Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase by Four Phenolic Acids: Kinetic, Spectroscopic, Molecular Simulation, and Cellular Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Assessment of Antioxidant Activity
2.2.1. Evaluation of Reducing Power
2.2.2. Measurement of ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.2.3. Determination of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.2.4. Evaluation of Oxygen Radical Absorption Capacity (ORAC)
2.3. Determination of XOD Inhibitory Activity In Vitro
2.4. Kinetic Mechanisms of XOD Inhibition
2.5. Fluorescence Spectra Measurement
2.6. CD Spectroscopic Analysis
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.9. Assessment of UA-Lowering Activity in BRL-3a Cells
2.9.1. Cell Culture
2.9.2. CCK-8 Method
2.9.3. Determination of UA Levels in BRL-3A Cells
2.10. ADMET Computational Simulation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
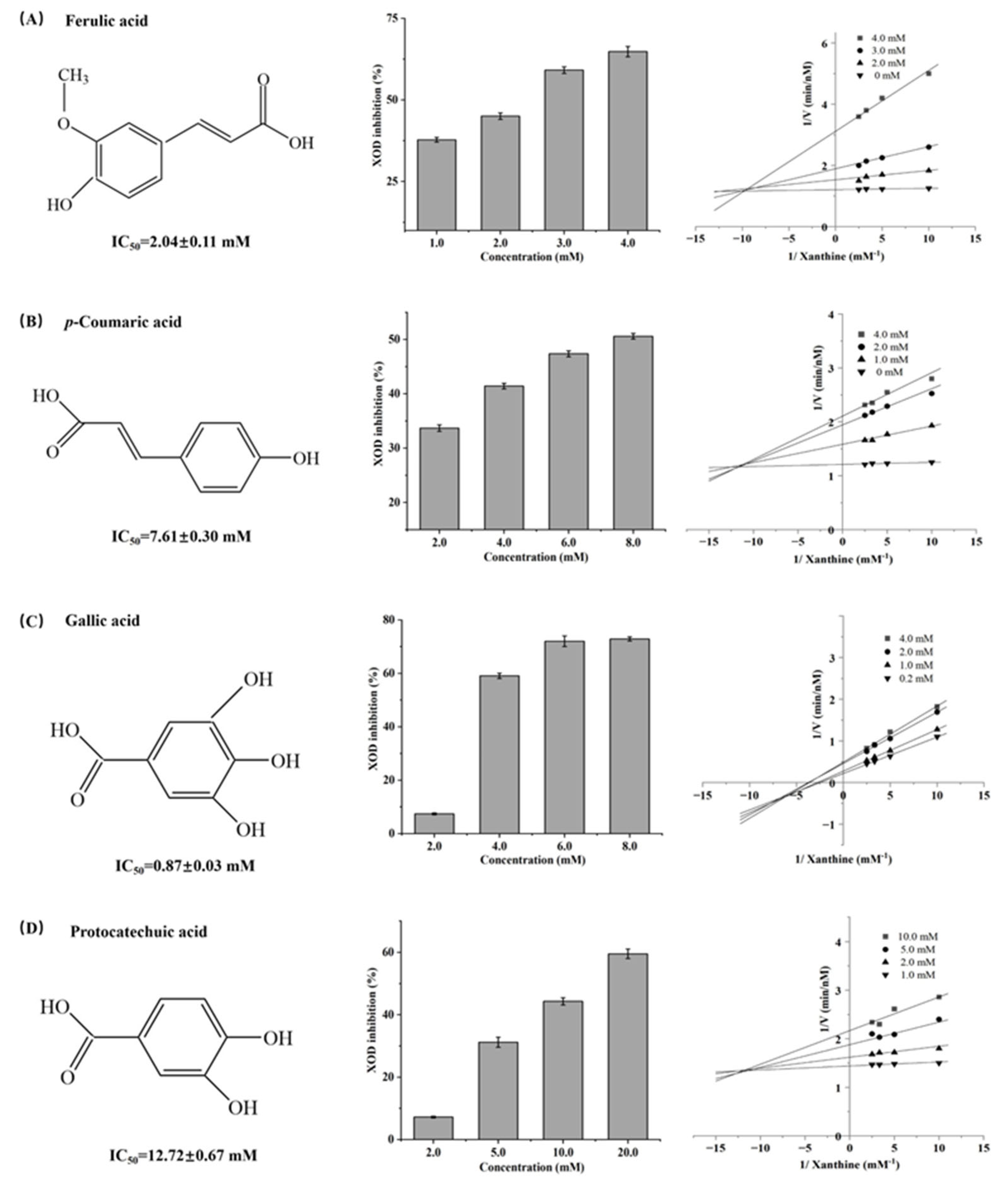
3.1. Antioxidant and XOD Inhibitory Activities of FA, CA, GA, and PA
3.2. Types of XOD Inhibition by FA, CA, GA, and PA
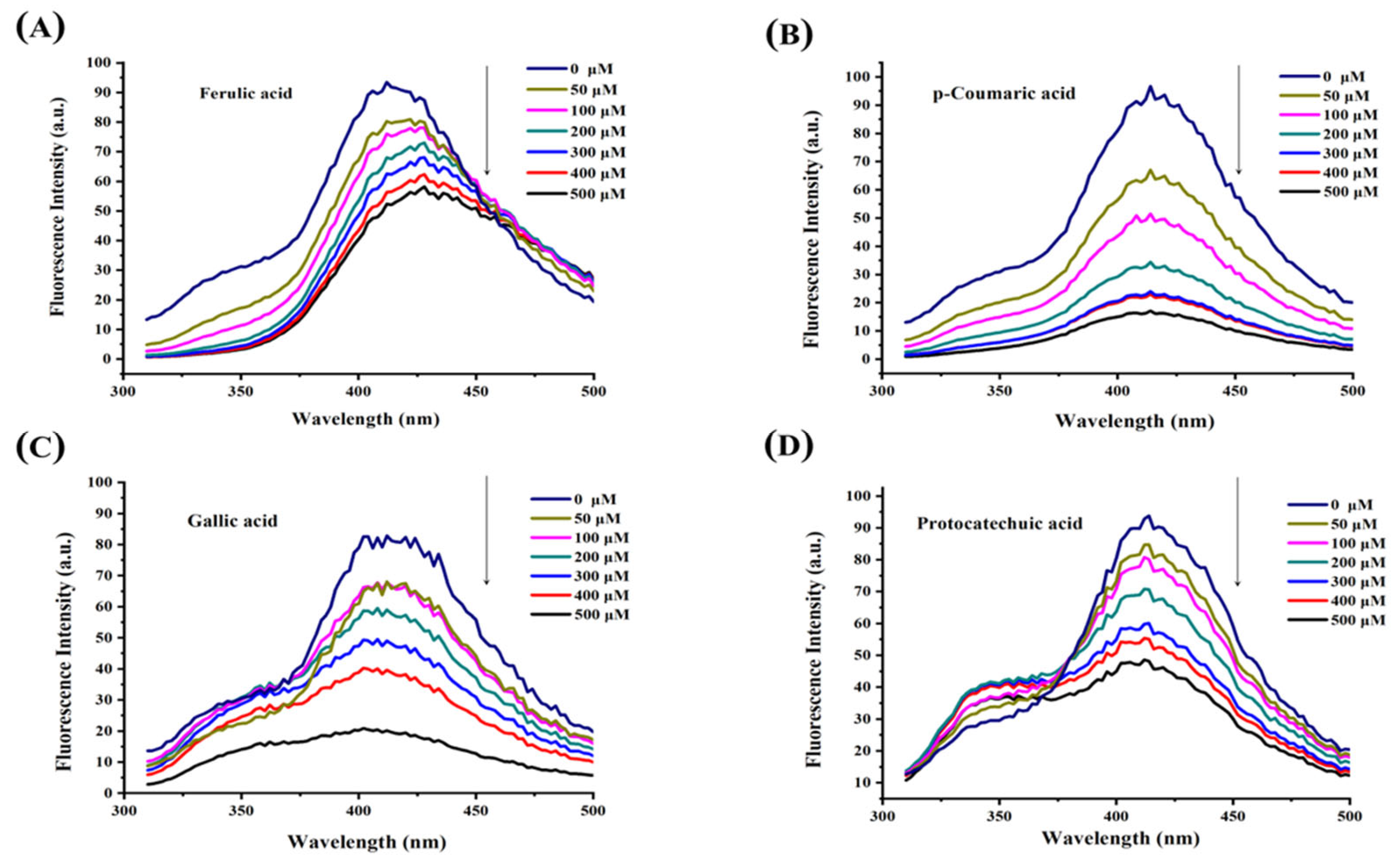
3.3. Fluorescence Quenching Analysis
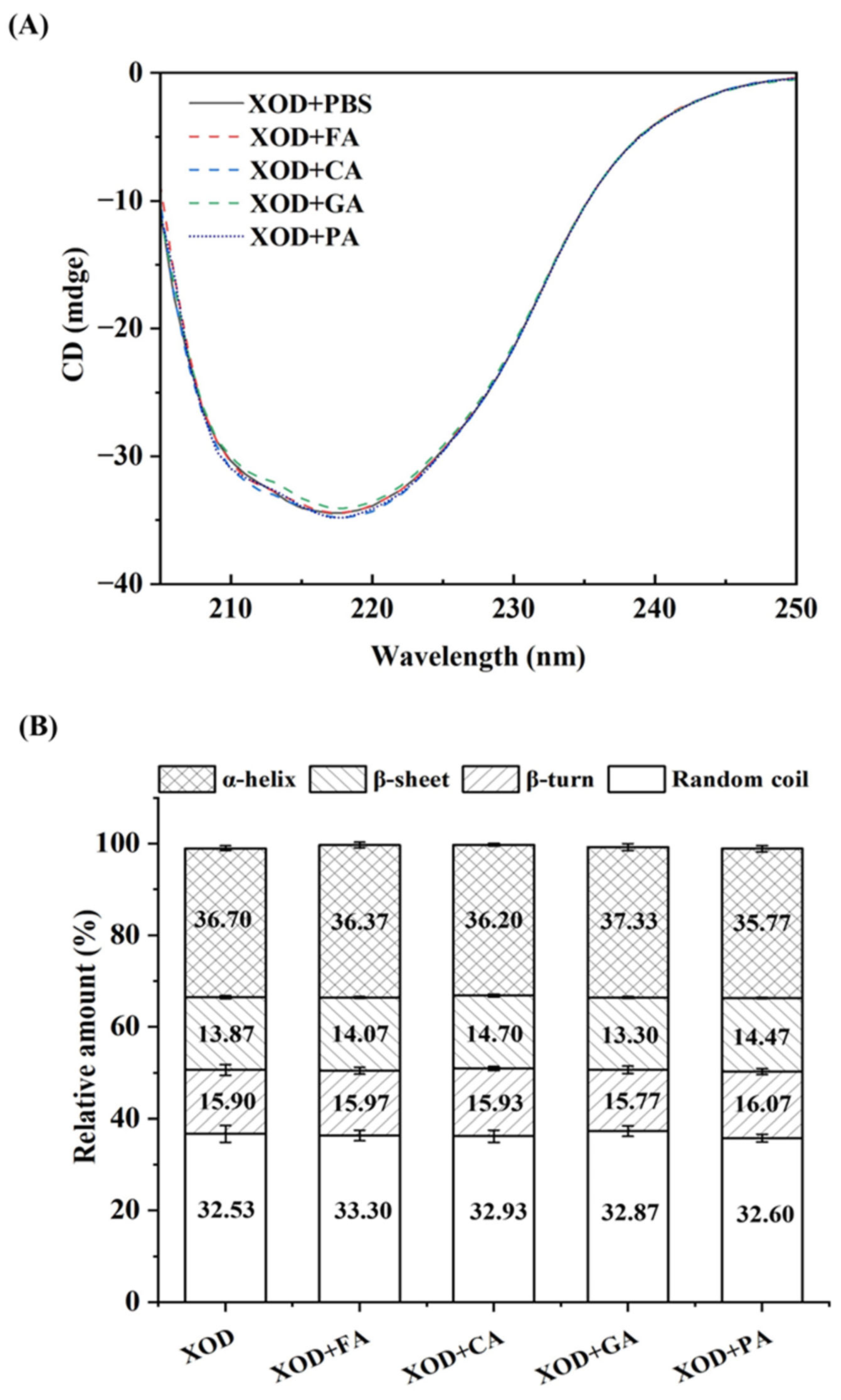
3.4. CD Spectroscopy
3.5. Molecular Docking
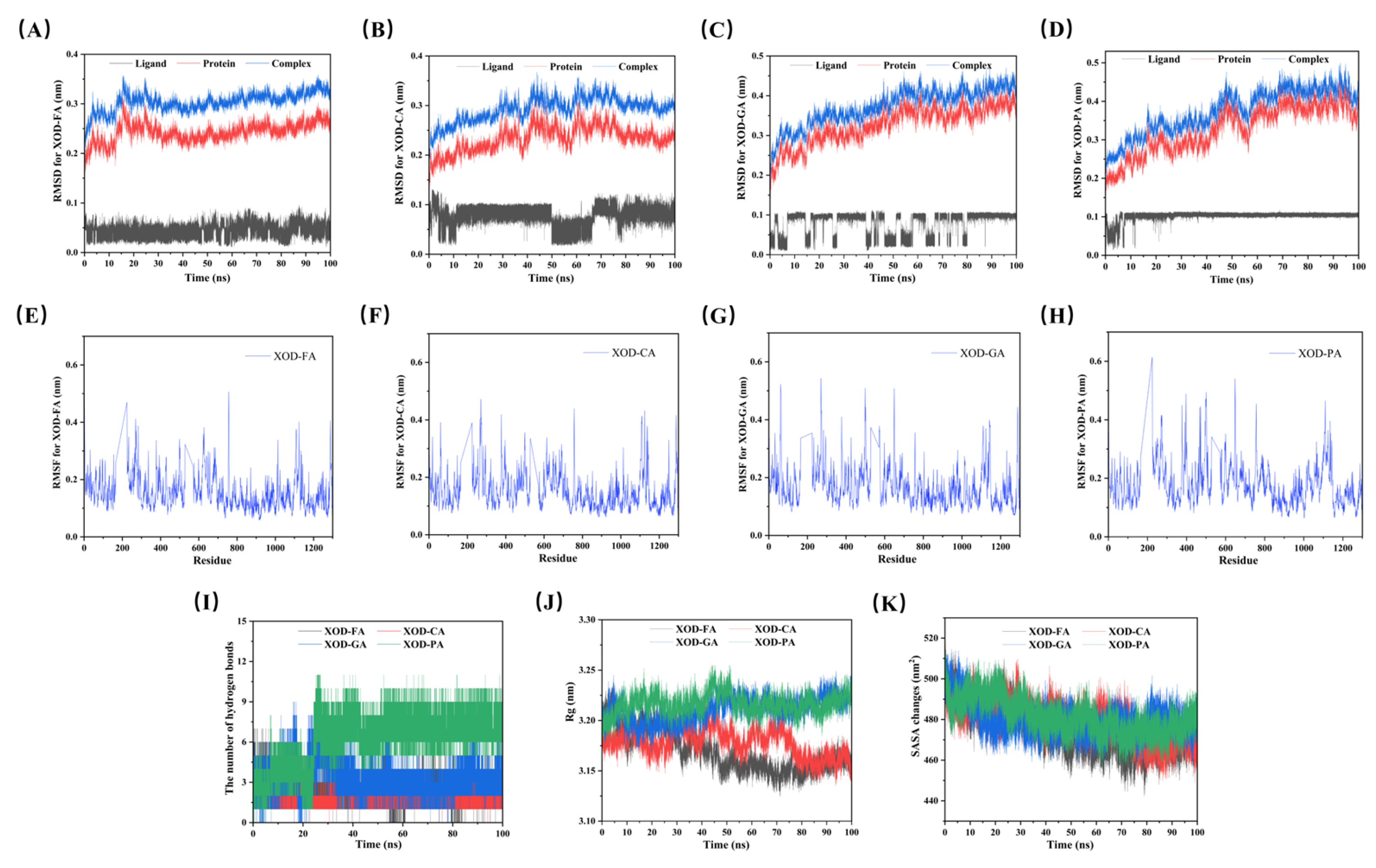
3.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
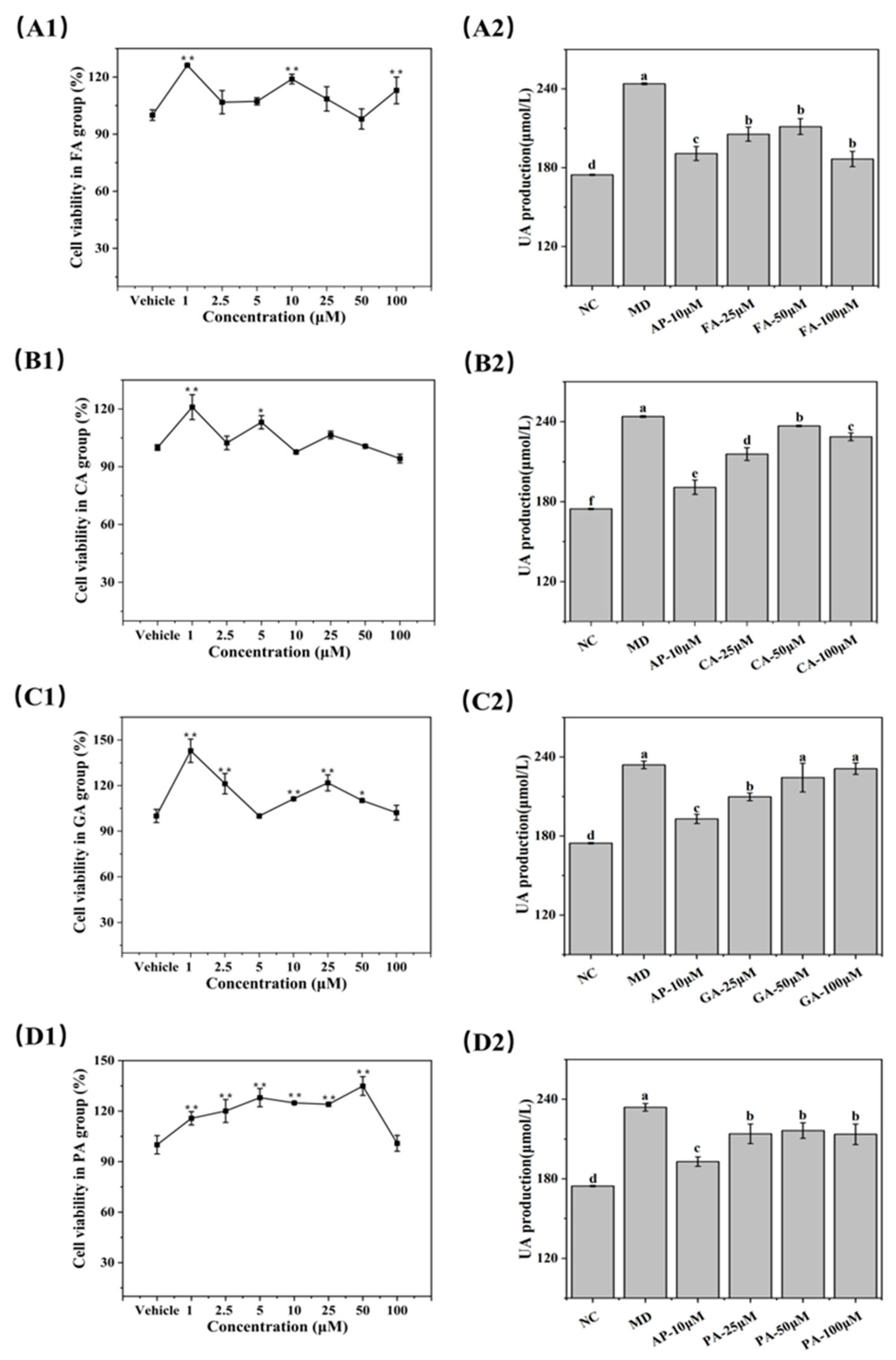
3.7. UA-Lowering Activity of Phenolic Acids in BRL-3A Cells
3.8. Physicochemical and ADMET Performance Prediction
3.9. Physicochemical and ADMET Performance Prediction Structure-Activity Relationship of XOD Inhibition by Phenolic Acids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, D.; Du, J.; He, P.; Wang, N.