Advances in Atmospheric Cold Plasma Technology for Plant-Based Food Safety, Functionality, and Quality Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of Atmospheric Cold Plasma
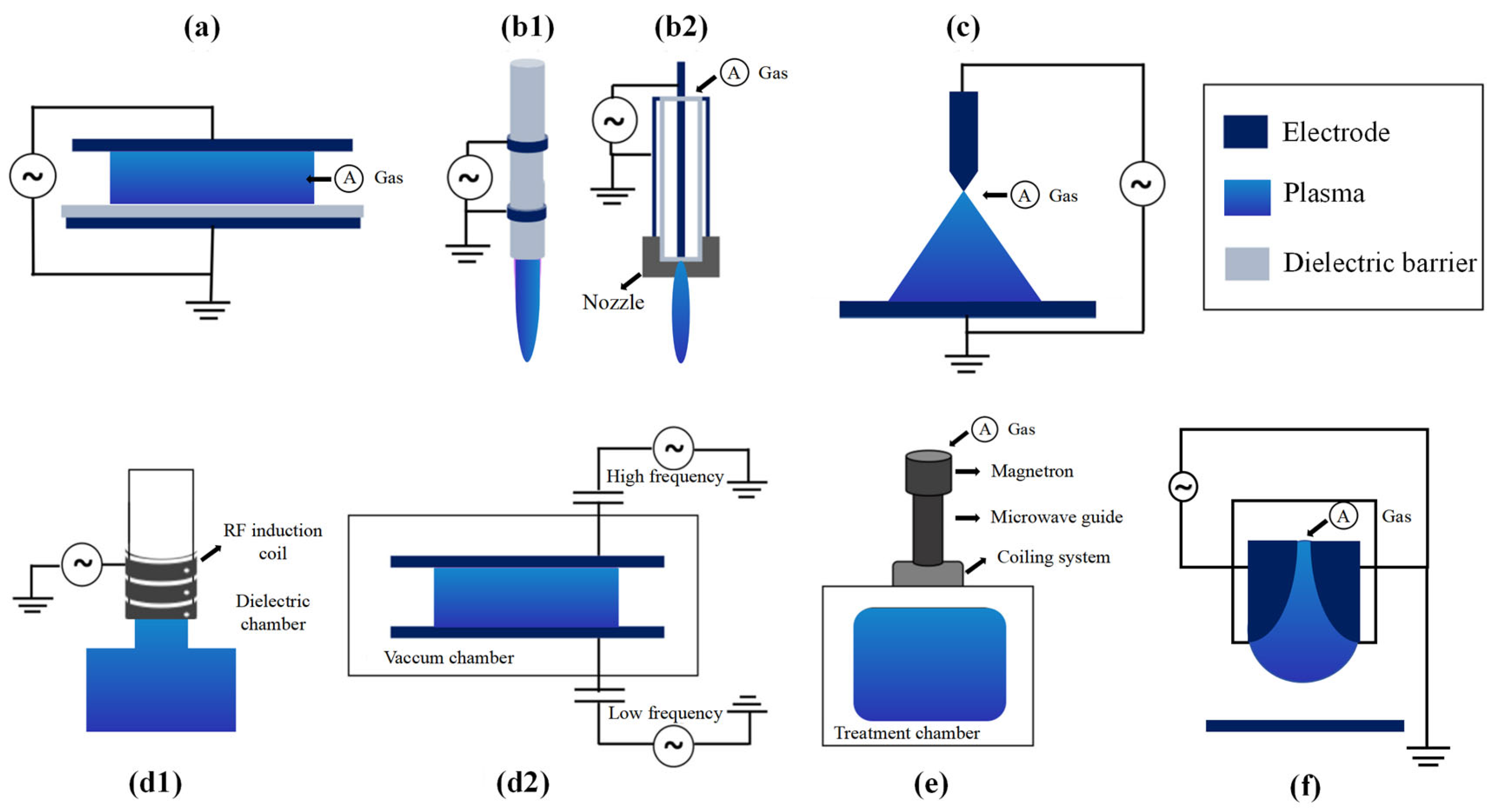
2.1. Dielectric Barrier Discharge
2.2. Corona Discharge
2.3. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet
2.4. Gliding Arc Discharge
2.5. Glow Discharge
2.6. Radio Frequency Discharge
2.7. Microwave Discharge
2.8. Plasma-Activated Liquid
3. ACP Applications for Plant-Based Foods
3.1. Microbial Inactivation
| No. | Sample | Microorganism | Equipment | Parameters | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Juglans regia L. | Coliforms, Molds | RF | 20, 30, 40, 50 W; 10, 15, 20 min | Microbial activity decreased gradually with increasing power and time | [78] |
| 2 | Black peppercorns | Indigenous bacteria, Bacillus tequilensis spores | DBD | 9.7, 9.8, 10.2, 10.5, 10.6 kV; 7.9, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, 22.1 min | Microbial inactivation improved with increased water activity, treatment time, and voltage | [79] |
| 3 | Black pepper grains | Bacillus subtilis vegetative cells and spores | APPJ | 280 GHz, 50 mA, 600 W, 30 min | Microbial activity decreased with increased voltage and treatment time | [82] |
| 4 | Black pepper seeds, allspice berries, and juniper berries | Aspergillus niger, Bacillus subtilis | MW | Argon, 20 L/min, 2.45 GHz, 600 W, 15–60 s | Degree of bacterial inactivation increased with prolonged treatment time | [83] |
| 5 | Black pepper | Bacillus cereus | APPJ | 40, 50, 60 L/min; 800, 900, 1000 W; 0–10 min | Significant reduction in vegetative cells of Bacillus cereus | [84] |
| 6 | Coriandrum sativum | Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts | APPJ | 47 GHz; 549 W; 0, 30, 90, 180 s | Microbial activity decreased with increased treatment time | [87] |
| 7 | Curcuma longa var. Suvarna | Aerobic viable cell | DBD | 25 kV; 3, 5, 7 min | Antibacterial effect declined with prolonged processing time | [91] |
| 8 | Dried saffron stigma | Molds, Yeasts, Escherichia coli | APPJ | Air/Argon, 1 L/min; 40, 70, 100 W; 1, 5, 10 min | Microbial load decreased with increased exposure time | [92] |
| 9 | Crocus sativus L. | Escherichia coli (E. coli) | APPJ | Helium, 1 L/min; 12 GHz; 5, 6, 7 kV; 0–12 min | Complete E. coli inactivation | [80] |
| 10 | Crocus sativus L. | TVC, Coliforms, Molds, Yeasts | RF | Oxygen, 70, 90, 110 W; 5, 10, 15, 30 min | Maximum microbial log reduction at 110 W for 30 min | [93] |
| 11 | Red mini-roses | Microbiota diversity | DBD, GD | 962 Hz, 18 kV, 20 min | Reduced microbial diversity without altering dominant populations | [94] |
| 12 | Agaricus bisporus | Aerobic colony | DBD | Optimal: 95 kV, 130 Hz, 10 min | Effective spoilage microbe reduction, minimizing contamination risk | [86] |
| 13 | Pleurotus ostreatus | Soil-borne pathogens | DBD | 2 L/min, 6 kV; 5–25 min | Optimal at 25 min; colony count decreased with time | [95] |
| 14 | Flammulina velutipes | Adherent Bacteria, Escherichia coli | APPJ, PAW | 83 kHz, 0.68 kV, 77 mA, 0–30 min | CFU reduction proportional to treatment time; NTAPPJ reduced bacterial adhesion; PAW increased cell death and lipid peroxidation | [96] |
| 15 | Shiitake mushrooms | Bacteria | DBD, GAD-PAW | N2-O2 (3:1), 200 W, 1200 W, 20 min | PAW outperformed DBD in postharvest quality preservation | [97] |
| 16 | Vitis vinifera | Aerobic bacteria, E. coli | APPJ | Helium, 20 kHz, 6.5 W, 4–5.5 kV, 1–3 min | Complete aerobic bacteria reduction; extended shelf-life (28 days) | [98] |
| 17 | D. longan | Diutina catenulata | DBD | Argon/air mixtures, 4 L/min, 5 kHz, 53 W, 24 kV, 180–360 s | Reduced microbial density; expanded antibacterial zones over time | [90] |
| 18 | Dried jujube | Aspergillus niger spores | DBD | 50 Hz; 50–70 kV; 0–20 min | Reduced spore viability and toxicity | [99] |
| 19 | Palm dates | Aspergillus niger | DBD | 10 kHz, 8–30 W, 5–10 kV, 3 min | Inhibited A. niger growth | [100] |
| 20 | Cowpea | Callosobruchus maculatus | DBD | 65% O2/30% N2/5% CO2; 20–70 kV, 1–3 min | Mortality/sterility increased with time and voltage | [101] |
| 21 | Cichorium intybus L. | Biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E. coli | APPJ | Helium, 2 SLM, 25 kHz, 8 kV, 3 min | Membrane disruption; E. coli more sensitive than P. aeruginosa | [102] |
| 22 | Camellia sinensis var. sinensis | Molds, yeasts, E. coli, Enterococcus faecalis | DBD | 20–25 kV; 2–8 min | Complete inactivation at 25 kV/8 min; E. coli required higher MIC/MBC than S. aureu | [103] |
| 23 | Almond slices | Molds, yeasts, Staphylococcus aureus | APPJ | Helium, 10 SLM, 17 V, 2.26 A, 5–20 min | Microbial reduction proportional to treatment duration after 20 min | [104] |
| 24 | Mulberries | E. coli | DBD | 0.1–1 A, 30 s | ROS accumulation induced apoptosis; damage intensity current-dependent | [105] |
| 25 | Vegetables/fruits/nuts/ powders | E. coli O157:H7, S. Typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes | DBD | 14.4 kHz, 51.7 W, 8 kV, 30 min | Surface roughness negatively correlated with inactivation efficiency | [106] |
3.2. Enzyme Activity

3.3. Mycotoxin Degradation
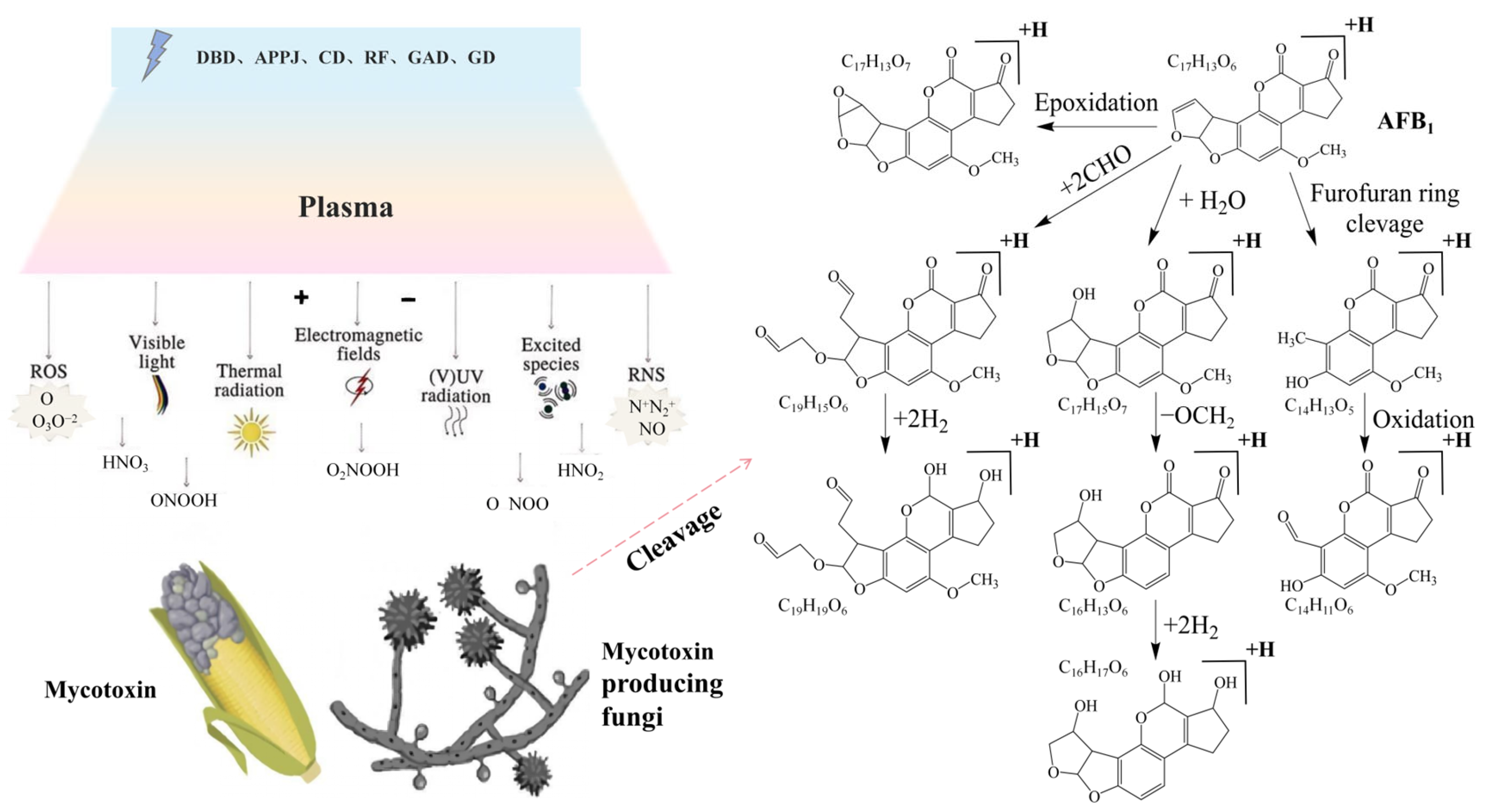
| No. | Sample | Mycotoxin | Equipment | Parameters | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pistacia vera L. | Aflatoxin | DBD | Oxygen, 25 kHz, 89 W, 15 kV, 60/120 s | Significantly reduced the number of molds and yeasts after 120 days of storage; notably decreased aflatoxin content | [125] |
| 2 | Pistacia vera L. | Aspergillus flavus, Aflatoxin | DBD-APPJ | Air–argon (0%, 50%, 100%), 10–20 kV, 5–15 min | High degradation rate under optimal treatment conditions; no significant difference between control and cold plasma-treated samples | [126] |
| 3 | Pistacia vera L. | Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) | RF | 12.56 kHz, 80 W; 10, 15 min | Aflatoxin content significantly decreased | [129] |
| 4 | Wheat | Deoxynivalenol (DON) | DDBD | 160–240 Hz, 60–140 V, duty cycles 20–99%, 25 min | ACP achieved a degradation efficiency of up to 98% in aqueous DON solutions, while 61% degradation in wheat samples | [123] |
| 5 | Corn kernels | Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) | DBD | 0.18 W/cm–0.31 W/cm, 30–480 s | Complete removal of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) | [130] |
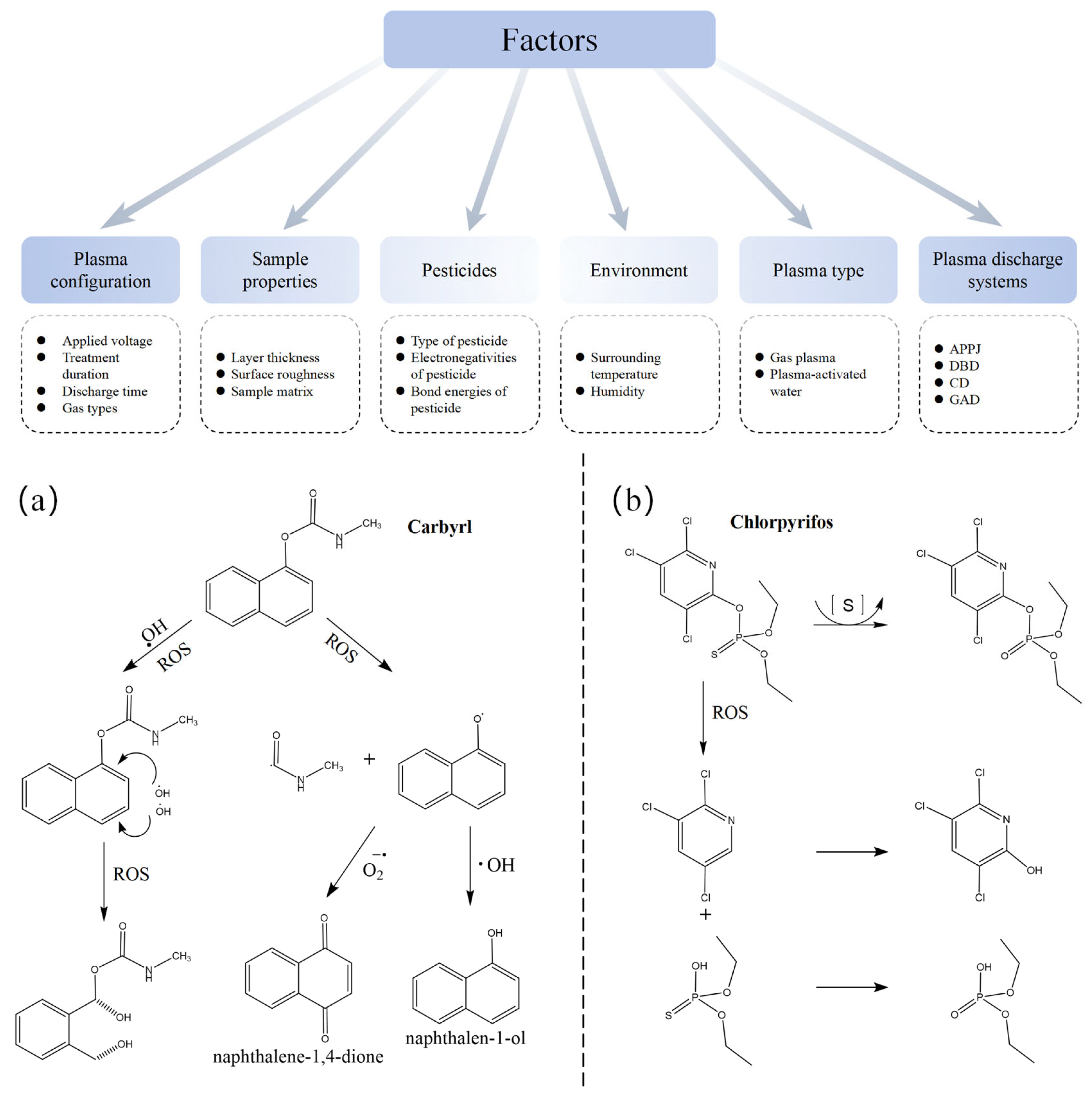
3.4. Pesticide Degradation
| No. | Sample | Pesticide | Equipment | Parameters | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fresh Spinacia oleracea L. | Chlorpyrifos, Malathion | Volume DBD | 100 W, 20 kV, 20 min | Microbial contamination and pesticide residue analysis showed that cold plasma treatment significantly reduced spinach contamination; chlorpyrifos and malathion decreased by 90% | [139] |
| 2 | Glycine. max (L.) Merr. | Chlorpyrifos | DBD | 1–2 kV, 2–6 min | Cold plasma (CP) treatment achieved a degradation rate of 65% for pesticides on soybeans, even high concentrations degraded by 50% | [140] |
| 3 | Blueberry | Boscalid, Imidacloprid | DBD | 60/80 kV; 2, 5 min | Degradation rates: Boscalid 80%, Imidacloprid 76%; after 1 min of cold plasma treatment, polyphenol and flavonoid content increased | [141] |
| 4 | Grape, Strawberry | Chlorpyrifos, Carbaryl | PAW | 1 kHz, 5.66 W, 5–30 min | Chlorpyrifos reduction: grape 79%, strawberry 69%; carbaryl reduction: grape 86%, strawberry 73%; no significant changes in color and firmness; slight changes in ascorbic acid levels | [62] |
| 5 | Lettuces | Chlorpyrifos, Malathion | DBD | 60–80 kV, 30–180 s | DBD treatment significantly degraded malathion and chlorpyrifos in water and lettuce; at 80 kV for 180 s, degradation efficiencies were 64.6% and 62.7%, respectively; no noticeable damage to lettuce quality including color and chlorophyll content; ascorbic acid significantly decreased | [142] |
| 6 | Corn | Chlorpyrifos, Carbaryl | DBD | 100–1200 Hz, 150–1500 mL·min−1, 4–20 W, 20–60 s | Under 1000 mL·min−1, 20 W, 1200 Hz for 60 s, chlorpyrifos degradation efficiency reached 86.2%, Carbaryl 66.6%; moisture and starch content significantly decreased, acid value increased, vitamin B2 unchanged | [143] |
| 7 | Edible Wolfberry | Omethoate | Surface DBD | 9 kHz, 0–20 kV, 0.1–30 min | At 10 kV for 30 min, optimal degradation rate reached 99%, with complete conversion into non-toxic species (e.g., PO43−, H2O, SO42−, CO2) | [144] |
| 8 | Lycium barbarum | Omethoate, Dichlorvos (DDVP) | Gas Phase Surface Discharge Plasma (GPSD) | 5–15 kV, 0.5–30 min | Maximum degradation rates reached 99.55% and 96.83%; completely degraded into non-toxic species with no impact on Lycium barbarum quality | [145] |
| 9 | Solanum lycopersicum | Chlorothalonil | PAL-U (PAW, PABS) | 600 W, 7 kV, 20 L/min; solution treatment 1–10 min, soaking for 15 min | Maximum reduction in residue was 89.23%, with no impact on sample quality | [146] |
| 10 | Solanum lycopersicum | Chlorothalonil (CTL), Thiram (THM) | PAW, Plasma activated buffer solution (PABS) | Argon/Oxygen = 98/2, 600 W, 2–7 kV, 1–10 min | Degradation rates: 85.3% and 74.2%, respectively; oxidation–reduction potential (ORP) and electrical conductivity (EC) of the solution significantly increased; pH decreased with activation time; no significant effect on tomatoes | [147] |
3.5. Bioactive Compound Extraction
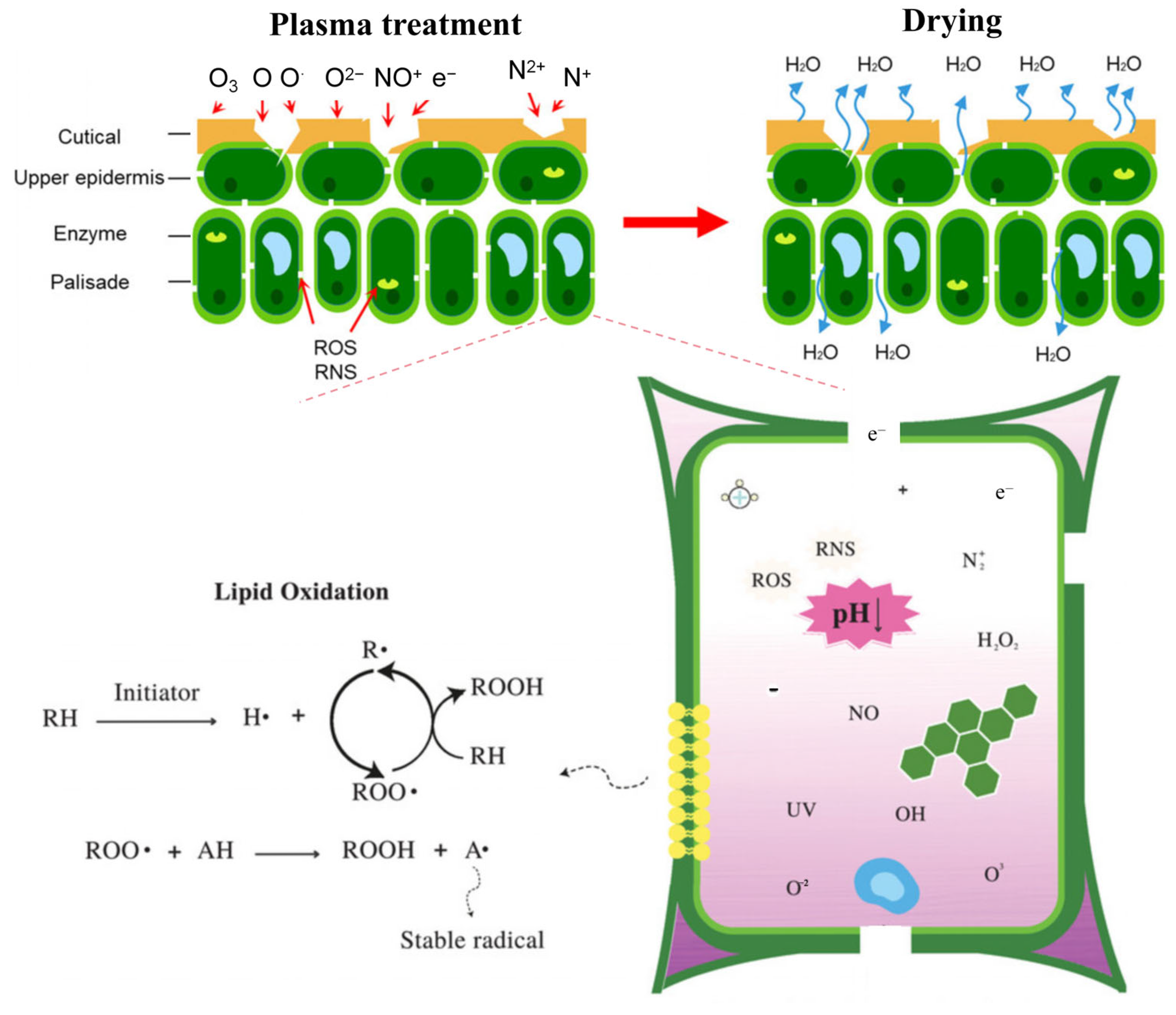
3.6. Drying
3.7. Germination
3.8. Food Packaging Applications
4. Cold Plasma Effects on Plant-Based Food Quality
4.1. Sensory Attributes and Physicochemical Properties
4.1.1. Color
4.1.2. Texture
4.1.3. Flavor and Aroma
4.1.4. Acidity and pH
4.1.5. Hydrophilicity and Hydrophobicity
4.1.6. Water Activity
4.2. Nutritional Value
4.2.1. Antioxidants
4.2.2. Proteins
4.2.3. Lipids
4.2.4. Carbohydrates
