In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Arecanut Polysaccharides: Effects on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Extraction and Purification of PAP1b
2.3. In Vitro Digestion of PAP1b
2.3.1. Simulated Digestive Solution Preparation
2.3.2. Oral Digestion
2.3.3. Gastric Digestion
2.3.4. Small Intestinal Digestion
2.4. In Vitro Fermentation of PAP1b
2.4.1. Design for Fecal Fermentation
2.4.2. pH Determination
2.4.3. Determination of SCFAs by GC
2.4.4. Determination of Gas Production During In Vitro Fermentation
2.5. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.6. Analysis of Intestinal Microbial Metabolites
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
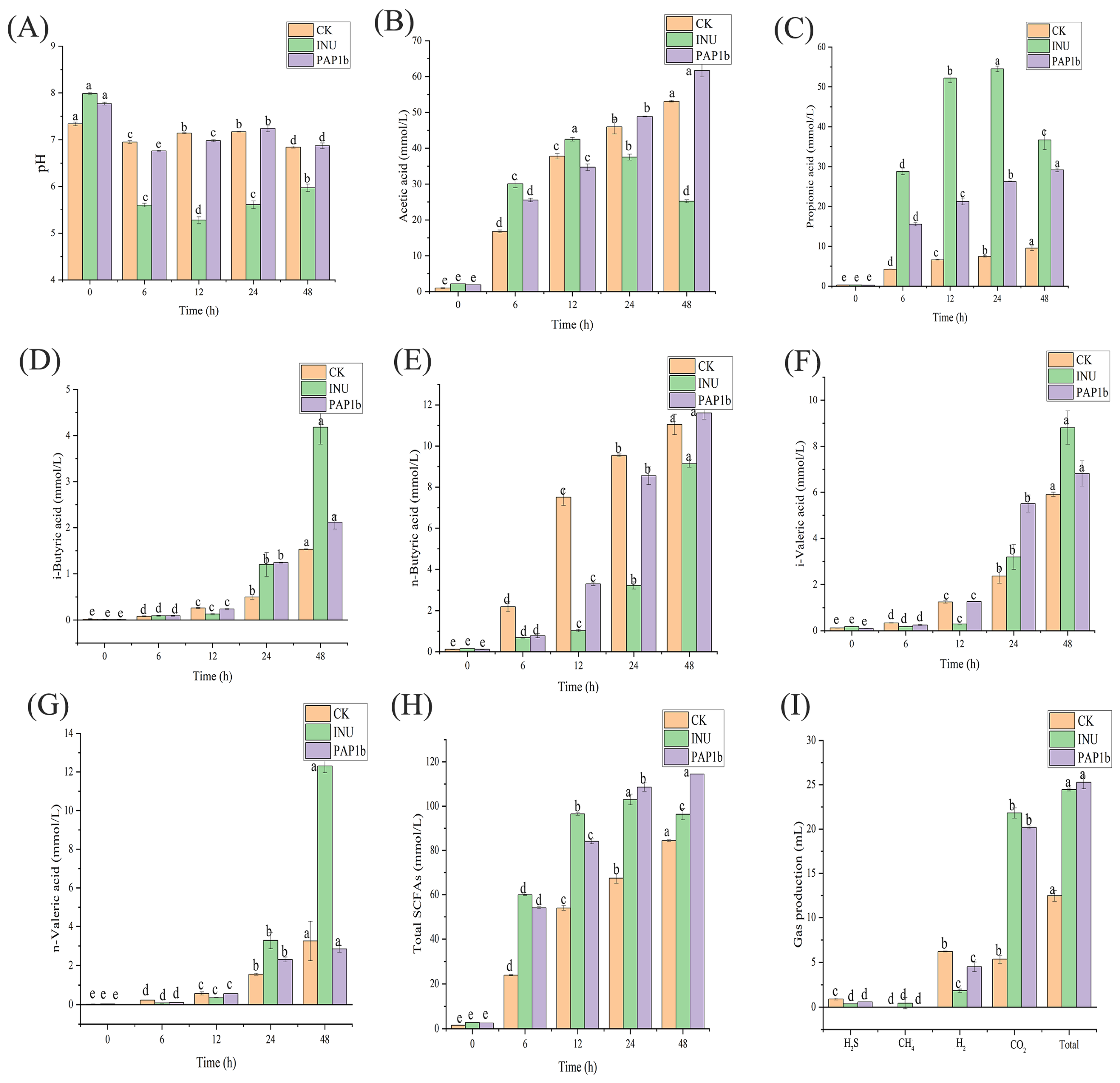
3.1. Impacts of PAP1b on pH and SCFAs in In Vitro Fermentation
3.2. Impacts of PAP1b on Gas Volume in In Vitro Fermentation
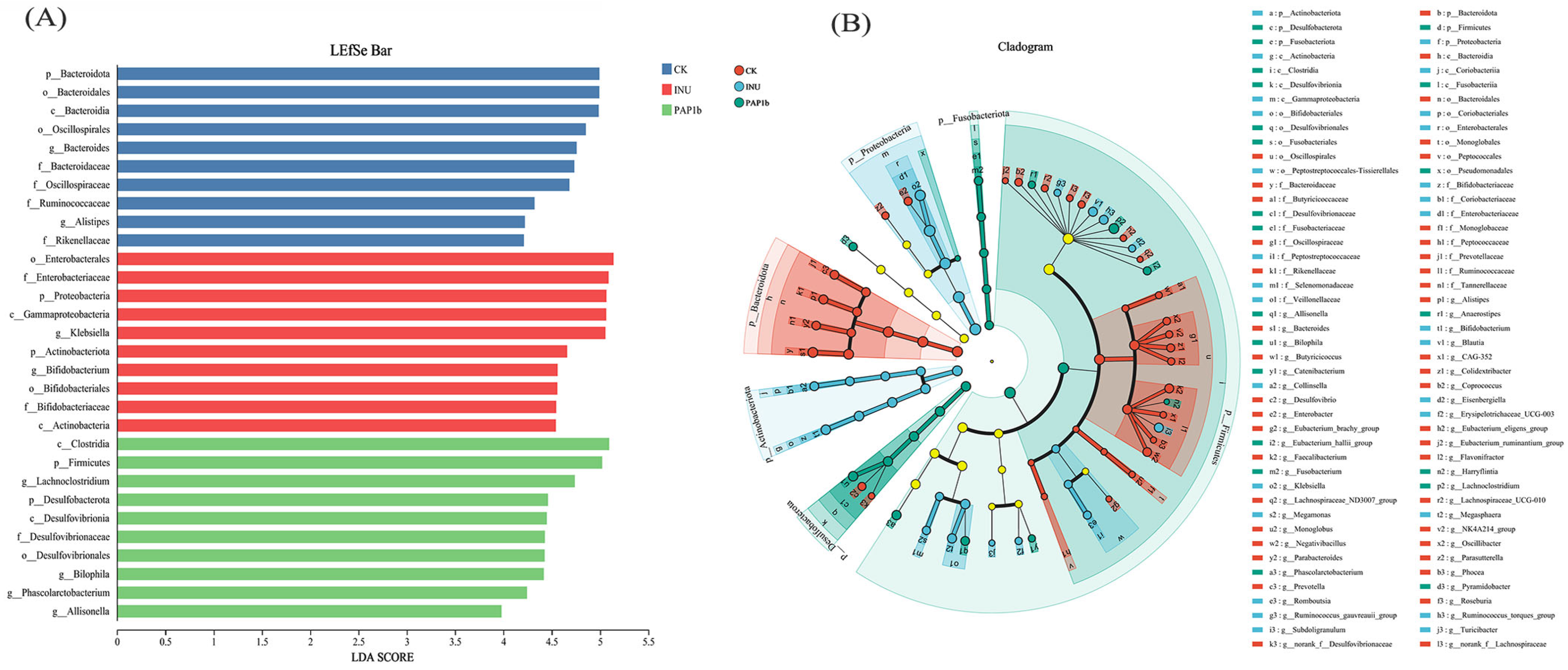
3.3. Impacts of PAP1b on Microbial Communities
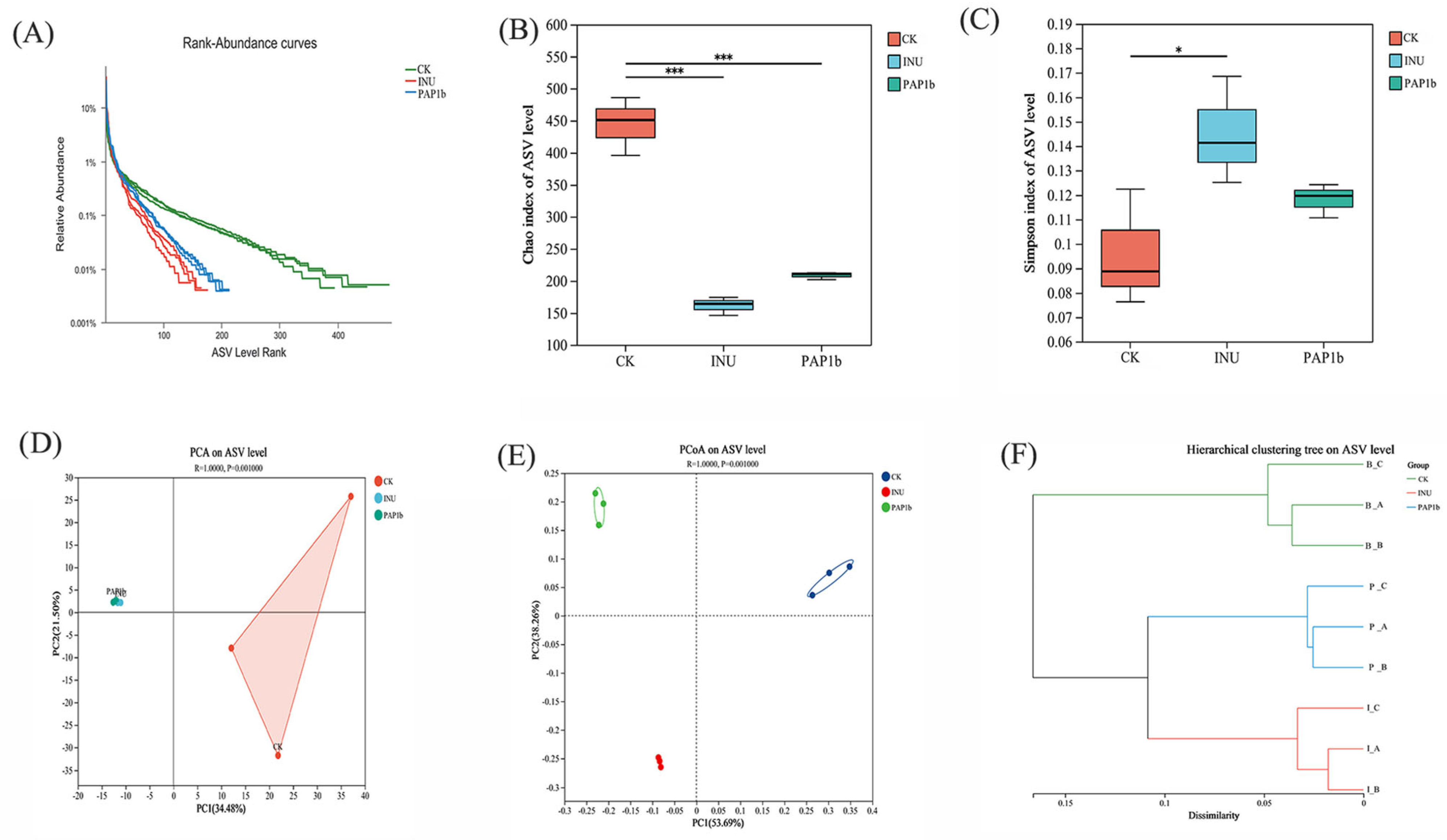
3.3.1. Impacts of PAP1b on Microbial Diversity
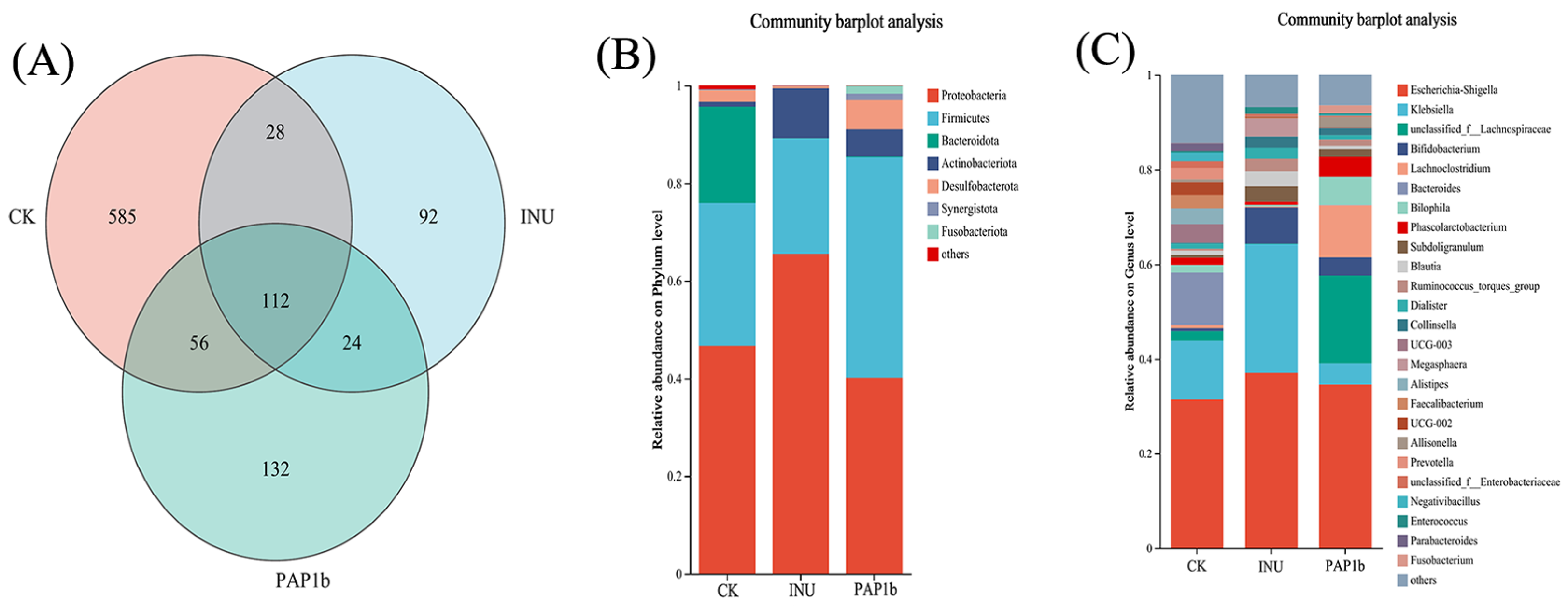
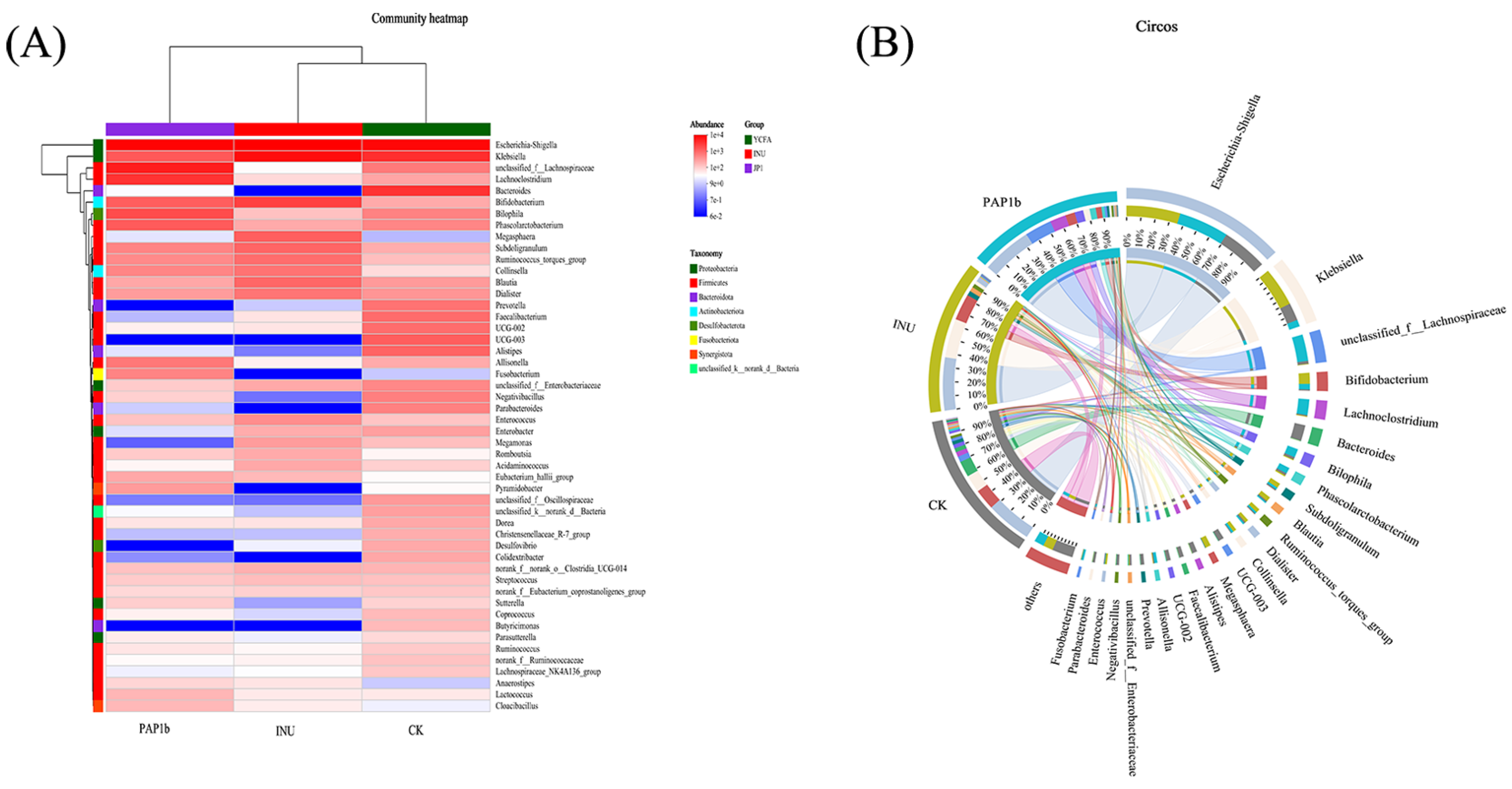
3.3.2. Impacts of PAP1b on Microbial Component
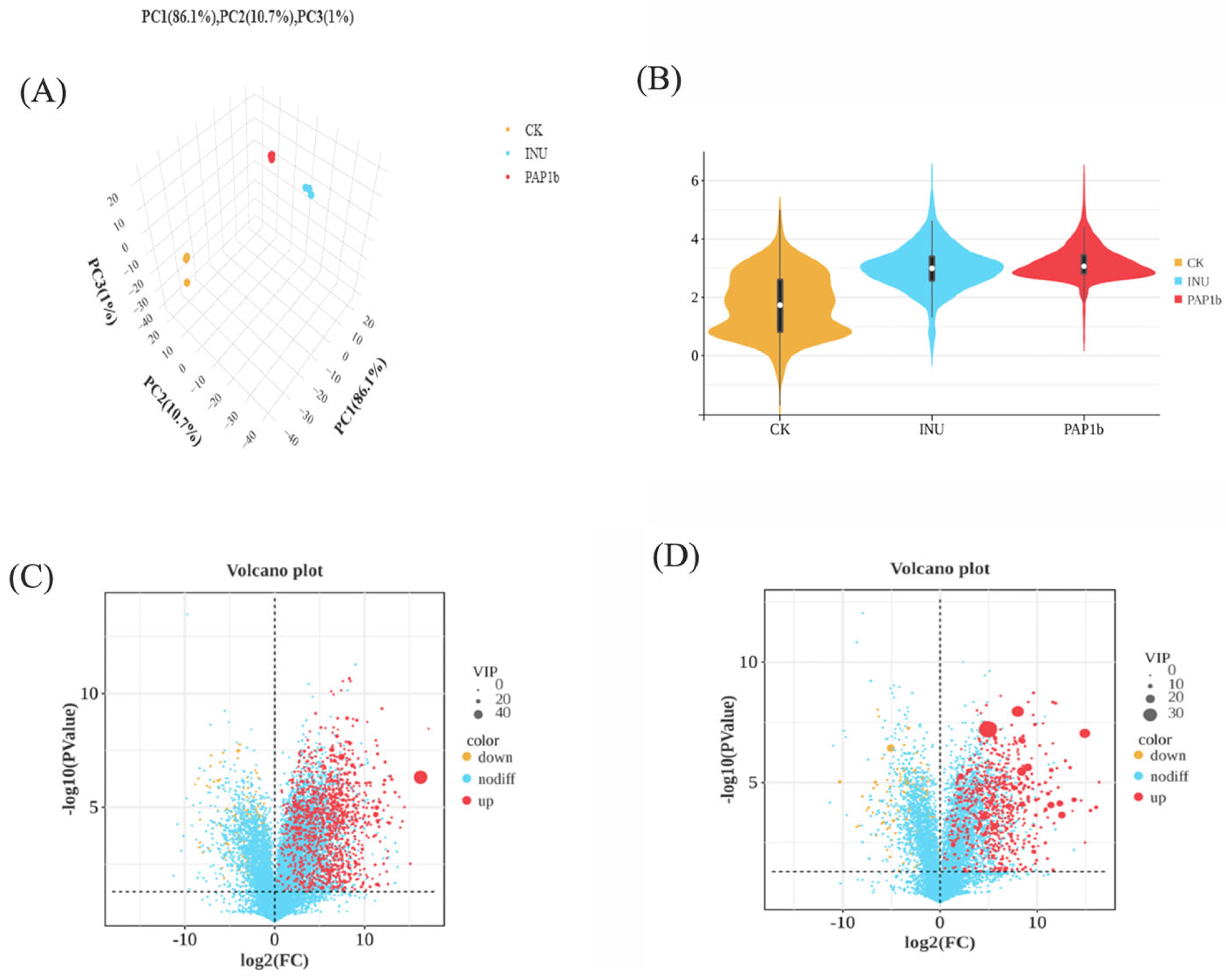
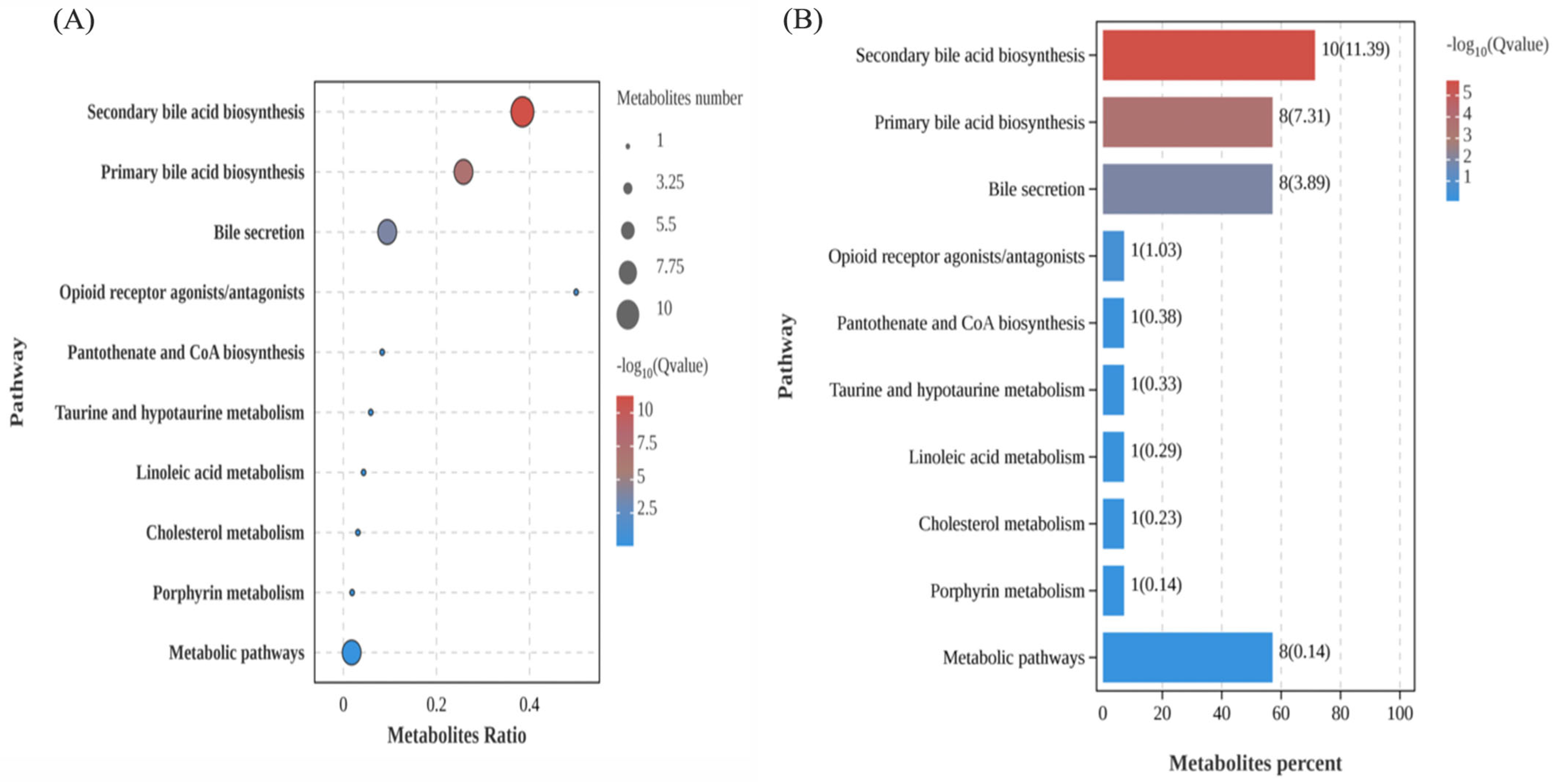
3.4. Impacts of PAP1b on Gut Fermentation Metabolites
3.4.1. Metabolite Composition and Diversity
3.4.2. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Gut Microbes and Metabolites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, W.; Liu, Y.J.; Wu, N.; Sun, T.; He, X.Y.; Gao, Y.X.; Wu, C.J. Areca catechu L. (Arecaceae): A review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.S.; Pan, F.B.; Guo, J.H.; Ji, X.L.; Liu, Y.Q. Research into chemical constituents and pharmacological activities in Areca catechu L. Food Res. Dev. 2021, 42, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.F.; Zhuang, H.N.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Fu, X.; Chen, S.; Yao, L.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Sun, M.; Yu, C.; et al. Structural characteristics of areca nut seed neutral polysaccharide and its impact on gut microbiota from human feces. Food Hydrocolloid. 2023, 171, 113006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Guo, J.H.; Pan, F.B.; Kuang, F.J.; Chen, H.M.; Guo, X.D.; Liu, Y.Q. Structural elucidation and antioxidant activities of a neutral polysaccharide from arecanut (Areca catechu L.). Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 853115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J.; Yao, J.X.; Gao, R.N.; Hao, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. Interactions of non-starch polysaccharides with the gut microbiota and the effect of non-starch polysaccharides with different structures on the metabolism of the gut microbiota: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, H.L.; Tan, Y.Z.; Feng, W.W.; Peng, C. Interactions between polysaccharides and gut microbiota: A metabolomic and microbial review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Song, C.; Li, F.; Hou, J.; Shen, T.; et al. Simulated digestion and in vitro fermentation of a polysaccharide from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera gaertn.) root residue by the human gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.R.; Meng, Y.; Li, X.Q. Digestion characteristics of jujube polysaccharide and its regulatory effect on intestinal microbiota and metabolites during in vitro fermentation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 210, 116869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Chen, X.F.; Gong, P.; Chen, F.X.; Cui, D.D.; Wang, M.R. Advances in the in vitro digestion and fermentation of polysaccharides. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 4970–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.X.; Shah, B.R.; Li, J.; Liang, H.S.; Zhan, F.C.; Geng, F.; Li, B. A critical review on interplay between dietary fibers and gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.X.; Dong, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Zhao, R.H.; Zha, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.K.; Zhang, B.S.; Ma, A.M. The effect of mushroom dietary fiber on the gut microbiota and related health benefits: A review. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L.Z.; Ji, X.L. An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.K.; Tang, Y.Q.; Zha, M.; Xie, K.F.; Tan, J.Q. The structure-function relationships and interaction between polysaccharides and intestinal microbiota: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 139063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.F.; Song, B.B.; Chen, J.P.; Li, R.; Jia, X.J.; Huang, R.M.; Xiang, W.Z.; Zhong, S.Y. Regulatory effects of marine polysaccharides on gut microbiota dysbiosis: A review. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.L.; Kei, N.; Yang, F.; Lauw, S.; Chan, P.L.; Chen, L.; Cheung, P.C.K. In vitro fermentation characteristics of fungal polysaccharides derived from Wolfiporia cocos and their effect on human fecal microbiota. Carbohyd. Polym. 2025, 350, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.D.; Brito, F.O.; Lopes, J.D.; Fabiano, G.A.; Lazarone, C.S.; Citelli, M.; Zago, L.; Antunes, A.E.C.; Evans, M.