Formation Mechanism of Characteristic Flavor Substances in 3-Year-Old Diannan Small-Ear Pig Ham: Lipidomics and Flavoromics Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Main Reagents
2.3. Sensory Analysis
2.4. Lipidomics Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Free Amino Acid Content
2.6. Analysis of Volatile Flavor Compounds
2.7. Calculation of Relative Odor Activity Value (ROAV)
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
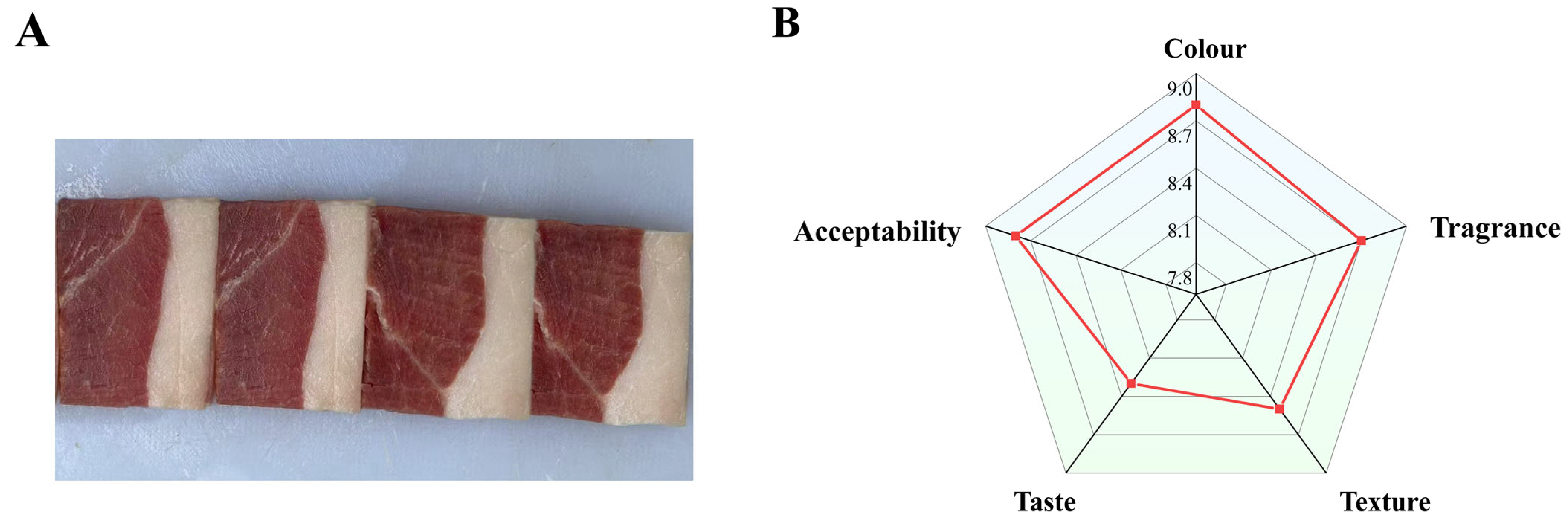
3.1. Sensory Analysis of DSP Ham
3.2. Reveal the Characteristic Lipids of DSP Ham
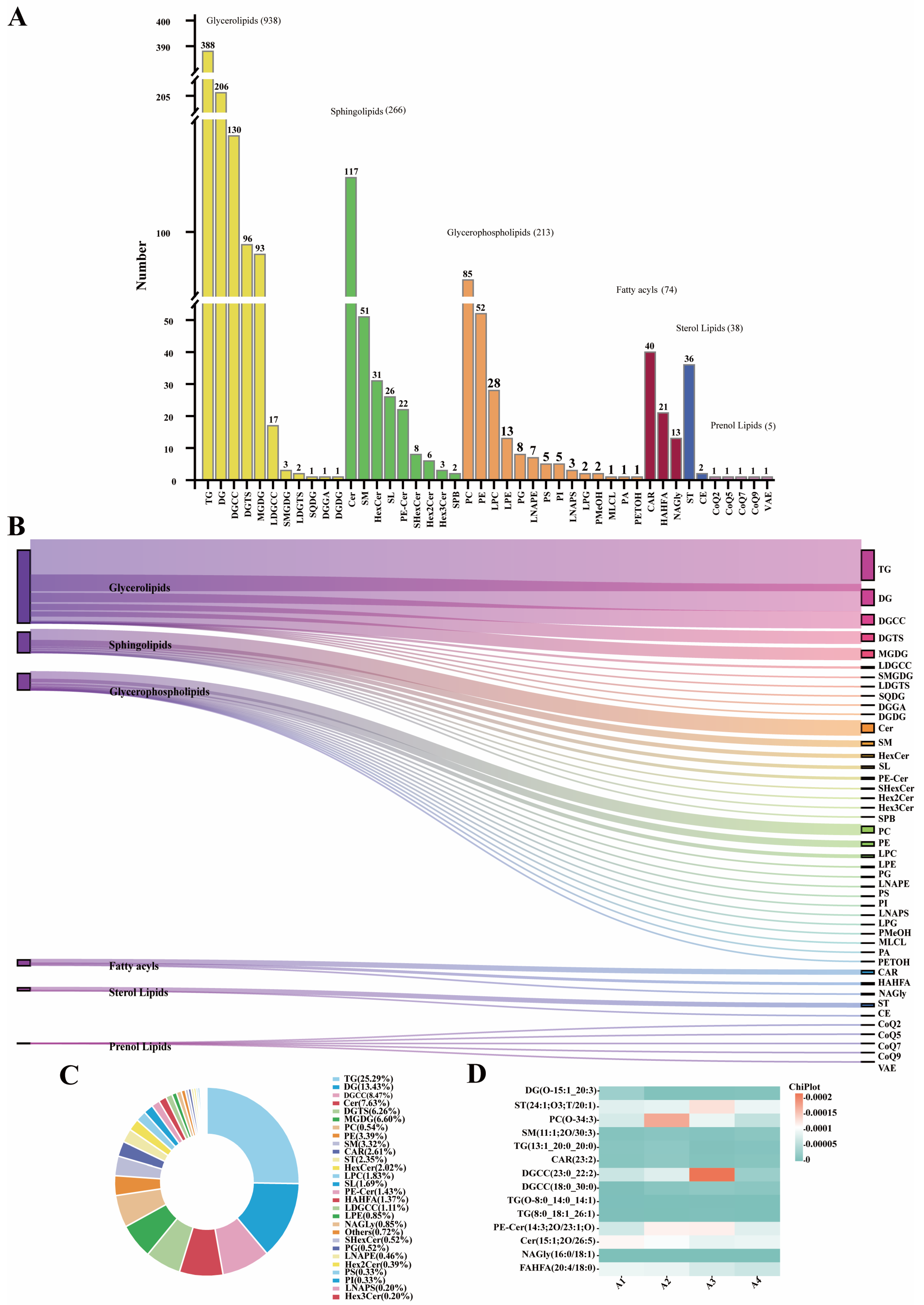
3.2.1. Lipid Composition of DSP Ham
3.2.2. Characteristic Lipids in DSP Ham
3.3. Flavor Compounds of DSP Ham Revealed by UPLC-MRM-MS/MS and Flavoromics
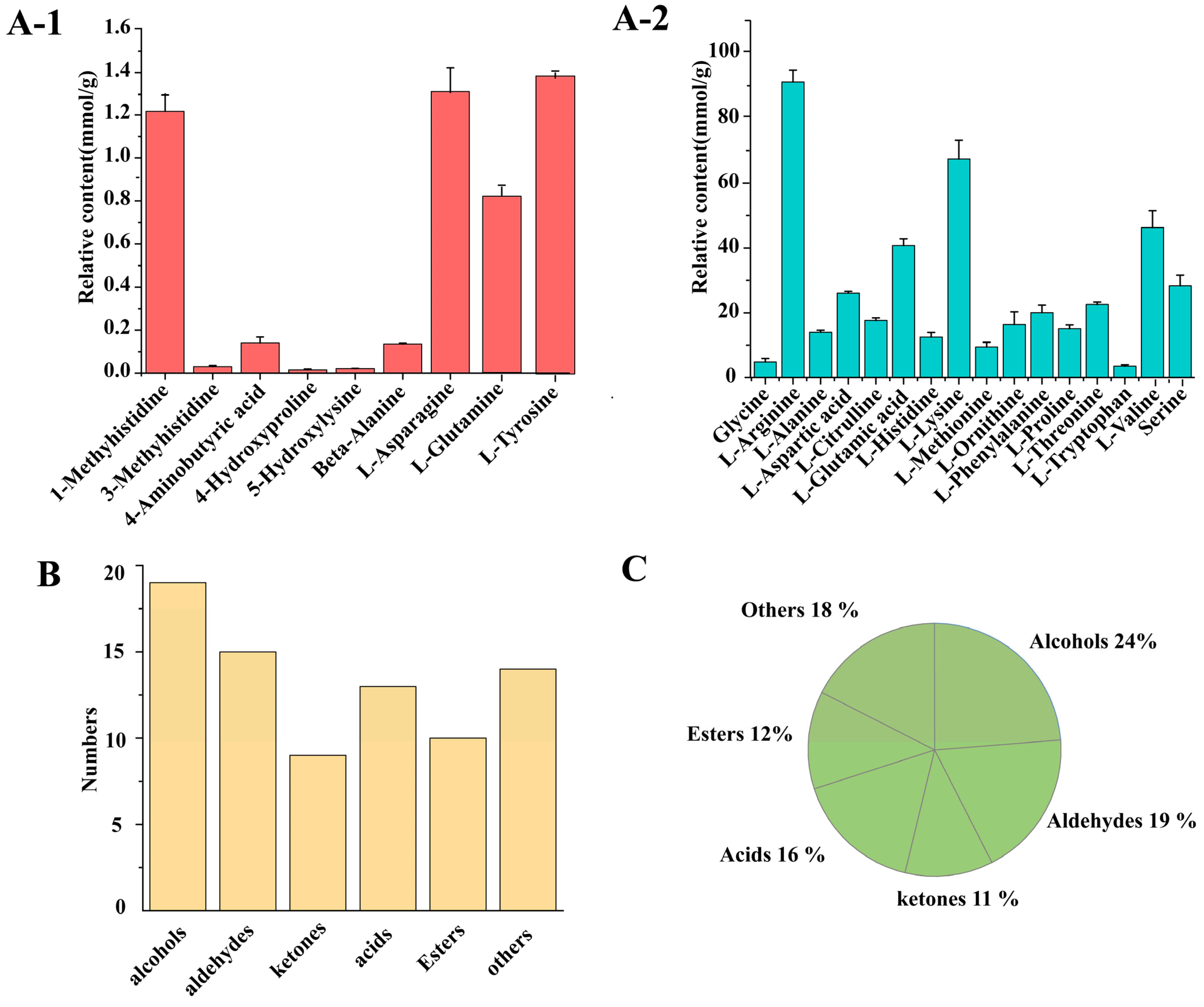
3.3.1. Non-Volatile Compounds in DSP Ham
3.3.2. Composition of Volatile Compounds in DSP Ham
3.3.3. Characteristic Volatile Flavor Compounds in DSP Ham
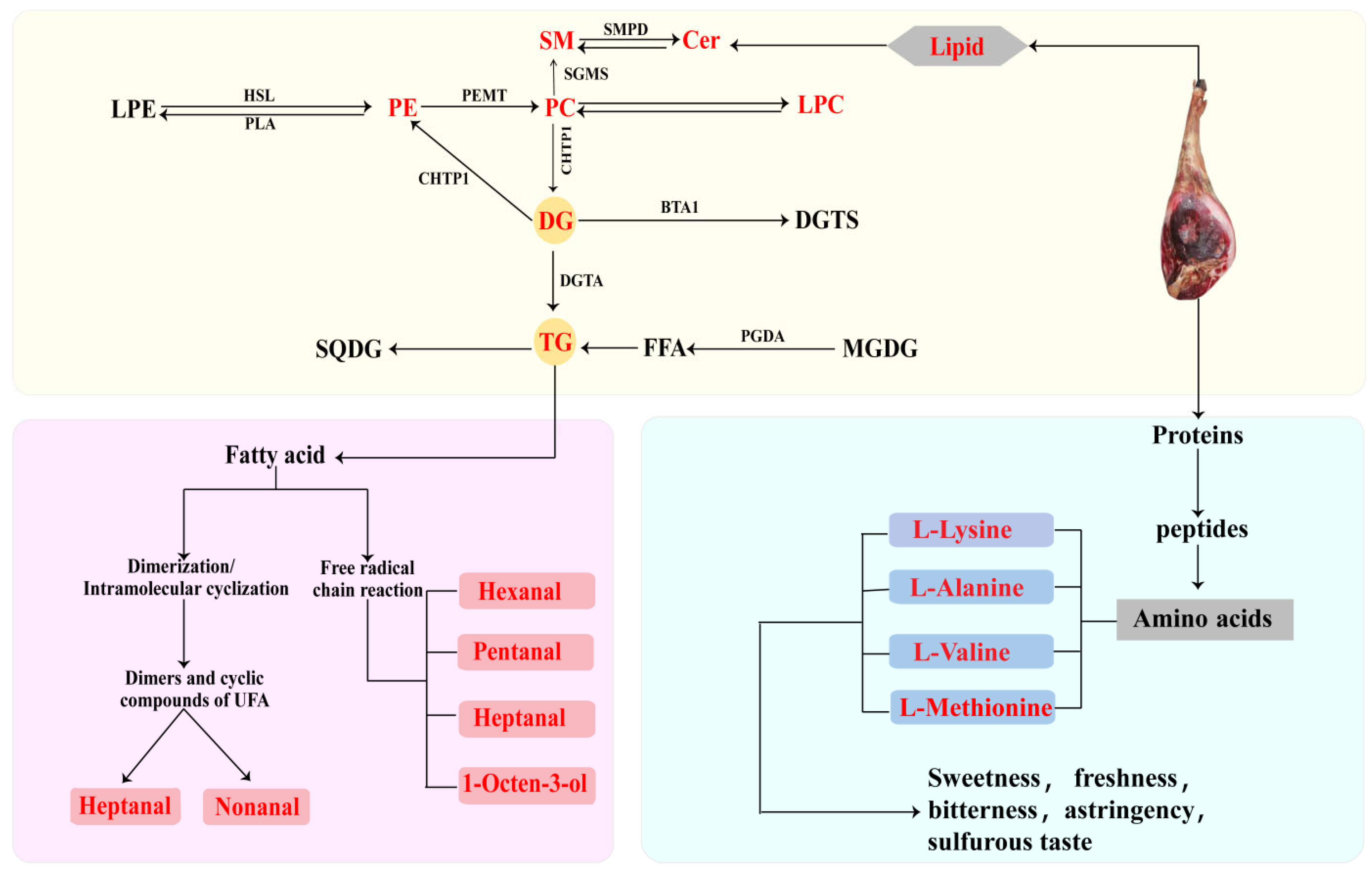
3.4. Flavor Formation Mechanism of DSP Ham
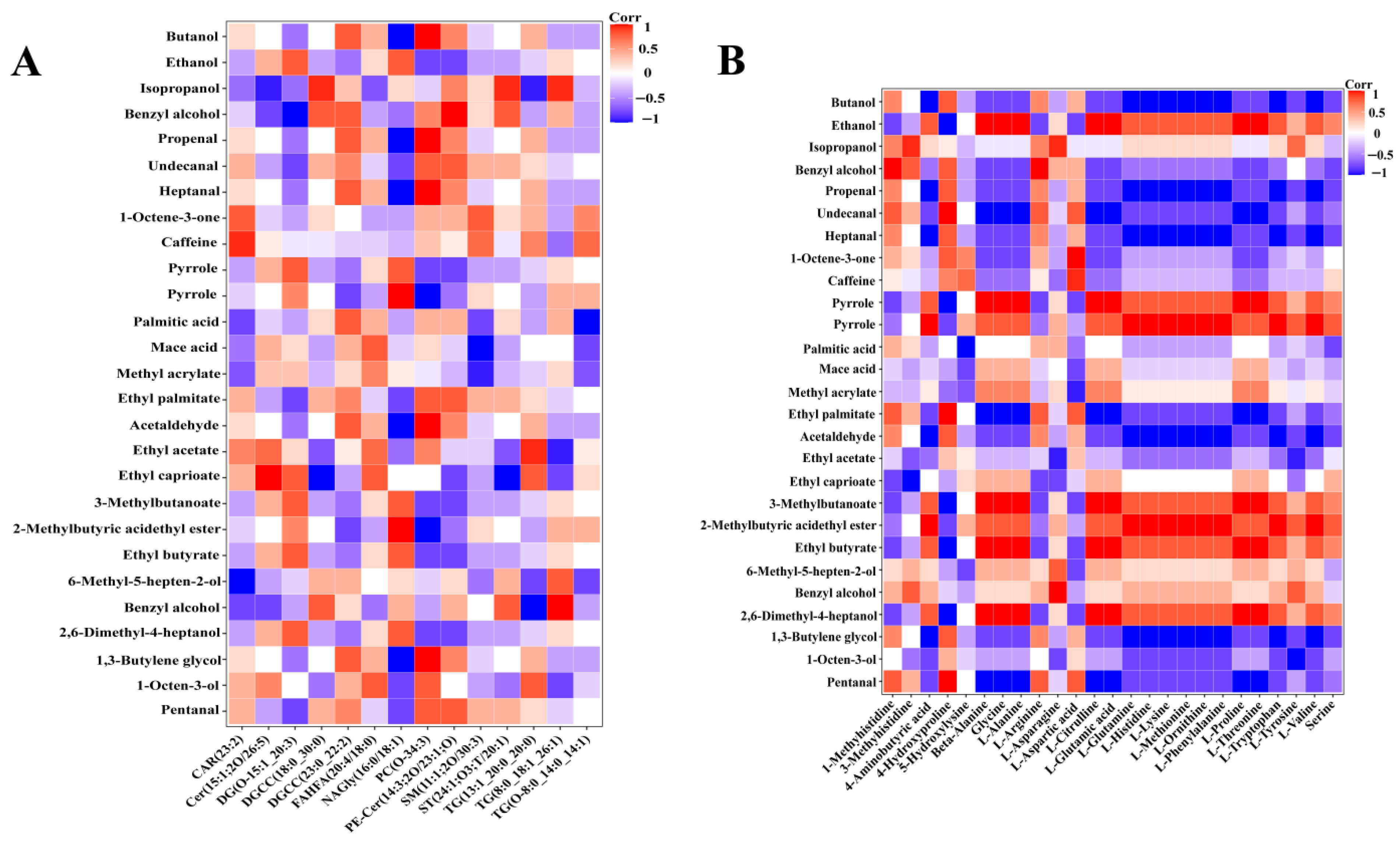
3.4.1. Effect of Lipids on the Flavor of Ham
3.4.2. Effect of Free Amino Acids on the Flavor of Ham
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bosse, R.; Müller, A.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, A.; Schmidt, H.; Weiss, J. Recent advances in cured raw ham manufacture. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 58, 610–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabio, E.; Vidal-Aragon, M.C.; Bernalte, M.J.; Gata, J.L. Volatile compounds present in six types of dry-cured ham from south european countries. Food Chem. 1998, 61, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bai, L.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, D.; Yao, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Characterization of Jinhua ham aroma profiles in specific to aging time by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS). Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkouss, R.; Astruc, T.; Lebert, A.; Gatellier, P.; Loison, O.; Safa, H.; Mirade, P.S. Quantitative study of the relationships among proteolysis, lipid oxidation, structure and texture throughout the dry-cured ham process. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Xu, W.; Chen, L.; Tang, H. Physicochemical property, volatile flavor quality, and microbial community composition of Jinhua fatty ham and lean ham: A comparative study. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1124770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; Wen, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. Correlation between the characteristic flavour and microbial community of xuanwei ham after ripening. Fermentation 2024, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Tang, C.; Yue, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, J. Changes in lipids and aroma compounds in intramuscular fat from Hu sheep. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Liao, G.; Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G. UHPLC-MS/MS-based lipidomics for the evaluation of the relationship between lipid changes and Zn-protoporphyrin formation during Nuodeng ham processing. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fan, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Sun, Y.; Du, L.; Pan, D. Effect of different salt substitutions on the decomposition of lipids and volatile flavor compounds in restructured duck ham. LWT 2023, 176, 114541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. A novel porcine gene, MAPKAPK3, is differentially expressed in the pituitary gland from mini-type Diannan small-ear pigs and large-type Diannan small-ear pigs. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3345–3349. [Google Scholar]
- Huan, W.; Yang, X.J.; Cao, Z.Y. Determination of chemical composition of small-ear pork in southern Yunnan by near infrared spectroscopy. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2016, 31, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Tang, C.B.; Li, G.; Dai, C.; Bai, Y.; Cao, J.X. Comparing the proteomic profile of proteins and the sensory characteristics in Jinhua ham with different processing procedures. Food Control 2019, 106, 106694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, G.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, C.; Liao, G. Evaluation of small molecular metabolites and sensory properties of Xuanwei ham salted with partial replacement of NaCl by KCl. Meat Sci. 2021, 175, 108465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Xia, Q.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Dang, Y.; Ou, C.; Pan, D.; Cao, J.; Zhou, G. Improvement of ultrasound-assisted thermal treatment on organoleptic quality, rheological behavior and flavor of defective dry-cured ham. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Nie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, B.; Shang, J.; Guo, X.