Metabolic Modulation of Yogurt Fermentation Kinetics and Storage Stability by Lactobacillus-Starter Culture Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Cultivation Conditions
2.2. Preparation of Yogurt Samples
2.3. Measurement of pH, TA, and Viable Counts
2.4. Determination of the Lactic Acid Content
2.5. Extraction and Analysis of Non-Volatile Metabolites
2.5.1. Sample Preparation
2.5.2. Liquid Chromatography Conditions
2.5.3. Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Acidification Properties of Yogurt During Fermentation
3.2. Viable Counts of Yogurt During Fermentation
3.3. Metabolite Changes During Fermentation
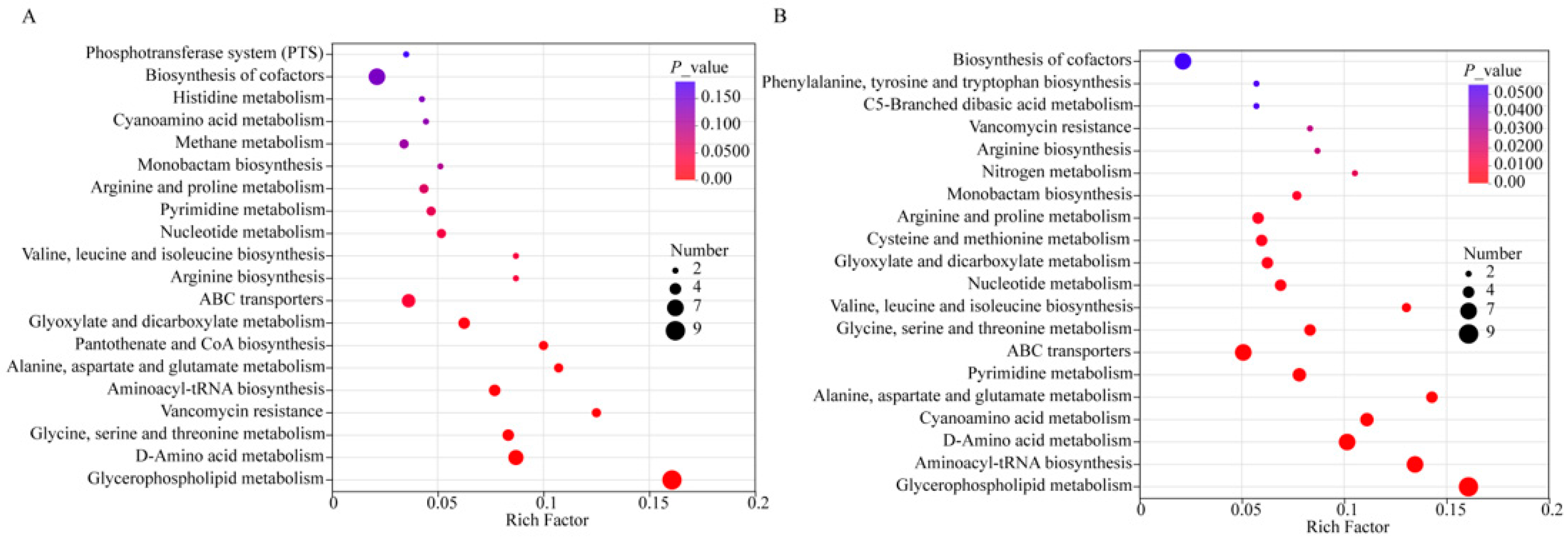
3.4. Metabolic Pathway Analysis During the Fermentation Period
3.5. Storage Period Performance of Different Strains of Yogurt
3.6. Metabolite Changes During Storage
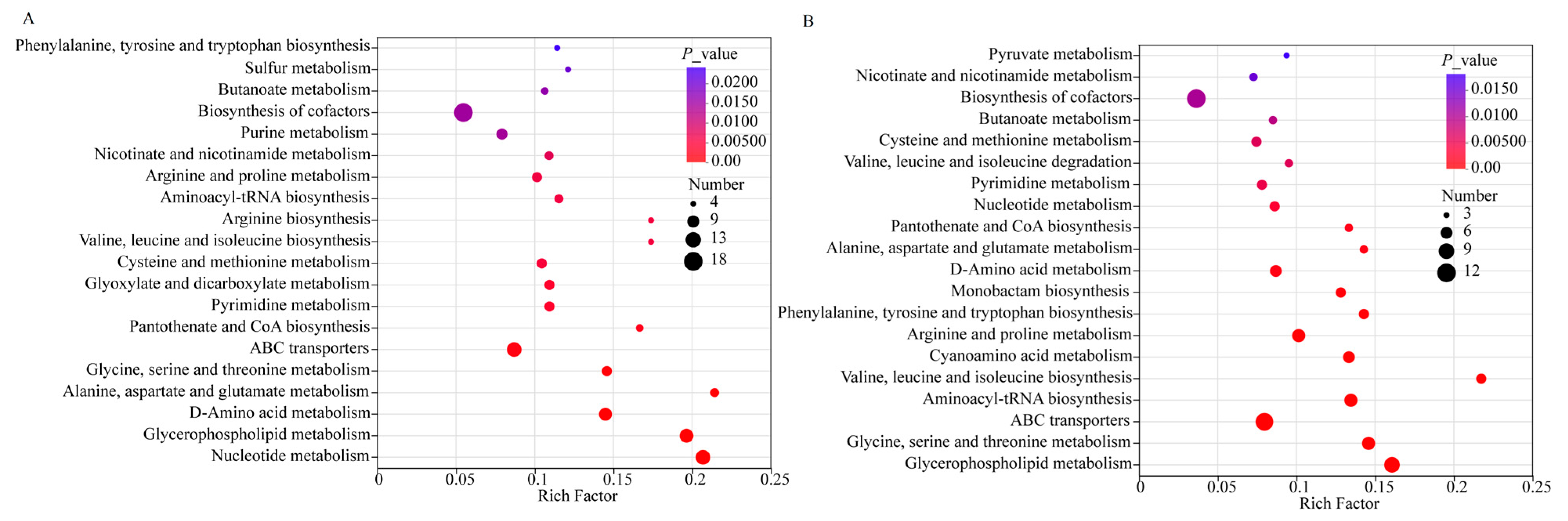
3.7. Metabolic Pathway Analysis During the Storage Period
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saleem, G.N.; Gu, R.X.; Qu, H.X.; Khaskheli, G.B.; Rajput, I.R.; Qasim, M.; Chen, X. Therapeutic potential of popular fermented dairy products and its benefits on human health. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, R.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.P.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Ibrahim, S.A. A review of factors influencing the quality and sensory evaluation techniques applied to Greek yogurt. J. Dairy Res. 2022, 89, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, H.; Inoue, N.; Liu, E.; Fukui, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Sasaki, T. A method for manufacturing superior set yogurt under reduced oxygen conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4112–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.F. Volatile flavor compounds in yogurt: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, M.; Yousefi, M.; Khanniri, E.; Azari, M.; Ghasemzadeh-Mohammadi, V.; Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N. A comprehensive review on yogurt syneresis: Effect of processing conditions and added additives. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.X.; Cui, Y.H.; Qu, X.J.; Li, B.L.; Zhang, L.W. Post-acidification of fermented milk and its molecular regulatory mechanism. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 426, 110920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G. Lactic metabolism revisited: Metabolism of lactic acid bacteria in food fermentations and food spoilage. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, F.; Delgado, S.; Ruiz, L.; Margolles, A.; Ruas-Madiedo, P. Functional bacterial cultures for dairy applications: Towards improving safety, quality, nutritional and health benefit aspects. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 133, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrellou, D.; Kandylis, P.; Kourkoutas, Y. Assessment of freeze-dried immobilized Lactobacillus casei as probiotic adjunct culture in yogurts. Foods 2019, 8, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, B.N.P.; Vasijevic, T.; McKechnie, S.; Donkor, O.N. Effect of probiotics on antioxidant and antimutagenic activities of crude peptide extract from yogurt. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.X.; Shen, Y.B.; Yu, H.Y.; He, Y.J.; Chen, C. Effects of 4 probiotic strains in coculture with traditional starters on the flavor profile of yogurt. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhang, F.X.; Wang, B.N.; Liu, Y.F. Storage stability of texture, organoleptic, and biological properties of goat milk yogurt fermented with probiotic bacteria. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Sun, H.T.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.R.; Kwok, L.