Effect of Different Microwave Times on the Nutritional Properties of Glycosylated Soybean 7S
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Glycosylated Soybean 7S Protein
2.2.1. Preparation of Soybean 7S Protein
2.2.2. Preparation of Glucose Glycosylation Products
2.2.3. Microwave Treatment of Samples
2.3. In Vitro Simulated Digestion Assay
2.4. Measurement of Protein Hydrolysis
2.5. Amino Acid Determination
2.5.1. Sample Preparation
2.5.2. Chromatographic Conditions for Amino Acid Analysis
2.5.3. Nutritional Evaluation of Amino Acids
- Amino acid score (AAS)
- Essential amino acid index (EAAI)
- Chemical score (CS)
- Biological value (BV)
- Score of ratio coefficient of amino acid (SRCAA)
- Protein efficiency ratio (C-PER)
- Protein digestibility corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Digestibility
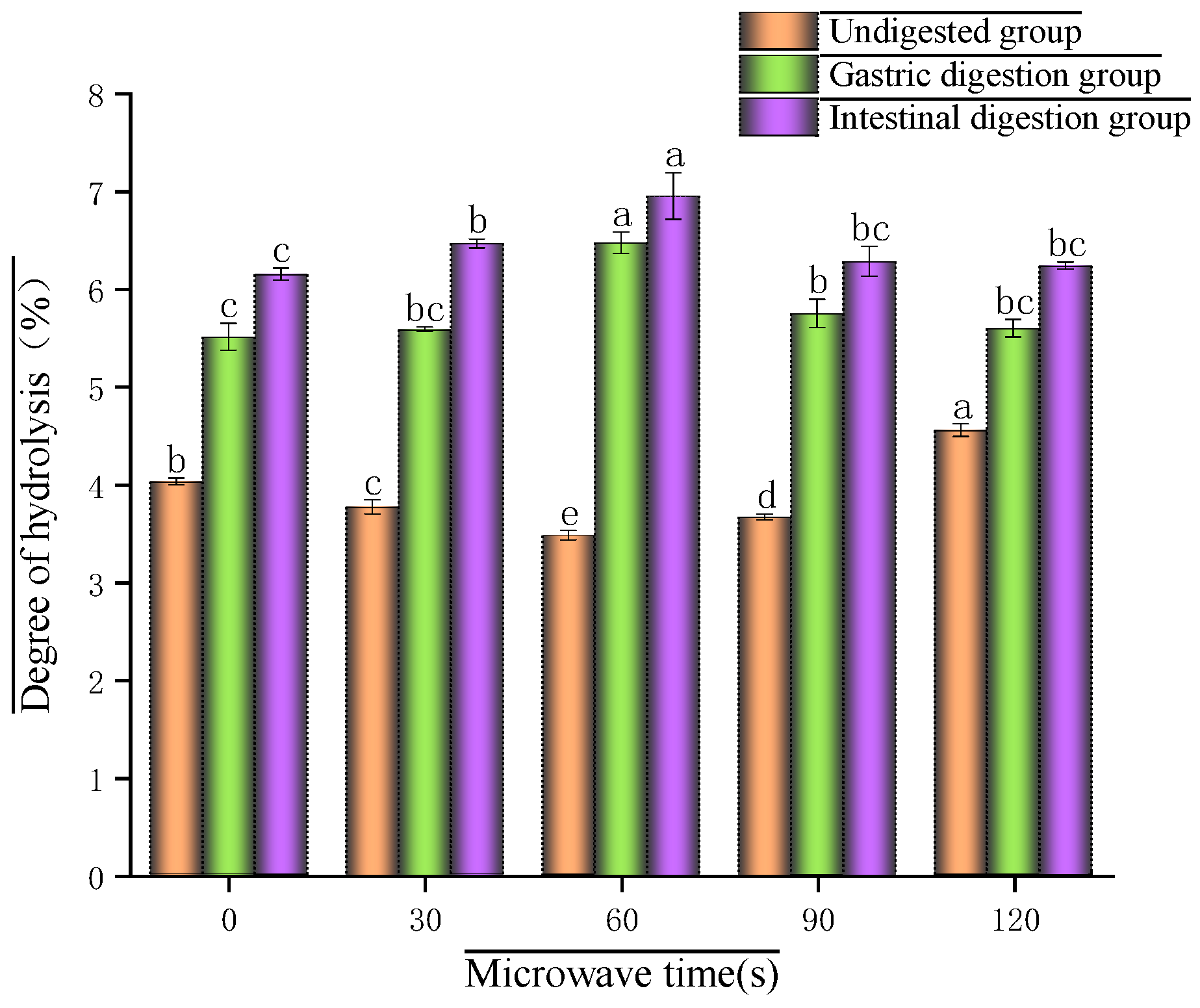
3.2. Hydrolysis
3.3. Amino Acid Composition
3.4. Nutritional Evaluation of Amino Acids
3.5. Analysis of Flavor-Presenting Amino Acids
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SGF | simulated gastric fluid |
| SIF | simulated intestinal fluid |
| AAS | amino acid score |
| CS | chemistry scoring |
| EAAI | essential amino acid index |
| BV | commodity prices |
| SRCAA | score of the ratio coefficient of the amino acid |
| C-PER | protein efficiency ratio |
| PDCAAS | protein digestibility corrected amino acid score |
| DH | hydrolysis |
| EAA | essential amino acid |
| NEAA | non-essential amino acids |
| TAA | total amino acids |
References
- Ashaolu, T.J.; Greff, B.; Varga, L. The structure-function relationships and techno-functions of β-conglycinin. Food Chem. 2024, 462, 140950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F. Thermal processing implications on the digestibility of meat, fish and seafood proteins. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4511–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, J.L.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Shen, R.L.; Wu, L.G.; Zhang, K.Y. Effects of Microwave Heating, Steaming, Boiling and Baking on the Structure and Functional Properties of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Protein Isolates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Mu, D.C.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, M.L. Microwave-assisted maillard reaction between rice protein and dextran induces structural changes and functional improvements. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 97, 103134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, F.F.; Mudgil, P.; Maqsood, S. Unveiling differential impact of heat and microwave extraction treatments on the structure, functionality, and digestibility of jack bean proteins extracted under varying extraction pH. Food Res. Int. 2024, 191, 114686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinonyerem, A.N.; Obioha, O.; Ebere, U. Amino acid Composition, Amino Acid Scores and Predicted Protein Efficiency Ratio of Raw and Cooked African Yam Bean (Sphenostylis sternocarpa). J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 2017, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Amino-Acid Content of Foods and Biological Data on Proteins; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, H.H. An integrated essential amino acid index for predicting the biological value of proteins. In Protein and Amino Acid Nutrition; Oser, B.L., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1959; pp. 281–295. [Google Scholar]
- Ware, K.; Kashyap, P.; Gorde, P.M.; Yadav, R.; Sharma, V. Comparative analysis of RSM and ANN-GA based modeling for protein extraction from cotton seed meal: Effect of extraction parameters on amino acid profile and nutritional characteristics. Food Bioprod. Process. 2025, 150, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, G. The Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS)—A concept for describing protein quality in foods and food ingredients: A critical review. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, J. Effects of Transglutaminase-Induced β-Conglycinin Gels on Intestinal Morphology and Intestinal Flora in Mice at Different High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment Time. Foods 2024, 13, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet-Cabero, A.-I.; Egger, L.; Portmann, R.; Ménard, O.; Marze, S.; Minekus, M.; Le Feunteun, S.; Sarkar, A.; Grundy, M.M.-L.; Carrière, F.; et al. A standardised semi-dynamic in vitro digestion method suitable for food-an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.M.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved Method for Determining Food Protein Degree of Hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2006, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 5009.124-2003; Determination of Amino Acids in Food. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC): Beijing, China.