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Integration of GC-MS, ROAV, and chemometrics to characterize key differential volatile compounds in wild and cultivated blueberries from Northeast China. LWT 2025, 225, 117950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Tian, M.; Liao, G.; Chen, G.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G. Evaluation of the effects of compound curing agents on the lipid profiles and volatile flavors in Nuodeng ham based on lipidomics and GC-IMS analysis. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, G.; Chen, G.; Zhou, N.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, C.; Liao, G. Revealing the intrinsic relationship between microbial communities and physicochemical properties during ripening of Xuanwei ham. Food Res. Int. 2024, 186, 114377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lin, S.; Xue, J.; Shen, Q.; Feng, J.; Jin, R.; Dai, Z. The characterization of myoglobin and myoglobin-Induced lipid oxidation in frigate mackerel. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2016, 40, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, H.; Gu, B.; Lyu, B.; Wang, Q. Changes in proteolysis, protein oxidation, flavor, color and texture of dry-cured mutton ham during storage. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 111860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lu, S.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Dong, J.; Ji, H.; Wang, Q.L. Correlations among flavor compounds, lipid oxidation indices, and endogenous enzyme activity during the processing of Xinjiang dry-cured mutton ham. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alencar Figueira Angelotti, J.A.; Battaglia Hirata, D.B.; Rodrigues Dos Santos, M.R. Lipases: Sources of acquisition, ways of production, and recent applications. Catal. Res. 2022, 2, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Pan, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J. The effect of coating incorporated with black pepper essential oil on the taste quality of jinhua ham after storage for four months. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ji, H.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Lu, Y. Shrimp lipids improve flavor by regulating characteristic aroma compounds in hot air-dried shrimp. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamphuis, M.M.; Mela, D.J.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Diacylglycerols affect substrate oxidation and appetite in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kennelly, J.P.; Wan, S.