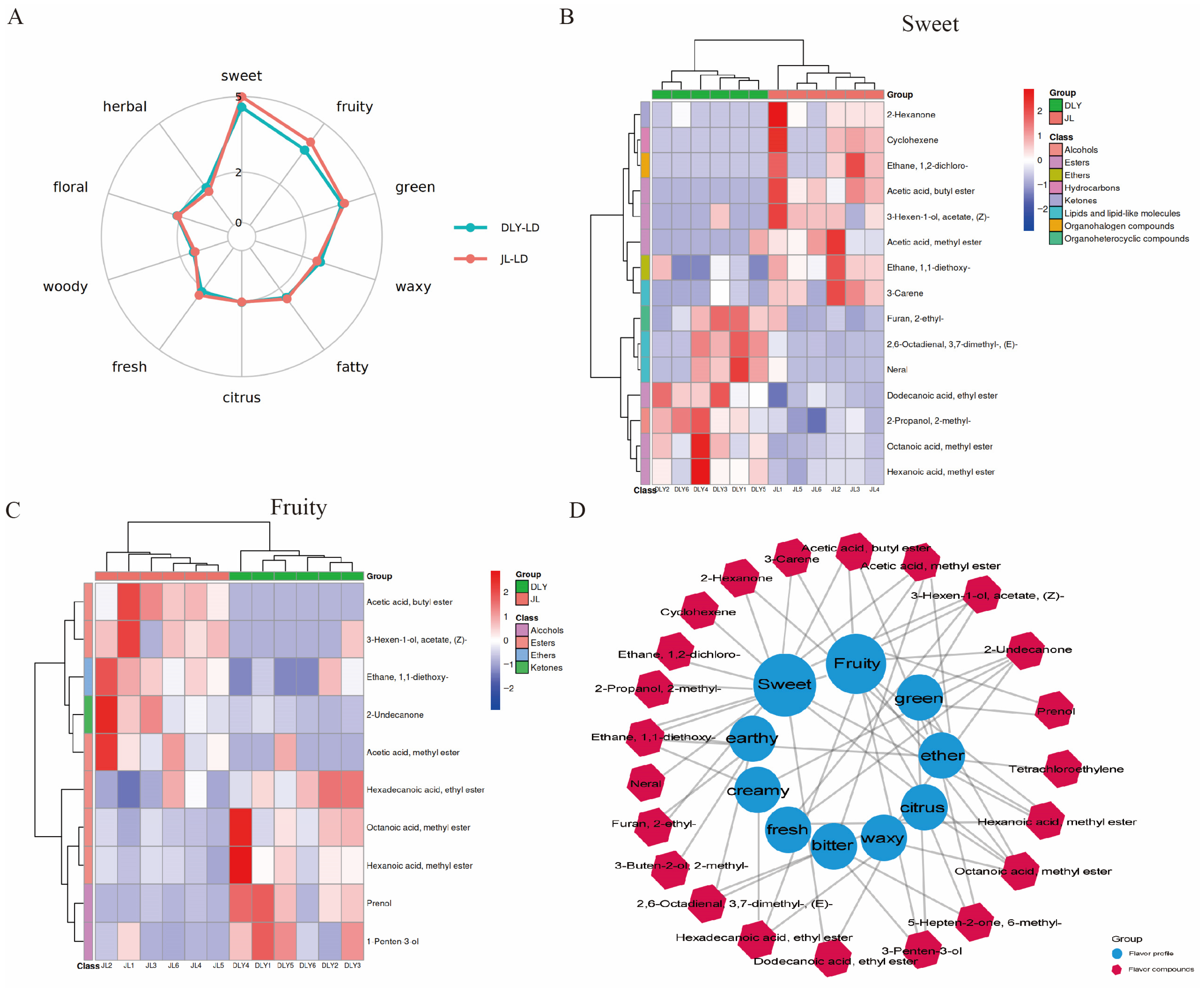
3.1. Comparative Analysis of Flavor Characteristics Between JL and DLY Pigs
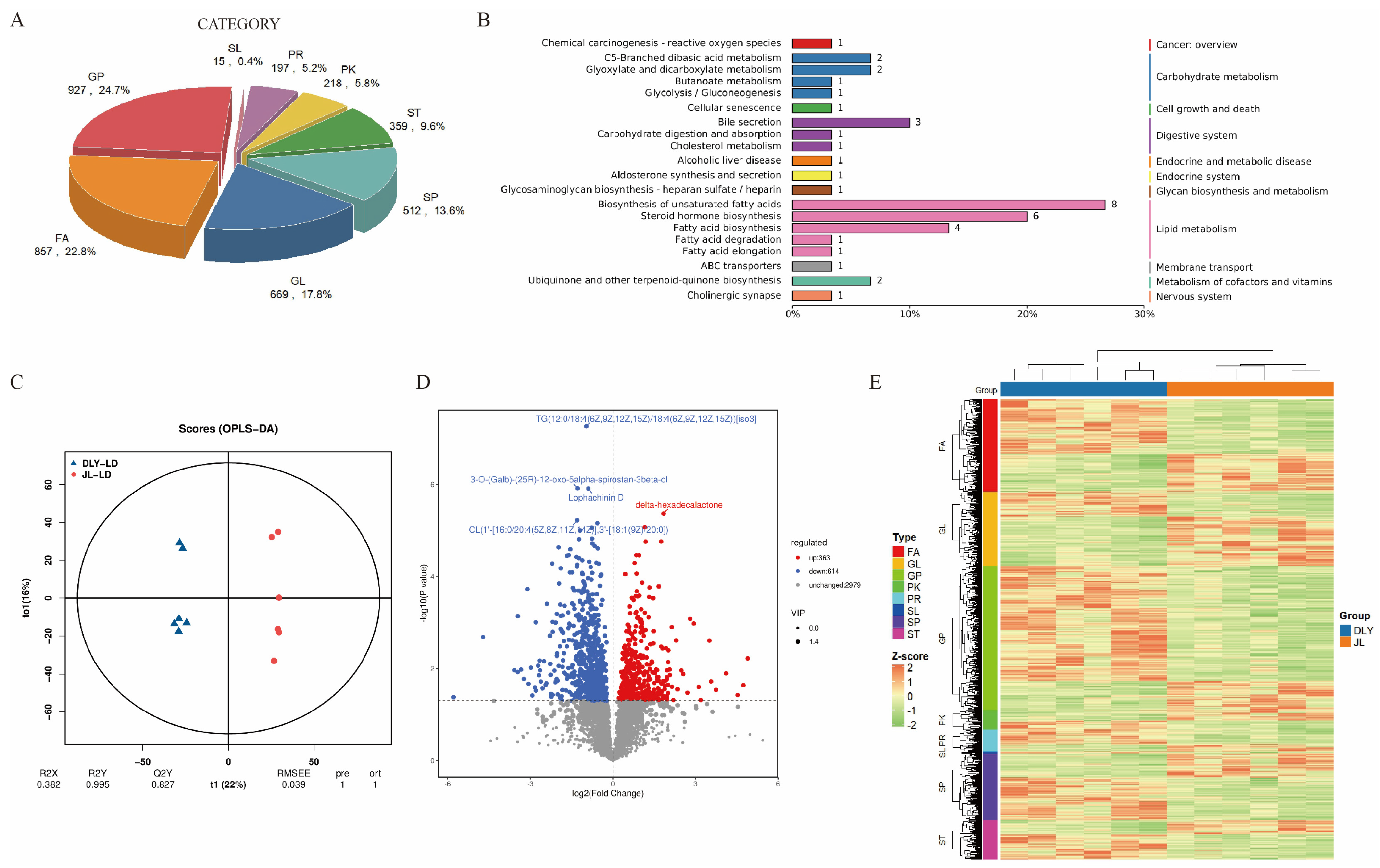
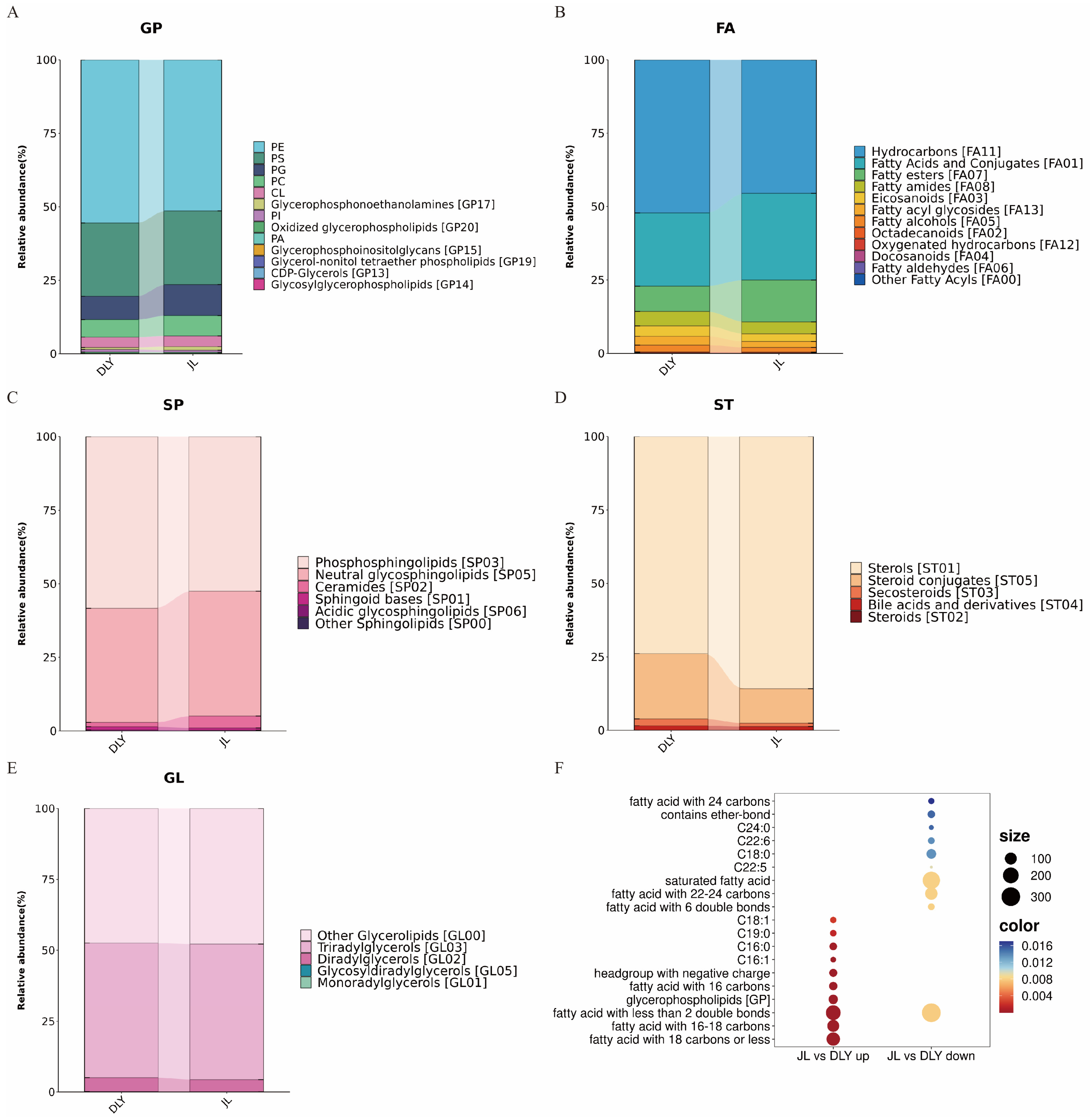
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Lipidomic Profiles Between JL and DLY Pigs
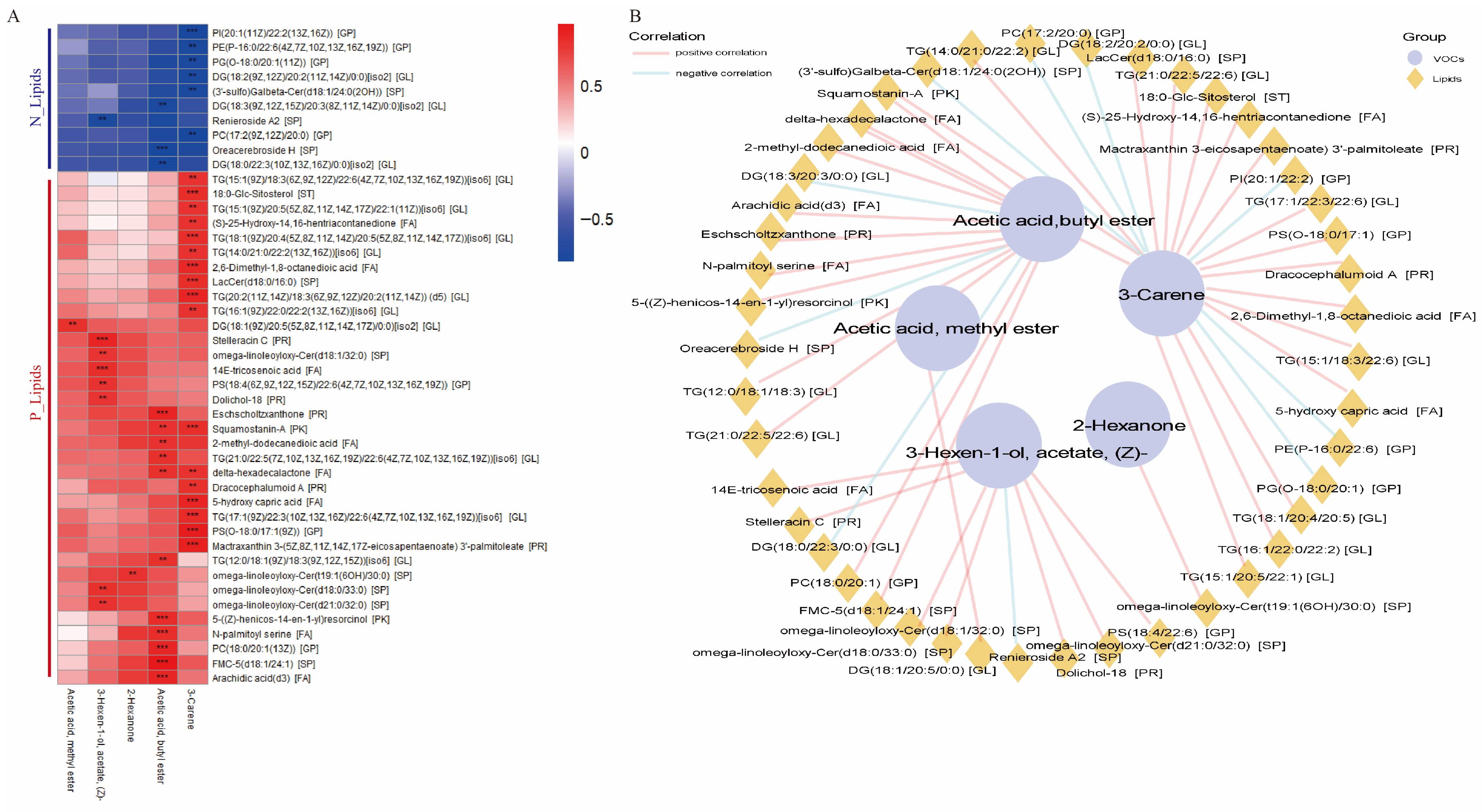
3.3. Correlation Analysis Identified the Precursor Lipids Associated with the Flavor of JL Pigs
3.4. The Expression Patterns of Fatty Acid Metabolism-Related Genes Are Significantly Different Between JL and DLY Pigs
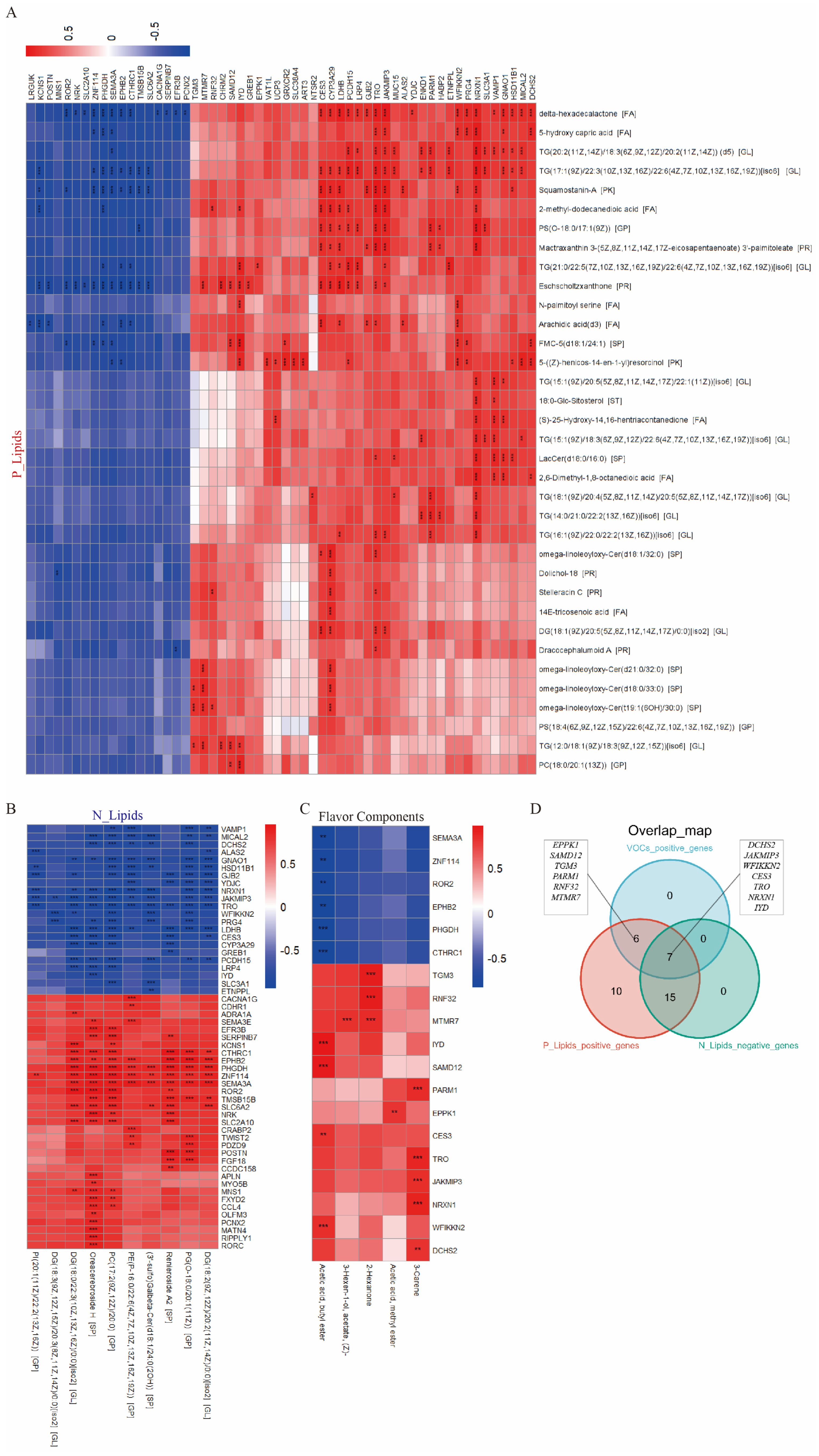
3.5. Integrative Analysis Revealed Key Regulatory Genes in the Flavor Formation of JL Pigs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Xie, J.; Zhao, M.; Hou, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J. Volatile flavor constituents in the pork broth of black-pig. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Tong, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, M.; Lin, Z.; Cai, S.; Chen, Y.; Mo, D. Characterization of different meat flavor compounds in Guangdong small-ear spotted and Yorkshire pork using two-dimensional gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multi-omics. LWT 2022, 169, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, H.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, G.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Yin, Y.; Xu, K. Comprehensive characterization of the differences in metabolites, lipids, and volatile flavor compounds between Ningxiang and Berkshire pigs using multi-omics techniques. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 139807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, T.; Jia, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Xia, N.; Qian, Q.; Peng, H.; et al. Comparison of Nutrition and Flavor Characteristics of Five Breeds of Pork in China. Foods 2022, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, L.; Sun, Q.; Wu, F.