Phytochemical Analysis and Characterisation of Brewers’ Spent Grain Properties as Affected by Fermentation and Ultrasonication Pretreatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Sample Pretreatments
2.2.1. Fermentation
2.2.2. Ultrasonication
2.3. pH and Titratable Acidity
2.4. Colour Measurement
2.5. Proximate Analysis of BSG Flour
2.6. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents and Antioxidant Activity
2.6.1. Methanolic BSG Flour Extraction
2.6.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC) of BSG
2.6.3. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC) of BSG
2.6.4. Estimation of Antioxidant Efficacy (DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP Assays)
2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH)
ABTS (2,2′-Azinobis(3-Ethyl-Benzothiazoline-6-Sulfonic Acid))
Ferric Ion-Reducing Antioxidant Power
2.7. Thermal Properties Using Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Colour Analysis of BSG Powder
3.2. Physicochemical Properties (pH, Total Titratable Acidity, and Soluble Solids) of Native BSG and Pretreated BSG Flours
3.3. Proximate Composition of BSG Flour
3.4. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
3.5. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
3.6. Antioxidant Activity of Native BSG and Pretreated BSG
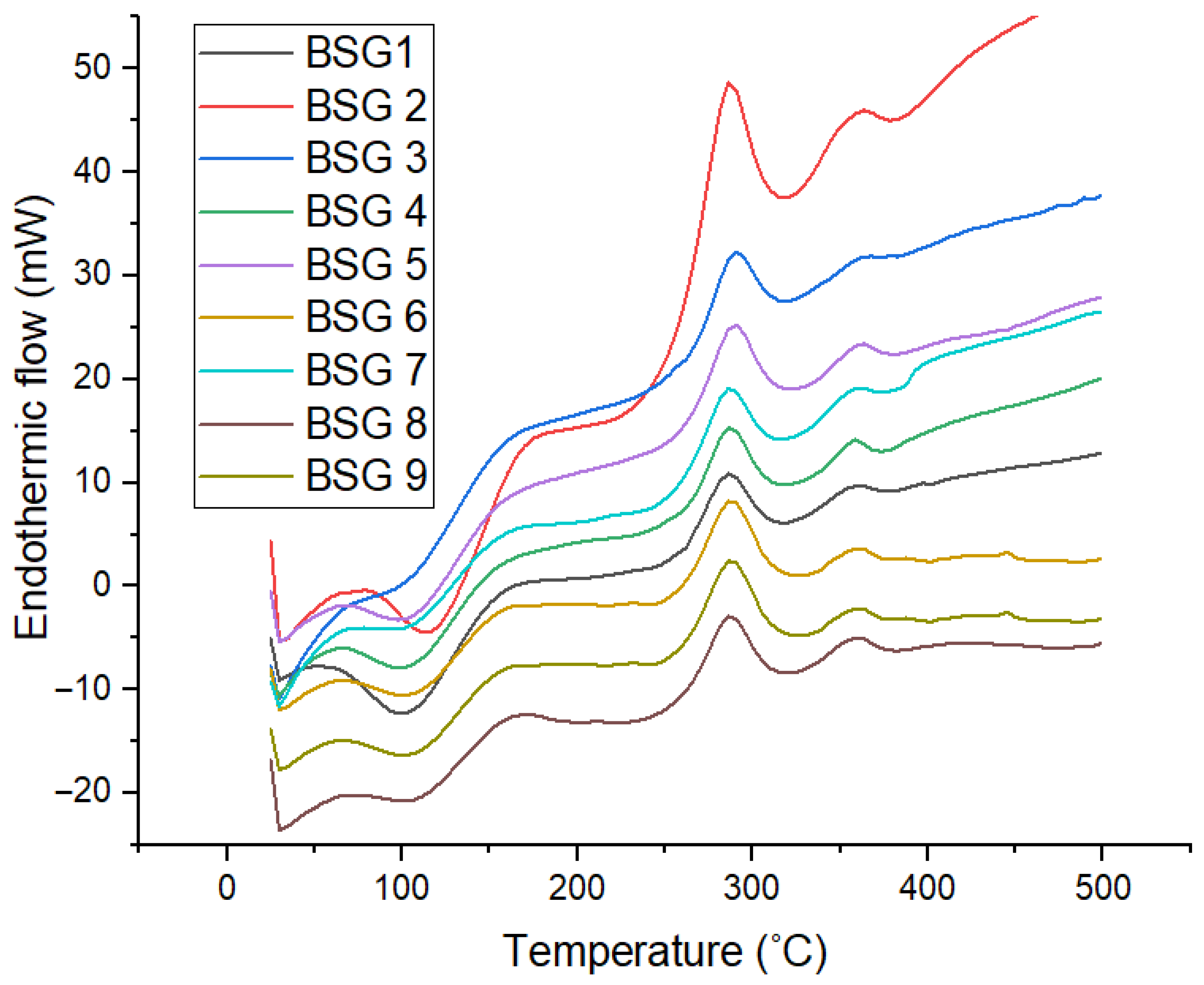
3.7. Thermal Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czubaszek, A.; Wojciechowicz-Budzisz, A.; Spychaj, R.; Kawa-Rygielska, J. Effect of added brewer’s spent grain on the baking value of flour and the quality of wheat bread. Molecules 2022, 27, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, L.C.; Barbosa, J.R.; da Costa, A.L.C.; Bezerra, F.W.F.; Pinto, R.H.H.; de Carvalho Junior, R.N. From waste to sustainable industry: How can agro-industrial wastes help in the development of new products? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers’ spent grain: Generation, characteristics and potential applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, L.; Dos Santos, B.P.; Ossanes, D.S.; de Souza Schwarz, P.; Bachmann, S.A.L.; Sebben, V.C.; Eller, S.; de Oliveira, T.F. Brewer’s spent grain as a potential sorbent for toxicology methods: Application to antidepressant analysis in urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 254, 116564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.X.; Mok, W.K.; Chen, W.N. In vitro evaluation of enriched brewers’ spent grains using Bacillus subtilis WX-17 as potential functional food ingredients. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, S.A.L.; Calvete, T.; Féris, L.A. Potential applications of brewery spent grain: Critical an overview. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Budroni, M.; Zara, S.; Mannazzu, I.; Fancello, F.; Zara, G. The role of microorganisms on biotransformation of brewers’ spent grain. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8661–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-León, C.; Ramírez-Guzman, N.; Londoño-Hernandez, L.; Martinez-Medina, G.A.; Díaz-Herrera, R.; Navarro-Macias, V.; Alvarez-Pérez, O.B.; Picazo, B.; Villarreal-Vázquez, M.; Ascacio-Valdes, J. Food waste and byproducts: An opportunity to minimize malnutrition and hunger in developing countries. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaș, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Tofană, M.; Mureşan, C.; Mudura, E.; Salanţă, L.; Scrob, S. Nutritional properties and volatile profile of brewer’s spent grain supplemented bread. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 19, 9705–9714. [Google Scholar]