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. Identification of natural xanthine oxidase inhibitors: Virtual screening, anti-xanthine oxidase activity, and interaction mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsans, J.; Palomäki, A.; Kauppi, M. Gout and Hyperuricemia: A Narrative Review of Their Comorbidities and Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dierckx, R.; Mohee, K.; Clark, A.L.; Cleland, J.G. Xanthine oxidase inhibition for the treatment of cardiovascular disease: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2017, 4, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Tsukui, D.; Kono, H. Uric Acid in Inflammation and the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-Y.; Shen, L.-J.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Lin, L.-Y.; Lin, F.-J. Comparing Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in the Real World: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouakkaz, H.; Djeridane, A.; Mahfoudi, R.; Yilmaz, M.A.; Cakir, O.; Tarhan, A.; Lassakeur, Z.; Yousfi, M. Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity and Uric Acid Dissolution Power of Some Plant Extracts: In Vitro Therapeutical Approach for Gout Treatment. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2024, 34, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Yue, P.; Mao, G.; Zhang, M.; Liu, P.; Wu, X.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L. A comprehensive review on recent xanthine oxidase inhibitors of dietary based bioactive substances for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout: Molecular mechanisms and perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, M.F.; Ahiduzzaman, M.; Islam, M.N.; Shozib, H.B. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and Southeast Asia: A Review. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, A.; Pandey, V.K.; Dar, A.H.; Fayaz, U.; Dash, K.K.; Shams, R.; Ahmad, S.; Bashir, I.; Fayaz, J.; Singh, P.; et al. Rice bran: Nutritional, phytochemical, and pharmacological profile and its contribution to human health promotion. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.I.; Song, G.S.; Yang, E.I.; Youn, Y.; Kim, Y.S. Antioxidant activities and phenolic compounds of pigmented rice bran extracts. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Song, D.; Zhao, X. Potential applications and preliminary mechanism of action of dietary polyphenols against hyperuricemia: A review. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Călinoiu, L.F.; Vodnar, D.C. Whole Grains and Phenolic Acids: A Review on Bioactivity, Functionality, Health Benefits and Bioavailability. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Gao, Q.; Fan, M.; Waleed, A.A.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, H. Ferulic acid ameliorates hyperuricemia by regulating xanthine oxidase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, L. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of quercetin and its derivatives: Interaction mechanism and evaluation methods. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Jiao, Q.C.; Qin, P. Discovery of coumaric acid derivatives hinted by coastal marine source to seek for uric acid lowering agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2163241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.; Lai, X.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J.; Wen, S.; Lai, Z.; et al. Tea and its components reduce the production of uric acid by inhibiting xanthine oxidase. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Su, G.; Cai, M.; Zhou, C.; Huang, J.; Li, L. The antioxidant activities and the xanthine oxidase inhibition effects of walnut (Juglans regia L.) fruit, stem and leaf. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, K.; Przybyłowicz, K.E.; Sawicki, T. Antioxidant activity and profile of phenolic compounds in selected herbal plants. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakbi, A.; Issaoui, M.; Dabbou, S.; Koubaa, N.; Echbili, A.; Hammami, M.; Attia, N. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of phenolic compounds from two extra virgin olive oils. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2010, 23, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, J.; Bhullar, K.S.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Su, D.; Ma, X. Identification, in silico selection, and mechanistic investigation of antioxidant peptides from corn gluten meal hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bhullar, K.S.; Fu, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Su, D.; Wu, S.; He, H.; Wang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Unraveling novel antioxidant peptides from Asian swamp eel: Identification, in silico selection, and mechanistic insights through quantum chemical calculation and molecular docking. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhao, M. Screening of bioactivity-oriented extraction approach and quality control standards of lotus leaf extracts with dual functions. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Tong, S.; Li, Y.; Cai, R.; Zhang, X.; Gao, F. Inhibitory Activity of Quercetin, Rutin, and Hyperoside Against Xanthine Oxidase: Kinetics, Fluorescence, and Molecular Docking. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2025, 26, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Characterization of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities of phenols from pickled radish with molecular simulation. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Study on the interaction mechanism between luteoloside and xanthine oxidase by multi-spectroscopic and molecular docking methods. J. Mol. Recognit. 2022, 35, e2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Ye, Y.; Ran, M.; Ruan, Z.; Jin, N. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by theaflavin: Possible mechanism for anti-hyperuricaemia effect in mice. Process Biochem. 2020, 97, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, W.; Jiao, W.; Lian, Y.; Mi, S.; Chitrakar, B.; Sang, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of ferulic acid and p-coumaric acid on lowering uric acid through network pharmacology and in vitro studies. Food Saf. Health 2024, 2, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Fu, R.; Lin, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L. Investigating the inhibition of xanthine oxidase by five catechins: Kinetic studies, spectroscopy, molecular docking, and dynamics simulations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefin, A.; Ismail Ema, T.; Islam, T.; Hossen, S.; Islam, T.; Al Azad, S.; Uddin Badal, N.; Islam, A.; Biswas, P.; Alam, N.U.; et al. Target specificity of selective bioactive compounds in blocking alpha-dystroglycan receptor to suppress Lassa virus infection: An in silico approach. J. Biomed. Res. 2021, 35, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhu, D.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Su, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y. In vitro and in vivo studies on adlay-derived seed extracts: Phenolic profiles, antioxidant activities, serum uric acid suppression, and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2014, 62, 7771–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, J.X.; Zhang, J.L.; Su, G.H. Hypouricemic effect in hyperuricemic mice and xanthine oxidase inhibitory mechanism of dietary anthocyanins from purple sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, L.; Sun, C.; Zhao, D.; Tang, H. Studies on the structure-activity relationship and interaction mechanism of flavonoids and xanthine oxidase through enzyme kinetics, spectroscopy methods and molecular simulations. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.; Qi, R.; Chang, H.; Han, L.; Han, W. Molecular dockings and molecular dynamics simulations reveal the potency of different inhibitors against xanthine oxidase. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11639–11649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, N.M.F.S.A.; Gesto, D.; Oliveira, E.F.; Santos-Martins, D.; Brás, N.F.; Sousa, S.F.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Receptor-based virtual screening protocol for drug discovery. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 582, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, K.A. SwissADME and pkCSM webservers predictors: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions for in silico ADME/T properties of artemisinin and its derivatives. Kompleks. Ispolz. Miner. Syra 2023, 325, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Ren, L.; Xie, Y. Advances in structures required of polyphenols for xanthine oxidase inhibition. Food Front. 2020, 1, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Reducing Power (mM) | IC50 Values of ABTS Assay (mM) | IC50 Values of DPPH Assay (mM) | ORAC Value (mmol TE/mmol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferulic acid | 0.74 ± 0.05 c | 0.30 ± 0.00 c | 0.80 ± 0.03 b | 7.99 ± 0.24 c |
| p-Coumaric acid | 6.98 ± 0.13 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 c | 19.39 ± 1.24 a | 9.64 ± 0.27 b |
| Gallic acid | 0.20 ± 0.01 d | 0.02 ± 0.00 d | 0.18 ± 0.01 b | 20.12 ± 0.74 a |
| Protocatechuic acid | 0.12 ± 0.01 d | 0.40 ± 0.02 b | 0.62 ± 0.00 b | 6.63 ± 0.09 d |
| Positive control | 2.62 ± 0.20 b (Trolox) | 3.41 ± 0.12 a (Trolox) | 0.68 ± 0.01 b (Trolox) |
| Compound | Ferulic Acid | p-Coumaric Acid | Gallic Acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mw | 194.18 | 164.16 | 170.12 |
| H-Ac | 4 | 3 | 5 |
| H-Do | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Log P | 1.25 | 1.43 | 0.59 |
