Characterization of Rapeseed Oil Oleogels Produced by the Emulsion Template Method Using Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and the Drying Kinetics of the Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Emulsions
2.3. Drying of the Emulsion
2.4. Oleogel Preparation
2.5. Rheological Characterization
2.6. Textural Properties
2.7. Oil Binding Capacity (OBC)
2.8. Oxidation Degree
2.8.1. Primary Oxidation
2.8.2. Secondary Oxidation
2.9. Colour
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Emulsion
3.2. Drying Kinetics
3.3. Drying Kinetics Modelling
3.4. Characterization of Oleogels
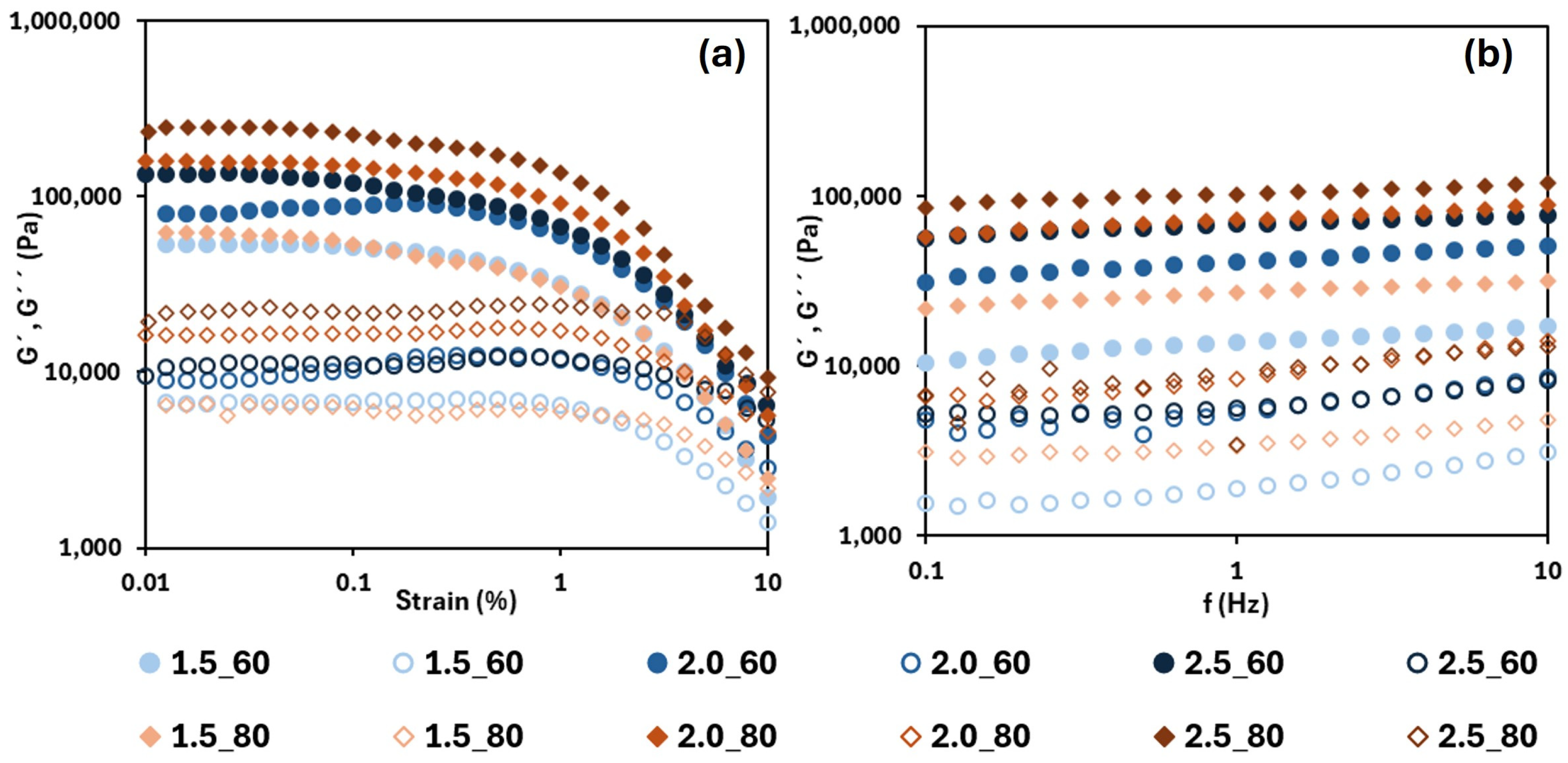
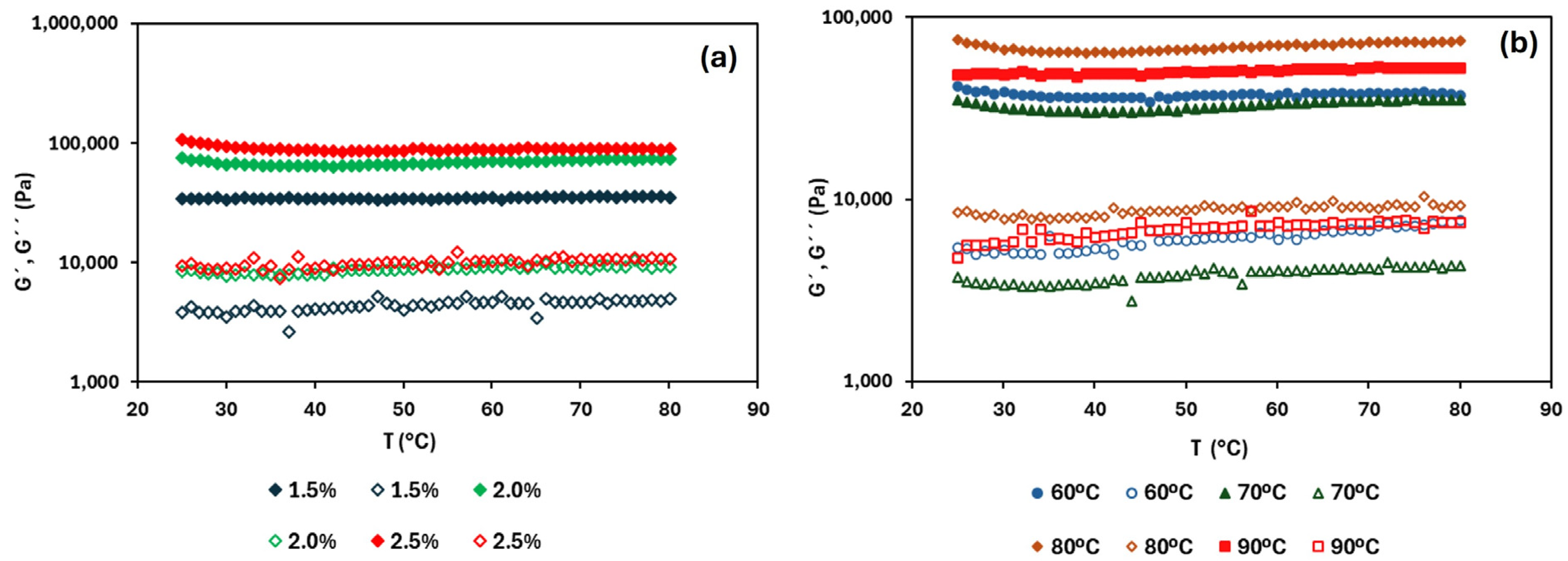
3.4.1. Rheology
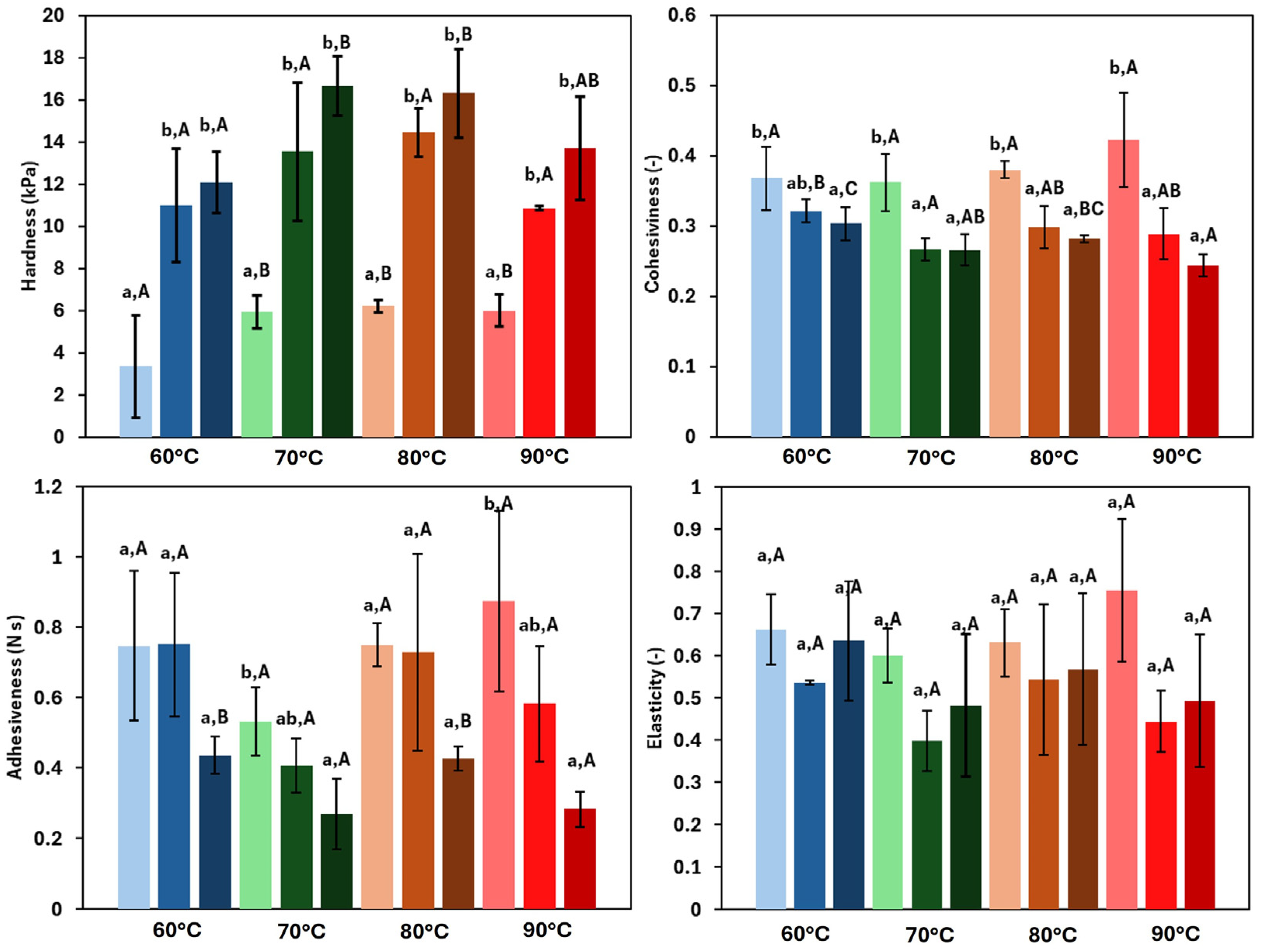
3.4.2. Texture
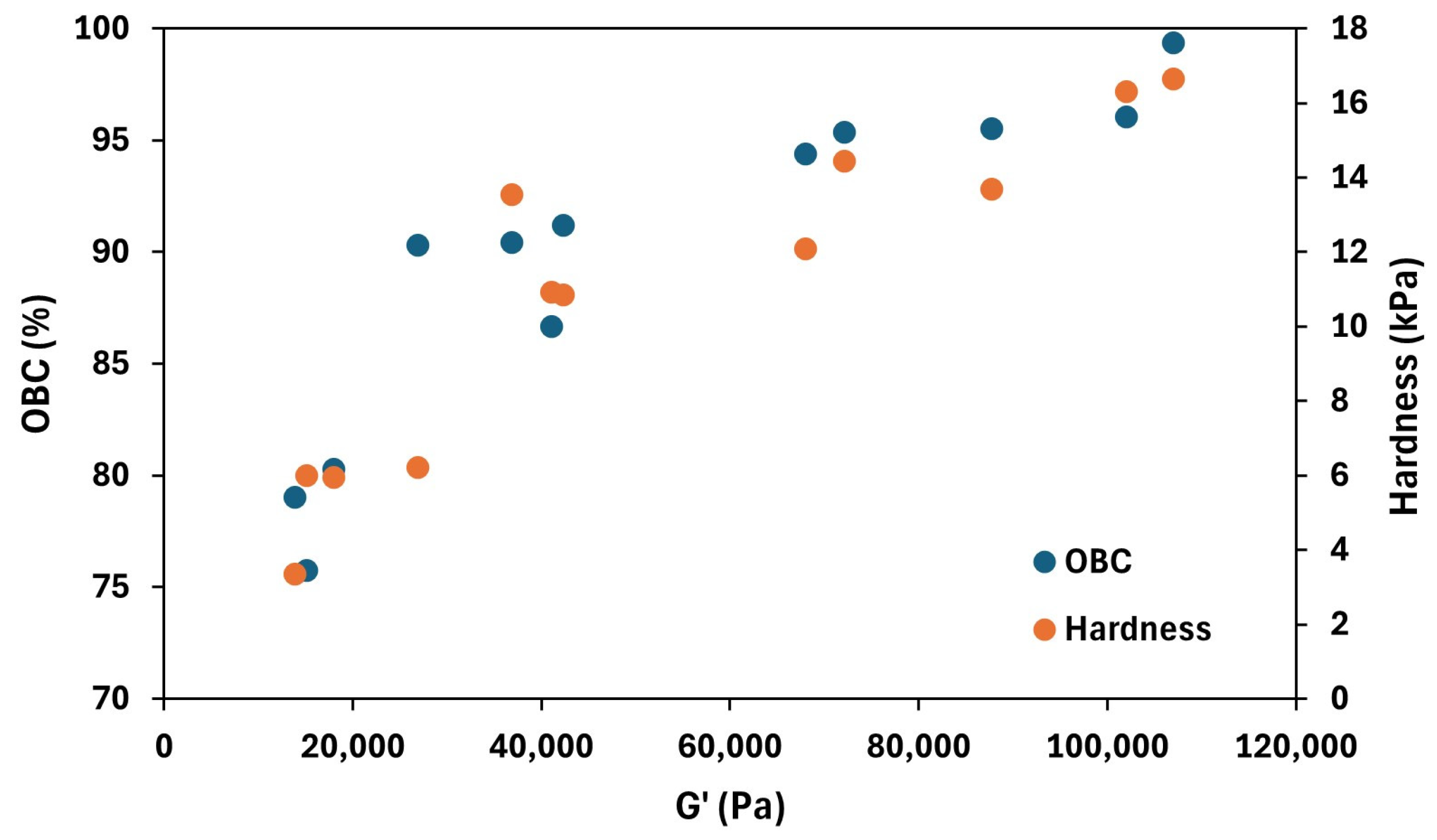
3.4.3. Oil Binding Capacity
3.4.4. Oil Oxidation
3.4.5. Oleogels Colour
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AV | Anisidine Value |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| HPMC | Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose |
| LVR | Linear Viscoelastic Region |
| MC | Methylcellulose |
| OBC | Oil Binding Capacity |
| O/W | Oil in Water |
| PI | Peroxide Index |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
References
- Reynolds, A.N.; Hodson, L.; de Souza, R.; Tran Diep Pham, H.; Vlietstra, L.; Mann, J. Saturated Fat and Trans-Fat Intakes and Their Replacement with Other Macronutrients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Patel, A.; Nicholson, R.; Marangoni, A. Applications of fat mimetics for the replacement of saturated and hydrogenated fat in food products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 33, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, C.; Valoppi, F. Advanced in Oleogel Development, Characterization, and Nutritional Aspects; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Du, L.; Meng, Z. Edible polysaccharide-based oleogels and novel emulsion gels as fat analogues: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 322, 121328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guo, B.