- Wang, P.-Y.; Shuang, F.-F.; Yang, J.-X.; Jv, Y.-X.; Hu, R.-Z.; Chen, T.; Yao, X.-H.; Zhao, W.-G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.-Y. A rapid and efficient method of microwave-assisted extraction and hydrolysis and automatic amino acid analyzer determination of 17 amino acids from mulberry leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 186, 115271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, Z.; Rajarathnam, S. Pleurotus mushroom as a nutritious food. In Tropical Mushrooms-Biological Nature and Cultivated Methods; Chang, S.T., Quimio, T.H., Eds.; The Chinese University Press: Hongkong, 1982; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Sá, A.G.A.; Wan, Z.; Jha, A.B.; Gali, K.K.; Warkentin, T.D.; House, J.D. Influence of different amino acid scoring patterns on the protein quality of field peas. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 127, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y. Study on the Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestive and Nutritional Properties of Soybean Protein. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, L.T.; Moughan, P.J.; Darragh, A.J. In vitro digestion and fermentation methods, including gas production techniques, as applied to nutritive evaluation of foods in the hindgut of humans and other simple-stomached animals. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2005, 123, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Portmann, R.; Dubois, S.; Recio, I.; Egger, L. Protein digestion of different protein sources using the INFOGEST static digestion model. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P. Protein secondary structures (α-helix and β-sheet) at a cellular level and protein fractions in relation to rumen degradation behaviours of protein: A new approach. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M.; Yao, Y.; Wu, N.; Du, H.; Tu, Y. Recent Progress in Understanding the Relationship between Protein Structure Change and in Vitro Digestibility after Different Treatments. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Impact of Microwave Time on the Structure and Functional Properties of Glycosylated Soy 7S Globulins. Foods 2025, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sui, X.; Qi, B.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, N.; Huang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Structural Characteristics ofinVitro Digestion Products of Heat-Treated Soybean Protein. Food Sci. 2017, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- El, S.N.; Karakaya, S.; Simsek, S.; Dupont, D.; Menfaatli, E.; Eker, A.T. In vitro digestibility of goat milk and kefir with a new standardised static digestion method (INFOGEST cost action) and bioactivities of the resultant peptides. Food Funct. 2015, 7, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohi, B.F.C.A.; Du, J.; Zeng, H.-Y.; Cao, X.-J.; Zou, K.M. Microwave Pretreatment and Enzymolysis Optimization of the Lotus Seed Protein. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Balam, M.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Gallegos-Tintoré, S.; Castellanos-Ruelas, A.; Rodríguez-Canto, W.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Nutritional characterization of quality protein maize (QPM) (Zea mays L.) protein concentrates. Food Humanit. 2023, 1, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosworthy, M.G.; Medina, G.; Lu, Z.-H.; House, J.D. Plant Proteins: Methods of Quality Assessment and the Human Health Benefits of Pulses. Foods 2023, 12, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Jie, G. Taste Characteristics Analysis of Compound Umami Products Based on Free Amino Acids and Sensory Evaluation of Umami Taste. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Reagents | Stock Conc. | SGF | SIF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| moL/L | mL | mmoL/L | mL | mmoL/L | |
