Triacylglycerol Crystallinity and Emulsion Colloidal Acid Stability Influence In Vitro Digestion Lipolysis and Bioaccessibility of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Rich Nanoemulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of Emulsions at Baseline
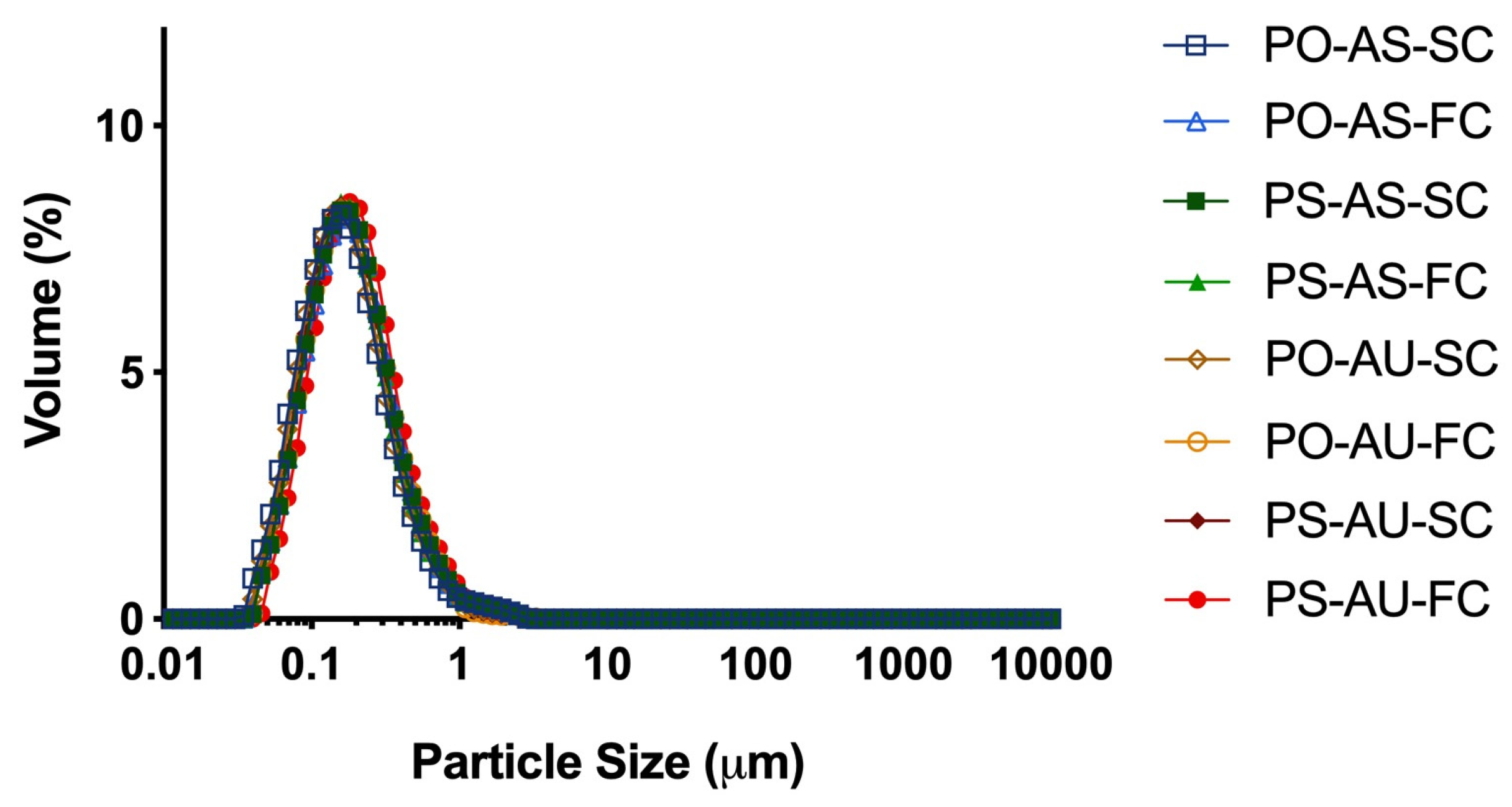
3.1.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
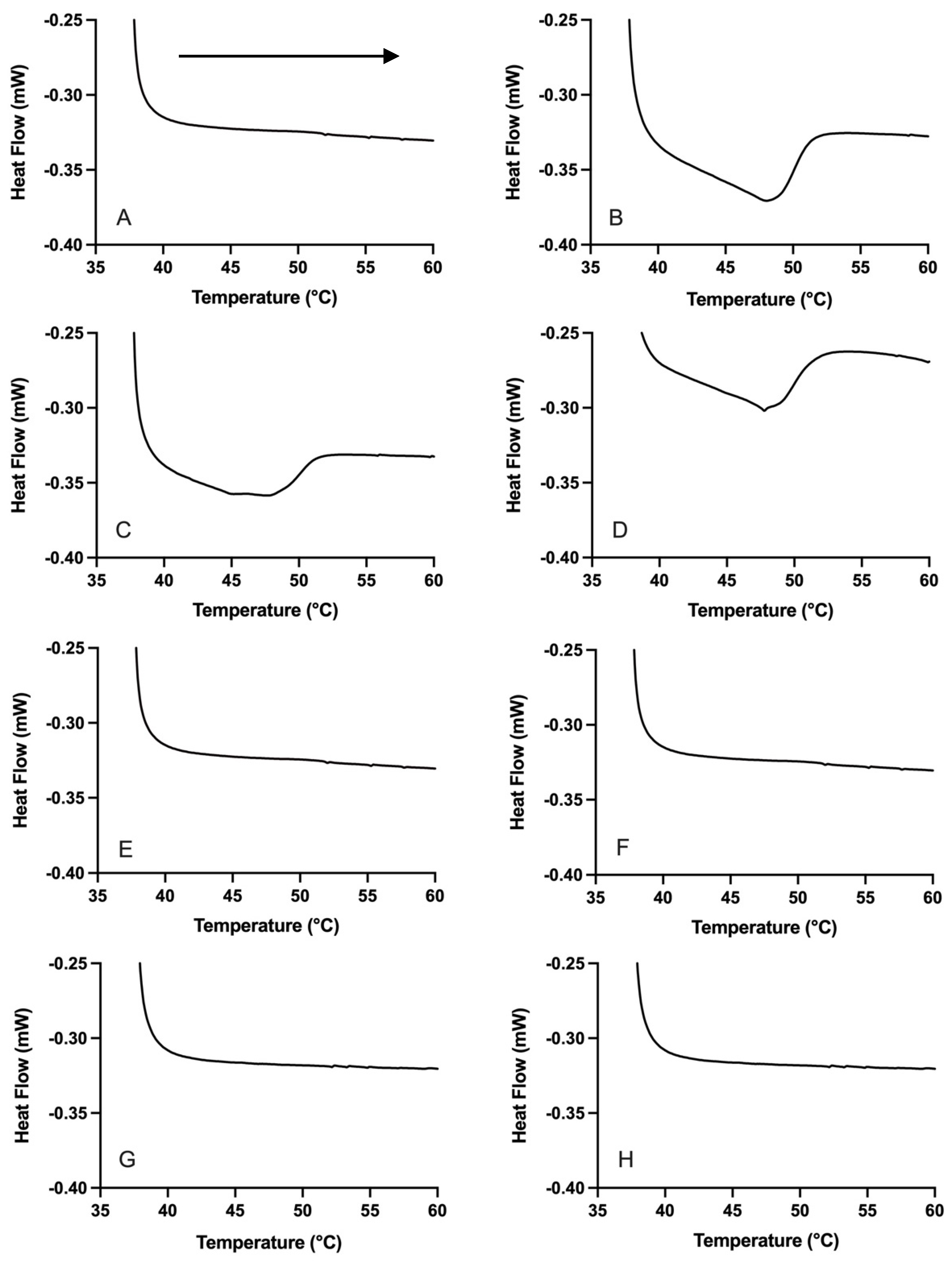
3.1.2. Emulsion Droplet Crystallinity
3.1.3. Emulsion Droplet Microstructure
3.2. Emulsion In Vitro Digestion
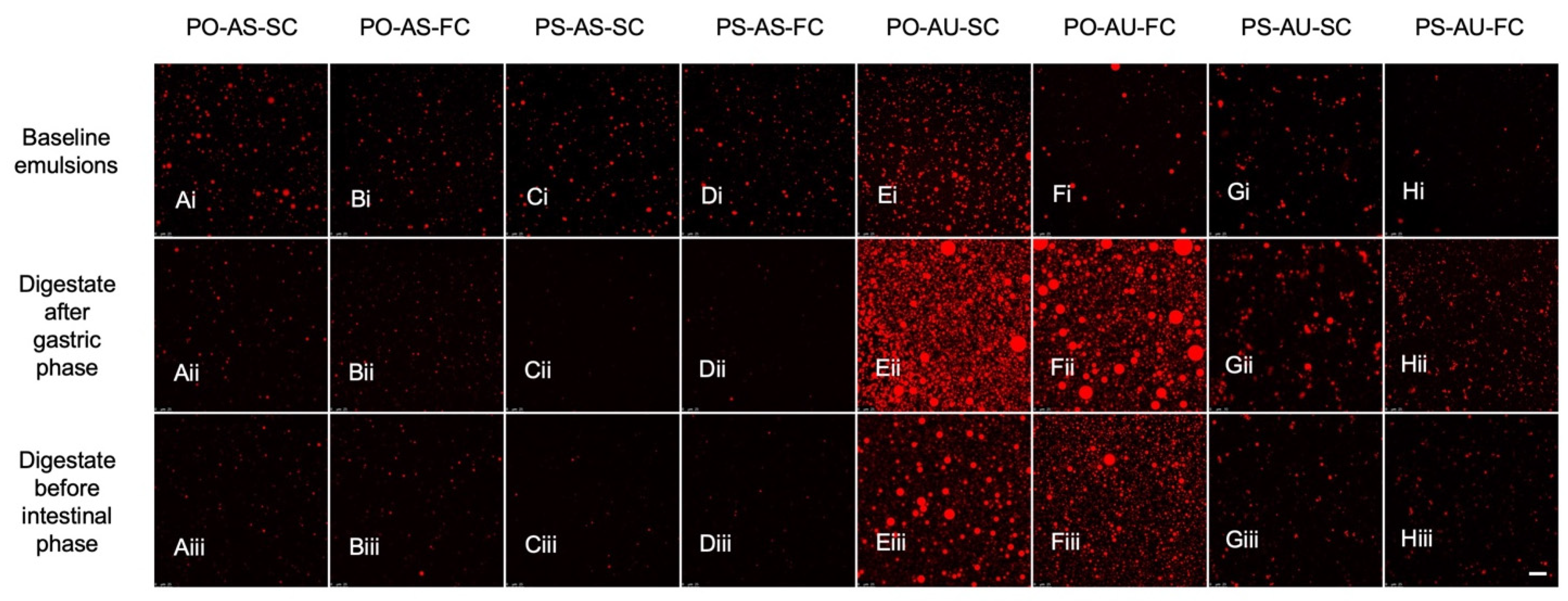
3.2.1. Digestate Microstructure
3.2.2. TAG Lipolysis and Relationship to Microstructure
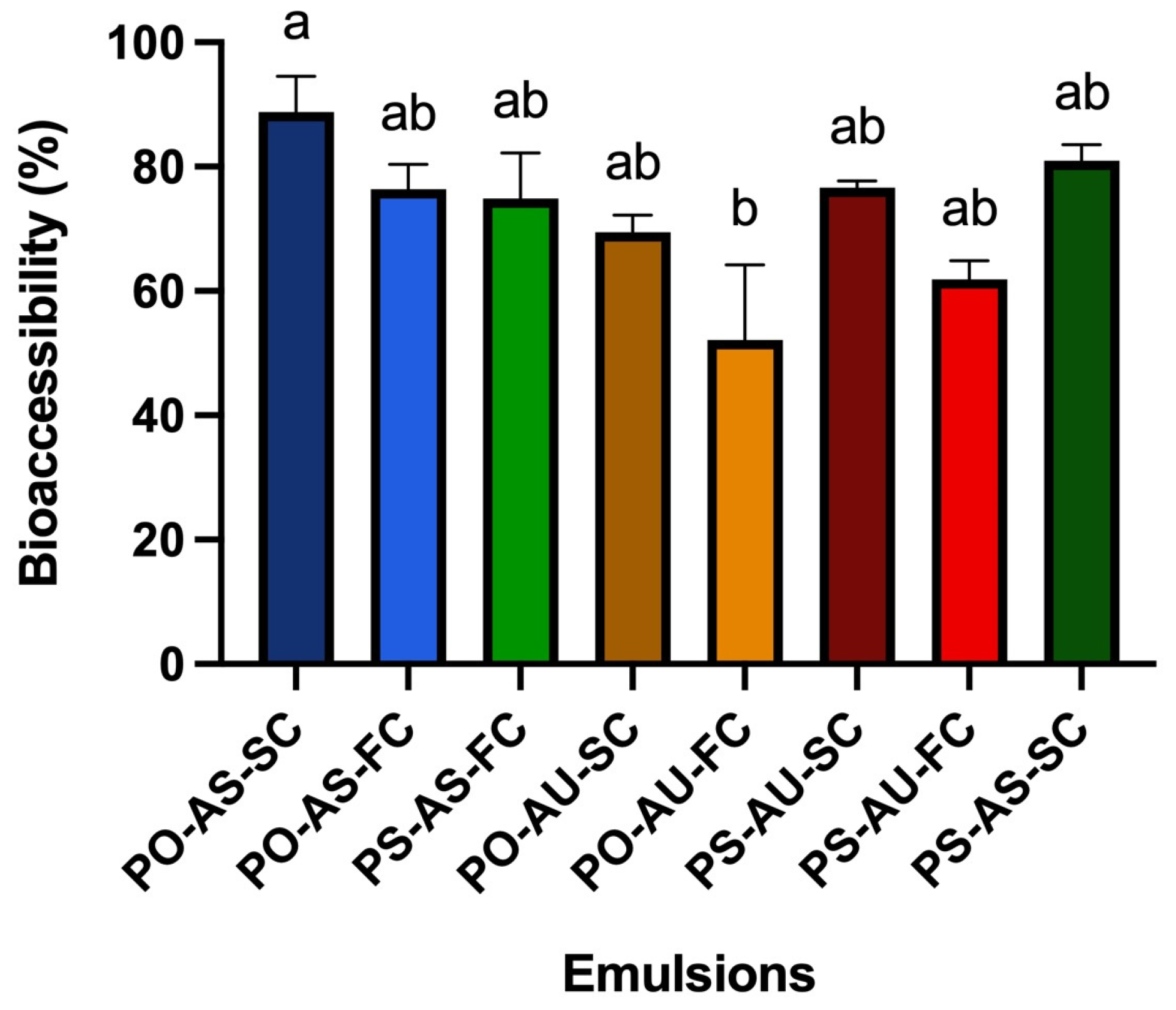
3.2.3. DHA Bioaccessibility
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tur, J.A.; Bibiloni, M.M.; Sureda, A.; Pons, A. Dietary sources of omega 3 fatty acids: Public health risks and benefits. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, S23–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Health Benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zou, Q.; Wang, Y.-H. Health effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in common diseases. Int. Food Res. J. 2021, 28, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Development of food-grade nanoemulsions and emulsions for delivery of omega-3 fatty acids: Opportunities and obstacles in the food industry. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayoso, L.; Ansorena, D.; Astiasarán, I. DHA rich algae oil delivered by O/W or gelled emulsions: Strategies to increase its bioaccessibility. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Høy, C.E. The digestion of dietary triacylglycerols. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Weiss, J. Emulsion-based delivery systems for lipophilic bioactive components. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R109–R124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raatz, S.K.; Redmon, J.B.; Wimmergren, N.; Donadio, J.V.; Bibus, D.M. Enhanced Absorption of n-3 Fatty Acids from Emulsified Compared with Encapsulated Fish Oil. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y. Controlling lipid bioavailability through physicochemical and structural approaches. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.C.; Genot, C.; Gayet, C.; Lopez, C.; Fine, F.; Joffre, F.; Vendeuvre, J.L.; Bouvier, J.; Chardigny, J.M.; Raynal-Ljutovac, K. Multiscale structures of lipids in foods as parameters affecting fatty acid bioavailability and lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lane, K.E.; Li, W. Evaluating the Stability and Digestibility of Long-Chain Omega-3 Algal Oil Nanoemulsions Prepared with Lecithin and Tween 40 Emulsifiers Using an In Vitro Digestion Model. Foods. 2024, 13, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.E.; Miller, G.; Sanders, T.A. The solid fat content of stearic acid-rich fats determines their postprandial effects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1486–1494. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/85/6/1486/4754388 (accessed on 13 June 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, S.M.; Lin, X.; Thilakarathna, S.H.; Wright, A.J. Emulsion droplet crystallinity attenuates early in vitro digestive lipolysis and beta-carotene bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Wright, A.J. Emulsification of algal oil with soy lecithin improved DHA bioaccessibility but did not change overall in vitro digestibility. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.S.; Lee, J. Melting, crystallization, and in vitro digestion properties of fats containing stearoyl-rich triacylglycerols. Molecules 2022, 27, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathna, S.H.; Wright, A.J. Attenuation of Palm Stearin Emulsion Droplet In Vitro Lipolysis with Crystallinity and Gastric Aggregation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10292–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Wei, W.