Comparative Electrophoretic Analysis Between the Protein Content in Human and Donkey Milk Samples—A Study Covering the Long-Term Lactation Period
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
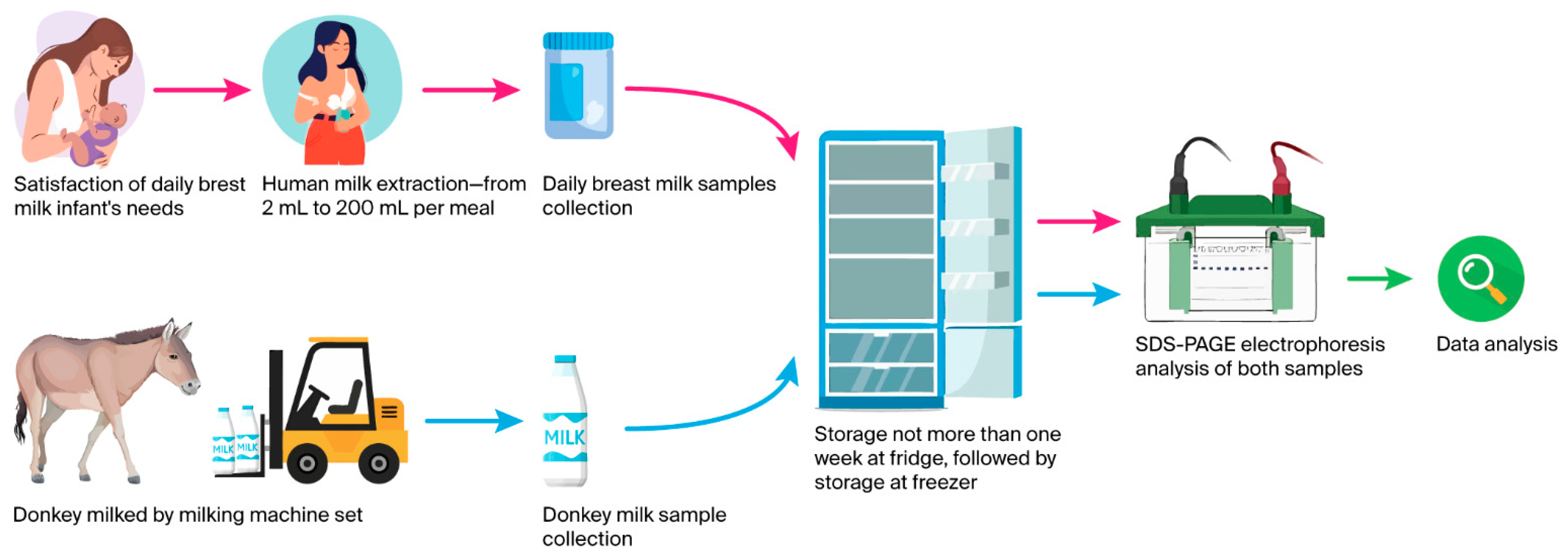
2.1. Human Milk Sample Collection
2.2. Donkey Milk Sample Collection
2.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of Protein Fractions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
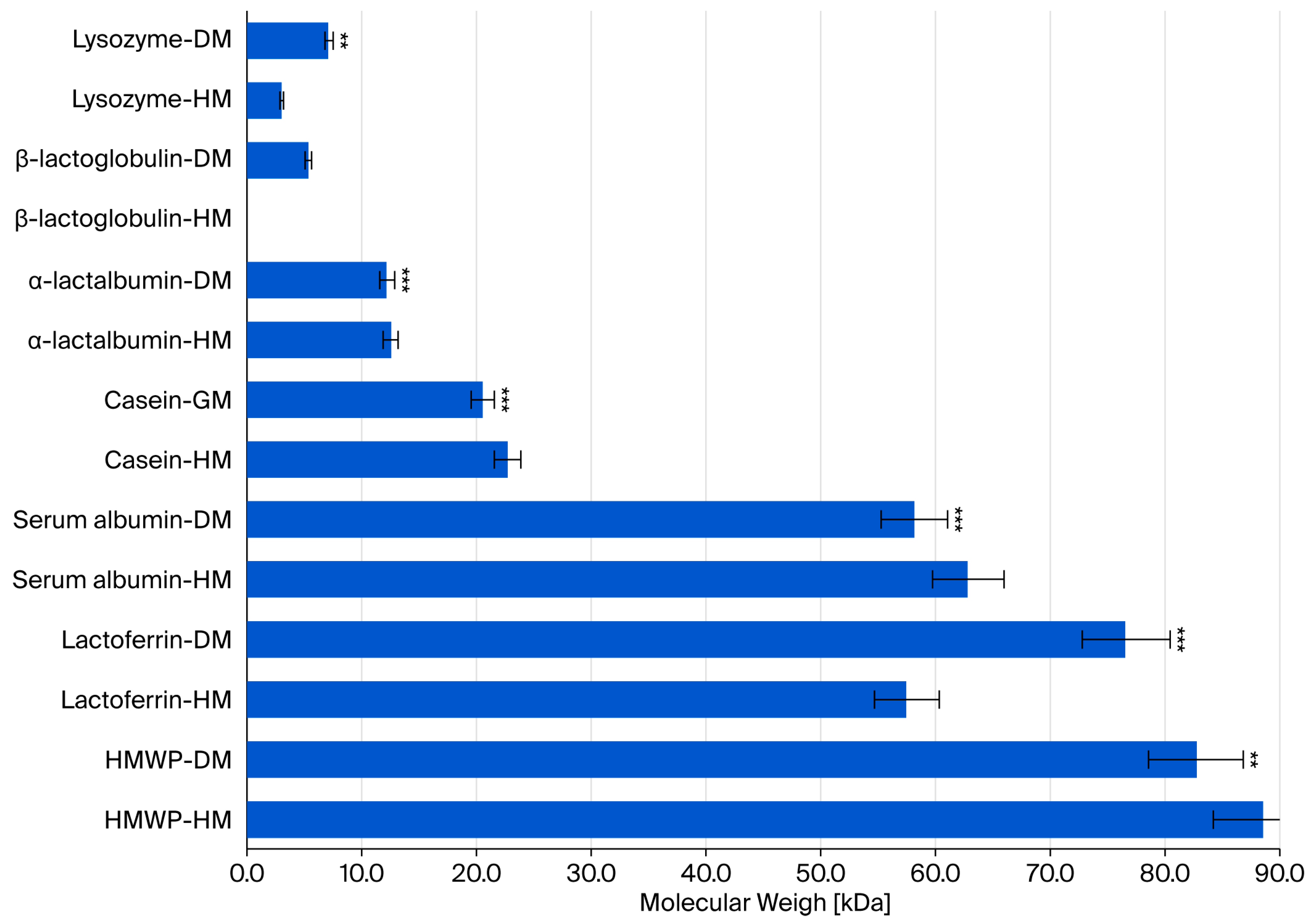
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lönnerdal, B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1537S–1543S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidelman, A.I.; Schanler, R.J.; Johnston, M.; Landers, S.; Noble, L.; Szucs, K.; Viehmann, L. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Paediatrics 2012, 129, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.S.; Kakuma, R. Optimal duration of exclusive breastfeeding. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD003517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.G.; Martin, R.M.; Whincup, P.H.; Smith, G.D.; Cook, D.G. Effect of infant feeding on the risk of obesity across the life course: A quantitative review of published evidence. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.; França, G.V.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.G.; Martin, R.M.; Whincup, P.H.; Smith, G.D.; Cook, D.G. Does breastfeeding influence risk of type 2 diabetes in later life? A quantitative analysis of published evidence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, K.; Gao, M.; Allen, G.; Lee, A.C.C. Breastfeeding in a global context: Epidemiology, impact, and future directions. Clin. Ther. 2022, 44, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Components of human breast milk: From macronutrient to microbiome and microRNA. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarelli, C.; Giannetti, A.; Buono, E.V.; Cunico, D.; Carbone, R.; Tonello, F.; Ricci, G. Cow’s milk allergy in breastfed infants: What we need to know about mechanisms, management and maternal role. Nutrients 2025, 7, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukou, Z.; Papadopoulou, E.; Panteris, E.; Papadopoulou, S.; Skordou, A.; Karamaliki, M.; Diamanti, E. The Effect of breastfeeding on food allergies in newborns and infants. Children 2023, 10, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition: Nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzikowska-Jura, A.; Czerwonogrodzka-Senczyna, A.; Olędzka, G.; Szostak-Węgierek, D.; Weker, H.; Wesołowska, A. Maternal nutrition and body composition during breastfeeding: Association with human milk composition. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimmino, F.; Catapano, A.; Villano, I.; Di Maio, G.; Petrella, L.; Traina, G.; Pizzella, A.; Tudisco, R.; Cavaliere, G. Invited review: Human, cow, and donkey milk comparison: Focus on metabolic effects. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 3072–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdak, R.; Sakoui, S.; Pop, O.L.; Muresan, C.I.; Vodnar, D.C.; Addoum, B.; Vulturar, R.; Chis, A.; Suharoschi, R.; Soukri, A.; et al. Insights on health and food applications of Equus asinus (Donkey) milk bioactive proteins and peptides-an overview. Foods 2020, 9, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, N. Bioactive components of donkey milk. Food Sci. Appl. Biotechnol. 2022, 5, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, L.; Martini, M.; Brajon, G.; Barni, S.; Salari, F.; Altomonte, I.; Ragona, G.; Mori, F.; Pucci, N.; Muscas, G.; et al. Donkey’s milk in the management of children with cow’s milk protein allergy: Nutritional and hygienic aspects. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2019, 45, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keitshweditse, B.; Tsvakirai, C.Z.; Mabuza, M.L.; Tshehla, M. Towards the expansion of the functional dairy market: Determining donkey milk value propositions and identifying possible consumers. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, M.; Criscione, A.; Franceschi, P.; Bordonaro, S.; Formaggioni, P.; Marletta, D.; Summer, A. New insights into chemical and mineral composition of donkey milk throughout nine months of lactation. Animals 2019, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Živkov Baloš, M.; Ljubojević Pelić, D.; Jakšić, S.; Lazić, S. Donkey milk: An overview of its chemical composition and main nutritional properties or human health benefit properties. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2023, 121, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massouras, T.; Triantaphyllopoulos, K.A.; Theodossiou, I. Chemical composition, protein fraction and fatty acid profile of donkey milk during lactation. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 75, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosuè, C.; Alabiso, M.; Russo, G.; Alicata, M.L.; Torrisi, C. Jennet milk production during the lactation in a Sicilian farming system. Animal 2008, 2, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Polidori, P.; Mariani, P.; Cammertoni, N.; Fantuz, F.; Vita, A. Donkey’s milk protein fractions characterization. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, L.; Calabrese, M.G.; Ferranti, P.; Mauriello, R.; Garro, G.; De Simone, C.; Quarto, M.; Addeo, F.; Cosenza, G.; Ramunno, L. Proteomic characterization of donkey milk “caseome”. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4834–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polidori, P.; Vincenzetti, S. Use of donkey milk in children with cow’s milk protein allergy. Foods 2013, 2, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Sandström, B.; Lönnerdal, B. The effect of casein phosphopeptides on zinc and calcium absorption from high phytate infant diets assessed in rat pups and Caco-2 cells. Pediatr. Res. 1996, 40, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz-Ahrens, K.E.; Schrezenmeir, J. Effects of bioactive substances in milk on mineral and trace element metabolism with special reference to casein phosphopeptides. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, S147–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudehope, D.I. Human milk and the nutritional needs of preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, S17–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Loly, M.M. Colostrum ingredients, its nutritional and health benefits—An overview. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2022, 44, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.; Barton, L.D.; Sanders, J.T.; Zhang, Q. Exploration of bovine milk proteome in colostral and mature whey using an ion-exchange approach. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. The nutritional ingredients and antioxidant activity of donkey milk and donkey milk powder. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Mauriello, R.; Garro, G.; Auzino, B.; Iannaccone, M.; Costanzo, A.; Chianese, L.; Pauciullo, A. Casein composition and differential translational efficiency of casein transcripts in donkey’s milk. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Z.; Chen, W.; Li, M.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Ullah, Q.; Wei, L.; Wang, T.; Khan, A.; et al. Is there sufficient evidence to support the health benefits of including donkey milk in the diet? Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1404998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignone, L.E.; Wu, T.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Whey protein: The “whey” forward for treatment of type 2 diabetes? World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Effects of donkey milk on oxidative stress and inflammatory response. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, V.; Ferranti, P.; Chianese, L.; Salimei, E.; Addeo, F.; Picariello, G. Antibacterial potential of donkey’s milk disclosed by untargeted proteomics. J. Proteom. 2021, 231, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnykowska-Łukacka, M.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M.; Broers, B.; Królak-Olejnik, B. Lactoferrin in human milk of prolonged lactation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Erdmann, P.; Thakkar, S.K.; Sauser, J.; Destaillats, F. Longitudinal evolution of true protein, amino acids and bioactive proteins in breast milk: A developmental perspective. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ren, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z. Lactoferrin: A glycoprotein that plays an active role in human health. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1018336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, V.A.D.O.; Assis, A.M.O.; Júnior, R.H.D.C. Protective effect of human lactoferrin in the gastrointestinal tract. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2013, 31, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, T.J.; Cleary, T.G. Effect of lactoferrin on enteric pathogens. Biochimie 2009, 91, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueiros-Cendón, T.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Iglesias-Figueroa, B.F.; García-Montoya, I.A.; Salazar-Martínez, J.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.; Xie, A.; Jiang, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Li, M.; Yue, X. A review of the biological activities of lactoferrin: Mechanisms and potential applications. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8182–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago-Serrano, M.E.; Campos-Rodríguez, R.; Carrero, J.C.; de la Garza, M. Lactoferrin: Balancing ups and downs of inflammation due to microbial infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esener, O.; Balkan, B.M.; Armutak, E.I.; Uvez, A.; Yildiz, G.; Hafizoglu, M.; Yilmazer, N.; Gurel-Gurevin, E. Donkey milk kefir induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation of Ehrlich ascites carcinoma by decreasing iNOS in mice. Biotech. Histochem. 2018, 93, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likaa, H.M.; Neihaya, H.Z.; Istabreq, M.; Luma, A. Immunostimulatory, antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of purified donkey colostrums lactoferrin on multidrug resistance Serratia liquefaciens producing Intl gene. J. Fac. Med. Baghdad 2017, 59, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Mudjihartini, N.; Shahab, M.A. Comparison of serum albumin levels in the breast