Effects of Various Drying Parameters on the Volatile and Non-Volatile Compositions of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Tea Sample Preparation
2.3. Sensory Evaluation
2.4. E-Tongue Evaluation
2.5. Non-Volatile Metabolomics Analysis
2.6. Volatile Metabolomics Analysis
2.6.1. HS-SPME Extraction
2.6.2. GC-MS Analysis
2.6.3. Identification and Quantification of Volatile Compounds
2.6.4. Relative Odor Activity Value Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
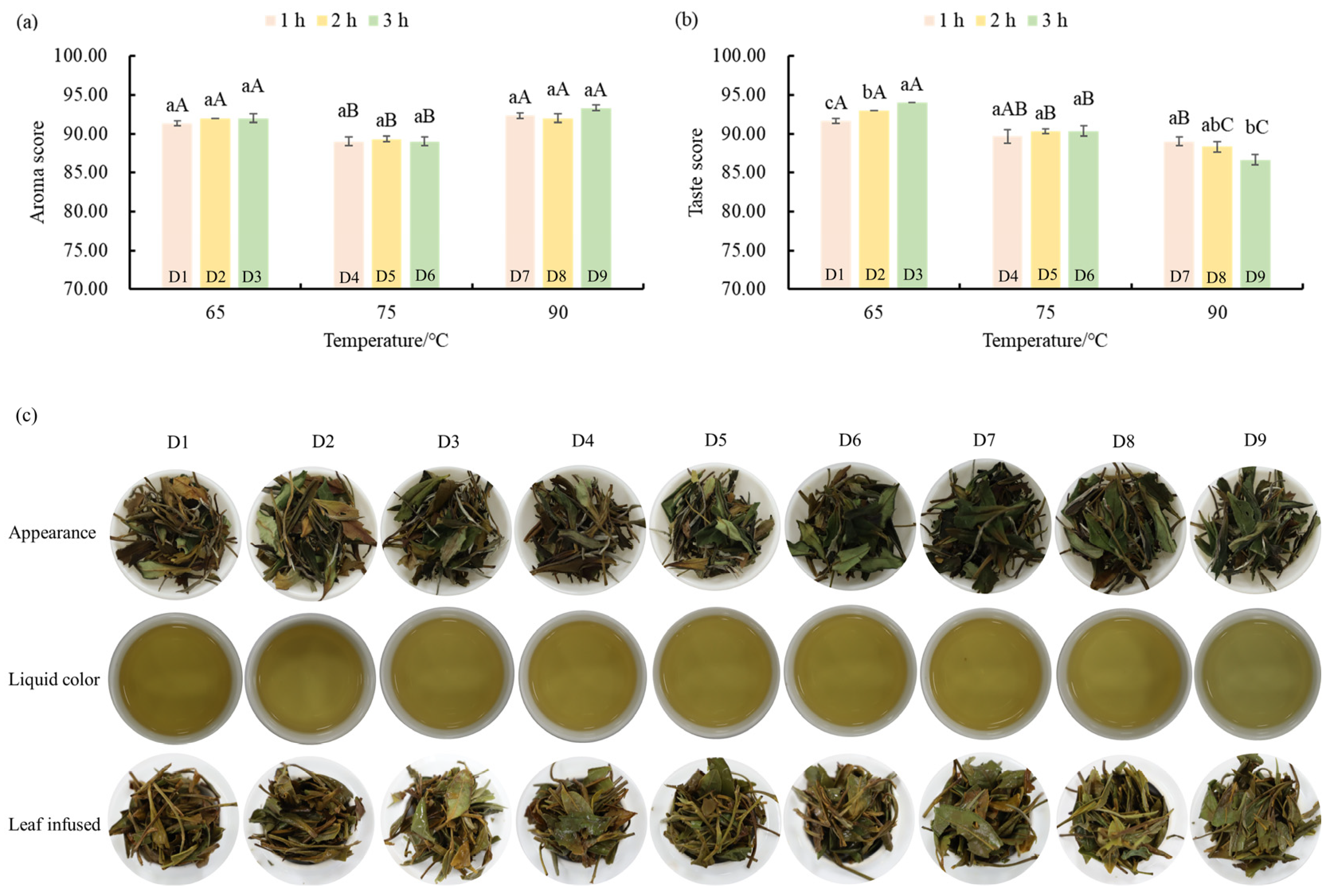
3.1. Sensory Analysis of White Tea Samples with Different Drying Treatments
3.2. Effect of Different Drying Treatments on the Taste Characteristics of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea
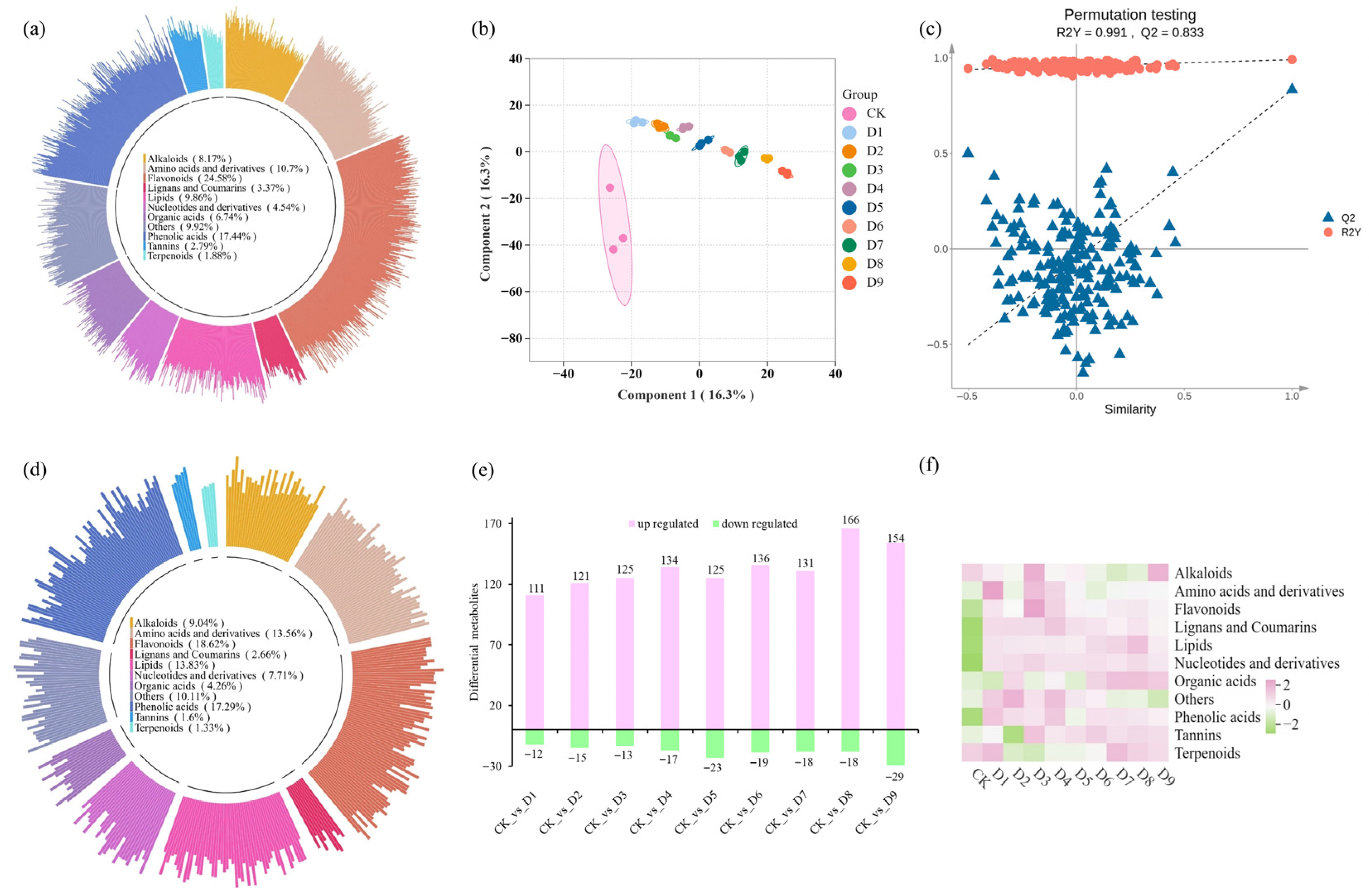
3.3. Non-Volatile Metabolite Analysis of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea
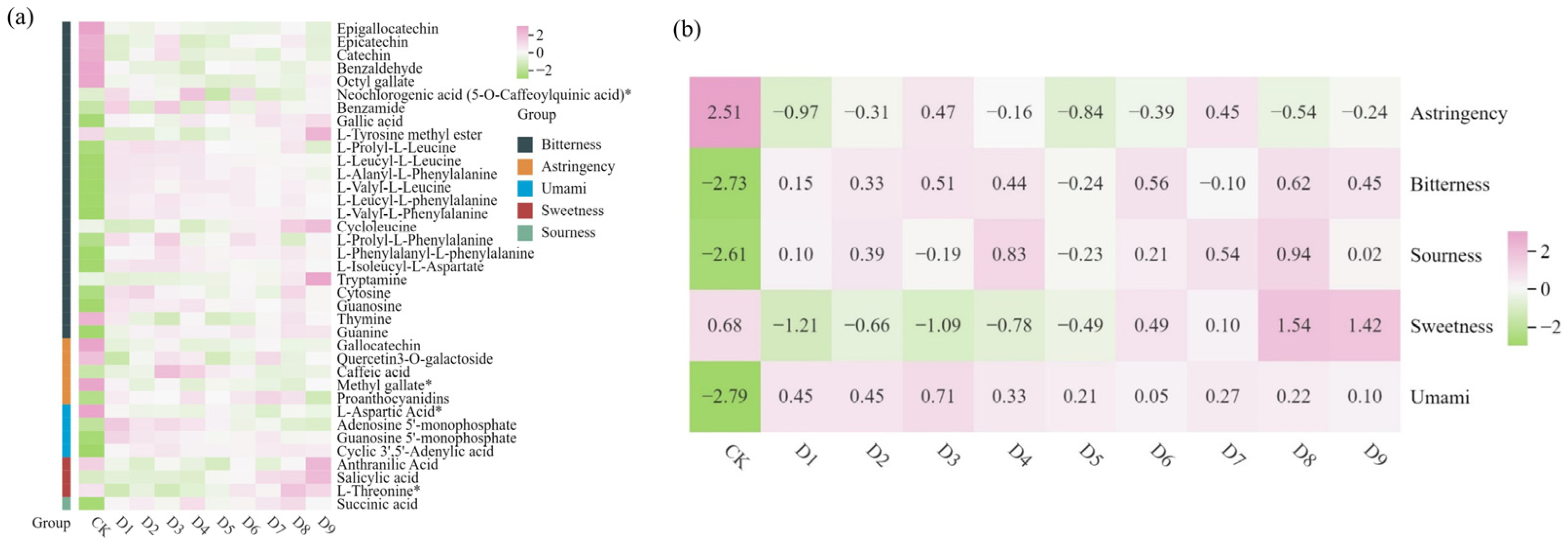
3.4. Key Taste-Related Metabolite Analysis
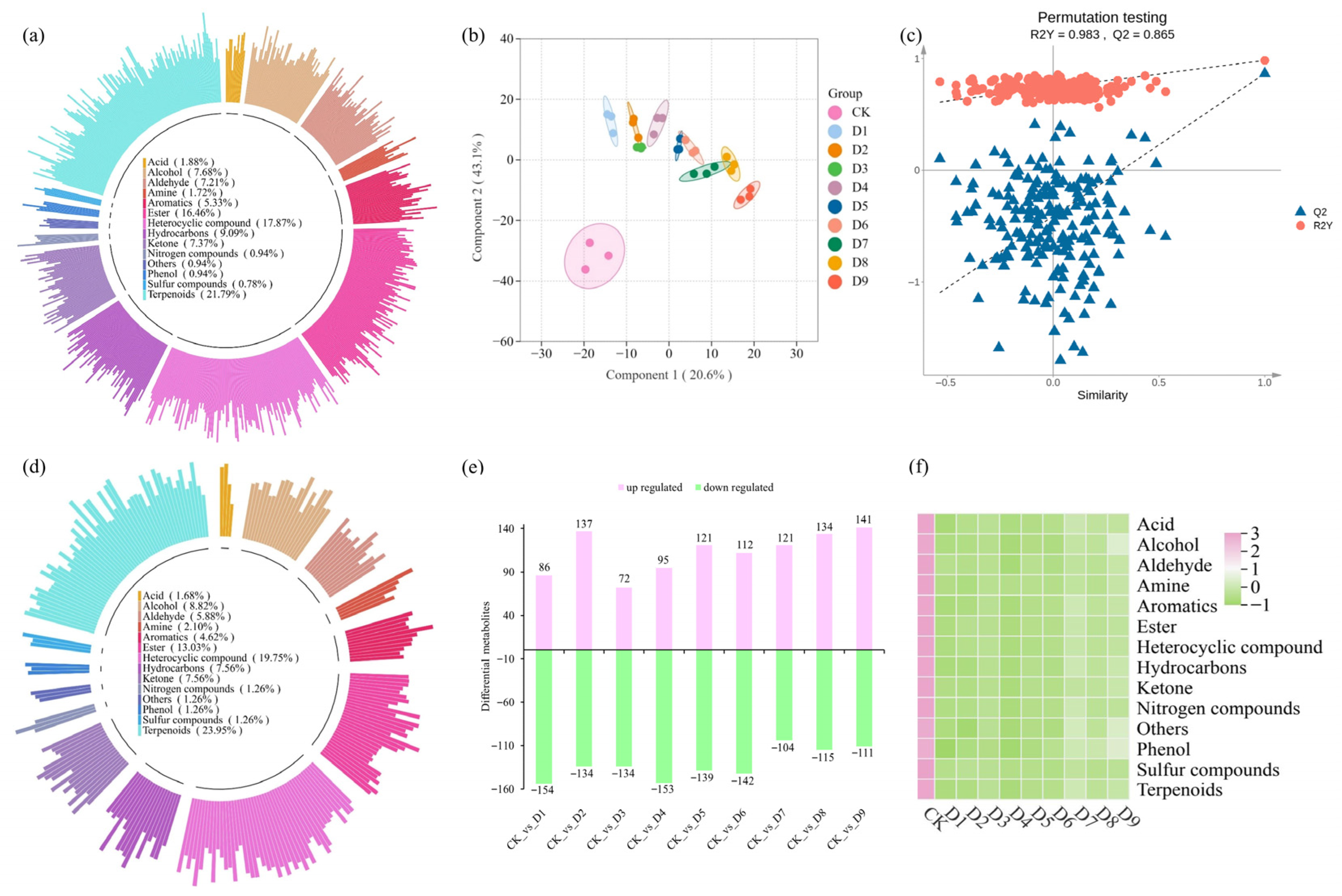
3.5. Volatile Metabolite Analysis of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea
3.5.1. Key Volatile Metabolite Analysis
3.5.2. ROAV Analysis for Key Volatile Metabolites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.; Yang, T.; Luo, J.; Fang, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Pan, K. Changes in Alkaloids and Their Related Metabolites during the Processing of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea Based on Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis. LWT 2025, 218, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Xue, C.; Huang, X. Enhancing Virus-Induced Gene Silencing Efficiency in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis L.) and the Functional Analysis of CsPDS. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 337, 113585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Qiao, D.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Camellia Sinensis Cultivar ‘Qiancha1’ from Guizhou Province, China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2022, 7, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Ma, Y.; Ran, J.; Shen, Q.; Fang, W. Characterizing Flavor Determinants and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Components in Ancient Tea Plants and ‘Qiancha 1’ White Teas. Food Chem. X 2025, 27, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Shan, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Dynamic Changes of Volatile and Non-Volatile Metabolites during Oolong Tea Manufacture. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Ou, C.; Feng, X.; Pan, Y.; Gong, S.; Fan, F.; Chen, P.; Chu, Q. Recent Advances on White Tea: Manufacturing, Compositions, Aging Characteristics and Bioactivities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-Y.; Huang, C.