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. In vitro gastrointestinal digestion of broccolis sprout extract: Impact on the bioaccesibility of sulforaphane and total phenolic. Food Res. Int. 2025, 217, 116795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Fan, C.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Z.L.; Wang, J.Q.; Nie, S.P. Structural characterization and in vitro fermentation of the polysaccharide from fruits of Gardenia jasminoides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 142678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.X.; Yao, S.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, Q.B.; Xu, F.; Wu, G.; Dong, W.J.; Tan, L.H. Effects of in vitro saliva, gastric and intestinal digestion on the chemical properties, antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (Jackfruit) Pulp. Food Hydrocolloid. 2019, 87, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, T.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Ou, S.; Zeng, X.; Ye, H. In vitro digestion by saliva, simulated gastric and small intestinal juices and fermentation by human fecal microbiota of sulfated polysaccharides from Gracilaria rubra. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; You, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.F.; Xiong, L.; Song, H.Z.; Shen, X.C. Structural characterization and in vitro fermentation properties of polysaccharides from Dragon fruit (Hylocereus undatus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 5981–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.P.; Li, H.Y.; Li, J.Q.; Zou, G.Y.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.F.; Hu, B.; Wu, W.J.; Li, X.L.; Zeng, Z.; et al. In vitro simulated digestion and fermentation behaviors of polysaccharides from Pleurotus cornucopiae and their impact on the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 10051–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, R.F.; Su, D.X.; Jia, X.C.; Deng, M.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhang, M.W.; Huang, F. Effects of molecular weight on simulated digestion and fecal fermentation of polysaccharides from longan pulp in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.L.; Hou, C.Y.; Yan, Y.Z.; Shi, M.M.; Liu, Y.Q. Comparison of structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.F.; Liu, M.Q.; Yao, A.N.; Cui, W.C.; Wei, Y.; Guo, S.; Duan, J.L.; Kang, H.J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Su, S.L.; et al. In vitro fermentation characteristics and interaction of neutral and acidic polysaccharides from Lycii fructus on human gut microbiota. Food Hydrocolloid. 