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.D.; Wang, J.W. Ceramide de novo synthesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 202, 115157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Dong, J.; Shi, W.; Zhao, H.; Bai, Y. Research progress on quality detection of livestock and poultry meat based on machine vision, hyperspectral and multi-Source information fusion technologies. Foods 2024, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Qiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Human milk sphingomyelin: Function, metabolism, composition and mimicking. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Fu, Y. Lipid degradation contributes to flavor formation during air-dried camel jerky processing. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Saghatelian, A. The measurement, regulation and biological activity of FAHFAs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2025, 21, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ard, Y. Flavour formation by amino acid catabolism. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Kong, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Zeng, X.; Bai, W.; Qian, M.; Dong, H. Flavor evolution and identification of the warmed-over flavor (WOF) in pre-cooked goose meat by means of HS-SPME-GC-MS and GC-IMS. Food Chem. 2025, 481, 143979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, B. Correlation of characteristic flavor and microbial community in Jinhua ham during the post-ripening stage. LWT 2022, 71, 114067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Weng, L.; Yu, C.; Hu, M.; Peng, B.; Tu, Z. Integration of lipidomics and flavoromics reveals the lipid-flavor transformation mechanism of fish oil from silver carp visceral with different enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, T.T.; To, K.V.; Schilling, M.W. Fatty acid composition of meat animals as flavor precursors. Meat Muscle Biol. 2021, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez-Rivas, M.; Gallardo, E.; León-Camacho, M. Evolution of volatile hydrocarbons from subcutaneous fat during ripening of Iberian dry-cured ham. A tool to differentiate between ripening periods of the process. Food Res. Int. 2015, 67, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriel, E.; Andres, A.I.; Petron, M.J.; Antequera, T.; Ruiz, J. Lipolytic and oxidative changes in Iberian dry-cured loin. Meat Sci. 2007, 75, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lan, Q.; Yang, L.; Deng, Q.; Wei, T.; Zhao, H.; Peng, P.