| KCl | 0.5 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 6.8 |
| KH2PO4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| NaHCO3 | 1 | 12.5 | 25 | 42.5 | 85 |
| NaCl | 2 | 11.8 | 47.2 | 9.6 | 38.4 |
| MgCl2(H2O)6 | 0.15 L | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 0.33 |
| (NH4)2CO3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| pH | 3 | 7 | |||
| ultrapure water | 400 mL | 400 mL | |||
| Hydrolyzed Amino Acids | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amino acid type | 0 s | 30 s | 60 s | 90 s | 120 s |
| aspartic acid(Asp) | 90.8 | 93.2 | 100 | 103 | 92.7 |
| threonine(Thr) | 29.4 | 32.3 | 34.6 | 35.7 | 29.8 |
| serine(Ser) | 40.6 | 41.9 | 45 | 44.8 | 41.6 |
| glutamic acid(Glu) | 148 | 136 | 147 | 148 | 151 |
| glycine(Gly) | 31.2 | 32.5 | 34.9 | 35.7 | 31.2 |
| alanine(Ala) | 32.7 | 35 | 37.4 | 38.2 | 33.1 |
| cysteine(Cys) | 2.4 | 3.3 | 4.3 | 3.4 | 1.7 |
| valine(Val) | 40.2 | 42.2 | 45.1 | 46.3 | 40.1 |
| methionine(Met) | 1 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 5 | 2.4 |
| isoleucine(IIe) | 34.4 | 35.5 | 38 | 39.2 | 34.6 |
| leucine(Leu) | 60.4 | 64.7 | 69.8 | 71.6 | 61.1 |
| tyrosine(Tyr) | 24.4 | 27.6 | 29.9 | 30.2 | 24.2 |
| phenylalanine(Phe) | 40.2 | 42.7 | 46 | 47.4 | 41 |
| lysine(Lys) | 60.2 | 59 | 63.8 | 65.9 | 61.3 |
| histidine(His) | 18.8 | 19.6 | 21.2 | 21.8 | 18.8 |
| arginine(Arg) | 65.7 | 66.1 | 71.2 | 73.1 | 66.4 |
| proline(Pro) | 31.9 | 35 | 36.6 | 37.6 | 32.3 |
| EAA | 292.6 | 308.5 | 335.3 | 344.7 | 296.2 |
| NEAA | 459.7 | 459.3 | 493.3 | 502.2 | 467.1 |
| TAA | 752.3 | 767.8 | 828.6 | 846.9 | 763.3 |
| EAA/TAA | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.39 |
| NEAA/TAA | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.59 | 0.61 |
| EAA/NEAA | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.63 |
| Free Amino Acids | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amino acid type | 0 s | 30 s | 60 s | 90 s | 120 s |
| aspartic acid(Asp) | 0.069 | 0.074 | 0.059 | 0.057 | 0.096 |
| threonine(Thr) | 0.0085 | 0.014 | 0.0057 | 0.0084 | 0.018 |
| serine(Ser) | 0.029 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.056 | 0.048 |
| glutamic acid(Glu) | 0.017 | 0.032 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.063 |
| glycine(Gly) | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.021 | 0.028 | 0.033 |
| alanine(Ala) | N.d. (<0.0097) | N.d. (<0.0097) | N.d. (<0.0097) | N.d. (<0.0097) | N.d. (<0.0097) |
| cysteine(Cys) | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.015 | 0.029 | 0.019 |
| valine(Val) | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.0063 | 0.0074 | 0.013 |
| methionine(Met) | N.d. (<0.0075) | N.d. (<0.0075) | N.d. (<0.0075) | N.d. (<0.0075) | N.d. (<0.0075) |
| isoleucine(IIe) | 0.016 | 0.023 | 0.028 | 0.021 | 0.017 |
| leucine(Leu) | N.d. (<0.0036) | N.d. (<0.0036) | N.d. (<0.0036) | N.d. (<0.0036) | N.d. (<0.0036) |
| tyrosine(Tyr) | N.d. (<0.0095) | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| phenylalanine(Phe) | N.d. (<0.0083) | N.d. (<0.0083) | N.d. (<0.0083) | N.d. (<0.0083) | N.d. (<0.0083) |
| lysine(Lys) | 0.02 | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.02 | 0.042 |
| histidine(His) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) |
| arginine(Arg) | N.d. (<0.0065) | N.d. (<0.0065) | N.d. (<0.0065) | N.d. (<0.0065) | N.d. (<0.0065) |
| proline(Pro) | N.d. (<0.0087) | N.d. (<0.0087) | N.d. (<0.0087) | N.d. (<0.0087) | N.d. (<0.0087) |
| EAA | 0.0675 | 0.211 | 0.181 | 0.1958 | 0.219 |
| NEAA | 0.139 | 0.165 | 0.124 | 0.152 | 0.24 |
| TAA | 0.2065 | 0.376 | 0.305 | 0.3478 | 0.459 |
| EAA/TAA | 0.33 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.48 |
