Tailoring Interfacial Activity of pH-Driven Shellac–Chitosan Nanocomposites via Solution Addition Sequence for Pickering Emulsion Stabilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SH-CS Nanocomposites
2.3. Turbidity and Zeta Potential at Different pH Levels
2.4. Effect of Composition Ratio on Nanocomposite Properties
2.4.1. Turbidity
2.4.2. Particle Size, PDI, and Zeta Potential
2.4.3. Dispersed Fraction After Storage
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.7. Dissociation Experiment
2.8. Interfacial Activity
2.8.1. Three-Phase Contact Angle
2.8.2. Interfacial Tension
2.9. Emulsification Performance
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
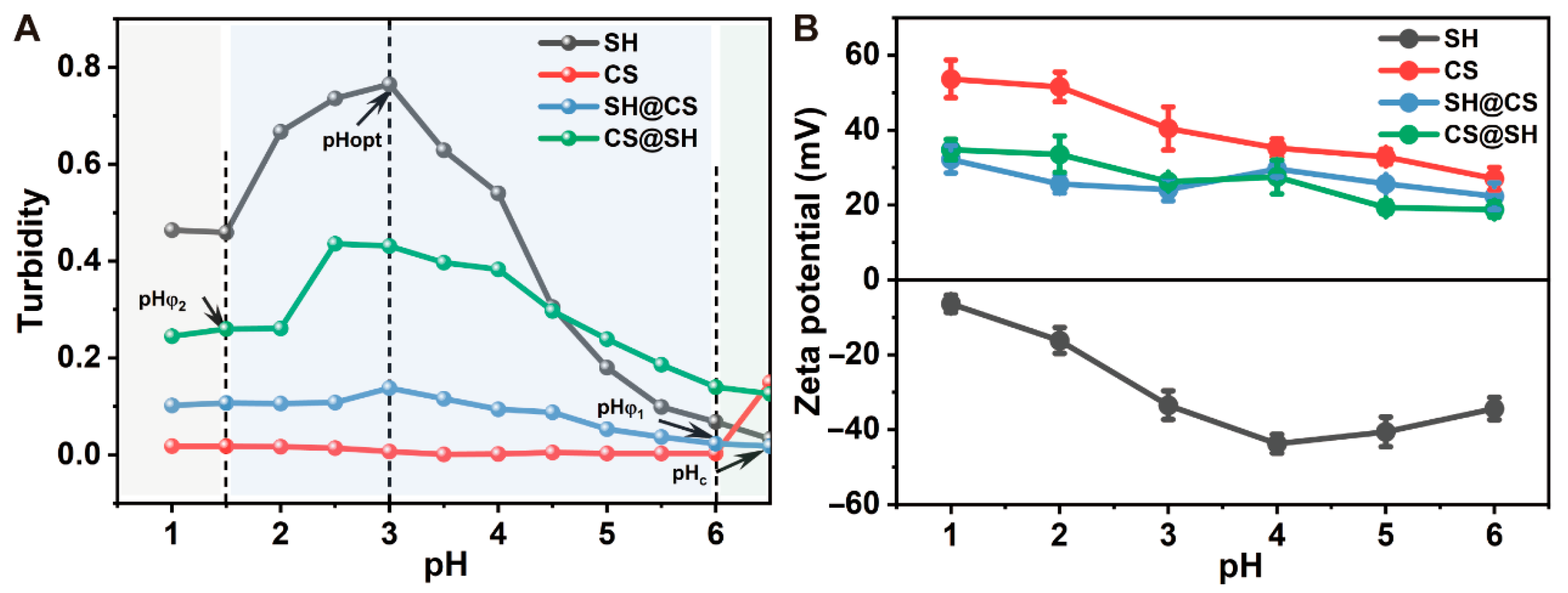
3.1. Effect of pH on the Formation of Nanocomposites
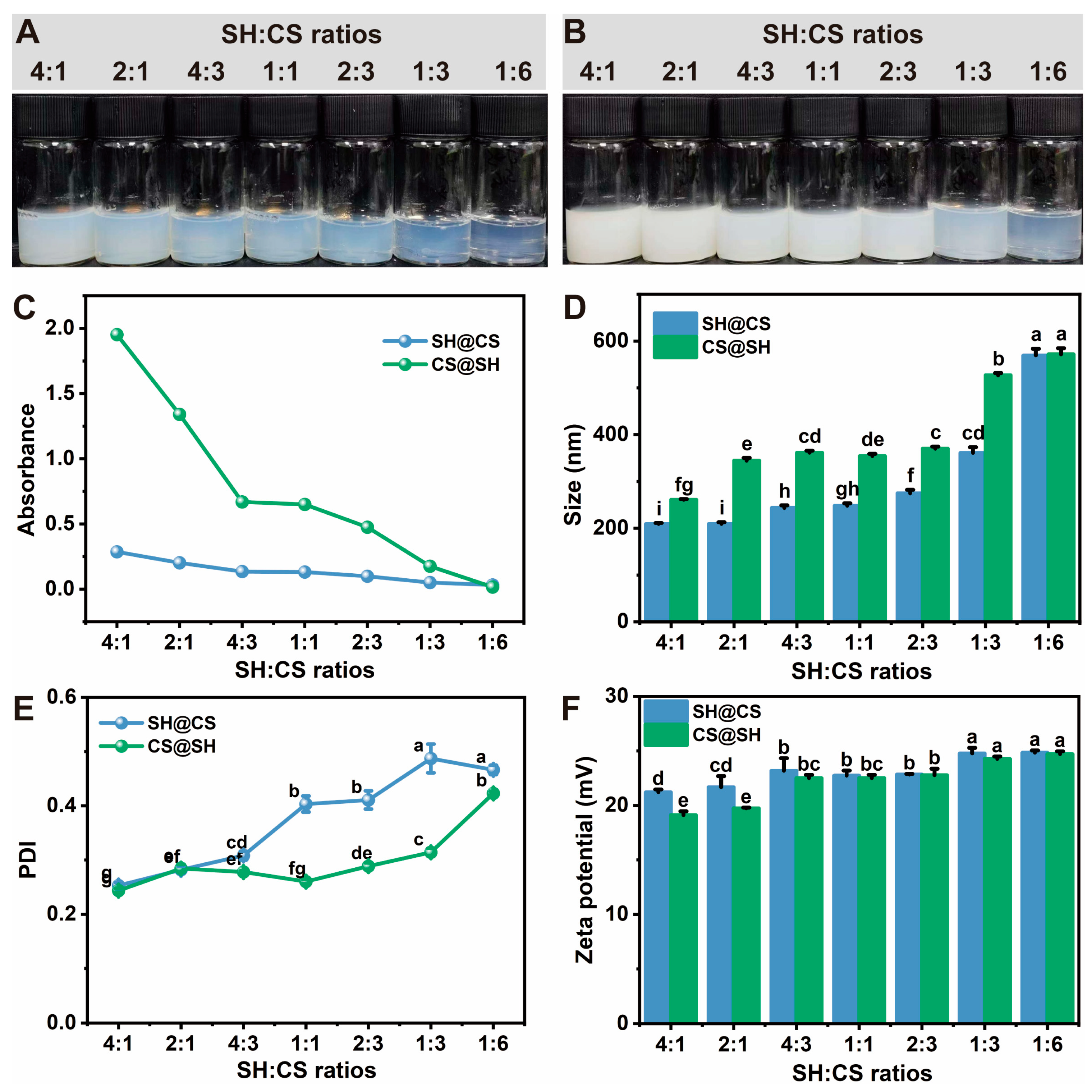
3.2. Effect of Composition Ratio on the Performance of Nanocomposites
3.2.1. Turbidity, Particle Size, PDI, and Zeta Potential
3.2.2. Sedimentation Tendency of Nanocomposites After Storage
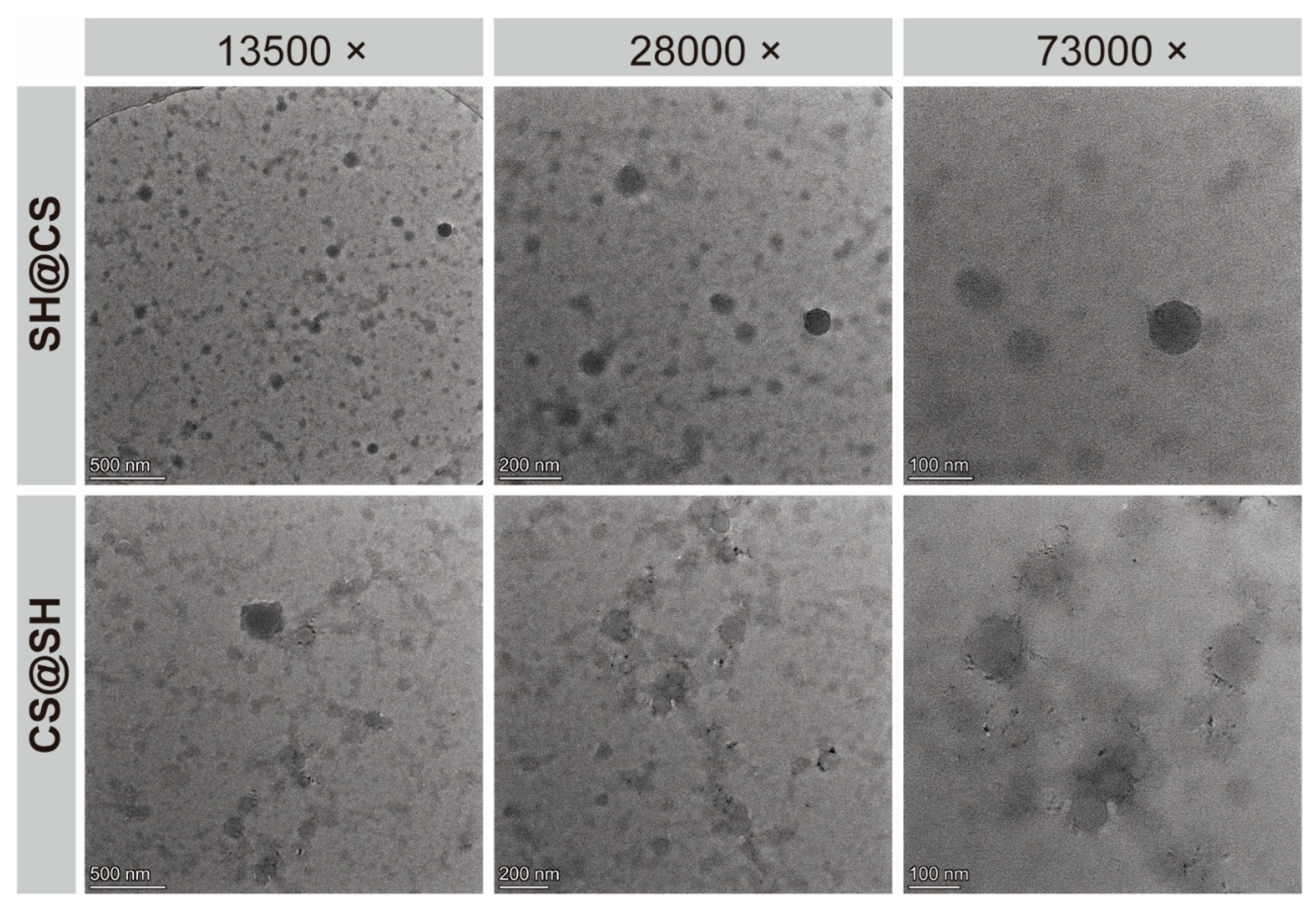
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
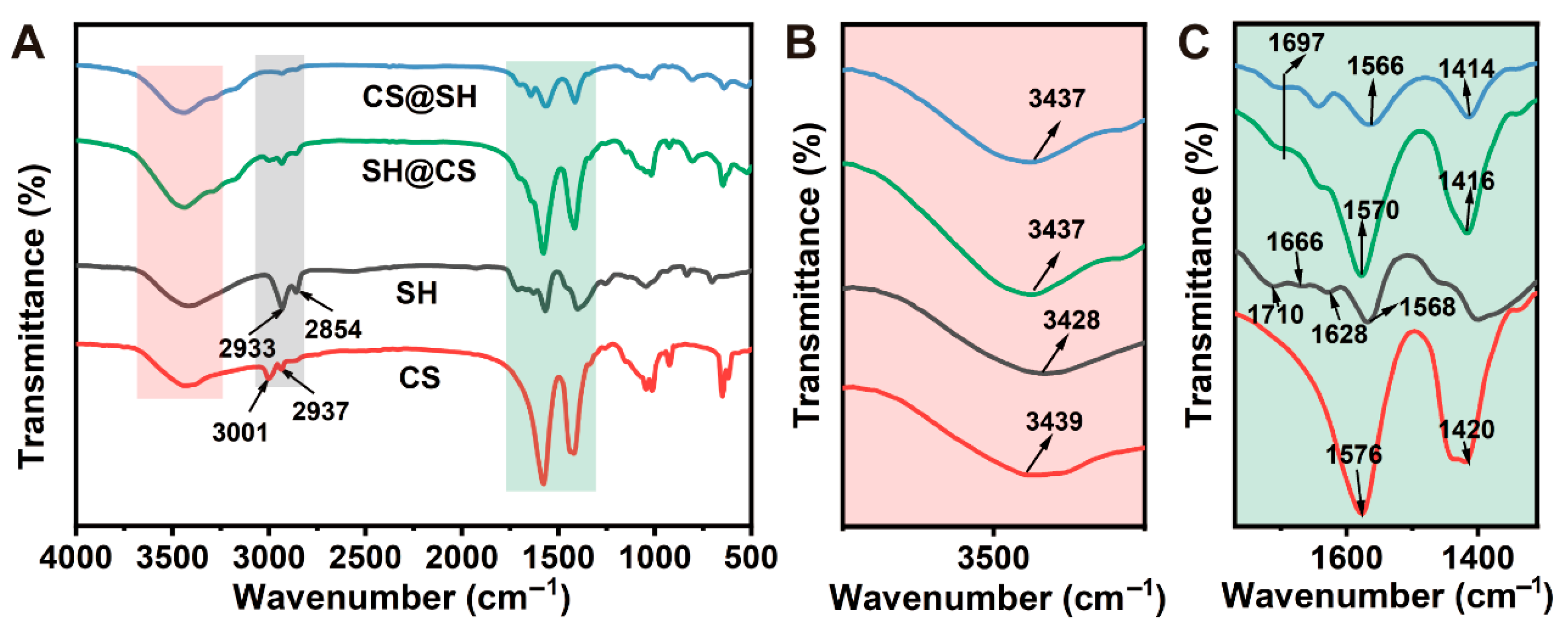
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.5. Molecular Interaction Analysis
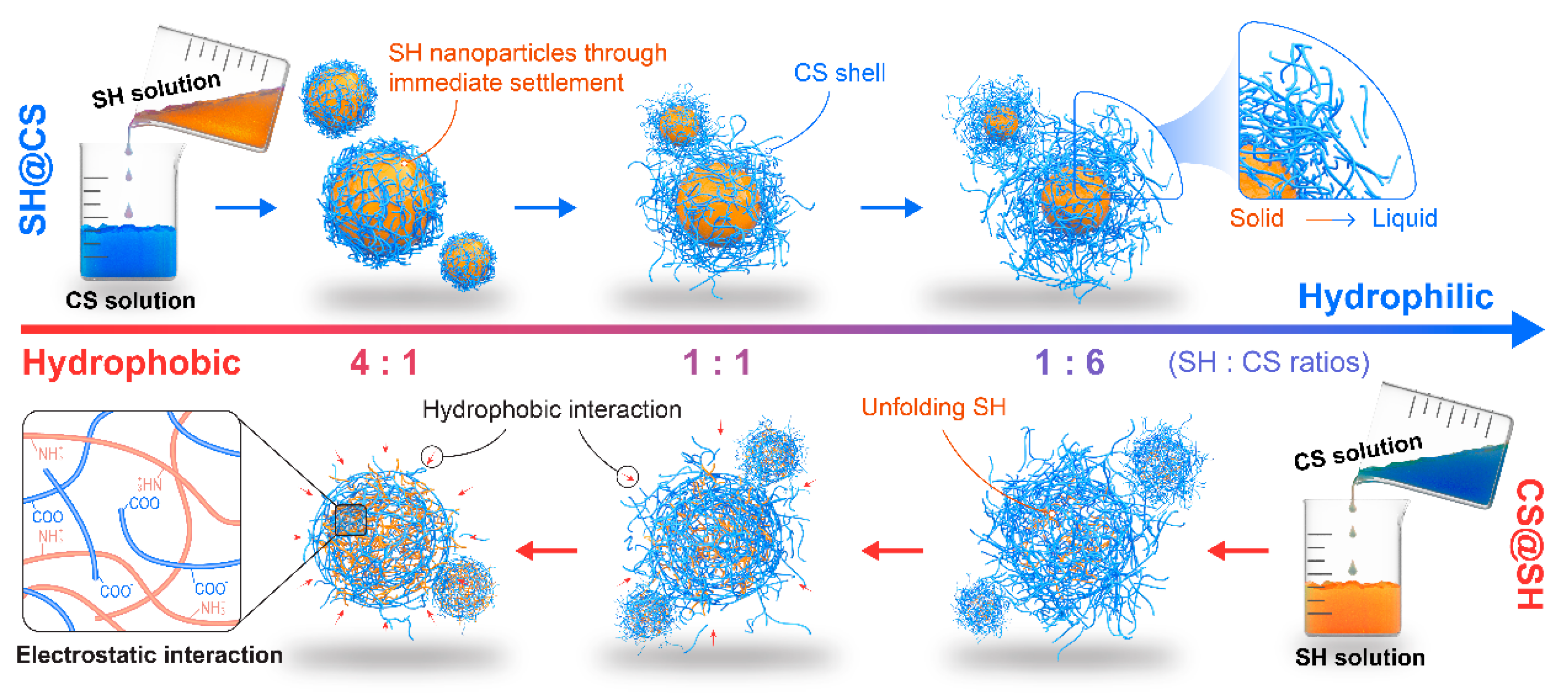
3.6. Potential Mechanism of Nanocomposite Formation
3.7. Interface Properties
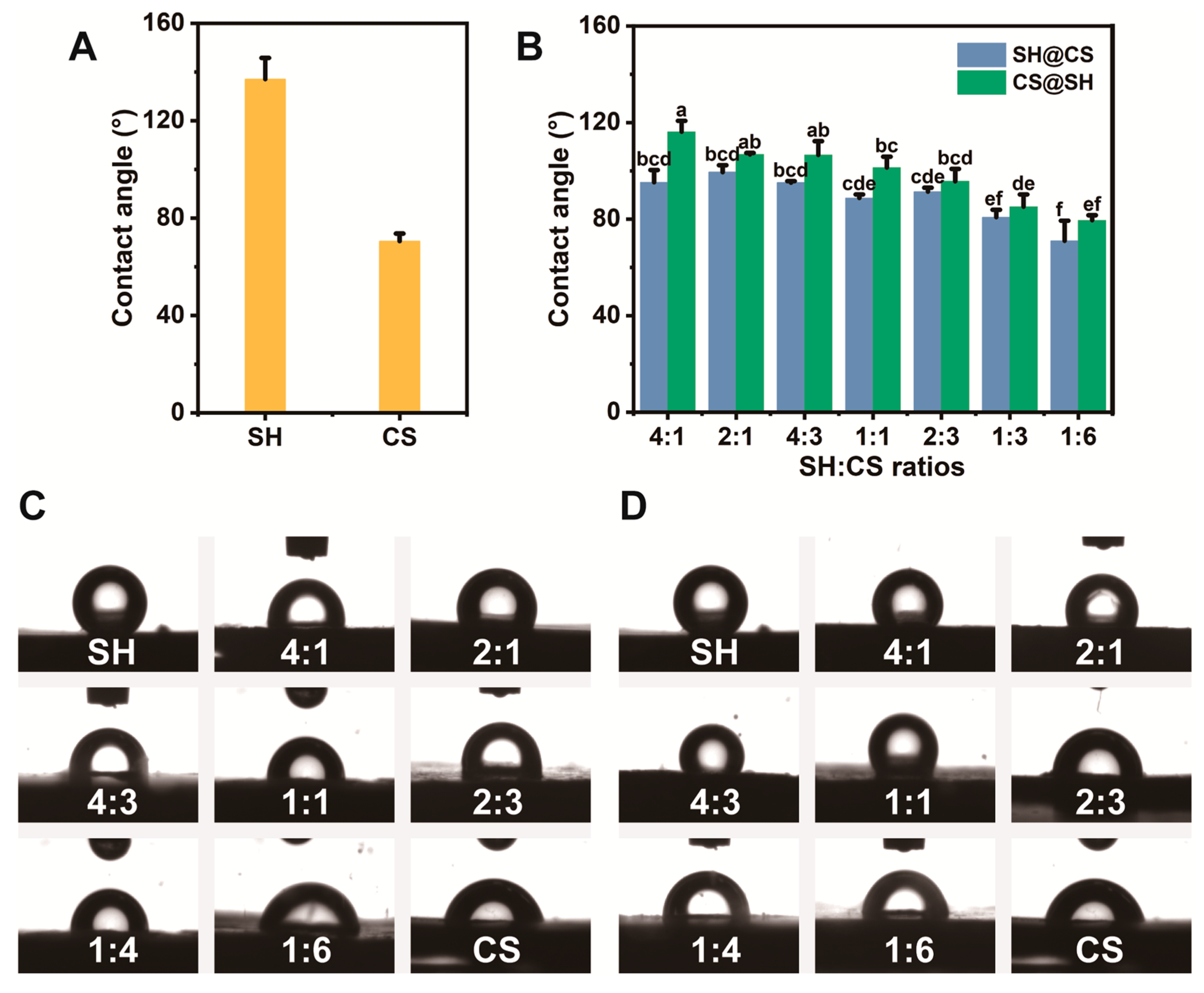
3.7.1. Three-Phase Contact Angle Analysis
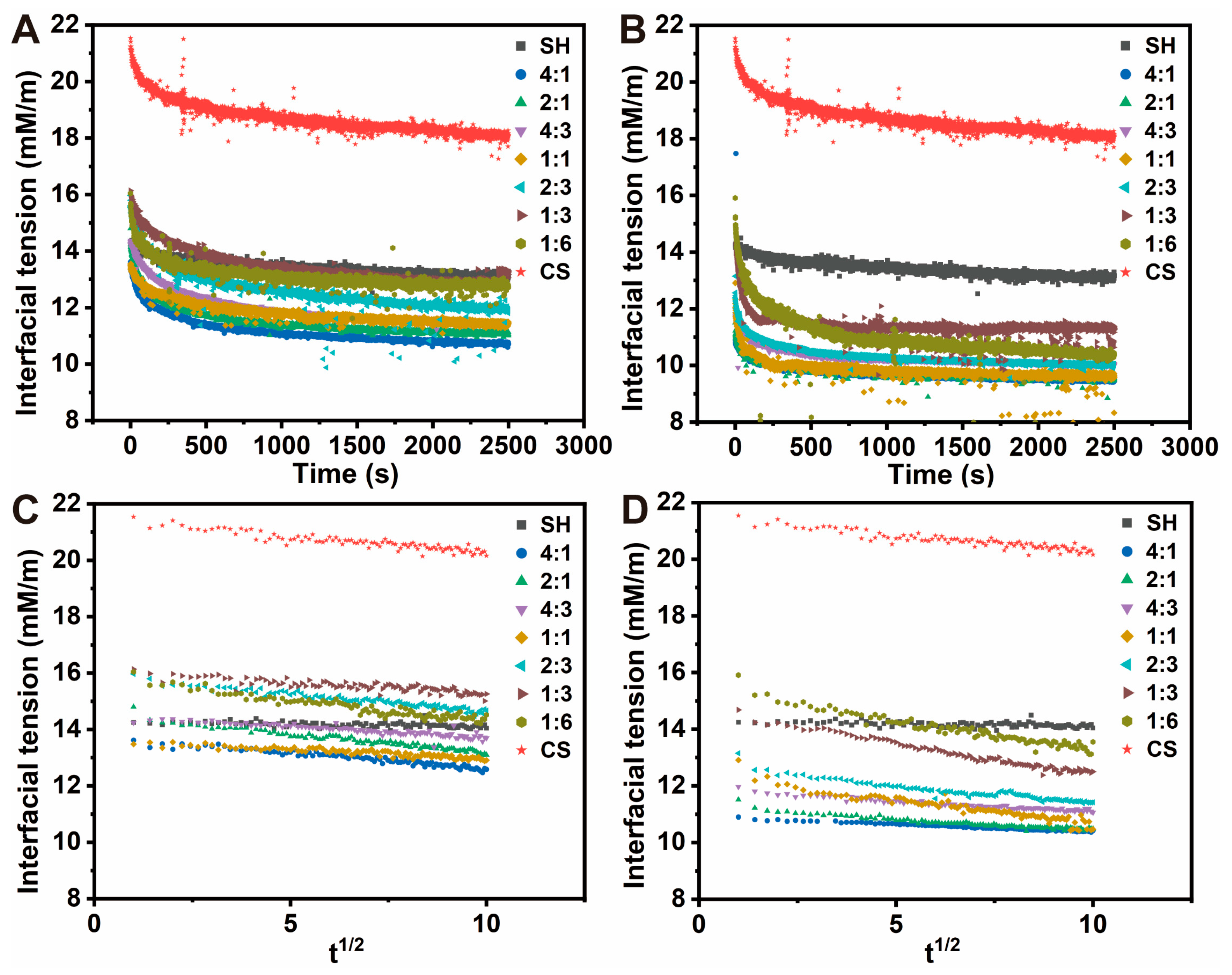
3.7.2. Interfacial Tension Analysis
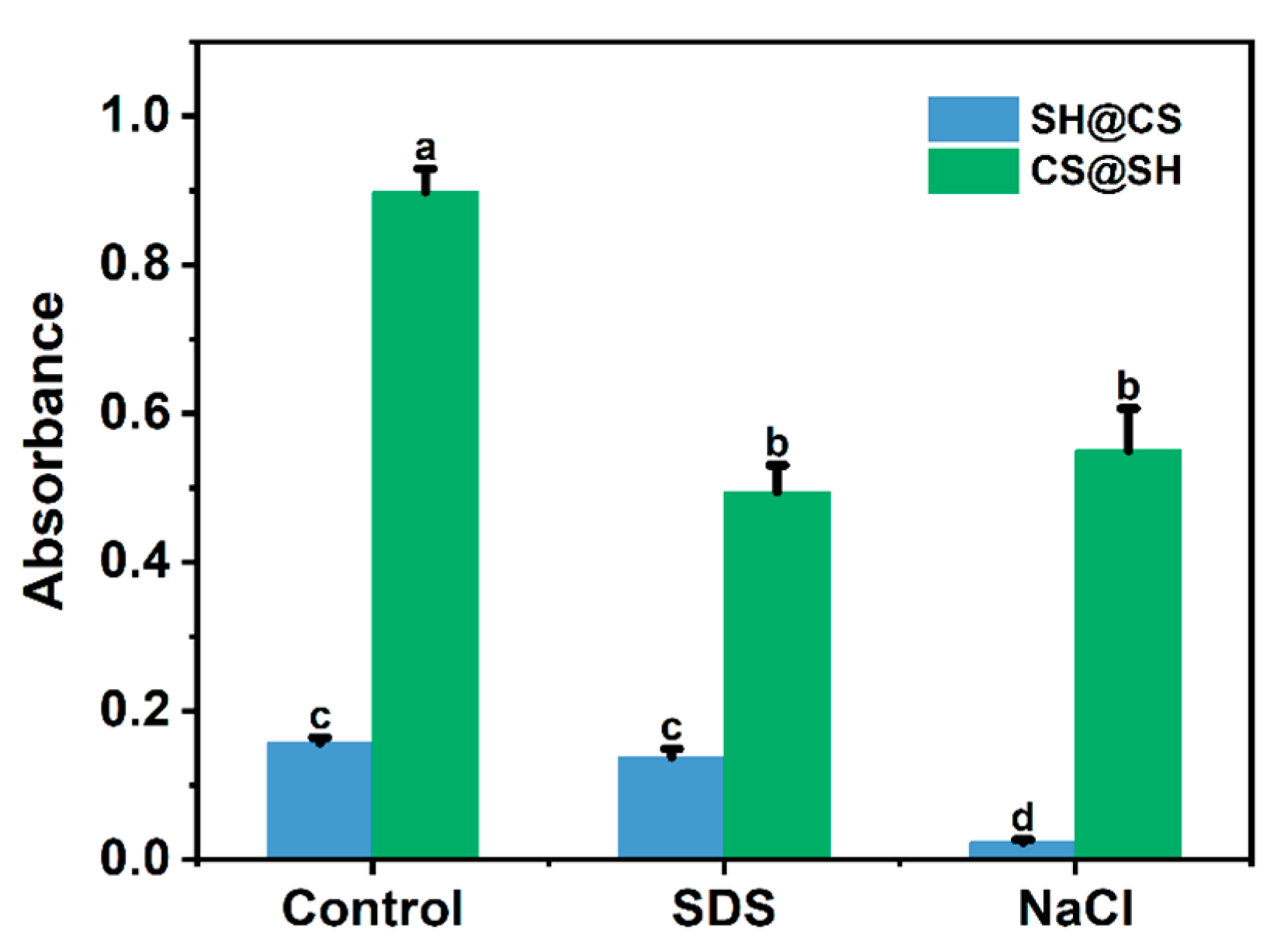
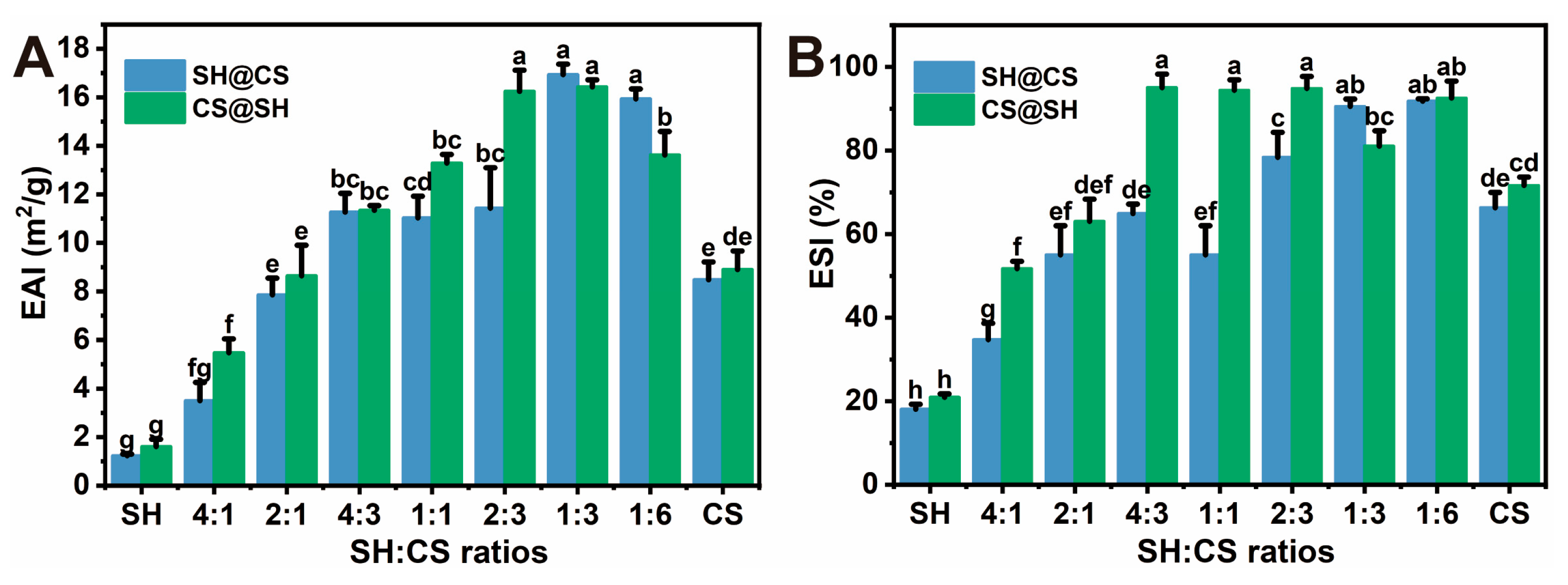
3.8. Emulsification Properties
3.9. Potential Food Industry Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, T.; Qiao, G.; Chen, X.-W. Fabrication of complex interface and pH-switchable Pickering emulsions prepared by electrostatic associative of zein nanoparticles with QS-coated nanodroplets. Food Hydrocoll. 