Machine Learning and Multi-Omics Integration to Reveal Biomarkers and Microbial Community Assembly Differences in Abnormal Stacking Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.4. Identification of Functional Genes and Metabolic Pathways
2.5. Analysis of Volatile Compounds by HS-SPME-GC-MS
2.6. Mechanisms of Microbial Community Assembly
2.7. Machine Learning Model Construction
2.8. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
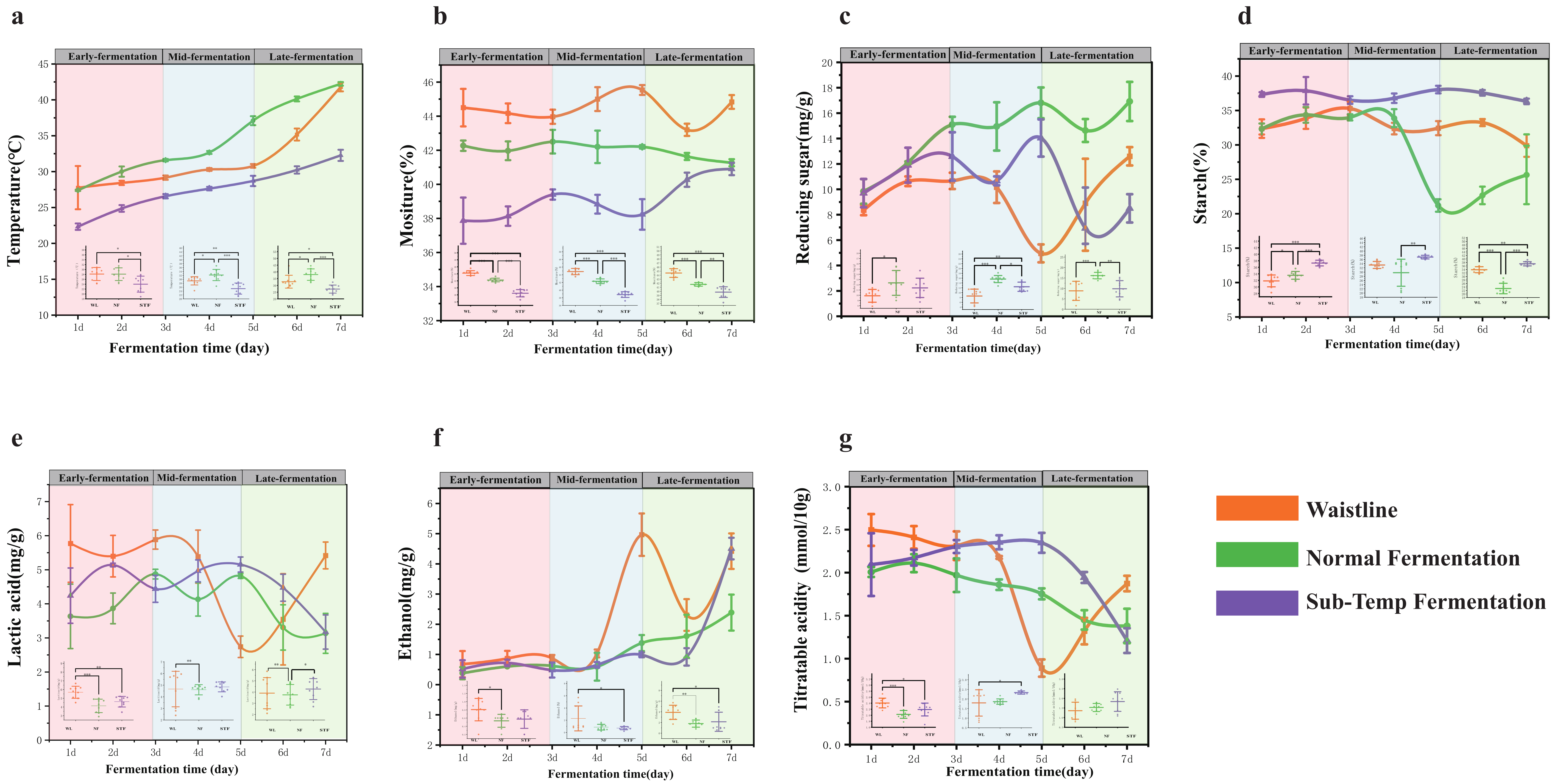
3.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Index Differences
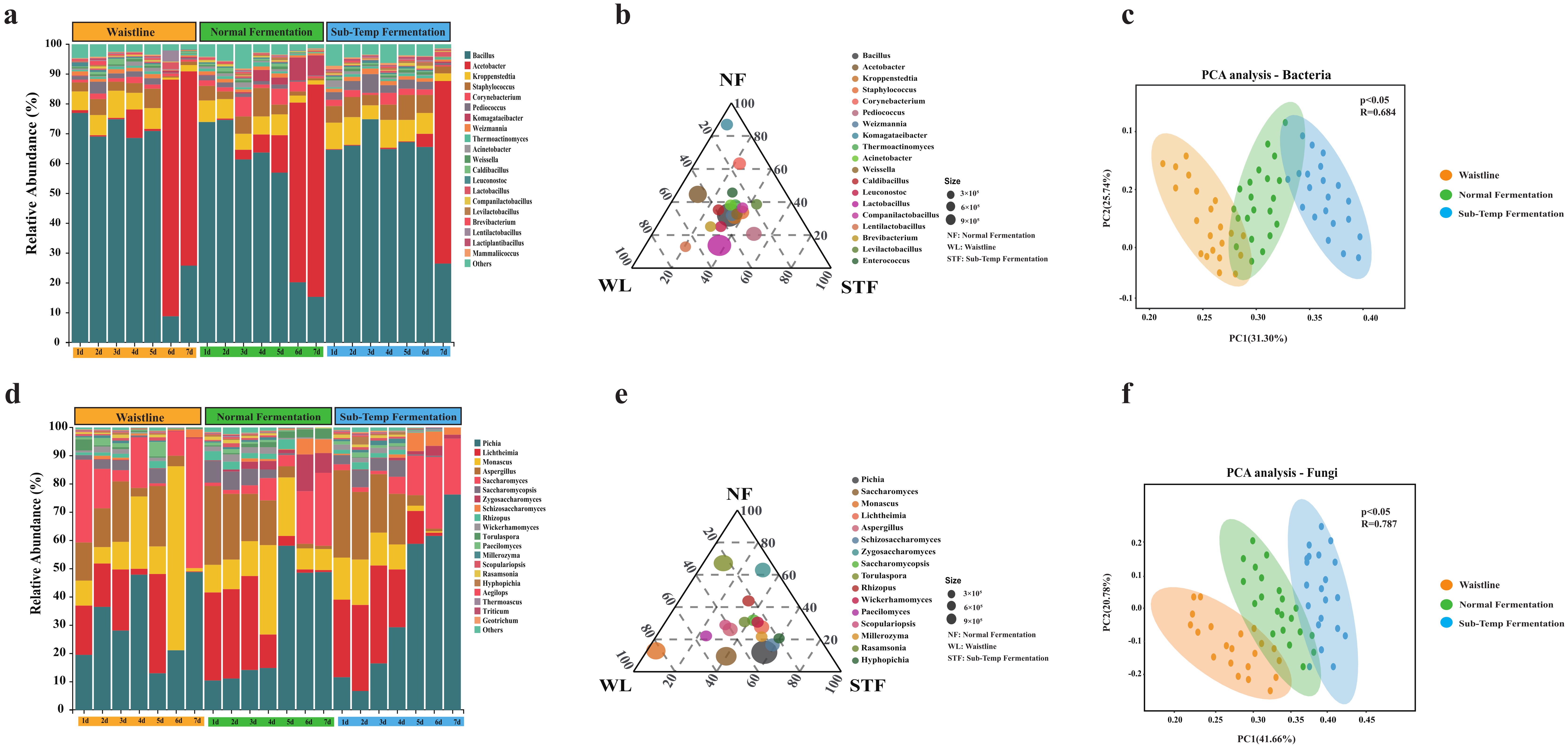
3.2. Differences in Microbial Community Composition
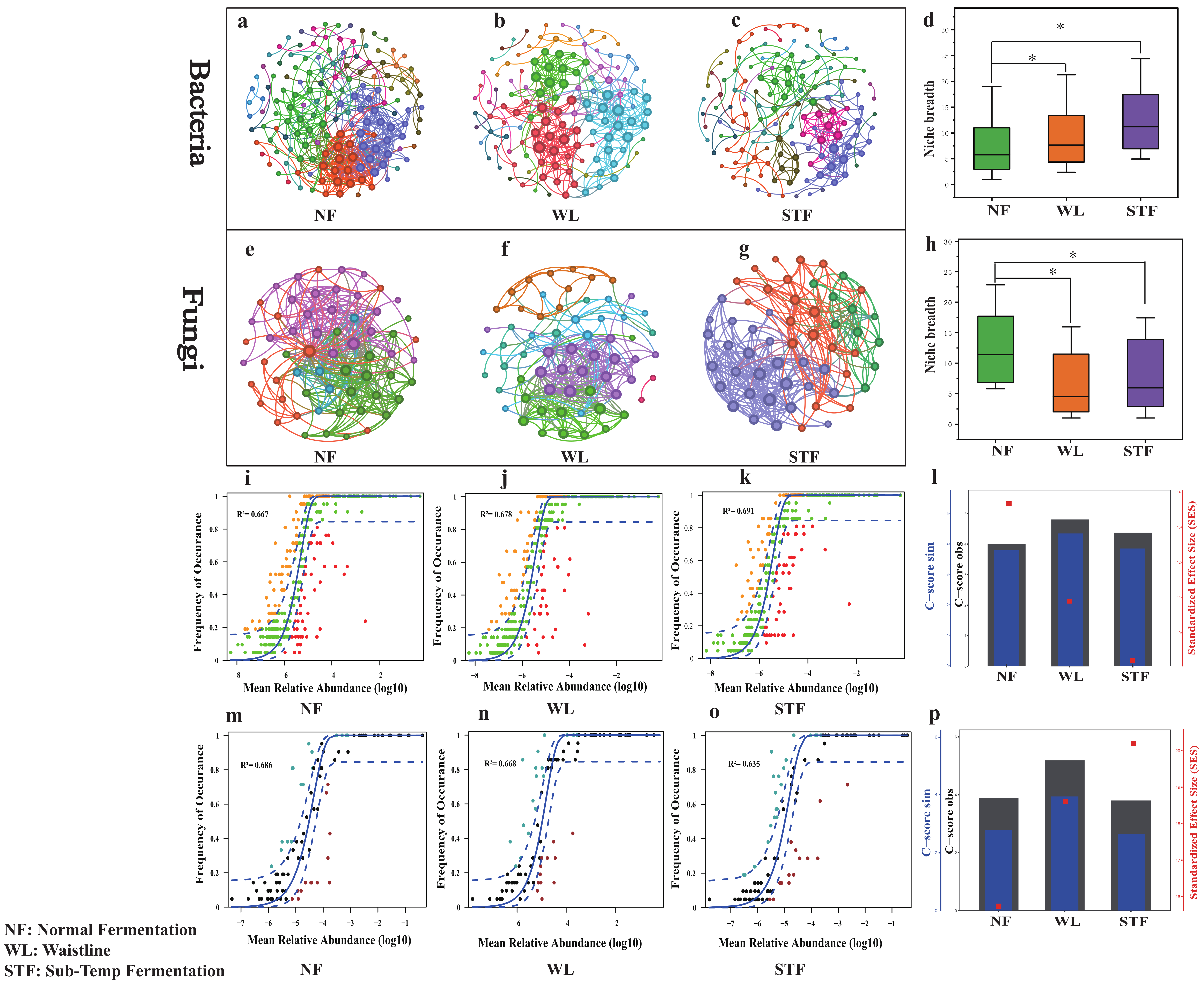
3.3. Differences in Microbial Community Assembly Mechanisms
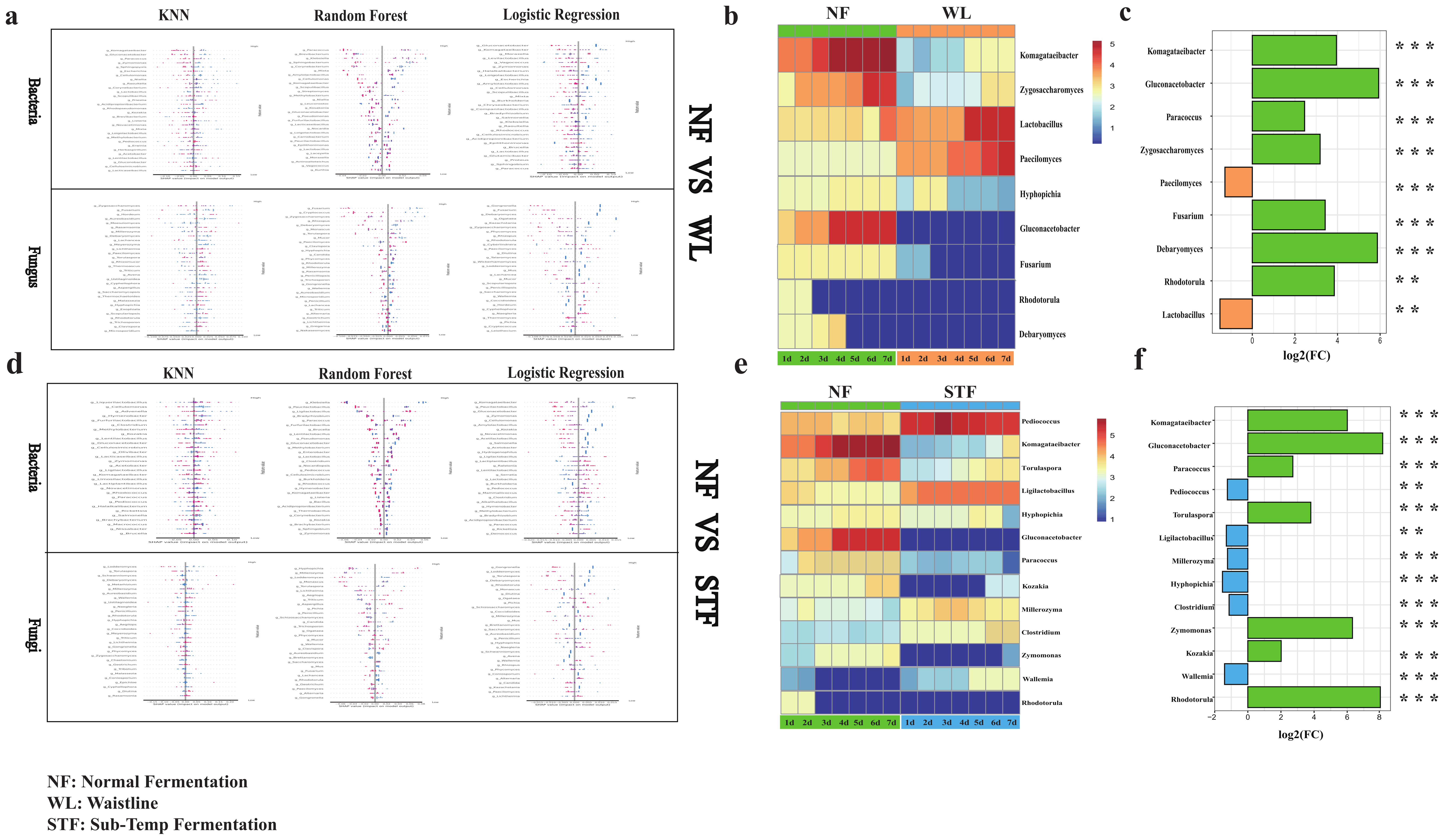
3.4. Screening of Microbial Biomarkers Based on Machine Learning
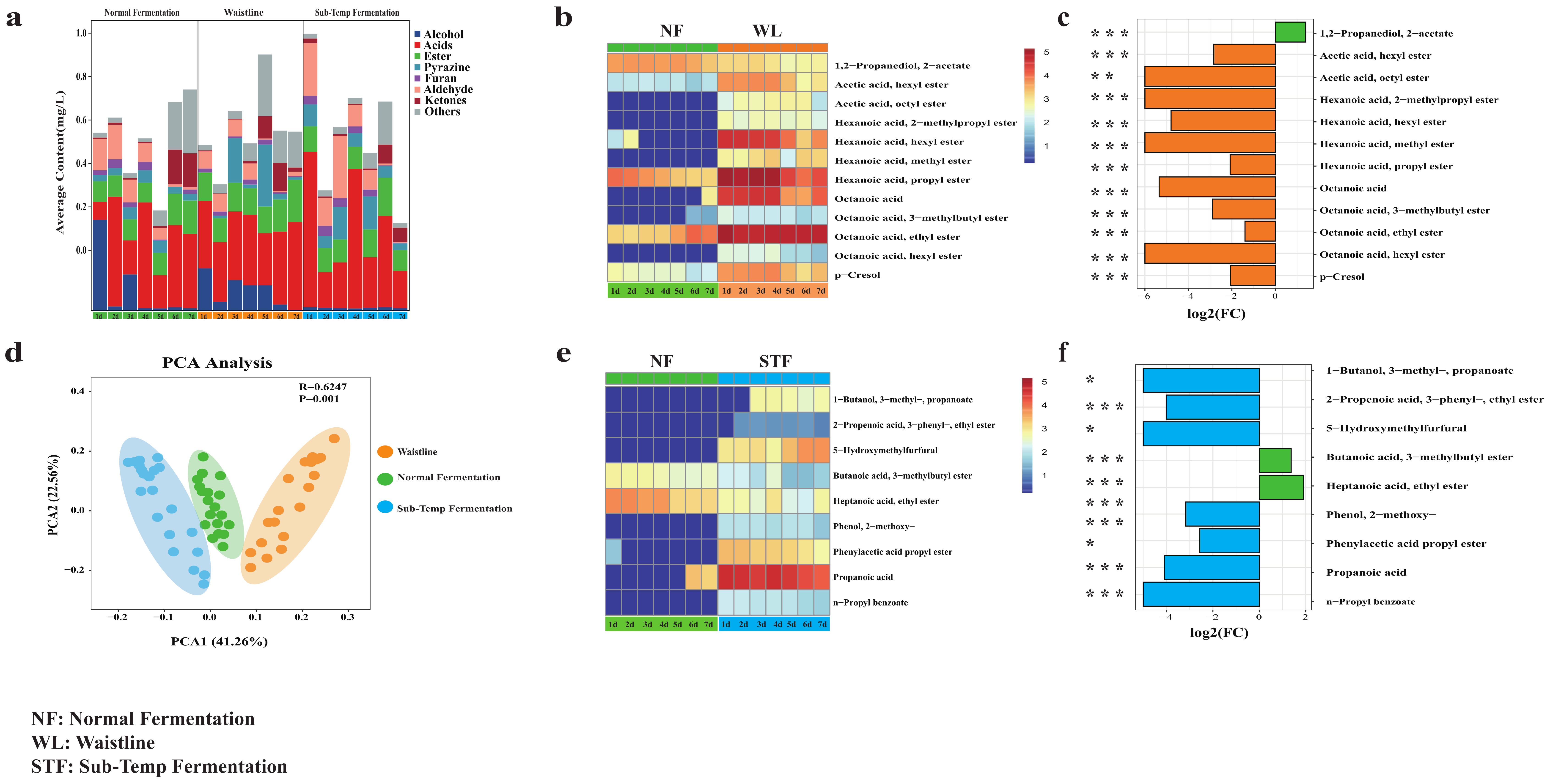
3.5. Analysis of Volatile Compound Differences and Screening of Flavor Biomarkers
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Biomarkers and Environmental Driving Factors
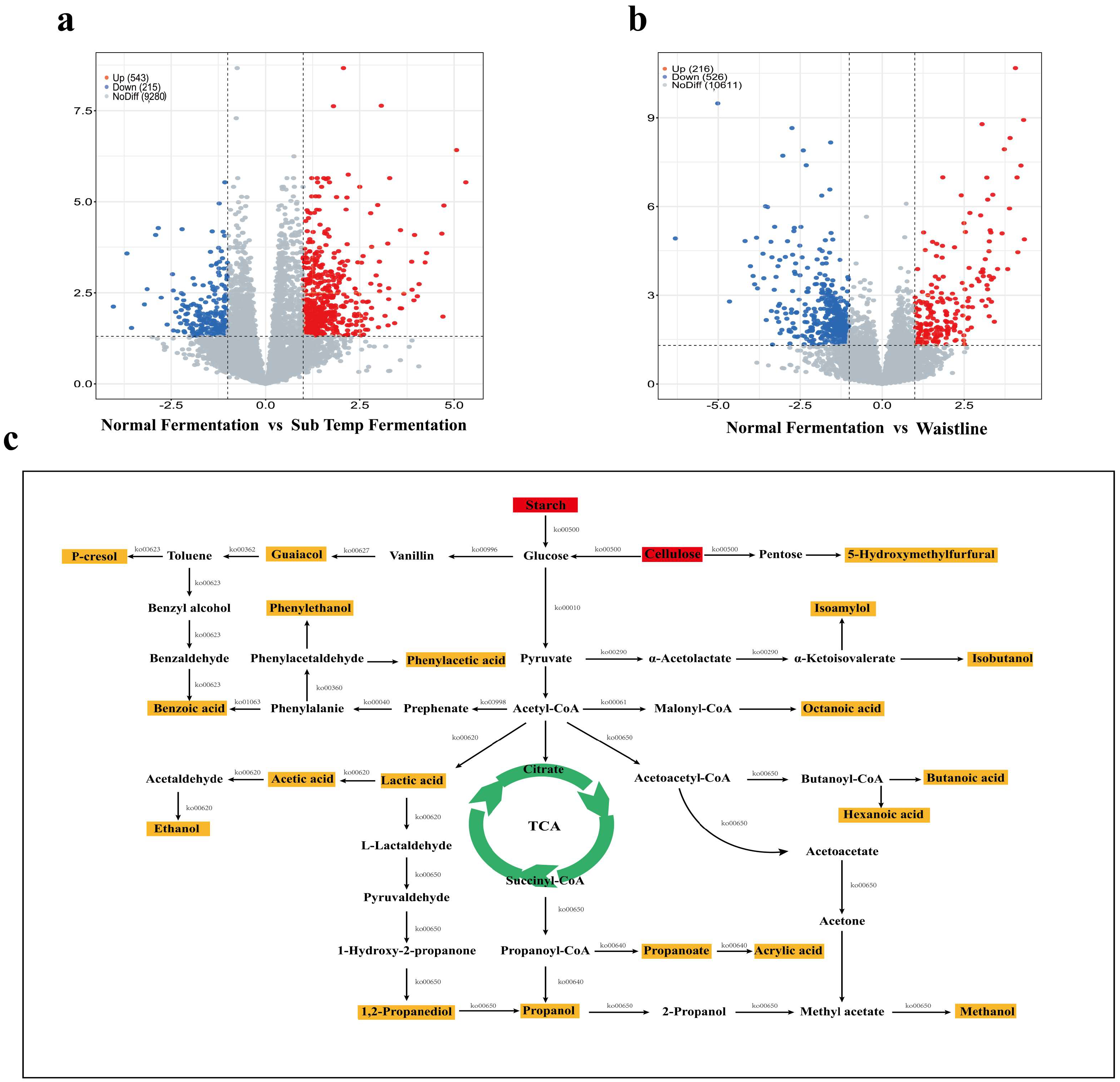
3.7. Differential Gene Pathway Enrichment and Predicted Metabolic Network Analysis for Characteristic Flavor Formation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, C.; Wijffels, R.H.; Xu, Y. Can we control microbiota in spontaneous food fermentation?—Chinese liquor as a case example. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, F. A review on flavor of Baijiu and other world-renowned distilled liquors. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Research trends in Jiang-flavor baijiu fermentation: From fermentation microecology to environmental ecology. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, B. Effect of Fermentation Processing on the Flavor of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, R.