Lactoferrin-Loaded Liposomal Nanoparticles: Enhanced Intestinal Stability and Bioactivity for Mitigating Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Lip-LF
2.3. Drug Loading Determination
2.4. Physicochemical Characterization
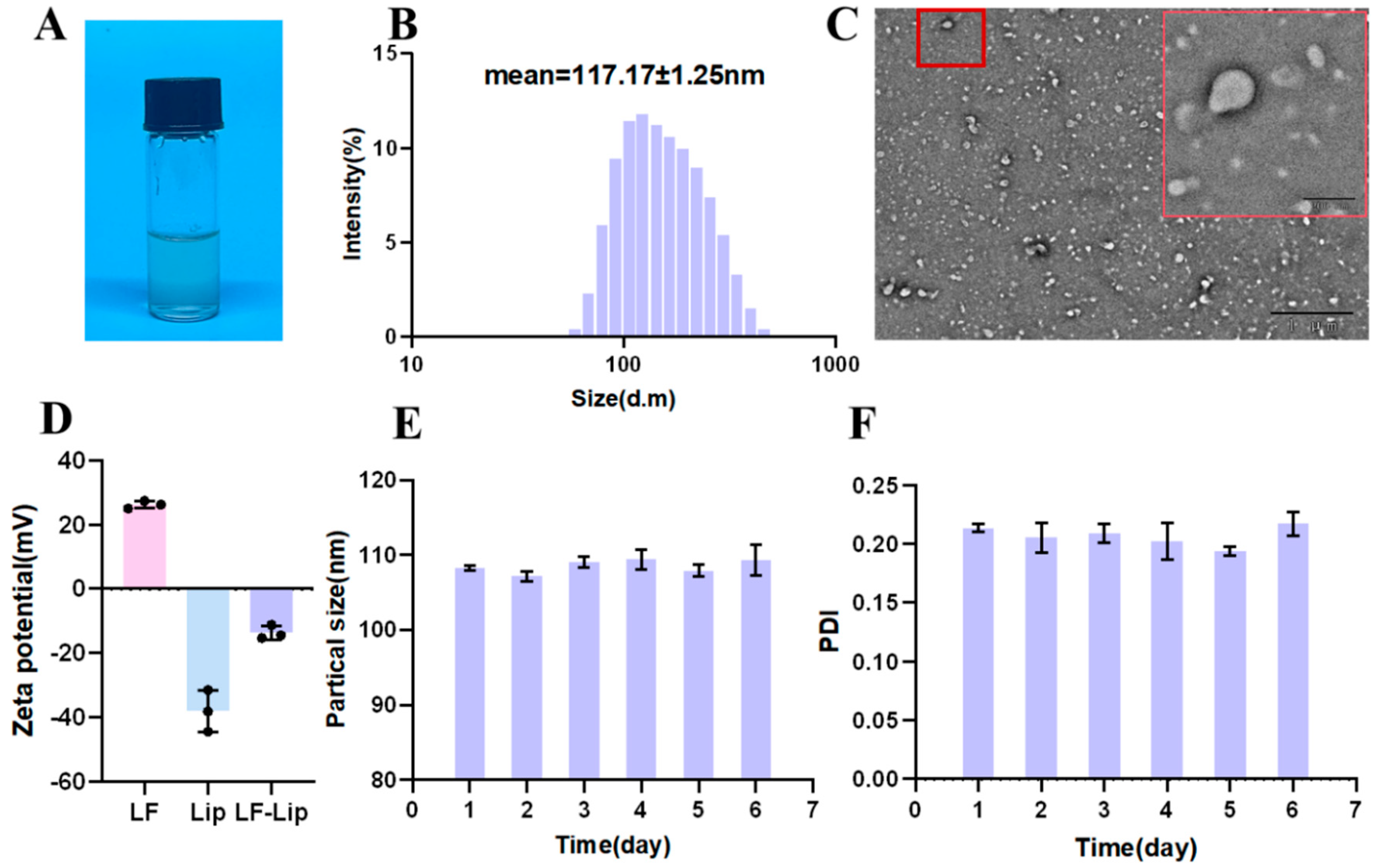
2.4.1. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
2.4.2. Morphology
2.4.3. Zeta Potential
2.4.4. Storage Stability
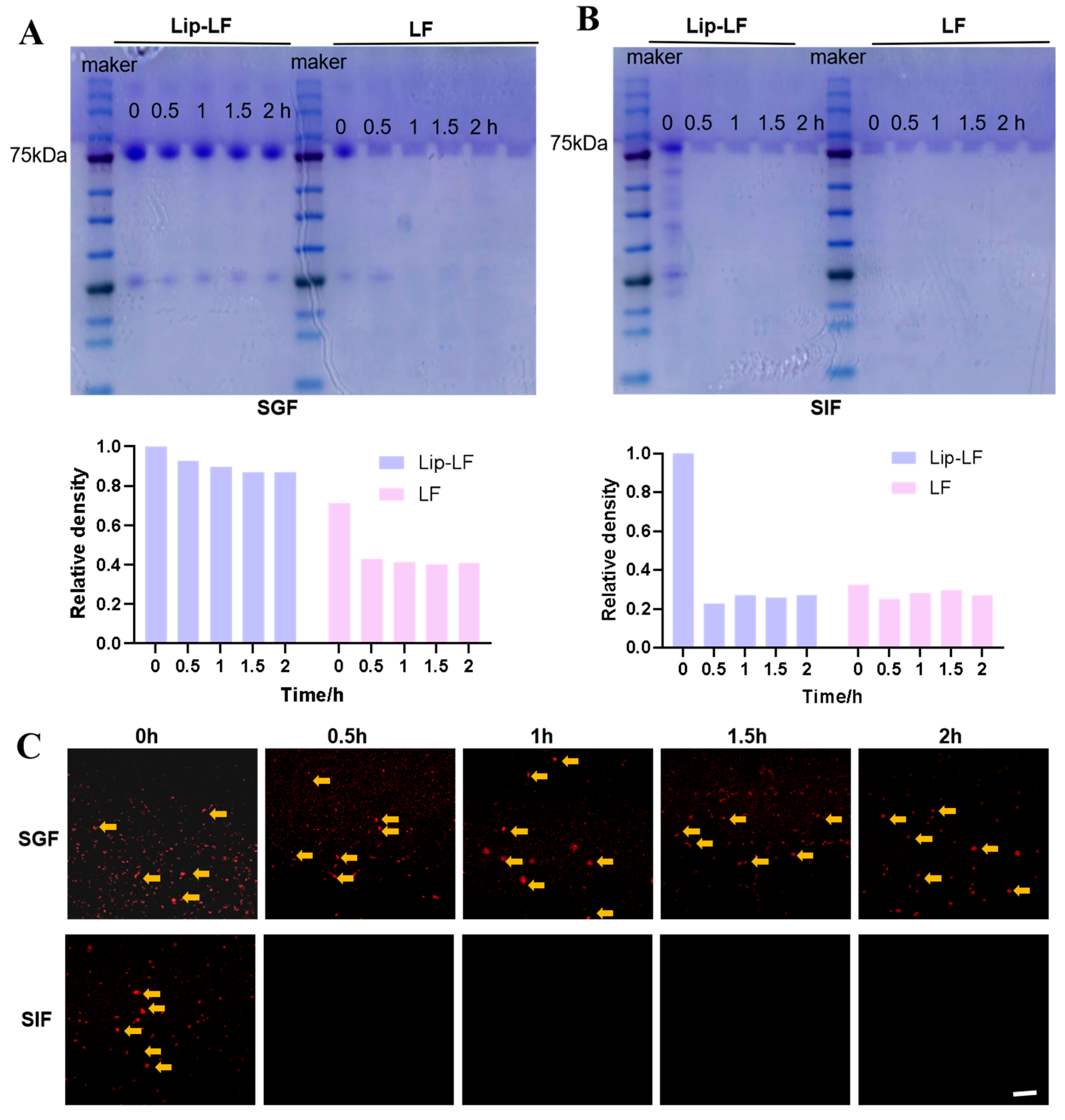
2.5. In Vitro Digestive Stability
2.5.1. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.5.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.5.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
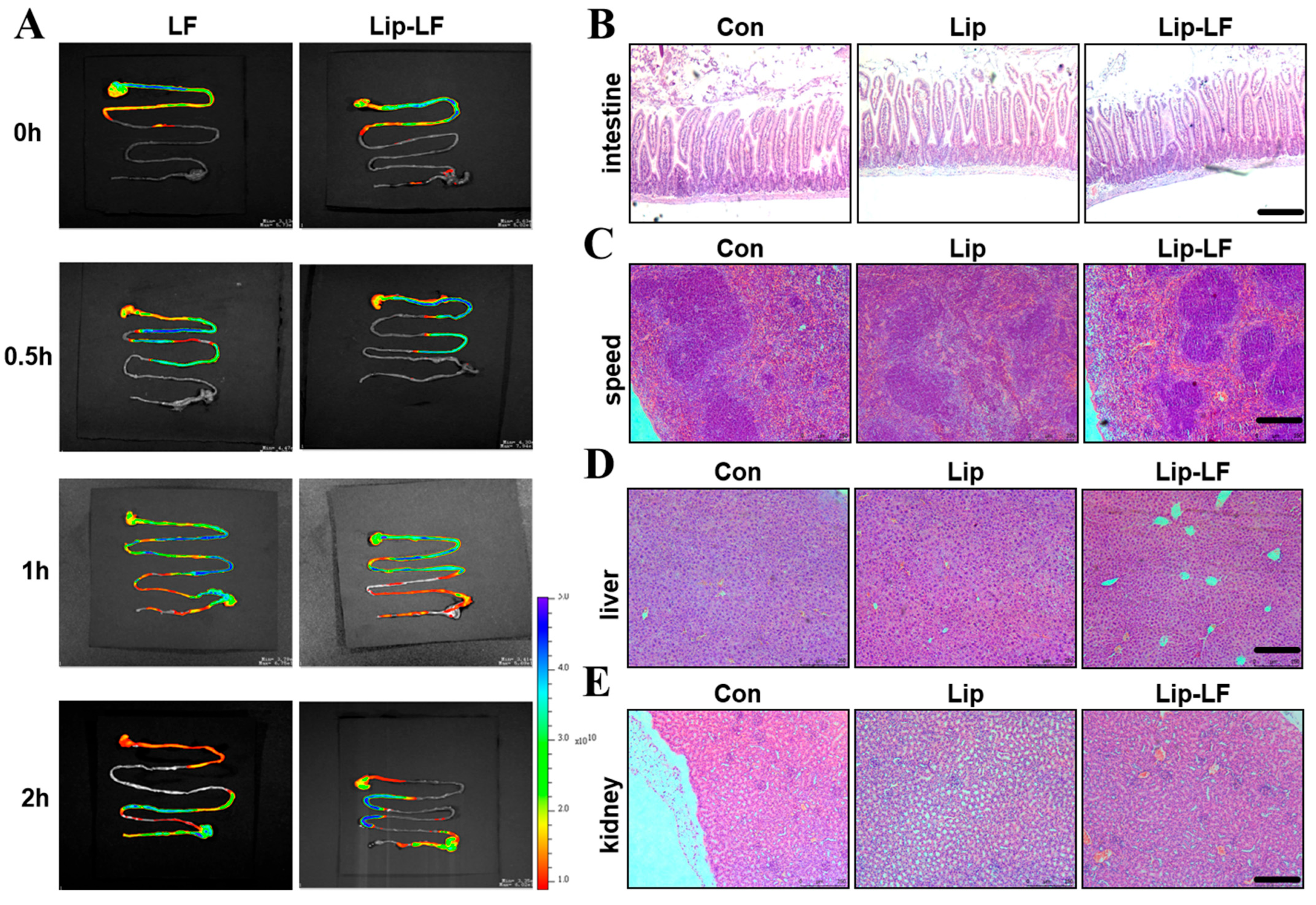
2.6. In Vivo Gastrointestinal Distribution
2.6.1. Fluorescent Labeling of LF
2.6.2. Animal Imaging
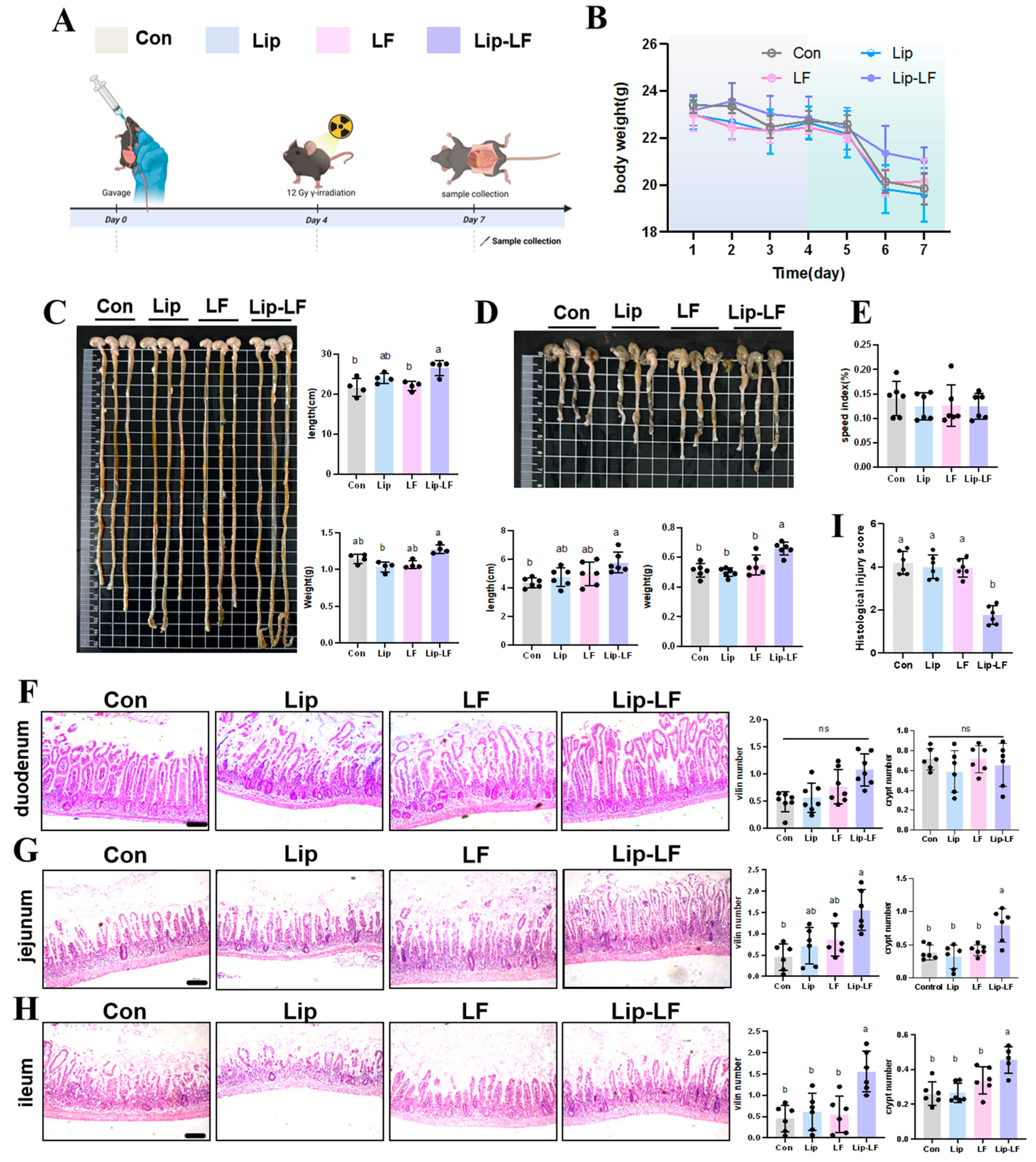
2.7. Animal Ethics and Experimental Design
2.7.1. Animals and Husbandry
2.7.2. Radiation Enteropathy Model and Treatments
2.7.3. Systemic Toxicity Evaluation
2.8. Hematoxylin-Eosin (H&E)
2.9. Histological Injury Score
2.10. Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Staining
2.11. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.12. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.13. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Lip-LF Formulation
3.1.1. Influence of Lipid Composition on Particle Size and PDI
3.1.2. Drug-Loading Optimization
3.2. Comprehensive Characterization of Lip-LF
3.3. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Protection and Release
3.4. In Vivo Gastrointestinal Biodistribution
3.5. Lip-LF Against RIII
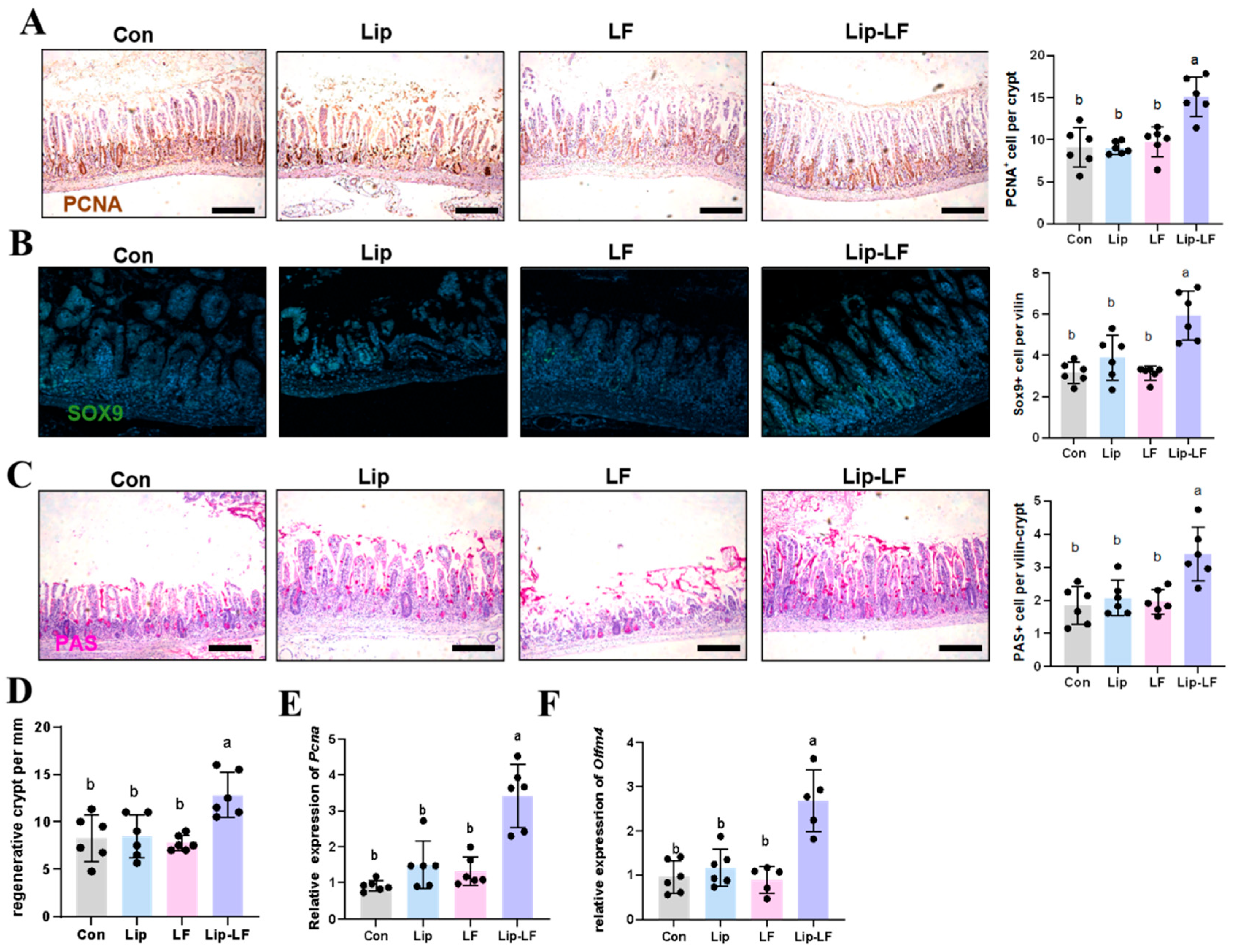