-S.; Tong, Y.-L.; Guo, H.-W.; Zhou, S.-J.; Ye, J.-H.; Gong, S.-Y. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis of White Peony Teas with Different Storage Time and Association with Sensory Attributes. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, J.; Mu, B.; Chen, Z.; Dai, W.; Lin, Z. Metabolomics Combined with Proteomics Provides a Novel Interpretation of the Changes in Nonvolatile Compounds during White Tea Processing. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wu, W.; Gao, C.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, F.; Sun, W. The Effect of Different Drying Temperatures on Flavonoid Glycosides in White Tea: A Targeted Metabolomics, Molecular Docking, and Simulated Reaction Study. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Lv, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, X.; Qian, Y.; Zeng, X.; He, W.; Ye, Y. Comparison of Volatile and Nonvolatile Metabolites in Green Tea under Hot-Air Drying and Four Heat-Conduction Drying Patterns Using Widely Targeted Metabolomics. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Long, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wen, M.; Han, Z.; Zhou, F.; Ke, J.; Wan, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Zhang, L. Chemical, Sensory and Biological Variations of Black Tea under Different Drying Temperatures. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, M.; Hu, D.; Fan, L.; Li, R.; Wang, S. Developing a Novel Radio Frequency Dehydration Process Based on Heating Uniformity, Drying Characteristics, and Product Quality of White Tea. J. Food Eng. 2025, 398, 112606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, R.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Wen, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, L.; et al. Characterization of Aroma Differences on Three Drying Treatments in Rucheng Baimao (Camellia pubescens) White Tea. LWT 2023, 179, 114659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Xu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, P. Thermochemical Reactions in Tea Drying Shape the Flavor of Tea: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, T.; Fang, S.; Dai, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Shen, Q.; Long, L.; Pan, K.; et al. Effect of Spreading Time on the Taste Quality of Steamed Green Tea Based on E-Tongue Evaluation and Chemometric Statistical Analysis. Food Meas. 2024, 18, 3176–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.; Xu, S.-S.; Wei, Y.-M.; Bao, G.-H.; Dai, Q.-Y.; Deng, W.-W.; Ning, J.