Elemental Analysis and Chemometric Assessment of Edible Part and Peel of Mango Fruits (Mangifera indica L.) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
- ultra-pure nitric acid, HNO3 conc. (w = 60%) (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany);
- hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 conc. (w = 30%) (Gram-mol, Zagreb, Croatia);
- standard multi-element solution VI of spectral purity for ICP (γ = 1000 mg/L) (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany);
- high-purity deionised water from inhouse facility, specific resistance ≥ 18 MΩ cm−1;
- Rh, internal standard solution (γ = 1 μg/L) (Merck; Darmstadt; Germany);
- NIST SRM 1547—peach leaves;
- NIST SRM 1573a—tomato leaves.
2.2. Instruments
2.2.1. Microwave Digestion System
2.2.2. ICP-MS
2.3. Sample Description and Pretreatment
2.4. Microwave-Assisted Digestion Procedure
2.5. Data Evaluation and Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
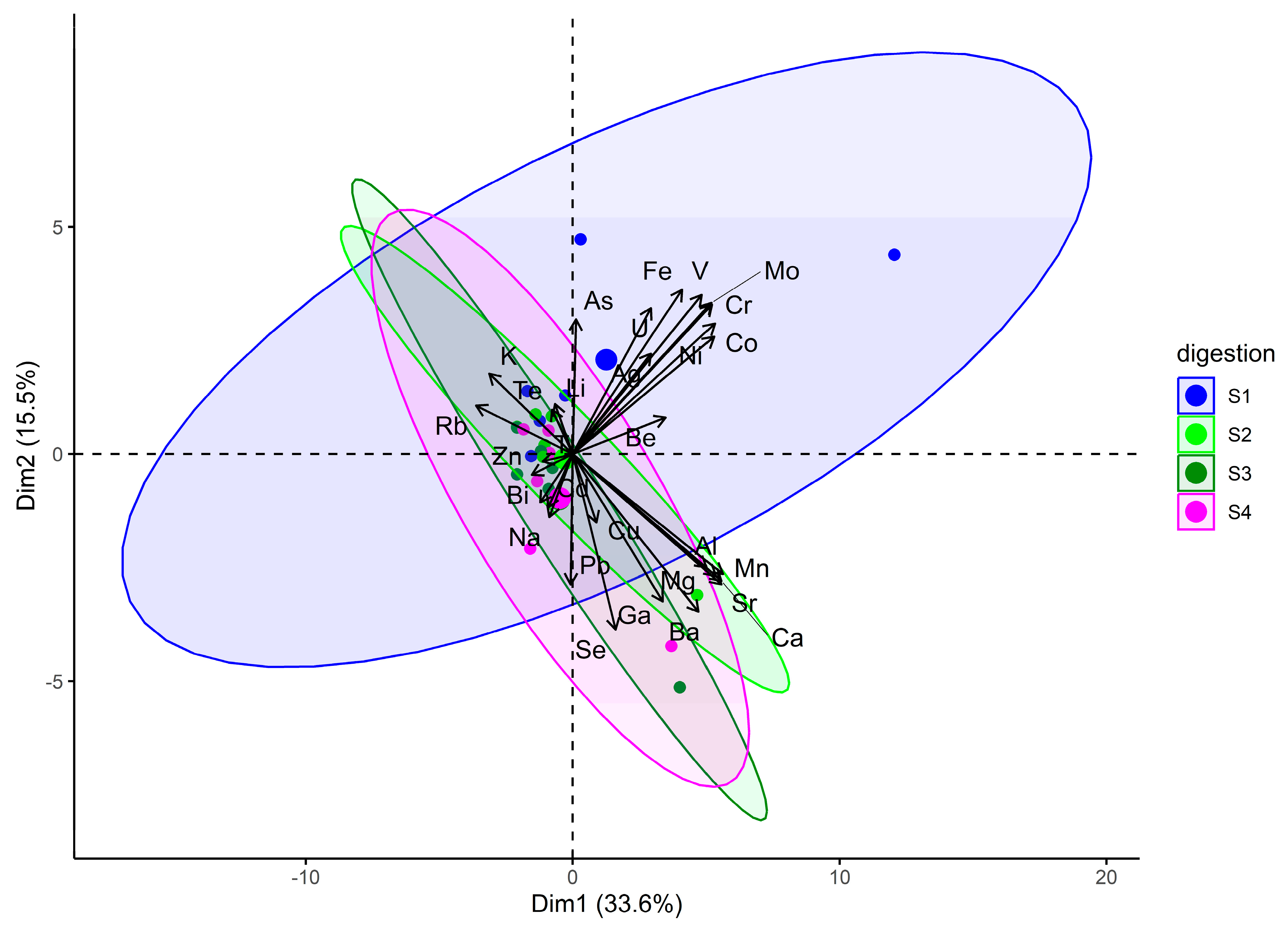
3.1. Optimisation of the Digestion Procedure
3.2. Applicability of the Analytical Method
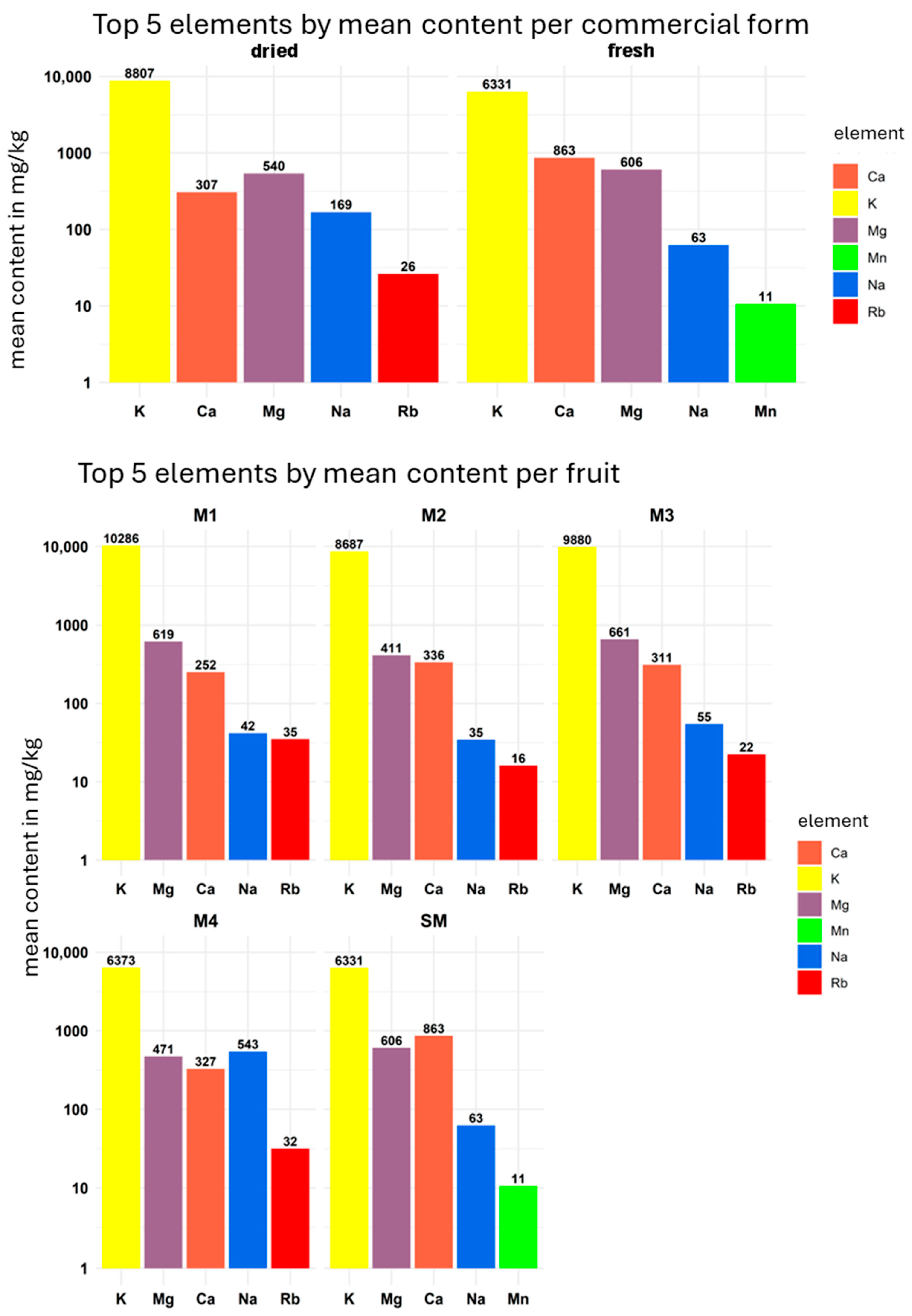
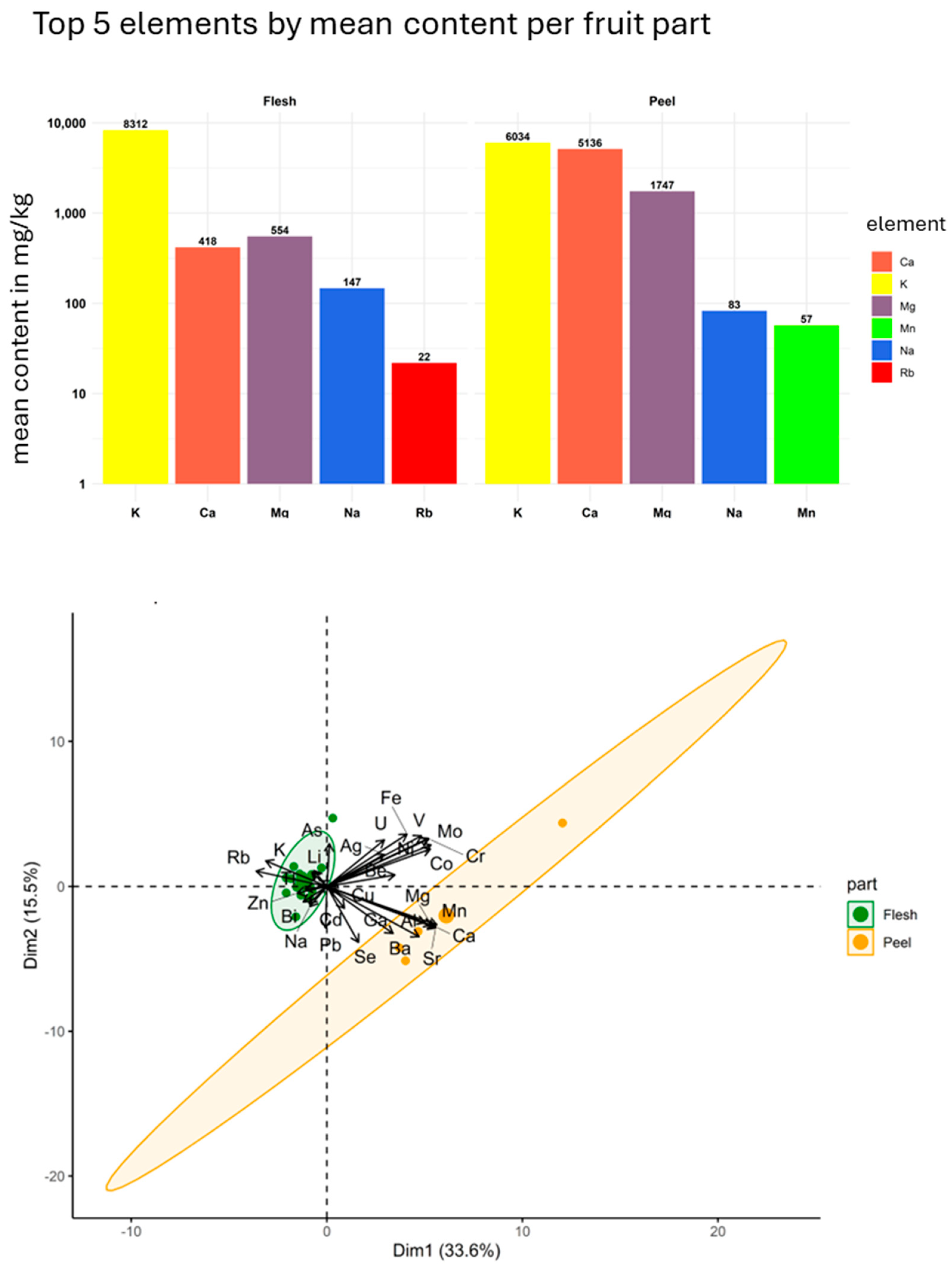
3.3. Elemental Composition of Mango
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, S.K.; Alasalvar, C.; Shahidi, F. Review of dried fruits: Phytochemicals, antioxidant efficacies, and health benefit. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.K.; Sidhu, J.; Barta, J.; Wu, J.; Cano, M.P. Handbook of Fruits and Fruit Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Nabrzyski, M. Functional Role of Some Minerals in Foods. In Mineral Components in Foods; Szefer, P., Nriagu, J.O., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clase, C.M.; Carrero, J.J.; Ellison, D.H.; Grams, M.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Jardine, M.J.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kline, G.A.; Lindner, G.; Obrador, G.T.; et al. Potassium homeostasis and management of dyskalemia in kidney diseases: Conclusions from a KDIGO Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omolola, A.O.; Jideani, A.I.; Kapila, P.F. Quality properties of fruits as affected by drying operation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Zhao, Y. Photooxidation of phytochemicals in food and control: A review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1398, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzaman, A.N.; Abdullah, A.H.; Chua, S.T.; Arshad, K.; Megat Mokhtar, M.A.; Shafie, F.A. Determination of Sulfites in Dried Fruits and Its Health Risk Assessment. MAEH J. Environ. Health 2020, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Encyclopaedia Britannica. Mango. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/plant/mango-plant-and-fruit (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Mirza, B.; Croley, C.R.; Ahmad, M.; Pumarol, J.; Das, N.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Mango (Mangifera indica L.): A magnificent plant with cancer preventive and anticancer therapeutic potential. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2125–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warschefsky, E.J.; von Wettberg, E.J.B. Population genomic analysis of mango (Mangifera indica) suggests a complex history of domestication. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 2023–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Redondo, J.; Bertoldi, D.; Tonon, A.; Ziller, L.; Camin, F.; Moreno-Rojas, J. Tracing the geographical origin of Spanish mango (Mangifera indica L.) using stable isotope ratios and multi-element profiles. Food Control. 2021, 125, 107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, I. History of Mango—‘King of Fruits’. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2017, 6, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Ihli, N. Atomic absorption and atomic emission spectrometry for the determination of the trace element content of selected fruits consumed in the United States. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1996, 9, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, R.; Mehta, B. Trace metal content in market samples of mango jam. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mysore 2003, 40, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lebaka, V.; Wee, Y.; Ye, W.; Korivi, M. Nutritional composition and bioactive compounds in three different parts of mango fruit. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierson, J.; Monteith, G.; Roberts-Thomson, S.; Dietzgen, R.; Gidley, M.; Shaw, P. Phytochemical extraction, characterisation and comparative distribution across four mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit varieties. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, D.G. A Basic Guide to Drying Fruits and Vegetables; University of Guelph, Department of Food Science: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lewicki, P.P. Design of hot air drying for better foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablani, S.S. Drying of fruits and vegetables: Retention of nutritional/functional quality. Dry. Technol. 