Biological Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) Reared in Two Different Culture Modes in Cold Regions of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Experimental Design and Culture Management
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Biological Characteristics
2.5. Proximate Composition
2.6. Fatty Acid Profile and Evaluation
2.7. Free Amino Acid and Taste Activity Value Analysis
2.8. Mineral Element Composition and Evaluation
- -
- recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for Mg, Fe, Cu, Zn, and Se;
- -
- adequate intake (AI) for Na, K, Ca, and Mn;
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biological Characteristics
3.2. Proximate Composition
3.3. Fatty Acid Profile and Evaluation
3.4. Free Amino Acid and Taste Activity Value Analysis
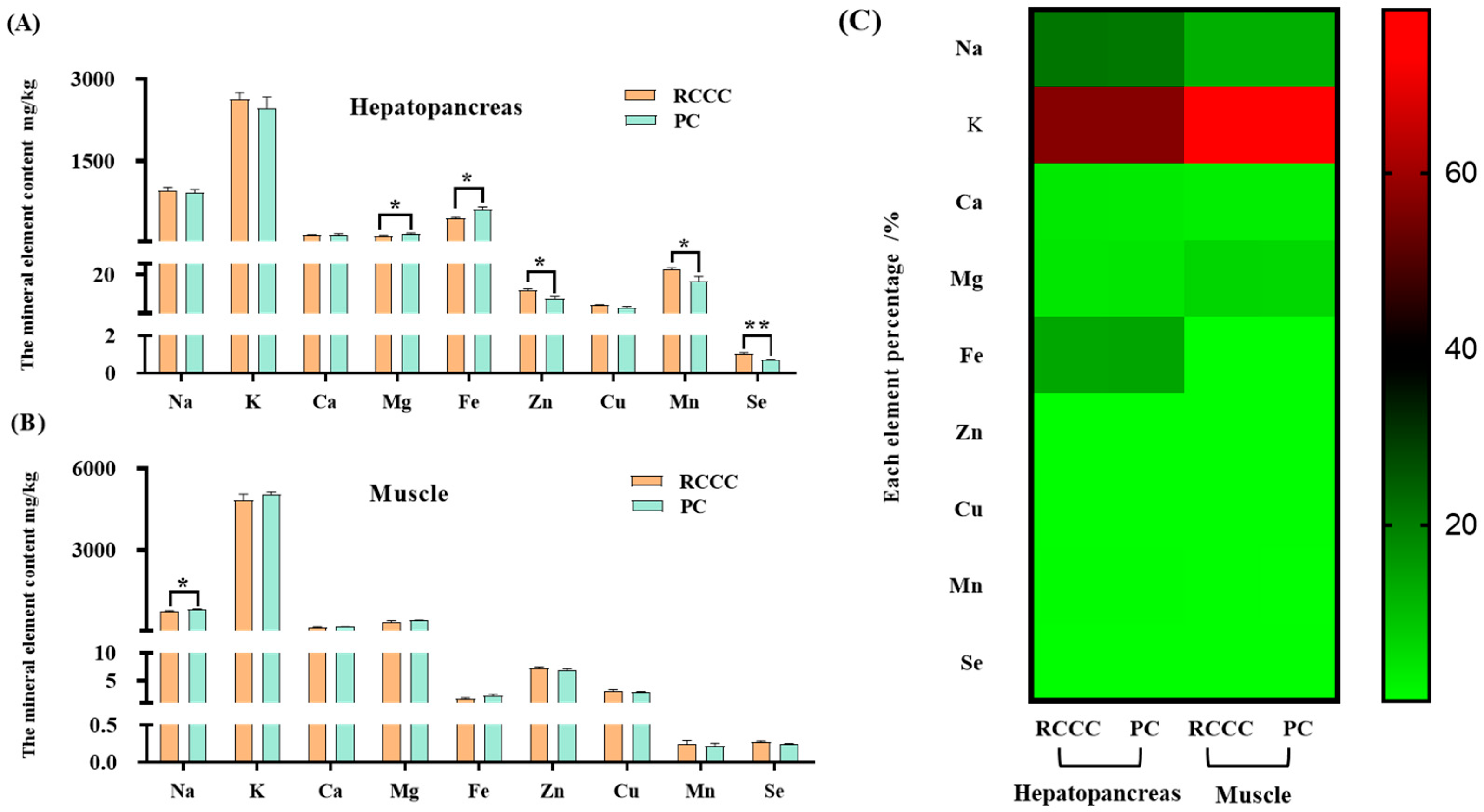
3.5. Mineral Element Composition and Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Biological Characteristics of RCCC and PC
4.2. Proximate Composition of RCCC and PC
4.3. Fatty Acid Profile of RCCC and PC
4.4. Free Amino Acid of RCCC and PC
4.5. Mineral Elements of RCCC and PC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yang, B.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.T.; Lu, J.F.; Lin, L. Comparison of the nutritional qualities of the pond, rice-field and wild crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) meat. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmietana, N.; Panicz, R.; Sobczak, M.; Śmietana, P.; Nędzarek, A. Spiny-Cheek Crayfish, Faxonius limosus (Rafinesque, 1817), as an alternative food source. Animals 2021, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrag, M.M.S.; El-Geddawy, M.A.M.A.; Ahmed, Z.S.A. More evidences for the nutritional quality and future exploitation of the invasive crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) from the River Nile, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2022, 48, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.Y.; Wu, Q.Q.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.L.; Ning, Y.Q.; Xie, S.Y.; Huang, W.M.; Bi, X.Y. Enrichment of trace elements in red swamp crayfish: Influences of region and production method, and human health risk assessment. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Q.; Chen, Z.J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Han, C.; Yue, L.; Kong, Q.L.; Zheng, Q.; Tian, W.H.; Xu, B.G. Multi-frequency power ultrasound (MFPU) pretreatment of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): Effect on the enzymatic hydrolysis process and subsequent Maillard reaction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 111, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishery Administration of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Areas; National Aquatic Technology Promotion Station; China Fisheries Society. 2024 China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Huang, J.; Li, C.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hou, S.Q.; Cheng, Y.X.; Li, J.Y. Evaluation of the nutritional quality of edible tissues (muscle and hepatopancreas) of cultivated Procambarus clarkii using biofloc technology. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Ye, J.W.; Zhang, Z.X.; An, Z.H.; Wang, T.; Dong, X.J. Comparison of the nutrient value, nonspecific immunity, and intestinal microflora of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in different culture modes. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 31, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Huang, J.N.; Wen, B.; Gao, J.Z.; Chen, Z.Z. Comprehensive assessment of three crayfish culture modes: From production performance to environmental sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.Y.; Jacquin, L.; Xiong, M.T.; Li, R.J.; Lek, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, T.L. Reproductive pattern and population dynamics of commercial red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) from China: Implications for sustainable aquaculture management. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Aquatic Technology Promotion Station; China Fisheries Society. The report on the development of China’s crayfish industry in 2024. China Fish. 2024, 7, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Luo, L.; Zhang, R.; Guo, K.; Bai, S.Y.; Qin, D.L.; Zhao, Z.G. Comparison of edible yield and quality of female Chinese mitten crab between two-year-old and three-year-old. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 112, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Su, J.J.; Zhang, S.Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, R.; Guo, K.; Zhao, Z.G. Nutritional quality and heavy metal safety risk assessment of Chinese mitten crab and crayfish cultivated in cold ponds. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2025, 40, 396–405. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.168-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Fatty Acids in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhang, L.; Yin, M.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, C.H.; Tao, N.P.; Wu, X.G.; Wang, X.C. Brackish water improves the taste quality in meat of adult male Eriocheir sinensis during the postharvest temporary rearing. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Wen, M.L.; Lv, J.X.; Bian, H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, D.Y.; Geng, Z.M.; Xu, W.M.; Zhang, F.X.; Yao, T.Y. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis for evaluating free amino acids in Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) from different co-culture modes. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.268-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Multi Elements in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Nędzarek, A.; Czerniejewski, P. The edible tissues of the major European population of the invasive Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) in the Elbe River, Germany, as a valuable and safe complement in essential elements to the human diet. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R. Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: History, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.W.; She, M.; Zhou, J.S.; Xiong, G.Q.; Bai, C.; Qiu, L.; Yang, J.S.; Liao, T. Nutritional analysis and evaluation of different parts of Procambarus clarkia with different size and gender. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2023, 14, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.R.; Ge, M.T.; Chen, H.F.; Jiang, S.T.; Lin, L.; Lu, J.F. Comparison between the nutritional qualities of wild-caught and rice-field male Chinese mitten crabs (Eriocheir sinensis). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kause, A.; Ritola, O.; Paananen, T.; Mäntysaari, E.; Eskelinen, U. Coupling body weight and its composition: A quantitative genetic analysis in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 2002, 211, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, G. Life-cycle and functional cytology of the hepatopancreatic cells of Astacus astacus (Crustacea, Decapoda). Zoomorphology 1994, 114, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.F.; Song, R.; Xiang, J.; Liu, L.; Tian, X.; Wang, D.W.; Liu, M.Q.; Xie, Z.G.; Wang, J.L. Analysis and evaluation of different farming modes and nutrient composition of wild crawfish (Procambarus clarkia) muscle. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, I.A.; Wanders, A.J.; Katan, M.B. Effect of animal and industrial trans-fatty acids on HDL and LDL cholesterol levels in humans—A quantitative review. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, M.D.; Gil, F.; Olmedo, P.; Gil, A. Nutritional importance of selected fresh fishes, shrimps and mollusks to meet compliance with nutritional guidelines of n-3 LC-PUFA intake in Spain. Nutrients 2021, 13, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.W.; Zhang, M.; Shrestha, S. Compositional characteristics and nutritional quality of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufarelli, V.; Valentini, L.; Dario, M.; Laudadio, V. Effect of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on hare reproductive performances. Animal 2010, 4, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Fats and Oils in Human Nutrition; Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Mapiye, C.; Chimonyo, M.; Dzama, K.; Hugo, A.; Strydom, P.; Muchenje, V. Fatty acid composition of beef from Nguni steers supplemented with Acacia karroo leaf-meal. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevrkla, P.; Kapelanski, W.; Václavková, E.; Hadas, Z.; Cebulska, A.; Horky, P. Meat quality and fatty acid profile of pork and backfat from an indigenous breed and a commercial hybrid of pigs. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2017, 17, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.E.; Vasconcelos, M.A.D.S.; Ribeiro, M.D.A.; Sarubbo, L.A.; Andrade, S.A.C.; Filho, A.B.D.M. Nutritional and lipid profiles in marine fish species from Brazil. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.S. Comparative composition of free amino acids in wild and cultured Procambarus clarkii. Food Sci. 2014, 35, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, B.; Hu, M.M.; Zhong, B.Z.; Yu, C.W.; Tu, Z.K. Exploration on the quality changes and flavour characteristics of freshwater crayfish (Procambarus clarkia) during steaming and boiling. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 190, 115582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Zeng, Q.X.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhang, L.Y. Chemical and sensory changes associated Yu-lu fermentation process—A traditional Chinese fish sauce. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Long, Y.N.; Li, B.; Zhao, L.L.; Luo, J.; Xu, L.; Luo, W.; Du, Z.J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S. Rice-shrimp culture: A better intestinal microbiota, immune enzymatic activities, and muscle relish of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in Sichuan Province. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9413–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.C.; Gupta, S.C. Sources and deficiency diseases of mineral nutrients in human health and nutrition: A review. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbance, O.; De Bels, D.; Honoré, P.M.; Bargalzan, D.; Tolwani, A.; Ismaili, K.; Biarent, D.; Redant, S. Potassium disorders in pediatric emergency department: Clinical spectrum and management. Arch. Pédiatr. 2020, 27, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandil, M.; Jaber, S.; Desai, D.; Cruz, S.N.; Lomotan, N.; Ahmad, U.; Cirone, M.; Burkins, J.; McDowell, M. MAGraine: Magnesium compared to conventional therapy for treatment of migraines. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 39, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, E.L.; Zheng, H.D.; Liu, X.G.; Lin, C.C.; Guan, L.; Zhou, Y.M. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution and risk assessment of dietary intake of pollutants in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) in main aquaculture areas of northeast China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2016, 15, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fatty Acids | Hepatopancreas | Muscle | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCCC | PC | RCCC | PC | |
| C14:0 | 0.99 ± 0.04 | 1.72 ± 0.06 ** | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.57 ± 0.03 |
| C15:0 | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 1.17 ± 0.03 ** | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.01 |
| C16:0 | 17.80 ± 0.20 | 21.03 ± 0.55 ** | 16.31 ± 0.25 ** | 14.78 ± 0.18 |
| C17:0 | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 1.04 ± 0.05 ** | 1.29 ± 0.04 | 1.38 ± 0.01 |
| C18:0 | 4.03 ± 0.07 | 4.62 ± 0.27 | 10.80 ± 0.06 ** | 10.50 ± 0.05 |
| C20:0 | 0.58 ± 0.03 | 0.58 ± 0.03 | 0.35 ± 0.02 * | 0.27 ± 0.01 |
| C21:0 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.01 ** | ND | ND |
| C22:0 | 0.53 ± 0.03 | 0.53 ± 0.03 | ND | ND |
| C23:0 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.47 ± 0.02 | ND | ND |
| C24:0 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | ND | ND |
| ∑SFA | 26.46 ± 0.26 | 31.84 ± 0.98 ** | 30.05 ± 0.22 ** | 28.20 ± 0.21 |
| C15:1n5 | 0.27 ± 0.01 ** | 0.10 ± 0.01 | ND | 2.80 ± 0.03 ** |
| C16:1n7 | 5.03 ± 0.53 | 6.15 ± 0.31 | 2.31 ± 0.22 | 1.97 ± 0.14 |
| C17:1n7 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.87 ± 0.02 ** | 2.90 ± 0.12 | 3.74 ± 0.05 ** |
| C18:1n9 | 35.70 ± 0.93 * | 32.57 ± 0.64 | 27.55 ± 0.14 ** | 24.90 ± 0.16 |
| C20:1n9 | 2.23 ± 0.11 * | 1.95 ± 0.05 | 1.90 ± 0.03 ** | 1.64 ± 0.02 |
| C22:1n9 | 3.15 ± 0.24 ** | 1.36 ± 0.08 | ND | ND |
| C24:1n9 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.02 ** | ND | ND |
| ∑MUFA | 47.21 ± 0.79 ** | 43.23 ± 0.53 | 34.65 ± 0.15 | 35.04 ± 0.21 |
| C18:2n6 (LA) | 17.38 ± 0.40 ** | 14.07 ± 0.68 | 8.22 ± 0.19 ** | 6.94 ± 0.14 |
| C18:3n6 (GLA) | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | ND | ND |
| C18:3n3 (ALA) | 5.74 ± 0.44 | 5.75 ± 0.50 | 4.18 ± 0.12 ** | 3.47 ± 0.12 |
| C20:2n6 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.02 ** | 0.96 ± 0.03 | 1.07 ± 0.01 ** |
| C20:3n6 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.02 ** | ND | 0.30 ± 0.01 ** |
| C20:4n6 (ARA) | 0.61 ± 0.05 | 1.29 ± 0.09 ** | 4.33 ± 0.13 | 6.12 ± 0.15 ** |
| C20:3n3 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.02 ** | 0.57 ± 0.03 | 0.53 ± 0.03 |
| C20:5n3 (EPA) | 1.00 ± 0.12 | 1.36 ± 0.14 | 13.23 ± 0.08 | 12.94 ± 0.19 |