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Peng, C.T. Comparison of the effects of single probiotic strains Lactobacillus casei Zhang and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis Probio-M8 and their combination on volatile and nonvolatile metabolomic profiles of yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7509–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenea, G.N.; Suárez, J. Probiotic potential and technological properties of bacteriocinogenic Lactococcus lactis subsp. Lactis UTNGt28 from a native amazonian fruit as a yogurt starter culture. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranadheera, C.S.; Evans, C.A.; Adams, M.C.; Baines, S.K. Probiotic viability and physico-chemical and sensory properties of plain and stirred fruit yogurts made from goat’s milk. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niamah, A.K.; Al-fekaiki, D.F.; Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Verma, D.K.; Patel, A.R.; Singh, S. Investigating the effect of addition of probiotic microorganisms (bacteria or yeast) to yoghurt on the viability and volatile aromatic profiles. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5463–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Shi, S.Q.; Hao, Y.L.; Zhai, Z.Y.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, X.; Yang, J.J.; Zhao, L.; Luo, J.; Ge, S.Y.; et al. Surface hydrophilic amino acids of sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase SacA play a key role in high acid production rates in Lacticaseibacillus casei. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 218, 117465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseenko, K.V.; Glazunova, O.A.; Savinova, O.S.; Shabaev, A.V.; Fedorova, T.V. Changes in composition of some bioactive molecules upon inclusion of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei probiotic strains into a standard yogurt starter culture. Foods 2023, 12, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, O.N.; Henriksson, A.; Vasiljevic, T.; Shah, N.P. Effect of acidification on the activity of probiotics in yoghurt during cold storage. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, S.Q.; Li, D.D.; Sang, Y.; Wang, P.J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.Q.; Fang, B.; Chen, S.X.; et al. Flavor properties of post-heated fermented milk revealed by a comprehensive analysis based on volatile and non-volatile metabolites and sensory evaluation. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 9, 100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.K.; Song, J.H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Dong, Y.; Yu, H.J.; Hou, Q.C.; Zhang, H.P.; Chen, Y.F. Influence of Lactobacillus plantarum on yogurt fermentation properties and subsequent changes during postfermentation storage. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2512–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Zhai, Z.Y.; Hao, Y.L.; Zhang, M.; Hou, C.Y.; He, J.J.; Shi, S.Q.; Zhao, Z.; Sang, Y.; Ren, F.Z.; et al. The plasmid-encoded lactose operon plays a vital role in the acid production rate of Lacticaseibacillus casei during milk beverage fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ye, H.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhu, C.L.; Tang, J.N. Physicochemical properties, antioxidant activities, and aromatic profile of yogurt co-fermented by Weissella cibaria G232 with traditional starters. Foods 2025, 14, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.H.; Huo, Y.X.; Gao, W.Y.; Dai, M.X.; Zhao, G.Y.; Zhang, S.S. Physicochemical, microbiological and sensory characterization of yogurt fermented by Weissella confusa SW1 and traditional starters. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 201, 116229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Fazeli, M.R.; Ezzatpanah, H.; Mohammadi, R. The effects of inoculant variables on the physicochemical and organoleptic properties of Doogh. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2012, 65, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Pourjafar, H.; Homayouni, A. Effect of calcium alginate and resistant starch microencapsulation on the survival rate of Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and sensory properties in Iranian white brined cheese. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Svensson, B.; Henrissat, B.; Moller, M.S. Functional roles of n-terminal domains in pullulanase from human gut Lactobacillus acidophilus. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 18898–18908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, D.; Mital, B.K.; Garg, S.K. Utilization of sugars by Lactobacillus acidophilus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 10, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.L.; Yin, B.X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, M.R.; Chang, Z.Q.; Zhou, J.P.; Yue, M.Z.; Chen, J.X.; Liu, F.; Feng, Z. Nutrient consumption patterns of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5982–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshayesh, R.V.; Panahi, B.; Hejazi, M.A.; Nami, Y. Metabolite profiling of different Iranian traditional yogurts using an untargeted metabolomics approach. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Schnacke, P.; Frei, M.S.; Koch, B.; Hiblot, J.; Wombacher, R.; Fabritz, S.; Johnsson, K. Probing coenzyme A homeostasis with semisynthetic biosensors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, Y.R.; Yang, D.; Zhao, L.; Rao, L.; Liao, X.J. High-pressure-induced viable but non-culturable lactic acid bacteria inhibit its post-acidification. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 422, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.Z.; Wang, S.L.; He, J.; Ma, X.; Sun, T.; Li, J.D.; De Souza, C.; Yi, H.X.; Zhang, L.W.; Lin, K. Characterization of key lipid components in the cell membrane of freeze-drying resistant Lacticaseibacillus paracasei strains using nontargeted lipidomics. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2025, 73, 2696–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, K.S.; Zheng, Y.R.; Tan, X.H.; Wang, L.B.; Tong, C.M.; Huang, S.Q.; Cai, X.T.; Zhou, C.Y.; Cao, J.X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Influence of sonication-assisted fermentation on the physicochemical features and antioxidant activities of yogurts fortified by polyphenol-rich pineapple peel powder with varied chemical profiling. Food Res. Int. 2024, 198, 115333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuru, E.; Lambert, C.; Rittichier, J.; Till, R.; Ducret, A.; Derouaux, A.; Gray, J.; Biboy, J.; Vollmer, W.; VanNieuwenhze, M.; et al. Fluorescent D-amino-acids reveal bi-cellular cell wall modifications important for Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus predation. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Bai, M.; Kwok, L.Y.; Zhong, Z.; Sun, Z.H. The intricate symbiotic relationship between lactic acid bacterial starters in the milk fermentation ecosystem. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 728–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.X.; He, T.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhang, G.L.; Ma, X. Branched chain amino acids: Beyond nutrition metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, D.K.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R.Q.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.D. Arginine deiminase pathway of Tetragenococcus halophilus contributes to improve the acid tolerance of lactic acid bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2023, 113, 104281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez, L.; Solopova, A.; Fernández-Pérez, R.; González, M.; Tenorio, C.; Kuipers, O.P.; Ruiz-Larrea, F. Transcriptome analysis shows activation of the arginine deiminase pathway in Lactococcus lactis as a response to ethanol stress. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 257, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutella, G.S.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Solieri, L. Survival and bioactivities of selected probiotic lactobacilli in yogurt fermentation and cold storage: New insights for developing a bi-functional dairy food. Food Microbiol. 