Study on the Probiotic Properties of Xinjiang-Characteristic Selenium-Enriched Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Distribution of Selenium Element
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Reagents
2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.3. Experimental Method
2.3.1. Exploring the Optimal Selenium Enrichment Concentration for LAB
2.3.2. Exploring the Effects of Environmental Factors on the Growth of Selenium Content LAB
2.3.3. Determination of Selenium Content in LAB by 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine Method
2.3.4. Determination of Probiotic Properties of Selenium-Enriched LAB
2.3.5. Exploring the Distribution of Selenium in LAB
2.3.6. Metabolomics
2.3.7. Proteomics
2.3.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tolerance of LAB to Selenium
3.2. Determination Results of Selenium Enrichment Rate
3.3. Growth Status of 8 Selenium-Enriched LAB Strains Under Different Temperatures
3.4. Growth Status of Selenium-Enriched LAB Under Different Salt Concentration Conditions
3.5. Growth Status of Selenium-Enriched LAB Under Different pH Conditions
3.6. Results of DPPH and ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Capacities
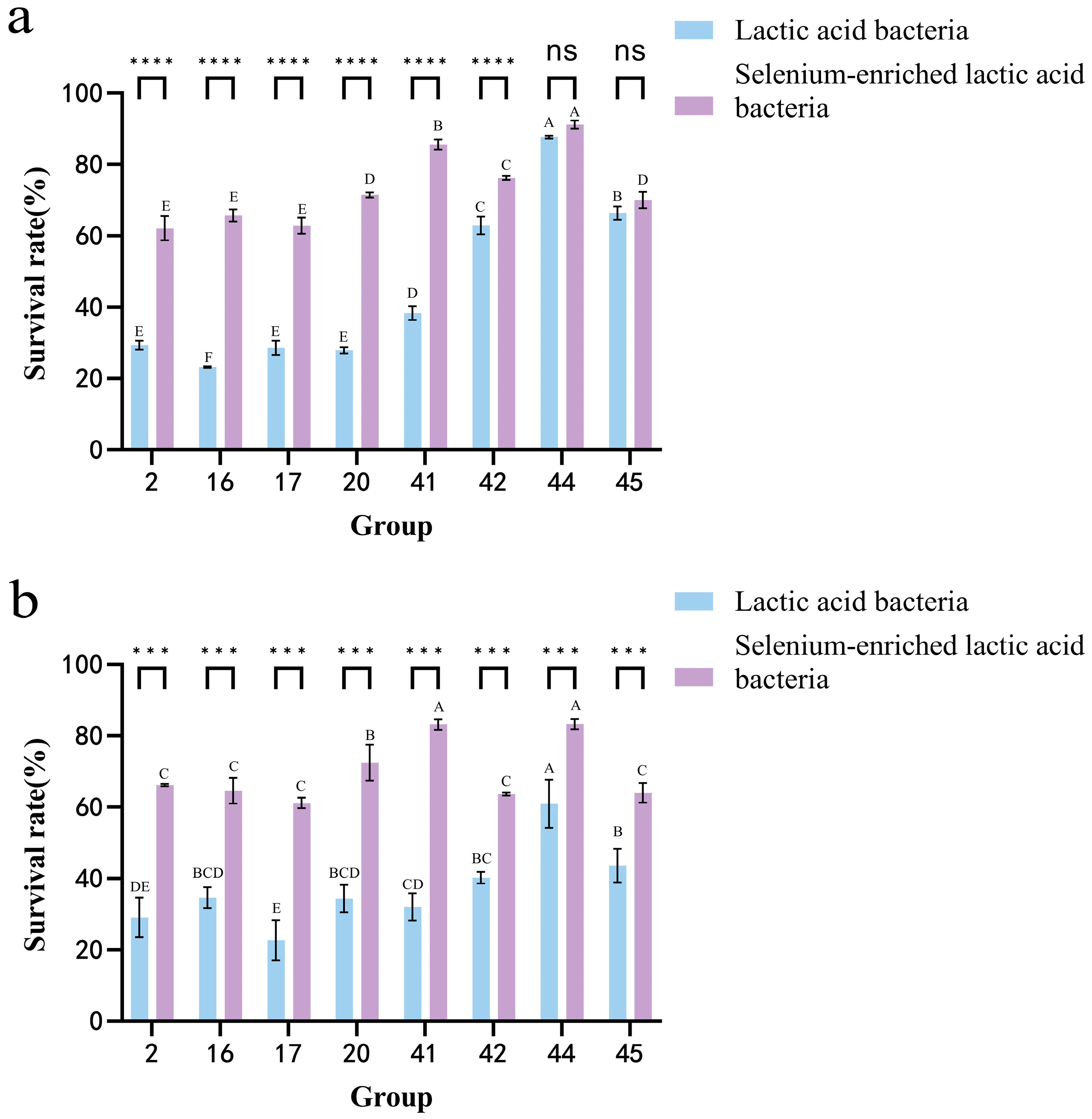
3.7. Analysis of the Survival Rate of LAB in Artificial Gastric Juice and Intestinal Juice Before and After Selenium Enrichment
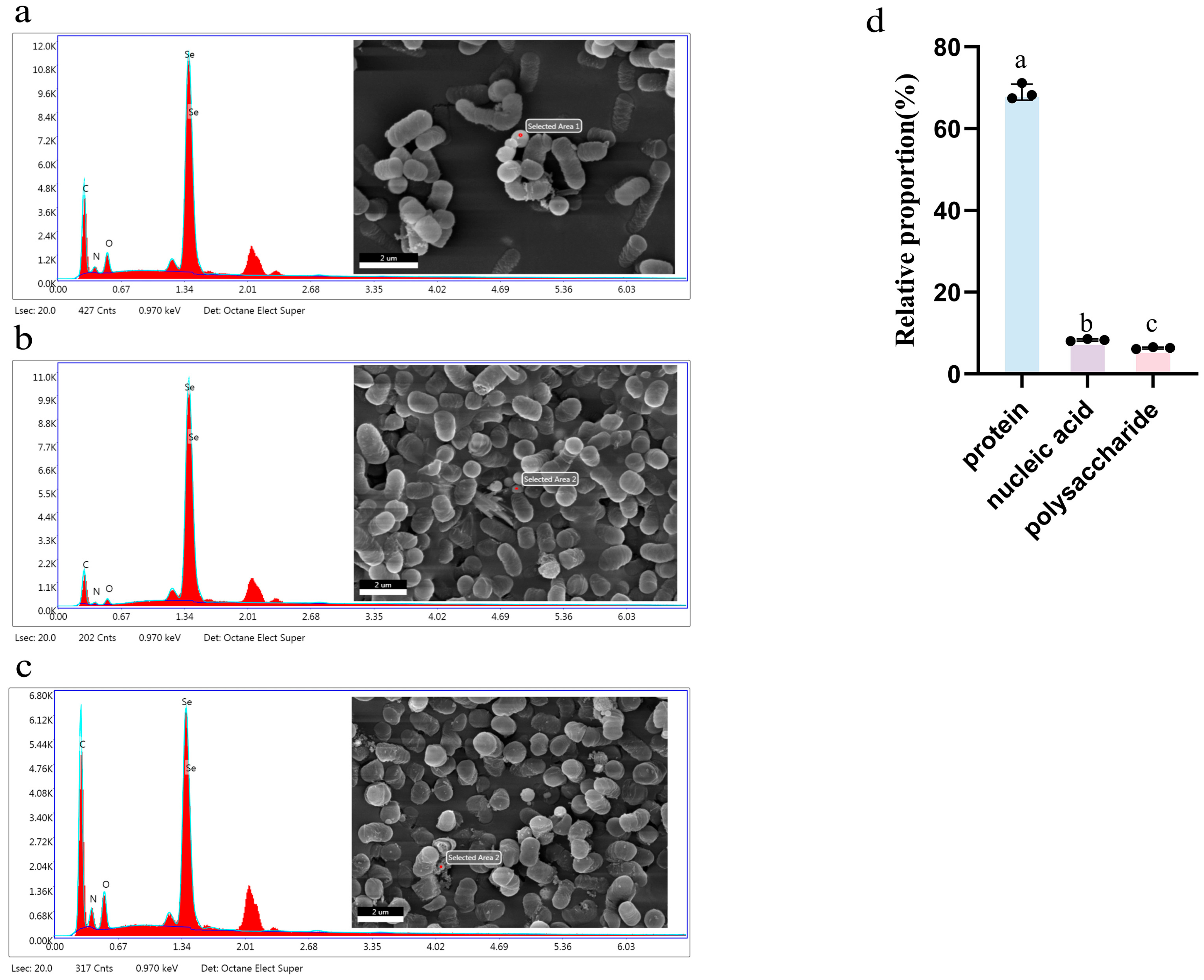
3.8. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Spectroscopy
3.9. Distribution of Selenium Element
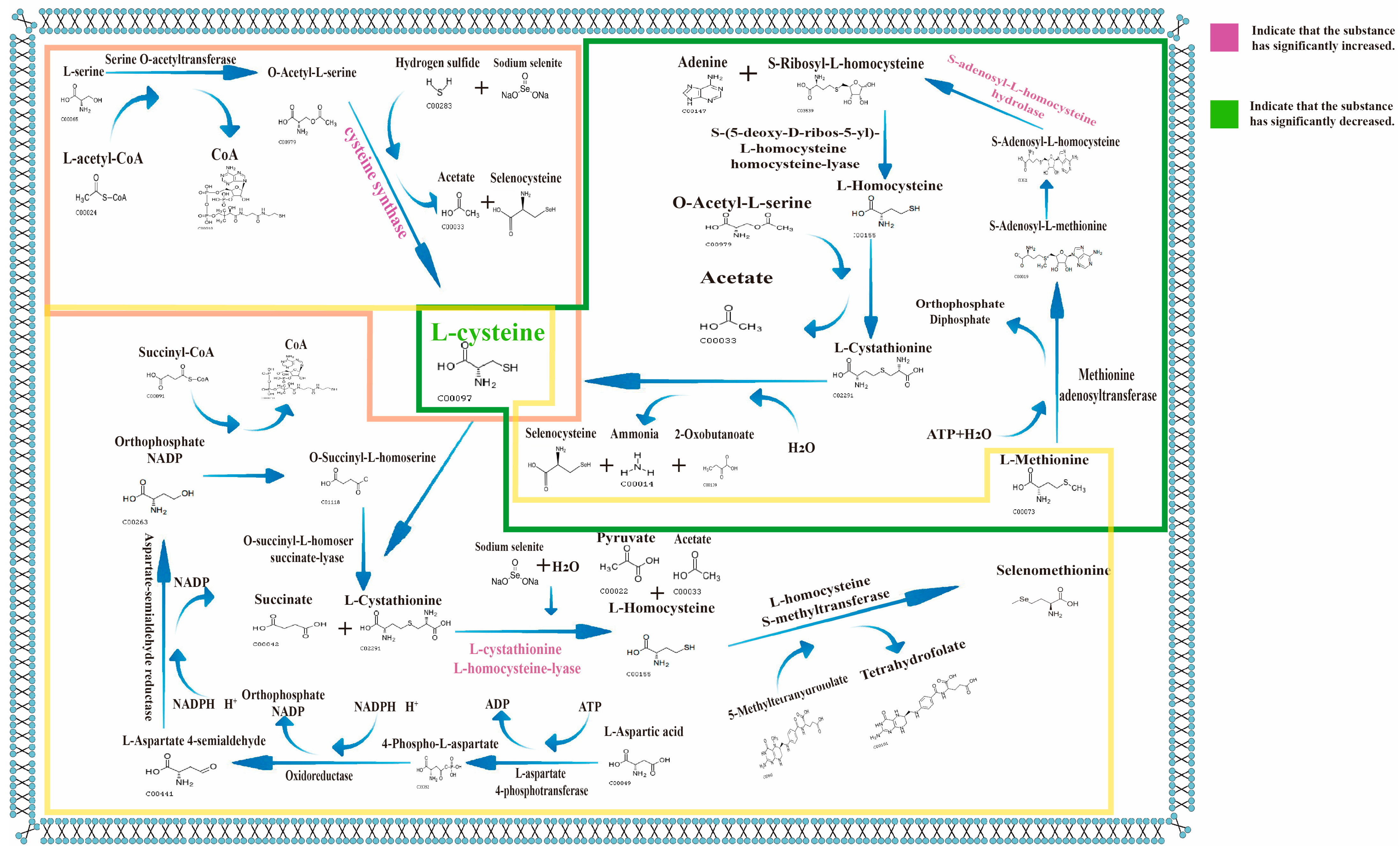
3.10. Dntargeted Metabolomics
3.11. Proteomics
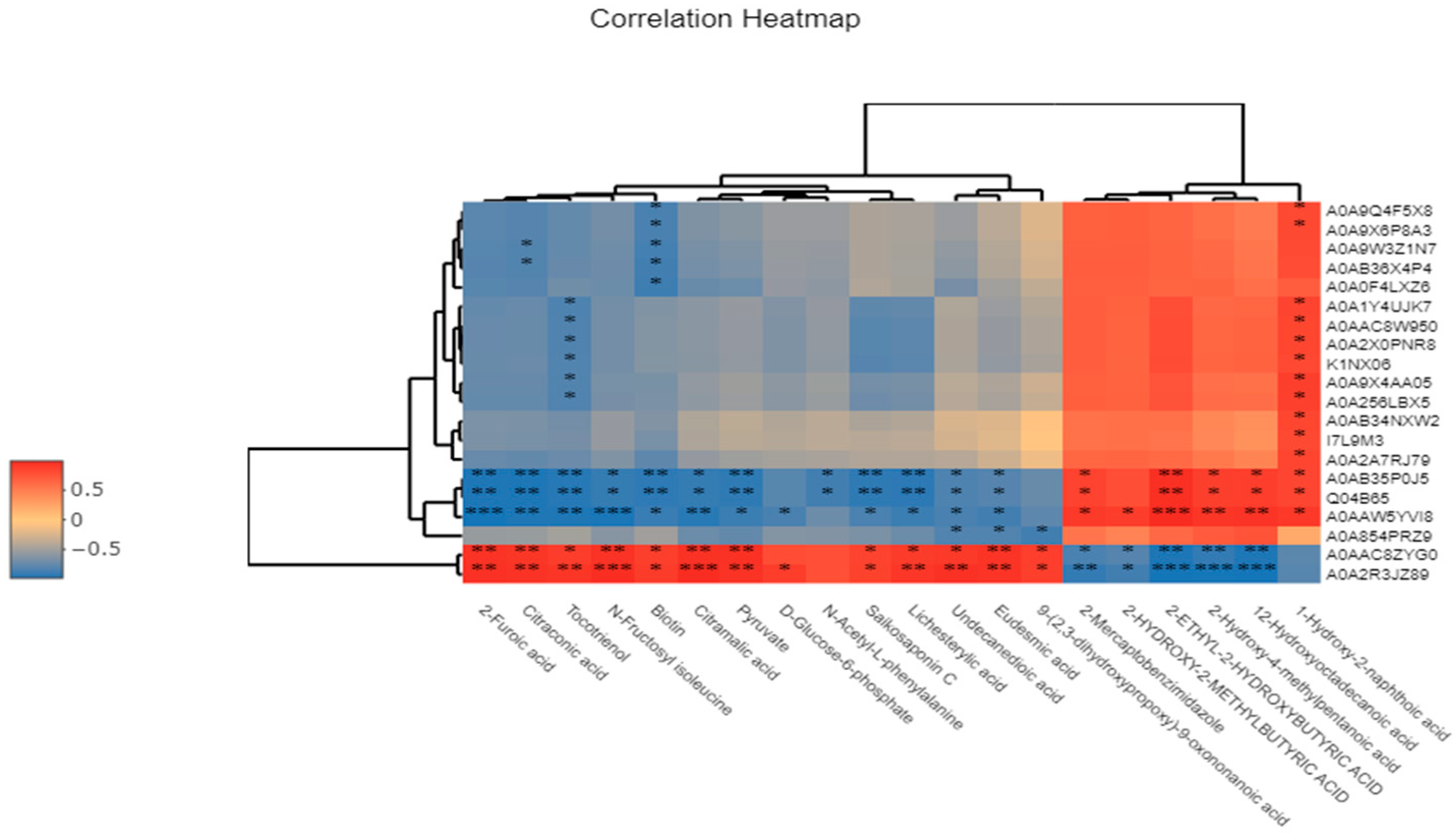
3.12. Correlation Analysis of Significantly Differential Metabolites Using Metabolomics Combined with Proteomics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamed, A.A.; Hawwa, M.T.; Baraka, D.M.; El-Shora, H.M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Al-Hazmi, N.E.; Hassan, M.G. Understanding antimicrobial activity of biogenic selenium nanoparticles and selenium/chitosan nano-incorporates via studying their inhibition activity against key metabolic enzymes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 298, 140073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Tran, T.A.T.; Wang, D.; Yang, W.; Zhou, F.