Investigation on Precursor Aromas and Volatile Compounds During the Fermentation of Blackened Pear Vinegar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of BPV
2.3. Determination of TPC, TFC, Polysaccharides, and 5-HMF During the Fermentation of BPV
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Organic Acids by HPLC
2.5. Analysis of Free Amino Acids by Amino Acid Analyzer
2.6. Determination of Volatile Flavor Compounds
2.7. Analysis of Characteristic Flavor Compounds Based on Odor Activity Value (OAV)
2.8. E-Nose and E-Tongue Analysis of BPV
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
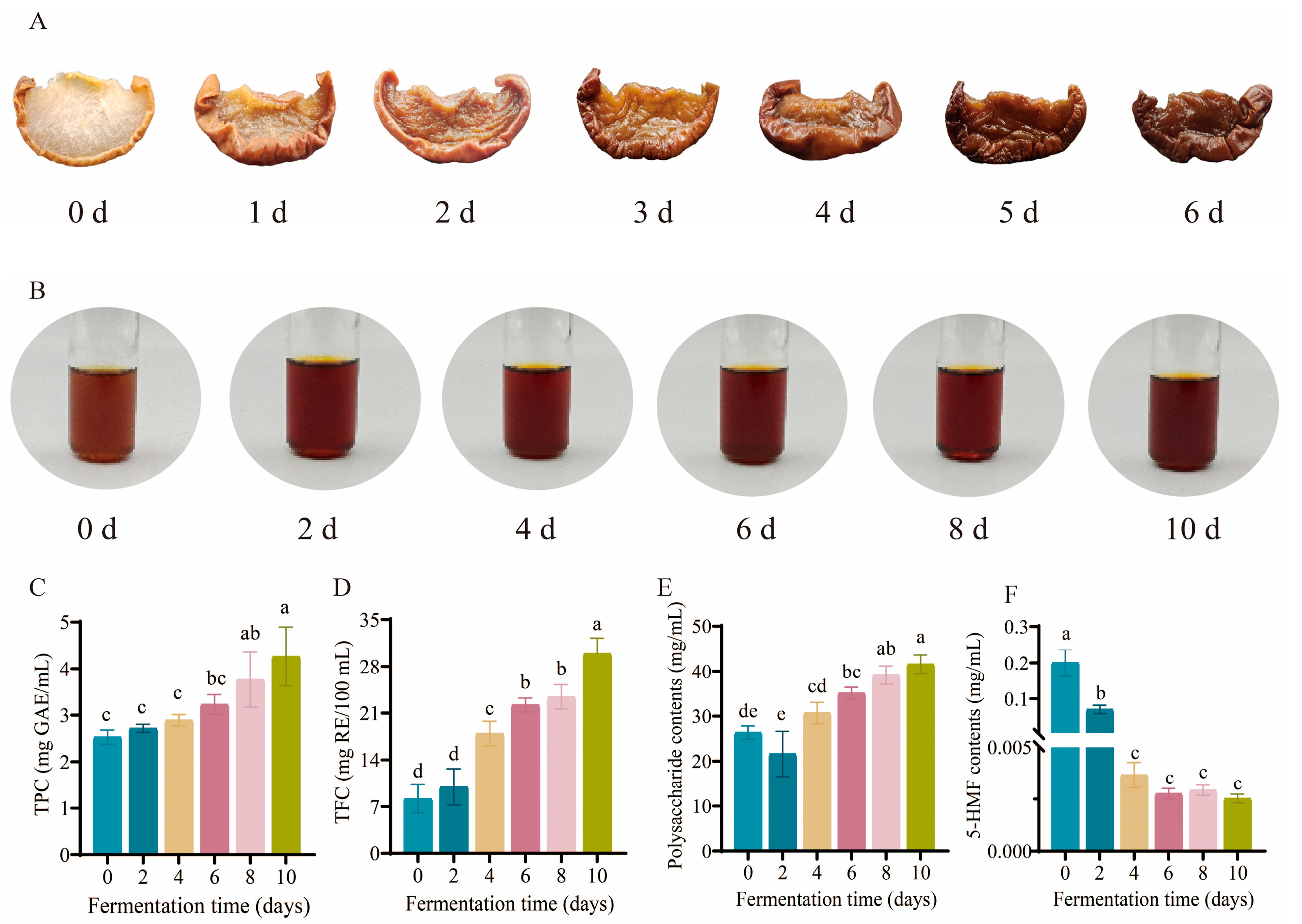
3.1. Analysis of Morphological and Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Dynamic Changes in Organic Acids
3.3. Dynamic Variation in Free Amino Acids
3.4. Dynamic Changes in Volatile Flavor Compounds During the Fermentation of BPV Analyzed by HS-SPME-GC–MS and OAV
3.5. Differences in Aroma Characteristics Analyzed by Multivariate Data Analysis
3.6. Results of E-Nose and E-Tongue
3.7. Correlation Between Volatile Flavor Compounds and Nonvolatile Flavor Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Qi, K.; Li, H.; Tian, R.; Wu, X.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Comparative analysis of volatile aromatic compounds from a wide range of pear (Pyrus L.) germplasm resources based on HS-SPME with GC–MS. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, S.; Vaateri, L.; Ma, X.; Haikonen, T.; Yang, B.; Laaksonen, O. Comparison of phenolic composition and sensory quality among pear beverages made using Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Torulaspora delbrueckii. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gu, D.Y.; Fu, Q.B.; Gao, L.; Shi, C.; Zhang, R.T.; Qiao, X.G. Content variations in compositions and volatile component in jujube fruits during the blacking process. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.R.; Chen, C.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pan, Z.L.; Zhang, R.T. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of jujubes (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.): Effect of blackening process on different cultivars. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 1576–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.C.; Zheng, Z.J.; Zhang, B.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Qiao, X.G. Formation, nutritional value, and enhancement of characteristic components in black garlic: A review for maximizing the goodness to humans. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 801–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.X.; Wu, F.; Gu, D.Y.; Tao, H.X.; Zhang, R.T. Organic acid and aromatic compounds create distinctive flavor in the blackening process of jujube. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Peng, S.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, T.; Gong, X.; Liao, L.; Li, J.; et al. Effects of acetic acid fermentation on the phytochemicals content, taste and aroma of pineapple vinegar. LWT 2024, 210, 116861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Chen, T.; Giudici, P.; Chen, F.S. Vinegar Functions on Health: Constituents, Sources, and Formation Mechanisms. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Xiong, J.; Sun, J.; Du, F.; Xu, G.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Lou, X. Dynamic transformation in flavor during hawthorn wine fermentation: Sensory properties and profiles of nonvolatile and volatile aroma compounds coupled with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 139982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J. Dynamic changes of quality and flavor characterization of Zhejiang rosy vinegar during fermentation and aging based on untargeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Qu, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Characterization of the flavor and nutritional value of coconut water vinegar based on metabolomics. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Bao, Y.; Wu, B.; Lao, F.; Hu, X.; Wu, J. Chemical analysis and flavor properties of blended orange, carrot, apple and Chinese jujube juice fermented by selenium-enriched probiotics. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Z.; Song, Y.R.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Zhang, R.T. Physicochemical properties, and volatile compounds of blackened jujube vinegar as prepared by optimized fermentation process. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wen, J.-J.; Hu, J.-L.; Nie, Q.-X.; Chen, H.-H.; Nie, S.-P.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M.-Y. Momordica charantia juice with Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation: Chemical composition, antioxidant properties and aroma profile. Food Biosci. 2019, 29, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Qiang, X.; Geng, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Changes in the Phytochemical and Bioactive Compounds and the Antioxidant Properties of Wolfberry during Vinegar Fermentation Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Mazza, G.; Zhang, X. Metagenomic analysis revealing the metabolic role of microbial communities in the free amino acid biosynthesis of Monascus rice vinegar during fermentation. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.P.; Lu, Y.R.; Ma, J.X.; Zhang, W.B.; Wen, P.C. Co-decoding dynamics in volatiles and sensory profiles of Zhaiji millet vinegar during aging by integrating multiple flavor characterization techniques and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2025, 479, 143803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Remize, F.; Poucheret, P. Fruits and vegetables, as a source of nutritional compounds and phytochemicals: Changes in bioactive compounds during lactic fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 104, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Medina-Meza, I.G. Impact of Fermentation on the Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Whole Cereal Grains: A Mini Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Cheng, F.S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, T.H.; Sun, Y.K.; Jiang, X.Q. Dynamic changes and correlation of quality, flavor and microorganisms of Mei (Prunus mume) vinegar during fermentation and clarification. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.-G.; Zhu, W.-L.; Yu, Y.-S.; Zou, B.; Xu, Y.-J.; Xiao, G.-S.; Wu, J.-J. The variation on structure and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharide during the longan pulp fermentation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünsche, J.; Schmid, J. Acetobacteraceae as exopolysaccharide producers: Current state of knowledge and further perspectives. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1166618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Deng, H.; Huang, L.; Teng, J.; Wei, B.; Xia, N.; Pang, B. Degradation of Cell Wall Polysaccharides during Traditional and Tank Fermentation of Chinese Liupao Tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 4195–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Su, D.; Lee, Y.-K.; Zou, X.; Dong, L.; Deng, M.; Zhang, R.; Huang, F.; Zhang, M. Accumulation of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides during Lychee Pulp Fermentation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Involves Endoglucanase Expression. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 3669–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Chen, K.T.; Lin, J.A.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, Y.A.; Wu, J.T.; Hsieh, C.W. Recent advances in processing technology to reduce 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastoriza de la Cueva, S.; Álvarez, J.; Végvári, Á.; Montilla-Gómez, J.; Cruz-López, O.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Rufián-Henares, J.A. Relationship between HMF intake and SMF formation in vivo: An animal and human study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanderley, B.; de Lima, N.D.; Deolindo, C.T.P.; Kempka, A.P.; Moroni, L.S.; Gomes, V.V.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Amboni, R.; Aquino, A.; et al. Impact of pre-fermentative maceration techniques on the chemical characteristics, phenolic composition, in vitro bioaccessibility, and biological activities of alcoholic and acetic fermented products from jaboticaba (Plinia trunciflora). Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Dang, B.; Yang, X.; Nie, M.; Chen, Z.; Lin, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.-T. Deeply analyzing dynamic fermentation of highland barley vinegar: Main physicochemical factors, key flavors, and dominate microorganisms. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.H.; Ding, N.A.; Han, R.H.; Deng, Y. Metabolic engineering and fermentation optimization strategies for producing organic acids of the tricarboxylic acid cycle by microbial cell factories. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 379, 128986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Barrao, C.; Saad, M.M.; Ferrete, E.C.; Bravo, D.; Chappuis, M.L.; Pérez, R.O.; Junier, P.; Perret, X.; Barja, F. Metaproteomics and ultrastructure characterization of Komagataeibacter spp. involved in high-acid spirit vinegar production. Food Microbiol. 2016, 55, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, K.; Lu, J.; Wu, D. Optimization of fermentation conditions and analysis of the changes in flavor compounds for lemon vinegar. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelwood Lucie, A.; Daran, J.-M.; van Maris Antonius, J.A.; Pronk Jack, T.; Dickinson, J.R. The Ehrlich Pathway for Fusel Alcohol Production: A Century of Research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae Metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2008, 74, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dalatony, M.M.; Saha, S.; Govindwar, S.P.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.I.; Jeon, B.H. Biological Conversion of Amino Acids to Higher Alcohols. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, T.; Lu, Y.; Hadiatullah, H.; Li, P.; Ding, K.; Zhao, G. Effects of amino acid composition of yeast extract on the microbiota and aroma quality of fermented soy sauce. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, B.F.; Qiao, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, X.B.; Cheng, S.Z.; Du, M. Impact of Cooking Processes on Volatile Flavor Compounds and Free Amino Acids in Fish Sauce. Foods 2025, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, R.; Xia, M.; Bai, X.; Mou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Effect of aspartic acid and glutamate on metabolism and acid stress resistance of Acetobacter pasteurianus. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.H.; Cui, C.F.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, Y.T.; Feng, S.B. Insight into the dynamic changes and relationship between organic acids, amino acids and microbial communities during the fermentation of highland barley wine. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 140, 107260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Zhang, Z.H.; He, R.H.; Zhao, G.Z.; Yu, Y.J.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X.L. Research advances in technologies and mechanisms to regulate vinegar flavor. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özen, M.; Özdemir, N.; Filiz, B.E.; Budak, N.H.; Kök-Tas, T. Sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) vinegars produced from fresh fruit or juice concentrate: Bioactive compounds, volatile aroma compounds and antioxidant capacities. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Jiang, J.; Ma, X.; Xie, Y.; Cui, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Gao, F. Dynamic changes of physicochemical parameters, antioxidant activity, organic acids, polyphenols, and volatile components in prune vinegar during fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalali, S.; Zheng, F.P.; Sun, B.G.; Rahman, T.; Chen, F. Tracking volatile flavor changes during two years of aging of Chinese vinegar by HS-SPME-GC-MS and GC-O. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Kuang, G.; Li, J.; Hadiatullah, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Pan, Z.-H.; Wang, Y. Characterization of aldehydes and hydroxy acids as the main contribution to the traditional Chinese rose vinegar by flavor and taste analyses. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, D.; Kim, G.