2024, 152, 109940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Hou, C.Y.; Gao, Y.G.; Xue, Y.Q.; Yan, Y.Z.; Guo, X.D. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota modulatory effects of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) polysaccharides in a colorectal cancer mouse model. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Cai, W.H.; Li, X.X.; Deng, Y.X.; Li, J.J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.Y.; Wang, C.; Li, X.Q. The effect of type 2 resistant starch and indole-3-propionic acid on ameliorating high-fat-diet-induced hepatic steatosis and gut dysbiosis. Foods 2024, 13, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.X.; Li, W.; Ma, L.N.; Liu, X.L.; Ding, Q.T.; Yu, W.M.; Yu, T.J.; Ding, C.B.; Liu, W.C. Research progress of natural plant polysaccharides inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways and regulating intestinal flora and metabolism to protect inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Liang, X.N.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, L.H.; Xiao, W.; Ma, Y.H.; Wang, R.; Gu, Y.; Li, S.; Qiu, Y.B.; et al. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation of basidiospore-derived exopolysaccharides from Naematelia aurantialba. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.P.; Qiu, Z.H.; Yang, Y.T.; Wang, T.Z.; Inam, M.; Ma, H.X.; Zhang, H.P.; He, C.G.; Guan, L.L. Comprehensive evaluation of Flammulina velutipes residues polysaccharide based on in vitro digestion and human fecal fermentation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.S.; Zhang, J.N.; Chen, K.N.; Xiao, C.X.; Fan, L.N.; Zhang, B.Z.; Ren, J.L.; Fang, B.S. An in vitro fermentation study on the effects of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides on human intestinal microbiota from fecal microbiota transplantation donors. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 53, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Nie, X.R.; Gan, R.Y.; Guo, H.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, W. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation behaviors of a pectic polysaccharide from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) and its impacts on human gut microbiota. Food Hydrocolloid. 2021, 114, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Guo, Q.B.; Zhang, K.L.; Wang, N.F.; Li, C.R.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, A.L.; Wang, C.L. Polysaccharide from Pleurotus nebrodensis: Physicochemical, structural characterization and in vitro fermentation characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; An, L.Y.