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.; Liang, D. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review. Environ. Int. 2018, 112, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Xi, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, S.; Yi, Q. Effects of dietary bio-fermented selenium supplementation on growth, immune performance, and intestinal microflora of Chinese mitten crabs, eriocheir sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, I.; Hassan, M.F.; Kieliszek, M. A comprehensive review of selenium as a key regulator in thyroid health. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tao, H.; Xu, C.; Song, J.; Teng, C.; Pan, C.; Wei, S. Selenium-enriched green tea extracts: Chemical constituents and effects on antioxidant and anti-inflammatory factors and four major intestinal flora in mice with intestinal disorders. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 4472–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Peng, M.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; et al. Effect of lactobacillus plantarum enriched with organic/inorganic selenium on the quality and microbial communities of fermented pickles. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Luo, D.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Tian, X.; Nie, Y. Different effects of selenium speciation on selenium absorption, selenium transformation and cadmium antagonism in garlic. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Yang, X.; He, J.; Liu, P.; Shi, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, D. Bioconversion of inorganic selenium to less toxic selenium forms by microbes: A review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1167123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Wang, C. Factors affecting selenium-enrichment efficiency, metabolic mechanisms and physiological functions of selenium-enriched lactic acid bacteria. J. Future Foods 2022, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zou, X.; Lan, A.