3.6. Lip-LF Promote the Proliferation and Goblet-Cell Differentiation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, J.; Lin, B.; Fan, M.; Niu, T.; Gao, F.; Tan, B.; Du, X. Research progress on the mechanism of radiation enteritis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 888962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luvhengo, T.; Khan, U.; Marumo, T.K. Paneth Cells and Lgr5+ Intestinal Stem Cells in Radiation Enteritis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrey, E.K.; Pathak, R. Radiation-Induced Intestinal Normal Tissue Toxicity: Implications for Altered Proteome Profile. Genes 2022, 13, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.S.; Liu, B.; Lin, Y.Y.; Xue, P.; Lu, Y.; Song, S.J.; Li, Y.X.; Szeto, I.M.Y.; Ren, F.Z.; Guo, H.Y. The application of lactoferrin in infant formula: The past, present and future. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 5748–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, C.; Bellés, A.; Grasa, L.; Sánchez, L. The Role of Lactoferrin in Intestinal Health. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, K.; Iwasa, A.; Amano, Y.; Okubo, K.; Hirahashi, J.; Kawakami, H. Preventive effect of lactoferrin peptides on ulcerative colitis. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 150, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Cheng, Z.M.; Wang, X.; An, Q.; Huang, K.L.; Dai, Y.P.; Meng, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Lactoferrin, a Critical Player in Neonate Intestinal Development: RHLF may be a Good Choice in Formula. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8726–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Robinson, S.C.; Lee, C.; O’Connell, J.S.; Bindi, E.; Zheng, S.; Sherman, P.M.; Pierro, A. Lactoferrin Reduces Necrotizing Enterocolitis Severity by Upregulating Intestinal Epithelial Proliferation. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 30, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jin, S.S.; Chen, H.X.; Cao, Y.M.; Dong, X.B.