Analysis of Global Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages from 2015 to 2024
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection on Microbial Safety Incidents of Frozen Beverages in Global Import and Export Trade
2.2. Criteria for Data Inclusion and Exclusion
2.3. Data Collection on Microbial Safety Incidents of Frozen Beverages in the Chinese Market
2.4. Geographic Information Visualization Analysis of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages
2.5. Analysis of the Contamination Spectrum of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages
2.6. Analysis of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverage
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
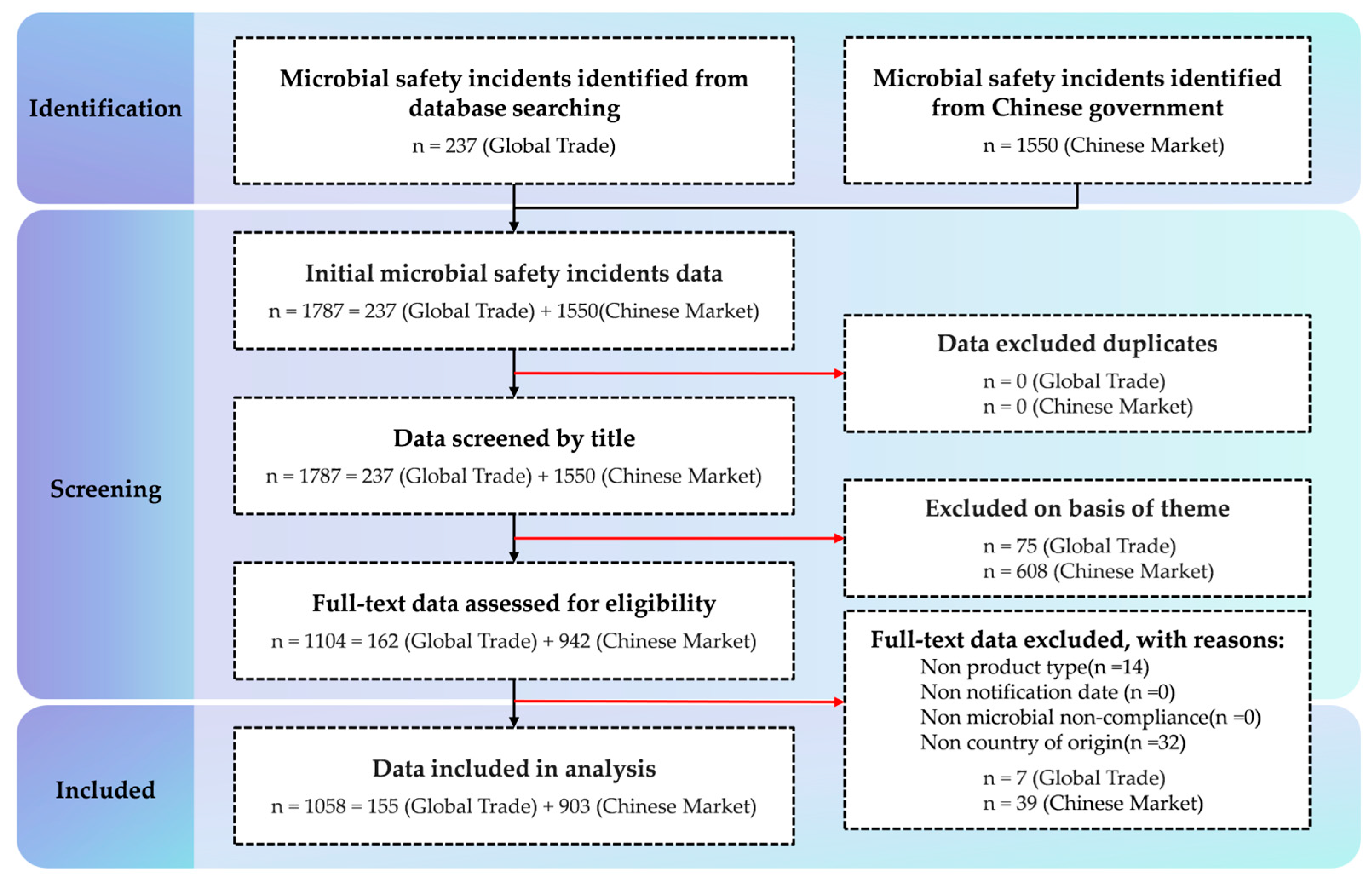
3.1. Screening Results of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages
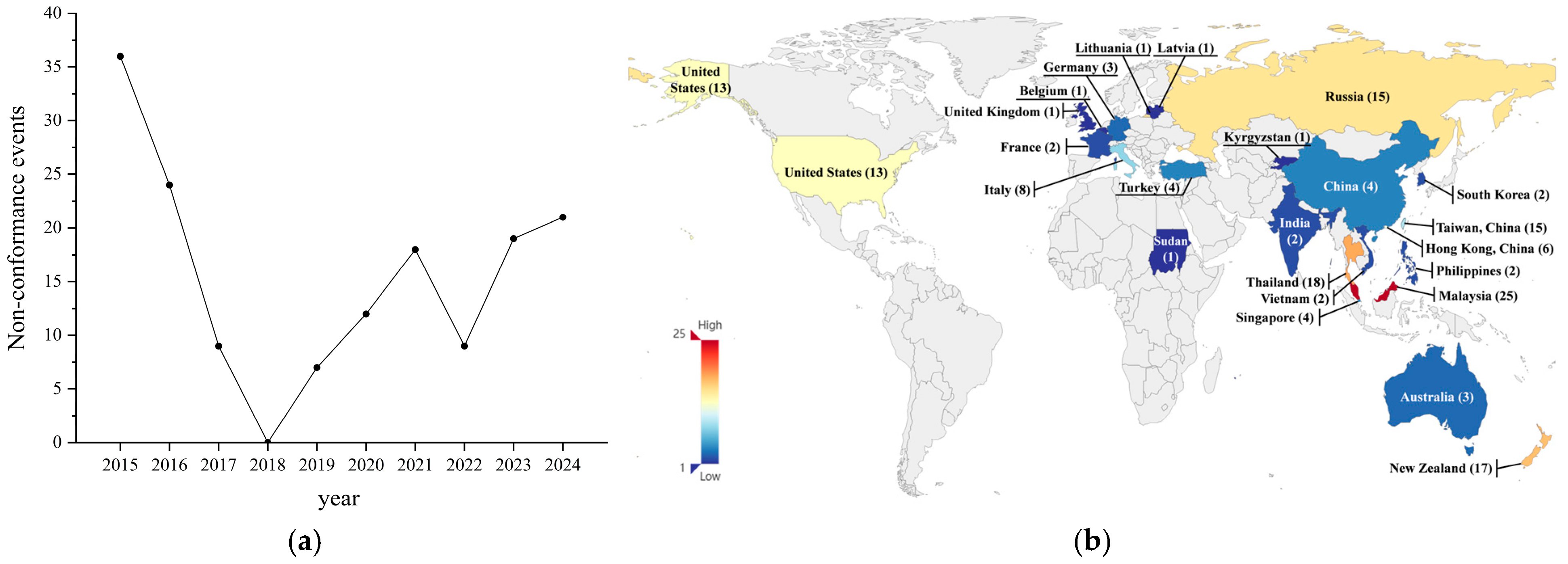
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages Imports and Exports Among Major Global Trading Nations
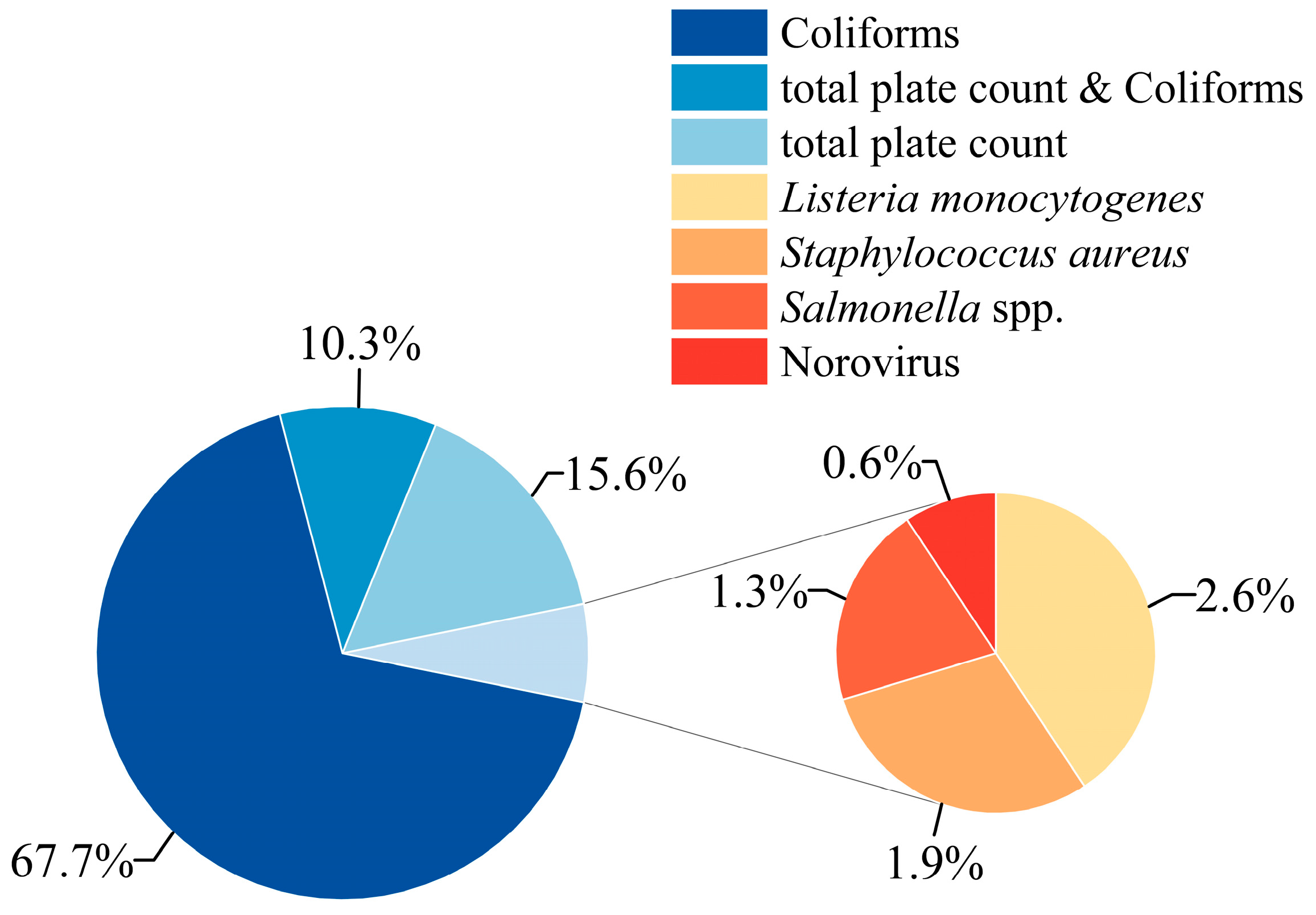
3.3. Microbial Safety Incident Contamination Spectrum of Frozen Beverages Imports and Exports Among Major Global Trading Nations
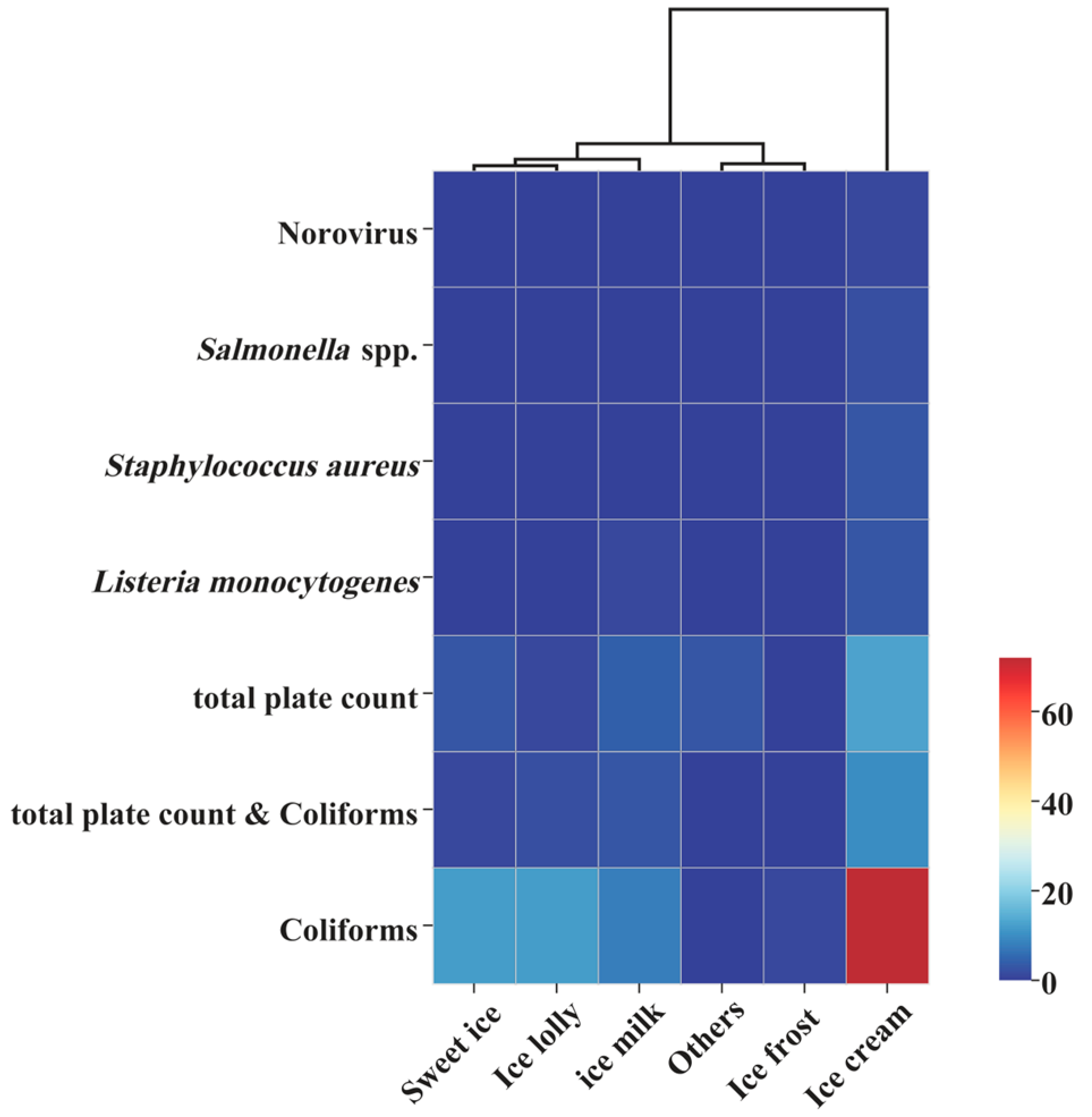
3.4. Cluster Analysis of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverage Imports and Exports Among Major Global Trading Countries
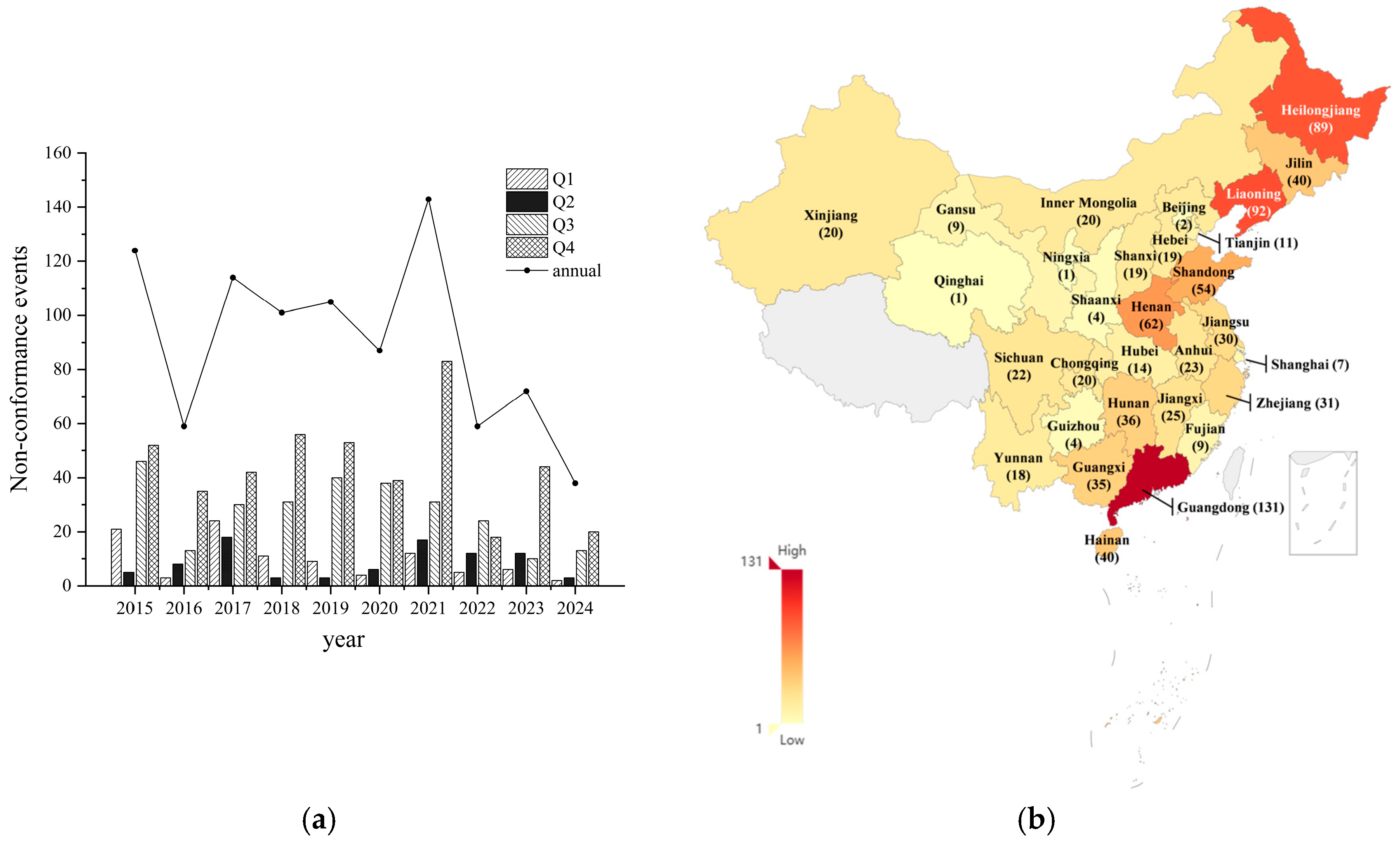
3.5. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages in the Chinese Market
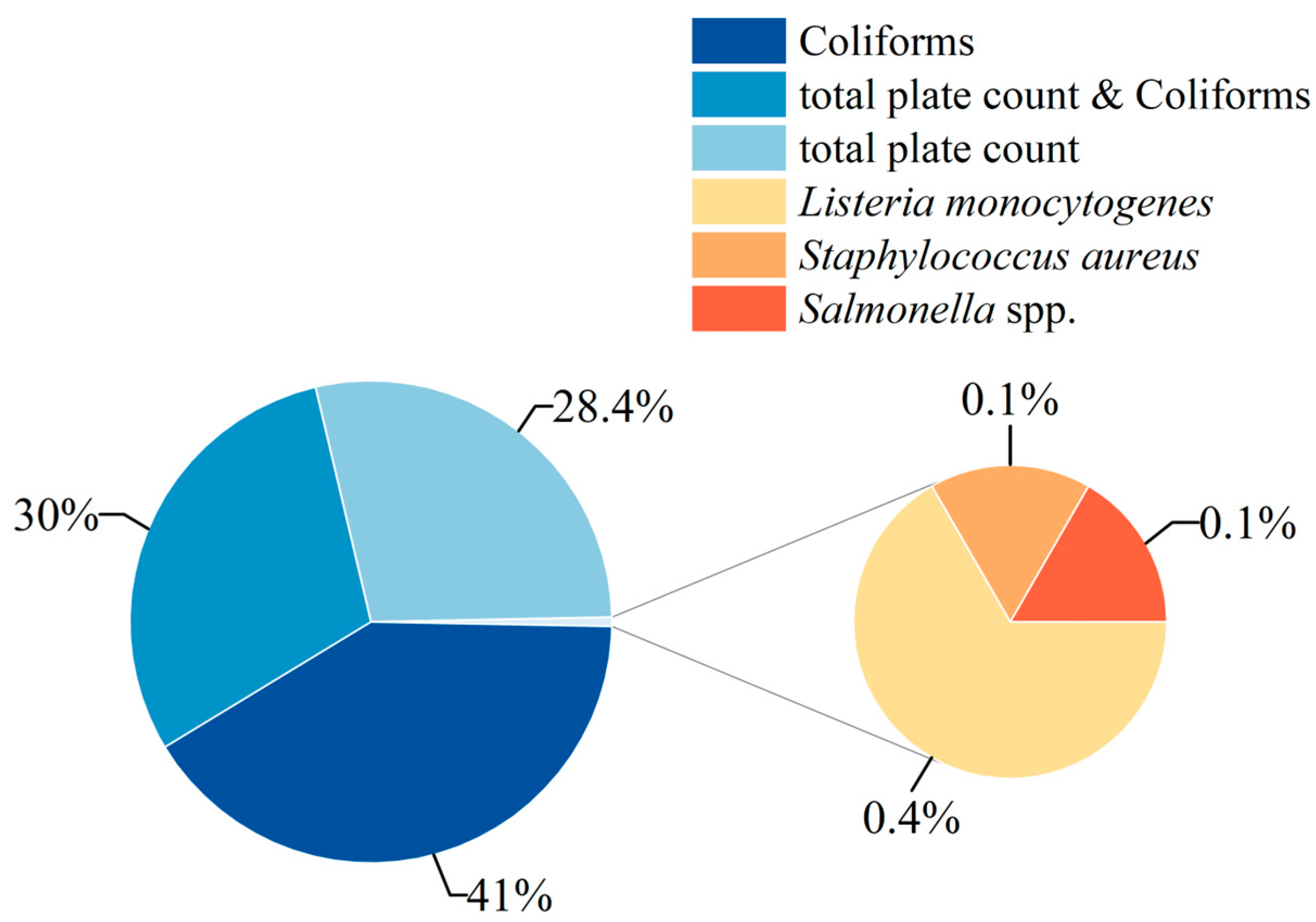
3.6. Microbial Safety Incident Contamination Spectrum of Frozen Beverages in the Chinese Market
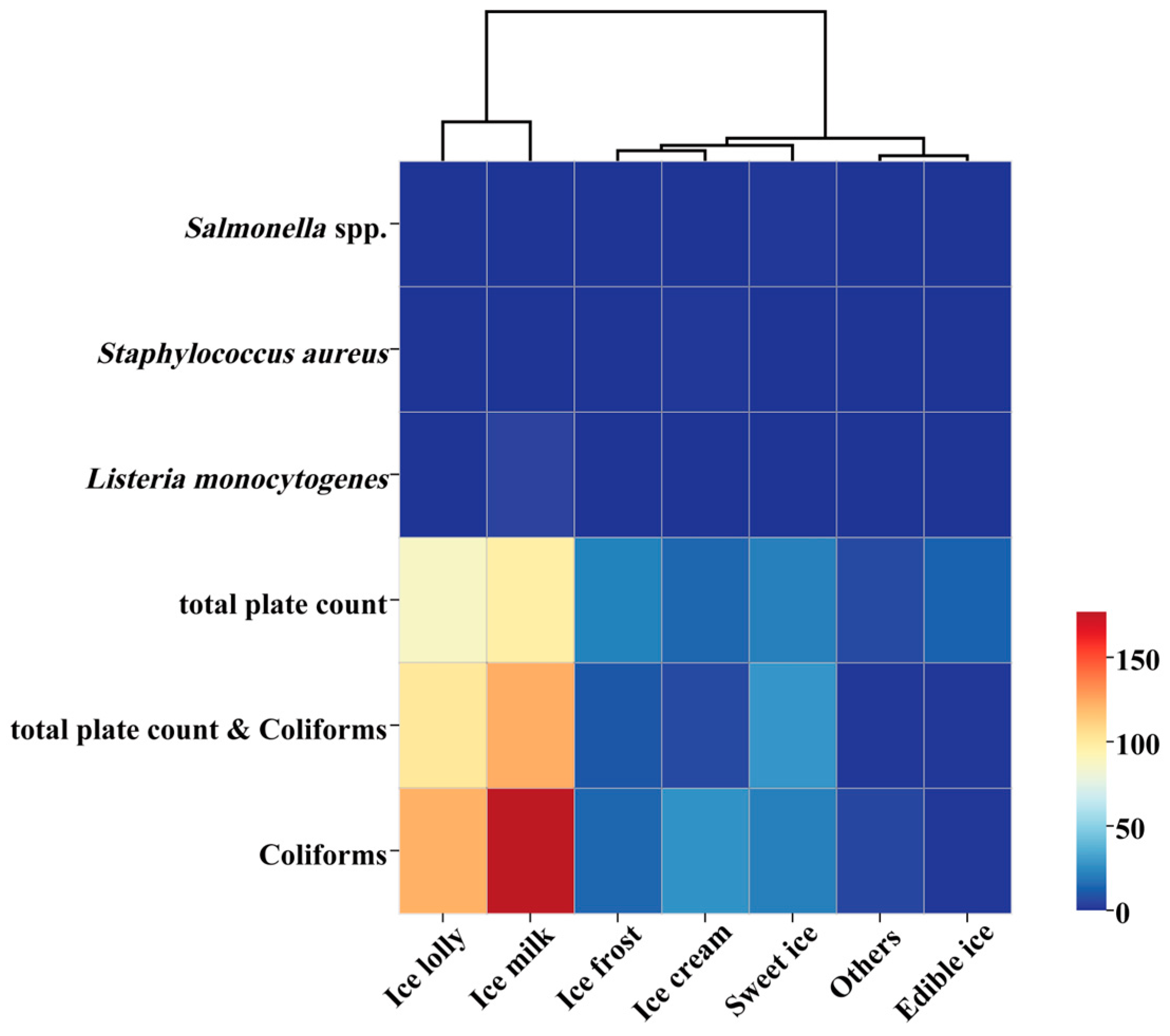
3.7. Cluster Analysis of Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverage Market in China
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RASFF | Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed |
| GEMS | Global Environment Monitoring System |
References
- Nalbone, L.; Vallone, L.; Giarratana, F.; Virgone, G.; Lamberta, F.; Marotta, S.M.; Donato, G.; Giuffrida, A.; Ziino, G. Microbial Risk Assessment of Industrial Ice Cream Marketed in Italy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Eskandari, M.H.; Davoudi, Z. Application and functions of fat replacers in low-fat ice cream: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassagh, M.H.; Movassagh, A.; Mahmoodi, H.; Servatkhah, F.; Sourorbakhsh, M.R. Microbiological