Non-Destructive and Real-Time Discrimination of Normal and Frozen-Thawed Beef Based on a Novel Deep Learning Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Pre-Processing
2.2. The Proposed YOLO-NF Model
2.2.1. Overall Network Structure of the YOLO-NF Model
2.2.2. Network Structure of YOLOv7 Model
2.2.3. SimAM Module
2.2.4. SE Attention Mechanism Module
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
2.4. Supplementary Model Analyses
2.5. Model Deployment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Experimental Training Process
3.3. Quantitative Analysis
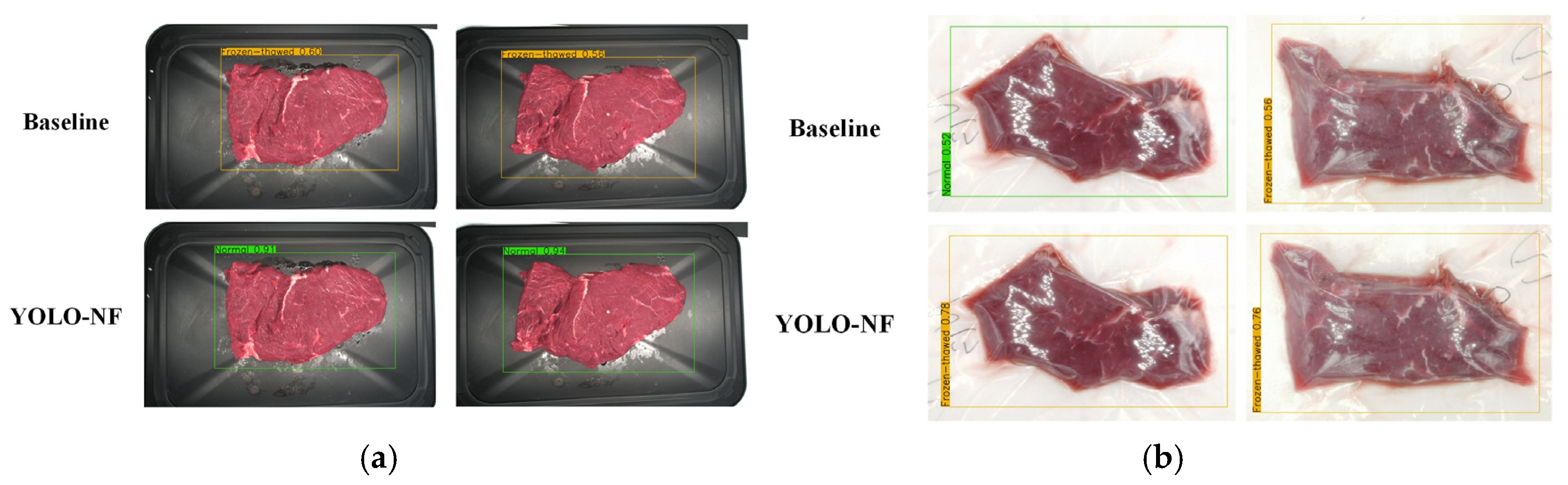
3.4. Qualitative Analysis
3.5. Ablation Experiments
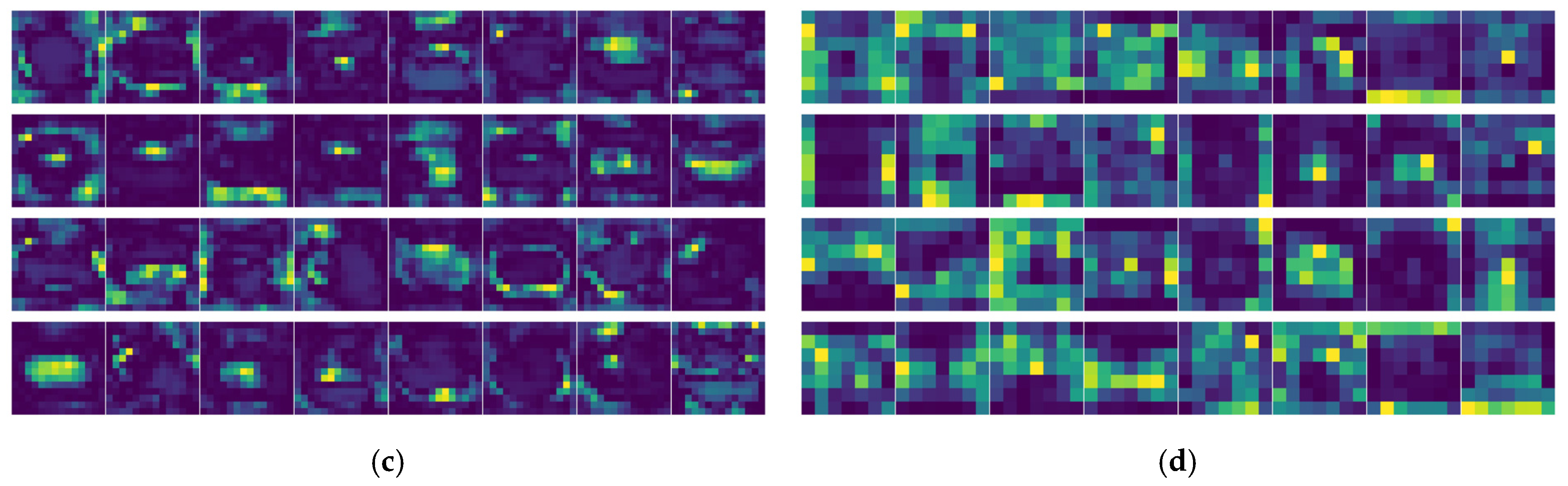
3.6. Model Interpretations
3.7. Deployment of the YOLO-NF Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, Y.; Lv, J.; Lou, A.; Quan, W.; Shen, Q.W. Protein Lysine Acetylation Regulates Beef Color Stability During Storage. LWT 2025, 220, 117468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Seo, J.-K.; Romanyk, M.; Shin, D.-J.; Kim, Y.H.B. Effects of Aging and Repeated Freeze-thaw Cycles on Quality Attributes, Physicochemical and Biochemical Properties, and Sensory Characteristics of Beef Sirloins. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lu, P.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Fowler, S.; Liang, R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Characterization and Identification of Frozen-thawed Beef: The Interactions of Frozen Storage and Chilled Display Time. Food Sci. Anim. Prod. 2025, 3, 9240098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.D.; Nott, K.P.; Kshirsagar, A.A.; Hall, L.D. The Effect of Freezing and Thawing on the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Parameters of Water in Beef, Lamb and Pork Meat. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejerina, D.; Oliván, M.; García-Torres, S.; Franco, D.; Sierra, V. Use of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Discriminate DFD Beef and Predict Meat Quality Traits in Autochthonous Breeds. Foods 2022, 11, 3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antequera, T.; Caballero, D.; Grassi, S.; Uttaro, B.; Perez-Palacios, T. Evaluation of Fresh Meat Quality by Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A review. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hong, S.-J.; Kim, S.; Ryu, J.; Roh, S.; Kim, G. Classification of Fresh and Frozen-Thawed Beef Using a Hyperspectral Imaging Sensor and Machine Learning. Agriculture 2023, 13, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Non-Destructive Detection of Water Content in Pork Based on NIR Spatially Resolved Spectroscopy. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Toldrá, F.; Kang, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y. Benefits of Ultrasonic Technology Application in Meat Field and Its Influential Mechanism: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulat, J.; Monteils, V.; Andueza, D. The Freezing Duration and the Number of Freeze-thaw Cycles Influence the Near Infrared Spectra of Ageing Beef Muscles. LWT 2024, 214, 117147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Zhong, X.; Zheng, O.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, M. Innovations in Seafood Freshness Quality: Non-destructive Detection of Freshness in Litopenaeus vannamei using the YOLO-Shrimp Model. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Pi, J.; Wang, D. Research on Beef Marbling Grading Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv8x. Foods 2025, 14, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Li, C. Discrimination among Fresh, Frozen–Stored and Frozen–Thawed Beef Cuts by Hyperspectral Imaging. Foods 2024, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Qiu, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Bouhile, Y.; Ma, H. Ultrasonic-Assisted Flowing Water Thawing of Frozen Beef with Different Frequency Modes: Effects on Thawing Efficiency, Quality Characteristics and Microstructure. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Palacios, T.; Ávila, M.; Antequera, T.; Torres, J.P.; González-Mohino, A.; Caro, A. MRI-Computer Vision on Fresh and Frozen-Thawed Beef: Optimization of Methodology for Classification and Quality Prediction. Meat Sci. 2023, 197, 109054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; LeCun, Y.; Sahani, M.; Precup, D.; Silver, D.; Sugiyama, M.; Uchibe, E.; Morimoto, J. Deep Learning, Reinforcement Learning, and World Models. Neural Netw. 2022, 152, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, M.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Hazra, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Garg, D. Development of IoT Enabled Deep Learning Model for Indian Food Classification: An Approach Based on Differential Evaluation. Food Anal. Methods 2025, 18, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhu, R.; He, D.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z. Adulteration Detection of Pork in Mutton Using Smart Phone with the CBAM-Invert-ResNet and Multiple Parts Feature Fusion. Foods 2023, 12, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Wang, S.; Yong, C.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X. Non-Destructive Detection of Chicken Freshness Based on Electronic Nose Technology and Transfer Learning. Agriculture 2023, 13, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, İ.Y.; Gürfidan, R.; Açikgözoğlu, E. Quality Determination of Frozen-Thawed Shrimp Using Machine Learning Algorithms Powered by Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Food Anal. Methods 2025, 18, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, İ.Y.; Gürfidan, R.; Yiğit, T. Quality Prediction of Seabream Sparus Aurata by Deep Learning Algorithms and Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elfattah, M.; Ewees, A.A.; Darwish, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Detection and Classification of Meat Freshness Using an Optimized Deep Learning Method. Food Chem. 2025, 489, 144783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ma, J.; Sun, D.-W.; Cheng, J.-H.; Zhou, C. Fast Real-Time Monitoring of Meat Freshness Based on Fluorescent Sensing Array and Deep Learning: From Development to Deployment. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhan, W.; Du, Z.; Hong, S.; Dong, T.; She, J.; Min, C. Pork Primal Cuts Recognition Method via Computer Vision. Meat Sci. 2022, 192, 108898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Duan, X.; Li, K.; Cheng, H.; Sun, G.; Luo, X.; Hopkins, D.L.; Holman, B.W.B.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Investigation of Oxygen Packaging to Maintain Beef Color Stability and Microbiology Safety after Periods of Long-Term Superchilled Storage. Meat Sci. 2024, 215, 109548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Holman, B.W.B.; Mao, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, X.; Hopkins, D.L.; Zhang, Y. Determination of a pH Threshold for Dark Cutting Beef Based On Visual Evaluation By Asian Consumers. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xue, S.; Li, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhu, T.; Ni, C. A Candy Defect Detection Method Based on StyleGAN2 and Improved YOLOv7 for Imbalanced Data. Foods 2024, 13, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Zhou, H.; Yi, H.; Ma, L.; Nie, J.; Huang, T. YOLOv7-GCM: A Detection Algorithm for Creek Waste Based on Improved YOLOv7 Model. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2024, 27, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Ma, J.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Visible Detection of Chilled Beef Freshness Using a Paper-Based Colourimetric Sensor Array Combining with Deep Learning Algorithms. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kılcı, O.; Koklu, M. Automated Classification of Biscuit Quality Using YOLOv8 Models in Food Industry. Food Anal. Methods 2025, 18, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chu, L.; Pei, J.; Liu, W.; Bian, J. Model Complexity of Deep Learning: A survey. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2021, 63, 2585–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| Hyperparameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Epoch | 80 |
| Initial learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Final learning rate | 0.1 |
| Batch size | 4 |
| Momentum | 0.97 |
| Weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Input image size | 640 × 640 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | FLOPs (G) | Running Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 79.3 | 83.3 | 81.2 | 84.8 | 15.8 | 0.015 |
| YOLOv8 | 73.6 | 84.6 | 78.7 | 85.0 | 28.4 | 0.011 |
| YOLOv7 | 82.8 | 79.7 | 81.2 | 89.9 | 103.2 | 0.0214 |
| YOLO-NF | 95.5 | 95.2 | 95.3 | 98.6 | 103.4 | 0.022 |
| Samples | Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Baseline | 82.8 | 79.7 | 81.2 | 89.9 |
| YOLO-NF | 95.5 | 95.2 | 95.3 | 98.6 | |
| Normal | Baseline | 94.2 | 79.3 | 86.1 | 94.9 |
| YOLO-NF | 93.1 | 99.6 | 96.2 | 98.7 | |
| Frozen-thawed | Baseline | 71.4 | 80.2 | 75.5 | 85.0 |
| YOLO-NF | 97.9 | 90.9 | 94.3 | 98.5 |
| Scheme | Baseline | SimAM | SE | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | √ | - | - | 82.8 | 79.7 | 81.2 | 89.9 |
| B | √ | √ | - | 94.4 | 88.7 | 91.5 | 96.8 |
| C | √ | - | √ | 87.6 | 94.2 | 91.8 | 97.1 |
| D | √ | √ | √ | 95.5 | 95.2 | 95.3 | 98.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, R.; Lyu, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, P.; Duan, X.; Hopkins, D.L.; Zhang, Y. Non-Destructive and Real-Time Discrimination of Normal and Frozen-Thawed Beef Based on a Novel Deep Learning Model. Foods 2025, 14, 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193344
Xi R, Lyu X, Yang J, Lu P, Duan X, Hopkins DL, Zhang Y. Non-Destructive and Real-Time Discrimination of Normal and Frozen-Thawed Beef Based on a Novel Deep Learning Model. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193344
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Rui, Xiangyu Lyu, Jun Yang, Ping Lu, Xinxin Duan, David L. Hopkins, and Yimin Zhang. 2025. "Non-Destructive and Real-Time Discrimination of Normal and Frozen-Thawed Beef Based on a Novel Deep Learning Model" Foods 14, no. 19: 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193344
APA StyleXi, R., Lyu, X., Yang, J., Lu, P., Duan, X., Hopkins, D. L., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Non-Destructive and Real-Time Discrimination of Normal and Frozen-Thawed Beef Based on a Novel Deep Learning Model. Foods, 14(19), 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193344