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. The structure of triglycerides impacts the digestibility and bioaccessibility of nutritional lipids during in vitro simulated digestion. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, M.; Wooster, T.J.; Day, L.; Xu, M.; Lundin, L.; Keogh, J.; Cliftonx, P. Impact of gastric structuring on the lipolysis of emulsified lipids. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3513–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.; Tari, N.R.; Mathiyalagan, G.; Wright, A.J. Emulsion acid colloidal stability and droplet crystallinity modulate postprandial gastric emptying and short-term satiety: A randomized, double-blinded, crossover, controlled trial in healthy adult males. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Ulbikas, J.D.; Hamad, S.; Chen, R.; Maw, J.; Nasr, P.; Rogers, M.; Wright, A.J. Comparison of static and dynamic in vitro digestibility and bioaccessibility of palm-based emulsions and correlation to a human study: Effects of triacylglycerol crystallinity. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4302–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Dickson, E.; Dungan, S.R.; Kinsella, J.E.; Ma, J.G.; Povey, M.J.W. Effect of Emulsifier Type on the Crystallization Kinetics of O W Emulsions Containing a Mixture of Solid and Liquid Droplets. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 160, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.; Narine, S.S.; Marangoni, A.G. Effect of cooling rate on the structure and mechanical properties of milk fat and lard. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, M.; Wooster, T.J. The influence of emulsion structure and stability on lipid digestion. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Li, L.; Harro, J.M.; Hoag, S.W.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Shirtliff, M.E. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Palm Olein and Palm Stearin-in-Water Emulsions with Different Physical States and Fat Contents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7062–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borduas, M.; Spagnuolo, P.A.; Marangoni, A.G.; Corradini, M.G.; Wright, A.J.; Rogers, M.A. Lipid crystallinity of oil-in-water emulsions alters in vitro. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathna, S.H.; Hamad, S.; Cuncins, A.; Brown, M.; Wright, A.J. Emulsion Droplet Crystallinity Attenuates Postprandial Plasma Triacylglycerol Responses in Healthy Men: A Randomized Double-Blind Crossover Acute Meal Study. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.; Thilakarathna, S.H.; Cuncins, A.; Brown, M.; Wright, A.J. Emulsion Droplet Crystallinity Attenuates Short-Term Satiety in Healthy Adult Males: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Crossover, Acute Meal Study. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, P.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Enhancing omega-3 fatty acids nanoemulsion stability and in-vitro digestibility through emulsifiers. J. Food Eng. 2016, 187, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Herrera, M.L.; Hartel, R.W. Effect of cooling rate on nucleation behavior of milk fat—Sunflower oil blends. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2001, 39, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Herrera, M.L.; Hartel, R.W. Effect of cooling rate on crystallization behavior of milk fat fraction: Sunflower oil blends. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippetts, M.; Martini, S. Effect of cooling rate on lipid crystallization in oil-in-water emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wright, A.J. Pectin and gastric pH interactively affect DHA-rich emulsion in vitro digestion microstructure, digestibility and bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecques, J.D.; Kerr, B.J.K.; Hillyer, L.M.; Kang, J.X.; Robinson, L.E.; Ma, D.W.L. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ameliorate neurobehavioral outcomes post-mild traumatic brain injury in the fat-1 mouse model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldemnawy, H.Y.; Wright, A.J.; Corredig, M. A Better Understanding of the Factors Affecting In vitro Lipolysis Using Static Mono-compartmental Models. Food Dig. 2015, 6, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; McClements, D.J. New mathematical model for interpreting pH-stat digestion profiles: Impact of lipid droplet characteristics on in vitro digestibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8085–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkar, A.; Rosen-Kligvasser, J.; Lesmes, U.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M. Controlling lipid intestinal digestibility using various oil structuring mechanisms. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7495–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, T.; Takata, Y.; Ueno, S.; Sato, K. DSC and synchrotron-radiation X-ray diffraction studies on crystallization and polymorphic behavior of palm stearin in bulk and oil-in-water emulsion states. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, V.; Deman, J.M.; Deman, L. Short Spacings and Polymorphic Forms of Natural and Commercial Solid Fats: A Review. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1990, 67, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaire, M.; Di Bari, V.; Norton, J.E.; Sullo, A.; Lillford, P.; Norton, J.E.; Sullo, A.; Lilliford, P.; Norton, I.T. Fat crystallisation at oil–water interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 203, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantes-Garcia, M.R.; Verkempinck, S.H.E.; Gonzalez-Fuentes, P.G.; Hendrickx, M.E.; Grauwet, T. Lipolysis products formation during in vitro gastric digestion is affected by the emulsion interfacial composition. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Chang, M.; Wang, X. Medium and long-chain structured triacylglycerol enhances vitamin D bioavailability in an emulsion-based delivery system: Combination of in vitro and in vivo studies. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Ba, G.; Hu, S.; He, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, K.; Tan, W.; Du, H.; Luo, Y.; et al. Differences in DHA bioaccessibility and fat digestion of DHA-enriched milks: An in vitro infant digestion model. Food Res. Int. 2025, 213, 116602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsokoti, L.; Panozzo, A.; Pallares Pallares, A.; Jaiswal, S.; Van Loey, A.; Grauwet, A.; Hendrickx, M. Carotenoid bioaccessibility and the relation to lipid digestion: A kinetic study. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuro, P.K.; Viau, M.; Marze, S.; Laurent, S.; Cunha, R.L.; Berton-Carabin, C.; Meynier, A. In vitro digestion of high-lipid emulsions: Towards a critical interpretation of lipolysis. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10868–10881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Cao, C.; Xu, Y.J.; Cao, P.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Fatty acid profiles of typical dietary lipids after gastrointestinal digestion and absorbtion: A combination study between in-vitro and in-vivo. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, B.R.; Lee, J.H. In Vitro and In Vivo Digestibility of Soybean, Fish, and Microalgal Oils, and Their Influences on Fatty Acid Distribution in Tissue Lipid of Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, D.; Verkempinck, S.H.E.; Spaepen, R.; Vermeulen, K.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; del Castillo-Santaella, T.; Wealleans, A.; Grauwet, T. An in-depth interfacial study uncovering the effect of emulsifier mixes on small intestinal in vitro lipid digestion kinetics. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

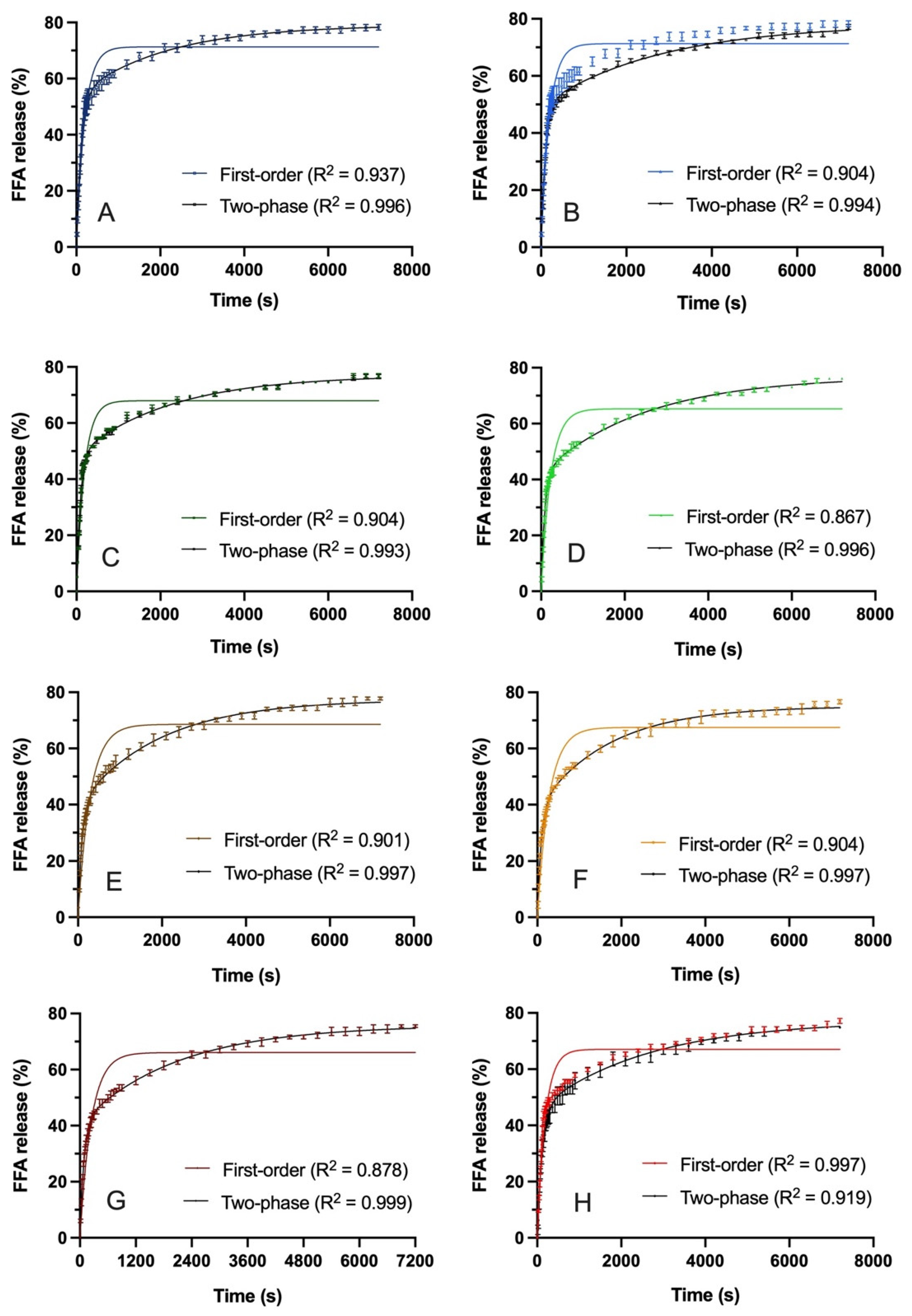
| Emulsion | 5 min Lipolysis (%) | 2 h Lipolysis (%) | First-Order Rate Constant | Two-Phase Exponential Association Rate Constant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k (min−1) | kearly (min−1) | klate (min−1) | |||
| PO-AS-SC | 3.6 a | 1.0 a | 0.313 0.045 ab | 0.542 0.067 a | 0.0278 0.005 a |