2026, 170, 111737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.K.M.M.; Cai, Q.; Manir, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Fang, L.; Mamun, M.A.; Chowdhury, M.N.K.; Cai, X.; Musiol, R.; Shubhra, Q.T.H. Shellac: A Sustainable Natural Bio-Resin for Emerging Biomedical and Technological Applications—Properties, Modifications, and Challenges. Polym. Rev. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Ortiz, D.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Cambedouzou, J.; Bechelany, M.; Miele, P. Current Trends in Pickering Emulsions: Particle Morphology and Applications. Engineering 2020, 6, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Lin, Y.; Tian, J.; Cai, J.; Hao, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H. Tea tree oil Pickering emulsions stabilized by sodium lignosulfonate-zein covalent conjugate for fungicide delivery and enhanced control efficacy against peanut sclerotium blight. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 513, 162876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, W.; Liang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W. High inner phase emulsion of fish oil stabilized with rutin-grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) myofibrillar protein: Application as a fat substitute in surimi gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Du, P.; Dong, P.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, W.; Feng, C.; et al. Synergistic effect of dextran and ergosterol: A venue for fabricating a water-in-oil pickering emulsion gel as a solid fat substitute in cream cheese. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 164, 111188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Weiss, J.; Ahmad, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. A review of recent progress on high internal-phase Pickering emulsions in food science. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Li, X.; Zhai, J.; Su, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Stability of protein particle based Pickering emulsions in various environments: Review on strategies to inhibit coalescence and oxidation. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K. Recent progress on Pickering emulsions stabilized by polysaccharides-based micro/nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 296, 102522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; He, N.; Xue, Q.; Guo, Q.; Dong, L.; Haruna, M.H.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Li, L. Shellac: A promising natural polymer in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; He, N.; Dong, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Li, L. Multiscale Shellac-Based Delivery Systems: From Macro- to Nanoscale. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18794–18821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, A.; Wu, C.; Hei, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Jiao, B.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, Q. Natural Amphiphilic Shellac Nanoparticle-Stabilized Novel Pickering Emulsions with Droplets and Bi-continuous Structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 57350–57361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Amstad, E.; Zhao, C.-X.; Cai, L.; Fan, J.; Chen, Q.; Hai, M.; Koehler, S.; Zhang, H.; Liang, F.; et al. Biocompatible Amphiphilic Hydrogel–Solid Dimer Particles as Colloidal Surfactants. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11978–11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, F.; Wu, B.; Shao, B.; Li, Z.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Liu, K. Biocompatible and pH-Responsive Colloidal Surfactants with Tunable Shape for Controlled Interfacial Curvature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9365–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmar, K.; Bianco-Peled, H. Shellac-based nanoparticles provide highly stable Pickering emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 141941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; Fang, M.; Liu, X.; Gong, Z. Preparation of shellac nanoparticles-chitosan complexes stabilized Pickering emulsion gels and its application in β-carotene delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yan, R.; He, Y.; Yang, B.; Zheng, K.; Guan, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Ca2+ induced irregular spherical oat protein-shellac nanoparticles as Pickering emulsions stabilizer to improve emulsion storage stability. Food Chem. 2025, 480, 143975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Bhutto, R.; Hira Bhutto, N.U.A.; Wang, M.; Iqbal, S.; Yi, J. Curcumin-loaded Pickering emulsion stabilized by pH-induced self-aggregated chitosan particles: Effects of degree of deacetylation and molecular weight. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, V.K.; Amiri, H.; Pan, J.; Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Rajaei, A. Recent developments in improving the emulsifying properties of chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y. Water-in-oil Pickering emulsions stabilized by phytosterol/chitosan complex particles. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 657, 130489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Yin, S.-W.; Wu, L.-Y.; Qi, J.-R.; Guo, J.; Yang, X.-Q. Fabrication and characterization of Pickering emulsions and oil gels stabilized by highly charged zein/chitosan complex particles (ZCCPs). Food Chem. 2016, 213, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, Q. Edible Pickering emulsions stabilized by ovotransferrin–gum arabic particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Ge, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Li, W. Assembly mechanism of glycosylated soybean protein isolate-chitosan nanocomposite particles and its Pickering emulsion construction for stabilization of Alpinia galanga essential oil: A mechanistic investigation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 217, 118869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Yu, D.; Ban, Q. Stabilization mechanisms and digestion properties of Pickering emulsions prepared with tempo-oxidized hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanoparticles: From the perspective of oxidation degree. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Qin, L.; Niu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, M. Maintained particulate integrity of soy protein nanoparticles during gastrointestinal digestion via genipin crosslinking enhancing stability and bioavailability of curcumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Li, Q.-M.; Pan, L.-H.; Luo, J.-P.; Li, X.-Y.; Zha, X.-Q. Co-assembly of quinoa protein isolate and shellac as nano-vehicles for naringenin: Characterization, formation mechanism, release behavior and cellular uptake. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J. Ultrasonic engineering of bovine serum albumin nanoparticles for high internal phase Pickering emulsions: Interfacial behavior, microstructural evolution and stabilization enhancement. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 121, 107543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, L. Preparation of a novel nanoparticle with extruded soy protein isolate-oat β-glucan: Interfacial properties and mechanism of emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Hua, Y. Emulsifying behaviors and interfacial properties of different protein/gum arabic complexes: Effect of pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Spice aldehydes improve emulsification stability of β-carotene by Schiff base reaction binding sodium caseinate as emulsion surface stabilizer. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Guo, P.; Qu, A.; Liang, W.; Zheng, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. The curcumin-loaded zein-shellac nanoparticles using pH-driven method: Fabrication, characterization, and anti-inflammatory effect. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 125, 106692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chai, J.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Saini, R.K.; Xu, M.; Li, S.; Shang, X. Phase behavior, thermodynamic and rheological properties of ovalbumin/dextran sulfate: Effect of biopolymer ratio and salt concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Roos, Y.H.; Miao, S. Phase behavior and complex coacervation of whey protein isolate-Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Lin, W.; Gao, G.; Zhou, J.; Chen, T.; Ke, L.; Rao, P.; Wang, Q. Purification and characterization of the major protein isolated from Semen Armeniacae Amarum and the properties of its thermally induced nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, D.; Pandey, K.; Singh, A.; Yoo, H. Impact of particle structure on the storage stability and release kinetics of essential oil encapsulated in shellac particle for high-barrier paper coatings for food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 323, 146221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calumba, K.F.; Zhong, Q. Shellac-based microgels for enhanced delivery of Lactobacillus bulgaricus ATCC 11842. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 321, 146358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Meng, Z. pH and CO2/N2 dual responsive Pickering emulsion stabilized by shellac nanoparticle-enzyme conjugates for synthesis of phytosterol esters. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Han, J.; Chen, F.; Gao, C.; Tang, X. Chitosan/gum arabic complexes to stabilize Pickering emulsions: Relationship between the preparation, structure and oil-water interfacial activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Cao, X.; Guan, Y.; Zeng, T.; Li, J. Fabrication of fucoxanthin-loaded composite nanoparticles based on lactoferrin and carboxymethyl chitosan: Interaction mechanism, stability and the application in filled hydrogel beads. Food Res. Int. 2025, 214, 116614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Du, G.; Charrier, B.; Essawy, H.; Pizzi, A.; Liao, J.; et al. Development of novel sustainable lignin nanoparticles-caseinate nanocomposite films with properties for application as food packaging materials. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 167, 111413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Piao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, D. Covalent modulation of zein surface potential by gallic acid to enhance the formation of electrostatic-driven ternary antioxidant complex coacervates with chitosan. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.-C.; Gong, P.-X.; Li, H.-J. Co-assembly of foxtail millet prolamin-lecithin/alginate sodium in citric acid–potassium phosphate buffer for delivery of quercetin. Food Chem. 2022, 381, 132268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Preparation and Characterization of Insulin-Loaded Zein/Carboxymethylated Short-Chain Amylose Complex Nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9335–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y. Emulsifier synergism in aerated emulsions: Coordinated regulation of fat crystallization and protein interfacial adsorption. Food Hydrocoll. 2026, 170, 111725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, X. Improving the interfacial performance of pea protein via mild fractionation for enhanced lubrication behavior in plant-based emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 164, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimaming, N.; Sadeghpour, A.; Murray, B.S.; Sarkar, A. Hybrid particles for stabilization of food-grade Pickering emulsions: Fabrication principles and interfacial properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Feng, J.; Binkley, L.; Tan, L.; Kong, L. Enhancing lutein stability and bioaccessibility with high internal phase emulsions stabilized by octenylsuccinylated starch. Food Front. 2025, 6, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ai, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Teng, H.; Xiao, J.; Chen, L. Emulsion and its application in the food field: An update review. eFood 2023, 4, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xiao, N.; Guo, S.; Ai, M. Egg white grafts weak-gels efficiently stabilize high internal phase emulsions and interfere with lipid hydrolysis: As delivery vehicles for hydrophobic actives. Food Saf. Health 2024, 2, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, L.; Fang, S.; Li, Z.; Hu, R.; Chen, W.; Xiao, J. Development and Textural Property Regulation of Pickering Type Bigel-Based Low-Fat Spread. Food Front. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SH:CS Ratios | The DF of SH-CS Nanocomposites (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| SH@CS | CS@SH | |
| 4:1 | 63.06 ± 4.040 d | 74.41 ± 4.294 c |
| 2:1 | 63.06 ± 4.876 d | 76.48 ± 4.624 c |
| 4:3 | 65.62 ± 2.221 d | 85.33 ± 1.177 b |
| 1:1 | 87.24 ± 4.084 b | 95.65 ± 0.602 a |
| 2:3 | 100.00 ± 0.000 a | 97.54 ± 1.475 a |
| 1:3 | 100.00 ± 0.000 a | 100.00 ± 0.000 a |
| 1:6 | 100.00 ± 0.000 a | 100.00 ± 0.000 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Qu, L.; Zheng, T.; Yang, T.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Tailoring Interfacial Activity of pH-Driven Shellac–Chitosan Nanocomposites via Solution Addition Sequence for Pickering Emulsion Stabilization. Foods 2025, 14, 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203556
Yuan Y, Qu L, Zheng T, Yang T, Liu H, Li Y, Liu S. Tailoring Interfacial Activity of pH-Driven Shellac–Chitosan Nanocomposites via Solution Addition Sequence for Pickering Emulsion Stabilization. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203556
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yi, Luping Qu, Tingyong Zheng, Tangyu Yang, Huan Liu, Yajun Li, and Shutao Liu. 2025. "Tailoring Interfacial Activity of pH-Driven Shellac–Chitosan Nanocomposites via Solution Addition Sequence for Pickering Emulsion Stabilization" Foods 14, no. 20: 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203556
APA StyleYuan, Y., Qu, L., Zheng, T., Yang, T., Liu, H., Li, Y., & Liu, S. (2025). Tailoring Interfacial Activity of pH-Driven Shellac–Chitosan Nanocomposites via Solution Addition Sequence for Pickering Emulsion Stabilization. Foods, 14(20), 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203556






