Effects of Thermal Treatments on the Physicochemical and Flavor Profiles of Chili Powders and Their Derived Chili Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Chili Powder and Chili Oil with Different Processing
2.3. Color Analysis
2.4. Volatile Organic Compounds Analysis
2.4.1. The Electronic Nose (E-Nose) Analysis
2.4.2. GC-IMS Analysis
2.4.3. HS-SPME-GC-MS Analysis
2.4.4. Identification of Relative Odor Activity Values (ROAVs)
2.5. LC-MS/MS for Non-Volatile Flavor Compounds Analysis
2.6. Sensory Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Color
3.2. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds
3.2.1. Analysis of E-Nose
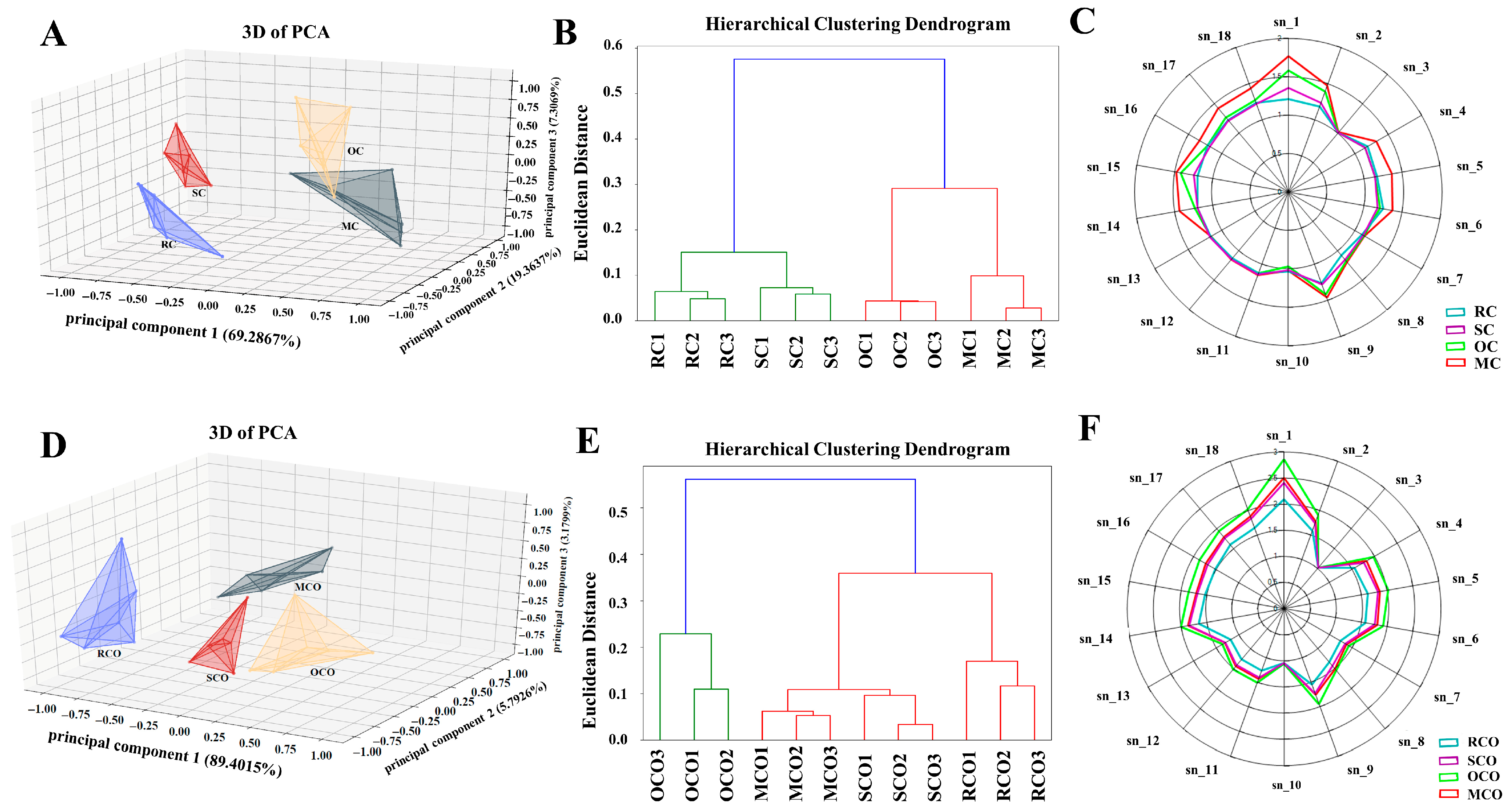
3.2.2. Analysis of GC-IMS
Topographic Map Analysis
Fingerprint Analysis of Differences in VOCs in CPs and COs
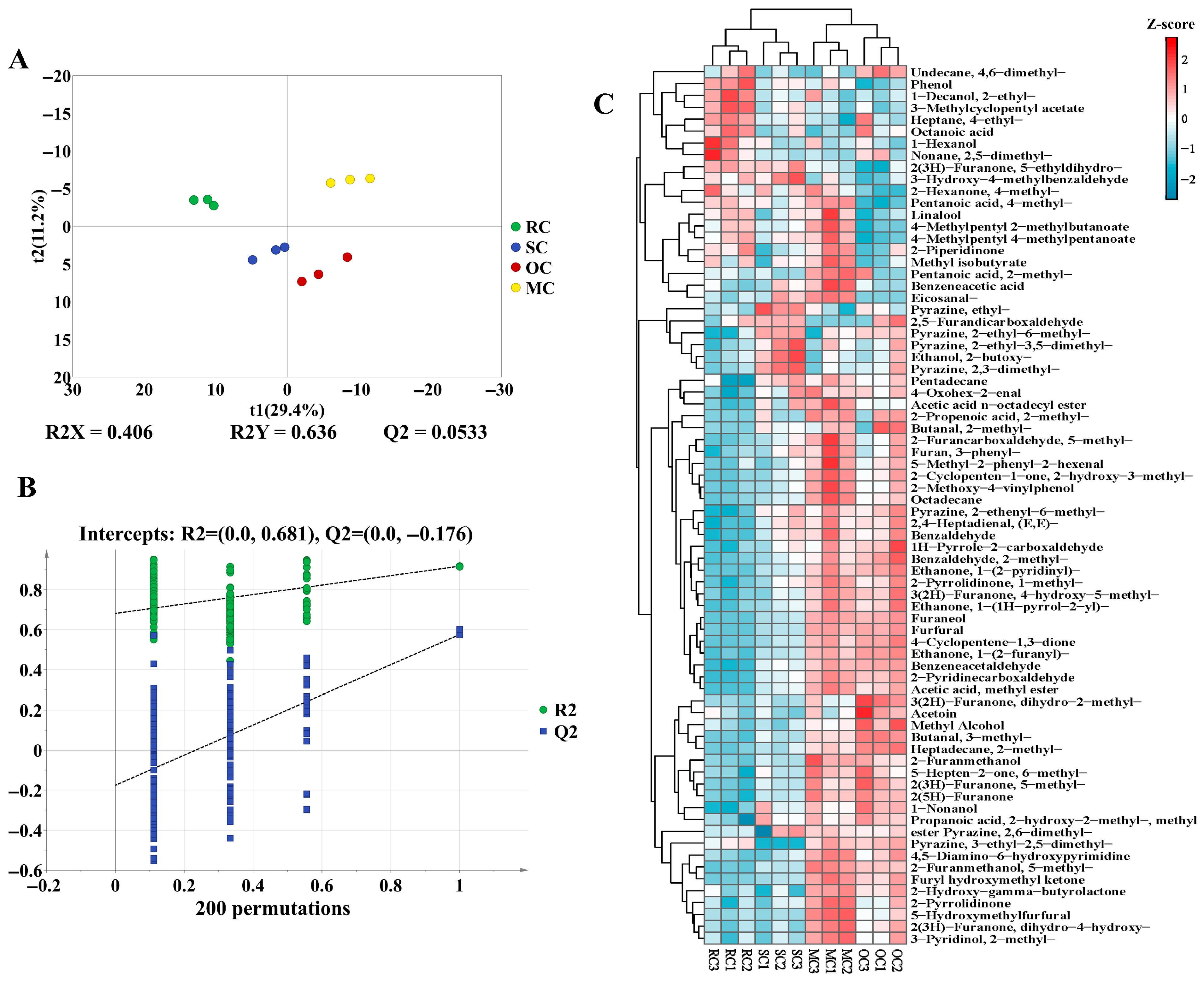
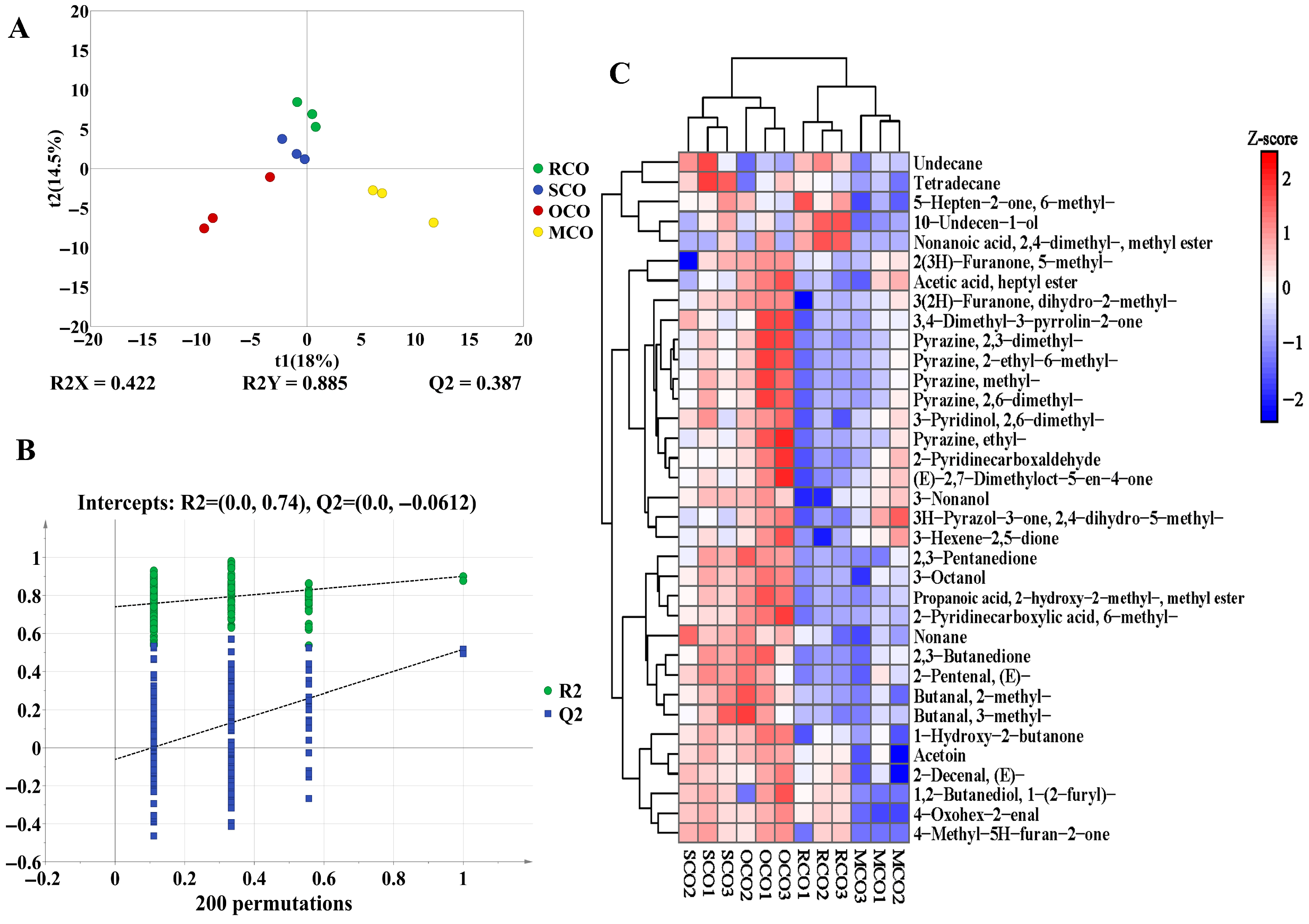
3.2.3. Analysis of HS-SPME-GC-MS
Analysis of Key Aroma-Active Volatiles
Influence of Different Thermal Treatments on the Flavor of CPs
Influence of Secondary Heat Activation on the Flavor of COs
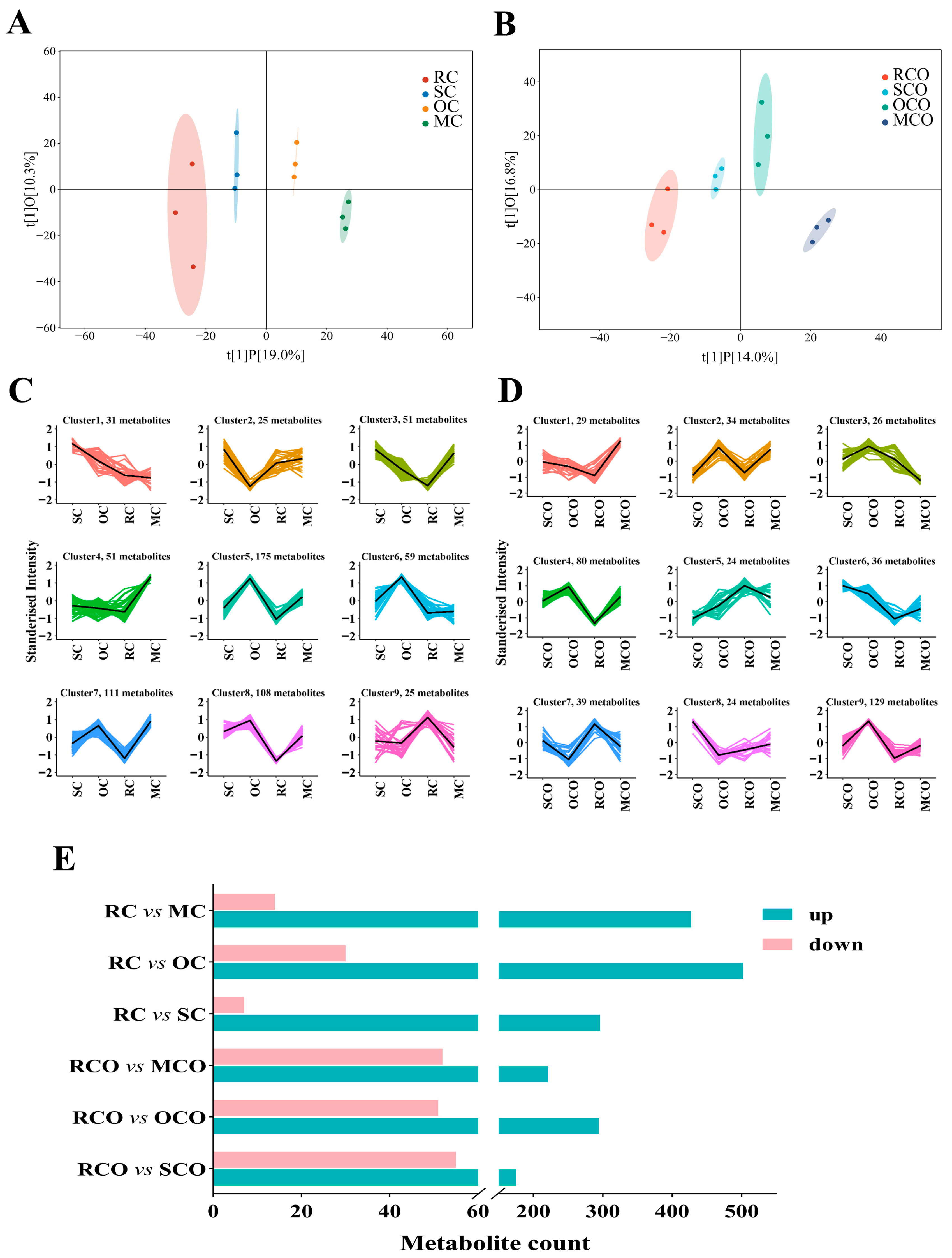
3.3. Analysis of LC-MS/MS
3.3.1. Influence of Different Thermal Treatments on the Capsaicinoids
3.3.2. Influence of Different Thermal Treatments on the Non-Volatile Compound Profiles
3.4. Analysis of Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPs | chili powders |
| RC | untreated raw chili powder |
| SC | stir-fried chili powder |
| OC | oven-baked chili powder |
| MC | microwave-treated chili powder |
| COs | chili oils |
| RCO | untreated raw chili oil |
| SCO | stir-fried chili oil |
| OCO | oven-baked chili oil |
| MCO | microwave-treated chili oil |
| E-nose | electronic nose |
| GC-IMS | chromatography-ion mobility spectrometr |
| HS-SPME-GC-MS | headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
| VOCs | volatile organic compounds |
References
- Liu, M.; Hu, L.; Deng, N.; Cai, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J. Effects of different hot-air drying methods on the dynamic changes in color, nutrient and aroma quality of three chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) varieties. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Xing, L.; Song, W.; Lu, S. Analysis of Volatile and Non-Volatile Components of Dried Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Foods 2025, 14, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Geng, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Han, J.; Yang, H.; Cao, S. Effect of blanching times and drying temperatures on the color, moisture migrations, microstructures, phytochemicals, and flavors of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Chem. 2025, 486, 144690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Karrar, E.