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoev, S.D. Food Safety and Increasing Hazard of Mycotoxin Occurrence in Foods and Feeds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskovac, A.; Petrović, S. Pesticide Use and Degradation Strategies: Food Safety, Challenges and Perspectives. Foods 2023, 12, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenyorege, E.A.; Ma, H.; Ayim, I.; Zhou, C.; Wu, P.; Hong, C.; Osae, R. Effect of Multi-frequency Ultrasound Surface Washing Treatments on Escherichia coli Inactivation and Some Quality Characteristics of Non-heading Chinese Cabbage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenyorege, E.A.; Ma, H.; Ayim, I.; Aheto, J.H.; Hong, C.; Zhou, C. Effect of Multi-Frequency Multi-Mode Ultrasound Washing Treatments on Physicochemical, Antioxidant Potential and Microbial Quality of Tomato. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hassane Hamadou, A.; Li, B.; Xu, B. Gentle Debranning as a Technology to Reduce Microbial and Deoxynivalenol Levels in Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Its Application in Milling Industry. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 107, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Okonkwo, C.E.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C. Multimode Ultrasonic-Assisted Decontamination of Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Apaliya, M.T.; Mahunu, G.K.; Chen, L.; Li, W. Control of Ochratoxin A-Producing Fungi in Grape Berry by Microbial Antagonists: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.M.R.; Ma, H.; Xu, B.; Devi, S.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Stanley, S.L.; Bhandari, B.; Zhu, J. Efficacy of Ultrasound Treatment in the Removal of Pesticide Residues from Fresh Vegetables: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenyorege, E.A.; Ma, H.; Ayim, I.; Zhou, C. Ultrasound Decontamination of Pesticides and Microorganisms in Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. J. Food Saf. Food Qual.-Arch. Leb. 2018, 69, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Antimicrobial Mechanism of Pulsed Light for the Control of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Its Application in Carrot Juice. Food Control 2019, 106, 106751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, R.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Jia, M.; Jiang, Y. Influencing Factors, Kinetics, and Pathways of Pesticide Degradation by Chlorine Dioxide and Ozone: A Comparative Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huangfu, X.; Huang, R.; Liang, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, H.; Witkowski, B.; Gierczak, T.; Li, S. Evaluating Degradation Efficiency of Pesticides by Persulfate, Fenton, and Ozonation Oxidation Processes with Machine Learning. Environ. Res. 2025, 277, 121548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnew, M.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, A.; Li, M.; Zhao, C. A Review of Various Advanced Oxidation Techniques for Pesticide Degradation for Practical Application in Aqueous Environments. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, G.; Hou, M.; Du, S.; Han, J.; Yu, Y.; Gao, H.; He, D.; Shi, J.; Lee, Y.-W.; et al. New Hydrolase from Aeromicrobium sp. HA for the Biodegradation of Zearalenone: Identification, Mechanism, and Application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Garba, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, P. Isolation and Characterization of a Bacillus subtilis Strain with Aflatoxin B 1 Biodegradation Capability. Food Control 2017, 75, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Pang, B.; Solairaj, D.; Hu, W.; Legrand, N.N.G.; Ma, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of Rhodotorula Mucilaginosa on Patulin Degradation and Toxicity of Degradation Products. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.-Z.; Guo, L.-P.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, D.; Kang, L.-P.; He, Y.-L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.-Y. Discussion on Present Situation of Study on Pesticide Residues in Chinese Herbal Medicines. China J. Chin. Mate. Med. 2016, 41, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhou, C.; Wang, B.; Zeng, S.; Mu, R.; Li, G.; Li, B.; Lv, W. Research Progress and Application of Ultrasonic- and Microwave-Assisted Food Processing Technology. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 3707–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaguthevar, R.; Packialakshmi, J.S.; Murugesan, B.; Rhim, J.; Thiyagamoorthy, U. In-package Cold Plasma Treatment to Extend the Shelf Life of Food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Han, Z.; Brennan, C.S. Non-thermal Technologies and Its Current and Future Application in the Food Industry: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osae, R.; Essilfie, G.; Alolga, R.N.; Akaba, S.; Song, X.; Owusu-Ansah, P.; Zhou, C. Application of Non-thermal Pretreatment Techniques on Agricultural Products Prior to Drying: A Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2585–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng, I.D.; Yang, X. Thermal and Non-Thermal Processing Affect Maillard Reaction Products, Flavor, and Phytochemical Profiles of Ginkgo Biloba Seed. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I.D.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Saalia, F.K.; Yang, X. Non-thermal Pretreatment Affects Ginkgo biloba L. Seed’s Product Qualities, Sensory, and Physicochemical Properties. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, S.; Dar, A.H.; Dash, K.K.; Srivastava, S.; Pandey, V.K.; Ayoub, W.S.; Pandiselvam, R.; Manzoor, S.; Kaur, M. Cold Plasma Treatment Advancements in Food Processing and Impact on the Physiochemical Characteristics of Food Products. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonks, L. Oscillations in Ionized Gases. In Plasma and Oscillations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1961; pp. 122–139. ISBN 978-1-4831-9913-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pogorzelska-Nowicka, E.; Hanula, M.; Pogorzelski, G. Extraction of Polyphenols and Essential Oils from Herbs with Green Extraction Methods—An Insightful Review. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherif, M.M.; Assadi, I.; Khezami, L.; Ben Hamadi, N.; Assadi, A.A.; Elfalleh, W. Review on Recent Applications of Cold Plasma for Safe and Sustainable Food Production: Principles, Implementation, and Application Limits. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Carbone, K.; Gervasi, F.; Parandi, E.; Rouhi, M.; Rostami, O.; Abedi-Firoozjah, R.; Kolahdouz-Nasiri, A.; Garavand, F.; Mohammadi, R. Cold Plasma-Assisted Extraction of Phytochemicals: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, B.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Saleemi, M.K.; Nawaz, M.Y.; Li, M.; Xu, Y. Cold Plasma: A Success Road to Mycotoxins Mitigation and Food Value Edition. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Huangfu, L.; Dong, S.; Ma, Y.; Li, K.; Niu, L.; Bai, Y. Feasibility of Atmospheric Cold Plasma for the Elimination of Food Hazards: Recent Advances and Future Trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 4431–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojithamporn, P.; Leksakul, K.; Sawangrat, C.; Charoenchai, N.; Boonyawan, D. Degradation of Pesticide Residues in Water, Soil, and Food Products via Cold Plasma Technology. Foods 2023, 12, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Yadav, S.K. Recent Advances in Cold Plasma Technology for Food Processing. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroque, D.A.; Seó, S.T.; Valencia, G.A.; Laurindo, J.B.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Cold Plasma in Food Processing: Design, Mechanisms, and Application. J. Food Eng. 2022, 312, 110748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoux, C.M.G.; Patange, A.; Lamba, S.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Tiwari, B.K.; Scannell, A.G.M. Applications of Nonthermal Plasma Technology on Safety and Quality of Dried Food Ingredients. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feizollahi, E.; Misra, N.N.; Roopesh, M.S. Factors Influencing the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Atmospheric Cold Plasma (ACP) in Food Processing Applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 666–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiru, M.M.; Frimpong, E.B.; Muhammad, U.; Qian, J.; Mustapha, A.T.; Yan, W.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, J. Dielectric Barrier Discharge Cold Atmospheric Plasma: Influence of Processing Parameters on Microbial Inactivation in Meat and Meat Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2626–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Pedrow, P.D. A Novel Active Needle Probe in an Atmospheric Pressure Corona-Based Cold Plasma Reactor with Admixtures of Helium and Dry Air. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2020, 48, 2418–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feklistov, E.G. Measurement Approach for Custom Designed Cold Plasma Generator. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-S.; Lawless, P.A.; Yamamoto, T. Corona Discharge Processes. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1991, 19, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamsen, N.; Akkarachanchainon, A.; Fookiat, K.; Srisala, J.; Chomchuen, S.; Kanokbannakorn, W.; Srisonphan, S. Atmospheric Cold Plasma via Fringe Field Enhanced Corona Discharge on Single Dielectric Barrier for Large-Volume Applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 86, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, Z.; Yao, C.; Zhang, G. Non-Thermal Equilibrium Atmospheric Pressure Glow-like Discharge Plasma Jet. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, Z.; Zhong, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bai, S. Inactivation of Escherichia coli Using Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Jet with Thin Quartz Tubes. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 455204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Saman, N.; Ahmad, M.H.; Buntat, Z. Experimental Analysis of Cold Plasma with Glow Discharge Mechanism under a Variety of Input Parameters. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2022, 50, 2110–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Z.; Longjin, J.; Shun, Z.; Guohua, N.I. Review of Research on VOCs Treatment by Gliding Arc Plasma. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2024, 14, 425–436. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarasimhan, J.; Lakshminarayana, R.; Anand, M.S.; Dasappa, S. Influence of Gas Dynamics on Arc Dynamics and the Discharge Power of a Rotating Gliding Arc. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, 85012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Li, X.-S.; Liu, J.-B.; Liu, J.-L.; Li, H.-P.; Zhu, A.-M. Dimensionless Factors for an Alternating-Current Non-Thermal Arc Plasma. Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 120707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wei, S.; Zhang, D. Cold Plasma Pretreatment Technology for Enhancing the Extraction of Bioactive Ingredients from Plant Materials: A Review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 209, 117963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Nath, P.C.; Rustagi, S.; Sharma, M.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Dikkala, P.K.; Nayak, P.K.; Sridhar, K. Cold Plasma—A Sustainable Energy-efficient Low-carbon Food Processing Technology: Physicochemical Characteristics, Microbial Inactivation, and Industrial Applications. Int. J. Food Sci. 2025, 2025, 4166141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denes, F. Macromolecular Plasma-Chemistry: An Emerging Field of Polymer Science. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 815–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Ran, Y.; Zhai, S.; Xia, Y. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Promising and Safe Therapeutic Strategy for Atopic Dermatitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 184, 1184–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.E.; Fernandes, F.A.N. Diazinon Degradation in Water Applying Glow Discharge Plasma Technology. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 42, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saman, N.M.; Ahmad, M.H.; Buntat, Z. Application of Cold Plasma in Nanofillers Surface Modification for Enhancement of Insulation Characteristics of Polymer Nanocomposites: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 80906–80930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Chauhan, A.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Rajesh; Dhanprakash; Singh, S. Investigating the Effect of Combined Radiofrequency Cold Plasma (RF-CP) Treatment on Techno-Functional Attributes of Cashewnut. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 109, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puligundla, P.; Mok, C. Microwave- and Radio-Frequency-Powered Cold Plasma Applications for Food Safety and Preservation. In Advances in Cold Plasma Applications for Food Safety and Preservation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 309–329. ISBN 978-0-12-814921-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ionita, M.D.; Teodorescu, M.; Acsente, T.; Bazavan, M.; Ionita, E.R.; Dinescu, G. Remote Surface Modification of Polymeric Foils by Expanding Atmospheric Pressure Radiofrequency Discharges. Rom. J. Phys. 2011, 56, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Despax, B.; Pascal, O.; Gherardi, N.; Naude, N.; Belinger, A.; Pitchford, L.C. Influence of Electromagnetic Radiation on the Power Balance in a Radiofrequency Microdischarge with a Hollow Needle Electrode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 144104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, Y.; Chaniel, G.; Bormashenko, E. Surface Charging by the Cold Plasma Discharge of Lentil and Pepper Seeds in Comparison with Polymers. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 172, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihe, T. Microwave Plasmas in Food Safety. A Review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 96, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Cheng, T.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.; Lu, X. Ionization Process and Distinctive Characteristic of Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Jet Driven Resonantly by Microwave Pulses. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2022, 24, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, T.; Wang, X.; Bao, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Monto, A.R.; Jin, W.; Yuan, L.; Gao, R. Plasma-Activated Water Promoted the Aggregation of Aristichthys Nobilis Myofibrillar Protein and the Effects on Gelation Properties. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.; Jin, W.; Bao, Y.; Monto, A.R.; Yuan, L.; Gao, R. Mechanism of Plasma-Activated Water Promoting the Heat-Induced Aggregation of Myofibrillar Protein from Silver Carp (Aristichthys nobilis). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 91, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangapani, C.; Scally, L.; Gulan, M.; Cullen, P.J. Dissipation of Pesticide Residues on Grapes and Strawberries Using Plasma-Activated Water. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 1728–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, K.; Bai, Y. A Review on Recent Advances in Plasma-Activated Water for Food Safety: Current Applications and Future Trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2250–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.S.; Chew, N.S.L.; Low, M.; Tan, M.K. Plasma-Activated Water: Physicochemical Properties, Generation Techniques, and Applications. Processes 2023, 11, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Xu, M.; Pan, S.; Gan, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Lu, X.; Ostrikov, K.K. Plasma Activated Oil: Fast Production, Reactivity, Stability, and Wound Healing Application. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Ma, C.; Lin, L. Synergetic Antibacterial Efficacy of Cold Nitrogen Plasma and Clove Oil against Escherichia coli O157:H7 Biofilms on Lettuce. Food Control 2016, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Plasma Enhanced-Nutmeg Essential Oil Solid Liposome Treatment on the Gelling and Storage Properties of Pork Meat Batters. J. Food Eng. 2020, 266, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Lin, L. Synergistic Effect between Helichrysum italicum Essential Oil and Cold Nitrogen Plasma against Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms on Different Food-contact Surfaces. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liao, X.; Cui, H. Cold Plasma Treated Thyme Essential Oil/Silk Fibroin Nanofibers against Salmonella Typhimurium in Poultry Meat. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liao, X.; Li, C.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.; Cui, H. Inhibitory Effect of Cold Nitrogen Plasma on Salmonella Typhimurium Biofilm and Its Application on Poultry Egg Preservation. LWT 2020, 126, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia Bangar, S.; Suri, S.; Nayi, P.; Phimolsiripol, Y. Cold Plasma for Microbial Safety: Principle, Mechanism, and Factors Responsible. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Lin, L. Promoting Anti-listeria Activity of Lemongrass Oil on Pork Loin by Cold Nitrogen Plasma Assist. J. Food Saf. 2017, 37, e12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Dai, C.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Umego, E.C.; He, R.; Ma, H. The Selective Breeding and Mutagenesis Mechanism of High-yielding Surfactin Strains with Atmospheric and Room Temperature Plasma. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, S.; Yang, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, B.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, L. Cold Plasma Controls Nitrite Hazards by Modulating Microbial Communities in Pickled Radish. Foods 2023, 12, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, E.; Başaran, P.; Kartal, S.; Akan, T. Cold Plasma Application to Fresh Green Leafy Vegetables: Impact on Microbiology and Product Quality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 4484–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Ma, C.; Li, C.; Lin, L. Enhancing the Antibacterial Activity of Thyme Oil against Salmonella on Eggshell by Plasma-Assisted Process. Food Control 2016, 70, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravlje, J.; Regvar, M.; Vogel-Mikuš, K. Development of Cold Plasma Technologies for Surface Decontamination of Seed Fungal Pathogens: Present Status and Perspectives. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, M.; Ramezan, Y.; Khani, M.R. Effect of Low Pressure Cold Plasma Treatment on Microbial Decontamination and Physicochemical Properties of Dried Walnut Kernels. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, I.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Min, S.C. Microbial Decontamination of Black Peppercorns by Simultaneous Treatment with Cold Plasma and Ultraviolet C. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 63, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Rasouli, M.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Momeni, M.; Ostrikov, K.K. Synergistic Cellulose-Based Nanocomposite Packaging and Cold Plasma Decontamination for Extended Saffron Preservation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, A.; Marino, M.; Innocente, N.; Celotto, M.; Maifreni, M. Antimicrobial Effect of Oxidative Technologies in Food Processing: An Overview. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoux, C.M.G.; Free, L.; Hinds, L.M.; Vijayaraghavan, R.K.; Daniels, S.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Effect of Non-Thermal Plasma Technology on Microbial Inactivation and Total Phenolic Content of a Model Liquid Food System and Black Pepper Grains. LWT 2020, 118, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiktor, A.; Hrycak, B.; Jasiński, M.; Rybak, K.; Kieliszek, M.; Kraśniewska, K.