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Screening, characterization and probiotic properties of selenium-enriched lactic acid bacteria. Fermentation 2024, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, H. Recent development in se-enriched yeast, lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Barajas, E.; Díaz-Pérez, C.; Ramírez-Díaz, M.I.; Riveros-Rosas, H.; Cervantes, C. Bacterial transport of sulfate, molybdate, and related oxyanions. Biometals 2011, 24, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ju, J.; Xie, H.; Qiao, F.; Luo, Q.; Zhou, L. Comparative study on growth and metabolomic profiles of six lactobacilli strains by sodium selenite. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Fang, Q.; He, P.; Tu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, B. Unveiling the potential of selenium-enriched tea: Compositional profiles, physiological activities, and health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 104356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tian, Z.; Yuan, W.; Peng, X.; Zhou, H.; Shen, Q.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, X.; et al. Anti-aging effect of limosilactobacillus fermentum CGMCC 17434 in mice fed with fermented selenium-enriched yogurt. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Mudgil, P.; Al Hashmi, S.; Hamed, F.; Jafari, S.M.; Maqsood, S. Conception of novel protein-polysaccharide complex coacervation based on hemp proteins and kudzu starch for the microencapsulation of limosilactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 probiotic strain. Food Res. Int. 2025, 219, 116941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Chang, M.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y.; Shi, Y. Distribution characteristics of organic selenium in se-enriched lactobacillus (lactobacillus paracasei). LWT 2022, 165, 113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Long, R.; Huang, G.; Huang, H. Extraction and antioxidant activities in vivo of pumpkin polysaccharide. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 146, 112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Li, T.; Huang, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, J. Advances in the study of selenium-enriched probiotics: From the inorganic se into se nanoparticles. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 2300432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Yue, Y.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Guo, Q.; Yan, X.; Du, G.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Enrichment and distribution of selenium in Pediococcus acidilactici MRS-7: Impact on its biochemical composition, microstructure, and gastrointestinal survival. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14877–14885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, N.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, T.; Guo, L.; Ma, M.; Fan, M.; Wei, X. Selenium-enriched lactobacillus plantarum improves the antioxidant activity and flavor properties of fermented pleurotus eryngii. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averina, O.V.; Poluektova, E.U.; Marsova, M.V.; Danilenko, V.N. Biomarkers and utility of the antioxidant potential of probiotic lactobacilli and bifidobacteria as representatives of the human gut microbiota. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Duan, B.; Tan, W.; Wang, Z.; Cai, R.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Enhancing functional metabolites and flavor volatiles of kiwifruit juice fermented with selenium-enriched limosilactobacillus fermentum ln-9. Food Microbiol. 2025, 134, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.G.; Cuencas Barrientos, M.E.; Mozzi, F.; Pescuma, M. Survival of selenium-enriched lactic acid bacteria in a fermented drink under storage and simulated gastro-intestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampis, S.; Zonaro, E.; Bertolini, C.; Bernardi, P.; Butler, C.S.; Vallini, G. Delayed formation of zero-valent selenium nanoparticles by bacillus mycoides SeITE01 as a consequence of selenite reduction under aerobic conditions. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Rensing, C.; Zheng, S. Microbial reduction and resistance to selenium: Mechanisms, applications and prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, P.; Li, D. Biosynthesis and structural characteristics of selenium nanoparticles by pseudomonas alcaliphila. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Allawadhi, P.; Singh, V.; Khurana, I.; Yadav, P.; Sathua, K.B.; Allwadhi, S.; Banothu, A.K.; Navik, U.; Bharani, K.K. Antimicrobial and anti-viral effects of selenium nanoparticles and selenoprotein based strategies: COVID-19 and beyond. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Nishimura, K.; Nomura, M.; Shigehiro, T.; Suzuki, T.; Zang, W.; Tatara, Y.; Ito, H.; Hayashi, Y.; et al. Selenoprotein-mediated redox regulation shapes the cell fate of HSCs and mature lineages. Blood 2025, 145, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.A.D.; Melo, A.A.R.D.; Silva, V.M.; Reis, A.R.D. Selenium enhances ROS scavenging systems and sugar metabolism increasing growth of sugarcane plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Oltra, E.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Chillon, T.S.; Seemann, P.; Asaad, S.; Demircan, K.; Espejo-Oltra, J.A.; Sánchez-Fito, T.; Martín-Martínez, E.; et al. Autoantibodies to selenoprotein P in chronic fatigue syndrome suggest selenium transport impairment and acquired resistance to thyroid hormone. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinova, A.; Blinov, A.; Kravtsov, A.; Nagdalian, A.; Rekhman, Z.; Gvozdenko, A.; Kolodkin, M.; Filippov, D.; Askerova, A.; Golik, A.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and potential antimicrobial activity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized with cetyltrimethylammonium chloride. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Liu, B.; Lv, Z.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H. Effects of selenium on apoptosis and abnormal amino acid metabolism induced by excess fatty acid in isolated rat hepatocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Wen, P. Revealing the impact of organic selenium-enriched lactiplantibacillus plantarum NML21 on yogurt quality through volatile flavor compounds and untargeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Chang, S.; Dong, H.; Duan, H.; Liu, W.; Menghe, B. The revelation of high-yield amino acids and probiotic characteristics of an intestinal lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus X9C17. Food Chem. 2025, 467, 142245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanweert, F.; Schrauwen, P.; Phielix, E. Role of branched-chain amino acid metabolism in the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes-related metabolic disturbances BCAA metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2022, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Li, Q.; Long, B.; Li, B.; Shen, Z.; Xu, N.