2006, 24, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Singh, J.; Chauhan, H.; Anjum, P.G.A.; Kour, H. Different drying methods: Their applications and recent advances. Int. J. Food Nutr. Saf. 2013, 4, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Radojčin, M.; Pavkov, I.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P.; Wiktor, A.; Stamenković, Z.; Kešelj, K.; Gere, A. Effect of selected drying methods and emerging drying intensification technologies on the quality of dried fruit: A review. Processes 2021, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajila, C.; Bhat, S.; Rao, U. Valuable components of raw and ripe peels from two Indian mango varieties. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaurah, P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, N.; Panghal, A.; Attkan, A.; Singh, V.; Garg, M. Physicochemical characteristics, bioactive compounds and industrial applications of mango kernel and its products: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2421–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiner, M.; Fiedler, H.; Juranović Cindrić, I.; Nemet, I.; Toma, D.; Habinovec, I. Preliminary study of pepper types based on multielement content combined with chemometrics. Foods 2023, 12, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiner, M.; Juranović Cindrić, I.; Nemet, I.; Šola, I.; Fiedler, H. Chemometric evaluation of inorganic and organic parameters found in Rosaceae plants proposed as food supplements. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, B.G.; Casagrande, T.A.; Cardoso, L.A. Food additives and their health effects: A review on preservative sodium benzoate. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvard, T.H.; Chan School of Public Health. The Nutrition Source—Vitamins and Minerals. Available online: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/vitamins (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Monro, J.A.; Holloway, W.D.; Lee, J. Elemental analysis of fruit and vegetables from Tonga. J. Food Sci. 1986, 51, 522–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ullah, R.; Ali, H.; Waheed, A.; Abbas, Q. Elemental analysis of mango ripened by different postharvest treatments using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Optik 2021, 246, 167770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, P.; Singh, D. Deficiency symptoms in mango due to the absence of trace elements. Indian J. Hortic. 