2016, 60, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbent, J.R.; Larsen, R.L.; Deibel, V.; Steele, J.L. Physiological and transcriptional response of Lactobacillus casei ATCC 334 to acid stress. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocer, E.M.C.; Ergin, F.; Kücükcetin, I.O.; Kücükcetin, A. In vitro gastrointestinal resistance of Lactobacillus acidophilus in some dairy products. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2319–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Zhao, W.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.R.; Yao, K.; Liu, Z.Z.; Sun, Z.H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Peng, C.T. Different growth behaviors and metabolomic profiles in yogurts induced by multistrain probiotics of Lactobacillus casei Zhang and Bifidobacterium lactis V9 under different fermentation temperatures. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 10528–10539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Cui, Y.L.; Yue, F.F.; Liu, L.H.; Shan, Y.Y.; Liu, B.F.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacteria: Structures, physiochemical functions and applications in the food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boram, T.J.; Benjamin, A.B.; de Sousa, A.S.; Stunkard, L.M.; Stewart, T.A.; Adams, T.J.; Craft, N.A.; Velázquez-Marrero, K.G.; Ling, J.H.; Nice, J.N.; et al. Activity of fatty acid biosynthesis initiating ketosynthase FabH with acetyl/malonyl-oxa/aza(dethia)CoAs. ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.Q.; Lu, F.X.; Du, H.C.; Nie, T.; Zhu, X.Y.; Connerton, I.F.; Zhao, H.Z.; Bie, X.M.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Z.X.; et al. Acetate and auto-inducing peptide are independent triggers of quorum sensing in Lactobacillus plantarum. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 116, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Xiao, M.Y.; Xu, Y.Z.; Li, D.Y.; Zhu, W.H.; Huang, T.; Peng, F.; Guan, Q.Q.; Peng, Z.; Xie, M.Y.; et al. Effect of homo- and hetero-fermentative lactic acid bacteria on physicochemical properties, amino acid, and volatile flavor compounds during paocai fermentation by pure culture. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, 17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.M. Arginine metabolism revisited. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedley, A.M.; Benkovic, S.J. A new view into the regulation of purine metabolism: The purinosome. Trends Biochem. Sci 2017, 42, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yang, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, G.; Hou, B.; He, J.; Hung, W.-L.; et al. Metabolic Modulation of Yogurt Fermentation Kinetics and Storage Stability by Lactobacillus-Starter Culture Interactions. Foods 2025, 14, 2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172935
An M, Zhao Z, Zhao L, Yang J, Gao H, Zhang L, Zhao G, Hou B, He J, Hung W-L, et al. Metabolic Modulation of Yogurt Fermentation Kinetics and Storage Stability by Lactobacillus-Starter Culture Interactions. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172935
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Meilun, Zhi Zhao, Liang Zhao, Jianjun Yang, Haina Gao, Lele Zhang, Guoping Zhao, Baochao Hou, Jian He, Wei-Lian Hung, and et al. 2025. "Metabolic Modulation of Yogurt Fermentation Kinetics and Storage Stability by Lactobacillus-Starter Culture Interactions" Foods 14, no. 17: 2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172935
APA StyleAn, M., Zhao, Z., Zhao, L., Yang, J., Gao, H., Zhang, L., Zhao, G., Hou, B., He, J., Hung, W.-L., Li, B., Yu, Y., Ge, S., Li, X., & Wang, R. (2025). Metabolic Modulation of Yogurt Fermentation Kinetics and Storage Stability by Lactobacillus-Starter Culture Interactions. Foods, 14(17), 2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172935




