Alterations in Biochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community During the Storage of Suancai
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Suancai
2.2. Determination of Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Determination of Non-Volatile Compounds
2.3.1. Organic Acids
2.3.2. Free Amino Acids
2.3.3. Biogenic Amines
2.3.4. Taste Activity Value
2.4. Determination of Volatile Compounds
2.5. DNA Extraction and Sequence Analysis of Microorganisms
2.5.1. DNA Extraction of Microorganisms
2.5.2. Sequence Data Analysis
2.6. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Analysis of Non-Volatile Compounds
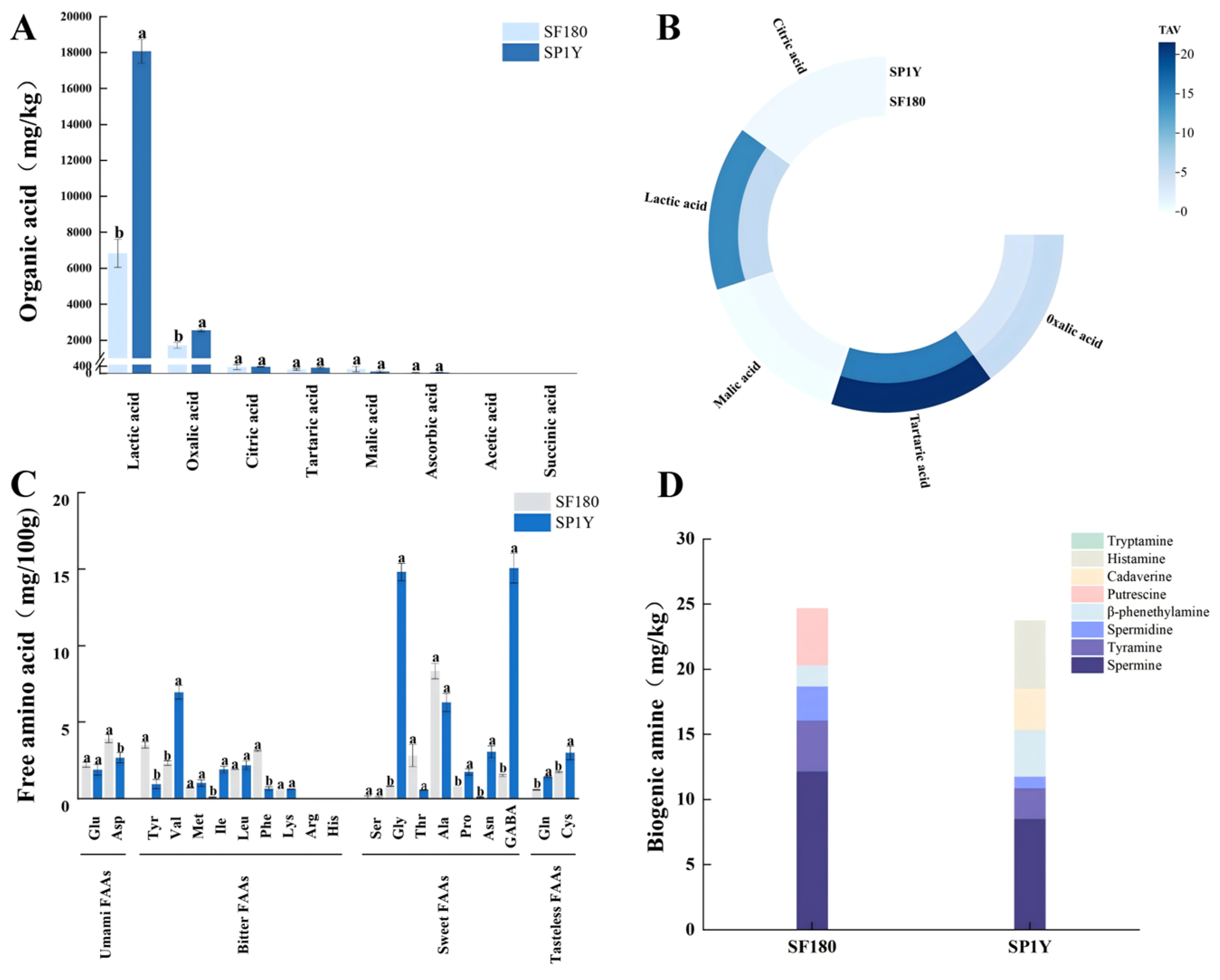
3.2.1. Organic Acids
3.2.2. Free Amino Acids
3.2.3. Biogenic Amines
3.3. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
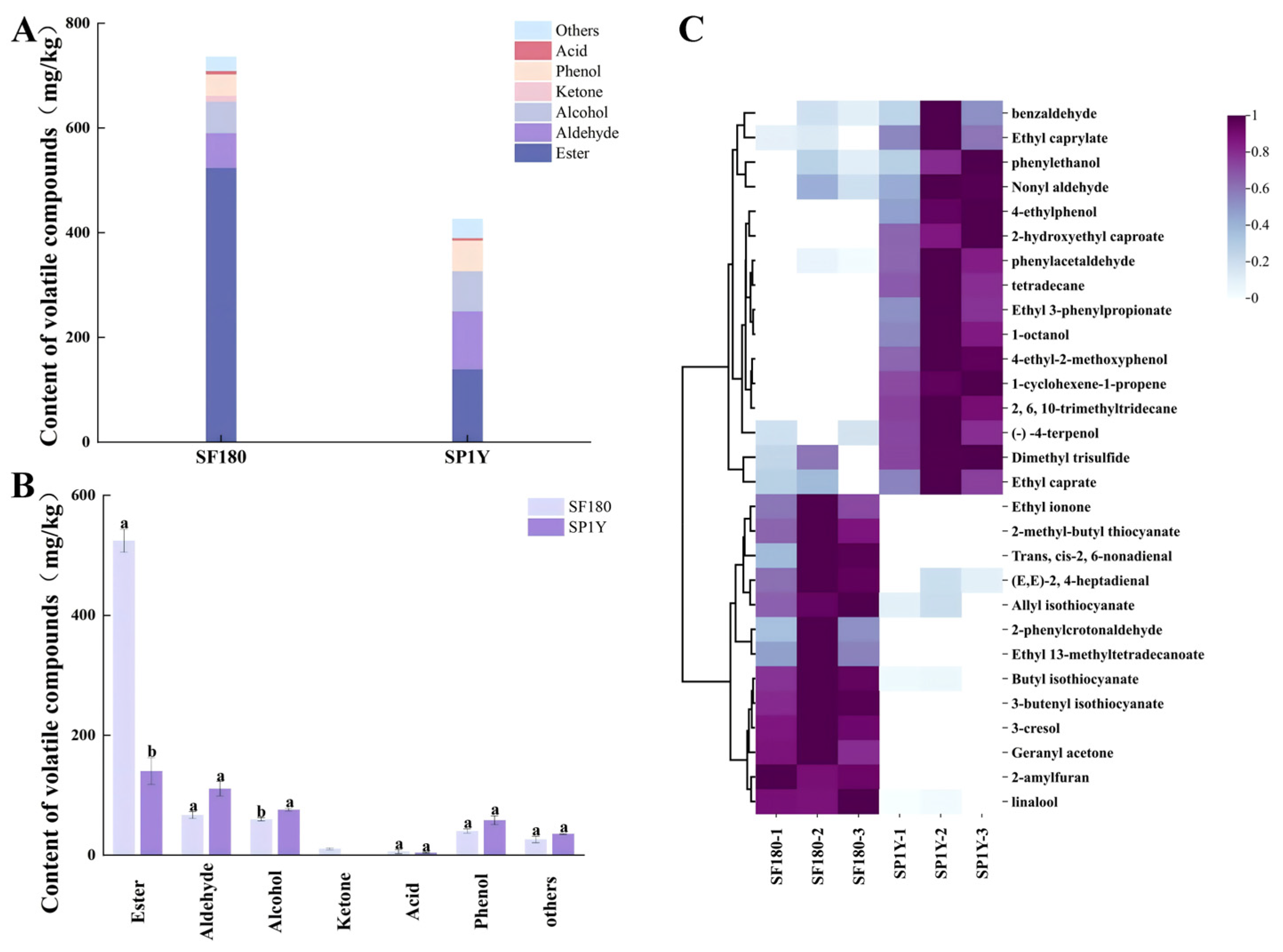
3.3.1. Qualitative Analysis of Volatile Flavor Compounds
3.3.2. Analysis of Differential Volatile Compounds
3.4. Analysis of Microbial Diversity
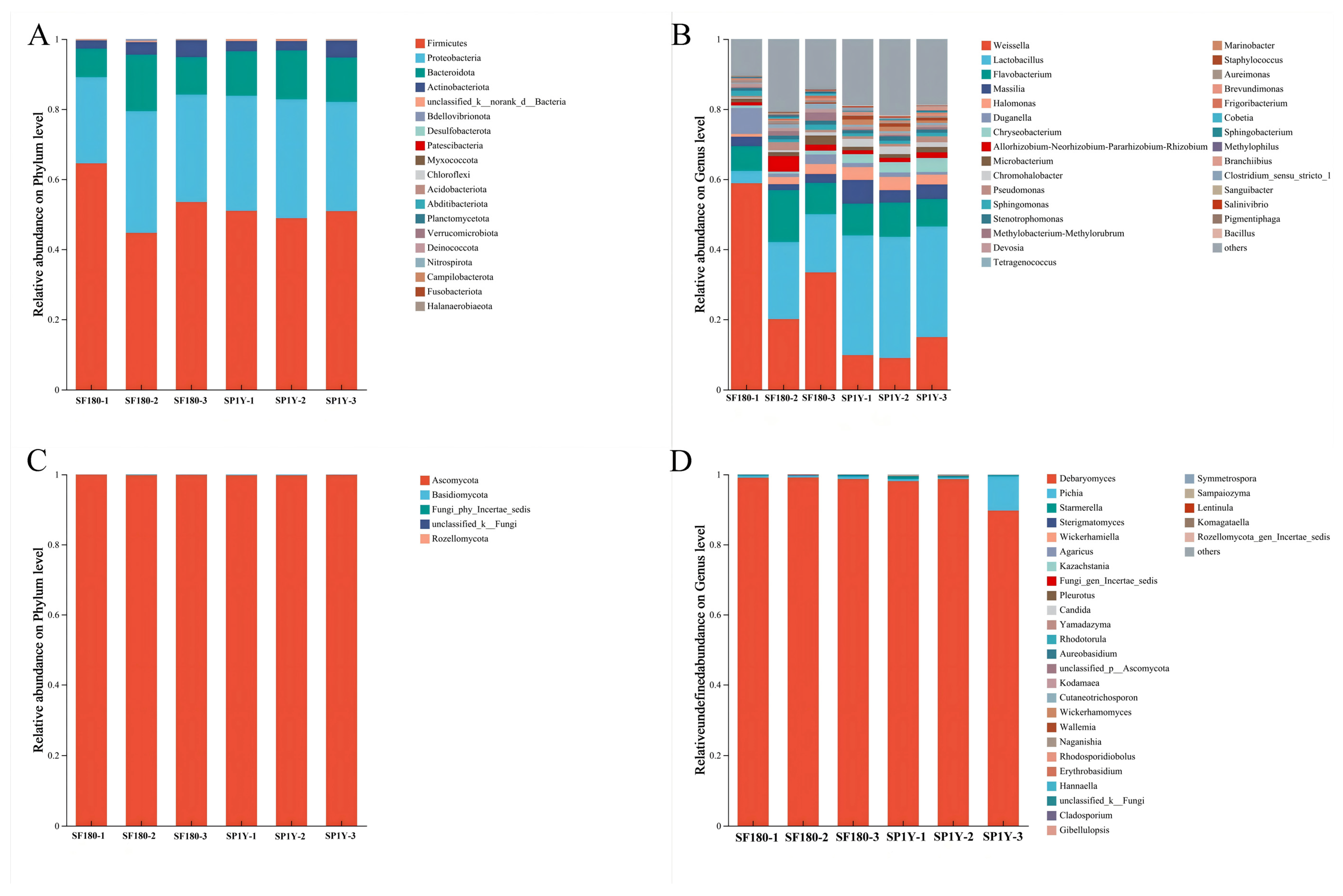
3.4.1. Succession of Bacterial and Fungal Communities
3.4.2. Analysis of Species Differences
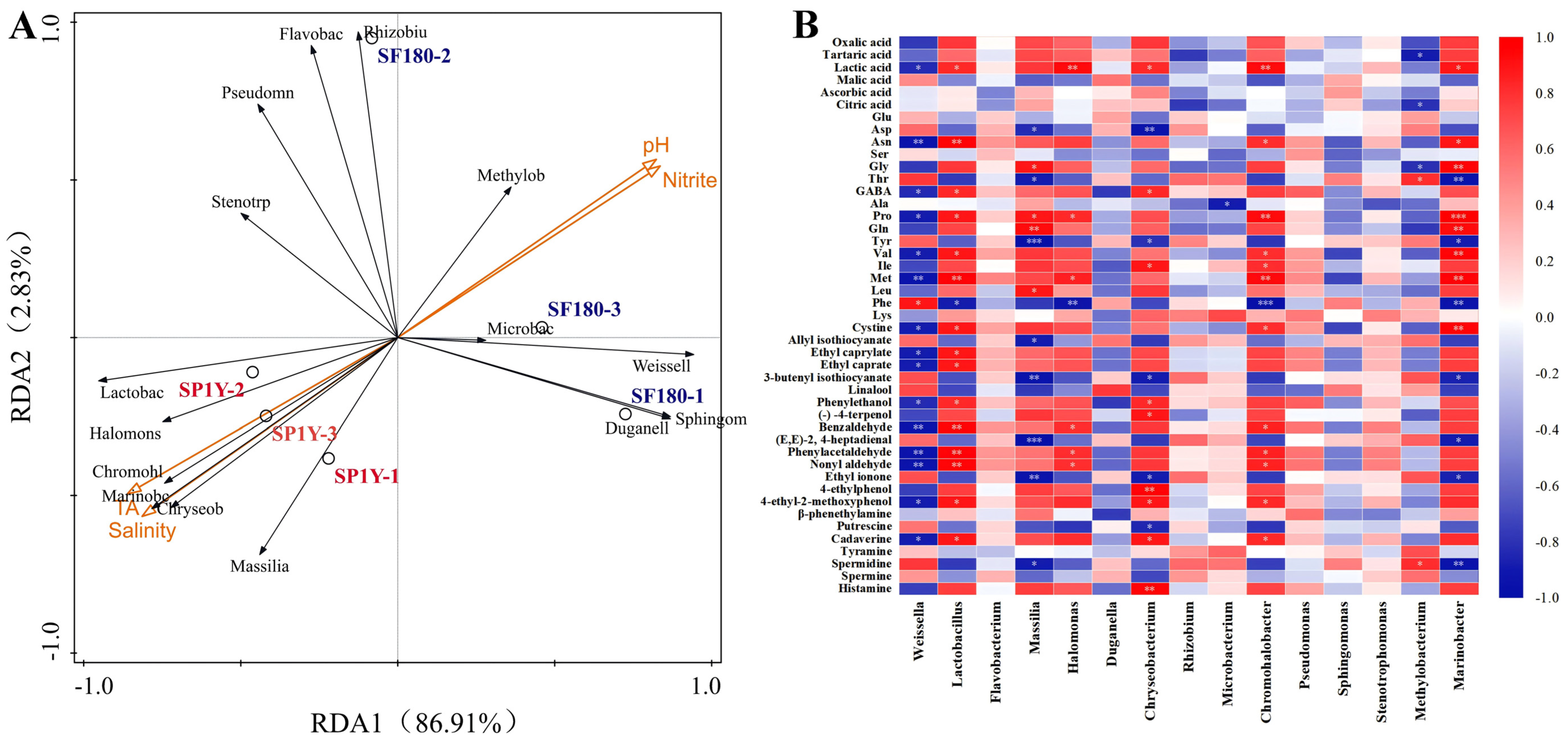
3.5. Correlation Between Physicochemical Factors and Microorganisms
3.6. Associations Among Microorganisms, Organic Acids, Free Amino Acids, Biogenic Amines, and Volatile Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Q.; Zang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X. Dynamic Changes of Bacterial Communities and Nitrite Character during Northeastern Chinese Sauerkraut Fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Peng, Z.; Hardie, W.J.; Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Exploring the Typical Flavours Formation by Combined with Metatranscriptomics and Metabolomics During Chinese Sichuan Paocai Fermentation. LWT 2022, 153, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Sui, Y.; Kong, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q. Effects of Different Fermentation Temperatures and Salt Concentrations on the Physicochemical Properties, Quality, Safety, Bacterial Composition of Northeastern Sauerkraut. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Xin, L.; Xu, S.; Meng, X. Effect of Rapid Fermentation on the Quality of Northeastern Sauerkraut Analyzed Based on HSSPME-GC-MS and LC-MS. LWT 2024, 198, 116005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Qiu, D.; Xu, X.; Du, T.; Peng, Z.; Xiao, M.; Huang, T.; Huang, J.; Ren, H.; Xie, M.; et al. Heterogeneity of Microbiome and Flavor Profiles of Industrial-Scale Laotan Suancai: Fermentation Craft Plays Important Roles. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Hu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Yuan, L.; Liu, G. The Dynamic Changes and Correlations between Biochemical Properties, Flavor and Microbial Community during Fermentation of Asparagus by-Products. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, R.; Ye, M.; Ming, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Lai, X.; et al. Correlation Between Autochthonous Microbial Communities and Flavor Profiles During the Fermentation of Mustard Green Paocai (Brassica juncea Coss.), a Typical Industrial-Scaled Salted Fermented Vegetable. LWT 2022, 172, 114212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, M.; Tian, Y.; Jian, C.; Lv, B.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y. The Potential Correlation Between Microbial Communities and Flavors in Fermented Bamboo Shoots. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Chu, C.; Yi, J.; Liu, Z. Enhancing Fermented Vegetable Flavor with Lactobacillus plantarum and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa. Food Res. Int. 2025, 200, 115500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yao, S.; Hao, L.; Jin, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C. Utilization of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum to Enhance the Flavor Quality and Safety Properties of Radish Paocai. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 12456-2021; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Total Acid in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB 5009.33-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Karrar, E.; Wu, D.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. A Cooperative Combination of Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Electronic Tongue Evaluation Reveals the Dynamic Changes in Metabolites and Sensory Quality of Radish during Pickling. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, D.; Hu, R.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ming, J.; Chi, Y. Effects of Dry-Salting and Brine-Pickling Processes on the Physicochemical Properties, Nonvolatile Flavour Profiles and Bacterial Community During the Fermentation of Chinese Salted Radishes. LWT 2022, 157, 113084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Li, T.