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Wang, X. Capsaicinoids and volatile flavor compounds profile of Sichuan hotpot as affected by cultivar of chili peppers during processing. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chu, B.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Gu, Q. The difference analysis of physicochemical indexes and volatile flavor compounds of chili oil prepared from different varieties of chili pepper. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Peng, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Guo, X. Combination of Flos Sophorae and chili pepper as a nitrite alternative improves the antioxidant, microbial communities and quality traits in Chinese sausages. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Jin, Y.; Wu, C. Exploring major variable factors influencing flavor and microbial characteristics of Pixian Doubanjiang. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Shang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Ren, H.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Effect of ripening and variety on the physiochemical quality and flavor of fermented Chinese chili pepper (Paojiao). Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Ren, H.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Dynamic analysis of flavor properties and microbial communities in Chinese pickled chili pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.): A typical industrial-scale natural fermentation process. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, M.; Lin, H.; Tang, H.; Jiang, H.; Fu, Q.; Yuan, Y. Investigation of the physicochemical properties and the chemical components of chili rapeseed oil via different preparation oil temperatures. LWT 2024, 204, 116432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dadmohammadi, Y.; Abbaspourrad, A. Flavor components, precursors, formation mechanisms, production and characterization methods: Garlic, onion, and chili pepper flavors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8265–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Hossain, A. Role of Lipids in Food Flavor Generation. Molecules 2022, 27, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Fang, X.-M.; Wang, J.; Pei, Y.-P.; Wu, W.; Zielinska, M.; Xiao, H.