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. Multi-Omics Reveals the Effect of Crossbreeding on Some Precursors of Flavor and Nutritional Quality of Pork. Foods 2023, 12, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhan, J.; Tang, X.; Li, T.; Duan, S. Characterization and identification of pork flavor compounds and their precursors in Chinese indigenous pig breeds by volatile profiling and multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Lin, R.; Song, Z.; et al. Genome-wide detection of selection signatures in Jianli pigs reveals novel cis-regulatory haplotype in EDNRB associated with two-end black coat color. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Jo, C.; Tariq, M.R. Meat flavor precursors and factors influencing flavor precursors—A systematic review. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Su, Y.; He, L.; Wu, H.; Shui, S. Analysis of volatile compounds in pork from four different pig breeds using headspace solid-phase micro-extraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Appelqvist, I.; Piyasiri, U.; Delahunty, C. In vitro measurement of volatile release in model lipid emulsions using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaslyng, M.D.; Meinert, L. Meat flavour in pork and beef—From animal to meal. Meat Sci. 2017, 132, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Wu, W.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E.; Bak, K.H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Maillard reaction of food-derived peptides as a potential route to generate meat flavor compounds: A review. Food Res Int. 2022, 151, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, D.; Crecente, S.; Vazquez, J.A.; Gómez, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Effect of cross breeding and amount of finishing diet on growth parameters, carcass and meat composition of foals slaughtered at 15 months of age. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Rodriguez, E.; Purrinos, L.; Crecente, S.; Bermúdez, R.; Lorenzo, J.M. Meat quality of “Galician Mountain” foals breed. Effect of sex, slaughter age and livestock production system. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Peng, X.; Gao, X.; Luo, Q.; Luo, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, X. Linking lipidomics to meat quality: A review on texture and flavor in livestock and poultry. Food Chem. 2025, 492 Pt 1, 145402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Cui, L.; Yang, J.; Ji, J.; et al. A large-scale comparison of meat quality and intramuscular fatty acid composition among three Chinese indigenous pig breeds. Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Hossain, A. Role of Lipids in Food Flavor Generation. Molecules 2022, 27, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, F.; Han, D.; Xu, Y.; Shen, S.; Luan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. Elucidation of potential lipid precursors and formation pathways for the warmed-over flavor (WOF) in precooked Chinese stewed beef through lipid oxidation mechanisms. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Q.; Xing, J.; Li, P.; Gao, P.; Hamid, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Gong, H. Exploring the formation and retention of aroma compounds in ready-to-eat roasted pork from four thermal methods: A lipidomics and heat transfer analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, Q.; Guo, Q.; Duan, Y.; Li, J.; et al. A Comprehensive Characterization of the Differences in Meat Quality, Nonvolatile and Volatile Flavor Substances Between Taoyuan Black and Duroc Pigs. Foods 2025, 14, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Raza, S.H.A.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Tu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Tan, Y. Flavor characterization of pork cuts in Chalu black pigs using multi-omics analysis. Meat Sci. 2025, 219, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Wu, W.; Tang, X.; Ge, Q.; Zhan, J. Screening out important substances for distinguishing Chinese indigenous pork and hybrid pork and identifying different pork muscles by analyzing the fatty acid and nucleotide contents. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jo, K.; Park, M.K.; Choi, Y.-S.; Jung, S. Role of lipids in beef flavor development: A review of research from the past 20 years. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, A.; Al-Dalali, S.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Shakoor, A.; Asimi, S.; Shah, H.; Patil, P. Aroma compounds identified in cooked meat: A review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorraiz, C.; Beriain, M.J.; Chasco, J.; Insausti, K. Effect of Aging Time on Volatile Compounds, Odor, and Flavor of Cooked Beef from Pirenaica and Friesian Bulls and Heifers. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Suleman, R.; Gao, P.; Li, P.; Xing, J.; Ma, Q.; Hamid, N.; Wang, P.; Gong, H. Understanding the role of lipids in aroma formation of circulating non-fried roasted chicken using UHPLC-HRMS-based lipidomics and heat transfer analysis. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173 Pt 2, 113370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.S.; Mottram, D.S.; Enser, M.; Wood, J.D. Effect of the polyunsaturated fatty acid composition of beef muscle on the profile of aroma volatiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Dunshea, F.R.; Lisle, A.; Roura, E. Feeding a high oleic acid (C18:1) diet improves pleasing flavor attributes in pork. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, E.E.; Hamblen, H.; Leal-Gutierrez, J.D.; Carr, C.; Scheffler, T.; Scheffler, J.M.; Mateescu, R.G. Exploring the impact of fatty acid composition on carcass and meat quality in Bos taurus indicus influenced cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Pei, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Guo, X.; Yan, P. Effect of Lipids in Yak Muscle under Different Feeding Systems on Meat Quality Based on Untargeted Lipidomics. Animals 2022, 12, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhong, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Identification and expression patterns of adipokine genes during adipocyte differentiation in the Tibetan goat (Capra hircus). Gene 2018, 643, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Dong, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, Z.; Pei, Y. Differences in histomorphology and expression of key lipid regulated genes of four adipose tissues from Tibetan pigs. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, R.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Xing, J.; Gao, P.; Liu, H.; et al. Unraveling the formation mechanism of aroma compounds in pork during air frying using UHPLC-HRMS and Orbitrap Exploris GC-MS. Food Res. Int. 2024, 192, 114816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mao, H.; Peng, G.; Zeng, Q.; Wei, Q.; Ruan, J.; Huang, J. Effect of JAK-STAT pathway in regulation of fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome in chickens. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travez, A.; Rabanal-Ruiz, Y.; Lopez-Alcala, J.; Molero-Murillo, L.; Díaz-Ruiz, A.; Guzmán-Ruiz, R.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Frühbeck, G.; Tinahones, F.J.; et al. The caveolae-associated coiled-coil protein, NECC2, regulates insulin signalling in Adipocytes. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5648–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghlool, S.B.; Sharma, S.; Molnar, M.; Matías-García, P.R.; Elhadad, M.A.; Waldenberger, M.; Peters, A.; Rathmann, W.; Graumann, J.; Gieger, C.; et al. Revealing the role of the human blood plasma proteome in obesity using genetic drivers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.S.; Xu, H.Y.; Fang, J.C.; Yin, B.Z.; Wang, B.B.; Pang, Z.; Xia, G.J. Integrated microRNA-mRNA analysis reveals the roles of microRNAs in the muscle fat metabolism of Yanbian cattle. Anim. Genet. 2021, 52, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Wei, E.; Wang, S.P.; Quiroga, A.D.; Li, L.; Di Pardo, A.; van der Veen, J.; Sipione, S.; Mitchell, G.A.; Lehner, R. Liver specific inactivation of carboxylesterase 3/triacylglycerol hydrolase decreases blood lipids without causing severe steatosis in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Quiroga, A.D.; Li, L.; Lehner, R. Ces3/TGH deficiency improves dyslipidemia and reduces atherosclerosis in Ldlr−/− mice. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrutta, L.C.; Layerenza, J.P.; Bronsoms, S.; Trejo, S.A.; Ves-Losada, A. Nuclear-lipid-droplet proteome: Carboxylesterase as a nuclear lipase involved in lipid-droplet homeostasis. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Igarashi, M.; Yamamuro, D.; Ohshiro, T.; Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Enkhtuvshin, B.; Sekiya, M.; Okazaki, H.; Osuga, J.-I.; et al. Critical role of neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase 1 in cholesteryl ester hydrolysis in murine macrophages. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, X.; Tang, H.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Sun, K. A Unique Role of Carboxylesterase 3 (Ces3) in beta-Adrenergic Signaling-Stimulated Thermogenesis. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1178–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, K.; Liu, L.; Yan, N.; Farag, M.A.; Liu, L. Dissecting Maillard reaction production in fried foods: Formation mechanisms, sensory characteristic attribution, control strategy, and gut homeostasis regulation. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Xie, J.; Xiao, Q.F.; Du, W.B.; Wang, Y.X. Meat flavor generation from different composition patterns of initial Maillard stage intermediates formed in heated cysteine-xylose-glycine reaction systems. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yu, M.; Liu, Z.; Deng, D.; Cui, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wang, G. Effect of amino acids and their derivatives on meat quality of finishing pigs. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Chen, L.; Wu, W.; Soladoye, O.P.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y. The potential meat flavoring generated from Maillard reaction products of wheat gluten protein hydrolysates-xylose: Impacts of different thermal treatment temperatures on flavor. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Items | DLY | JL | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carcass fat percentage (%) | 19.33 ± 2.79 | 35.48 ± 3.60 ** | 0.00 |