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Peng, C.; Li, Z. Correlations Between Microbiota Succession and Volatile Profiles Development and Biogenic Amine Formation Involved in the Ripening of Chinese Sour Meat. LWT 2025, 215, 117238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Wang, L.; Kong, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, W.; Fu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Xue, C. The Rapid Fermentation of Euphausia Superba Sauce and Revealing of the Relationship Between Key Flavor Compounds and Core Microorganisms. Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, T.; Huang, T.; Huang, J.; Ren, H.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Integrated Metatranscriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Microbial Succession and Flavor Formation Mechanisms During the Spontaneous Fermentation of Laotan Suancai. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Ren, H.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Dynamic Analysis of Flavor Properties and Microbial Communities in Chinese Pickled Chili Pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.): A Typical Industrial-Scale Natural Fermentation Process. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Ma, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, B. Volatile Organic Compound Dynamics in Ugni Blanc and Vidal Wines During Fermentation in the Hexi Corridor (China): Insights from E-Nose, GC-MS, GC-IMS, and Multivariate Statistical Models. LWT 2025, 217, 117440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Song, J.; Mumby, W.; Suo, H.; Zhang, Y. The Correlation Between Flavor Formation and Microbial Community Dynamics During the Fermentation of Zha Cai. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 6233–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Peng, M.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum Enriched with Organic/Inorganic Selenium on the Quality and Microbial Communities of Fermented Pickles. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Tang, T.; Zhang, M.; Lim Law, C.; Mujumdar, A.S. Novel Strategies for Controlling Nitrite Content in Prepared Dishes: Current Status, Potential Benefits, Limitations and Future Challenges. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 112984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, P.; Wu, J.; Tao, D.; Wu, R. Effects of Leuconostoc mesenteroides on Physicochemical and Microbial Succession Characterization of Soybean Paste, Da-Jiang. LWT 2019, 115, 108028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Guo, H.; Bai, J.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wan, H.; Huang, Y.; Gao, H. Metabolomics and Metatranscriptomics Reveal the Influence Mechanism of Endogenous Microbe (Staphylococcus succinus) Inoculation on the Flavor of Fermented Chili Pepper. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 406, 110371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Ge, L.; Lai, H.; Wang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Su, Y.; Shi, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Unraveling the Contribution of Pre-Salting Duration to Microbial Succession and Changes of Volatile and Non-Volatile Organic Compounds in Suancai (a Chinese Traditional Fermented Vegetable) During Fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, E.J.; Kleerebezem, M. Production of Aroma Compounds in Lactic Fermentations. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feixia, D.; Ya, L.; Dafei, L.; Dingjiang, Z.; Guiping, H.; Zeliang, W.; Lirong, J. Kaili Red Sour Soup: Correlations in Composition/Microbial Metabolism and Flavor Profile during Post-Fermentation. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Xu, X.; Du, T.; Liu, Q.; Huang, T.; Ren, H.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Organic Acids Drove the Microbiota Succession and Consequently Altered the Flavor Quality of Laotan Suancai Across Fermentation Rounds: Insights from the Microbiome and Metabolome. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hu, W.; Xiu, Z.; Jiang, A.; Yang, X.; Saren, G.; Ji, Y.; Guan, Y.; Feng, K. Effect of Salt Concentration on Microbial Communities, Physicochemical Properties and Metabolite Profile During Spontaneous Fermentation of Chinese Northeast Sauerkraut. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1458–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Huang, T.; Huang, C.; Hardie, J.; Peng, Z.