-W. High-humidity hot air impingement blanching (HHAIB) efficiently inactivates enzymes, enhances extraction of phytochemicals and mitigates brown actions of chili pepper. Food Control 2020, 111, 107050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, D.; Dong, Y.; Ju, H.; Wu, C.; Lin, S. Characteristic volatiles fingerprints and changes of volatile compounds in fresh and dried Tricholoma matsutake Singer by HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1099, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guclu, G.; Keser, D.; Kelebek, H.; Keskin, M.; Sekerli, Y.E.; Soysal, Y.; Selli, S. Impact of production and drying methods on the volatile and phenolic characteristics of fresh and powdered sweet red peppers. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Kang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, C. Flavor profiles and active compounds release in noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) fruit tea: A comparison among different drying approaches. J. Future Foods, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, S.; Qin, L.; Wang, S.; Geng, Y.; Chen, D. Lipid molecule profiling in Lentinula edodes during hot air drying via untargeted lipidomics: Composition, dynamic variations and contribution to characteristic flavor. Food Biosci. 2025, 71, 107386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Tang, H.; Huang, Q.; Meng, P.; Deng, H.; He, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, P.; Li, T.; et al. Investigation of the flavor profiles on chili rapeseed oil: A study on flavor generation by chili addition and frying oil temperature. LWT 2025, 228, 118064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Li, M.; Ren, H.; Cai, S.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Dynamics of microbial communities, flavor, and physicochemical properties of pickled chayote during an industrial-scale natural fermentation: Correlation between microorganisms and metabolites. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrzak, T.; Wojnowski, W.; Dymerski, T.; Gebicki, J.; Namiesnik, J. Electronic noses in classification and quality control of edible oils: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zou, Y.; Liao, G.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G. Identification of characteristic flavor compounds and small molecule metabolites during the ripening process of Nuodeng ham by GC-IMS, GC–MS combined with metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Liu, C.; Yao, Z.; Wan, H.; Ruan, M.; Wang, R.; Ye, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, Y. Detection and Analysis of VOCs in Cherry Tomato Based on GC-MS and GC×GC-TOF MS Techniques. Foods 2024, 13, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhong, Q. Comprehensive