| PO-AS-FC | 0.78 ab | 0.9 ab | 0.317 0.023 ab | 0.671 0.045 a | 0.027 0.002 a |
| PS-AS-SC | 0.77 ab | 0.7 ab | 0.329 0.017 a | 0.630 0.040 a | 0.031 0.002 a |
| PS-AS-FC | 1.49 b | 0.3 ab | 0.262 0.016 ab | 0.717 0.025 a | 0.029 0.000 a |
| PO-AU-SC | 2.09 b | 0.6 ab | 0.208 0.018 b | 0.596 0.038 a | 0.023 0.003 a |
| PO-AU-FC | 0.69 b | 0.7 ab | 0.213 0.004 b | 0.709 0.041 a | 0.024 0.002 a |
| PS-AU-SC | 1.42 ab | 0.5 ab | 0.248 0.022 ab | 0.643 0.071 a | 0.033 0.005 a |
| PS-AU-FC | 3.26 ab | 0.4 b | 0.237 0.031 ab | 0.504 0.040 a | 0.024 0.000 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulbikas, J.D.; Ghazani, S.M.; Marangoni, A.G.; Wright, A.J. Triacylglycerol Crystallinity and Emulsion Colloidal Acid Stability Influence In Vitro Digestion Lipolysis and Bioaccessibility of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Rich Nanoemulsions. Foods 2025, 14, 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213631
Ulbikas JD, Ghazani SM, Marangoni AG, Wright AJ. Triacylglycerol Crystallinity and Emulsion Colloidal Acid Stability Influence In Vitro Digestion Lipolysis and Bioaccessibility of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Rich Nanoemulsions. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213631
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlbikas, Jessica D., Saeed Mirzaee Ghazani, Alejandro G. Marangoni, and Amanda J. Wright. 2025. "Triacylglycerol Crystallinity and Emulsion Colloidal Acid Stability Influence In Vitro Digestion Lipolysis and Bioaccessibility of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Rich Nanoemulsions" Foods 14, no. 21: 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213631
APA StyleUlbikas, J. D., Ghazani, S. M., Marangoni, A. G., & Wright, A. J. (2025). Triacylglycerol Crystallinity and Emulsion Colloidal Acid Stability Influence In Vitro Digestion Lipolysis and Bioaccessibility of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Rich Nanoemulsions. Foods, 14(21), 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213631