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M. Selenium-enriched lactic acid bacteria inoculation enhances the quality of paocai by imparting the microbiome and metabolome. Food Chem. 2025, 486, 144644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xing, Y.; Yan, T.; Li, Y.; Tian, R.; Hou, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, J. Regulation of artificial supramolecular transmembrane signal transduction by selenium-containing artificial enzyme receptors. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gervacio, A.D.J.; Qui-Zapata, J.A.; Barrera-Martínez, I.; Montero-Cortés, M.I.; García-Morales, S. Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) inhibit the growth and proliferation of reproductive structures in phytophthora capsici by altering cell membrane stability. Agronomy 2025, 15, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liphardt, J.; Onoa, B.; Smith, S.B.; Tinoco, I.; Bustamante, C. Reversible unfolding of single RNA molecules by mechanical force. Science 2001, 292, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescure, A.; Allmang, C.; Yamada, K.; Carbon, P.; Krol, A. cDNA cloning, expression pattern and RNA binding analysis of human selenocysteine insertion sequence (SECIS) binding protein 2. Gene 2002, 291, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, H.; Luo, D.; Chen, D.; Fan, J.; Shao, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W. A rational combination of cyclocarya paliurus triterpene acid complex (TAC) and se-methylselenocysteine (MSC) improves glucose and lipid metabolism via the PI3K/akt/GSK3β pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbariyan, A.; Haghighat, S.; Yazdi, M.H.; Bidgoli, S.A.; Tabriz, H.M.; Mahdavi, M. Immunogenic potential of biogenic vs. synthetic selenium nanoparticles in vaccine candidate against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Vaccine X 2025, 24, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
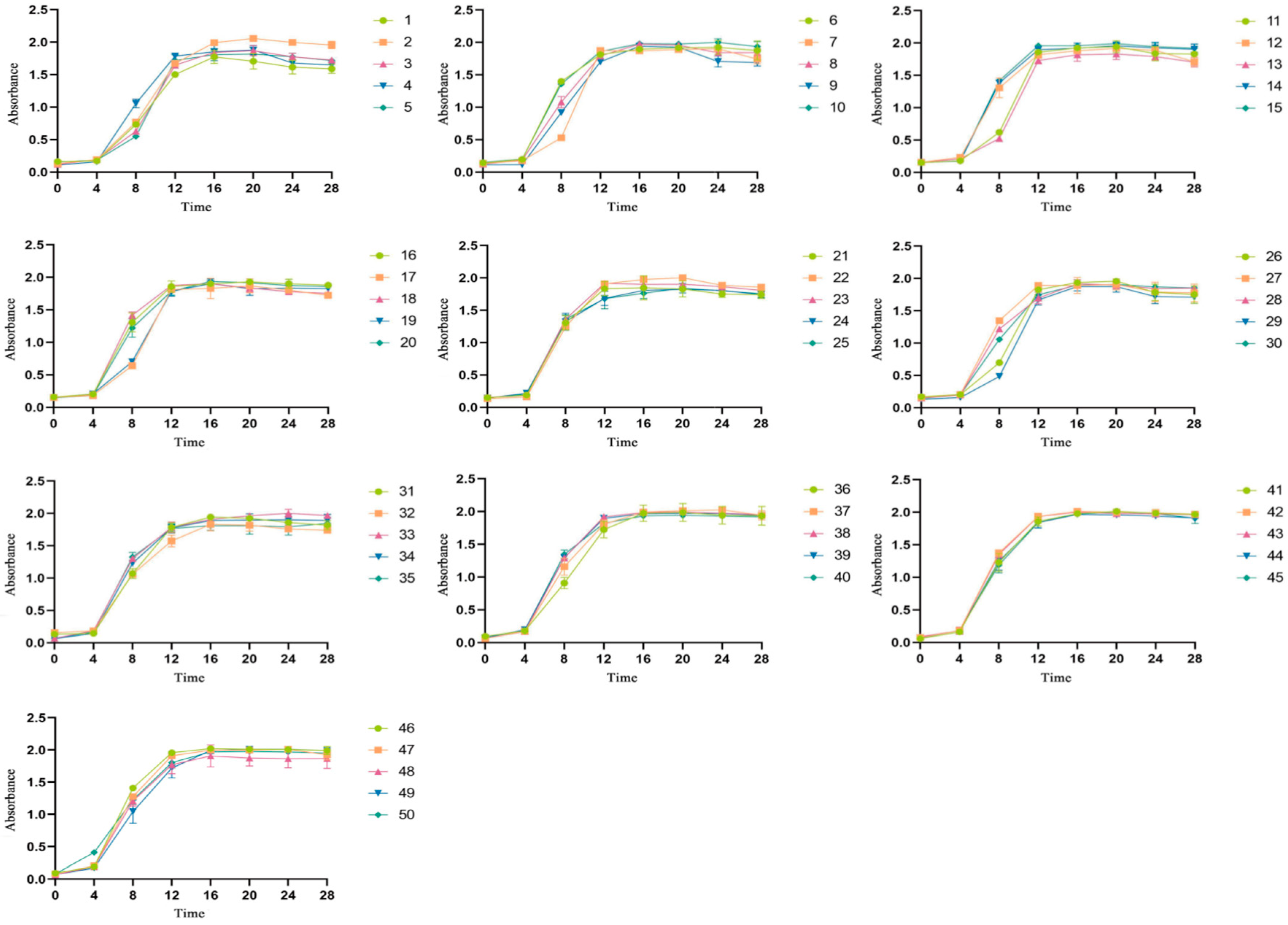