- Fărcaş, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Dulf, F.V.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Diaconeasa, Z. Volatile profile, fatty acids composition and total phenolics content of brewers’ spent grain by-product with potential use in the development of new functional foods. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 64, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huige, N.J. Brewery by-products and effluents. In Handbook of Brewing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 670–729. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, A.L.; O’Callaghan, Y.C.; Piggott, C.O.; FitzGerald, R.J.; O’Brien, N.M. Brewers’ spent grain; bioactivity of phenolic component, its role in animal nutrition and potential for incorporation in functional foods: A review. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2013, 72, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habschied, K.; Košir, I.J.; Krstanović, V.; Kumrić, G.; Mastanjević, K. Beer polyphenols—Bitterness, astringency, and off-flavors. Beverages 2021, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio-Lopes, T.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pintado, M. Current extraction techniques towards bioactive compounds from brewer’s spent grain–A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Alva, A.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T.; Baigts-Allende, D.K. Brewer’s spent grain (BSG) as an ingredient for leavened bread making: Challenges and opportunities. J. Cereal Sci. 2025, 124, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.; Ravindran, R.; Jaiswal, S.; Tiwari, B.K.; Williams, G.A.; Jaiswal, A.K. An evaluation of sonication pretreatment for enhancing saccharification of brewers’ spent grain. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Colpini, L.M.S. All-around characterization of brewers’ spent grain. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, N.; Fatkullin, R.; Popova, N.; Ruskina, A.; Kalinina, I.; Morozov, R.; Avdin, V.V.; Antonova, A.; Vasileva, E. Effect of a combination of ultrasonic germination and fermentation processes on the antioxidant activity and γ-aminobutyric acid content of food ingredients. Fermentation 2023, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleke, M.S.; Adebo, O.A.; Wilkin, J.; Ledbetter, M.; Feng, X.; Gieng, J.; Molelekoa, T.B.J. Effect of fermentation, malting and ultrasonication on sorghum, mopane worm and Moringa oleifera: Improvement in their nutritional, techno-functional and health promoting properties. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1469960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kewuyemi, Y.O.; Adebo, O.A. Complementary nutritional and health promoting constituents in germinated and probiotic fermented flours from cowpea, sorghum and orange fleshed sweet potato. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Zhu, F. Effect of ultrasound on structural and physicochemical properties of sweetpotato and wheat flours. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 66, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Najafi, M.A.; Haddadi, T. Effect of fermentation process, wheat bran size and replacement level on some characteristics of wheat bran, dough, and high-fiber Tafton bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 85, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, I.; Kim, Y. Cookies formulated from fresh okara using starch, soy flour and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose have high quality and nutritional value. LWT 2015, 63, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. American association of cereal chemists. In Approved Methods of the AACC (10th ed.) Method 38-10; AACC: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Xu, T.; Lu, B.; Liu, R. Guidelines for antioxidant assays for food components. Food Front. 2020, 1, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasina, F.; Carabio, C.; Celano, L.; Thomson, L. Analysis of two methods to evaluate antioxidants. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2012, 40, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeboye, A.S.; Emmambux, N.M. Composition, functional and nutritional quality of marama (Tylosema esculentum) storage root. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4391–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathare, P.B.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Said, F.A.-J. Colour measurement and analysis in fresh and processed foods: A review. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, D.M.; Jacob, F.; Titze, J.; Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Fibre, protein and mineral fortification of wheat bread through milled and fermented brewer’s spent grain enrichment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Ortiz, A.; Hernández-Rodríguez, L.; Sandoval-Castilla, O.; Lobato-Calleros, C.; Cuevas-Bernardino, J.C. Impact of spontaneous fermentation and heat treatment on the physicochemical, functional and antioxidant properties of BSG. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2025, 19, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudau, M.; Adebo, O.A. Effect of traditional and novel processing technologies on the thermo-pasting, microstructural, nutritional, and antioxidant properties of finger millet and Bambara groundnut flours. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 60, vva2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliopoulos, C.; Arapoglou, D.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Markou, G.; Haroutounian, S.A. Conversion of brewers’ spent grain into proteinaceous animal feed using solid state fermentation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29562–29569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudau, M.; Adebo, O.A. Impact of ultrasonication on the metabolite profile, nutritional quality, and antioxidant properties of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf powder. Appl. Food Res. 2025, 5, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla-Bertholdt, A.M.; Baier, A.K.; Rauh, C. Potential of modification of techno-functional properties and structural characteristics of citrus, apple, oat, and pea dietary fiber by high-intensity ultrasound. Foods 2023, 12, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewuyemi, Y.O.; Kesa, H.; Adebo, O.A. Biochemical properties, nutritional quality, colour profile and techno—Functional properties of whole grain sourdough and malted cowpea and quinoa flours. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 1527–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, M. Composition and nutrient value proposition of brewers spent grain. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2232–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekatorou, A.; Bountas, Y.; Banat, I.M.; Kanellakl, M. Upgrading brewer’s spent grains by treatment with Aspergillus species. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2017, 13, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, S.T.; Chen, W.N. Valorization of brewer’s spent grain using fungi solid-state fermentation to enhance nutritional value. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Wang, Q.; Lu, T.; Ma, H.; Chen, X. The effects of ultrasonication on the phytochemicals, antioxidant, and polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase activities in coffee leaves. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaș, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Chiș, M.S.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; García-Segovia, P.; Becze, A.; Török, A.I.; Cadar, O.; Coldea, T.E.; Igual, M. In vitro digestibility of minerals and B group vitamins from different brewers’ spent grains. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Dang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, W.; Yang, X. Enhancement of polyphenols and antioxidant activity in germinated black highland barley by ultrasonication. Molecules 2023, 28, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabhane, J.; William, S.P.; Vaidya, A.N.; Anand, D.; Wate, S. Pretreatment of garden biomass by alkali-assisted ultrasonication: Effects on enzymatic hydrolysis and ultrastructural changes. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoff, M.M.; Babji, A.S.; Ismail, N. Structural modification of plant polysaccharides induced by ultrasound: Mechanisms and functional implications. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 68, 105221. [Google Scholar]
- Mudau, M.; Chinma, C.E.; Ledbetter, M.; Wilkin, J.; Adebo, O.A. Gas chromatography—mass spectrometry analysis of metabolites in finger millet and Bambara groundnut as affected by traditional and novel food processing. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 6394–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruíz Suarez, C.B.; Schalchli Sáez, H.L.; Melo, P.S.; Moreira, C.d.S.; Sartori, A.G.d.O.; de Alencar, S.M.; Scheuermann Salinas, E.S. Effect of physical separation with ultrasound application on brewers’ spent grain to obtain powders for potential application in foodstuffs. Foods 2024, 13, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalić, A.; Jagelavičiūtė, J.; Rezić, T.; Trivunović, Z.; Žadeikė, D.; Bašinskienė, L. From bakery leftovers to brewing sustainability: Fermentation of spent grain with Yarrowia lipolytica and Lactobacillus acidophilus. Sustainability 2025, 17, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| BSG | L* | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 57.43 ± 0.85 b | 3.47 ± 0.30 ab | 9.88 ± 0.29 bcd |
| 2 | 57.10 ± 0.21 bc | 3.26 ± 0.02 ab | 9.61 ± 0.02 d |
| 3 | 57.84 ± 0.61 ab | 3.18 ± 0.07 c | 9.71 ± 0.08 cd |
| 4 | 57.75 ± 0.52 ab | 3.63 ± 0.04 a | 10.55 ± 0.29 a |
| 5 | 57.45 ± 0.88 b | 3.59 ± 0.06 ab | 10.48 ± 0.27 ab |
| 6 | 57.08 ± 0.59 bc | 3.45 ± 0.16 ab | 10.41 ± 0.27 abc |
| 7 | 56.92 ± 0.08 c | 3.27 ± 0.07 bc | 10.16 ± 0.15 ab |
| 8 | 56.33 ± 0.45 b | 3.58 ± 0.09 ab | 9.91 ± 0.92 bcd |
| 9 | 59.09 ± 0.13 a | 3.31 ± 0.04 bc | 10.70 ± 0.41 a |
| BSG | pH | TTA (mg/g) | TSS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.97 ± 1.00 a | 1.50 ± 0.10 de | 1.50 ± 0.10 c |
| 2 | 4.31 ± 0.03 a | 2.00 ± 0.10 c | 1.40 ± 0.00 c |