| Average backfat thickness (mm) | 25.67 ± 6.11 | 34.86 ± 6.15 * | 0.026 |
| IMF content (%) | 2.63 ± 0.61 | 3.15 ± 0.97 | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Lu, S.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Qiao, M.; Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Peng, X.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Flavoromics, Lipidomics, and Transcriptomics Reveals the Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Unique Meat Flavor of Jianli Pigs. Foods 2025, 14, 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223838
Chen T, Lu S, Zhou J, Xu Z, Feng Y, Qiao M, Chen D, Li Z, Sun H, Peng X, et al. Integrative Analysis of Flavoromics, Lipidomics, and Transcriptomics Reveals the Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Unique Meat Flavor of Jianli Pigs. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223838
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tong, Sujian Lu, Jiawei Zhou, Zhong Xu, Yue Feng, Mu Qiao, Dake Chen, Zipeng Li, Hua Sun, Xianwen Peng, and et al. 2025. "Integrative Analysis of Flavoromics, Lipidomics, and Transcriptomics Reveals the Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Unique Meat Flavor of Jianli Pigs" Foods 14, no. 22: 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223838
APA StyleChen, T., Lu, S., Zhou, J., Xu, Z., Feng, Y., Qiao, M., Chen, D., Li, Z., Sun, H., Peng, X., Mei, S., & Wu, J. (2025). Integrative Analysis of Flavoromics, Lipidomics, and Transcriptomics Reveals the Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Unique Meat Flavor of Jianli Pigs. Foods, 14(22), 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223838







