Beyond Sugar: A Holistic Review of Sweeteners and Their Role in Modern Nutrition
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Sweetener | Type of Treatments | Chemical Formulas | Glycemic Index (GI) | Potency * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maltose | enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis | C12H22O11 | 105 | 0.3 | [8] |
| Dextrose | hydrolysis | C6H12O6 | 100 | 0.7 | [9] |
| Glucose | hydrolysis | C6H12O6 | 100 | [10] | |
| Trehalose | Enzymatic or/and fermentation processes | C12H22O11 | 70 | 0.4–0.5 | [11] |
| Sucrose | acid catalysts and heat | C12H22O11 | 65 | 1.0 | [12] |
| Fructose | enzymatically converting glucose | C6H12O6 | [13] | ||
| Galactose | isomerization of glucose | C6H12O6 | 20 | 0.5–0.7 | [14] |
| Lactose | concentration, crystallization, and purification from dairy | C12H22O11 | 46 | 0.2–0.4 | [15] |
| Tagarose | Isomerization of D-galactose | C6H12O6 | 1–3 | 0.9 | [16] |
| Isomaltose | Starch hydrolyzation | C12H22O4 | 35 | 3.5 | [17] |
2. Artificial Sweeteners and Other Sugar Substitutes
| Sweetener 1 | Potency * | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Advantame | 20,000 | [10] |
| Acesulfame-K | 200 | [58] |
| Alitame | 2000 | [59] |
| Aspartame | 180 | [60] |
| Cyclamate | 30–40 | [61] |
| Neotame | 8000 | [62] |
| Neohesperidin dihidrochalcon (NHDC) | 1500–1800 | [63] |
| Saccharin | 300 | [64] |
| Sucralose | 600 | [65] |
2.1. Saccharin
2.2. Aspartame
2.3. Acesulfame K
2.4. Neohesperidin Dihidrochalcone (NHDC)
2.5. Sucralose
2.6. Cyclamate
2.7. Alitame
2.8. Neotame
2.9. Advantame
2.10. Lugduname
3. Polyols
| Sweetener | Chemical Structure | IUPAC Name | Glycemic INDEX (GI) | kcal/g | Potency * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caramel | C24H36O18 | (2S,3aS,6aS)-1-[(2S)-2-{[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino}propanoyl]-octahydrocyclopenta[b]pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid | 60 | 3–5.5 | 1.1 | [117] |
| Golden syrup | C6H12O6 | mixture of glucose and fructose, of various ratio | 60 | 3.2 | 1.1 | [118] |
| Inverted sugar | C12H24O12 | 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal, and fructose is 1,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexan-2-1 | 60 | 4 | 1.2 | [119] |
| Maltodextrin 1 | C6nH(10n + 2)O(5n + 1) | mixture of polysaccharide chains of varying lengths | 110 | 4 | 0.01–0.03 | [120] |
| Xylitol | C5H12O5 | (2R,3r,4S)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | 12 | 2.4 | 0.8–1.1 | [121] |
| Sorbitol | C6H14O6 | 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexanehexol | 4 | 2.6 | 0.5 | [122] |
| Lactitol | C12H24O11 | (2S,3R,4R,5R)-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl) oxan-2-yl] oxyhexane-1,2,3,5,6-pentol | 3 | 2.0 | 0.4 | [123] |
| Isomalt | C12H24O11 | (2R,3R,4R,5R)-6-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl) oxan-2-yl] oxyhexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | 2 | 2.1 | 0.5 | [124] |
| Mannitol | C12H24O11 | hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol | 2 | 1.6 | 0.5–0.6 | [125] |
| Maltitol | C12H24O11 | 4-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-glucitol | 35 | 2.1 | 0.7–0.9 | [104] |
| Erythritol | C4H10O4 | 1,2,3,4-butanetetrol | 0 | 0.2 | 0.65 | [126] |
3.1. Xylitol
3.2. Mannitol
3.3. Sorbitol
3.4. Maltitol
3.5. Lactitol
4. Plant Origin Sweetener’s
| Sweetener | Method of Production | Glycemic Index (GI) | Potency * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molasse | mechanical extraction and boiling, followed by a separation process | 55 | - | [153] |
| Maple syrup | collecting sap from maple trees and then evaporating the water | 54 | 1.0 | [154] |
| Honey | centrifugal extraction | 50 | 1.1 | [155] |
| Sorghum syrup | pressing the stalks of sweet sorghum to release the juice, which is then boiled down | 50 | 1.0 | [156] |
| Sugarcane juice | crystallization, membrane filtration, and solvent extraction | 43 | - | [157] |
| Coconut palm sugar | physical indirect heating | 35 | 1 | [158] |
| HFCS-90 (high-fructose corn syrup containing 90% fructose) | corn starch extraction, liquefaction, saccharification, and isomerization, with concern to the degree matters | 31 | 1.6 | [159] |
| HFCS-55 | 58 | 1.2 | [160] | |
| HFCS-42 | 68 | 1.1 | [161] | |
| Brown rice syrup | enzymatic hydrolysis of rice starch | 25 | 0.5 | [162] |
| Fructose | acid hydrolysis of inulin or enzymatic conversion of glucose | 23 | 1.17–1.75 | [163] |
| Agave syrup | pressing or shredding the cooked agave to extract the juice, and then concentrating the juice | 15 | 1.5 | [164,165,166] |
4.1. Steviol Glycosides
4.2. Curculin
4.3. Glycyrrhizin (Liquorice)
4.4. Thaumatin
4.5. Luo Han Guo (Monk Fruit)
4.6. Miraculin
4.7. Monellin
4.8. Hernandulcin
4.9. Brazzein
4.10. Pentadin
4.11. Phyllodulcin
5. Mechanisms of Sweet Taste Perception
6. Comparison Between Natural and Artificial (Synthetic) Sweeteners
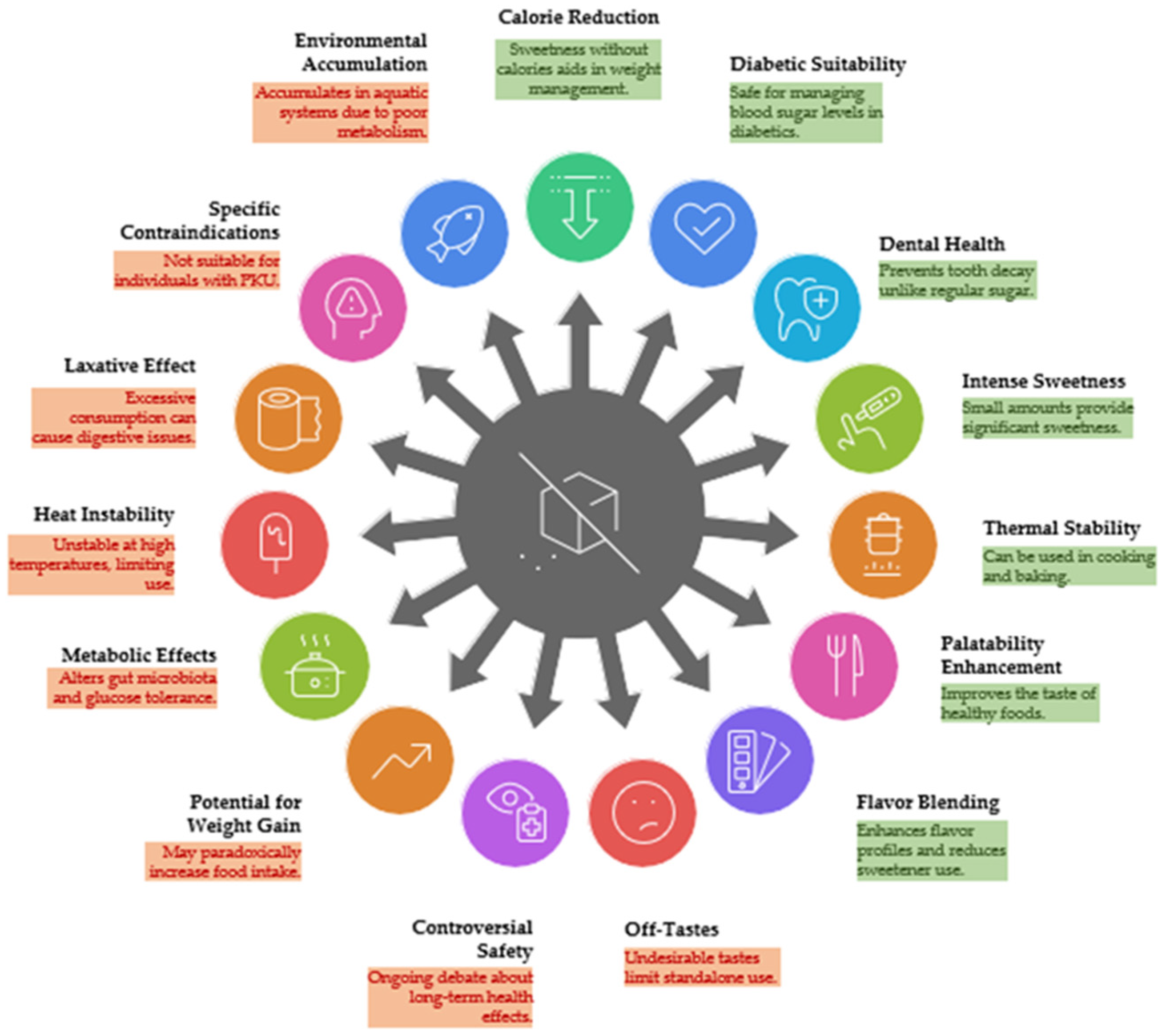
7. Controversies and Limitations of Sweeteners
7.1. Health Implications
7.2. Health and Safety Data
7.3. Sensory and Consumers’ Acceptance
7.4. Process Feasibility and Market Application Trends
7.5. Environmental Sustainability
7.6. Commercialisation Challenges
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asănică, A.; Tudor, V.; Teodorescu, R. Distinctive behaviour of somes weet cherry cultivars related to roots to CK type. AgroLife Sci. J. 2013, 2, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, F.; Malorgio, G. Food Policies: Balancing Health and Market in the Era of Ubiquitous Ultra-Processed Foods. Agric. Food Econ. 2024, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Ahmad, I.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, A.; Tang, W.; Ding, Y.; Lyu, F. Recent Advance in Technological Innovations of Sugar-Reduced Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 5128–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsato, M. “Edible Aesthetics”: Blurring Boundaries between Pastry and Art. Humanities 2023, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, N.; Bahaciu, G.V.; Ianitchi, D.; Defta, N. Research on Obtaining Organic Gluten-Free Cookies With Amaranth Flour and Pumpkin Pulp. Sci. Pap. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2022, LXV, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomir, N.; Stan, A.; Ion, V.A.; Nicolae, C.G.; Bujor-Nenita, O.C.; Bordei, I.S.; Frincu, M.; Petre, A.; Dobrin, A.; Bădulescu, L. Product Development of Organic Macarons Enriched With Freeze Dried Apple Powder. Sci. Pap. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2021, LXIV, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Szenderák, J.; Fróna, D.; Rákos, M. Consumer Acceptance of Plant-Based Meat Substitutes: A Narrative Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, R.; Jeyakumar, P.; Sassikumar, D.; Vijayalakshmi, D.; Arul, L.; Manimekalai, R.; Thirumurugan, T.; Nageswari, R.; Jayachandran, M.; Vanitha, K.; et al. Assessing Sugarcane Clones’ Resilience to Waterlogging Stress and Comprehending the Physiological and Morphological Processes. Plant Sci. Today 2025, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Thoo, Y.Y.; Tan, C.P.; Siow, L.F. Moisture Absorption Behavior and Thermal Properties of Sucrose Replacer Mixture Containing Inulin or Polydextrose. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K. Is the Use of Artificial Sweeteners Beneficial for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus? The Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Sweeteners. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvorogova, A.A.; Landikhovskaya, A.V.; Kazakova, N.V.; Zakirova, R.R.; Pivtsaeva, M.M. Scientific and Practical Aspects of Trehalose Contain in Ice Cream without Sucrose. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 640, 052017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.; Manasa, V.S.; Abirami, K.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Gayathri, R.; Geetha, G.; RamyaBai, M.; Padmavathi, S.; Rajalakshmi, M.; Pradeepa, R.; et al. Effect of Replacing Sucrose in Beverages with Nonnutritive Sweetener Sucralose on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors Among Asian Indian Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A 12-Week Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 2061–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieronimus, B.; Medici, V.; Lee, V.; Nunez, M.V.; Sigala, D.M.; Bremer, A.A.; Cox, C.L.; Keim, N.L.; Schwarz, J.M.; Pacini, G.; et al. Effects of Consuming Beverages Sweetened with Fructose, Glucose, High-Fructose Corn Syrup, Sucrose, or Aspartame on OGTT-Derived Indices of Insulin Sensitivity in Young Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homolak, J.; Babic Perhoc, A.; Knezovic, A.; Kodvanj, I.; Virag, D.; Osmanovic Barilar, J.; Riederer, P.