-R.; Yeo, S.-H.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Noh, B.S.; Kwon, J.-H. Analysis of aroma compounds of commercial cider vinegars with different acidities using SPME/GC-MS, electronic nose, and sensory evaluation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela-Moura, A.; Schuller, D.; Mendes-Faia, A.; Côrte-Real, M. Effects of acetic acid, ethanol, and SO2 on the removal of volatile acidity from acidic wines by two Saccharomyces cerevisiae commercial strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Li, Y.J.; Zheng, L.Y.; Qin, Y.F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.J.; Zhang, H.; Du, L.P. Impact of organic acids on aroma release in light-flavor Baijiu: A focus on key aroma-active compounds. Food Biosci. 2025, 65, 106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.N.; Jing, S.; Wang, X.L.; Zheng, F.P.; Li, H.H.; Sun, B.G.; Li, Z.X. Evaluation of the Perceptual Interaction among Ester Odorants and Nonvolatile Organic Acids in Baijiu by GC-MS, GC-O, Odor Threshold, and Sensory Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13987–13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, S.; Burin, V.M.; Caliari, V.; Bordignon-Luiz, M.T. Profiling of free amino acids in sparkling wines during over-lees aging and evaluation of sensory properties. LWT 2021, 140, 110847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkwitz, F.; Nicolau, L.; Lund, C.; Beresford, M.; Wohlers, M.; Kilmartin, P.A. Evaluation of Key Odorants in Sauvignon Blanc Wines Using Three Different Methodologies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6293–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Martínez-Lapuente, L.; Ayestarán, B.; Guadalupe, Z. Volatile and sensory characterization of Tempranillo wines aged in Quercus alba oak barrels of different geographical origins in USA. LWT 2023, 173, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gemert, L.J. Compilations of Odour Threshold Values in Air, Water and Other Media, 2nd ed.; Oliemans Punter & Partners BV: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.A.; Sanchez-Palomo, E.; Alises, M.O.; Vinas, M.A.G. Chemical and sensory aroma typicity of La Mancha Petit Verdot wines. LWT 2022, 162, 113418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sensor Name | Main Applications | Reference Material |
|---|---|---|
| W1W | Sensitive to sulfides compounds | H2S, 1 mg kg−1 |
| W1C | Sensitive to aromatic compounds | Toluene, 10 mg kg−1 |
| W3C | Sensitive to ammonia and aromatic compounds | Benzene, 10 mg kg−1 |
| W6S | Mainly sensitive to hydrogen | H2, 100 µg kg−1 |
| W5C | Sensitive to alkenes and aromatic compounds | Propane, 1 mg kg−1 |
| W3S | Mainly sensitive to alkenes | CH3, 10 CH3, 100 mg kg−1 |
| W1S | Sensitive to methane | CH3, 100 mg kg−1 |
| W2S | Sensitive to alcohols, partially aromatic compounds | CO, 100 mg kg−1 |
| W5S | Broad sensitivity and very sensitive to nitrogen oxides | NO2, 1 mg kg−1 |
| W2W | Sensitive to aromatic compounds and organic sulfides | H2S, 1 mg kg−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Han, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Gao, L.; Zhang, R. Investigation on Precursor Aromas and Volatile Compounds During the Fermentation of Blackened Pear Vinegar. Foods 2025, 14, 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162905
Chen S, Wang Y, Sun X, Han Z, Jiang Q, Gao L, Zhang R. Investigation on Precursor Aromas and Volatile Compounds During the Fermentation of Blackened Pear Vinegar. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162905
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shangjing, Yuxiao Wang, Xin Sun, Zhizhen Han, Qiyong Jiang, Lin Gao, and Rentang Zhang. 2025. "Investigation on Precursor Aromas and Volatile Compounds During the Fermentation of Blackened Pear Vinegar" Foods 14, no. 16: 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162905
APA StyleChen, S., Wang, Y., Sun, X., Han, Z., Jiang, Q., Gao, L., & Zhang, R. (2025). Investigation on Precursor Aromas and Volatile Compounds During the Fermentation of Blackened Pear Vinegar. Foods, 14(16), 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162905