| C22:6n3 (DHA) | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.72 ± 0.07 ** | 4.14 ± 0.08 | 5.37 ± 0.07 ** |
| ∑PUFA | 26.27 ± 0.97 | 24.86 ± 1.50 | 35.63 ± 0.18 | 36.75 ± 0.30 * |
| ∑EFA | 18.01 ± 0.41 ** | 14.30 ± 0.70 | 8.22 ± 0.19 ** | 6.94 ± 0.14 |
| ∑HUFA | 8.09 ± 0.64 | 10.10 ± 0.84 | 26.45 ± 0.14 | 28.73 ± 0.32 ** |
| ∑n-3 PUFA | 7.16 ± 0.58 | 8.17 ± 0.72 | 22.12 ± 0.08 | 22.31 ± 0.21 |
| ∑n-6 PUFA | 19.11 ± 0.46 * | 16.69 ± 0.83 | 13.51 ± 0.24 | 14.44 ± 0.11 ** |
| n-3/n-6 PUFA | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.03 * | 1.64 ± 0.03 ** | 1.55 ± 0.01 |
| DHA + EPA | 1.25 ± 0.15 | 2.08 ± 0.21 ** | 17.37 ± 0.12 | 18.31 ± 0.24 * |
| DHA/EPA | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.01 ** | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 0.42 ± 0.00 ** |
| h/H | 3.27 ± 0.06 ** | 2.49 ± 0.10 | 3.65 ± 0.04 | 3.92 ± 0.05 ** |
| AI | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.01 ** | 0.27 ± 0.00 ** | 0.24 ± 0.00 |
| TI | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.00 ** | 0.28 ± 0.00 |
| Free Amino Acids | Hepatopancreas | Muscle | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCCC | PC | Percentage of RCCC/% | Percentage of PC/% | RCCC | PC | Percentage of RCCC/% | Percentage of PC/% | |
| Aspartic acid | 33.28 ± 3.49 ** | 18.04 ± 1.00 | 3.83 | 2.90 | 4.25 ± 0.34 ** | 2.58 ± 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.19 |
| Arginine | 163.62 ± 14.05 | 186.79 ± 11.07 | 18.83 | 30.07 | 851.16 ± 20.89 | 933.18 ± 37.79 | 57.81 | 68.28 |
| Alanine | 57.38 ± 8.48 | 43.42 ± 1.54 | 6.60 | 6.99 | 107.54 ± 1.55 ** | 86.05 ± 3.96 | 7.30 | 6.30 |
| Cysteine | 10.72 ± 2.05 * | 4.17 ± 0.27 | 1.23 | 0.67 | 2.30 ± 0.28 ** | 1.15 ± 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.08 |
| Glutamic acid | 112.33 ± 14.98 | 75.11 ± 3.62 | 12.92 | 12.09 | 25.94 ± 1.20 ** | 18.45 ± 0.60 | 1.76 | 1.35 |
| Glycine | 70.22 ± 10.19 | 64.64 ± 3.34 | 8.08 | 10.41 | 188.49 ± 20.32 ** | 87.13 ± 16.63 | 12.80 | 6.38 |
| Histidine | 17.72 ± 2.86 | 16.49 ± 1.15 | 2.04 | 2.65 | 55.97 ± 3.61 | 50.67 ± 1.75 | 3.80 | 3.71 |
| Proline | 29.56 ± 4.61 ** | 11.48 ± 0.86 | 3.40 | 1.85 | 51.74 ± 10.35 * | 21.24 ± 3.35 | 3.51 | 1.55 |
| Serine | 4.93 ± 0.72 | 11.17 ± 0.43 ** | 0.57 | 1.80 | 4.38 ± 0.14 | 21.00 ± 2.81 ** | 0.30 | 1.54 |
| Tyrosine | 43.87 ± 5.60 ** | 19.13 ± 1.07 | 5.05 | 3.08 | 15.47 ± 0.68 ** | 9.37 ± 0.67 | 1.05 | 0.69 |
| Isoleucine ▲ | 35.69 ± 6.04 * | 16.55 ± 0.75 | 4.11 | 2.66 | 12.65 ± 0.75 | 10.73 ± 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.79 |
| Leucine ▲ | 68.72 ± 9.93 * | 32.28 ± 1.32 | 7.91 | 5.20 | 23.17 ± 1.17 * | 17.69 ± 1.71 | 1.57 | 1.29 |
| Lysine ▲ | 76.19 ± 8.94 ** | 39.52 ± 2.04 | 8.77 | 6.36 | 34.22 ± 3.26 | 36.64 ± 3.23 | 2.32 | 2.68 |
| Methionine ▲ | 21.96 ± 2.47 ** | 11.63 ± 0.42 | 2.53 | 1.87 | 41.28 ± 6.02 * | 19.11 ± 2.53 | 2.80 | 1.40 |
| Phenylalanine ▲ | 42.40 ± 6.12 * | 20.70 ± 1.15 | 4.88 | 3.33 | 8.97 ± 0.64 ** | 5.63 ± 0.29 | 0.61 | 0.41 |
| Threonine ▲ | 38.66 ± 5.92 | 25.83 ± 0.84 | 4.45 | 4.16 | 18.87 ± 2.24 | 27.11 ± 2.35 * | 1.28 | 1.98 |
| Valine ▲ | 41.93 ± 8.02 | 24.22 ± 1.08 | 4.82 | 3.90 | 25.96 ± 1.06 ** | 18.88 ± 1.53 | 1.76 | 1.38 |
| ∑EFAA | 325.54 ± 46.25 * | 170.74 ± 6.93 | 37.45 | 27.49 | 165.12 ± 10.62 | 135.80 ± 12.34 | 11.21 | 9.94 |
| ∑FAA | 869.16 ± 93.76 * | 621.18 ± 21.86 | 1472.36 ± 20.81 | 1366.61 ± 47.39 | ||||