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. Oleogel-structured emulsions: A review of formation, physicochemical properties and applications. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradabbasi, M.; Hossein Goli, S.A.; Fayaz, G. Effect of biopolymers concentration and drying methods on physicochemical properties of emulsion-templated oleogel. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1994–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, M.; Montes, L.; Franco, D.; Franco-Uría, A.; Moreira, R. Chitosan-based oleogels: Emulsion drying kinetics and physical, rheological, and textural characteristics of olive oil oleogels. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espert, M.; Wang, Q.; Sanz, T.; Salvador, A. sunflower oil-based oleogel as fat replacer in croissants: Textural and sensory characterisation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.J.; Um, I.C. Examination of thermo-gelation behaviour of HPMC and HEMC aqueous solutions using rheology. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2013, 25, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espert, M.; Borreani, J.; Hernado, I.; Quiles, A.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T. Relationship between cellulose chemical substitution, structure and fat digestion in o/w emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, M.Y.; Montes, L.; Franco, D.; Franco-Uría, A.; Moreira, R. Drying kinetics modeling of hot air drying of emulsion templated oleogels employing hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as structuring agent. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Miao, J.; Tan, H.; Feng, R.; Zheng, Q.; Cao, Y.; Lan, Y. Oleogel-structured emulsion for enhanced oxidative stability of perilla oil: Influence of crystal morphology and cooling temperature. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 139, 110560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Velasco, A.; Trujillo-Ramírez, D.; Bustos-Vázquez, G.; Cervantes-Arista, C. The use of candelilla wax/rapeseed oil oleogel in the formulation of sponge cake bread improves morphostructural and sensory properties. Discov. Food 2024, 4, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettlaufer, T.; Brykczynski, H.; Flöter, E. Wax-based oleogels-properties in medium chain triglycerides and canola oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 2100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrah, K.; Adegoke, S.C.; Tahergorabi, R. Physicochemical and microbial quality of coated raw and oleogel-fried chicken. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.G.; Lee, S. Feasibility of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose oleogel as an animal fat replacer for meat patties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espert, M.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T. Cellulose ether oleogels obtained by emulsion-templated approach without additional thickeners. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Callau, M.; Sow-Kébé, K.; Nicolas-Morgantini, L.; Fameau, A.-L. Effect of the ratio between behenyl alcohol and behenic acid on the oleogel properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Oil Chemists’ Society. Peroxide Value, Acetic Acid, Isooctane Method (AOCS Official Method Cd 8b-90); AOCS: Urbana, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- American Oil Chemists’ Society. Anisidine Value (AOCS Official Method Cd 18-90); AOCS: Urbana, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krstonosic, V.; Pavlovic, N.; Nikolic, I.; Milutinov, J.; Cirin, D. Physicochemical properties and stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by