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, D.; Sun, B. Can the Maillard reaction affect the characteristic aroma of Sesame aroma baijiu—A research on the methional during the stacking fermentation stage of Jiupei. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y. Microbiome diversity and evolution in stacking fermentation during different rounds of Jiang-flavoured Baijiu brewing. LWT 2021, 143, 111119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, X.; Hu, J.; Deng, H.; He, J.; Zhang, C. The spatiotemporal heterogeneity of microbial community assembly during pit fermentation of soy sauce flavor Baijiu. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, R.; Herbert, R.A.; Jaffe, A.L.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Power, M.E.; Koskella, B. Priority effects in microbiome assembly. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.R.; Karunaratne, S.; Campbell, C.D.; Yao, H.; Robinson, L.; Singh, B.K. Deterministic processes vary during community assembly for ecologically dissimilar taxa. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeily, R.; Razavi, M.A.; Razavi, S.H. A step forward in food science, technology and industry using artificial intelligence. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrocino, I.; Rantsiou, K.; McClure, R.; Kostic, T.; de Souza, R.S.C.; Lange, L.; FitzGerald, J.; Kriaa, A.; Cotter, P.; Maguin, E.; et al. The need for an integrated multi-OMICs approach in microbiome science in the food system. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 1082–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Qu-omics elucidates the formation and spatio-temporal differentiation mechanism underlying the microecology of high temperature Daqu. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Piergiovanni, M.; Franceschi, P.; Mattivi, F.; Vrhovsek, U.; Carlin, S. Application of Comprehensive 2D Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry in Beer and Wine VOC Analysis. Analytica 2023, 4, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, E.; Han, J.; Luo, W.; Zhou, J.; An, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.H.; Li, H. On fusion methods for knowledge discovery from multi-omics datasets. Comp. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellazzi, R. Big Data and Biomedical Informatics: A Challenging Opportunity. Yearb. Med. Inform. 2014, 23, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Pu, D.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances and application of machine learning in food flavor prediction and regulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Thomas, A.M.; Passerini, A.; Waldron, L.; Segata, N. Machine learning for microbiologists. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokhirev, M.N.; Johnson, A.A. An integrative machine-learning meta-analysis of high-throughput omics data identifies age-specific hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 81, 101721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xian, C.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C. The spatio-temporal diversity and succession of microbial community and its environment driving factors during stacking fermentation of Maotai-flavor baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Du, H.; Jin, G.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y. Mucorpepsin from Rhizomucor pusillus relates the quality of medium-temperature Daqu. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zuo, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wei, J.; Huang, Y. Unraveling the core microorganisms and metabolic pathways related to off-flavor compounds formation during Jiang-flavor Baijiu fermentation. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Hao, F.; Lv, X.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of Pichia on shaping the fermentation microbial community of sauce-flavor Baijiu. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 336, 108898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Verdegem, M.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, S. Co-occurrence patterns in biofloc microbial communities revealed by network analysis and their impact on the host. Aquaculture 2023, 577, 739964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, Ö.; Drakare, S.; Kritzberg, E.S.; Langenheder, S.; Logue, J.B.; Lindström, E.S. Regional invariance among microbial communities. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, L.; Roberts, A. The checkerboard score and species distributions. Oecologia 1990, 85, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Peng, F.; Gao, X.; Xiao, P.; Logares, R.; Jeppesen, E.; Ren, K.; Xue, Y.; Yang, J. Low shifts in salinity determined assembly processes and network stability of microeukaryotic plankton communities in a subtropical urban reservoir. Microbiome 2021, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, S.H.M.; Javanmardi, S.; Jahanbanifard, M.; Martynenko, A.; Verbeek, F.J. Detection of Mulberry Ripeness Stages Using Deep Learning Models. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 100380–100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Covert, I.C.; Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S. Algorithms to estimate Shapley value feature attributions. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2023, 5, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Turning over fermented grains elevating heap temperature and driving microbial community succession during the heap fermentation of sauce-flavor baijiu. LWT 2022, 172, 114173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, C. Comprehensive genomic and metabolomic analysis revealed the physiological characteristics and pickle like odor compounds metabolic pathways of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ZZ7 isolated from fermented grains of Maotai-flavor baijiu. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1295393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, T.; Zhong, X.; Chai, L.; Lu, Z.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Komagataeibacter europaeus improves community stability and function in solid-state cereal vinegar fermentation ecosystem: Non-abundant species plays important role. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. Diverse structure and characteristics of the fungal community during the different rounds of Jiang-flavoured Baijiu production in Moutai town. LWT 2022, 161, 113313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Qi, Q.; Bao, X.; Hou, J. Quorum sensing-mediated protein degradation for dynamic metabolic pathway control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 2021, 64, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Beniwal, A.; Kokkiligadda, A.; Vij, S. Response and tolerance of yeast to changing environmental stress during ethanol fermentation. Process Biochem. 2018, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Nie, Y.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Serine Improves Lactic Acid Stress Tolerance and Ethanol Production in Zygosaccharomyces bailii in Baijiu Fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20295–20303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, X.; Ye, J.