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.C.; Wang, S.P.; Zou, L. In vitro fecal fermentation properties of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis and related modulation effects on gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringseis, R.; Gessner, D.K.; Eder, K. The gut-liver axis in the control of energy metabolism and food intake in animals. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2020, 8, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Aweya, J.J.; Huang, Z.X.; Kang, Z.Y.; Bai, Z.H.; Li, K.H.; He, X.T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.Q.; Cheong, K.L. In vitro fermentation of Gracilaria lemaneiformis sulfated polysaccharides and its agaro-oligosaccharides by human fecal inocula and its impact on microbiota. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 234, 115894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.R.; Guo, D.D.; Bau, T.; Lei, J.Y.; Xu, L.J.; Cheng, Y.F.; Feng, C.P.; Meng, J.L.; Chang, M.C. Effects of in vitro digestion and fecal fermentation on physico-chemical properties and metabolic behavior of polysaccharides from Clitocybe squamulosa. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Aru, V.; Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Qin, P.Y.; Jiang, Q.Q.; Li, Z.D.; Engelsen, S.B.; Zhao, X.Y. Deciphering the interplay between pectin structural variability, intestinal bioavailability and gut microbiota metabolism: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2025, 360, 123596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, C.; Hua, H.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Cheng, Y.L.; Yao, W.R.; Qian, H. Comprehensive analysis of Sparassis crispa polysaccharide characteristics during the in vitro digestion and fermentation model. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.S.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, Z.Z. Regulating effects of three polysaccharides on gut microbiota in felines and canines: Insights from in vitro digestion, fecal fermentation, and lactic acid bacterial fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 9618–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Yan, Y.Z.; Hou, C.Y.; Shi, M.M.; Liu, Y.Q. Structural characterization of a galacturonic acid-rich polysaccharide from Ziziphus jujuba cv. Muzao. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.X.; Chen, X.F.; Gong, P.; Wang, M.R.; Yao, W.B.; Yang, W.J.; Chen, F.X. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation of Siraitia grosvenorii polysaccharide and its impact on human gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9443–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonero, F.; Benefiel, A.C.; Alizadeh-Ghamsari, A.H.; Gaskins, H.R. Microbial pathways in colonic sulfur metabolism and links with health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Su, J.; Wu, J.H.; Zhao, D.; Huang, M.Q.; Lu, Y.P.; Zheng, J.; Li, H.H. The prebiotic activity of a novel polysaccharide extracted from Huangshui by fecal fermentation in vitro. Foods 2024, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.J.; Fan, J.T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Cao, Y.X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, W.; Deng, J.M.; Tan, B.P. Effects of dietary non-starch polysaccharides level on the growth, intestinal flora and intestinal health of juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquaculture 2022, 557, 738343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Huang, L.X.; Shen, M.Y.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.H. Review of the relationships among polysaccharides, gut microbiota, and human health. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Aweya, J.J.; Li, N.; Deng, R.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Tang, J.; Cheong, K. Microbial catabolism of Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides by human gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.X.; Chen, L.L.; Xian, J.C.; An, G.Q.; Wei, H.B.; Ma, Y.T. Digestive characteristics of Gastrodia elata Blume polysaccharide and related impacts on human gut microbiota in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 328, 118064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Miyake, T.; Maekawa, T.; Mori, H.; Yasukawa, D.; Ohno, M.; Nishida, A.; Andoh, A.; Tani, M. High abundance of Lachnospiraceae in the human gut microbiome is related to high immunoscores in advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immun. 2023, 72, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, V.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Maloney, C.A.; Raipuria, M.; Huinao, K.D.; Mitchell, H.M.; Morris, M.J. Changes in gut microbiota in rats fed a high fat diet correlate with obesity-associated metabolic parameters. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.F.; Zhong, Y.D.; Liu, H.; Hu, J.L. Lipid metabolism regulation by dietary polysaccharides with different structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, K.; Tsukahara, T.; Yamada, K.; Koyama, H.; Ushida, K. Megasphaera elsdenii JCM1772T normalizes hyperlactate production in the large intestine of fructooligosaccharide-fed rats by stimulating butyrate production. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3187–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Ye, Y.W.; Sang, S.Y.; Luo, X.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Shan, K.; Ou, C.R.; Jia, L.L. Recent progress of Clostridium butyricum in fish culture: Maintenance of intestinal homeostasis, improvement of disease resistance, activation of immune signaling pathways, and positive effects on fish. Aquaculture 2025, 596, 741723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.B.; Hu, J.L.; Geng, F.; Nie, S.P. Bacteroides utilization for dietary polysaccharides and their beneficial effects on gut health. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2022, 11, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.K.; Liang, B.M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.Y.; Fang, S.S.; Xie, K.F.; Tan, J.Q. The regulatory effect of polysaccharides on the gut microbiota and their effect on human health: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, H.; Rajca, S.; Rainteau, D.; Benarous, D.; Maubert, M.A.; Quervain, E.; Thomas, G.; Barbu, V.; Humbert, L.; Despras, G.; et al. Connecting dysbiosis, bile-acid dysmetabolism and gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 2013, 62, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Q.; Ren, D.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.B. Fuzhuan brick tea polysaccharide improved ulcerative colitis in association with gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8448–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayin, S.I.; Wahlström, A.; Felin, J.; Jäntti, S.; Marschall, H.U.; Bamberg, K.; Angelin, B.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Oresic, M.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. 2013, 13, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, L.L.; Zhai, Q.X.; Zhao, R.H.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Tian, F.W. In vitro fermentation of heparin by the human gut microbiota: Changes in the microbiota community and metabolic functions. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 135010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.R.; Huang, R.; Zhu, S.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, X.L.; Zhu, Z.J. Polysaccharide from Caulerpa lentillifera alleviates hyperlipidaemia through altering bile acid metabolism mediated by gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 306, 141663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.Y.; Lam, K.L.; Li, X.J.; Kong, A.P.S.; Cheung, P.C.K. Circadian disruption-induced metabolic syndrome in mice is ameliorated by oat β-glucan mediated by gut microbiota. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 267, 118216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Bäckhed, F. Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Li, W.D.; Xiao, L.; Liu, C.D.; Qi, H.M.; Zhang, Z.S. In vivo antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant activity of porphyran in hyperlipidemic mice. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 174, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly-Y, M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic treg cell homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.C.; Johansson, M.E.V. The inner of the two Muc2 mucin-dependent mucus layers in colon is devoid of bacteria. Gut Microbes 2008, 105, 15064–15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Nilsson, A.; Akrami, R.; Lee, Y.S.; De Vadder, F.; Arora, T.; Hallen, A.; Martens, E.; Björck, I.; Bäckhed, F. Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soret, R.; Chevalier, J.; De Coppet, P.; Poupeau, G.; Derkinderen, P.; Segain, J.P.; Neunlist, M. Short-chain fatty acids regulate the enteric neurons and control gastrointestinal motility in rats. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Jiang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Du, J.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X. In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Arecanut Polysaccharides: Effects on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Foods 2025, 14, 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172954
Ji X, Jiang K, Liu Y, Zhao C, Du J, Chen L, Zhu Z, Li X. In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Arecanut Polysaccharides: Effects on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172954
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiaolong, Ke Jiang, Yuqing Liu, Chenyu Zhao, Jun Du, Liang Chen, Zhigang Zhu, and Xiaoqiong Li. 2025. "In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Arecanut Polysaccharides: Effects on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites" Foods 14, no. 17: 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172954
APA StyleJi, X., Jiang, K., Liu, Y., Zhao, C., Du, J., Chen, L., Zhu, Z., & Li, X. (2025). In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Arecanut Polysaccharides: Effects on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Foods, 14(17), 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172954