soy protein isolate and xanthan gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, L.; Abdolmaleki, K.; Nayebzadeh, K.; Bahmei, M. Characterization of sodium caseinate/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose concentrated emulsions: Effect if mixing ratio, concentration and wax addition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T. Rheology of Dispersions: Principles and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espert, M.; Gracia-Hernández, C.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T.; Hernández, M.J. Linear and nonlinear viscoelasticity of edible o/w emulsions used as saturated fat replacers. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 191, 115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, L.; Rosell, C.M.; Moreira, R. Rheological properties of corn starch gels with the addition of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose of different viscosities. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 866789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Talukder, S.; Zaman, A.U.; Sarkar, A.; Yasin, M. Effective drying process for Taikor (Garcinia pedunculata Roxb.) fruit by ultrasound-assisted osmotic pretreatment: Analysis of quality and kinetic models. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 103, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Du, Y.; Yan, J.; Xie, H.; Liao, X.; Wei, H. Study on the characteristics and kinetics of microwave hot air combined drying of peanuts pods. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 60, 104640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cheng, W.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Chen, H. Drying kinetic and upgraded grindability of biomass with torrefaction-assisted deep drying. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 226, 120659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divoux, T.; Mao, B.; Snabre, P. Syneresis and delayed detachment in agar plates. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho Pinheiro, M.N.; Castro, L.M. Effective moisture diffusivity prediction in two Portuguese fruit cultivars (Bravo de Esmolfe apple and Madeira banana) using drying kinetics data. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti-Mata, M.; Duarte, M.E.; Tolentino, M.; Mendes, F.; Batista, L.; de Lima, J.M.; Lisboa, H.M. Drying kinetics of industrial pineapple waste: Effective diffusivity and thermodynamic properties resulting from new mathematical models derived from the Fick equation. Processes 2024, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Espert, M.; Larrea, V.; Quiles, A.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T. Comparison of different indirect approaches to design edible oleogels based on cellulose ethers. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, X.; Bi, L. camellia saponin based oleogels by emulsion-templated method: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro digestion. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.; Chenlo, F.; Moreira, R. Viscoelastic and textural characteristics of gels obtained from potato starch roasted under several temperature-time conditions. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 7606359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Qi, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Macro-micro structure characterization and molecular properties of emulsion-templated polysaccharide oleogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y. Crystallization and structural properties of oleogel-based margarine. Molecules 2022, 27, 8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Ahmad, M.I.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H. Preparation, characterization and digestive mechanism of plant-derived oil bodies-based oleogels structured by chitosan and vanillin. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, G.; Di Sarli Peixoto, V.; Martins, M.; Rosário, D.; Ract, J.; Conte-Júnior, C.; Torres, A. Development of chitosan-based oleogels via crosslinking with vanillin using an emulsion templated approach: Structural characterization and their application as fat-replacer. Food Struct. 2022, 32, 100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Ijaz Ahmad, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Impact of interfacial layer number and Schiff base cross-linking on the microstructure, rheological properties and digestive lipolysis of plant-derived oil bodies-based oleogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo, C.; Montes, L.; Moreira, R.; Franco, D. Structuring olive oil with ethylcellulose of different molecular weights: Influence of concentration, viscosity and mixtures. Future Foods 2025, 11, 100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Jiang, L. Construction of soybean oil bodies-xantham gum composite oleogels by emulsion-templated method: Preparation, characterization and stability analysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Tang, L.; Dong, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Effect of oleogelation on physical properties and oxidative stability of camellia oil-based oleogels and oleogel emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, A.L.; Morozova, K.; Ferrentino, G.; Biasioli, F.; Scampicchio, M. Early detection of acrolein precursors in vegetable oils by using proton transfer reaction–mass spectrometry. Talanta 2024, 270, 125513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CXS 210-1999; Standard for Named Vegetable Oils (amended 2022–2023). Codex Alimentarius Commission, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Miao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Q.; McClements, D.J.; Ji, H.; Jiang, L.; Qiu, C. Preparation of emulsion-template oleogels: Tuning properties by controlling initial water content and evaporation method. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Prieto, B. A laboratory approach on the combined effects of granite bioreceptivity and parameters modified by climate change on the development of subaerial biofilms on cultural heritage. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 164, 105295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

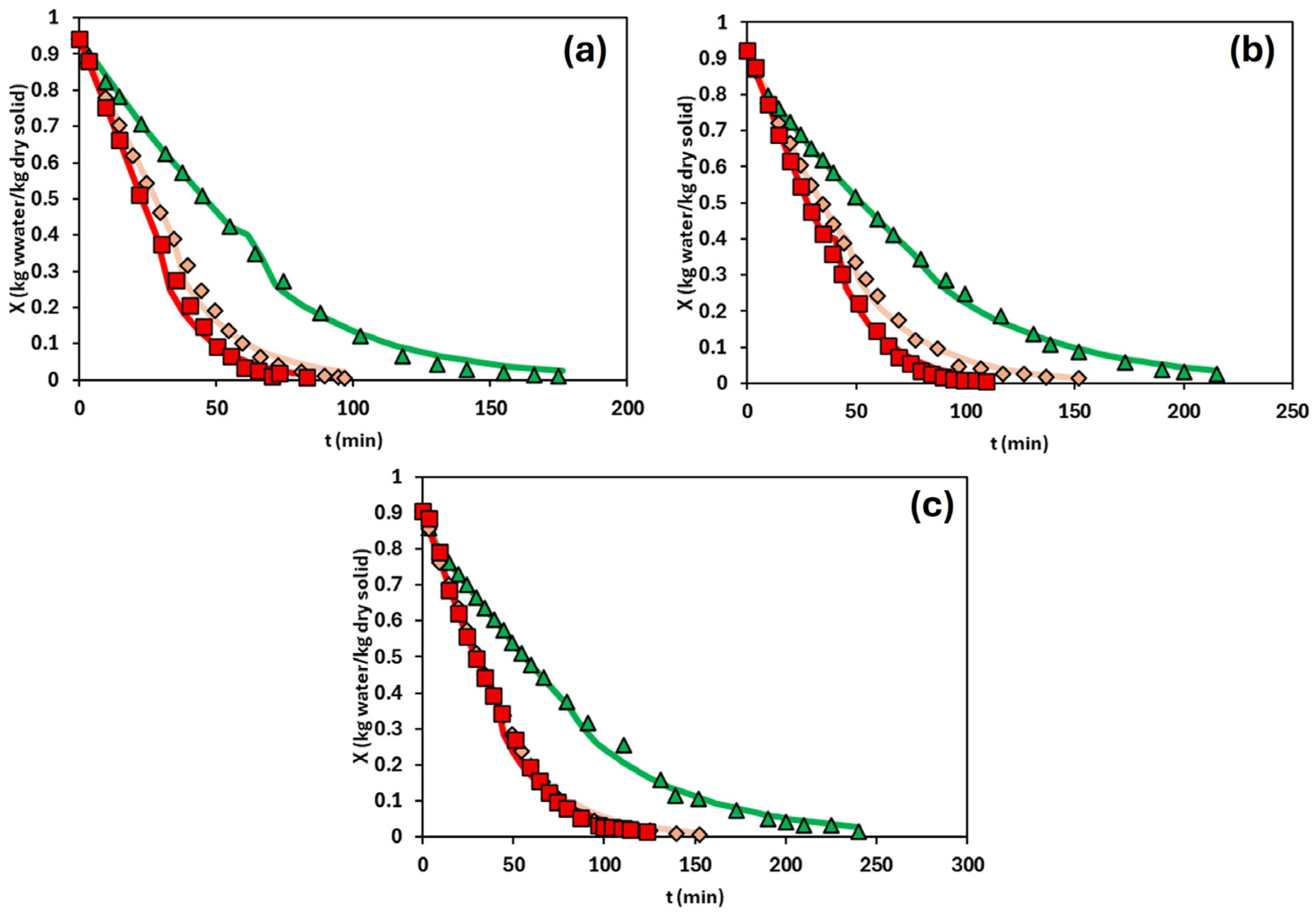

| HPMC Content (%, w/w) | Temperature (°C) | k (10−3 kg Water/(kg Dry Solid·min)) | Deff (10−11 m2/s) | R2 | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 70 | 8.9 ± 0.2 c,A | 5.21 c,A | 0.890 | 0.724 |
| 80 | 15.9 ± 0.2 c,B | 9.81 b,B | 0.993 | 0.073 | |
| 90 | 19.3 ± 0.5 b,C | 12.8 c,C | 0.994 | 0.087 | |
| 2.0 | 70 | 7.0 ± 0.4 b,A | 3.04 a,A | 0.994 | 0.040 |
| 80 | 11.4 ± 0.2 a,B | 6.85 a,B | 0.989 | 0.045 | |
| 90 | 12.7 ± 0.3 a,C | 10.3 b,C | 0.982 | 0.054 | |
| 2.5 | 70 | 6.24 ± 0.3 a,A | 3.63 b,A | 0.982 | 0.052 |
| 80 | 12.6 ± 0.3 b,B | 6.89 a,B | 0.992 | 0.053 | |
| 90 | 12.7 ± 0.4 a,B | 7.69 a,C | 0.989 | 0.053 |
| HPMC Content (%, w/w) | Drying Temperature (°C) | G’ (104 Pa) | OBC (%) | L* | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 60 | 1.39 ± 0.04 a,A | 79.0 ± 1.7 a,AB | 30.09 ± 2.07 a,A | −2.38 ± 0.25 a,A | 10.88 ± 0.79 a,AB | 0 |
| 70 | 1.80 ± 0.05 a,C | 80.3 ± 2.6 a,B | 31.50 ± 2.70 b,A | −2.19 ± 0.13 b,B | 10.33 ± 0.38 a,A | 1.53 | |
| 80 | 2.69 ± 0.07 a,D | 90.3 ± 1.4 a,C | 30.31 ± 0.61 b,A | −2.45 ± 0.12 a,A | 10.49 ± 0.49 a,A | 0.45 | |
| 90 | 1.51 ± 0.04 a,B | 75.7 ± 0.8 a,A | 31.04 ± 1.09 b,A | −2.35 ± 0.18 a,AB | 11.28 ± 0.92 a,B | 1.03 | |
| 2.0 | 60 | 4.11 ± 0.08 b,B | 86.7 ± 3.6 b,A | 30.17 ± 1.83 a,B | −2.34 ± 0.09 a,AB | 11.54 ± 0.72 b,B | 0.67 |
| 70 | 3.69 ± 0.07 b,A | 90.4 ± 1.4 b,A | 29.26 ± 0.73 a,AB | −2.28 ± 0.09 ab,BC | 10.97 ± 0.47 b,A | 0.84 | |
