Quality and Maturity Detection of Korla Fragrant Pears via Integrating Hyperspectral Imaging with Multiscale CNN–LSTM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
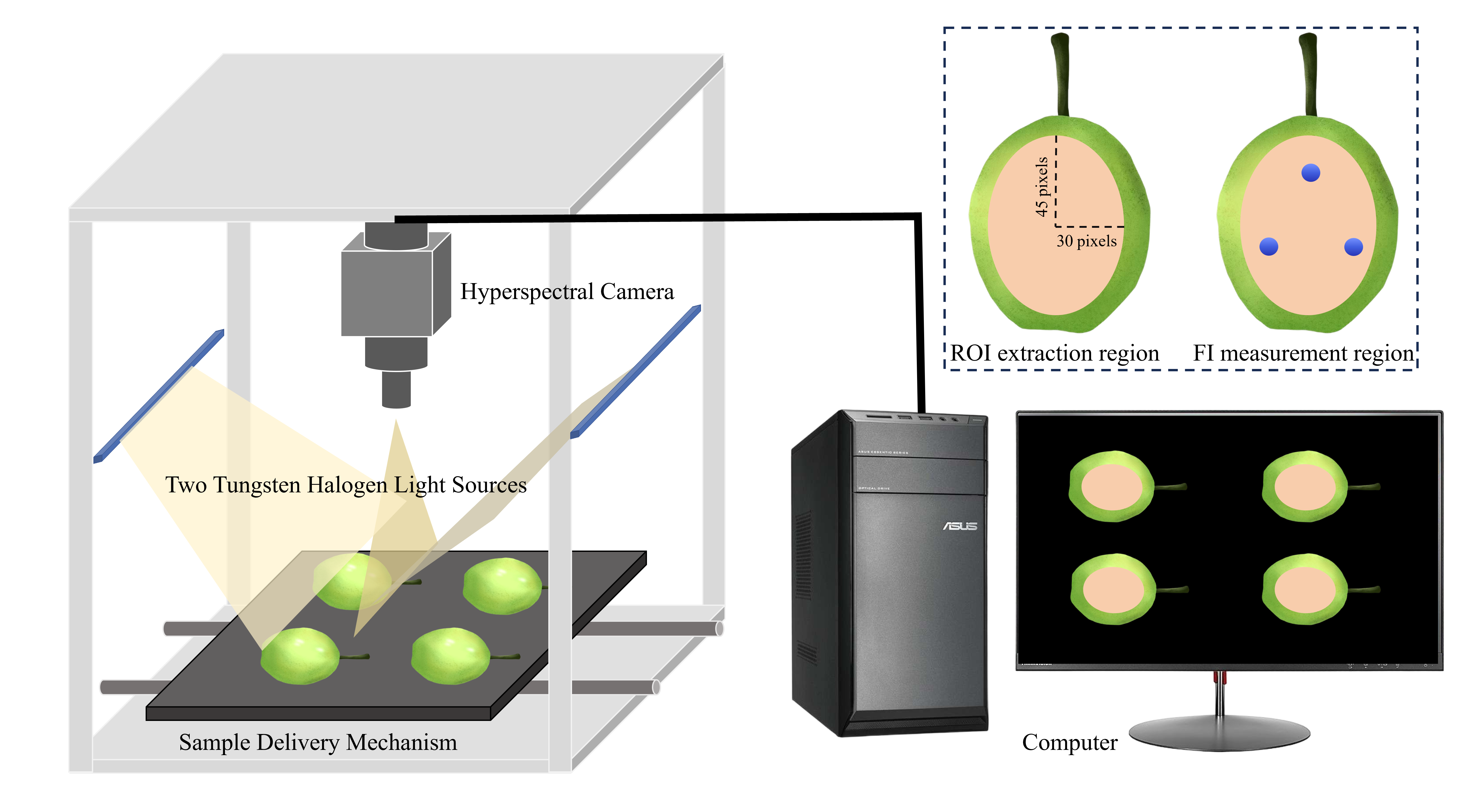
2.2. Hyperspectral Image Acquisition
2.3. Hyperspectral Image Correction and Spectral Data Extraction
2.4. Determination of FSR in Korla Fragrant Pears
2.5. Data Preprocessing and Partitioning
2.6. Construction of Machine Learning Regression Models
2.7. Construction of Deep-Learning Regression Models
2.7.1. Residual Neural Network 18 (ResNet18)
2.7.2. MSCNN
2.7.3. MSCNN–LSTM
2.8. Classification Models
2.9. Model Evaluation
2.9.1. Regression Model Evaluation
2.9.2. Classification Model Evaluation
3. Results and Analysis
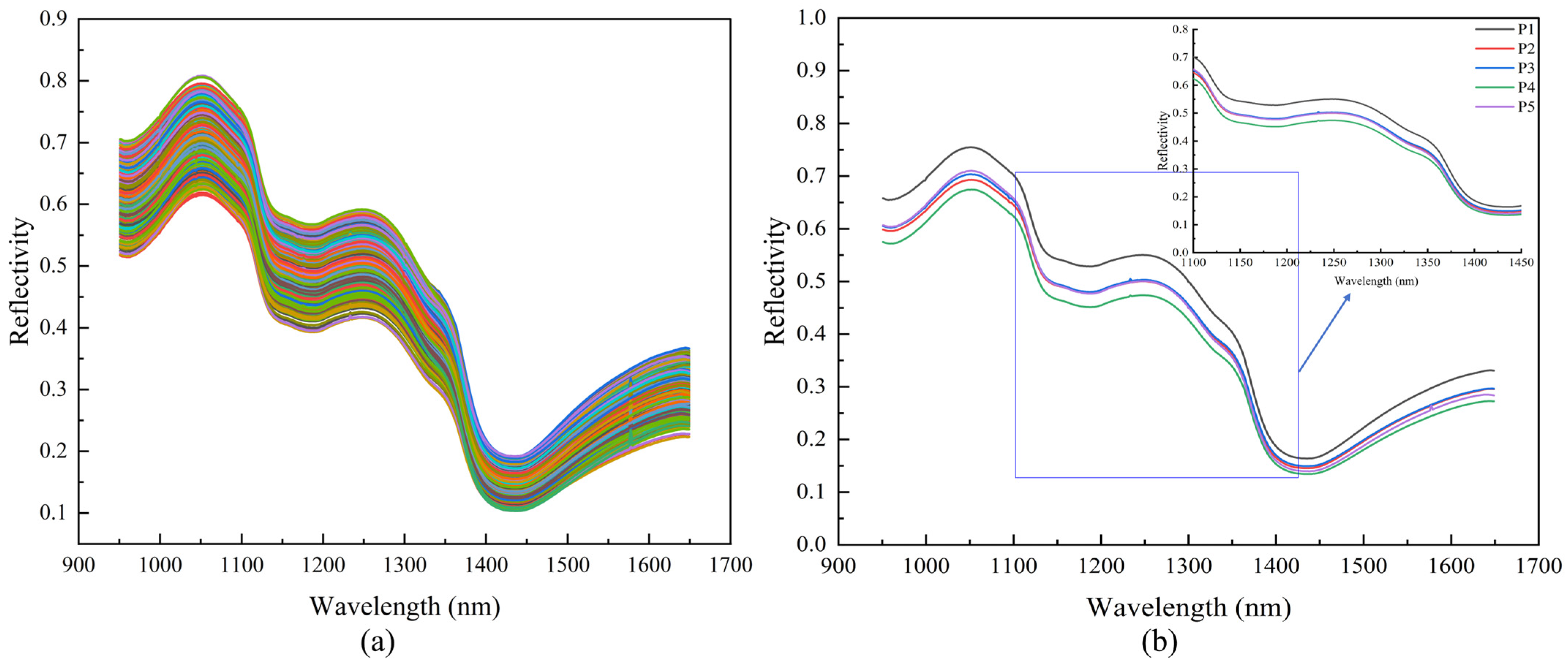
3.1. Spectral Analysis
3.2. Variation Patterns of FI, SSC, and FSR with Maturity
3.2.1. Variation Patterns of FI
3.2.2. Variation Patterns of SSC
3.2.3. Variation Patterns of FSR
3.3. Analysis of Regression Models
3.3.1. Analysis of Machine Learning Regression Models
3.3.2. Analysis of Deep-Learning Regression Models
3.4. Visualization and Analysis of Quality Indexes for Korla Fragrant Pears
3.5. Analysis of Maturity Prediction Models
4. Discussion
| Index | Fruit Type | Spectral Range | Model | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSC | Pear | 950–2500 nm | MSC-CARS-PLS | 0.8284 | 0.3655 | [62] |
| Apricot | 180–1100 nm | SG-MLP-XGBoost | 0.7182 | 1.7400 | [63] | |
| Pear | 380–1030 nm | RAW-PLSR | 0.8320 | 0.3300 | [8] | |
| FI | Peach | 400–1000 nm | Nor-RF-MLR | 0.8200 | 1.0270 | [64] |
| Apple | 200–1100 nm | RAW-Ridge | 0.8552 | 0.3386 | [65] | |
| Pear | 350–1100 nm | RAW-PLSR | 0.8100 | 3.8100 | [50] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FSR | Firmness–soluble solids ratio |
| FI | Firmness |
| SSC | Soluble solid content |
| MSCNN–LSTM | Multiscale convolutional neural network–long short-term memory |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| PCR | Principal component regression |
| NIR-HSI | Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| RPD | Residual prediction deviation |
| SVR | Support vector regression |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares-discriminant analysis |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
References
- Li, Y.; You, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.; Song, J.; Lan, W.; Tu, K.; Pan, L. Exploring the limit of detection on early implicit bruised ‘Korla’ fragrant pears using hyperspectral imaging features and spectral variables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 208, 112668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, H. Non-destructive quality assessment method for Korla fragrant pears based on electrical properties and adaptive neural-fuzzy inference system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.; Brandão, T.R.S.; Cassoni, C.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Ferrante, A.; Pintado, M. Firmness prediction of ‘Rocha’ pear based on non-destructive methods and shelf-life using PLS-regression modeling. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 205, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Nondestructive detection of SSC in multiple pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) cultivars using Vis-NIR spectroscopy coupled with the Grad-CAM method. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Hou, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hong, R.; Huang, Y. Pears characteristics (soluble solids content and firmness prediction, varieties) testing methods based on visible-near infrared hyperspectral imaging. Optik 2016, 127, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yao, M. Is this pear sweeter than this apple? A universal SSC model for fruits with similar physicochemical properties. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 226, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasi, S.; Minaei, S.; Jamshidi, B.; Fathi, D.; Khoshtaghaza, M.H. Rapid measurement of apple quality parameters using wavelet de-noising transform with Vis/NIR analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 252, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lu, H.; Wu, D. Development of deep learning method for predicting firmness and soluble solid content of postharvest Korla fragrant pear using Vis/NIR hyperspectral reflectance imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 141, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinobas, L.R.; Ruiz-Altisent, M.; de la Plaza Perez, J.L. Bruise development and fruit response of pear (cv. Blanquilla) under impact conditions. J. Food Eng. 1991, 14, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ruiz, M.; Lu, F.; Kader, A.A. Study of impact and compression damage on Asian pears. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1987, 30, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yin, H.; Liu, Y.D.; Zhang, F.; Yang, A.K.; Su, C.T.; Ou-yang, A.G. Study on qualitative impact damage of yellow peaches using the combined hyperspectral and physicochemical indicators method. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1265, 133407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Ju, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.-G.; Guo, S.; Pan, Z.; Wang, L.; Cheng, T. Construction of spectral detection models to evaluate soluble solids content and acidity in Dangshan pear using two different sensors. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Shen, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, C. Rapid and non-destructive determination of soluble solid content of crown pear by visible/near-infrared spectroscopy with deep learning regression. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Li, J. Nondestructive firmness measurement of the multiple cultivars of pears by Vis-NIR spectroscopy coupled with multivariate calibration analysis and MC-UVE-SPA method. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 104, 103154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yu, X.; Tu, K.; Lan, W.; Pan, L. Evaluating the microstructure and physicochemical properties of ‘Korla’ fragrant pear disease caused by Alternaria alternata: Vis-NIR hyperspectral microscope imaging coupled with convolutional neural network. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 212, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, T.; Faqeerzada, M.A.; Kim, Y.; Pahlawan, M.F.R.; Aline, U.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Cho, B.-K. Hyperspectral imaging with multivariate analysis for detection of exterior flaws for quality evaluation of apples and pears. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 223, 113453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieme, J.; Mollazade, K.; Malounas, I.; Zude-Sasse, M.; Zhao, M.; Gowen, A.; Argyropoulos, D.; Fountas, S.; Van Beek, J. Application of hyperspectral imaging systems and artificial intelligence for quality assessment of fruit, vegetables and mushrooms: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 222, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, C. Visible/near-infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging Facilitate the Rapid Determination of Soluble Solids Content in Fruits. Food Eng. Rev. 2024, 16, 470–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, G.; Dai, C. Soluble Solids Content prediction for Korla fragrant pears using hyperspectral imaging and GsMIA. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J. Nondestructive determination of SSC in Korla fragrant pear using a portable near-infrared spectroscopy system. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 116, 103785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Mei, M.; Diao, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, R.; Cai, Z. Detection of bruising in pear with varying bruising degrees and formation times by using SIRI technique combining with texture feature-based LS-SVM and ResNet-18-based CNN model. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 223, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, K.; Zhao, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Pan, L.; Tu, K. Information fusion of hyperspectral imaging and electronic nose for evaluation of fungal contamination in strawberries during decay. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 153, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, U.; Guha, P.; Mishra, S. Comparison of PLSR, MLR, SVM regression methods for determination of crude protein and carbohydrate content in stored wheat using near Infrared spectroscopy. Mater. Today: Proc. 2022, 48, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhan, B.; Liu, X.; Luo, W. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Nanfeng mandarin quality based on hyperspectral imaging and deep learning. Food Control 2025, 167, 110831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, L.; Fan, S.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, C. Variable Selection in Visible and Near-Infrared Spectral Analysis for Noninvasive Determination of Soluble Solids Content of ‘Ya’ Pear. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, K.; Gao, Z. Phenotyping of navel orange based on hyperspectral imaging technology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 237, 110642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, S.; An, T.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, W. Detection of Insect-Damaged Maize Seed Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Hybrid 1D-CNN-BiLSTM Model. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 137, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Lin, T.; Ying, Y. Food and agro-product quality evaluation based on spectroscopy and deep learning: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuquimarca, L.E.; Vintimilla, B.X.; Velastin, S.A. A review of external quality inspection for fruit grading using CNN models. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2024, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhu, R.; Yuan, H.; Song, C. Rapid quantitative analysis of cotton-polyester blended fabrics using near-infrared spectroscopy combined with CNN-LSTM. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, G.; Wu, Z. A graph convolutional LSTM approach for modeling nonlinear chemical process networks using spatial–temporal data. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2025, 201, 109242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Luo, J.; Tian, Q.; Li, J.; Cao, M.; Yang, S.; Guo, W. Nondestructive detection of internal quality in multiple peach varieties by Vis/NIR spectroscopy with multi-task CNN method. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 227, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sirisomboon, P.; Sumech, K.C.; Terdwongworakul, A.; Phetpan, K.; Kshetri, T.B.; Sangwanangkul, P. Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging combined with machine learning for physicochemical-based quality evaluation of durian pulp. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 200, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B. Accurate prediction of soluble solid content of apples from multiple geographical regions by combining deep learning with spectral fingerprint features. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Tian, T.; Cui, J.; Shi, X.; Song, J.; Li, T.; Li, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, W. Construction of spectral index based on multi-angle spectral data for estimating cotton leaf nitrogen concentration. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 201, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, M.; Mavaddati, S.; Koohi, H. ResNet deep models and transfer learning technique for classification and quality detection of rice cultivars. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 247, 123276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, P.; Raja, P.; Natarajan, S. MangoYieldNet: Fruit yield estimation for mango orchards using DeepLabv3+ with ResNet18 architecture. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2025, 84, 41329–41351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Dai, M.; Li, A.; Liang, Y.; Lu, W.; Zeng, J.; Peng, J.; Tian, J.; Chen, M. CLNet: A fusion network capturing spectral features and wavelength relationships for predicting sorghum protein and moisture content. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 142, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, N.; Othman, M.F.; Abdoulghafor, R.; Belhaouari, S.B.; Mamat, N.; Mohd Hussein, S.F. Advanced Technology in Agriculture Industry by Implementing Image Annotation Technique and Deep Learning Approach: A Review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Jayan, H.; Majeed, U.; Ashiagbor, K.; Jiang, S.; Zou, X. Multi-sensor fusion and deep learning for batch monitoring and real-time warning of apple spoilage. Food Control 2025, 172, 111174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X. Marine diesel engine piston ring fault diagnosis based on LSTM and improved beluga whale optimization. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 109, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunny, S.S.; Kurniawan, H.; Amanah, H.Z.; Baek, I.; Kim, M.S.; Chan, D.; Faqeerzada, M.A.; Wakholi, C.; Cho, B.-K. Hyperspectral imaging techniques for detection of foreign materials from fresh-cut vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 201, 112373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Lu, Y.; Stafne, E. Fusing spectral and spatial features of hyperspectral reflectance imagery for differentiating between normal and defective blueberries. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, L.; Li, R. Nondestructive detection of frying times for soybean oil by NIR-spectroscopy technology with Adaboost-SVM (RBF). Optik 2020, 206, 164248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, S.; Pan, L.; Huang, M.; Zhu, Q. Predictions of multiple food quality parameters using near-infrared spectroscopy with a novel multi-task genetic programming approach. Food Control 2023, 144, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, C.; Majeed, U.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; Zou, X. Optical properties of multilayered tissues of different varieties of apples and inspection models of internal quality. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 146, 107942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Gu, S.; Xu, J.; Jia, B.; Ye, Z.; Heng, W.; Jin, X. An early asymptomatic diagnosis method for cork spot disorder in ‘Akizuki’ pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) using micro near infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem X 2023, 19, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Xuan, G.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Liu, L. Determination of the bruise degree for cherry using Vis-NIR reflection spectroscopy coupled with multivariate analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, K.B.; McGlone, V.A.; Han, D.H. The uses of near infra-red spectroscopy in postharvest decision support: A review. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 163, 111139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Ji, T.; Cao, M.; Guo, W. Generation of fruit’s spectra with hundreds of wavelengths from obtained multi-spectra and spectral application using deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 210, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, K.; Hu, D. Assessment of firmness and soluble solids content of peaches by spatially resolved spectroscopy with a spectral difference technique. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Yao, K.; Zhou, X. Simultaneous detection for storage condition and storage time of yellow peach under different storage conditions using hyperspectral imaging with multi-target characteristic selection and multi-task model. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, G.; He, F. Nondestructive Analysis of Internal Quality in Pears with a Self-Made Near-Infrared Spectrum Detector Combined with Multivariate Data Processing. Foods 2021, 10, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sheng, X.; Zan, J.; Yuan, H.; Zong, X.; Jiang, Y. Monitoring the dynamic change of catechins in black tea drying by using near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 119, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fan, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, C.; Qing, R.; Li, K.; Kang, Z. Combining hyperspectral imaging technology and visible-near infrared spectroscopy with a data fusion strategy for the detection of soluble solids content in apples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 137, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, A.A.; Zulfahrizal; Meilina, H.; Pawelzik, E. Near infrared spectroscopy as a fast and non-destructive technique for total acidity prediction of intact mango: Comparison among regression approaches. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, W.; Chen, Y.; Huo, D.; Chao, K. Nondestructive detection of nutritional parameters of pork based on NIR hyperspectral imaging technique. Meat Sci. 2023, 202, 109204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jin, C.; Zhai, Y.; Pu, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, C. Simultaneous detection of citrus internal quality attributes using near-infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging with multi-task deep learning and instrumental transfer learning. Food Chem. 2025, 481, 143996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Efficient extraction of deep image features using convolutional neural network (CNN) for applications in detecting and analysing complex food matrices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.; Tammineni, D.K.; Rana, P.; Sharma, M.; Sridhar, K.; Chen, H.-H. Computer vision and deep learning-based approaches for detection of food nutrients/nutrition: New insights and advances. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chai, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Ren, Z.; Dong, H.; Chen, L. Quantitative predictions of protein and total flavonoids content in Tartary and common buckwheat using near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 141033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, J.-X.; Luo, S.-H.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.-L.; Hui, A.-L.; Liang, F.-X.; Wu, C.-Y.; Wang, L.; et al. An improved 1D CNN with multi-sensor spectral fusion for Detection of SSC in pears. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 144, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Ren, Z. Prediction of prunoideae fruit quality characteristics based on machine learning and spectral characteristic acquisition optimization. Food Control 2024, 165, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, G.; Gao, C.; Shao, Y. Spectral and image analysis of hyperspectral data for internal and external quality assessment of peach fruit. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 272, 121016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Ren, Z. Apple firmness detection method based on hyperspectral technology. Food Control 2024, 166, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Indicator | Statistic | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI (N) | Minimum | 10.97 | 9.58 | 7.99 | 6.90 | 6.75 |