1959, 16, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Xing-yang, L. The determination of selenium in mango in Panzhihua. J. Southwest China Norm. Univ. 2007, 6, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, N.; Devi, S.; Nand, K. Influence of trace elements on biogas production from mango processing waste in 1.5 m3 KVIC digesters. Biotechnol. Lett. 1991, 13, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obediah, G.; Elechi-Amadi, K. Determination of trace mineral elements in some tropical fruits. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 1228–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Schnug, E.; Haneklaus, N. Uranium in phosphate fertilizers–review and outlook. In Uranium—Past and Future Challenges, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Uranium Mining and Hydrogeology, Freiberg, Germany, 21–25 September 2014; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Duhan, S.S.; Khyalia, P.; Solanki, P.; Laura, J.S. Uranium sources, uptake, translocation in soil-plant system and its toxicity in plants and human: A critical review. Orient. J. Chem. 2023, 39, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardisson, A.; Revert, C.; González Weller, D.; Gutiérrez, Á.; Paz, S.; Rubio, C. Aluminium exposure through the diet. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleimi, N.; Kouki, R.; Hadj Ammar, M.; Ferreira, R.; Pérez-Clemente, R. Barium effect on germination, plant growth, and antioxidant enzymes in Cucumis sativus L. plants. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2086–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Širić, I.; Eid, E.M.; El-Morsy, M.H.E.; Osman, H.E.M.; Adelodun, B.; Abou Fayssal, S.; Mioč, B.; Goala, M.; Singh, J.; Bachheti, A.; et al. Health Risk Assessment of Hazardous Heavy Metals in Two Varieties of Mango Fruit (Mangifera indica L. var. Dasheri and Langra). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Hussain, S.; Arshad, P.; Hassan, A. Irrigation Water of Different Sources Affects Fruit Quality Attributes and Heavy Metals Contents of Un-Grafted and Commercial Mango Cultivars. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 281, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Ren, L.; Gong, M.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z. Transfer of Cadmium and Lead from Soil to Mangoes in an Uncontaminated Area, Hainan Island, China. Geoderma 2010, 155, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Condition |