| 80 | 7.22 ± 0.14 b,C | 95.4 ± 1.6 b,B | 29.27 ± 0.74 a,AB | −2.41 ± 0.16 a,A | 11.54 ± 0.21 c,B | 1.05 | |
| 90 | 4.22 ± 0.08 b,B | 91.2 ± 2.6 b,A | 28.78 ± 1.07 a,A | −2.23 ± 0.04 b,C | 11.47 ± 0.20 a,B | 1.44 | |
| 2.5 | 60 | 6.80 ± 0.75 c,A | 94.4 ± 1.4 c,A | 29.55 ± 1.15 a,A | −2.35 ± 0.09 a,A | 10.63 ± 0.38 a,A | 0.60 |
| 70 | 10.7 ± 1.28 c,B | 99.4 ± 0.5 c,B | 29.31 ± 0.81 a,A | −2.37 ± 0.10 a,A | 11.92 ± 0.49 c,B | 1.30 | |
| 80 | 10.2 ± 1.10 c,B | 96.0 ± 1.2 b,A | 30.17 ± 1.22 b,A | −2.32 ± 0.10 a,A | 11.05 ± 0.56 b,A | 0.20 | |
| 90 | 8.78 ± 0.97 c,B | 95.5 ± 2.1 c,A | 30.39 ± 1.89 b,A | −2.21 ± 0.09 b,B | 10.90 ± 0.69 a,A | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lama, M.; Franco-Uría, A.; Moreira, R. Characterization of Rapeseed Oil Oleogels Produced by the Emulsion Template Method Using Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and the Drying Kinetics of the Emulsions. Foods 2025, 14, 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162908
Lama M, Franco-Uría A, Moreira R. Characterization of Rapeseed Oil Oleogels Produced by the Emulsion Template Method Using Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and the Drying Kinetics of the Emulsions. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162908
Chicago/Turabian StyleLama, Mario, Amaya Franco-Uría, and Ramón Moreira. 2025. "Characterization of Rapeseed Oil Oleogels Produced by the Emulsion Template Method Using Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and the Drying Kinetics of the Emulsions" Foods 14, no. 16: 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162908
APA StyleLama, M., Franco-Uría, A., & Moreira, R. (2025). Characterization of Rapeseed Oil Oleogels Produced by the Emulsion Template Method Using Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and the Drying Kinetics of the Emulsions. Foods, 14(16), 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162908