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Is Galactose a Hormetic Sugar? An Exploratory Study of the Rat Hippocampal Redox Regulatory Network. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikova, E.; Bogdanova, E.; Paveleva, D.; Saranov, I.; Pandiselvam, R. Sucrose, Lactose, Thermogravimetry, and Differential Thermal Analysis: The Estimation of the Moisture Bond Types in Lactose-Containing Ingredients for Confectionery Products with Reduced Glycemic Index. Int. J. Food Sci. 2023, 2023, 8835418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Liu, X.G.; Ding, Z.R.; Liu, Q.P.; Liao, A.M.; Pan, L.; Hou, Y.C.; Xu, T.T.; Niu, Z.L.; Li, L.L.; et al. Impact of Tagatose on Physicochemical, Nutritional, and In Vitro Digestive Properties of Toast Bread. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalitto, S.; Ramirez-Gutierrez, A.; Ortiz, G.; Contreras-Esquivel, J. Isomaltulose: The Next Sweetener, A Quick Review. In Food Product Optimization for Quality and Safety Control; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA; Burlington, ON, Canada, 2020; p. 277. ISBN 9781003003144. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, A.; Bourbon, A.I.; Peixoto, A.R.; Silva, A.S.; Tasso, A.; Almeida, C.; Nobre, C.; Nunes, C.; Sánchez, C.; Gonçalves, D.A.; et al. Chapter 9—Strategies for the Reduction of Sugar in Food Products. In Food Structure Engineering and Design for Improved Nutrition, Health and Well-Being; Cerqueira, M.Â.P.R., Castro, L.M.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 219–241. ISBN 978-0-323-85513-6. [Google Scholar]
- Scapin, T.; Fernandes, A.C.; Curioni, C.C.; Pettigrew, S.; Neal, B.; Coyle, D.H.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Bernardo, G.L.; Uggioni, P.L.; Proença, R.P.C. Influence of Sugar Label Formats on Consumer Understanding and Amount of Sugar in Food Choices: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulais, L.; Corcuff, R.; Boonefaes, E. Natural and Healthy? Consumers Knowledge, Understanding and Preferences Regarding Naturalness and Healthiness of Processed Foods. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023, 31, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippe, J.M.; Angelopoulos, T.J. Relationship between Added Sugars Consumption and Chronic Disease Risk Factors: Current Understanding. Nutrients 2016, 8, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Meng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Added Sugar Intake and Its Forms and Sources in Relation to Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Results from the Tianjin Chronic Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and Health Cohort Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C. The Clustering of Cardiovascular, Renal, Adipo-Metabolic Eye and Liver Disease with Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolism 2022, 128, 154961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Nan, F.; Liang, H.; Shu, P.; Fan, X.; Song, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, D. Excessive Intake of Sugar: An Accomplice of Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 988481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, S.; Karmakar, S. Excess Dietary Sugar and Its Impact on Periodontal Inflammation: A Narrative Review. BDJ Open 2024, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, A.J.; Sinha, D.; Konwar, S.; Pegu, B.K.; Baruah, S. Sweeteners and Sugar- Their Impact on Human Metabolic Health and Chronic Diseases. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2024, 21, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, T.P.; Blanck, H.M.; Flores-Ayala, R.; Rose, K.; Galuska, D.A.; Gunn, J.; O’Connor, A.; Petersen, R.; Hacker, K. Five Priority Public Health Actions to Reduce Chronic Disease Through Improved Nutrition and Physical Activity. Health Promot. Pract. 2022, 23, 5S–11S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.R.; Dando, R. The Sensory Properties and Metabolic Impact of Natural and Synthetic Sweeteners. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1554–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.; Rehman, T.; Saif, S.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Hassoun, A.; Cropotova, J.; Trif, M.; Younas, A.; Aadil, R.M. Replacement of Refined Sugar by Natural Sweeteners: Focus on Potential Health Benefits. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonheim, L.E.; Austad, E.; Torheim, L.E.; Henjum, S. Plant-Based Meat and Dairy Substitutes on the Norwegian Market: Comparing Macronutrient Content in Substitutes with Equivalent Meat and Dairy Products. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council. European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35/EC of 30 June 1984 on Sweeteners for Use in Foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1984, L273, 196–205. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Khubber, S.; Dwivedi, M.; Misra, N.N. Strategies for Lowering the Added Sugar in Yogurts. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pineda, M.; Yagüe-Ruiz, C. The Risk of Undeclared Allergens on Food Labels for Pediatric Patients in the European Union. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliza, R.; Lima, M.F.; Ares, G. Rethinking Sugar Reduction in Processed Foods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 40, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Knutsen, H.K.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Tolerable Upper Intake Level for Dietary Sugars. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Guthrie, B.; Kim, S.K.; Balanda, S.; Kubicek, J.; Murtaza, B.; Khan, N.A.; Khakbaz, P.; Su, J.; Goddard, W.A. Steviol Rebaudiosides Bind to Four Different Sites of the Human Sweet Taste Receptor (T1R2/T1R3) Complex Explaining Confusing Experiments. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman-Petrycka, M.; Klimacka-Nawrot, E.; Ziora, K.; Suchecka, W.; Gorczyca, P.; Rojewska, K.; Błońska-Fajfrowska, B. Sweet, Salty, and Umami Taste Sensitivity and the Hedonic Perception of Taste Sensations in Adolescent Females with Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tyagi, P.K.; Gola, D.; Mishra, A.K.; Arya, A. Plant-Based Sweeteners and Their Applications in Modern Lifestyle. In Non-Timber Forest Products: Food, Healthcare and Industrial Applications; Husen, A., Bachheti, R.K., Bachheti, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 75–103. ISBN 978-3-030-73077-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Dang, Z.; Shu, X. Waste Natural Pyrite Activation of Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame Potassium: Efficiency, Influencing Factors, Degradation Mechanisms, and Toxicity Evaluation. Water 2025, 17, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchezan, G.; Carniciu, S.; Israel-Roming, F. Identifying Synthetic Sweeteners from Wine by UPLC. Sci. Bull. Ser. F Biotechnol. 2020, XXIV, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Moszczyński, P.; Tabarowski, Z. Recommended Diet for Diabetics: Hydrocarbons, Glycemic Impact, Glycemic Load, Glycemic Index, and Mediterranean Diet. In Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods in Human Health and Disease Prevention; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, D.; Narayanasamy, N.; Pratyusha, V.A.; Thakur, J.; Sinha, N. Dietary Carbohydrates and Health. In Textbook of Nutritional Biochemistry; Malik, D., Narayanasamy, N., Pratyusha, V.A., Thakur, J., Sinha, N., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 127–159. ISBN 978-981-19-4150-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sagili, V.S.; Chakrabarti, P.; Jayanty, S.; Kardile, H.; Sathuvalli, V. The Glycemic Index and Human Health with an Emphasis on Potatoes. Foods 2022, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, F.S.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Foster-Powell, K.; Buyken, A.E.; Goletzke, J. International Tables of Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Values 2021: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Dong, R.; Hu, X.; Ren, C.; Li, Y. Oat-Based Foods: Chemical Constituents, Glycemic Index, and the Effect of Processing. Foods 2021, 10, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzbieta, W. Sweeteners as Sugar Substitutes in Food Industry—Conditions of Use and Consumer. Adv. Food Process. Technol. 2021, 1, 186–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Zhu, J.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, L. Identification of Characteristic Compounds of Sweet Orange Oil and Their Sweetening Effects on the Sucrose Solution with Sweetness Meter, Sensory Analysis, Electronic Tongue, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Food Chem. 2024, 461, 140815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaposhnikov, I.; Kosovan, A.; Vedernikov, A.; Sergeev, S.; Tagiev, N. How Bakery Industry Is Changing to Comply with New Consumer Trends on Sustainability and Ecoconsciousness. BIO Web Conf. 2023, 64, 01015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, N.; Bahaciu, G.V. Studies regarding market trends gluten-free organic products. Sci. Pap. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2022, LXV, 378–384. [Google Scholar]