|---|---|
| RF power | 1500 W |
| Carrier gas flow (Ar) | 0.90 L/min |
| Additional gas flow (Ar) | 0.20 L/min |
| Nebulizer | MicroMist |
| Nebulizer pump | 0.10 rps |
| Spray chamber | Scott double pass |
| Integration time | 0.10 s |
| Repeated samples | Two |
| Calibration | External |
| Calibration solution | Multi-element VI (Merck) |
| Isotopes | 7Li, 9Be, 23Na, 24Mg, 27Al, 39K, 43Ca, 51V, 53Cr, 55Mn, 56Fe, 59Co, 60Ni, 63Cu, 66Zn, 69Ga, 75As, 82Se, 85Rb, 88Sr, 95Mo, 107Ag, 111Cd, 125Te, 137Ba, 205Tl, 208Pb, 209Bi, 238U |
| Internal standard (10 µg/L) | 103Rh |
| Collision chamber | Usage depending on analyte |
| Sample | Designation | Country | Water Content in % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dried Mango 1 | M1 | Burkina Faso | 17.31% |
| Dried Mango 2 | M2 | Burkina Faso | 15.15% |
| Dried Mango 3 | M3 | Burkina Faso | 14.75% |
| Dried Mango 4 | M4 | Ghana | 15.00% |
| Fresh Mango | SM | Brazil | 85.10% |
| Fresh Mango Peel | P | Brazil | 77.49% |
| Digestion Series Name | Designation | Digestion Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| Series 1 | S1 | 6 mL conc. nitric acid |
| Series 2 | S2 | 6 mL diluted nitric acid (7 mol/L) |
| Series 3 | S3 | 6 mL conc. nitric acid + 3 mL H2O2 (30%) |
| Series 4 | S4 | 6 mL diluted nitric acid (7 mol/L) + 3 mL H2O2 (30%) |
| Element | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | 0.053 | 0.006 | 0.013 | <LOD |
| Be | <LOD | <LOD | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Na | 53.4 | 37.0 | 76.8 | <LOD |
| Mg | 588 | 628 | 639 | 620 |
| Al | <LOD | 2.85 | 4.96 | <LOD |
| K | 9711 | 10,387 | 10,699 | 10,347 |
| Ca | 227 | 310 | 251 | 222 |
| V | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Cr | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Mn | 9.13 | 9.60 | 8.01 | 7.98 |
| Fe | 3.08 | 2.29 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Co | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ni | <LOD | 0.113 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Cu | 3.74 | 4.91 | 4.73 | 4.94 |
| Zn | 5.72 | 10.9 | 6.92 | 2.68 |
| Ga | 0.019 | 0.025 | 0.027 | 0.045 |
| As | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Se | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.081 |
| Rb | 33.0 | 35.5 | 36.6 | 35.1 |
| Sr | 0.718 | 0.804 | 0.828 | 0.764 |
| Mo | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ag | 2.03 | 0.257 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Cd | <LOD | <LOD | 0.0007 | <LOD |