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Microwave Plasma Treatment on Quality of Selected Spices. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Deng, J.; Cui, X.; Ma, Z.; Dai, R.; et al. A Systematic Investigation of Direct and Indirect-Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment on Bacillus Cereus and the Application in Black Pepper. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 92, 103583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahar, S.P.; Shelar, A.; Annapure, U.S. Effect of Pin-to-Plate Atmospheric Cold Plasma (ACP) on Microbial Load and Physicochemical Properties in Cinnamon, Black Pepper, and Fennel. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xia, S.; Shi, C.; Ma, N.; Pei, F.; Yang, W.; Hu, Q.; Kimatu, B.M.; Fang, D. The Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Storage Stability of Mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus). Foods 2024, 13, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craighead, S.; Hertrich, S.; Boyd, G.; Sites, J.; Niemira, B.A.; Kniel, K.E. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet Inactivates Cryptosporidium Parvum Oocysts on Cilantro. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvecká, V.; Mošovská, S.; Mikulajová, A.; Valík, Ľ.; Zahoranová, A. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Decontamination of Allspice Berries and Effect on Qualitative Characteristics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Fan, X. Cold Plasma Enhances the Efficacy of Aerosolized Hydrogen Peroxide in Reducing Populations of Salmonella Typhimurium and Listeria Innocua on Grape Tomatoes, Apples, Cantaloupe and Romaine Lettuce. Food Microbiol. 2020, 87, 103391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than, H.A.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Do, N.K.; Tran, M.A.N.; Pham, T.H. Inactivation of Diutina Catenulata Isolated from Longan Fruit Using Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma DBD in Argon, Air, and Argon-Air Mixture. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, V.; Garavand, F.; Goudarzi, M.; Sarlak, Z.; Cacciotti, I.; Tiwari, B.K. Cold Atmospheric-pressure Plasma Treatment of Turmeric Powder: Microbial Load, Essential Oil Profile, Bioactivity and Microstructure Analyses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birjandi Toroghi, Z.; Niazmand, R.; Moradinezhad, F.; Bayat, H. Potential of Cold Plasma Pretreatment for Preserving Biochemical Attributes and Ensuring the Microbiological Safety of Saffron Stigma. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 7417–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvish, H.; Ramezan, Y.; Khani, M.R.; Kamkari, A. Effect of Low-pressure Cold Plasma Processing on Decontamination and Quality Attributes of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Morais, J.S.; Cabral, L.; Fonteles, T.V.; Silva, F.A.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Dos Santos Lima, M.; Rodrigues, S.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Magnani, M. Effects of Different Cold Plasma Treatments on Chemical Composition, Phenolics Bioaccessibility and Microbiota of Edible Red Mini-Roses. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agun, L.; Ahmad, N.; Redzuan, N.; Idirs, N.A.S.; Taib, S.M.; Zakaria, Z.; Raja Ibrahim, R.K. Sterilization of Oyster Mushroom Crop Residue Substrate by Using Cold Plasma Technology. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 39, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Veerana, M.; Choi, E.-H.; Park, G. Effects of Pre-Treatment Using Plasma on the Antibacterial Activity of Mushroom Surfaces. Foods 2021, 10, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavahian, M.; Sheu, F.; Tsai, M.; Chu, Y. The Effects of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Gas and Plasma-activated Water on Texture, Color, and Bacterial Characteristics of Shiitake Mushroom. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 44, e14316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Mishra, A.; Jangra, S.; Pandey, S.; Chhabra, M.; Prakash, R. Process Parameters Optimization for Red Globe Grapes to Enhance Shelf-Life Using Non-Equilibrium Cold Plasma Jet. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 210, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Fungicidal Efficiency of DBD Cold Plasma against Aspergillus Niger on Dried Jujube. Food Microbiol. 2024, 121, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, K.; Al-Qahtani, S.M.; Al-Harbi, N.A.; El-Absy, K.M.; Bu Shulaybi, F.A.; Alali, S.A.; Mashtoly, T.A. Influence of Non-Thermal Plasma on the Quality and Nutritional Content of Palm Dates. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk-Bradley, N.T.; Salau, T.G.; Salzman, K.Z.; Moore, J.M. Atmospheric Cold Plasma (ACP) Treatment for Efficient Disinfestation of the Cowpea Weevil, Callosobruchus Maculatus. J. ASABE 2023, 66, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, H.; Dezhpour, A.; Jafari, S.; Moghaddam, M.J.M.; Nilkar, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Cold Atmospheric-Pressure Argon Plasma Combined with Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) Extract against P. aeruginosa and E. coli Biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmati, V.; Garavand, F.; Khorshidian, N.; Cacciotti, I.; Goudarzi, M.; Chaichi, M.; Tiwari, B.K. Impact of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on Microbial Safety, Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents, Antioxidant Activity, Volatile Compounds, Surface Morphology, and Sensory Quality of Green Tea Powder. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, K.; Shahidi, F.; Mortazavi, S.A. Investigation of Decontamination Effect of Argon Cold Plasma on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Almond Slices. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 335, 108892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menglu, H.; Can, Z.; Peiyao, C.; Yinxin, L.; Cui, S.; Shuhao, H.; Lingxia, H. Killing Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on Escherichia coli from Post-Harvest Mulberry Fruit. Sci. Seric. 2023, 49, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.-Y.; Song, W.-J.; Eom, S.; Kim, S.B.; Kang, D.-H. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Cold Plasma Treatment against Food-Borne Pathogens on Various Foods. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 204003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, B.; Yang, W.; Zhai, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Air and Argon Cold Plasma Effects on Lipolytic Enzymes Inactivation, Physicochemical Properties and Volatile Profiles of Lightly-Milled Rice. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Chen, W.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. The Effects of Cold Plasma (CP) Treatment on the Inactivation of Yam Peroxidase and Characteristics of Yam Slices. J. Food Eng. 2023, 359, 111693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, J.-H. Effects of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Cold Plasma on the Activity, Structure and Conformation of Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) and on the Activity of Litchi Peroxidase (POD). LWT 2021, 141, 111078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, N.; Ji, H.; Zhang, X.; Dong, C.; Yu, J.; Yan, S.; Chen, C.; Liang, L. Effects of Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment on the Storage Quality and Chlorophyll Metabolism of Postharvest Tomato. Foods 2022, 11, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, N.; Dong, C.; Zheng, P.; Ji, H.; Yu, J.; Yan, S.; Chen, C.; Liang, L. Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Softening of Winter Jujubes (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv. Dongzao). Horticulturae 2023, 9, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, F.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W. Improving Food Drying Performance by Cold Plasma Pretreatment: A Systematic Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 4402–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayookha, V.P.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; Padma Ishwarya, S.; Chandra Khanashyam, A.; Kutlu, N.; Rifna, E.J.; Kumar, M.; Panesar, P.S.; Abd El-Maksoud, A.A. Ozone and Cold Plasma: Emerging Oxidation Technologies for Inactivation of Enzymes in Fruits, Vegetables, and Fruit Juices. Food Control 2023, 144, 109399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Pankaj, S.K.; Segat, A.; Ishikawa, K. Cold Plasma Interactions with Enzymes in Foods and Model Systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 55, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Activities and Conformation Changes of Food Enzymes Induced by Cold Plasma: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R. Application of Electronic Nose as a Non-Invasive Technique for Odor Fingerprinting and Detection of Bacterial Foodborne Pathogens: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Mahoney, N.E.; Pan, Z.; Khir, R.; Wu, B.; Ma, H.; Zhao, L. Effectiveness of Pulsed Light Treatment for Degradation and Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Rough Rice and Rice Bran. Food Control 2016, 59, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godana, E.A.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Mehari, T.G.; Zhang, H. Biotechnological and Biocontrol Approaches for Mitigating Postharvest Diseases Caused by Fungal Pathogens and Their Mycotoxins in Fruits: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17584–17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; He, Y.; Yuan, B.; Li, L.; Luo, L.; You, T. Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Mycotoxins in Agricultural Products: Recent Advances in Optical and Electrochemical Sensing Methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, M.; Xu, K.; Song, W.; Chen, Q.; Wen, H. Safeguarding Food Safety: Nanomaterials-Based Fluorescent Sensors for Pesticide Tracing. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Yang, X.; Yu, B.; Zhuang, J.; Xu, H.; Xiang, Q.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z. Recent Advances in the Degradation Efficacy and Mechanisms of Mycotoxins in Food by Atmospheric Cold Plasma. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, N.N.; Yadav, B.; Roopesh, M.S.; Jo, C. Cold Plasma for Effective Fungal and Mycotoxin Control in Foods: Mechanisms, Inactivation Effects, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ye, Z.; Xing, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, W. Degradation of Deoxynivalenol in Wheat by Double Dielectric Barrier Discharge Cold Plasma: Identification and Pathway of Degradation Products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwabor, O.F.; Onyeaka, H.; Miri, T.; Obileke, K.; Anumudu, C.; Hart, A. A Cold Plasma Technology for Ensuring the Microbiological Safety and Quality of Foods. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan-Mahdavi, S.; Mirzazadeh, M.; Alam, Z.; Solaimanimehr, S. The Effect of Chitosan Coating Combined with Cold Plasma on the Quality and Safety of Pistachio during Storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 4296–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, Z.; Hosseinzadeh Samani, B.; Nazari, F.; Rostami, S.; Nemati, A. The Green Technology of Cold Plasma Jet on the Inactivation of Aspergillus flavus and the Total Aflatoxin Level in Pistachio and Its Quality Properties. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ileleji, K.; Stroshine, R.L.; Keener, K.; Jensen, J.L. Reduction of Aflatoxin in Corn by High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Bian, K. Structures of Reaction Products and Degradation Pathways of Aflatoxin B1 by Ultrasound Treatment. Toxins 2019, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, F.; Mosallaie, F.; Sanaei, F.; Falah, F.; Vasiee, A.; Yazdi, F.T. The Simultaneous Influence of Ultraviolet Rays and Cold Plasma on the Physicochemical Attributes and Shelf Life of Dried Pistachios during the Storage Period. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojnik, N.; Modic, M.; Žigon, D.; Kovač, J.; Jurov, A.; Dickenson, A.; Walsh, J.L.; Cvelbar, U. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma-assisted Removal of Aflatoxin B1 from Contaminated Corn Kernels. Plasma Process. Polym. 2021, 18, 2000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topolovec, B.; Škoro, N.; Puač, N.; Petrovic, M. Pathways of Organic Micropollutants Degradation in Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Processing—A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Jiang, W.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Residue Behaviors of Six Pesticides during Apple Juice Production and Storage. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Duan, J.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Z. Degradation of Pesticides in Wheat Flour during Noodle Production and Storage. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2022, 39, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hassan, M.M.; Ali, S.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Self-Cleaning-Mediated SERS Chip Coupled Chemometric Algorithms for Detection and Photocatalytic Degradation of Pesticides in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.M.R.; Ma, H.; Xu, B.; Devi, S.; Stanley, S.L.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Zhu, J. Multi-Frequency Multi-Mode Ultrasound Treatment for Removing Pesticides from Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and Effects on Product Quality. LWT 2021, 143, 111147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Azeem, A.; Sikandar Zaman, M.; Zia Ul Haq, M. From Field to Table: Ensuring Food Safety by Reducing Pesticide Residues in Food. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandiselvam, R.; Kaavya, R.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Divya, V.; Abdullah, S.K.; Aurum, F.S.; Dakshyani, R.; Kothakota, A.; Ramesh, S.V.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. Research Trends and Emerging Physical Processing Technologies in Mitigation of Pesticide Residues on Various Food Products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 45131–45149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavahian, M.; Sarangapani, C.; Misra, N.N. Cold Plasma for Mitigating Agrochemical and Pesticide Residue in Food and Water: Similarities with Ozone and Ultraviolet Technologies. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelakshmi, V.P.; Vendan, S.E.; Negi, P.S. Cold Plasma Treatment for Decontamination of Pesticide Residues and Preservation of Spinach Leaves. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 220, 113322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasan, R.; Jaspin, S.; Bhavadharini, B.; Pare, A.; Pandiselvam, R.; Mahendran, R. Chlorpyrifos Pesticide Reduction in Soybean Using Cold Plasma and Ozone Treatments. LWT 2022, 159, 113193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangapani, C.; O’Toole, G.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Atmospheric Cold Plasma Dissipation Efficiency of Agrochemicals on Blueberries. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yan, W. Effect of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma on the Degradation of Malathion and Chlorpyrifos on Lettuce. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, D.; Feng, X. Plasma Degradation of Pesticides on the Surface of Corn and Evaluation of Its Quality Changes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Zhou, R.; Liu, D.; Song, Y.; Niu, J. Treatment of Omethoate on Edible Wolfberry by Atmospheric Pressure Air Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Yu, F.; Xi, D.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Removal of Organophosphorus Pesticide Residues from Lycium Barbarum by Gas Phase Surface Discharge Plasma. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Sun, D.-W.; Cheng, J.-H.; Johnson Esua, O. Effects of Combined Treatment of Plasma Activated Liquid and Ultrasound for Degradation of Chlorothalonil Fungicide Residues in Tomato. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Effect of Plasma Activated Water and Buffer Solution on Fungicide Degradation from Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Fruit. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H. Recent Advances in the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds with Subcritical Water: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Martín, E.; Forbes-Hernández, T.; Romero, A.; Cianciosi, D.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Influence of the Extraction Method on the Recovery of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds from Food Industry By-Products. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 131918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, W.; Rehman, A.; Hussain, A.; Karim, A.; Sharif, H.R.; Siddiquy, M.; Lianfu, Z. Optimization of Extraction Process and Estimation of Flavonoids from Fenugreek Using Green Extracting Deep Eutectic Solvents Coupled with Ultrasonication. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchabo, W.; Ma, Y.; Kwaw, E.; Xiao, L.; Wu, M.; Apaliya, M.T. Impact of Extraction Parameters and Their Optimization on the Nutraceuticals and Antioxidant Properties of Aqueous Extract Mulberry Leaf. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, B.; Pang, Z.; Liu, X.; Jatoi, M.A.; Mehmood, A.; Rashid, M.T.; Ali, N.; Naveed, M. Flaxseed Gum: Extraction, Bioactive Composition, Structural Characterization, and Its Potential Antioxidant Activity. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; He, R.; Ma, H.; Wu-Chen, R.A.; Zhang, T. Influence of Nitrogen Protection on the Extraction Yield and Antioxidant Activities of Polyphenols by Ultrasonic-assisted Extraction from Rapeseed Meal. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Ji, D.; He, S.; Ma, H. Optimization of Ultrasonic-assisted Extraction Conditions for Bioactive Components from Coffee Leaves Using the Taguchi Design and Response Surface Methodology. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpabli-Tsigbe, N.D.K.; Ma, Y.; Ekumah, J.; Osabutey, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, M.; Johnson, N.A.N.; Mintah, B.K. Ultrasonic-assisted Extraction of Bioactive Chlorogenic Acid from Heilong48 Soybean Variety: Parametric Optimization and Evaluation of Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzah, C.S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Ma, H. The Effects of Ultrasound Assisted Extraction on Yield, Antioxidant, Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenol Extracts: A Review. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Ghobadian, B.; Ebadi, M.; Ghomi, H. Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Extracted Oil from Camelina Sativa Seed Treated by Discharge Cold Plasma. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2020, 60, e202000032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, Q.; Wang, L. Extraction of Anthocyanins from Haskap Using Cold Plasma-assisted Enzyme. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmizadeh, A.; Goli, S.A.H.; Rahimmalek, M. Application of Cold Plasma Pretreatment to Improve the Extraction Efficiency of Tanshinone Compounds from Salvia Subg. Perovskia Root. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 204, 117337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, X.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Brennan, C.S.; Yan, J. Application of Nonthermal Processing Technologies in Extracting and Modifying Polysaccharides: A Critical Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4367–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, F.; Ebadi, M.