- Slade, L.; Kweon, M.; Levine, H. Exploration of the Functionality of Sugars in Cake-Baking, and Effects on Cake Quality. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 283–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, P.J.; Appleton, K.M. The Effects of Low-Calorie Sweeteners on Energy Intake and Body Weight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Sustained Intervention Studies. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Wijaya, F.; Jiang, G.; Gibney, P.; Dando, R. Sensory Profiling of Natural Sweeteners and Sucrose–Sweetener Binary Mixtures. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 2984–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.D.; Goossens, G.H.; Blaak, E.E. The Impact of Artificial Sweeteners on Body Weight Control and Glucose Homeostasis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 598340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.D.; Cruz, R.; Casal, S. Sugars and Artificial Sweeteners in Soft Drinks: A Decade of Evolution in Portugal. Food Control 2021, 120, 107481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayo-Mendez, L.M.; Rodriguez-Llanos, J.H. Natural Sweeteners. In Natural Additives in Foods; Valencia, G.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 123–150. ISBN 978-3-031-17346-2. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, F.Z. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, ITC33–ITC48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.E. The Role of Allulose and Sugar Alcohols in Gut Microbiota Modulation and Metabolic Health: A Review. Univers. J. Pharm. Res. 2025, 9, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, M. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for Highly Selective and Sensitive Determination of Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame-K. Talanta Open 2023, 7, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, L.; Feng, H.; Shen, L.; Tian, X.; Niu, J. Chloride Ion Improving the Electro-Degradation of Artificial Sweetener Alitame by Porous Three-Dimensional Membrane Anode. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 107079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torigoe, K.; Torigoe, M.; Oka, S.; Obata, Y.; Mukae, H.; Nishino, T. Aspartame, as an Artificial Sweetener, Does Not Affect Renal Function and Antioxidative States in Mice. BMC Res. Notes 2024, 17, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, H.M.; Alkass, S.Y.; de Oliveira, D.S.P. Impact of Long-Term Cyclamate and Saccharin Consumption on Biochemical Parameters in Healthy Individuals and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Medicina 2023, 59, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shil, A.; Ladeira Faria, L.M.; Walker, C.A.; Chichger, H. The Artificial Sweetener Neotame Negatively Regulates the Intestinal Epithelium Directly through T1R3-Signaling and Indirectly through Pathogenic Changes to Model Gut Bacteria. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1366409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Manthey, J.A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y. Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone and Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone-O-Glycoside Attenuate Subcutaneous Fat and Lipid Accumulation by Regulating PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudure, R.; Ganorkar, K.; Beldar, V.; Ghosh, S.K.; Panda, A.K.; Jadhao, M. Effect of Artificial Sweetener Saccharin on Lysozyme Aggregation: A Combined Spectroscopic and in Silico Approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 290, 122269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Guerrero, J.A.; Méndez-García, L.A.; Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Viurcos-Sanabria, R.; Escobedo, G. Sucralose: From Sweet Success to Metabolic Controversies—Unraveling the Global Health Implications of a Pervasive Non-Caloric Artificial Sweetener. Life 2024, 14, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, T.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, W.; Xu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Lei, P.; Wang, R.; Xu, H.; et al. Comprehensive New Insights into Sweet Taste Transmission Mechanisms and Detection Methods. Foods 2025, 14, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, K.; Korytek, W.; Pelczyńska, M.; Moszak, M.; Bogdański, P. The Effect of Artificial Sweeteners Use on Sweet Taste Perception and Weight Loss Efficacy: A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, C.A.; Selani, M.M.; Saldaña, E.; Pimentel-Filho, N.d.J.; Fontenele Domingues, M.A. Sensory Dynamic Profile and Consumer Acceptance of Short-Dough Biscuits with Reduced Sucrose and Thaumatin Addition. Food Res. Int. 2025, 200, 115524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Redha, A.; Torquati, L.; Bows, J.R.; Gidley, M.J.; Cozzolino, D. Microencapsulation of Broccoli Sulforaphane Using Whey and Pea Protein: In Vitro Dynamic Gastrointestinal Digestion and Intestinal Absorption by Caco-2-HT29-MTX-E12 Cells. Food Funct. 2024, 16, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.M.; Reboredo, F.H.; Lidon, F.C. Sweetener Food Additives: A Synoptical Overview on Their Chemical Properties, Applications in Food Products and Side Effects. Emirates J. Food Agric. 2023, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B. Current Advances and Future Aspects of Sweetener Synergy: Properties, Evaluation Methods and Molecular Mechanisms. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, L.; Nissar, J.; Ahad, T.; Gull, A. Bakery, Confectionery and Beverages as Functional Foods. In Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals: Chemistry, Health Benefits and the Way Forward; Bashir, K., Jan, K., Ahmad, F.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 249–275. ISBN 978-3-031-59365-9. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarshini, S.R.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Determining the Glycaemic Responses of Foods: Conventional and Emerging Approaches. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2022, 35, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, S.; Gómez-martínez, S.; Díaz, L.E.; Nova, E.; Urrialde, R.; Marcos, A. Potential Effects of Sucralose and Saccharin on Gut Microbiota: A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecka, K.; Pilarz, A.; Rogut, A.; Maj, P.; Szymańska, J.; Olejnik, Ł.; Szymański, P. Aspartame—True or False? Narrative Review of Safety Analysis of General Use in Products. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, F.N.; Şahin, T.Ö.; Capasso, R.; Ağagündüz, D. Protein Substitutions as New-Generation Pharmanutrition Approach to Managing Phenylketonuria. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2023, 66, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.M.; Reboredo, F.H.; Lidon, F.C. Food Colour Additives: A Synoptical Overview on Their Chemical Properties, Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, E.G. Health Hazards. In The Oxford Handbook of Climate Change and Society; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-P.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ding, M.-Y. Investigations on the Degradation of Aspartame Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorb, S.; Gleiss, K.; Wedekind, R.; Suonio, E.; Kull, A.K.; Kuntz, M.; Walch, S.G.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Assessment of Aspartame (E951) Occurrence in Selected Foods and Beverages on the German Market 2000–2022. Foods 2023, 12, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Shendurse, A.M.; Sharma, V.; Wadhwa, B.K.; Singh, A.K. Assessment of Stability of Binary Sweetener Blend (Aspartame x Acesulfame-K) during Storage in Whey Lemon Beverage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, P.; Ahuja, S.; Sriram, K. Non-Nutritive Sweeteners: Review and Update. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flad, E.; Altstädt, A.; Beglinger, C.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C. Effects of Oral Xylitol, Sucrose, and Acesulfame Potassium on Total Energy Intake During a Subsequent Ad Libitum Test Meal: A Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial in Healthy Humans. Nutrients 2025, 17, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Wong, R.R.; Cha, Y.K.; Park, T.H.; Kim, Y.; Chung, S.-J. Sweet–Bitter Taste Interactions in Binary Mixtures of Sweeteners: Relationship between Taste Receptor Activities and Sensory Perception. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwig, G.J.; te Poele, E.M.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Kamerling, J.P. Chapter One—Stevia Glycosides: Chemical and Enzymatic Modifications of Their Carbohydrate Moieties to Improve the Sweet-Tasting Quality. In Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry; Baker, D.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 73, pp. 1–72. ISBN 9780128099834. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, A.C.; Fideles, S.O.M.; Reis, C.H.B.; Bellini, M.Z.; Pereira, E.S.B.M.; Pilon, J.P.G.; de Marchi, M.Â.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Flato, U.A.P.; Trazzi, B.F.M.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Citrus Flavonoids Neohesperidin, Hesperidin and Its Aglycone, Hesperetin on Bone Health. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Safwa, S.M.; Ahmed, T.; Talukder, S.; Sarkar, A.; Rana, M.R. Applications of Non-Thermal Technologies in Food Processing Industries—A Review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 100917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente-García, O.; Castillo, J.; Del Baño, M.J.; Lorente, J. Improved water solubility of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone in sweetener blends. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uniform Sanitary and Epidemiological and Hygienic Requirements for Goods Subject to Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision (Control). Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/document/download/d12ae437-8d70-4198-8335-899f6519c22c_en?filename=ia_eu-ru_sps-req_req_san-epi_chap-2_22_en.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Dhartiben, K.; Aparnathi, K.D. Chemistry and Use of Artificial Intense Sweeteners. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujral, J.; Carr, J.; Tonucci, D.; Darwen, C.; Grotz, V.L. Use of Sucralose in Foods Heated during Manufacturing Does Not Pose a Risk to Human Health. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2021, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS). Safety of the Proposed Extension of Use of Sucralose (E 955) in Foods for Special Medical Purposes in Young Children. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezovic, Z.; Jurcevic Zidar, B.; Pribisalic, A.; Luetic, S.; Jurcic, K.; Knezovic, N.; Sutlovic, D. Artificial Sweeteners in Food Products: Concentration Analysis, Label Practices, and Cumulative Intake Assessment in Croatia. Nutr. 2025, 17, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobach, A.R.; Roberts, A.; Rowland, I.R. Assessing the in Vivo Data on Low/No-Calorie Sweeteners and the Gut Microbiota. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šedivá, A.; Panovská, Z.; Pokorný, J. Sensory Profiles of Sweeteners in Aqueous Solutions. Czech J. Food Sci. 2006, 24, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Blank, K.; Meyerhof, W. Blends of Non-Caloric Sweeteners Saccharin and Cyclamate Show Reduced Off-Taste Due to TAS2R Bitter Receptor Inhibition. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1199–1204.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drasar, B.S.; Renwick, A.G.; Williams, R.T. The Role of the Gut Flora in the Metabolism of Cyclamate. Biochem. J. 1972, 129, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, S.A.; Ho, G.S.; Ho, C. Stability and Degradation of the High-intensity Sweeteners: Aspartame, Alitame, and Sucralose. Food Rev. Int. 1999, 15, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A. Sweeteners Permitted in the European Union: Safety Aspects. Scand. J. Food Nutr. 2006, 50, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.Q.; Zafar, T.; Shrivastava, V.K. Environmental Impact of the Presence, Distribution, and Use of Artificial Sweeteners as Emerging Sources of Pollution. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 6624569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel, E.; Faf, F.; Castle, L.; Andreassen, M.; Aquilina, G.; Lourdes, M.; Polly, B.; Biagio, B.; Reginald, F.; Jose, M.; et al. Evaluation of Neotame (E 961) as Food Additive. EFSA J. 2025, 23, e9480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otabe, A.; Fujieda, T.; Masuyama, T.; Ubukata, K.; Lee, C. Advantame—An Overview of the Toxicity Data. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, S2–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, Y.; Mohamed Elfadil, O.; Patel, S.; Ghanem, O.M.; Hurt, R.T.; Mundi, M.S. Rediscovering Sweetness: The Evolution and Impact of Non-Nutritive and Natural Sweeteners. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, R.S. Saccharide Sweet (SS) Principles, Classification and Structural and Functional Details of SS Sweeteners and Plants. In Alternative Sweet and Supersweet Principles; Springer: Singapore, 2022; ISBN 9789813363496. [Google Scholar]
- Baute-Pérez, D.; Santana-Mayor, Á.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Analysis of Alkylphenols, Bisphenols and Alkylphenol Ethoxylates in Microbial-Fermented Functional Beverages and Bottled Water: Optimization of a Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Protocol Based on Natural Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Lai, J.; Lin, H.; Ye, G.; Chen, Y.; Hu, F.; Wang, Z.; Yan, R. Direct and Accurate Purity Evaluation for Isovanillin Conversion to HMCA through Aldol Condensation by Using RID and Its Comparison with UV Detection. Arab. J. Chem. 2025, 18, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Fan, M.; Qian, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Maternal Dietary Carbohydrate and Pregnancy Outcomes: Quality over Quantity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadzadegan, S.; Summonte, S.; Ricci, F.; Sandmeier, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Intraoral Drug Delivery: Bridging the Gap Between Academic Research and Industrial Innovations. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2500157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Food Additives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008R1333 (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Tkach, V.V.; Morozova, T.V.; Kushnir, M.V.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Odyntsova, V.M.; Kras’ko, M.P.; Antonyuk, I.Y.; Hrabovska, O.V.; Fedorova, D.V.; Kormosh, Z.O.; et al. The Theoretical Description of Sucralose and Lugduname Electrochemical Determination in Beverages. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2024, 13, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, V.V.; Morozova, T.V.; Shapovalova, N.P. The Theoretical Description for the Electrochemical Determination of Sucralose and Aspartame in Drinks. Orbital 2024, 16, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basson, A.R.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A.; Cominelli, F. Artificial Sweeteners: History and New Concepts on Inflammation. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 746247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanišová, E.; Mošaťová, D.; Hlaváčová, Z.; Hlaváč, P.; Kunecová, D.; Gálik, B.; Čech, M.; Harangozo, Ľ.; Kubiak, P. Nutritional, Physical and Sensory Quality of Gingerbread Prepared Using Different Sweeteners. Agron. Res. 2023, 21, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, L.; Wouters, R.; Theis, S. Replacing Sugar with the Polyol Isomalt: Technological Advances and Nutritional Benefits Focusing on Blood Glucose Management. Nutrafoods 2024, 1, 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido-Romero, M.; Montilla, A.; Moreno, F.J. Dietary Carbohydrates: A Trade-off between Appealing Organoleptic and Physicochemical Properties and Ability to Control Glucose Release and Weight Management. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 49, 100976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, L.; Narvekar, U.; McDonald, A.; Mullany, P. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Oral Cavity and Mobile Genetic Elements That Disseminate Antimicrobial Resistance: A Systematic Review. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2022, 37, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.X.; Luo, C.; Geng, Z.Z.; Jiang, Z.R.; Ji, L.B.; Shentu, H.Q.; Xie, Y.F.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, D.L. Type I Caramel Products of Maltose and Sucrose with Water and Their Antioxidant Activities. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e58520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.; Dodd, S.; Mosca, S.; Matousek, P.; Parmar, B.; Kevei, Z.; Anastasiadi, M. Application of Spatial Offset Raman Spectroscopy (SORS) and Machine Learning for Sugar Syrup Adulteration Detection in UK Honey. Foods 2024, 13, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciursă, P.; Pauliuc, D.; Dranca, F.; Ropciuc, S.; Oroian, M. Detection of Honey Adulterated with Agave, Corn, Inverted Sugar, Maple and Rice Syrups Using FTIR Analysis. Food Control 2021, 130, 108266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staltner, R.; Sánchez, V.; Bergheim, I.; Baumann, A. Acute Intake of Sucrose but Not of the Intense Sweetener Sucralose Is Associated with Post-Prandial Endotoxemia in Healthy Young Adults—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadi, F.S.; Hasheminejad, N.; Mehdizadeh, A.; Eskandarizadeh, A.; Rostamizadeh, M. Dentists’ Knowledge and Clinical Experience towards Molar-Incisor-Hypomineralization in Iran. Pesqui. Bras. Odontopediatria Clin. Integr. 2021, 21, e0004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M. The Preparation of Sorbitol and Its Application in Polyurethane: A Review. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 2667–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertna, N.; Sansawat, N.; Neramittagapong, A.; Theerakulpisut, S.; Neramittagapong, S. Optimizing Sorbitol Double Dehydration: A Box-Behnken Design Approach with Commercial Sulfonic Acid Resin. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Z.; Guo, J. Strategies of Formulation and Lyophilization Process for Sodium Chloride-Mannitol-Protein-Based Products. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 114, 103671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Castle, L.; Degen, G.; Engel, K.H.; Fowler, P.J.; Frutos Fernandez, M.J.; Fürst, P.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Gürtler, R.; et al. Re-Evaluation of Erythritol (E 968) as a Food Additive. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, C.; Córdova, A.; Aburto, C.; Guerrero, C.; Suárez, S.; Illanes, A. Synthesis and Purification of Galacto-Oligosaccharides: State of the Art. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhart, A.; Chey, W.D. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Polyols on Gastrointestinal Health and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Bacteria, Colonic Fermentation, and Gastrointestinal Health. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinik, A.I.; Mehrabyan, A. Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy. Compr. Ther. 2003, 29, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.; Dempsey, E.; Cosantino, A.; Ghoreishi, N.; Cannon, M.; Dempsey, E.; Cosantino, A.; Ghoreishi, N. Analysis of Osmotic Pump-Administered Xylitol in a Syngeneic Mouse Melanoma Model. Preprints 2025, 2025070545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umai, D.; Kayalvizhi, R.; Kumar, V.; Jacob, S. Xylitol: Bioproduction and Applications-A Review. Front. Sustain. 2022, 3, 826190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Singh, E.; Shrivastava, S. Microbial Xylitol Production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauser, N.M.; Fit, C.G.; Cardozo, R.E.; Rivaldi, J.A.; Felissia, F.E.; Area, M.C.; Vallejos, M.E. Technical, Economic and Environmental Assessment of Xylitol Production in a Biorefinery Platform Toward a Circular Economy. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalabothu, R.L.; Fisher, K.J.; Labella, A.L.; Meyer, T.A.; Opulente, D.A.; Wolters, J.F.; Rokas, A.; Hittinger, C.T. Codon Optimization Improves the Prediction of Xylose Metabolism from Gene Content in Budding Yeasts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Peñalva, M.Á.; Barriuso, J.; Espeso, E.A.; Martínez, M.J. Improvement of β-Xylosidase and Endoxylanase Activities in Talaromyces Amestolkiae by Genetic Manipulation of the Transcriptional Activator XlnR. Microb. Biotechnol. 2025, 18, e70166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Vargas, B.; dos Santos, J.R.; Pereira, G.A.G.; da Silveira Bezerra de Mello, F. An Atlas of Rational Genetic Engineering Strategies for Improved Xylose Metabolism in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manaf, S.F.A.; Luthfi, A.A.I.; Tan, J.P.; Abdul, P.M.; Jamali, N.S. Kinetic Study and Model of Fermentation Parameters Affected Growth and Xylitol Production in Bioreactor by Kluyveromyces Marxianus ATCC 36,907. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 7247–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.A.; Antunes, F.A.F.; Terán-Hilares, R.; Díaz-Ruiz, E.; Jofre, F.M.; Arruda, G.L.; Cruz-Santos, M.M.; Melo, Y.C.S.; Santos, J.C. An Overview of Different Approaches and Bioreactors for Xylitol Production by Fermentation. In Current Advances in Biotechnological Production of Xylitol; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 9783031049422. [Google Scholar]
- Heianza, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Tiwari, S.; Watrous, J.D.; Rexrode, K.M.; Alotaibi, M.; Jain, M.; Mora, S.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Plasma Levels of Polyols Erythritol, Mannitol, and Sorbitol and Incident Coronary Heart Disease among Women. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2025, 32, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Tang, B.; Yang, X.; Vit, P.; Popova, M.; Bankova, V.; Wu, L.; Wang, K. Mannitol: A Novel Chemical Marker in Stingless Bee Honey. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán, J.O.; Henderson, W.A.; Walker, J.M.; Ronning, A.; Jones, D.R.; Walter, P.J.; Daniel, S.G.; Bittinger, K.; Vaughan, R.; MacArthur, R.; et al. Excess Dietary Fructose Does Not Alter Gut Microbiota or Permeability in Humans: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Study. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 5, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Sharma, S.; Kaurav, M.; Sharma, A. Characteristics and Analytical Methods of Mannitol: An Update. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2021, 13, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Miranda, J.G.; Chairez, I.; Durán-Páramo, E. Mannitol Production by Heterofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2762–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koju, N.; Mao, G.-H.; Sheng, R. Interconversion of Coenzyme I and II, Trans-Organelle Transport and Its Significance. In Biology of Nicotinamide Coenzymes: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications; Qin, Z.-H., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 197–214. ISBN 978-981-97-9877-3. [Google Scholar]
- Poka, M.S.; Milne, M.; Wessels, A.; Aucamp, M. Sugars and Polyols of Natural Origin as Carriers for Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.J.N.; Augusto, P.E.D.; Telis-Romero, J.; Polachini, T.C. Transport Properties of Saturated Sucrose and Maltitol Solutions as Affected by Temperature. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, H.; Sonia, A. Substituting Sugar in Pastry and Bakery Products with Functional Ingredients. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, D.E.; Wu, S.; Jayasinghe, D.N.D.S. Galacto-Oligosaccharides and Other Products Derived from Lactose. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry: Volume 3: Lactose, Water, Salts and Minor Constituents; McSweeney, P.L.H., O’Mahony, J.A., Kelly, A.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 125–228. ISBN 978-3-030-92585-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Chen, L.; Pan, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Lou, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; et al. Lactitol Supplementation Modulates Intestinal Microbiome in Liver Cirrhotic Patients. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 762930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokołowska, E.; Sadowska, A.; Sawicka, D.; Kotulska-Bąblińska, I.; Car, H. A Head-to-Head Comparison Review of Biological and Toxicological Studies of Isomaltulose, d-Tagatose, and Trehalose on Glycemic Control. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5679–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtuś, M.; Tomaszuk, S.; Wąsik, K. Polyols—What Do We Know about Their Impact on the Gut Microbiome? J. Educ. Health Sport 2022, 12, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordenti, A.L.; Giaretta, E.; Campidonico, L.; Parazza, P.; Formigoni, A. A Review Regarding the Use of Molasses in Animal Nutrition. Animals 2021, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, A.; Carrascosa, C.; Ramos, F.; Raheem, D.; Pedreiro, S.; Vega, A.; Raposo, A. Brazzein and Monellin: Chemical Analysis, Food Industry Applications, Safety and Quality Control, Nutritional Profile and Health Impacts. Foods 2023, 12, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Miura, Y.; Sone, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Lijima, H. High-level expression of a sweet protein, monellin, in the food yeast Candida utilis. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggleston, G.; Boue, S.; Bett-Garber, K.; Verret, C.; Triplett, A.; Bechtel, P. Phenolic Contents, Antioxidant Potential and Associated Colour in Sweet Sorghum Syrups Compared to Other Commercial Syrup Sweeteners. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, F.C.; Moraes, T.C.K.; Dacanal, G.C.; de Oliveira, A.L.; Petrus, R.R. The Potential Use of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide in Sugarcane Juice Processing. npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maryani, Y.; Rochmat, A.; Khastini, R.O.; Kurniawan, T.; Saraswati, I. Identification of Macro Elements (Sucrose, Glucose and Fructose) and Micro Elements (Metal Minerals) in the Products of Palm Sugar, Coconut Sugar and Sugar Cane. In Joint Proceedings of the 2nd and the 3rd International Conference on Food Security Innovation; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- Simsek, Y.; Topaloǧlu, U.S.; Dizdar, O.S. High-Fructose Corn Syrup Effects on Metabolic Parameters and Malignancy. J. Diabetol. 2021, 12, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, D.M.; Hieronimus, B.; Medici, V.; Lee, V.; Nunez, M.V.; Bremer, A.A.; Cox, C.L.; Price, C.A.; Benyam, Y.; Chaudhari, A.J.; et al. Consuming Sucrose- or HFCS-Sweetened Beverages Increases Hepatic Lipid and Decreases Insulin Sensitivity in Adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3248–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E. Effects of Natural Alternative Sweeteners on Metabolic Diseases. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2023, 12, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyıldız, İ.E.; Uzunöner, D.; Raday, S.; Acar, S.; Erdem, Ö.; Damarlı, E. Identification of the Rice Syrup Adulterated Honey by Introducing a Candidate Marker Compound for Brown Rice Syrups. LWT 2022, 154, 112618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Noh, E.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K.-G. Effect of Roasting after Sugar-Soaking on the Level of Volatile Compounds, Total Polyphenol, Total Flavonoid, and Isoflavones in Black Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). LWT 2023, 185, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, A.; Carrascosa, C.; Ramos, F.; Raheem, D.; Raposo, A. Agave Syrup: Chemical Analysis and Nutritional Profile, Applications in the Food Industry and Health Impacts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrete-Herrera, P.I.; López, M.G.; Medina-Torres, L.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; González-Ávila, M.; Ortiz-Basurto, R.I. Physicochemical Composition and Apparent Degree of Polymerization of Fructans in Five Wild Agave Varieties: Potential Industrial Use. Foods 2019, 8, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, A.; Carrascosa, C.; Ramos, F.; Raheem, D.; Lopes, M.; Raposo, A. Maple Syrup: Chemical Analysis and Nutritional Profile, Health Impacts, Safety and Quality Control, and Food Industry Applications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbrava, D.; Raba, D.; Moldovan, C.; Popa, M.; Misca, C.D.; Poiana, M.; Dogaru, D.; Petcu, C.D. Antioxidant and nutritional characteristics of two innovative sugar free fruit jellies. Sci. Papers. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2022, LXV, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Morini, G.; Bassoli, A.; Borgonovo, G. Molecular Modelling and Models in the Study of Sweet and Umami Taste Receptors. A Review. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2011, 26, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Sun, G.; Yu, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Hu, D.; Liang, L.; He, G.; Hu, J.; et al. Molecular Recognition and Modification Strategies of Umami Dipeptides with T1R1/T1R3 Receptors. Molecules 2025, 30, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaciu, G.V.; Dragomir, N.; Georgeta Nicolae, C. Study on The Incidence of GlutenIntolerance Associated Diseases with Consumption of Aglutenic Foods. Sci. Papers. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2022, LXV, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, Z.; Ahngar, T.A.; Nazir, A.; Dar, Z.A.; Khuroo, N.S.; Majeed, S.; Naseer, S.; Bashir, S.; Rakshanda, A.; Iqbal, S.; et al. Research Technology of Stevia. Cut.-Edge Res. Agric. Sci. 2021, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.I.; Rahanur Alam, M.; Raihan, M.M.; Rahman, T.; Islam, S.; Halima, O. Effect of Stevia Leaves (Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni) on Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2868–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, L.; Mustapha, A.T.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C.; Okonkwo, C.E. Natural and Low-Caloric Rebaudioside A as a Substitute for Dietary Sugars: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 615–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakütük, İ.A.; Şengül, M.; Zor, M.; Aksoy, S. The Effects of Using Different Plant Species and Sweeteners (Stevia and Sucrose) in Sherbet Production on Chemical and Sensory Quality of Sherbet. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5308–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, C.E.; Adeyanju, A.A.; Onyeaka, H.; Nwonuma, C.O.; Olaniran, A.F.; Alejolowo, O.O.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Oluyori, A.P.; Zhou, C. A Review on Rebaudioside M: The next Generation Steviol Glycoside and Noncaloric Sweetener. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 6946–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Díaz-Montes, E.; Cassano, A.; Gontarek, E. Membrane Separation Processes for the Extraction and Purification of Steviol Glycosides: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2152–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Degen, G.; Engel, K.H.; Fowler, P.; Frutos Fernandez, M.J.; Fürst, P.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Gürtler, R.; Husøy, T.; et al. Safety Evaluation of the Food Additive Steviol Glycosides, Predominantly Rebaudioside M, Produced by Fermentation Using Yarrowia Lipolytica VRM. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nawi, N.; Suboh, N.A. Exploring Consumer Awareness of Curculigo Latifolia as a Sugar Substitute. Malays. J. Agric. Econ. 2023, 30, a0000426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Aldholmi, M.; Alqathama, A.; Aldossary, S.; Bubshait, S.; Aljaber, M.; Abuhassan, A.; Aldarwish, A.; Alateeq, L. Green and Novel Ultrasonic Extraction with UHPLC-MSMS Analysis of Natural Sweetener (Glycyrrhizic Acid) from Glycyrrhiza Glabra; a Multifactorial Mechanistic Evaluation Based on Statistical Analysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 77, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; He, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Pang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, K.; Qian, S.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; et al. Physicochemical Parameters Combined with Sensory and Discriminant Regression, for Quality and Sensory Characterization of Licorice for Both Food and Medicine. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 3619–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, I.; Bala, K.; Khan, I.A.; Khan, S.I. A Review on Phytochemicals, Pharmacological Activities, Drug Interactions, and Associated Toxicities of Licorice (Glycyrrhiza Sp.). Food Front. 2021, 2, 449–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Castle, L.; Engel, K.H.; Fowler, P.; Frutos Fernandez, M.J.; Fürst, P.; Gürtler, R.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Husøy, T.; et al. Re-Evaluation of Thaumatin (E 957) as Food Additive. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Garba, A.; Unar, N.B.; Jude Kelechi, A. Chemistry of Food Sweeteners. In Food Additives—From Chemistry to Safety; Lagouri, V.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2024; ISBN 978-0-85014-430-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pomon, B.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, A.L.; Lin, T.; Freed, J.H.; Abbaspourrad, A. Thermal Degradation of Thaumatin at Low PH and Its Prevention Using Alkyl Gallates. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievenpiper, J.L.; Purkayastha, S.; Grotz, V.L.; Mora, M.; Zhou, J.; Hennings, K.; Goody, C.M.; Germana, K. Dietary Guidance, Sensory, Health and Safety Considerations When Choosing Low and No-Calorie Sweeteners. Nutrients 2025, 17, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, R.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, L. Research Progress of Pharmacological Effects of Siraitia Grosvenorii Extract. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Shi, M.; Sarengaowa; Xiao, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, K. Recent Advances in the Distribution, Chemical Composition, Health Benefits, and Application of the Fruit of Siraitia Grosvenorii. Foods 2024, 13, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Tang, X.; Nie, J. Metabolomics Combined with Network Pharmacology Reveals the Effects of Ripening Stages and Edible Parts on Bioactive Ingredients of Luohan Guo (Siraitia grosvenorii). Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benucci, I.; Lombardelli, C.; Esti, M. A Comprehensive Review on Natural Sweeteners: Impact on Sensory Properties, Food Structure, and New Frontiers for Their Application. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 4615–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, S.; Kathuria, D.; Mishra, A.; Sharma, R. Phytochemical Composition and Pharmacological Impact of Natural Non-Calorie Sweetener- Monk Fruit (Siraitia grosvenorii): A Review. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 51, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazir, M.; Verma, H.; Singh, J.; Singh, P.; Passey, S. The Battle of Natural Sweeteners: A Comprehensive Guide to Monk Fruit and Stevia. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2025, 13, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Du, P.; Li, P.; Lai, W.; Hu, H.; Luo, J.; Ding, Y. The Chromosome-Level Genome of Miracle Fruit (Synsepalum dulcificum) Provides New Insights Into the Evolution and Function of Miraculin. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 804662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, D.; Uleh, M. Phylogenetic Relationships in the Miracle Berry Genus, Synsepalum, Sensu Lato, and Relatives (Sapotaceae). Plants 2025, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of Dried Fruits of Synsepalum Dulcificum as a Novel Food Pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novik, T.S.; Koveshnikova, E.I.; Kotlobay, A.A.; Sycheva, L.P.; Kurochkina, K.G.; Averina, O.A.; Belopolskaya, M.V.; Sergiev, P.V.; Dontsova, O.A.; Lazarev, V.N.; et al. Sweet-Tasting Natural Proteins Brazzein and Monellin: Safe Sugar Substitutes for the Food Industry. Foods 2023, 12, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.-P.; Wang, Y.; Munger, S.D.; Tang, X. A Review on Natural Sweeteners, Sweet Taste Modulators and Bitter Masking Compounds: Structure-Activity Strategies for the Discovery of Novel Taste Molecules. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 2076–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharififar, F.; Ashrafzadeh, A.; Kavirimanesh Khanaman, M. A Review of Natural Peptide Sweeteners. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfi, M.; Emendato, A.; Leone, S.; Lampitella, E.A.; Porcaro, P.; Cardinale, G.; Petraccone, L.; Picone, D. A Super Stable Mutant of the Plant Protein Monellin Endowed with Enhanced Sweetness. Life 2021, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, M.; You, T.; Ye, S.; Liu, S. Computational Design towards a Boiling-Resistant Single-Chain Sweet Protein Monellin. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compadre, C.M.; Robbins, E.F.; Kinghorn, A.D. The intensely sweet herb, Lippia dulcis Trev.: Historical uses, field inquiries, and constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1986, 15, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Ruano, N.; Ramírez-García, S.A.; Landeta-Cortés, G.; Cunill-Flores, J.M.; Horta-Valerdi, G.M.; Hernández, Y.P. Comparative Effect of Resveratrol, Carnosic Acid and Hernandulcin on Target Enzymes and Biochemical Markers Linked to Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism in Mice. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2023, 35, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Zheng, W.; Shi, N.; Song, R.; Han, F.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Peng, C.; Li, B.; Chen, Y. Study on the Thermal Stability of the Sweet-Tasting Protein Brazzein Based on Its Structure–Sweetness Relationship. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 7374–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meetro, J.; Nahian, L.; Phipps, K.R.; Vo, T.D.; Dahms, I.; Lalpuria, M.; Omrani, H. Toxicological Evaluation of the Sweet Protein Brazzein Derived From Komagataella Phaffii for Use as a Sweetener in Foods and Beverages. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2025, 45, 1867–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Der Wel, H.; Larson, G.; Hladik, A.; Hladik, C.M.; Hellekant, G.; Glaser, D. Isolation and Characterization of Pentadin, the Sweet Principle of Pentadiplandra Brazzeana Baillon. Chem. Senses 1989, 14, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohstoffe, N.; Moll, M.D. Cultivation and Utilization of Hydrangea macrophylla Subsp. Serrata as Feedstock for Dihydroisocoumarins and Its Quality-Assessment through Non-Invasive Phenotyping. Master’s Thesis, Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, Bonn, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, L.R.; Sterneder, S.; Hasural, A.; Paetz, S.; Hans, J.; Ley, J.P.; Somoza, V. Reducing the Bitter Taste of Pharmaceuticals Using Cell-Based Identification of Bitter-Masking Compounds. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Molitor, E.; Riedel, K.; Krohn, M.; Rudolf, R.; Hafner, M.; Cesetti, T. An Alternative Pathway for Sweet Sensation: Possible Mechanisms and Physiological Relevance. Pflügers Arch—Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 1667–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikut-Ligaj, D.; Trzcielińska-Lorych, J. How Taste Works: Cells, Receptors and Gustatory Perception. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2015, 20, 699–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.; Simon, S.A. Physiology of Taste Processing in the Tongue, Gut, and Brain. Compr. Physiol. 2021, 11, 2489–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Lang, T. Extra-Oral Taste Receptors—Function, Disease, and Perspectives. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 881177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime-Lara, R.B.; Brooks, B.E.; Vizioli, C.; Chiles, M.; Nawal, N.; Ortiz-Figueroa, R.S.E.; Livinski, A.A.; Agarwal, K.; Colina-Prisco, C.; Iannarino, N.; et al. A Systematic Review of the Biological Mediators of Fat Taste and Smell. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 855–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunschi, S.; Munteanu, M.F.; Borcan, F.; Tașcău, G.; Pogurschi, E.N. Plasma Vitamin C Levels Associated with the Diet and Supplement Consumption. Med. Surg. J.—Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iaşi 2024, 128, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunschi, S.; Zugravu, C.A.; Munteanu, M.F.; Borcan, F.; Pogurschi, E.N. Determination of the Ascorbic Acid Content and the Antioxidant Activity of Different Varieties of Vegetables Consumed in Romania, from Farmers and Supermarkets. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragotoiu, D.; Dragotoiu, T.; Marin, M.; Pogurschi, E. Research Concerning the Influence of the Use of Energo-Protein Supplements-Eco Certificate upon Physical-Chemical Honey Indicators. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia. 2016, 10, 250–254. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Liu, W.W.; Bohórquez, D.V. The Neural Basis of Sugar Preference. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Shah, S.I.; Nawaz, H.; Nadeem, N. Historical and Current Perspectives on the Human Consumption of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners (Nns). J. Akhtar Saeed Med. Dent. Coll. 2023, 5, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/elena/interventions/free-sugars-adults-ncds (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-additives-petitions/aspartame-and-other-sweeteners-food (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, L. Natural Sweetener Glycyrrhetinic Acid Monoglucuronide Improves Glucose Homeostasis in Healthy Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 3483–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M, M.; Vellapandian, C. Exploring the Long-Term Effect of Artificial Sweeteners on Metabolic Health. Cureus 2024, 16, e70043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofides, E.A. POINT: Artificial Sweeteners and Obesity—Not the Solution and Potentially a Problem. Endocr. Pract. 2021, 27, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.J.; Li, C.H.; Wu, H.T.; Kuo, H.Y.; Wang, C.T.; Pai, H.L.; Chang, C.J.; Ou, H.Y. Long-Term Consumption of Sucralose Induces Hepatic Insulin Resistance through an Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2-Dependent Pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/14-07-2023-aspartame-hazard-and-risk-assessment-results-released (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/press/news/131210 (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Available online: https://www.fsai.ie/news-and-alerts/latest-news/aspartame-jefca-and-iarc-assessments (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Espinosa, A.; Mendoza, K.; Laviada-Molina, H.; Rangel-Méndez, J.A.; Molina-Segui, F.; Sun, Q.; Tobias, D.K.; Willett, W.C.; Mattei, J. Effects of Nonnutritive Sweeteners on the BMI of Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Prospective Cohort Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Sánchez, B.; Melgar-Locatelli, S.; López-Merchán, R.; Benítez-Marín, M.J.; Blasco-Alonso, M.; González-Mesa, E.; Tovar, R.; Rubio, P.; Suárez, J.; Sanjuan, C.; et al. Gestational Saccharin Consumption Disrupts Gut-Brain Axis Glucose Homeostasis Control in Adolescent Offspring Rats in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Biol. Sex Differ. 