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, C.Q. Dose effect of bovine lactoferrin fortification on diarrhea and respiratory tract infections in weaned infants with anemia: A randomized, controlled trial. Nutrition 2021, 90, 111288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, P.; Meyer, M.; Stolfi, I.; Rinaldi, M.; Cattani, S.; Pugni, L.; Romeo, M.G.; Messner, H.; Decembrino, L.; Laforgia, N.; et al. Bovine lactoferrin supplementation for prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in very-low-birth-weight neonates: A randomized clinical trial. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Shan, T.Z.; Xu, Z.R.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Effects of the lactoferrin (LF) on the growth performance, intestinal microflora and morphology of weanling pigs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2007, 135, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhao, F.Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.Y. Early-life lactoferrin intervention modulates the colonic microbiota, colonic microbial metabolites and intestinal function in suckling piglets. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6185–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Abe, F.; Shiga, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Shimizu, H.; Sato, A. Lactoferrin conjugated with 40-kDa branched poly(ethylene glycol) has an improved circulating half-life. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Han, T.; Tang, L. Effects of theaflavins on the structure and function of bovine lactoferrin. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ye, A.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Singh, H. Stability during in vitro digestion of lactoferrin-loaded liposomes prepared from milk fat globule membrane-derived phospholipids. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Feng, G.; Fang, J. Nanotechnology for research and treatment of the intestine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikado, A.; Imanaka, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Harada, E.; Makino, T. Liposomalization of lactoferrin enhanced it’s anti-inflammatory effects via oral administration. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, A.; Sakr, O.S.; Nasr, M.; Sammour, O. Ethanol injection technique for liposomes formulation: An insight into development, influencing factors, challenges and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hu, Z.; Song, F.; Xu, Y.; Han, X. Lipid nanoparticles: Composition, formulation, and application. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2025, 33, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assuncao, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carriere, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.J.; McArdle, A.H.; Brown, R.; Scott, H.J.; Gurd, F.N. Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. 1. A morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch. Surg. 1970, 101, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugleva, V.; Mihaylova, R.; Momekov, G.; Kamenova, K.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Petrova, M.; Ugrinova, I.; Momekova, D.; Petrov, P.D. pH-responsive niosome-based nanocarriers of antineoplastic agents. Rsc Adv. 2024, 14, 11124–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Y.; Harish, M.; Vijaya Kumar, V.; Haja Nazeer, A.; Thameemul Ansari, L.H. Descriptive Review on Liposomal Drug Delivery System. J. Pharma Insights Res. 2024, 2, 045–058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Han, J.; Ye, A.