| NRB | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TPSA | 66.76 | 57.53 | 97.99 |
| Water solubility (log mol/L) | −2.816 | −2.378 | −2.56 |
| HIA (%) | 77.579 | 93.494 | 43.374 |
| Caco-2 permeability (log Papp, cm/s) | 1.757 | 1.21 | −0.081 |
| BBB permeability (log BB) | 0.175 | −0.225 | −1.102 |
| CYP2D6 | No | No | No |
| CYP3A4 | No | No | No |
| Renal OCT2 substrate | No | No | No |
| Hepatotoxicity | No | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Su, D.; Luo, X.; Chen, B.; Bhullar, K.S.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; et al. Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase by Four Phenolic Acids: Kinetic, Spectroscopic, Molecular Simulation, and Cellular Insights. Foods 2025, 14, 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193404
Wang X, Su D, Luo X, Chen B, Bhullar KS, Liu H, Wang C, Zhang J, Wang L, Yang H, et al. Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase by Four Phenolic Acids: Kinetic, Spectroscopic, Molecular Simulation, and Cellular Insights. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193404
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao, Di Su, Xinyu Luo, Bingjie Chen, Khushwant S. Bhullar, Hongru Liu, Chunfang Wang, Jinglin Zhang, Longshen Wang, Hang Yang, and et al. 2025. "Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase by Four Phenolic Acids: Kinetic, Spectroscopic, Molecular Simulation, and Cellular Insights" Foods 14, no. 19: 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193404
APA StyleWang, X., Su, D., Luo, X., Chen, B., Bhullar, K. S., Liu, H., Wang, C., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Yang, H., & Zhou, W. (2025). Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase by Four Phenolic Acids: Kinetic, Spectroscopic, Molecular Simulation, and Cellular Insights. Foods, 14(19), 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193404







