Novel Insight into Metabolism Mechanism of Biogenic Amines During Fermentation of Chinese Traditional Fermented Mandarin Fish (Chouguiyu) Based on Metabolism Pathway and Correlation Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermentation of Chouguiyu
2.2. Metagenome Sequencing of Microbial Community in Chouguiyu
2.3. Gene Assembly and Functional Annotation
2.4. Determination of Biogenic Amines
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
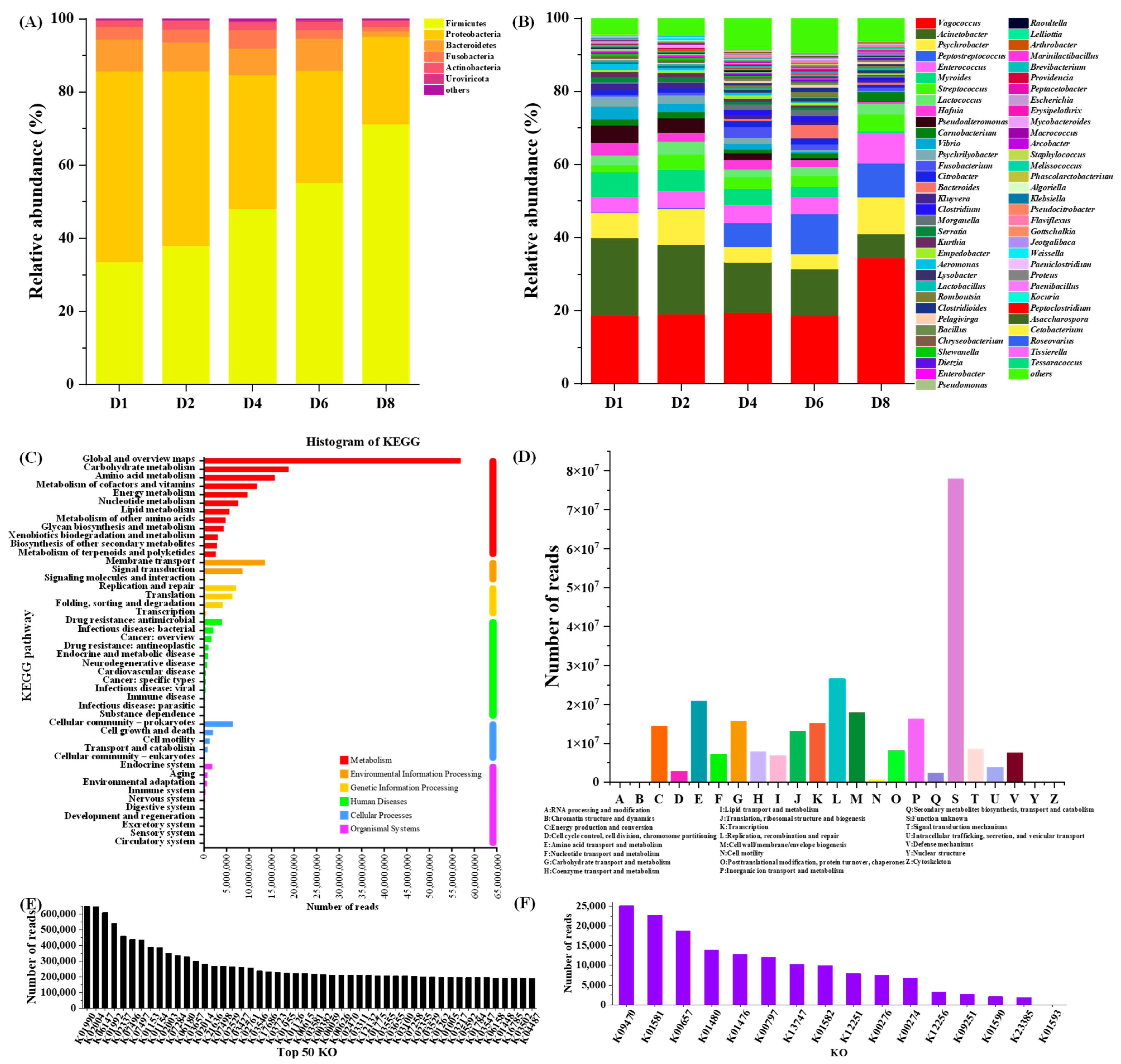