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, K.; Kong, Y.; Wei, F.; Zhou, W. Structural characterization and biological fate of lactoferrin-loaded liposomes during simulated infant digestion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, D.; Shene, C. Encapsulation of lactoferrin into rapeseed phospholipids based liposomes: Optimization and physicochemical characterization. J. Food Eng. 2019, 262, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Myung, H.; Kang, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Jang, W.S.; Lee, S.J.; Shim, S.; et al. Pravastatin Attenuates Acute Radiation-Induced Enteropathy and Improves Epithelial Cell Function. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, B.; Lee, C.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, S.; Pierro, A. Protective effects of lactoferrin on injured intestinal epithelial cells. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 2509–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Y.; Yang, M.; Guo, J.; Feng, Z.C. Effects of Bovine Lactoferrin on Rat Intestinal Epithelial Cells. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhao, F.Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.Y. Lactoferrin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses and barrier impairment through the modulation of NF-κB/MAPK/Nrf2 pathways in IPEC-J2 cells. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8516–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blais, A.; Takakura, N.; Grauso, M.; Puel-Artero, C.; Blachier, F.; Lan, A. Dietary Bovine Lactoferrin Reduces the Deleterious Effects of Lipopolysaccharide Injection on Mice Intestine. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hou, Y.M.; Xie, K.; Zhang, L.N.; Zhou, P. Digestive differences in immunoglobulin G and lactoferrin among human, bovine, and caprine milk following in vitro digestion. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 120, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlund, C.B.; Ulleberg, E.K.; Devold, T.G.; Flengsrud, R.; Jacobsen, M.; Sekse, C.; Holm, H.; Vegarud, G.E. Identification of lactoferrin peptides generated by digestion with human gastrointestinal enzymes. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Timilsena, Y.P.; Blanch, E.; Adhikari, B. Mild thermal treatment and in-vitro digestion of three forms of bovine lactoferrin: Effects on functional properties. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 64, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Timilsena, Y.P.; Blanch, E.; Adhikari, B. Lactoferrin: Structure, function, denaturation and digestion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 580–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.S.; Feng, K.; Li, S.F.; Hu, T.G.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H. Oral fate and stabilization technologies of lactoferrin: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6341–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Bunt, C.; Liu, M.; Quek, S.-Y.; Shaw, J.; Cornish, J.; Wen, J. Enhanced Cellular Uptake and Transport of Bovine Lactoferrin Using Pectin- and Chitosan-Modified Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda-Morszewski, P.; Poznanska, A.; Yus, C.; Arruebo, M.; Brindell, M. Encapsulation of Iron-Saturated Lactoferrin for Proteolysis Protection with Preserving Iron Coordination and Sustained Release. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ye, A.; Zhang, T.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Deng, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Han, J.; Liu, W. The novel lactoferrin and DHA-codelivered liposomes with different membrane structures: Fabrication, in vitro infant digestion, and suckling pig intestinal organoid absorption. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, T.; Dadmohammadi, Y.; Li, P.; Dong, H.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Meletharayil, G.; Kapoor, R.; Abbaspourrad, A. Using transglutaminase to cross-link complexes of lactoferrin and alpha-lactalbumin to increase thermal stability. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 5488–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.S.; Feng, K.; Li, S.F.; Hu, T.G.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H. Highly-hydrophobic nanofiber mat for efficient colonic delivery of lactoferrin: Preparation, characterization and release mechanism. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 78, 103015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopaeva, M.Y.; Alchinova, I.B.; Cherepov, A.B.; Demorzhi, M.S.; Nesterenko, M.V.; Zarayskaya, I.Y.; Karganov, M.Y. New Properties of a Well-Known Antioxidant: Pleiotropic Effects of Human Lactoferrin in Mice Exposed to Gamma Irradiation in a Sublethal Dose. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.L.; Jiang, R.L.; Lönnerdal, B. Biochemical and molecular impacts of lactoferrin on small intestinal growth and development during early life. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, D.M.; Wu, J.X.; Guo, Y.X.; Fan, J.B.; Wu, Q.Y.; Wang, H.P.; Wan, Z.X.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. Lactoferrin alleviates Western diet-induced cognitive impairment through the microbiome-gut-brain axis. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fan, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. The Protective Effects of Iron Free Lactoferrin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Inflammatory Injury via Modulating the NF-κB/PPAR Signaling Pathway. Foods 2022, 11, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Quan, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, J.; et al. Lactoferrin promotes intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial regeneration by activating Wnt signaling. Food Front. 