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H.; et al. Genome-Wide association analysis identifies genomic regions and candidate genes for growth and fatness traits in Diannan small-Ear (DSE) pigs. Animals 2023, 13, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezgebo, G.B.; Monahan, F.J.; McGee, M.; O’Riordan, E.G.; Richardson, I.R.; Brunton, N.P.; Moloney, A.P. Fatty acid, volatile and sensory characteristics of beef as affected by grass silage or pasture in the bovine diet-ScienceDirect. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, L.; Ren, W.; Qin, H.; Sun, M.; Yuan, S.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Li, M. Characterization of the relationship between lipids and volatile compounds in donkey, bovine, and sheep meat by UHPLC–ESI–MS and SPME–GC–MS. LWT 2023, 175, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hui, T.; Fang, F.; Ma, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Characterization and discrimination of key aroma compounds in pre- and postrigor roasted mutton by GC-O-MS, GC E-Nose and aroma recombination experiments. Foods 2021, 10, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Ge, L. Effects of production conditions on physicochemical and flavor quality of lard. Meat Res. 2020, 34, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, S.; Silcock, P.; Bremer, P. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) produced by Levilactobacillus brevis WLP672 fermentation in defined media supplemented with different amino acids. Molecules 2024, 29, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F. Research progress on extraction and analysis of volatile flavor compounds in aquatic products. Food Sci. 2015, 36, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, L.; Jin, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Zhao, L.; Su, L. Effect of feeding system on muscle fiber composition, antioxidant capacity, and nutritional and organoleptic traits of goat meat. Animals 2023, 13, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Shao, J.; Li, M.; Yue, X. A Review of Plant-based drinks addressing nutrients, flavor, and processing technologies. Foods 2023, 12, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Du, B.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Targeted microbial collaboration to enhance key flavor metabolites by inoculating Clostridium tyrobutyricum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the strong-flavor Baijiu simulated fermentation system. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Y.; Hong, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, D.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Molecular sensomics combined with random forest model can reveal the evolution of flavor type of Baijiu based on differential markers. Foods 2024, 13, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, T.; Chai, X.; Wang, P.; Duan, X. Comparative study of a liposome and emulsion system with cinnamon essential oil on the quality and proteolysis of refrigerated minced pork. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1341827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, I.; Aasen, I.M.; Rustad, T.; Eikevik, T.M. Manufacture of dry-cured ham: A review. Part 1. Biochemical changes during the technological process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, G. Dry cured ham quality as related to lipid quality of raw material and lipid changes during processing: A review. Grasas Aceites Int. J. Fats Oils 2009, 60, 297–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Geng, F. Molecular dynamics simulation of the interaction of food proteins with small molecules. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, F.; Han, D.; Xu, Y.; Shen, S.; Luan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. Elucidation of potential lipid precursors and formation pathways for the warmed-over flavor (WOF) in precooked Chinese stewed beef through lipid oxidation mechanisms. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Li, R.; Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Shi, L. Molecular mechanism of lipid transformation in cold chain storage of Tan sheep. Food Chem. 2021, 47, 129007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Q.; Xing, J.; Li, P.; Gao, P.; Hamid, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Gong, H. Exploring the formation and retention of aroma compounds in ready-to-eat roasted pork from four thermal methods: A lipidomics and heat transfer analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.X.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Pan, D.D.; Ou, C.R. The effect of dry-cured salt contents on accumulation of non-volatile compounds during dry-cured goose processing. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J. Enzymatic reaction-related protein degradation and proteinaceous amino acid metabolism during the black tea (Camellia sinensis) manufacturing process. Foods 2020, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrea, V.; Hernando, I.; Quiles, A.; Lluch, M.A.; Pérez-Munuera, I. Changes in proteins during Teruel dry-cured ham processing. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yoo, M.J.; Ross, A.B.; Farouk, M.M. Mechanisms and strategies to tailor dry-aged meat flavour. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Ventanas, J.; Cava, R.; Andrés, A.; García, C. Volatile compounds of dry-cured Iberian ham as affected by the length of the curing process. Meat Sci. 1999, 52, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Z.; Zhao, J.L.; Tian, W.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, M.Y.; Zhao, G.M. Contribution of histidine and lysine to the generation of volatile compounds in Jinhua ham exposed to ripening conditions via Maillard reaction. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar Sharma, P.; Chaturvedi, S.; Kumar, P.; Deepak Nannaware, A.; Kalra, A.; Kumar Rout, P. Biocatalyst for the synthesis of natural flavouring compounds as food additives: Bridging the gap for a more sustainable industrial future. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, R.; Gallardo, E.; Hidalgo, F.J. Strecker degradation of phenylalanine initiated by 2,4-decadienal or methyl 13-oxooctadeca-9,11-dienoate in model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canoy, T.; Wiedenbein, E.; Bredie, W.; Meyer, A.; Wösten, H.; Nielsen, S. Solid-state fermented plant foods as new protein sources. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Shi, Q.; Shi, L. Effect of irradiation treatment on the lipid composition and nutritional quality of goat meat. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NO. | Compounds | Threshold (µg/kg) | Relative Content (%) | ROAV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pentanal | 12.00 | 1.2274 | 2.3998 |
| 2 | Hexanal | 4.00 | 4.6181 | 27.0866 |
| 3 | Heptanal | 3.00 | 0.9151 | 7.1566 |
| 4 | Octanal | 1.40 | 0.6394 | 10.7155 |
| 5 | Nonanal | 1.00 | 0.1004 | 2.3544 |
| 6 | Benzaldehyde | 3.00 | 1.6205 | 12.6729 |
| 7 | Isopropyl Alcohol | 40,000.00 | 0.0010 | 5.7935 × 10−7 |
| 8 | Ethanol | 8.00 | 1.1285 | 3.3096 |
| 9 | 2-Butanol | 43,000.00 | 0.0324 | 1.7704 × 10−5 |
| 10 | 1-Octen-3-ol | 1.00 | 4.2624 | 100.0000 |
| 11 | 1-Heptanol | 3.00 | 0.5823 | 4.5535 |
| 12 | 4-Heptanol, 2,6-dimethyl- | 1300.00 | 0.0020 | 3.6283 × 10−5 |
| 13 | Benzyl alcohol | 1.20 | 0.0678 | 1.3258 |