3.1. Metagenomic Analysis of Microbial Community in Chouguiyu
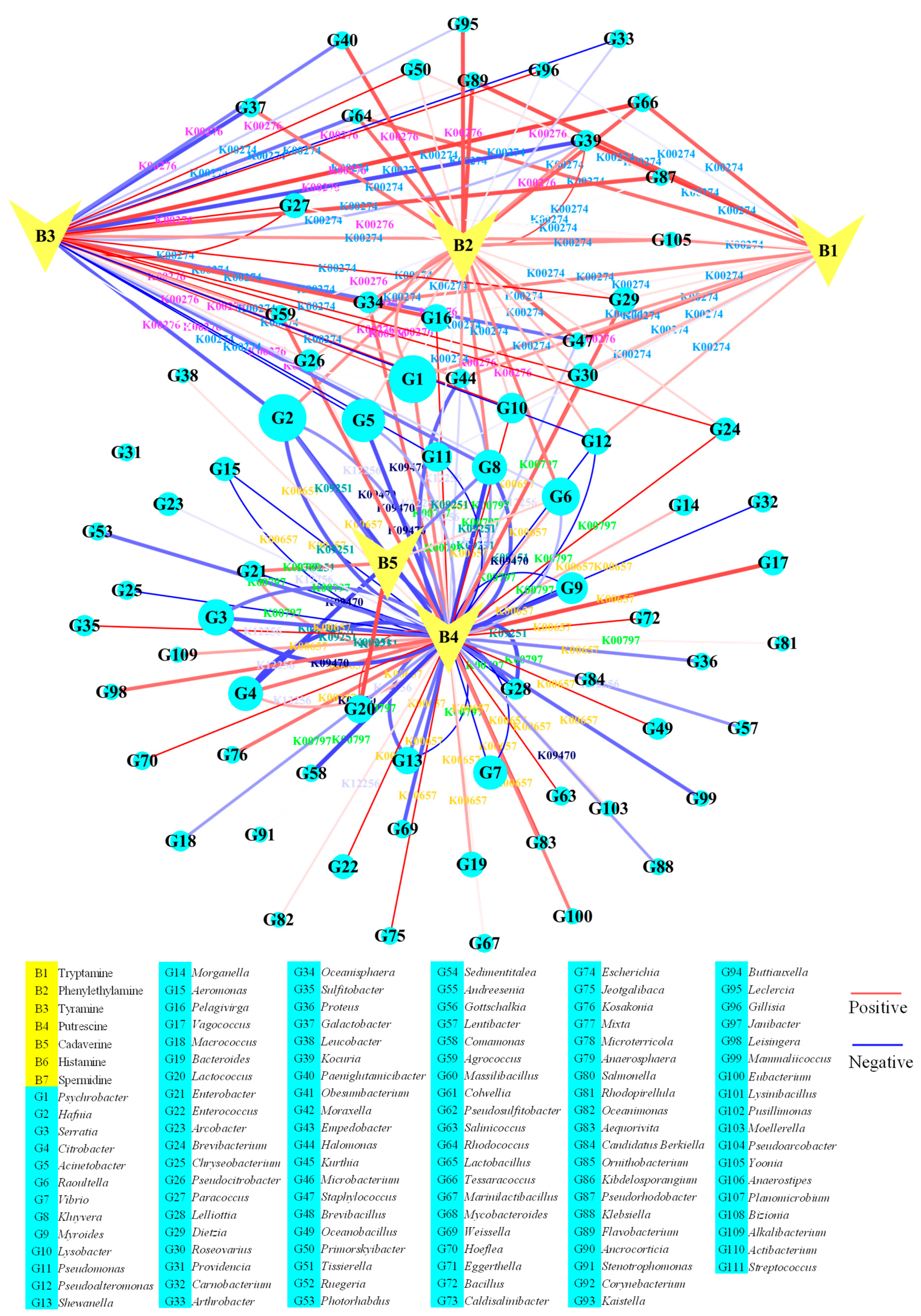
3.2. Enzymes Related to Biogenic Amine Metabolism in Chouguiyu Based on KO Functions
3.3. Microbial Genus Related to Biogenic Amine Metabolism in Chouguiyu Based on KO