milk of breastfeeding infants aged 1–3 months and 4–6 months. Ind. J. Med. Chem. Bio 2023, 2023, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Forsum, E.; Hambraeus, L. A longitudinal study of the protein, nitrogen, and lactose contents of human milk from Swedish well nourished mothers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1976, 29, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vusse, G.J. Albumin as fatty acid transporter. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 24, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, J.M. Future challenges of whey proteins. Int. J. Dairy. Scien 2015, 10, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkerroum, N. Antimicrobial activity of lysozyme with special relevance to milk. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 4856–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, W.L.; Verraes, C.; Cardoen, S.; De Block, J.; Huyghebaert, A.; Raes, K.; Dewettinck, K.; Herman, L. Consumption of raw or heated milk from different species: An evaluation of the nutritional and potential health benefits. Food Control 2014, 42, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, C.A. The natural antimicrobial enzyme lysozyme is upregulated in gastrointestinal inflammatory conditions. Pathogens 2014, 3, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvon, S.; Olier, M.; Leveque, M.; Jard, G.; Tormo, H.; Haimoud-Lekhal, D.A.; Peter, M.; Eutamène, H. Donkey milk consumption exerts anti-inflammatory properties by normalizing antimicrobial peptides levels in Paneth’s cells in a model of ileitis in mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraboschi, P.; Ciceri, S.; Grisenti, P. Applications of lysozyme, an innate immune defense factor, as an alternative antibiotic. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
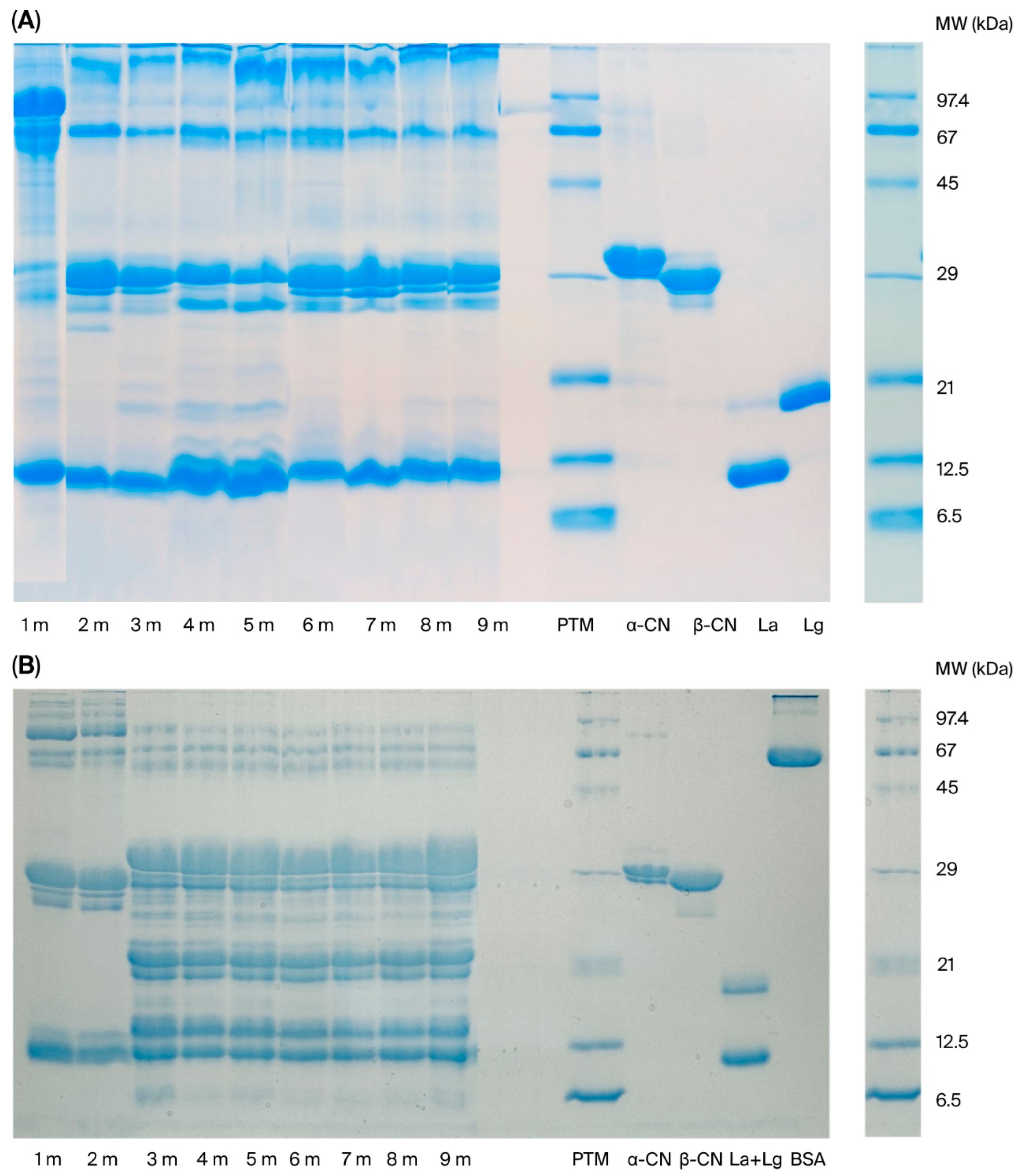
| Molecular Weight of Proteins from Human Breast Milk Samples | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Month | 2 Months | 3 Months | 4 Months | 5 Months | 6 Months | 7 Months | 8 Months | 9 Months |
| 123.5 | 123.3 | 95.0 | 125.9 | 92.2 | 126.2 | 130.6 | 125.8 | 89.7 |
| 83.6 | 84.1 | 80.5 | 83.1 | 68.3 | 114.9 | 82.5 | 91.8 | 69.5 |
| 69.4 | 72.1 | 68.4 | 68.3 | 27.4 | 85.7 | 65.9 | 81.9 | 27.7 |
| 27.4 | 65.1 | 27.7 | 26.8 | 26.8 | 69.5 | 27.1 | 66.3 | 26.1 |
| 23.9 | 54.6 | 24.4 | 25.4 | 24.5 | 26.6 | 26.7 | 50.1 | 24.5 |
| 18.2 | 49.2 | 16.1 | 23.7 | 17.1 | 23.5 | 23.3 | 26.5 | 16.2 |
| 16.0 | 28.9 | 14.6 | 16.5 | 13.7 | 21.4 | 17.0 | 24.2 | 13.7 |
| 14.3 | 26.7 | 13.5 | 13.6 | 16.4 | 15.1 | 16.3 | ||