| Maximum | 16.63 | 14.09 | 12.13 | 10.42 | 9.55 | |
| Mean | 13.98 | 11.42 | 10.09 | 8.43 | 8.03 | |
| Standard deviation | 1.24 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.75 | |
| SSC (%) | Minimum | 7.13 | 10.23 | 12.00 | 10.80 | 10.37 |
| Maximum | 12.10 | 14.53 | 17.00 | 15.10 | 14.50 | |
| Mean | 9.13 | 12.87 | 14.55 | 13.22 | 12.51 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 1.02 | 0.99 | |
| FSR | Minimum | 0.99 | 0.70 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.50 |
| Maximum | 2.22 | 1.23 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.87 | |
| Mean | 1.55 | 0.89 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.65 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Index | Model | Calibration Set | Prediction Set | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRD | ||||||
| FI (N) | SVR | 0.7740 | 1.0678 | 0.7853 | 1.2777 | 2.1581 |
| PLSR | 0.7768 | 1.0612 | 0.8355 | 1.1183 | 2.4658 | |
| PCR | 0.8220 | 0.9477 | 0.8612 | 1.0275 | 2.6837 | |
| MSCNN | 0.8869 | 0.7553 | 0.8506 | 1.0657 | 2.5873 | |
| Resnet18 | 0.9922 | 0.1987 | 0.8712 | 0.9895 | 2.7867 | |
| MSCNN–LSTM | 0.9215 | 0.6296 | 0.8934 | 0.9001 | 3.0634 | |
| SSC (%) | SVR | 0.8009 | 0.8743 | 0.7189 | 1.1853 | 1.8893 |
| PLSR | 0.7279 | 1.0221 | 0.7275 | 1.1689 | 1.9158 | |
| PCR | 0.7759 | 0.9274 | 0.7860 | 1.0359 | 2.1616 | |
| MSCNN | 0.8815 | 0.6744 | 0.8581 | 0.8437 | 2.6542 | |
| Resnet18 | 0.9949 | 0.1400 | 0.8591 | 0.8404 | 2.6645 | |
| MSCNN–LSTM | 0.8690 | 0.7092 | 0.8731 | 0.7976 | 2.8076 | |
| FSR | SVR | 0.9003 | 0.1073 | 0.8378 | 0.1810 | 2.4829 |
| PLSR | 0.8254 | 0.1419 | 0.7949 | 0.2035 | 2.2082 | |
| PCR | 0.8495 | 0.1318 | 0.8317 | 0.1844 | 2.4374 | |
| MSCNN | 0.8996 | 0.1076 | 0.8357 | 0.1822 | 2.4671 | |
| Resnet18 | 0.9859 | 0.0403 | 0.8539 | 0.1718 | 2.6159 | |
| MSCNN–LSTM | 0.9574 | 0.0701 | 0.8610 | 0.1676 | 2.6825 | |
| Model | Training Set | Test Set | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | |
| LDA | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| PLS-DA | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| SVM | 99.75 ± 0.08 | 99.75 ± 0.08 | 99.75 ± 0.08 | 99.75 ± 0.08 | 99.00 ± 0.62 | 99.05 ± 0.59 | 99.00 ± 0.62 | 99.00 ± 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Quality and Maturity Detection of Korla Fragrant Pears via Integrating Hyperspectral Imaging with Multiscale CNN–LSTM. Foods 2025, 14, 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203561
Long Z, Wang T, Zhang Z, Liu Y. Quality and Maturity Detection of Korla Fragrant Pears via Integrating Hyperspectral Imaging with Multiscale CNN–LSTM. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203561
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Zhengbao, Tongzhao Wang, Zhijuan Zhang, and Yuanyuan Liu. 2025. "Quality and Maturity Detection of Korla Fragrant Pears via Integrating Hyperspectral Imaging with Multiscale CNN–LSTM" Foods 14, no. 20: 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203561
APA StyleLong, Z., Wang, T., Zhang, Z., & Liu, Y. (2025). Quality and Maturity Detection of Korla Fragrant Pears via Integrating Hyperspectral Imaging with Multiscale CNN–LSTM. Foods, 14(20), 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203561