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. The Microbial Communities and Flavour Compounds of Jiangxi Yancai, Sichuan Paocai and Dongbei Suancai: Three Major Types of Traditional Chinese Fermented Vegetables. LWT 2020, 121, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mu, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, N.; Chen, L.; Wen, T.; Su, W. Analysis of Fermentation Characteristics in Fermented Grains Across Seven Rounds of Sauce-Flavored Baijiu: Microbial Communities Structure, Physicochemical Parameters, Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Compounds. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, H.X.; Viet, L.Q.; Chau, L.M.; Long, B.H.D.; Thanh, N.N.; Phat, D.T.; Truong, L.D. Isolation and Selection of Lactic Acid Bacteria with the Capacity of Producing γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) and Antimicrobial Activity: Its Application in Fermented Meat Product. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 19, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hu, W.; Xiu, Z.; Jiang, A.; Yang, X.; Sarengaowa; Ji, Y.; Guan, Y.; Feng, K. Comparison of Northeast Sauerkraut Fermentation Between Single Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains and Traditional Fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Li, C.; He, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Ho, C.-T. Research Advances on Biogenic Amines in Traditional Fermented Foods: Emphasis on Formation Mechanism, Detection and Control Methods. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sui, Y.; Liu, X.; Kong, B.; Qin, L.; Chen, Q. Exploring Potential Correlations between Fungal Communities, Safety, and Quality Properties of Traditional Fermented Sauerkraut from Northeast China. LWT 2023, 185, 115185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ren, H.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Integrated Metatranscriptomics and Metabolomics Revealed the Metabolic Pathways of Biogenic Amines During Laotan Suancai Fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Huang, Y.; Lai, H.; Wang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The Role of Abiotic and Biotic Factors of Aged Brine in Directing Microbial Assembly and Volatile Profiles of Paocai During Fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Huang, Y.; Lai, H.; Wang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Illumination and Reconstruction of Keystone Microbiota for Reproduction of Key Flavor-Active Volatile Compounds During Paocai (a Traditional Fermented Vegetable) Fermentation. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dong, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, M.; He, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, W.; et al. Screening of Strains from Pickles and Evaluation of Characteristics of Different Methods of Fast and Low Salt Fermented Mustard Leaves (Brassica juncea Var. Multiceps). Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Duan, J.; Wang, B.; Ma, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, B. Discrimination and Characterization of the Volatile Organic Compounds in Red and Black Raspberry Wines Fermented with Different Commercial Saccharomyces cerevisiae: An Integrated Analysis Using E-Nose, GC-MS, GC-IMS, and Multivariate Statistical Models. Food Chem. 2025, 478, 143678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, S.; Mith, H.; Tarayre, C.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Delvigne, F. Impact of Microbial Composition of Cambodian Traditional Dried Starters (Dombea) on Flavor Compounds of Rice Wine: Combining Amplicon Sequencing with HP-SPME-GCMS. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, A.; Li, J.; Shan, Y.; Gong, X.; Yao, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, M.; Liang, B.; Wang, F.; et al. Volatiles and Bacterial Composition of Pickled Bamboo Shoots Within 10 Pre-Packaged Chinese Luosifen Disclosed by GC–MS, GC-IMS, and High-Throughput Sequencing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 96, 103794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zheng, W.; Huang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Gong, D.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Comparison of Microbial Communities and Physiochemical Characteristics of Two Traditionally Fermented Vegetables. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Jia, Z.; Zhong, K.; Gao, H. Effects of Assorted Radishes on the Flavor Development and Bacterial Community Succession of Radish Paocai during Fermentation. LWT 2023, 187, 115377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Yan, K.; Li, G.; Luo, D.; Bai, W.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Q.; Deng, J.; Dong, H. Variations of Volatile Flavors and Microbial Communities in Chinese Chaozhou Pickle During Natural Fermentation Revealed by GC-IMS and High-Throughput Sequencing. LWT 2024, 191, 115610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, H.