2025, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Tien, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Garrido, D.; Farzi, A.; Herzog, H.; Fan, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C. Effect of Sucralose Intake on Human and Mouse/Rat Gut Microbiota Composition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Cohen, Y.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Mor, U.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Federici, S.; Zmora, N.; Leshem, A.; Heinemann, M.; Linevsky, R.; et al. Personalized Microbiome-Driven Effects of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on Human Glucose Tolerance. Cell 2022, 185, 3307–3328.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Bakshi, A. Effect of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on Insulin Regulation, Glycemic Response, Appetite and Weight Management: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 54, 100–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bai, J.; Miao, P.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Lan, H.; Qing, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Tang, R.; et al. The Key to Intestinal Health: A Review and Perspective on Food Additives. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1420358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, C.; Keim, K.S. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Use of Nutritive and Nonnutritive Sweeteners. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/saccharin-safety-threshold-increased (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/3301 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/6600 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Feteira-Santos, R.; Fernandes, J.; Virgolino, A.; Alarcão, V.; Sena, C.; Vieira, C.P.; Gregório, M.J.; Nogueira, P.; Costa, A.; Graça, P.; et al. Effectiveness of Interpretive Front-of-Pack Nutritional Labelling Schemes on the Promotion of Healthier Food Choices: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2020, 18, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, A.; Ahmadi, E.; Heshmati, A. Optimization of Physicochemical, Textural, and Rheological Properties of Sour Cherry Jam Containing Stevioside by Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, H.I. Physicochemical and Sensory Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Xylitol Candies Containing Yuja (Citrus Junos) Peels or Pulp. Foods 2024, 13, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompupor, P.; Süzer, Ö.; Kırmacı, H.A.; Pranil, T.; Ghuangpeng, S.; Nontasan, S. Effect of Erythritol Substitution on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Traditional Gaziantep Baklava. J. Food Qual. 2025, 2025, 8385433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, H. Postharvest Flavor Quality Changes and Preservation Strategies for Peach Fruits: A Comprehensive Review. Plants 2025, 14, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meenakshi, S.; Mohan, V. Decoding the Mystery of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2024, 44, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crakes, K.R.; Questell, L.; Soni, S.; Suez, J. Impacts of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on the Human Microbiome. Immunometabolism 2025, 7, e00060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 5. Facilitating Positive Health Behaviors and Well-Being to Improve Health Outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S68–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Rao, S.; Sun, X.; Liu, J. Advances in Molecular Epidemiology of Diabetic Retinopathy: From Genomics to Gut Microbiomics. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Peng, J.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Liu, C.W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Teitelbaum, T.; Wang, X.; Lu, K. Non/Low-Caloric Artificial Sweeteners and Gut Microbiome: From Perturbed Species to Mechanisms. Metabolites 2024, 14, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwonuma, C.; Igunnu, A.; Israel, F.; Okonkwo, C.; Bamgboye, F.; Ojekale, A.; Adeyanju, A. Non-Caloric Sweeteners: A Minireview. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Science, Engineering and Business for Driving Sustainable Development Goals (SEB4SDG), Omu-Aran, Nigeria, 2–4 April 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, R.; Ojito, S.; Pajaro, V.; Gutierrez, C.; Bolivar-anillo, H.; Hampel, M.; Anfuso, G. Artificial Sweeteners in Aquatic Ecosystems: Occurrence, Sources and Effects Artificial Sweeteners in Aquatic Ecosystems: Occurrence, Sources and Effects. Preprints 2025, 2025080839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemine, S.; Shibamori, S.; Sankoda, K.; Nishino, T.; Motegi, M.; Mishima, I. Applicability of Artificial Sweeteners as Markers of Wastewater Contamination in Japanese Surface Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 384, 127023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goveas, L.C. Artificial Sweeteners and the One Health Crisis: Toxicity Effects and Ecological Consequences. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Choe, D.-H.; Lee, C.-Y. The Impact of Artificial Sweeteners on Insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, F.; Yang, H.; Pan, Q.; Wu, X. Effect of Artificial Sugar Supplement on the Lifespan and Learning Memory Ability of Honey Bee (Apis Cerana) Worker Bee Offspring. J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cong, Q.; Shen, J.; Song, L.; Hallwachs, W.; Janzen, D.H.; Sourakov, A.; Grishin, N. V What One Genus of Showy Moths Can Say about Migration, Adaptation, and Wing Pattern. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319726121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryalls, J.M.W.; Langford, B.; Mullinger, N.J.; Bromfield, L.M.; Nemitz, E.; Pfrang, C.; Girling, R.D. Anthropogenic Air Pollutants Reduce Insect-Mediated Pollination Services. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/global-artificial-sweeteners-market (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/artificial-sweeteners-market (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Garg, R.K. The Alarming Rise of Lifestyle Diseases and Their Impact on Public Health: A Comprehensive Overview and Strategies for Overcoming the Epidemic. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2025, 30, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubhi, M.; Blake, M.; Nguyen, T.; Majmudar, I.; Moodie, M.; Ananthapavan, J. Consumer Willingness to Pay for Healthier Food Products: A Systematic Review. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M.; Hawkes, C. Sweetening of the Global Diet, Particularly Beverages: Patterns, Trends, and Policy Responses. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.; Baker, P.; Grimes, C.; Lindberg, R.; Lawrence, M.A. Global Trends in Added Sugars and Non-Nutritive Sweetener Use in the Packaged Food Supply: Drivers and Implications for Public Health. Public Health Nutr. 2023, 26, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Hilal, A.; Aseri, G.K.; Jain, N. Sweet or Sour? A Review of the Aspartame Market Landscape, Carcinogenicity, and Its Socioeconomic Impact. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 62, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sweetener-market (accessed on 20 August 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dragomir, N.; Grigore, D.-M.; Pogurschi, E.N. Beyond Sugar: A Holistic Review of Sweeteners and Their Role in Modern Nutrition. Foods 2025, 14, 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183182
Dragomir N, Grigore D-M, Pogurschi EN. Beyond Sugar: A Holistic Review of Sweeteners and Their Role in Modern Nutrition. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183182
Chicago/Turabian StyleDragomir, Nela, Daniela-Mihaela Grigore, and Elena Narcisa Pogurschi. 2025. "Beyond Sugar: A Holistic Review of Sweeteners and Their Role in Modern Nutrition" Foods 14, no. 18: 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183182
APA StyleDragomir, N., Grigore, D.-M., & Pogurschi, E. N. (2025). Beyond Sugar: A Holistic Review of Sweeteners and Their Role in Modern Nutrition. Foods, 14(18), 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183182