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Z.; Cao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, F.; Gao, C.X.; Qian, H. Impact of climate zones and seasons on indoor airborne microbial communities: Insights from a comprehensive analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, D.; Zhang, H. Rainfall seasonality shapes microbial assembly and niche characteristics in Yunnan Plateau lakes, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederdorfer, R.; Fragner, L.; Yuan, L.; Hausherr, D.; Wei, J.; Magyar, P.; Joss, A.; Lehmann, M.F.; Ju, F.; Bürgmann, H. Distinct growth stages controlled by the interplay of deterministic and stochastic processes in functional anammox biofilms. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprockett, D.; Fukami, T.; Relman, D.A. Role of priority effects in the early-life assembly of the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, S.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Differences in soil microbial community structure and assembly processes under warming and cooling conditions in an alpine forest ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannazza, P.; Rissanen, A.J.; Sarlin, E.; Guizelini, D.; Minardi, C.; Losoi, P.; Molinari, F.; Romano, D.; Mangayil, R. Characterization, genome analysis and genetic tractability studies of a new nanocellulose producing Komagataeibacter intermedius isolate. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasteva, P.V. Bacterial synthase-dependent exopolysaccharide secretion: A focus on cellulose. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 79, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agüero, A.; Lascano, D.; Ivorra-Martinez, J.; Gómez-Caturla, J.; Arrieta, M.P.; Balart, R. Use of bacterial cellulose obtained from kombucha fermentation in spent coffee grounds for active composites based on PLA and maleinized linseed oil. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 202, 116971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navya, P.V.; Gayathri, V.; Samanta, D.; Sampath, S. Bacterial cellulose: A promising biopolymer with interesting properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Cooperative Response of Pichia kudriavzevii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae to Lactic Acid Stress in Baijiu Fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4903–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, P.; Zhang, P.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, D.; Guo, X. Unraveling the aroma profiling of Baijiu: Sensory characteristics of aroma compounds, analytical approaches, key odor-active compounds in different Baijiu, and their synthesis mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Huang, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, B. Recent advances in the understanding of off-flavors in alcoholic beverages: Generation, regulation, and challenges. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 103, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, J. Evaluation of the Perceptual Interactions Between Higher Alcohols and Off-Odor Acids in Laimao Baijiu by σ–τ Plot and Partition Coefficient. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14938–14949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Structural and metabolic performance of p-cresol producing microbiota in different carbon sources. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.C.O.L.; Alcantara, G.M.R.N.; Silva, A.F.S.; Melchert, W.R.; Rocha, F.R.P. The role of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in food and recent advances in analytical methods. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryngajłło, M.; Jacek, P.; Cielecka, I.; Kalinowska, H.; Bielecki, S. Effect of ethanol supplementation on the transcriptional landscape of bionanocellulose producer Komagataeibacter xylinus E25. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6673–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Zhong, F.; Mao, J. Formation pathways and precursors of furfural during Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar production. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Zou, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhang, S. A metagenomic analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavor development in Shaoxing mechanized huangjiu fermentation mashes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 303, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Han, Y.; Yan, M.; Qiu, S.; Lu, J. Machine Learning and Multi-Omics Integration to Reveal Biomarkers and Microbial Community Assembly Differences in Abnormal Stacking Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu. Foods 2025, 14, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020245
Li S, Han Y, Yan M, Qiu S, Lu J. Machine Learning and Multi-Omics Integration to Reveal Biomarkers and Microbial Community Assembly Differences in Abnormal Stacking Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu. Foods. 2025; 14(2):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuai, Yueran Han, Ming Yan, Shuyi Qiu, and Jun Lu. 2025. "Machine Learning and Multi-Omics Integration to Reveal Biomarkers and Microbial Community Assembly Differences in Abnormal Stacking Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu" Foods 14, no. 2: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020245
APA StyleLi, S., Han, Y., Yan, M., Qiu, S., & Lu, J. (2025). Machine Learning and Multi-Omics Integration to Reveal Biomarkers and Microbial Community Assembly Differences in Abnormal Stacking Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu. Foods, 14(2), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020245