-W.; Cho, K.-M.; Kwon, S.J.; Roh, S.W.; Kwak, S.; Whon, T.W.; Son, H.-S. A Comparative Study of the Physicochemical, Microbial, and Metabolic Profiling of Kimchi During Long-Term Fermentation Under Varying Salinity Conditions. LWT 2024, 196, 115838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Li, T.; Wei, C.; Li, D.; Yan, Y.; Cao, W. Insight into the Succession Pattern of the Microbial Community of Fermented Grains and Driving Forces During Pit Fermentation of Maotai-Flavor Baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2025, 211, 116482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, W.; Kong, B.; Chen, Q. Improving the Bacterial Community, Flavor, and Safety Properties of Northeastern Sauerkraut by Inoculating Autochthonous Levilactobacillus brevis. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, B.; Deng, J.; Ren, Z.; Xie, J.; Wei, C. Succession of Microbial Community Structure in Fermented Grains during the Fermentation of Strong-Flavor Baijiu and Its Impact on the Metabolism of Acids, Alcohols, and Esters. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 3501–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sui, Y.; Lu, J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, H.; Kong, B.; Chen, Q. Exploring Potential Correlations Between Bacterial Communities, Organic Acids, and Volatile Metabolites of Traditional Fermented Sauerkraut Collected from Different Regions of Heilongjiang Province in Northeast China. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xin, X.; Liao, X. Metagenomics Reveals the Formation Mechanism of Flavor Metabolites During the Spontaneous Fermentation of Potherb Mustard (Brassica juncea var. Multiceps). Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| pH | Titratable Acidity (g/L) | Salinity (%) | Nitrite (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suancai fermented for 180 days | 4.88 ± 0.02 a | 3.35 ± 0.31 b | 16.10 ± 0.10 b | 0.67 ± 0.00 a |
| 1-year-aged Suancai post-fermentation | 3.62 ± 0.02 b | 7.54 ± 0.15 a | 18.90 ± 0.10 a | 0.09 ± 0.00 b |
| No. | Compounds | CAS | OT 1 (mg/kg) | Odor Description 2 | OAVs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suancai Fermented for 180 Days | 1-Year-Aged Suancai Post-Fermentation | |||||
| Esters | ||||||
| 1 | Allyl isothiocyanate | 57-06-7 | 0.046 | Pungent mustard smell | 5483.70 | 1390.87 |