contamination of the traditional chocolate ice cream sold in the northwest region of Iran. Glob. Vet. 2011, 6, 269–271. [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy, T.W.; Hedberg, C.W.; Slutsker, L.; White, K.E.; Besser-Wiek, J.M.; Moen, M.E.; Feldman, J.; Coleman, W.W.; Edmonson, L.M.; MacDonald, K.L.; et al. A national outbreak of Salmonella enteritidis infections from ice cream. The Investigation Team. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.H.; Valentin-Bon, I.E.; Brackett, R.E. Detection and enumeration of Salmonella enteritidis in homemade ice cream associated with an outbreak: Comparison of conventional and real-time PCR methods. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouillot, R.; Klontz, K.C.; Chen, Y.; Burall, L.S.; Macarisin, D.; Doyle, M.; Bally, K.M.; Strain, E.; Datta, A.R.; Hammack, T.S.; et al. Infectious Dose of Listeria monocytogenes in Outbreak Linked to Ice Cream, United States, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraccalvieri, R.; Bianco, A.; Difato, L.M.; Capozzi, L.; Del Sambro, L.; Simone, D.; Catanzariti, R.; Caruso, M.; Galante, D.; Normanno, G.; et al. Toxigenic Genes, Pathogenic Potential and Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacillus cereus Group Isolated from Ice Cream and Characterized by Whole Genome Sequencing. Foods 2022, 11, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schrijver, K.; Buvens, G.; Posse, B.; Van den Branden, D.; Oosterlynck, O.; De Zutter, L.; Eilers, K.; Pierard, D.; Dierick, K.; Van Damme-Lombaerts, R.; et al. Outbreak of verocytotoxin-producing E. coli O145 and O26 infections associated with the consumption of ice cream produced at a farm, Belgium, 2007. Euro Surveill. 2008, 13, 8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetsch, A.; Contzen, M.; Hartelt, K.; Kleiser, A.; Maassen, S.; Rau, J.; Kraushaar, B.; Layer, F.; Strommenger, B. Staphylococcus aureus food-poisoning outbreak associated with the consumption of ice-cream. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 187, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, A.; Son, S.; Kim, D. Using Import Data to Predict the Potential of Introduction of Alert Alien Species to South Korea. Diversity 2022, 14, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleter, G.A.; Prandini, A.; Filippi, L.; Marvin, H.J.P. Identification of potentially emerging food safety issues by analysis of reports published by the European Community’s Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) during a four-year period. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 932–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, J.L.; Stratakou, I.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Besten, H.M.W.d.; Zwietering, M.H. European alerting and monitoring data as inputs for the risk assessment of microbiological and chemical hazards in spices and herbs. Food Control 2016, 69, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, P.; Nucera, D.; Guardone, L.; Mariotti, M.; Nuvoloni, R.; Armani, A. Seafood products notifications in the EU Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) database: Data analysis during the period 2011–2015. Food Control 2018, 93, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beninger, P.; Murray, M. Review of FDA Amendments Act Section 921 Experience in Posting Data-mining Results from the FAERS Database. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frozen Drinks (SAC/TC 497). GB/T 30590-2014; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Li, D.; Mei, H.; Shen, Y.; Su, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Zu, M.; Chen, W. ECharts: A declarative framework for rapid construction of web-based visualization. Vis. Inform. 2018, 2, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.M.; Eltahan, A.; Hassan, H.A.; Abbas, N.H.; Hussien, H.; Shimamoto, T. Loads of Coliforms and Fecal Coliforms and Characterization of Thermotolerant Escherichia coli in Fresh Raw Milk Cheese. Foods 2022, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houmsi, M.; Ismail, Z.; Othman, K.; Ishak, D.; Magdy Hamed, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Syamsunur, D.; Shahid, S. Spatiotemporal Changes in Hourly Wet Bulb Globe Temperature in Peninsular Malaysia. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 2327–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, S.P. Effect of cold chain interruptions on the shelf-life of fluid pasteurised skim milk at the consumer stage. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2018, 21, e2017064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro Samuel, C.; Chukwuma Victor, U.; Isaiah, Y.; Aroh, K.E.; Owolabi, O.J.; Kalu, A.C.; Egwu-Ikechukwu, M.M.; Nnabugwu, C.C.; Azuama, O.C.; Ilang, D.C.; et al. Isolation, Identification and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Public Health Threat Enteric Bacteria from Milk and Dairy Products Retail in Abakaliki, South-East, Nigeria. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 17, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, A.K.; Yuksel, M. Determination of Certain Microbiological Quality Characteristics of Ice Cream, Detection of Salmonella by Conventional and Immunomagnetic Separation Methods and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Salmonella spp. Isolates. J. Food Saf. 2015, 35, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalew, K.; Pang, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, X. Recent Development in Detection and Control of Psychrotrophic Bacteria in Dairy Production: Ensuring Milk Quality. Foods 2024, 13, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.E.G.; Rossi, G.A.M.; Silva, H.O.; Oliveira, L.M.F.S.; Vasconcellos, A.N.; Fonseca, D.d.C.M.; Vaz, A.C.N.; de Souza, B.M.S.; Vidal, A.M.C. Gene Detection and Enzymatic Activity of Psychrotrophic Bacillus cereus s.s. Isolated from Milking Environments, Dairies, Milk, and Dairy Products. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Cold-adaptive mechanism of psychrophilic bacteria in food and its application. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 169, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mako, S.L.; Harrison, M.A.; Sharma, V.; Kong, F. Microbiological quality of packaged ice from various sources in Georgia. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundogan, N.; Güçlü, E. Occurrence and antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli, Stapylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus in raw milk and dairy products in Turkey. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2014, 67, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2759-2015; National Food Safety Standard—Frozen Drinks and Production Materials. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- (EC) No 2073/2005; Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. EC (European Commission): Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- Silk, B.J.; Date, K.A.; Jackson, K.A.; Pouillot, R.; Holt, K.G.; Graves, L.M.; Ong, K.L.; Hurd, S.; Meyer, R.; Marcus, R.; et al. Invasive listeriosis in the Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet), 2004-2009: Further targeted prevention needed for higher-risk groups. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54 (Suppl. 5), S396–S404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieschler-Lübbehüsen, S.; Kabisch, J.; Hetzer, B.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Böhnlein, C. Risk of Pseudomonas spp. in raw milk: Biofilm formation and enhanced peptidase production. Int. Dairy J. 2025, 171, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Burall, L.S.; Macarisin, D.; Pouillot, R.; Strain, E.; De Jesus, A.J.; Laasri, A.; Wang, H.; Ali, L.; Tatavarthy, A.; et al. Prevalence and Level of Listeria monocytogenes in Ice Cream Linked to a Listeriosis Outbreak in the United States. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Sarkar, P.K. Prevalence and characterization of Bacillus cereus group from various marketed dairy products in India. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 94, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, G.T.; Tuncel, G. Biofilm formation in an ice cream plant. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2006, 89, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundén, J.M.; Miettinen, M.K.; Autio, T.J.; Korkeala, H.J. Persistent Listeria monocytogenes Strains Show Enhanced Adherence to Food Contact Surface after Short Contact Times. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neha, N.; Anand, S.; Djira, G.; Kraus, B.; Sutariya, S. Listeria cross contamination levels in raw ice cream mix can serve as a predictor of their potential presence as heat-injured cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9659–9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xiaoyan, P.; Junjie, M.; Ying, L.; Shuran, Y.; Zixin, P.; Xiaorong, Y.; Lingling, M.; Qingwen, Y.; Huan, R.; et al. Surveillance and examination of microbial contamination in ice cream in China. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyac047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reij, M.W.; Den Aantrekker, E.D.; Microbio, I.E.R.A. Recontamination as a source of pathogens in processed foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warke, R.; Kamat, A.; Kamat, M.; Thomas, P. Incidence of pathogenic psychrotrophs in ice creams sold in some retail outlets in Mumbai, India. Food Control 2000, 11, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbakan, U.; Çon, A.H.; Ayar, A. Determination of microbiological contamination sources during ice cream production in Denizli, Turkey. Food Control 2004, 15, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Sources | Web Section | Website Link |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) | / | https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/screen/search (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Import Refusal Section, Import Alert Section | https://www.fda.gov/food/guidance-regulation-food-and-dietary-supplements/food-imports-exports (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan | Section on Violations in Food Monitoring Operations | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/shokuhin/yunyu_kanshi/index.html (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| Korea Food and Drug Administration | Imported Food Non-compliance Sector | https://www.mfds.go.kr/eng/wpge/m_11/de011002l001.do |
| Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry of Australia | Inspection and Testing of Imported Food Sector | https://bicon.agriculture.gov.au/BiconWeb4.0/Home/Notice (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| New Zealand Food Safety Authority | Food Recall and Complaints Division | https://www.mpi.govt.nz/food-safety-home/food-recalls-and-complaints/ (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| General Administration of Customs of China | Information on Prohibited Food and Cosmetics | http://jckspj.customs.gov.cn/spj/xxfw39/fxyj47/4677516/index.html (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| State Administration for Market Regulation and Provincial Bureaus | / | https://www.samr.gov.cn/ (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| Food Safety Center of Hong Kong | Food Alert | https://www.cfs.gov.hk/tc_chi/whatsnew/whatsnew_fa/whatsnew_fa.html (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| Taiwan Food and Drug Administration | Non-compliance of Food Information in Import Inspection | https://www.fda.gov.tw/TC/index.aspx (accessed on 10 September 2025) |