2024, 5, 2290–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznikov, E.A.; Comstock, S.S.; Yi, C.Y.; Contractor, N.; Donovan, S.M. Dietary Bovine Lactoferrin Increases Intestinal Cell Proliferation in Neonatal Piglets. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Forward Primer 5′–3′ | Reverse Primer 5′–3′ |
|---|---|---|
| Actb | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| Olfm4 | CAGCCACTTTCCAATTTCACTG | GCTGGACATACTCCTTCACCTTA |
| Pcna | TTTGAGGCACGCCTGATCC | GGAGACGTGAGACGAGTCCAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Ding, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, S.; Guo, H. Lactoferrin-Loaded Liposomal Nanoparticles: Enhanced Intestinal Stability and Bioactivity for Mitigating Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury. Foods 2025, 14, 3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193410
Lin Y, Ding R, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Song S, Guo H. Lactoferrin-Loaded Liposomal Nanoparticles: Enhanced Intestinal Stability and Bioactivity for Mitigating Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193410
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yingying, Rui Ding, Yuning Zhang, Yimeng Wang, Sijia Song, and Huiyuan Guo. 2025. "Lactoferrin-Loaded Liposomal Nanoparticles: Enhanced Intestinal Stability and Bioactivity for Mitigating Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury" Foods 14, no. 19: 3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193410
APA StyleLin, Y., Ding, R., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Song, S., & Guo, H. (2025). Lactoferrin-Loaded Liposomal Nanoparticles: Enhanced Intestinal Stability and Bioactivity for Mitigating Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury. Foods, 14(19), 3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193410