| 13.4 | 24.7 | 13.4 | 13.3 | 13.7 | ||||
| 17.2 | ||||||||
| 16.1 | ||||||||
| 13.4 | ||||||||
| Molecular Weight of Proteins in Donkey Milk Samples | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Month | 2 Months | 3 Months | 4 Months | 5 Months | 6 Months | 7 Months | 8 Months | 9 Months |
| 113.9 | 117.5 | 91.0 | 87.5 | 85.2 | 83.3 | 85.7 | 87.7 | 89.7 |
| 99.2 | 104.8 | 79.8 | 79.3 | 71.4 | 71.5 | 71.5 | 72.7 | 74.8 |
| 82.0 | 82.9 | 63.0 | 63.3 | 64.5 | 64.0 | 65.5 | 66.0 | 64.2 |
| 67.6 | 69.0 | 28.0 | 27.3 | 27.3 | 27.0 | 26.8 | 28.0 | 28.5 |
| 61.2 | 64.7 | 25.6 | 25.3 | 24.6 | 25.0 | 24.3 | 25.2 | 25.2 |
| 24.5 | 24.9 | 22.9 | 24.1 | 23.4 | 23.7 | 23.8 | 24.0 | 23.9 |
| 23.1 | 23.0 | 22.1 | 22.8 | 22.1 | 22.2 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 20.4 |
| 21.7 | 21.4 | 20.8 | 20.4 | 20.1 | 20.6 | 20.0 | 20.4 | 19.6 |
| 13.9 | 13.9 | 18.1 | 19.6 | 19.1 | 16.6 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 18.1 |
| 13.7 | 13.5 | 16.7 | 18.2 | 17.7 | 15.9 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 16.8 |
| 16.0 | 16.8 | 16.5 | 14.0 | 13.9 | 14.0 | 16.1 | ||
| 14.9 | 16.1 | 15.8 | 13.4 | 13.4 | 13.4 | 15.0 | ||
| 14.0 | 14.0 | 13.9 | 13.9 | |||||
| 13.4 | 13.5 | 13.4 | 13.4 | |||||
| Lysozyme | Lactalbumin | Caseins | Serum Albumin | Lactoferrin | HMWP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson’s correlation coefficient | 0.129 | 0.160 | <0.001 | 0.144 | 0.144 | 0.014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgieva, A.S.; Naydenova, N.; Ivanova, D. Comparative Electrophoretic Analysis Between the Protein Content in Human and Donkey Milk Samples—A Study Covering the Long-Term Lactation Period. Foods 2025, 14, 3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173083
Georgieva AS, Naydenova N, Ivanova D. Comparative Electrophoretic Analysis Between the Protein Content in Human and Donkey Milk Samples—A Study Covering the Long-Term Lactation Period. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173083
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgieva, Ana Stoyanova, Nikolina Naydenova, and Donika Ivanova. 2025. "Comparative Electrophoretic Analysis Between the Protein Content in Human and Donkey Milk Samples—A Study Covering the Long-Term Lactation Period" Foods 14, no. 17: 3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173083
APA StyleGeorgieva, A. S., Naydenova, N., & Ivanova, D. (2025). Comparative Electrophoretic Analysis Between the Protein Content in Human and Donkey Milk Samples—A Study Covering the Long-Term Lactation Period. Foods, 14(17), 3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173083