| Data Characteristics | Number of Data | |
|---|---|---|
| Incidents country & region | Southeast Asia | 51 |
| Other Asian region | 34 | |
| Europe | 32 | |
| Africa | 1 | |
| America | 13 | |
| Oceania | 20 | |
| South China | 215 | |
| North China | 71 | |
| East China | 63 | |
| Northeast China | 221 | |
| Southwest China | 64 | |
| Northwest China | 35 | |
| Central China | 73 | |
| Huang-Huai-Hai region | 146 | |
| Beverage category | ice cream | 152 |
| ice milk | 417 | |
| ice frost | 47 | |
| ice lolly | 325 | |
| sweet ice | 87 | |
| edible ice | 15 | |
| Non-compliance items | Coliforms | 472 |
| Total plate count | 284 | |
| Coliforms & total plate count | 286 | |
| L. monocytogenes | 8 | |
| S. aureus | 4 | |
| Salmonella | 3 | |
| Norovirus | 1 | |
| Region | Countries/Regions | Number of Data |
|---|---|---|
| Southeast Asia | Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, Vietnam, Philippines | 51 |
| Other Asia region | China Taiwan, China Hong Kong, China, India, South Korea, Turkey, Kyrgyzstan | 34 |
| Europe | Russia, Italy, Germany, France, Latvia, Lithuania, Belgium | 32 |
| Africa | Sudan | 1 |
| America | United States | 13 |
| Oceania | New Zealand, Australia | 20 |
| X2 | 61.623 | |
| p | <0.001 |
| Non-Compliant Items | Categories of Frozen Beverages | X2 | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ice Cream | Ice Lolly | Sweet Ice | Ice Milk | Ice Frost | Others | |||
| Norovirus | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | n.s | |
| Salmonella spp. | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | n.s | |
| S. aureus | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | n.s | |
| L. monocytogenes | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 0.317 |
| total plate count | 13 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 18.500 | <0.001 |
| total plate count & Coliforms | 10 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 12.500 | 0.006 |
| Coliforms | 72 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 158.667 | <0.001 |
| X2 | 264.577 | 14.800 | 12.875 | 6.500 | n.s | n.s | ||
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.090 | ||||
| Region | Provinces | Number of Data |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast China | Liaoning, Heilongjiang, Jilin | 221 |
| South China | Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi, Fujian | 215 |