| 3 | 4.27 ± 0.01 a | 2.30 ± 0.10 b | 1.40 ± 0.00 c |
| 4 | 4.27 ± 0.01 a | 2.40 ± 0.44 ab | 2.73 ± 0.11 b |
| 5 | 4.29 ± 0.01 a | 1.16 ± 0.01 c | 2.90 ± 0.00 ab |
| 6 | 4.25 ± 0.01 a | 1.50 ± 0.10 b | 3.23 ± 0.12 a |
| 7 | 4.29 ± 0.00 a | 1.70 ± 0.10 d | 2.80 ± 0.00 abc |
| 8 | 4.10 ± 0.56 a | 2.40 ± 0.10 ab | 1.57 ± 0.01 c |
| 9 | 4.43 ± 0.04 a | 2.70 ± 0.10 a | 3.03 ± 0.25 ab |
| BSG | Moisture Content (%) | Fibre (%) | Protein (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.89 ± 0.03 ab | 18.50 ± 0.21 d | 24.51 ± 0.03 a | 3.73 ± 1.16 a |
| 2 | 4.45 ± 0.03 cd | 20.05 ± 1.02 cd | 24.34 ± 0.19 bc | 2.97 ± 0.03 d |
| 3 | 7.11 ± 0.03 a | 24.86 ± 1.48 ab | 24.51 ± 0.25 a | 5.39 ± 0.13 ab |
| 4 | 5.20 ± 0.06 c | 22.18 ± 1.69 bc | 24.41 ± 0.25 abc | 4.94 ± 0.11 b |
| 5 | 5.52 ± 0.09 b | 24.53 ± 1.92 b | 23.96 ± 0.14 cd | 5.19 ± 0.11 b |
| 6 | 5.58 ± 0.07 b | 21.67 ± 1.48 c | 23.86 ± 0.16 d | 3.30 ± 0.11 cd |
| 7 | 3.65 ± 0.04 d | 28.12 ± 4.79 a | 24.40 ± 0.15 abc | 5.83 ± 0.00 a |
| 8 | 3.59 ± 0.06 d | 26.48 ± 14.78 ab | 24.46 ± 0.20 ab | 3.19 ± 0.05 d |
| 9 | 5.29 ± 0.80 bc | 18.79 ± 2.38 d | 24.26 ± 0.01 c | 2.99 ± 0.14 d |
| BSG | TPC (mg GAE/g) | TFC (mg QE/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.42 ± 2.2 a | 0.13 ± 0.0 b |
| 2 | 0.37 ± 0.05 d | 0.14 ± 0.00 ab |
| 3 | 0.86 ± 0.42 c | 0.14 ± 0.0 ab |
| 4 | 1.30 ± 0.08 ab | 0.13 ± 0.01 b |
| 5 | 1.30 ± 0.22 ab | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab |
| 6 | 1.12 ± 0.08 bc | 0.13 ± 0.01 b |
| 7 | 0.75 ± 0.08 d | 0.16 ± 0.01 a |
| 8 | 1.26 ± 0.01 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab |
| 9 | 0.79 ± 0.63 cd | 0.13 ± 0.01 b |
| BSG | FRAP (mgTE/g) | DPPH (% Inhibition) | ABTS (% Inhibition) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.10 ± 0.35 c | 65.87 ± 3.56 ab | 23.50 ± 0.90 bc |
| 2 | 4.35 ± 0.80 a | 66.76 ± 1.19 a | 37.29 ± 10.09 a |
| 3 | 3.44 ± 0.10 ab | 64.67 ± 3.65 bc | 20.29 ± 1.43 cd |
| 4 | 2.25 ± 0.42 bc | 57.63 ± 71.44 b | 27.60 ± 0.61 abc |
| 5 | 2.29 ± 0.25 bc | 63.92 ± 1.86 c | 24.48 ± 3.88 bc |
| 6 | 1.67 ± 0.12 d | 57.18 ± 30 d | 28.44 ± 10.46 ab |
| 7 | 2.01 ± 0.07 cd | 57.93 ± 1.58 cd | 22.25 ± 4.75 c |
| 8 | 2.43 ± 0.56 b | 61.23 ± 0.01 a | 22.25 ± 4.75 c |
| 9 | 2.14 ± 0.36 c | 65.27 ± 1.82 b | 30.58 ± 6.42 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olatunde, S.J.; Molelekoa, T.B.J.; Adebo, O.A. Phytochemical Analysis and Characterisation of Brewers’ Spent Grain Properties as Affected by Fermentation and Ultrasonication Pretreatments. Foods 2025, 14, 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203579
Olatunde SJ, Molelekoa TBJ, Adebo OA. Phytochemical Analysis and Characterisation of Brewers’ Spent Grain Properties as Affected by Fermentation and Ultrasonication Pretreatments. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203579
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlatunde, Sogo James, Tumisi Beiri Jeremiah Molelekoa, and Oluwafemi Ayodeji Adebo. 2025. "Phytochemical Analysis and Characterisation of Brewers’ Spent Grain Properties as Affected by Fermentation and Ultrasonication Pretreatments" Foods 14, no. 20: 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203579
APA StyleOlatunde, S. J., Molelekoa, T. B. J., & Adebo, O. A. (2025). Phytochemical Analysis and Characterisation of Brewers’ Spent Grain Properties as Affected by Fermentation and Ultrasonication Pretreatments. Foods, 14(20), 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203579