| 14 | 5-Hepten-2-ol,6-methyl- | 2000.00 | 0.0006 | 7.1909 × 10−6 |
| 15 | 1-Octen-3-one | 0.05 | 0.0627 | 29.4274 |
| 16 | Butanoic acid, ethyl ester | 0.10 | 0.0104 | 2.4337 |
| 17 | Butanoic acid, 2-methyl-, ethyl ester | 0.01 | 0.0024 | 5.7434 |
| 18 | Butanoic acid, 3-methyl-, ethyl ester | 0.01 | 0.0033 | 7.7816 |
| 19 | Hexanoic acid, ethyl ester | 0.30 | 0.0375 | 2.9309 |
| 20 | Acetic acid, 2-phenylethyl ester | 3000.00 | 0.0031 | 2.4501 × 10−5 |
| 21 | Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester | 2000.00 | 0.0064 | 7.5155 × 10−5 |
| 22 | Octanoic acid, methyl ester | 200.00 | 0.0004 | 4.5969 × 10−5 |
| 23 | Tetradecanoic acid | 10,000.00 | 0.0008 | 1.9034 × 10−6 |
| 24 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 10,000.00 | 0.0163 | 3.8225 × 10−5 |
| 25 | Pyrazine | 175,000.00 | 0.0449 | 6.0243 × 10−6 |
| 26 | Pyrrole | 20,000.00 | 0.0133 | 1.5546 × 10−5 |
| 27 | Ethanone, 1-(1H-pyrrol-2-yl)- | 170,000.00 | 0.0046 | 6.3212 × 10−7 |
| 28 | Caffeine | 29,000.00 | 0.0003 | 2.4773 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, W.; Li, Z.; Wei, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Chai, Y.; Mao, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Formation Mechanism of Characteristic Flavor Substances in 3-Year-Old Diannan Small-Ear Pig Ham: Lipidomics and Flavoromics Study. Foods 2025, 14, 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173098
Tao W, Li Z, Wei G, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang W, Zhang C, Chai Y, Mao H, Li Y, et al. Formation Mechanism of Characteristic Flavor Substances in 3-Year-Old Diannan Small-Ear Pig Ham: Lipidomics and Flavoromics Study. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173098
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Wenli, Zhenzhu Li, Guangqiang Wei, Yue Wang, Yuzhu Wang, Wenbin Zhang, Chenghao Zhang, Yunmei Chai, Huaming Mao, Yufang Li, and et al. 2025. "Formation Mechanism of Characteristic Flavor Substances in 3-Year-Old Diannan Small-Ear Pig Ham: Lipidomics and Flavoromics Study" Foods 14, no. 17: 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173098
APA StyleTao, W., Li, Z., Wei, G., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, C., Chai, Y., Mao, H., Li, Y., & Huang, A. (2025). Formation Mechanism of Characteristic Flavor Substances in 3-Year-Old Diannan Small-Ear Pig Ham: Lipidomics and Flavoromics Study. Foods, 14(17), 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173098