| Huang-Huai-Hai region | Henan, Shandong, Jiangsu | 146 |
| Central China | Hunan, Anhui, Hubei | 73 |
| North China | Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Hebei, Tianjin, Beijing | 71 |
| Southwest China | Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Guizhou | 64 |
| East China | Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Shanghai | 63 |
| Northwest China | Xinjiang, Gansu, Shaanxi, Qinghai, Ningxia | 35 |
| X2 | 337.60 | |
| p | <0.001 |
| Non-Compliant Items | Categories of Frozen Beverages | X2 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ice Milk | Ice Lolly | Sweet Ice | Ice Cream | Ice Frost | Edible Ice | Others | |||
| Salmonella spp. | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | n.s | |
| S. aureus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | n.s | |
| L. monocytogenes | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | n.s | |
| total plate count | 97 | 87 | 21 | 14 | 22 | 13 | 6 | 232.800 | <0.001 |
| total plate count & Coliforms | 123 | 101 | 28 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 410.607 | <0.001 |
| Coliforms | 177 | 122 | 21 | 27 | 14 | 1 | 5 | 540.997 | <0.001 |
| X2 | 156.436 | 6.006 | 22.915 | 32.167 | 4.870 | 19.200 | 3.500 | ||
| p | <0.001 | 0.050 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.088 | <0.001 | 0.174 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Fu, G.; Wang, X. Analysis of Global Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages from 2015 to 2024. Foods 2025, 14, 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183238
Qin Y, Li W, Zhang Z, Lu Y, Fu G, Wang X. Analysis of Global Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages from 2015 to 2024. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183238
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Yulong, Wenbo Li, Zhaohuan Zhang, Yuying Lu, Gui Fu, and Xu Wang. 2025. "Analysis of Global Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages from 2015 to 2024" Foods 14, no. 18: 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183238
APA StyleQin, Y., Li, W., Zhang, Z., Lu, Y., Fu, G., & Wang, X. (2025). Analysis of Global Microbial Safety Incidents in Frozen Beverages from 2015 to 2024. Foods, 14(18), 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183238