metabolite profiling reveals the dynamic changes of volatile and non-volatile metabolites in albino tea cultivar ‘Ming guan’ (MG) during white tea withering process. Food Res. Int. 2025, 202, 115784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Multi-dimensional pungency and sensory profiles of powder and oil of seven chili peppers based on descriptive analysis and Scoville heat units. Food Chem. 2023, 411, 135488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wan, P.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.; Chen, D.-W. Investigation on the changes of carotenoids and capsaicinoids in chili oil at different frying temperature by using 1H NMR. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Kan, J. Thermostability and kinetics analysis of oil color, carotenoids and capsaicinoids in hotpot oil models (butter, rapeseed oil, and their blends). LWT 2021, 152, 112216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Al-Dalali, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Zhou, H. Investigation of volatile flavor compounds and characterization of aroma-active compounds of water-boiled salted duck using GC-MS-O, GC-IMS, and E-nose. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yu, J.; Yan, S.; Bai, J.; Xu, H.; Li, M. Volatile flavor behavior characterization of Hericium erinaceus during postharvest storage using E-nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC–MS after treated with electron-beam generated X-ray irradiation. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zi, L.; Xu, N.; Yang, H.; Dong, S.; Qin, F.; Guo, L. Identification of characteristic flavor compounds of boletus edulis from different regions based on by E-nose, HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC–MS. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, D.; Lin, S. Development of a flavor fingerprint by HS-GC–IMS with PCA for volatile compounds of Tricholoma matsutake Singer. Food Chem. 2019, 290, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Ma, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M. Flavor profile analysis of grilled lamb seasoned with classic salt, chili pepper, and cumin (Cuminum cyminum) through HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-GC-IMS, E-nose techniques, and sensory evaluation on Sonit sheep. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Xu, X.; Ji, C.; Liang, H.; Dong, L. Deep exploration of lipid oxidation into flavor compounds: A density functional theory study on (E)-2-decenal thermal oxidative reaction. Food Chem. 2023, 428, 136725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Zhang, C.; Xie, J.; Yang, X. Maillard reaction chemistry in formation of critical intermediates and flavour compounds and their antioxidant properties. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Sun, R.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; Deng, W.; Liao, X.; Ling, J. Novel application of HS-GC-IMS with PCA for characteristic fingerprints and flavor compound variations in NFC Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) juice during storage. LWT 2022, 167, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.-S.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Ma, R.-H.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. Effects of roasting level on physicochemical, sensory, and volatile profiles of soybeans using electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, W.; Du, S.; Yu, X. Key volatile compound formation of rapeseed oil induced via the Maillard reaction during seed roasting. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Chen, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, L.; Yi, Y.; Deng, F.; Wang, R. Changes in volatile flavor compounds of peppers during hot air drying process based on headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3087–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Laaksonen, O.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Battino, M.; Yang, B.; Gu, Q. Aroma characteristics of volatile compounds brought by variations in microbes in winemaking. Food Chem. 2023, 420, 136075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.N.; Liu, F.F.; Pan, F.; Li, H.H.; Zheng, F.P.; Ye, X.Q.; Sun, B.G.; Cheng, H. Study on the Interaction between Polyol Glycerol and Flavor Compounds of Baijiu: A New Perspective of Influencing Factors of Baijiu Flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 26832–26845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Xu, B.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, X.; Sun, Y. Effects of different thermal treatment temperatures on volatile flavour compounds of water-boiled salted duck after packaging. LWT 2022, 154, 112625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Riaño, P.; Illera, A.E.; Benito-Román, O.; Melgosa, R.; Bermejo-López, A.; Beltrán, S.; Sanz, M.T. Degradation kinetics of sugars (glucose and xylose), amino acids (proline and aspartic acid) and their binary mixtures in subcritical water: Effect of Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Kao, T.-H.; Chen, B.-H. Development of a GC–MS/MS method coupled with HS-SPME-Arrow for studying formation of furan and 10 derivatives in model systems and commercial foods. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Y.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Wang, Z. Characterization of aroma profiles of chinese four most famous traditional red-cooked chickens using GC–MS, GC-IMS, and E-nose. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, R.; Wu, M.; Ge, Q.; Yu, H. A review on aroma-active compounds derived from branched-chain amino acid in fermented meat products: Flavor contribution, formation pathways, and enhancement strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y. Maillard reaction intermediates in Chinese Baijiu and their effects on Maillard reaction related flavor compounds during aging. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.-L.; Zhao, F.; Xin, R.; Huang, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhou, D.; Qin, L. Unraveling the Thermal Oxidation Products and Peroxidation Mechanisms of Different Chemical Structures of Lipids: An Example of Molecules Containing Oleic Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 16410–16423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, H.; Bolat, I.; Cook, D. Modelling flavour formation in roasted malt substrates under controlled conditions of time and temperature. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Deng, N.; Hou, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Characterisation of flavour profiles and microbial communities of fermented peppers with different fermentation years by combining flavouromics and metagenomics. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspardo, B.; Procida, G.; Toso, B.; Stefanon, B. Determination of volatile compounds in San Daniele ham using headspace GC–MS. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Mai, R.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, J. The contribution of inoculated probiotics to increased protein-derived volatile flavor compounds. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Jian, W.; Sun, Z.; Qi, P.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, S. Capsaicin from chili peppers and its analogues and their valued applications: An updated literature review. Food Res. Int. 2025, 208, 116034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; He, W.; Guo, D.; Xu, W. Effect of Capsaicin and Dihydrocapsaicin in Capsicum on Myofibrillar Protein in Duck Meat. Foods 2023, 12, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Bi, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, T.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, S.; Chen, C. Thermal degradation of capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin: Mechanism and hazards of volatile products. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 182, 106714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, C. Preserving pungency and color: Thermal/storage stability of bioactive compounds in chili oil and shelf-life extension strategies. Food Biosci. 2025, 71, 107212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, V.K.; Gothandam, K.M.; Ranjan, V.; Shakya, A.; Pareek, S. Effect of drying methods (microwave vacuum, freeze, hot air and sun drying) on physical, chemical and nutritional attributes of five pepper (Capsicum annuum var. annuum) cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3492–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| L* | a* | b* | ∆E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPs | ||||
| RC | 43.84 ± 0.17 a | 10.53 ± 0.36 b | 10.11 ± 0.53 b | |
| SC | 43.36 ± 0.65 a | 12.16 ± 0.63 a | 11.12 ± 0.77 ab | 2.15 ± 0.56 a |
| OC | 43.94 ± 0.64 a | 12.77 ± 0.57 a | 11.59 ± 0.67 a | 2.75 ± 0.80 a |
| MC | 44.14 ± 0.20 a | 12.96 ± 0.37 a | 12.09 ± 0.47 a | 3.15 ± 0.56 a |
| COs | ||||
| RCO | 26.04 ± 0.15 a | 12.68 ± 0.47 c | 4.74 ± 0.56 c | |
| SCO | 25.22 ± 0.17 b | 14.89 ± 0.63 b | 5.78 ± 0.31 b | 2.62 ± 0.44 b |
| OCO | 23.94 ± 0.30 c | 16.43 ± 0.44 a | 6.92 ± 0.32 a | 4.84 ± 0.32 a |
| MCO | 25.08 ± 0.25 b | 15.03 ± 0.48 b | 5.91 ± 0.39 b | 2.82 ± 0.45 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Fang, Z.; Hu, B.; Chen, H.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Z. Effects of Thermal Treatments on the Physicochemical and Flavor Profiles of Chili Powders and Their Derived Chili Oils. Foods 2025, 14, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173129
Jiang C, Zhang L, Yu L, Fang Z, Hu B, Chen H, Wu W, Liu Y, Zeng Z. Effects of Thermal Treatments on the Physicochemical and Flavor Profiles of Chili Powders and Their Derived Chili Oils. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173129
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Chunping, Lijia Zhang, Linman Yu, Zhengfeng Fang, Bin Hu, Hong Chen, Wenjuan Wu, Yuntao Liu, and Zhen Zeng. 2025. "Effects of Thermal Treatments on the Physicochemical and Flavor Profiles of Chili Powders and Their Derived Chili Oils" Foods 14, no. 17: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173129
APA StyleJiang, C., Zhang, L., Yu, L., Fang, Z., Hu, B., Chen, H., Wu, W., Liu, Y., & Zeng, Z. (2025). Effects of Thermal Treatments on the Physicochemical and Flavor Profiles of Chili Powders and Their Derived Chili Oils. Foods, 14(17), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173129