| 2 | Ethyl caprylate | 106-32-1 | 0.82 | Brandy’s fragrant sweetness | 3.24 | 6.29 |
| 3 | Ethyl caprate | 110-38-3 | 0.005 | Fruity aroma, brandy-like aroma | 174 | 614 |
| 4 | 3-butenyl isothiocyanate | 3386-97-8 | 0.017 | Strong, pungent smell reminiscent of rubber | 2325.29 | / |
| Alcohols | ||||||
| 5 | Linalool | 78-70-6 | 0.006 | Sweet, typical floral | 3321.67 | 353.33 |
| 6 | Phenethyl alcohol | 60-12-8 | 0.564 | Floral scent | 40.09 | 74.10 |
| 7 | (-)-4-terpenol | 20126-76-5 | 0.04 | Peppery, woody | 15.75 | 114.25 |
| Aldehydes | ||||||
| 8 | Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0.35 | Bitter almond scent | 34.31 | 58.4 |
| 9 | (E,E)-2,4-heptadienal | 4313-03-5 | 0.0154 | fatty | 881.82 | 203.90 |
| 10 | phenylacetaldehyde | 122-78-1 | 0.004 | Hyacinth fragrance | 2035 | 7760 |
| 11 | Nonyl aldehyde | 124-19-6 | 0.0011 | Strong fatty odor, sweet orange scent. | 5554.54 | 8436.36 |
| Ketones | ||||||
| 12 | Ethyl ionone | 79-77-6 | 0.000007 | Violet fragrance | 1,440,000 | / |
| Phenols | ||||||
| 13 | 4-ethylphenol | 123-07-9 | 0.013 | castoreum | / | 1070 |
| 14 | 4-ethyl-2-methoxyphenol | 2785-89-9 | 0.05 | Herbaceous fragrance | / | 836.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Suo, H.; Zalán, Z.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Alterations in Biochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community During the Storage of Suancai. Foods 2025, 14, 3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203490
Xie X, Li Z, Liu H, Suo H, Zalán Z, Song J, Zhang Y. Alterations in Biochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community During the Storage of Suancai. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203490
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xingyun, Zehui Li, Hong Liu, Huayi Suo, Zsolt Zalán, Jiajia Song, and Yu Zhang. 2025. "Alterations in Biochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community During the Storage of Suancai" Foods 14, no. 20: 3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203490
APA StyleXie, X., Li, Z., Liu, H., Suo, H., Zalán, Z., Song, J., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Alterations in Biochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community During the Storage of Suancai. Foods, 14(20), 3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203490