-T.; Ayyari, M. Qualitative Changes in Hyssop (Hyssopus officinalis L.) as Affected by Cold Plasma, Packaging Method and Storage Duration. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 22, 100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi-Sadr, J.; Ebadi, M.; Ayyari, M.; Ghomi, H. Optimization of Ultrasonic Bath and Cold Plasma Pre-treatments in the Spearmint Essential Oil Isolation Process. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1904–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, F.; Ebadi, M.; Ghomi, H.; Rezaeinezhad, A.R.; Faghih Haghani, S. Increasing the Efficiency of Cumin Essential Oil Extraction Using Cold Plasma Pretreatments. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5001–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alashti Fatemeh, J.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Ahmadian, S.; Kenari, R.E.; Nazifi, E. Impact of Atmospheric Cold Plasma Pretreatment on Morphology, Structure, and Chemical Properties of Clove (Syzygium aromaticum). LWT 2024, 191, 115639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Bae, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, S.; Jo, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Park, S. Structural and Functional Changes in Soybean Protein via Remote Plasma Treatments. Molecules 2023, 28, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Bao, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Huang, J.-Y. Effect of High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma on Extraction of Fenugreek Galactomannan and Its Physicochemical Properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.-J.; Lin, T.-C.; Chao, H.-R.; Tsai, C.-H.; Lu, J.-H.; Tsai, M.-H.; Chang, C.-T.; Hsieh, H.; Lu, I.-C.; Arcega, R.D.; et al. The Impact of Air or Nitrogen Non-Thermal Plasma on Variations of Natural Bioactive Compounds in Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.) Seed and the Potential Effects for Human Health. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, B.; ElGasim, A.; Yagoub, A.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C. Role of Drying Techniques on Physical, Rehydration, Flavor, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Characteristics of Garlic. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Fakayode, O.A.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, C. Combinative Effect of Cutting Orientation and Drying Techniques (Hot Air, Vacuum, Freeze and Catalytic Infrared Drying) on the Physicochemical Properties of Ginger (Zingiber Officinale Roscoe). LWT 2021, 144, 111238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Sun, Y.; Arun, M.S.; Ma, H.; Zhou, C. Role of Thermal and Non-thermal Drying Techniques on Drying Kinetics and the Physicochemical Properties of Shiitake Mushroom. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanor-Atiemoh, R.; Zhou, C.; Mujumdar, A.; Osae, R.; Taiye Mustapha, A.; Wahia, H.; Sampson, G.; Amoa-Owusu, A.; Ma, H. Effect of Simultaneous Dual-frequency Ultrasound Aided Ethanolic Pretreatment on Drying Kinetics, Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Physicochemical Properties of Apple Slices Using Pulsed Vacuum Dryer. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Sun, W.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Shang, N.; Lv, W.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Effect of Different Drying Techniques on Drying Kinetics, Nutritional Components, Antioxidant Capacity, Physical Properties and Microstructure of Edamame. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Sylvain Tiliwa, E.; Yan, W.; Roknul Azam, S.M.; Wei, B.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Bhandari, B. Recent Development in High Quality Drying of Fruits and Vegetables Assisted by Ultrasound: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, M.; Chitrakar, B.; Wei, B.; Wang, B.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, B.; Chang, L.; Ren, G.; et al. Selection of Drying Techniques for Pingyin Rose on the Basis of Physicochemical Properties and Volatile Compounds Retention. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Mohanty, P.; Sahu, J.K.; Sahu, J.N. A Critical Review on Drying of Food Materials: Recent Progress and Key Challenges. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 158, 107863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobot, M.; Kozłowska, M.; Ignaczak, A.; Kowalska, H. Development of Drying and Roasting Processes for the Production of Plant-Based pro-Healthy Snacks in the Light of Nutritional Trends and Sustainable Techniques. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 149, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, W.; Aziz, T.; Khojah, E.; Al-Asmari, F.; Alamri, A.S.; Alhomrani, M.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Drying Kinetics and Moisture Migration Mechanism of Yam Slices by Cold Plasma Pretreatment Combined with Far-Infrared Drying. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 95, 103730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.-W.; Li, D.-D.; Abulaiti, R.; Wang, M.; Wu, X.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, J. Cold Plasma as a Novel Pretreatment to Improve the Drying Kinetics and Quality of Green Peas. Foods 2025, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wei, B.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Chalamaiah, M.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Z. Dielectric Pretreatment of Rapeseed 1: Influence on the Drying Characteristics of the Seeds and Physico-Chemical Properties of Cold-Pressed Oil. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkari, A.; Dadashi, S.; Heshmati, M.K.; Dehghannya, J.; Ramezan, Y. The Effect of Cold Plasma Pretreatment on Drying Efficiency of Beetroot by Intermittent Microwave-Hot Air (IMHA) Hybrid Dryer Method: Assessing Drying Kinetic, Physical Properties, and Microstructure of the Product. LWT 2024, 212, 117010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Zhong, C.-S.; Zheng, Z.-A.; An, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, Q.; Xiao, H.-W. Cold Plasma Enhances Drying and Color, Rehydration Ratio and Polyphenols of Wolfberry via Microstructure and Ultrastructure Alteration. LWT 2020, 134, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namjoo, M.; Moradi, M.; Dibagar, N.; Niakousari, M. Cold Plasma Pretreatment Prior to Ultrasound-Assisted Air Drying of Cumin Seeds. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 2065–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Shishir, M.R.I.; Bao, T.; Chen, W. Effect of Cold Plasma Pretreated Hot-air Drying on the Physicochemical Characteristics, Nutritional Values and Antioxidant Activity of Shiitake Mushroom. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6271–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miraei Ashtiani, S.-H.; Rafiee, M.; Mohebi Morad, M.; Khojastehpour, M.; Khani, M.R.; Rohani, A.; Shokri, B.; Martynenko, A. Impact of Gliding Arc Plasma Pretreatment on Drying Efficiency and Physicochemical Properties of Grape. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 63, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obajemihi, O.I.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Novel Cold Plasma Functionalized Water Pretreatment for Improving Drying Performance and Physicochemical Properties of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Fruits during Infrared-Accelerated Pulsed Vacuum Drying. J. Food Eng. 2024, 379, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Effect of High-Voltage Electrostatic Field on Inorganic Nitrogen Uptake by Cucumber Plants. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, C.; Bian, Z.; Ye, Z.; Meng, L.; Xia, L.; Bao, E.; Cao, K. Abscisic Acid and Reactive Oxygen Species Were Involved in Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water-Promoted Seed Germination in Watermelon. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 291, 110581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, A.; Javed, Q.; Sun, J.; Ullah, I.; Buttar, N.A.; Saifullah, M.; Du, D. Effect of Salt Stress on Seed Germination and Seedling Vigour in Okra. Indian J. Hortic. 2020, 77, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Park, G. The Effects of Plasma on Plant Growth, Development, and Sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Li, Y.; Dhaliwal, H.; Feng, M.; Xiang, Q.; Roopesh, M.S.; Pan, D.; Du, L. The Application of Cold Plasma Technology in Low-Moisture Foods. Food Eng. Rev. 2023, 15, 86–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namjoo, M.; Moradi, M.; Dibagar, N.; Taghvaei, M.; Niakousari, M. Effect of Green Technologies of Cold Plasma and Airborne Ultrasound Wave on the Germination and Growth Indices of Cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) Seeds. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e14166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabderrahim, M.A.; Bettaieb, I.; Hannachi, H.; Rejili, M.; Dufour, T. Cold Plasma Treatment Boosts Barley Germination and Seedling Vigor: Insights into Soluble Sugar, Starch, and Protein Modifications. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 116, 103852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsimaab, S.P.; Makarian, H.; Ghasimi Hagh, Z.; Gholipoor, M. Scanning Electron Microscopy, Biochemical and Enzymatic Studies to Evaluate Hydro-Priming and Cold Plasma Treatment Effects on the Germination of Salvia Leriifolia Benth. Seeds. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1035296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Lyu, X.; Shi, L. Effects of Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Continuous and Interval Treatments on Oat Seed Germination. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Darmanin, M.; Fröhling, A.; Bußler, S.; Durek, J.; Neugart, S.; Schreiner, M.; Blundell, R.; Gatt, R.; Schlüter, O.; Valdramidis, V.P. Aqueous and Gaseous Plasma Applications for the Treatment of Mung Bean Seeds. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Lan, Q.; Pritchard, H.W.; Xue, H.; Wang, X. Reactive Oxygen Species Induced by Cold Stratification Promote Germination of Hedysarum Scoparium Seeds. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 109, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sajib, S.A.; Rahi, M.S.; Tahura, S.; Roy, N.C.; Parvez, S.; Reza, M.A.; Talukder, M.R.; Kabir, A.H. Mechanisms and Signaling Associated with LPDBD Plasma Mediated Growth Improvement in Wheat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildažienė, V.; Aleknavičiūtė, V.; Žūkienė, R.; Paužaitė, G.; Naučienė, Z.; Filatova, I.; Lyushkevich, V.; Haimi, P.; Tamošiūnė, I.; Baniulis, D. Treatment of Common Sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) Seeds with Radio-Frequency Electromagnetic Field and Cold Plasma Induces Changes in Seed Phytohormone Balance, Seedling Development and Leaf Protein Expression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.Y.; Prendeville, J.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Cold Plasma Technology in Food Packaging. Coatings 2022, 12, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.A.; Ayub, A.; Wani, A.K. Bioactive Compounds in Active Food Packaging (ACP): Health and Safety Considerations. In Green Materials for Active Food Packaging; Islam, S.u., Shahid, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 335–357. ISBN 978-981-96-0369-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Kumar, Y.; Singh, V.; Kaur, J.; Panesar, P.S. Cold Plasma Technology: Reshaping Food Preservation and Safety. Food Control 2024, 163, 110537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, P. Effects of In-package Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment on the Qualitative, Metabolic and Microbial Stability of Fresh-cut Pears. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4473–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, Y.; Bai, J.; Cai, J. Effects of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment on the Quality and Cellulose Modification of Brown Rice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 96, 103744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.-W.; Li, D.-D.; Aheto, J.H.; Qi, Z.-Y.; Reziwanguli, A.; Cai, J.-R.; Tian, X.-Y. Effects of Three Emerging Non-Thermal Pretreatments on Drying Kinetics, Physicochemical Quality, and Microstructure of Garlic Slices. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 4325–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezan, Y.; Kamkari, A.; Lashkari, A.; Moradi, D.; Tabrizi, A.N. A Review on Mechanisms and Impacts of Cold Plasma Treatment as a Non-thermal Technology on Food Pigments. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 1502–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.-W.; Xiao, H.-W.; Ma, H.-L.; Zhou, C.-S. Artificial Neural Network Modeling of Drying Kinetics and Color Changes of Ginkgo Biloba Seeds during Microwave Drying Process. J. Food Qual. 2018, 1, 3278595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osae, R.; Zhou, C.; Xu, B.; Tchabo, W.; Tahir, H.E.; Mustapha, A.T.; Ma, H. Effects of Ultrasound, Osmotic Dehydration, and Osmosonication Pretreatments on Bioactive Compounds, Chemical Characterization, Enzyme Inactivation, Color, and Antioxidant Activity of Dried Ginger Slices. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladejo, A.O.; Ma, H.; Qu, W.; Zhou, C.; Wu, B.; Yang, X. Influence of Ultrasound Pretreatments on Diffusion Coefficients, Texture and Colour of Osmodehydrated Sweet Potato (Ipomea batatas). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Qin, Y.; Gao, X. Recent Research and Prospects of Non-Thermal Physical Technologies in Green and High-Efficient Extraction of Natural Pigments: A Review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 92, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, D.S.; Amorim, I.S.; Chisté, R.C.; Filho, J.T.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Godoy, H.T. Effects of Cold Plasma on Chlorophylls, Carotenoids, Anthocyanins, and Betalains. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umair, M.; Jabbar, S.; Nasiru, M.M.; Senan, A.M.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, J. Sequential Application of High-Voltage Electric Field Cold Plasma Treatment and Acid Blanching Improves the Quality of Fresh Carrot Juice (Daucus carota L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15311–15318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varilla, C.; Marcone, M.; Annor, G.A. Potential of Cold Plasma Technology in Ensuring the Safety of Foods and Agricultural Produce: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ju, S.; Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Du, M.; Zhuang, J.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z.; Zhou, R.; Cullen, P.J. Effect of Cold Atmospheric Surface Microdischarge Plasma on the Inactivation of Fusarium Moniliforme and Physicochemical Properties of Chinese Yam Flour. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Guha, P.; Srivastav, P.P. Effect of High Voltage Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment on Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Taro (Colocasia esculenta) Starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Park, H.H.; Min, S.C. Microbial Decontamination of Red Pepper Powder Using Pulsed Light Plasma. J. Food Eng. 2020, 284, 110075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, A.; Lv, Z.; Gao, Z. Nondestructive Measurement of Kiwifruit Firmness, Soluble Solid Content (SSC), Titratable Acidity (TA), and Sensory Quality by Vibration Spectrum. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, B.; Guo, X.; Liu, D.; Qiu, C.; Ma, H. Effect of Thermosonication on Texture Degradation of Carrot Tissue in Relation to Alterations in Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Structure. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.; Tuly, J.A. Physicochemical Indicators Coupled with Statistical Tools for Comprehensive Evaluation of the Novel Infrared Peeling on Tomatoes. LWT 2024, 191, 115634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Liu, B.; Wu, B.; Guo, Y.; Song, C.; Nan, S.; Dai, J.; Shen, Y.; Ma, H. A Study on the Effect Mechanism of Pectin Modification on the Carrot Cell Wall’s Texture Formation under Ultrasonic and Infrared Drying. Agriculture 2024, 14, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, M.A.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Pandiselvam, R.; Joshi, T.J.; Thomas, P.E.; Zhang, Y.; Rustagi, S.; Bharti, S.; Thirumdas, R.; Kumar, M.; et al. Implications of Cold Plasma and Plasma Activated Water on Food Texture—A Review. Food Control 2023, 151, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarghuei, F.M.; Etemadi, M.; Ramezanian, A.; Esehaghbeygi, A.; Alizargar, J. An Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Basil. Plants 2021, 10, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargarchi, S.; Esatbeyoglu, T. Assessing the Impact of Cold Plasma Rotational Dynamics on Ginger’s Total Phenolic Content, Antioxidant Activity, Surface Structure and Color Using Response Surface Methodology. LWT 2024, 208, 116682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xue, Y.; Guo, J.; Ren, H.; Jiang, S.; Li, D.; Song, J.; Zhang, Z. Citric Acid and Sucrose Pretreatment Improves the Crispness of Puffed Peach Chips by Regulating Cell Structure and Mechanical Properties. LWT 2021, 142, 111036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, J.; Yuan, J.; Azam, S.R.; Zhang, M. Effect of Different Thawing Methods on the Efficiency and Quality Attributes of Frozen Red Radish. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3237–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Song, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, C.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, M.; et al. Effects of Pre-Drying Treatments Combined with Explosion Puffing Drying on the Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities and Flavor Characteristics of Apples. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.T.; Ma, H.; Safdar, B.; Ahmed Jatoi, M.; Wali, A.; Sarpong, F.; Zhou, C. Synergy of Ultrasound and Osmotic Dehydration in Improving Drying Kinetics and Quality of Dried Sweet Potato (Ipomea batatas L.). J. Food Saf. Food Qual.-Arch. Leb. 2019, 70, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, M.; Chitrakar, B.; Cheng, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, B.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H. Multi-Frequency Power Thermosonication Treatments of Clear Strawberry Juice: Impact on Color, Bioactive Compounds, Flavor Volatiles, Microbial and Polyphenol Oxidase Inactivation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 84, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhao, S.; Sun, H.; Pei, J.; Gao, R.; Jiang, P. Characterization and Discrimination of Flavor Volatiles of Different Colored Wheat Grains after Cooking Based on GC-IMS and Chemometrics. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Mehmood, A.; Lu, T.; Chen, X. Unraveling the Temporal Changes of Maillard Reaction Products and Aroma Profile in Coffee Leaves during Hot-Air Drying. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 128, 106055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Gu, D.; Tao, H.; Zhang, R. Organic Acid and Aromatic Compounds Create Distinctive Flavor in the Blackening Process of Jujube. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sruthi, N.U.; Josna, K.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; Gavahian, M.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. Impacts of Cold Plasma Treatment on Physicochemical, Functional, Bioactive, Textural, and Sensory Attributes of Food: A Comprehensive Review. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Gao, R. Analysis of the Changes of Volatile Flavor Compounds in a Traditional Chinese Shrimp Paste during Fermentation Based on Electronic Nose, SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, T.; Qi, X.; Lu, D.; Chen, B. Analyzing Changes of Volatile Components in Dried Pork Slice by Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectroscopy. CyTA J. Food 2020, 18, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Characterization of Selected Chinese Soybean Paste Based on Flavor Profiles Using HS-SPME-GC/MS, E-Nose and E-Tongue Combined with Chemometrics. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y. Characterization of the Volatile Flavor Profiles of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar Combining a Novel Nanocomposite Colorimetric Sensor Array with HS-SPME-GC/MS. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, R.; Arun Prasath, V.; Karpoora Sundara Pandian, N.; Patra, A.; Sharma, P.; Arulkumar, M.; Sivaranjani, S.; Govindarasu, P. Investigating the Influence of Pin-to-Plate Atmospheric Cold Plasma on the Physiochemical, Nutritional, and Shelf-Life Study of Two Raisins Varieties during Storage. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 7774–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, S.; Kenari, R.E.; Amiri, Z.R.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Khodaparast, M.H.H. Effect of Ultrasound-Assisted Cold Plasma Pretreatment on Cell Wall Polysaccharides Distribution and Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Hyssop (Hyssopus officinalis L.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirabadi, S.; Milani, J.M.; Sohbatzadeh, F. Application of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma to Hydrophobically Modification of Gum Arabic with Enhanced Surface Properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, F.; Ebadi, M.-T.; Ghomi, H.; Ayyari, M. Changes in Qualitative Characteristics of Garden Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) as Affected by Cold Plasma. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2022, 31, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chai, Z.; Hutabarat, R.P.; Zeng, Q.; Niu, L.; Li, D.; Yu, H.; Huang, W. Blueberry Leaves from 73 Different Cultivars in Southeastern China as Nutraceutical Supplements Rich in Antioxidants. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.-C.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S.; Ee, K.-Y.; Chai, T.-T. Advances on the Antioxidant Peptides from Edible Plant Sources. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cai, M.; Chen, G. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Polyphenolic Compounds from Red Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Bran and Their Biological Activities and Polyphenolic Compositions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremnezhad, S.; Soltani, M.; Faraji, A.; Hayaloglu, A.A. Chemical Changes of Food Constituents during Cold Plasma Processing: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Pipliya, S.; Srivastav, P.P. Effect of Cold Plasma on Different Polyphenol Compounds: A Review. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakshayani, R.; Paul, A.; Mahendran, R. Cold Plasma-Induced Effects on Bioactive Constituents and Antioxidant Potential of Lotus Petal Powder. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2021, 49, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garimella, J.N.; Pradhan, R.C. Effect of (Multi Pin) Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment on Curcumin Extraction and Investigating Phytochemicals, Antioxidants, Physical and Morphological Properties of Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Powder. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibian, S.A.; Labbafi, M.; Askari, G.H.; Rezaeinezhad, A.R.; Ghomi, H. Effect of Gliding Arc Discharge Plasma Pretreatment on Drying Kinetic, Energy Consumption and Physico-Chemical Properties of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.). J. Food Eng. 2020, 270, 109766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H. Plant Protein-Derived Antioxidant Peptides: Isolation, Identification, Mechanism of Action and Application in Food Systems: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharini, M.; Jaspin, S.; Mahendran, R. Cold Plasma Reactive Species: Generation, Properties, and Interaction with Food Biomolecules. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, E.; Yin, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Ho, C.-T. Enhancing Activities of Salt-Tolerant Proteases Secreted by Aspergillus oryzae Using Atmospheric and Room-Temperature Plasma Mutagenesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N.; Yousefi, M.; Nematollahi, A.; Khorshidian, N. Effect of Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment on Technological and Nutrition Functionality of Protein in Foods. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukagoshi, H. Control of Root Growth and Development by Reactive Oxygen Species. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 29, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mintah, B.K.; Xu, H.; Dabbour, M.; Cheng, Y.; Dai, C.; He, R.; Ma, H. Effects of Nonthermal Physical Processing Technologies on Functional, Structural Properties and Digestibility of Food Protein: A Review. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e14010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of Plasma Chemistry on the Interfacial Performance of Protein and Polysaccharide in Emulsion. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalari, G.; Barreca, D.; Gervasi, T.; Roussell, M.A.; Klein, B.; Feeney, M.J.; Carughi, A. Pistachio Nuts (Pistacia vera L.): Production, Nutrients, Bioactives and Novel Health Effects. Plants 2021, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Peng, L.; Cao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, C. Insights into Cold Plasma Treatment on the Cereal and Legume Proteins Modification: Principle, Mechanism, and Application. Foods 2024, 13, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Aalim, H.; Cao, Y.; Peng, L.; Dou, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, X.; Guo, Z.; Cai, J.; et al. Cold Plasma-Assisted Pretreatment for Fabrication and Characterization of Rice Starch-Stearic Acid Complexes. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liao, X.; Li, C.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.; Siva, S.; Cui, H. Cold Nitrogen Plasma Modified Cuminaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex and Its Application in Vegetable Juices Preservation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopuk, B.; Gunes, R.; Palabiyik, I. Cold Plasma Modification of Food Macromolecules and Effects on Related Products. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.W.; Roobab, U.; Wang, Z.; Raza, M.M.; Nawazish, H.; Islam, F.; Aadil, R.M. Salt Reduction in Food Products: A Systematic Review of Clean-Label Ingredients and Non-Thermal Technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 153, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaddu, S.; Sonkar, S.; Seth, D.; Dwivedi, M.; Pradhan, R.C.; Goksen, G.; Kumar Sarangi, P.; Režek Jambrak, A. Cold Plasma: Unveiling Its Impact on Hydration, Rheology, Nutritional, and Anti-Nutritional Properties in Food Materials—An Overview. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarshini, A.; Rajauria, G.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Emerging Food Processing Technologies and Factors Impacting Their Industrial Adoption. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3082–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, S.-H.M.; Aghkhani, M.H.; Feizy, J.; Martynenko, A. Effect of Cold Plasma Pretreatment Coupled with Osmotic Dehydration on Drying Kinetics and Quality of Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 2854–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, E.; Hosseini, S.I.; Samadlouie, H.R.; Mohammadhosseini, B.; Cullen, P.J. Surface Barrier Discharge Remote Plasma Inactivation of Aspergillus Niger ATCC 10864 Spores for Packaged Crocus Sativus. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Srivastav, P.P. Effect of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma-Activated Water Pre-Treatment on the Drying Properties, Kinetic Parameters, and Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Centella asiatica Leaves. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelarat, W.; Sangwanna, S.; Panklai, T.; Chaosuan, N.; Bootchanont, A.; Wattanawikkam, C.; Subcharoen, A.; Subcharoen, N.; Chanchula, N.; Boonyawan, D.; et al. Enhanced Fruiting Body Production and Bioactive Phytochemicals from White Cordyceps militaris by Blending Cordyceps militaris and Using Cold Plasma Jet. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Hao, X.; Shishir, M.R.I.; Karim, N.; Chen, W. Green Alternative Methods for Pretreatment of Whole Jujube before the Drying Process. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Yang, D.; Huang, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, C. Advances in Atmospheric Cold Plasma Technology for Plant-Based Food Safety, Functionality, and Quality Implications. Foods 2025, 14, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172999
Liu S, Yang D, Huang J, Huang H, Sun J, Yang Z, Zhou C. Advances in Atmospheric Cold Plasma Technology for Plant-Based Food Safety, Functionality, and Quality Implications. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172999
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Siyao, Danni Yang, Jiangqi Huang, Huiling Huang, Jinyuan Sun, Zhen Yang, and Chenguang Zhou. 2025. "Advances in Atmospheric Cold Plasma Technology for Plant-Based Food Safety, Functionality, and Quality Implications" Foods 14, no. 17: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172999
APA StyleLiu, S., Yang, D., Huang, J., Huang, H., Sun, J., Yang, Z., & Zhou, C. (2025). Advances in Atmospheric Cold Plasma Technology for Plant-Based Food Safety, Functionality, and Quality Implications. Foods, 14(17), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172999