| NEAA/TAA | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.44 | 0.52 |
| EAA/NEAA | 0.49 | 1.28 | 1.46 | 1.29 | 0.91 |
| Nutritional Assessment | Unit | 0 s | 30 s | 60 s | 90 s | 120 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAS | % | 9.76 | 12.91 | 23.19 | 24.08 | 11.77 |
| CS | % | 14.67 | 18.40 | 30.41 | 30.72 | 17.47 |
| EAAI | % | 74.69 | 79.43 | 88.06 | 89.58 | 76.52 |
| SRCCA | 82.15 | 83.10 | 84.63 | 84.69 | 82.43 | |
| C-PER | 2.26 | 2.39 | 2.60 | 2.68 | 2.29 | |
| BV | % | 69.71 | 74.88 | 84.29 | 85.94 | 71.71 |
| PDCAAS | % | 7.30 | 10.51 | 20.65 | 19.84 | 9.55 |
| Free Amino Acids | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| types of amino acids | 0 s | 30 s | 60 s | 90 s | 120 s |
| aspartic acid (Asp) | 33.41 | 19.68 | 19.34 | 16.39 | 20.92 |
| threonine (Thr) | 4.12 | 3.72 | 1.87 | 2.42 | 3.92 |
| serine (Ser) | 14.04 | 9.31 | 11.80 | 16.10 | 10.46 |
| glutamic acid (Glu) | 8.23 | 8.51 | 2.62 | 3.16 | 13.73 |
| glycine (Gly) | 11.62 | 6.38 | 6.89 | 8.05 | 7.19 |
| alanine (Ala) | / | / | / | / | / |
| cysteine(Cys) | 7.26 | 5.05 | 4.92 | 8.34 | 4.14 |
| valine (Val) | 3.87 | 3.46 | 2.07 | 2.13 | 2.83 |
| methionine (Met) | / | / | / | / | / |
| isoleucine (IIe) | 7.75 | 6.12 | 9.18 | 6.04 | 3.70 |
| leucine (Leu) | / | / | / | / | / |
| tyrosine (Tyr) | / | 29.26 | 36.07 | 31.63 | 23.97 |
| phenylalanine (Phe) | / | / | / | / | / |
| lysine (Lys) | 9.69 | 8.51 | 5.25 | 5.75 | 9.15 |
| histidine (His) | / | / | / | / | / |
| arginine (Arg) | / | / | / | / | / |
| proline (Pro) | / | / | / | / | / |
| taste TAA/TAA | 83.05 | 57.18 | 53.77 | 54.28 | 62.75 |
| Types of Amino Acids | Threshold | TAV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 s | 30 s | 60 s | 90 s | 120 s | |||
| umami | aspartic acid (Asp) | 1 | 0.0690 | 0.0740 | 0.0590 | 0.0570 | 0.0960 |
| glutamic acid (Glu) | 0.3 | 0.0567 | 0.1067 | 0.0267 | 0.0367 | 0.2100 | |
| sweet taste | glycine (Gly) | 1.3 | 0.0185 | 0.0185 | 0.0162 | 0.0215 | 0.0254 |
| alanine (Ala) | 0.6 | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | |
| proline (Pro) | 3 | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | |
| serine (Ser) | 1.5 | 0.0193 | 0.0233 | 0.0240 | 0.0373 | 0.0320 | |
| threonine (Thr) | 2.6 | 0.0033 | 0.0054 | 0.0022 | 0.0032 | 0.0069 | |
| bitter taste | Valine (Val) | 0.4 | 0.0200 | 0.0325 | 0.0158 | 0.0185 | 0.0325 |
| isoleucine (IIe) | 0.9 | 0.0178 | 0.0256 | 0.0311 | 0.0233 | 0.0189 | |
| leucine (Leu) | 1.9 | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | |
| histidine (His) | 0.2 | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | |
| arginine (Arg) | 0.5 | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | |
| methionine (Met) | 0.3 | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | N.d. (<0.0020) | |
| phenylalanine (Phe) | 0.9 | N.d.(<0.0020) | N.d.(<0.0020) | N.d.(<0.0020) | N.d.(<0.0020) | N.d.(<0.0020) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. Effect of Different Microwave Times on the Nutritional Properties of Glycosylated Soybean 7S. Foods 2025, 14, 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213694
Cui T, Zhang J, Xu H. Effect of Different Microwave Times on the Nutritional Properties of Glycosylated Soybean 7S. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213694
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Tao, Jixin Zhang, and Huiqing Xu. 2025. "Effect of Different Microwave Times on the Nutritional Properties of Glycosylated Soybean 7S" Foods 14, no. 21: 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213694
APA StyleCui, T., Zhang, J., & Xu, H. (2025). Effect of Different Microwave Times on the Nutritional Properties of Glycosylated Soybean 7S. Foods, 14(21), 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213694