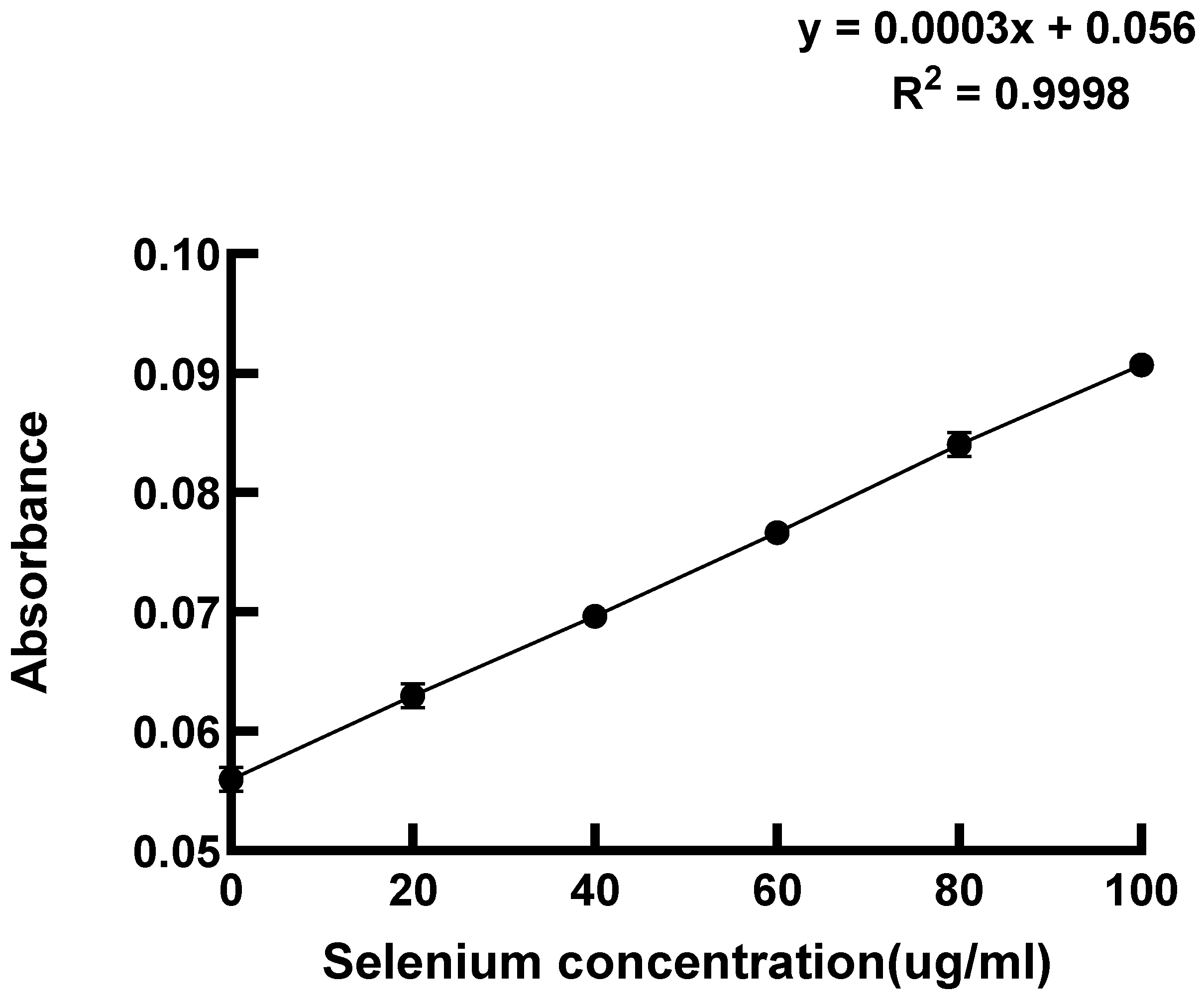
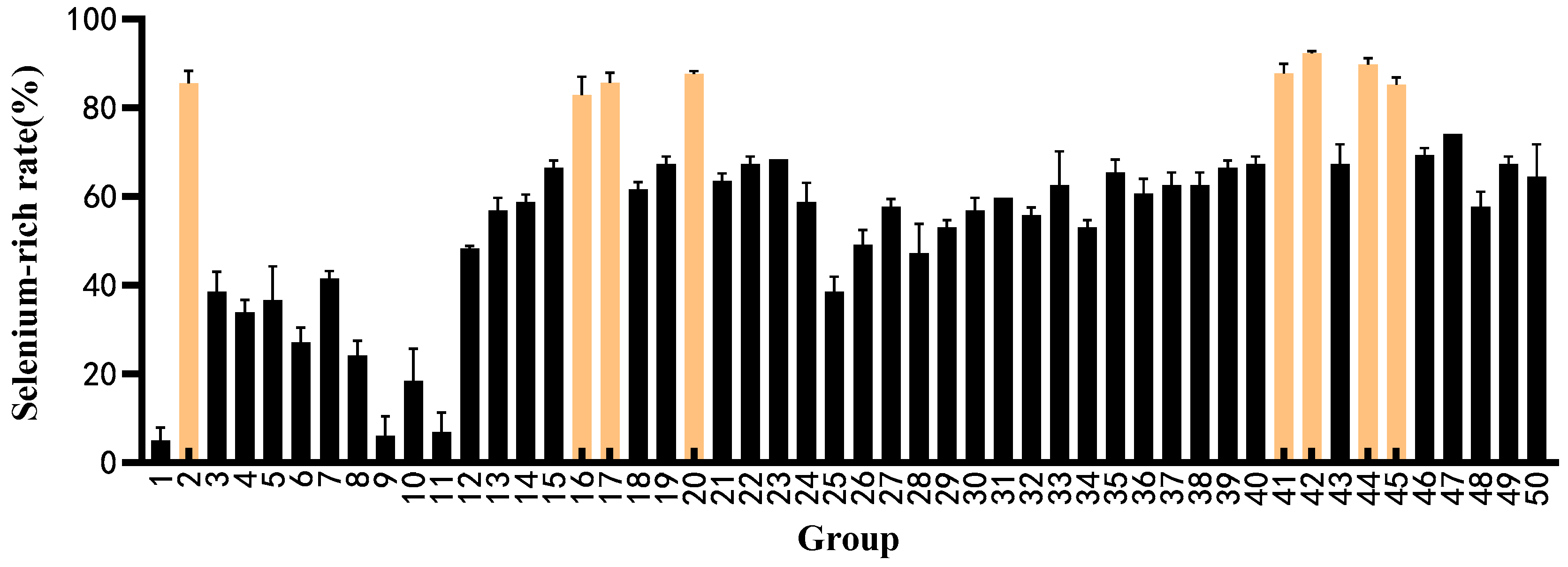

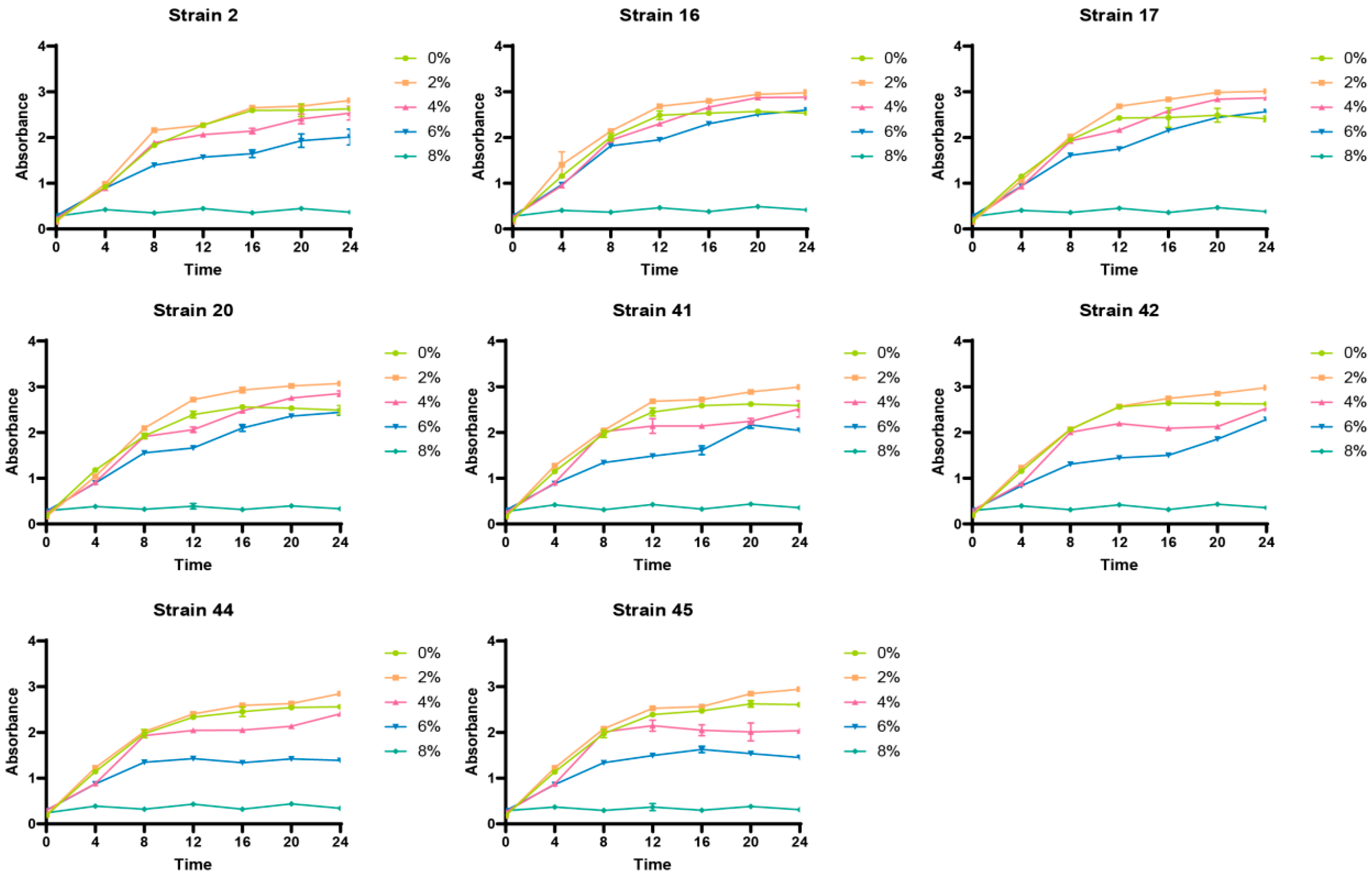




| Strain Number Sodium Selenite Concentration | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 2 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 3 | - | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 4 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 5 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 6 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 7 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 8 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 9 | - | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 10 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 11 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 12 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 13 | - | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 14 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 15 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 16 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 17 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 18 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 19 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 20 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 21 | - | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 22 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 23 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 24 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 25 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 26 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 27 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 28 | - | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 29 | - | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 30 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 31 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 32 | - | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 33 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 34 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 35 | - | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 36 