| Te | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ba | 0.741 | 1.085 | 1.082 | 0.740 |
| Tl | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.0003 |
| Pb | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Bi | <LOD | <LOD | 0.454 | 1.44 |
| U | <LOD | <LOD | 0.0006 | 0.003 |
| Element | Results | Certified Value SRM 1547 | Recovery in % | Results | Certified Value SRM 1573a | Recovery in % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | 0.084 | - | / | 0.366 | - | / |
| Be | 0.016 | - | / | 0.017 | - | / |
| Na | 25.3 | 23.8 ± 1.6 | 106% | 150.4 | 136.1 ± 3.7 | 110% |
| Mg | 4168 | 4320 ± 150 | 96% | 11,408 | 12,000 | 95% |
| Al | 258.2 | 248.9 ± 6.5 | 104% | 641 | 598.4 ± 7.1 | 107% |
| K | 23,241 | 24,330 ± 380 | 95% | 23,100 | 26,760 ± 480 | 86% |
| Ca | 16,100 | 15,590 ± 160 | 103% | 51,014 | 50,450 ± 550 | 101% |
| V | 0.298 | 0.367 ± 0.038 | 81% | 0.704 | 0.835 ± 0.034 | 84% |
| Cr | 1.1 | 1 | 110% | 2.12 | 1.988 ± 0.034 | 107% |
| Mn | 95.3 | 97.8 ± 1.8 | 97% | 240 | 246.3 ± 7.1 | 97% |
| Fe | 214 | 219.8 ± 6.8 | 97% | 378 | 367.5 ± 4.3 | 103% |
| Co | 0.1 | 0.07 | 143% | 0.593 | 0.5773 ± 0.0071 | 103% |
| Ni | 0.867 | 0.689 ± 0.095 | 126% | 1.20 | 1.582 ± 0.041 | 76% |
| Cu | 3.54 | 3.75 ± 0.37 | 94% | 4.62 | 4.70 ± 0.14 | 98% |
| Zn | 16.9 | 17.97 ± 0.53 | 94% | 31.8 | 30.94 ± 0.55 | 103% |
| Ga | 3.32 | - | / | 4.40 | - | / |
| As | 0.073 | 0.062 ± 0.014 | 118% | 0.129 | 0.1126 ± 0.0024 | 114% |
| Se | 0.201 | 0.120 ± 0.017 | 167% | 0.084 | 0.0543 ± 0.0020 | 155% |
| Rb | 18.7 | 19.65 ± 0.089 | 95% | 15.4 | 14.83 ± 0.31 | 104% |
| Sr | 48.4 | 53.0 ± 5.0 | 91% | 93 | 85 | 110% |
| Mo | 0.0681 | 0.0603 ±0.0068 | 113% | 0.42 | 0.46 | 91% |
| Ag | 1.16 | - | / | 0.020 | 0.017 | 118% |
| Cd | 0.0250 | 0.0261 ± 0.0022 | 96% | 1.49 | 1.517 ± 0.027 | 98% |
| Te | 1.5 × 10−3 | - | / | 0.001 | - | / |
| Ba | 111 | 123.7 ± 5.5 | 90% | 26.8 | - | / |
| Tl | 0.061 | - | / | 0.063 | - | / |
| Pb | 1.01 | 0.869 ± 0.018 | 116% | 1.12 | - | / |
| Bi | 0.067 | - | / | 0.012 | - | / |
| U | - | 0.018 | 0.035 | 51% |
| Element | Sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | SM | P | |
| Na | 76.7 | 48.1 | 81.8 | 551 | 70.2 | 40.9 |
| K | 10,699 | 8781 | 10,484 | 6600 | 6722 | 6194 |
| Ca | 251 | 354 | 328 | 360 | 921 | 5245 |
| Mg | 639 | 418 | 682 | 486 | 646 | 1771 |
| Cr | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Mn | 8.01 | 11.0 | 4.44 | 9.33 | 10.3 | 57.7 |