-M. Effects of Dynamic and Static Withering Technology on Volatile and Nonvolatile Components of Keemun Black Tea Using GC-MS and HPLC Combined with Chemometrics. LWT 2020, 130, 109547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zheng, J.Y.; Hou, Y.J.; Li, J.H.; Liu, W.H.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.P. Hot-Air Full Drying Driven Metabolome Changes in White Tea (Camellia sinensis L.). Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 2742–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Ouyang, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Yang, L.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Objective Quantification Technique and Widely Targeted Metabolomic Reveal the Effect of Drying Temperature on Sensory Attributes and Related Non-Volatile Metabolites of Black Tea. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, Z.; Luo, J.; Yang, T.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, T.; Fang, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Pan, K.; et al. Dynamic Evolution and Formation Mechanisms of Aroma Compounds in Qianmei 502 Black Tea during Processing: Insights from Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses. LWT 2025, 228, 118124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wei, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yu, B.; Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Lin, H.; Hao, Z. Effect of Drying Temperature on the Quality of Pressed White Tea Cake from Withered Leaves. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Comparative Volatiles Profiling in Milk-Flavored White Tea and Traditional White Tea Shoumei via HS-SPME-GC-TOFMS and OAV Analyses. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, H. Characterization of the Key Aroma Compounds in Semnostachya Menglaensis Tsui by Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry, Odor Activity Values, Aroma Recombination, and Omission Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Liu, M.; Shi, Y.; De Vos, R.C.H.; Ruan, J. Stimulated Biosynthesis of Delphinidin-related Anthocyanins in Tea Shoots Reducing the Quality of Green Tea in Summer. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, O.; Zehentbauer, G.; Hofmann, T. Bioresponse-Guided Decomposition of Roast Coffee Beverage and Identification of Key Bitter Taste Compounds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 222, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Hua, J.; Ning, J.; Yuan, H. Analysis of Volatile Metabolite Variations in Strip Green Tea during Processing and Effect of Rubbing Degree Using Untargeted and Targeted Metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hua, J.; Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Widely Targeted Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Dynamic Changes in Non-Volatile and Volatile Metabolites during Green Tea Processing. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hua, J.; Yuan, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Dong, C.; Zeng, J.; Jiang, Y. Investigation on Green Tea Lipids and Their Metabolic Variations during Manufacturing by Nontargeted Lipidomics. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hua, J.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qian, M.C.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Dong, C.; Yuan, H. Aroma Dynamic Characteristics during the Process of Variable-Temperature Final Firing of Congou Black Tea by Electronic Nose and Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography Coupled to Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Fang, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Pan, C.; Wu, H. Identification of Key Metabolites Based on Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Chemometrics Analyses Provides Insights into Bitterness in Kucha [Camellia kucha (Chang et Wang) Chang]. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Liu, P.; Guo, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Le, T.; Yin, J.; Ni, D.; Jiang, H. Profiling of Dynamic Changes in Non-Volatile Metabolites of Shaken Black Tea during the Manufacturing Process Using Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. LWT 2022, 156, 113010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Guo, C.; Sun, Y. Research Progress of Organic Acids in Tea. Subtrop. Agric. Res. 2015, 11, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Hong, L.; Kang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Jia, Y.; Jia, X.; Wu, Z.; et al. Effect of Processing on Aroma Intensity and Odor Characteristic of Shuixian (Camellia sinensis) Tea. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vant Gemert, L.J. Compilations of Flavour Threshold Values in Water and Other Media; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, L.; Tu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, W. Comparison of Volatile and Nonvolatile Metabolites in Black Tea under Four Second-Drying Methods Using Widely Targeted Metabolomics. Foods 2023, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Yonghui, L.; Xingfei, L.; Hao, M.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, R.; Qian, L.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; et al. Effects of Fermentation Duration on the Flavour Quality of Large Leaf Black Tea Based on Metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Feng, X.; Pan, Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Fan, F.; Gong, S.; Chen, P.; Chu, Q. Flowering in Aged White Tea: Recovering Umami Taste and Amplifying of Stale Aroma. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 141649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Fang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhuo, C.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W.-W.; Ning, J. Sensomics Analysis of the Effect of the Withering Method on the Aroma Components of Keemun Black Tea. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Liu, P.; Yin, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Le, T.; Ni, D.; Jiang, H. Dynamic Changes in Volatile Compounds of Shaken Black Tea during Its Manufacture by GC × GC–TOFMS and Multivariate Data Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Shen, S.; Huang, L.; Deng, G.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Wang, Y. Revelation of Volatile Contributions in Green Teas with Different Aroma Types by GC–MS and GC–IMS. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Discrimination and Characterization of the Volatile Profiles of Five Fu Brick Teas from Different Manufacturing Regions by Using HS–SPME/GC–MS and HS–GC–IMS. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1788–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, C.; Xu, K.; Tian, C.; Zhang, M.; Lu, L.; Zhu, C.; Lai, Z.; Guo, Y. A Comprehensive Investigation of Macro-Composition and Volatile Compounds in Spring-Picked and Autumn-Picked White Tea. Foods 2022, 11, 3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, C.; Zhu, J.; Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Feng, T. Characterization of Volatile Constituents and Odorous Compounds in Peach (Prunus persica L) Fruits of Different Varieties by Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry, Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry, and Relative Odor Activity Value. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 965796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, F.; Niu, Y. Characterization of the Key Aroma Compounds in Three World-Famous Black Teas. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 2237–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Zhong, X.-Y.; Zou, C.; Ning, J.; Dong, W.-J.; Wu, K.; Xu, Y.-Q. Aroma Compounds with Enhanced Sweet Perception in Tea Infusions: Screening, Characterization, and Sweetening Mechanism. J. Adv. Res. 2025, S2090123225003637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Cao, H.; Zhang, S.; Hao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Luo, L.; Zeng, L. Aroma Characteristics of Wuyi Rock Tea Prepared from 16 Different Tea Plant Varieties. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, W.; Lv, H.; Mu, B.; Li, P.; Tan, J.; Ni, D.; Lin, Z. Aroma Formation and Dynamic Changes during White Tea Processing. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Lv, H.-P.; Shao, C.-Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Dai, W.-D.; Tan, J.-F.; Peng, Q.-H.; Lin, Z. Identification of Key Odorants Responsible for Chestnut-like Aroma Quality of Green Teas. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Lv, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, P.; et al. Aroma Formation in Dianhong Black Tea: Effects of Baking. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, M.; Yang, C.; Xie, D.; Tan, J.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, D.; Dai, W.; et al. Variation Patterns in the Content of Glycosides during Green Tea Manufacturing by a Modification-Specific Metabolomics Approach: Enzymatic Reaction Promoting an Increase in the Glycosidically Bound Volatiles at the Pan Firing Stage. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X.; Yang, X. Tea Aroma Formation from Six Model Manufacturing Processes. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23776-2018; Methodology for Sensory Evaluation of Tea. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2018.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Liao, S.; Ding, F.; Dai, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, T.; Fang, S.; Li, Y.; Pu, L.; et al. Effects of Various Drying Parameters on the Volatile and Non-Volatile Compositions of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea. Foods 2025, 14, 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213787
Luo J, Liao S, Ding F, Dai Y, Liu Z, Yang T, Zhang T, Fang S, Li Y, Pu L, et al. Effects of Various Drying Parameters on the Volatile and Non-Volatile Compositions of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213787
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jinlong, Siyu Liao, Fengjiao Ding, Yuqiao Dai, Zhongying Liu, Ting Yang, Tuo Zhang, Shimao Fang, Yan Li, Lulu Pu, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Various Drying Parameters on the Volatile and Non-Volatile Compositions of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea" Foods 14, no. 21: 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213787
APA StyleLuo, J., Liao, S., Ding, F., Dai, Y., Liu, Z., Yang, T., Zhang, T., Fang, S., Li, Y., Pu, L., Pan, K., Fang, W., & Shen, Q. (2025). Effects of Various Drying Parameters on the Volatile and Non-Volatile Compositions of ‘Qiancha 1’ White Tea. Foods, 14(21), 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213787