| Free Amino Acids | Flavor Characteristics | Threshold (mg/100 g) | Hepatopancreas | Muscle | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCCC | PC | RCCC | PC | |||
| Aspartic acid | umami (+) | 100 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| Glutamic acid | umami (+) | 30 | 3.74 | 2.50 | 0.86 | 0.62 |
| ∑TUV | 4.08 | 2.68 | 0.91 | 0.64 | ||
| Alanine | sweetness (+) | 60 | 0.96 | 0.72 | 1.79 | 1.43 |
| Glycine | sweetness (+) | 130 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 1.45 | 0.67 |
| Serine | sweetness (+) | 150 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.14 |
| Threonine | sweetness (+) | 260 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.10 |
| Proline | sweetness/bitterness (+) | 300 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.07 |
| Arginine | sweetness/bitterness (+) | 50 | 3.27 | 3.74 | 17.02 | 18.66 |
| ∑TSV | 5.05 | 5.17 | 20.54 | 21.08 | ||
| Lysine | sweetness/bitterness (−) | 50 | 1.52 | 0.79 | 0.68 | 0.73 |
| Valine | sweetness/bitterness (−) | 40 | 1.05 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.47 |
| Methionine | bitterness/sweetness/sulphur (−) | 30 | 0.73 | 0.39 | 1.38 | 0.64 |
| Histidine | bitterness (−) | 20 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 2.80 | 2.53 |
| Isoleucine | bitterness (−) | 90 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| Leucine | bitterness (−) | 190 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.09 |
| Phenylalanine | bitterness (−) | 90 | 0.47 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| ∑TBV | 5.42 | 3.19 | 5.87 | 4.65 | ||
| Elements | DRI mg/day | Hepatopancreas | Muscle | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCCC | PC | RCCC | PC | ||
| RDA | |||||
| Mg | (335–255) | 4.00~5.25 | 5.11~6.72 | 10.45~13.75 | 11.95~15.70 |
| Fe | (18–8) | 253.01~569.26 | 335.58~755.05 | 0.96~2.16 | 1.26~2.84 |
| Cu | 0.9 | 64.78 | 53.89 | 35.42 | 32.77 |
| Zn | (11–8) | 11.69~16.08 | 8.04~11.05 | 6.56~9.02 | 6.32~8.68 |
| Se | 0.055 | 183.64 | 129.09 | 49.17 | 44.28 |
| AI | |||||
| Na | 1500 | 6.36 | 6.10 | 4.97 | 5.35 |
| K | 4700 | 5.59 | 5.26 | 10.28 | 10.75 |
| Ca | 1200 | 1.17 | 1.25 | 1.42 | 1.46 |
| Mn | (2.3–1.8) | 97.70~124.83 | 74.00~94.56 | 1.06~1.35 | 0.98~1.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Luo, L.; Zhang, R.; Guo, K.; Su, J.; Zhao, Z. Biological Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) Reared in Two Different Culture Modes in Cold Regions of China. Foods 2025, 14, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172998
Wang S, Zhang S, Luo L, Zhang R, Guo K, Su J, Zhao Z. Biological Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) Reared in Two Different Culture Modes in Cold Regions of China. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172998
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shihui, Shuqi Zhang, Liang Luo, Rui Zhang, Kun Guo, Junjie Su, and Zhigang Zhao. 2025. "Biological Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) Reared in Two Different Culture Modes in Cold Regions of China" Foods 14, no. 17: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172998
APA StyleWang, S., Zhang, S., Luo, L., Zhang, R., Guo, K., Su, J., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Biological Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) Reared in Two Different Culture Modes in Cold Regions of China. Foods, 14(17), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172998