| Fe | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Cu | 4.73 | 2.52 | 4.19 | 3.76 | 4.16 | 3.88 |
| Zn | 6.92 | 1.85 | 9.51 | 7.15 | 2.84 | 3.65 |
| Se | <LOD | <LOD | 0.020 | 0.020 | <LOD | 0.256 |
| Mo | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ni | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| V | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Li | 0.013 | <LOD | 0.050 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Co | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ga | 0.027 | 0.083 | 0.045 | 0.121 | 0.047 | 0.196 |
| Rb | 36.6 | 16.3 | 23.3 | 33.0 | 4.41 | 4.20 |
| Sr | 0.828 | 2.25 | 1.25 | 2.39 | 4.70 | 22.6 |
| Bi | 0.454 | 0.062 | 1.22 | <LOD | 0.576 | 0.571 |
| Te | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Al | 4.96 | 8.28 | 7.49 | 6.19 | 6.28 | 61.8 |
| Tl | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Be | 0.001 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.006 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ag | <LOD | 0.077 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ba | 1.08 | 3.31 | 1.64 | 5.17 | 2.02 | 7.55 |
| As | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Cd | 0.0008 | <LOD | 0.042 | 0.0017 | 0.0036 | 0.0059 |
| Pb | <LOD | <LOD | 0.058 | <LOD | 0.0039 | 0.056 |
| U | 0.001 | <LOD | 0.002 | <LOD | 0.001 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeiner, M.; Mihalić, E.; Juranović Cindrić, I.; Nemet, I.; Fiedler, H. Elemental Analysis and Chemometric Assessment of Edible Part and Peel of Mango Fruits (Mangifera indica L.). Foods 2025, 14, 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173096
Zeiner M, Mihalić E, Juranović Cindrić I, Nemet I, Fiedler H. Elemental Analysis and Chemometric Assessment of Edible Part and Peel of Mango Fruits (Mangifera indica L.). Foods. 2025; 14(17):3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173096
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeiner, Michaela, Ema Mihalić, Iva Juranović Cindrić, Ivan Nemet, and Heidelore Fiedler. 2025. "Elemental Analysis and Chemometric Assessment of Edible Part and Peel of Mango Fruits (Mangifera indica L.)" Foods 14, no. 17: 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173096
APA StyleZeiner, M., Mihalić, E., Juranović Cindrić, I., Nemet, I., & Fiedler, H. (2025). Elemental Analysis and Chemometric Assessment of Edible Part and Peel of Mango Fruits (Mangifera indica L.). Foods, 14(17), 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173096