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 37 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 38 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 39 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 40 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 41 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 42 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 43 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 44 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 45 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 46 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 47 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 48 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 49 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| 50 | - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Jia, Y.; Chensheng, H.; Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Jian, T.; Han, X.; Niu, X.; Xu, Q. Study on the Probiotic Properties of Xinjiang-Characteristic Selenium-Enriched Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Distribution of Selenium Element. Foods 2025, 14, 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203577
Chen J, Jia Y, Chensheng H, Feng L, Li Y, Jian T, Han X, Niu X, Xu Q. Study on the Probiotic Properties of Xinjiang-Characteristic Selenium-Enriched Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Distribution of Selenium Element. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203577
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jingshu, Yiming Jia, Huizi Chensheng, Lu Feng, Yawen Li, Tiantian Jian, Xue Han, Xiyue Niu, and Qian Xu. 2025. "Study on the Probiotic Properties of Xinjiang-Characteristic Selenium-Enriched Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Distribution of Selenium Element" Foods 14, no. 20: 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203577
APA StyleChen, J., Jia, Y., Chensheng, H., Feng, L., Li, Y., Jian, T., Han, X., Niu, X., & Xu, Q. (2025). Study on the Probiotic Properties of Xinjiang-Characteristic Selenium-Enriched Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Distribution of Selenium Element. Foods, 14(20), 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203577