3.3.1. Microbial Genera for BA Synthesis
3.3.2. Microbial Genera for BA Degradation
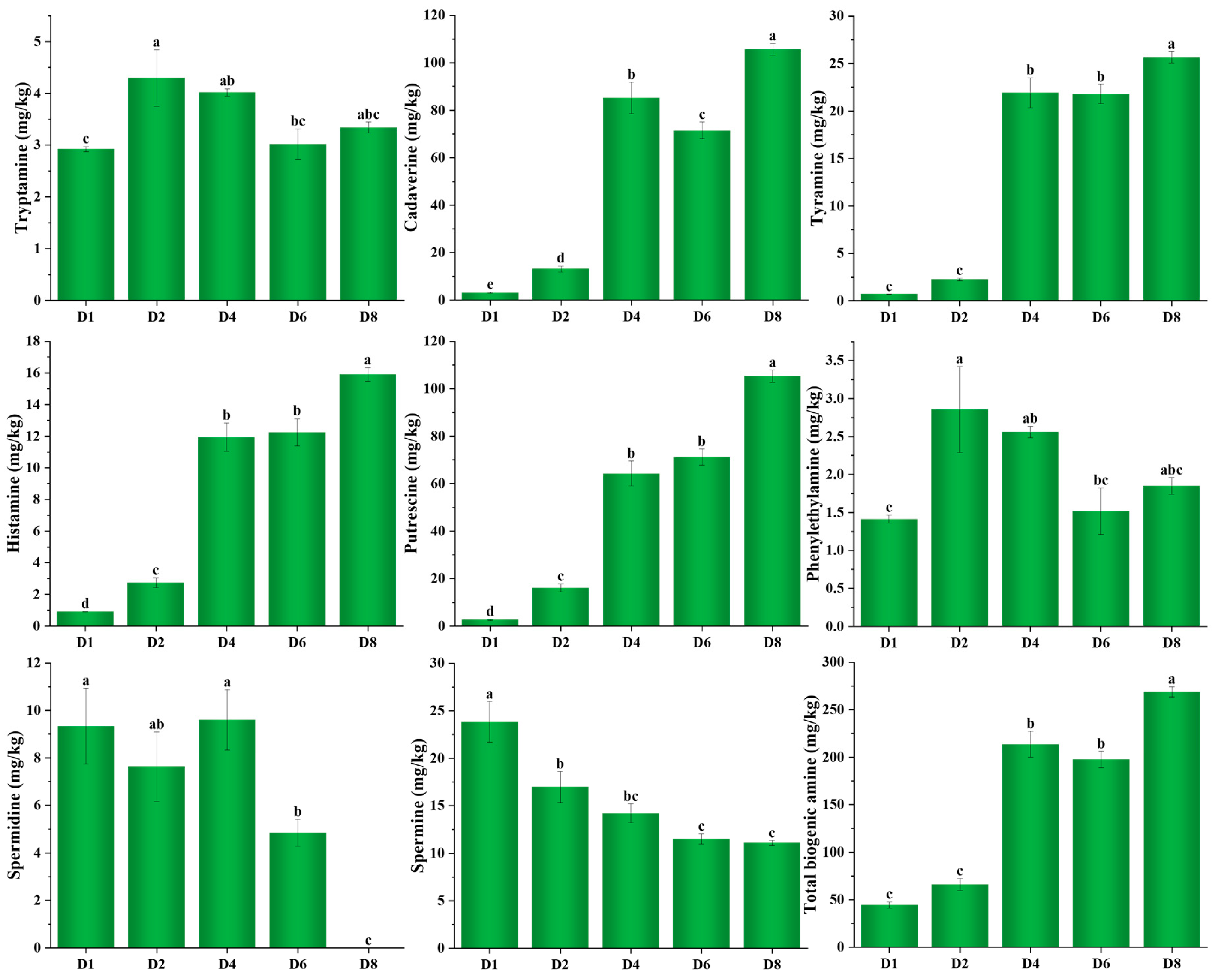
3.4. Change in Biogenic Amines During Fermentation of Chouguiyu
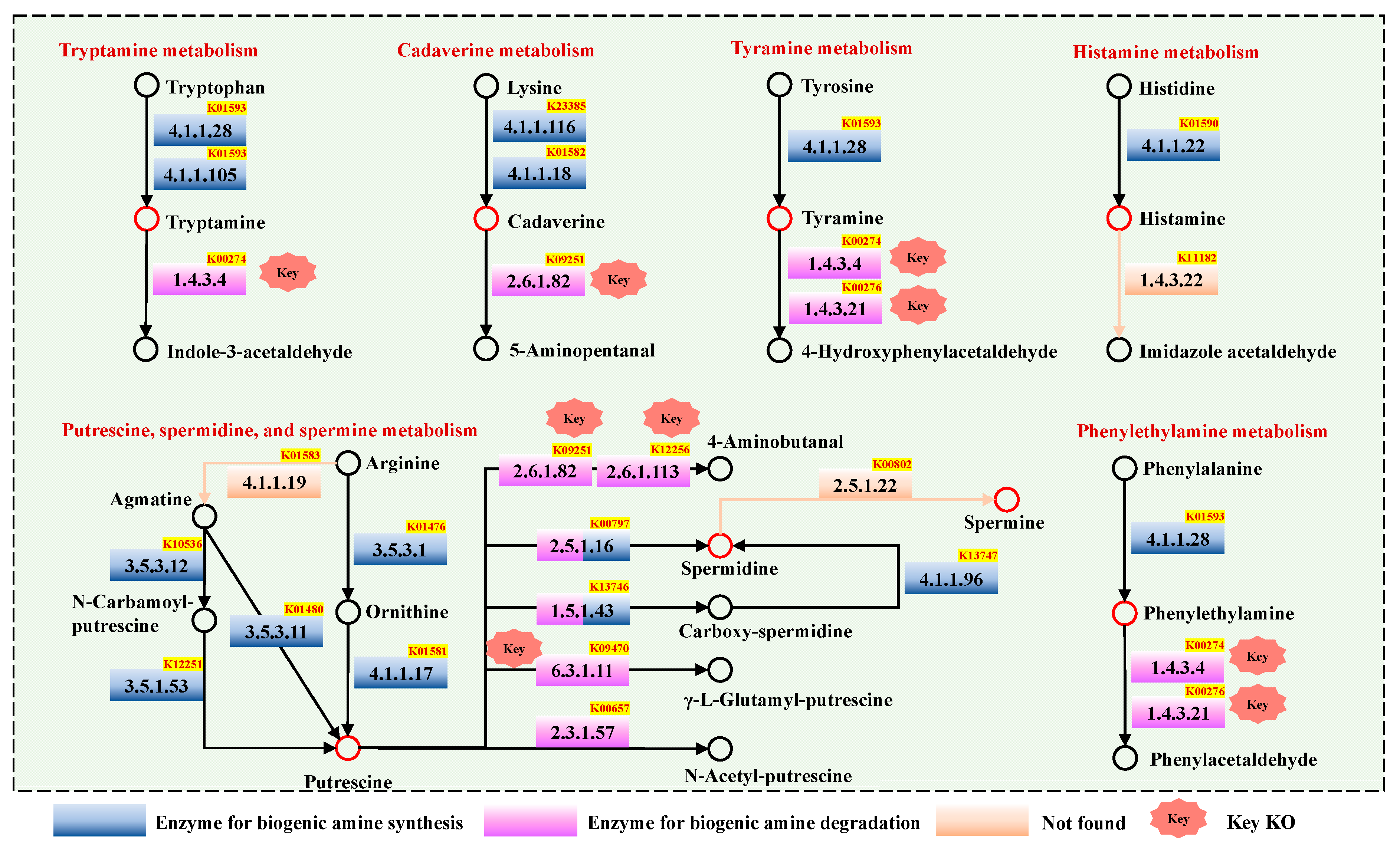
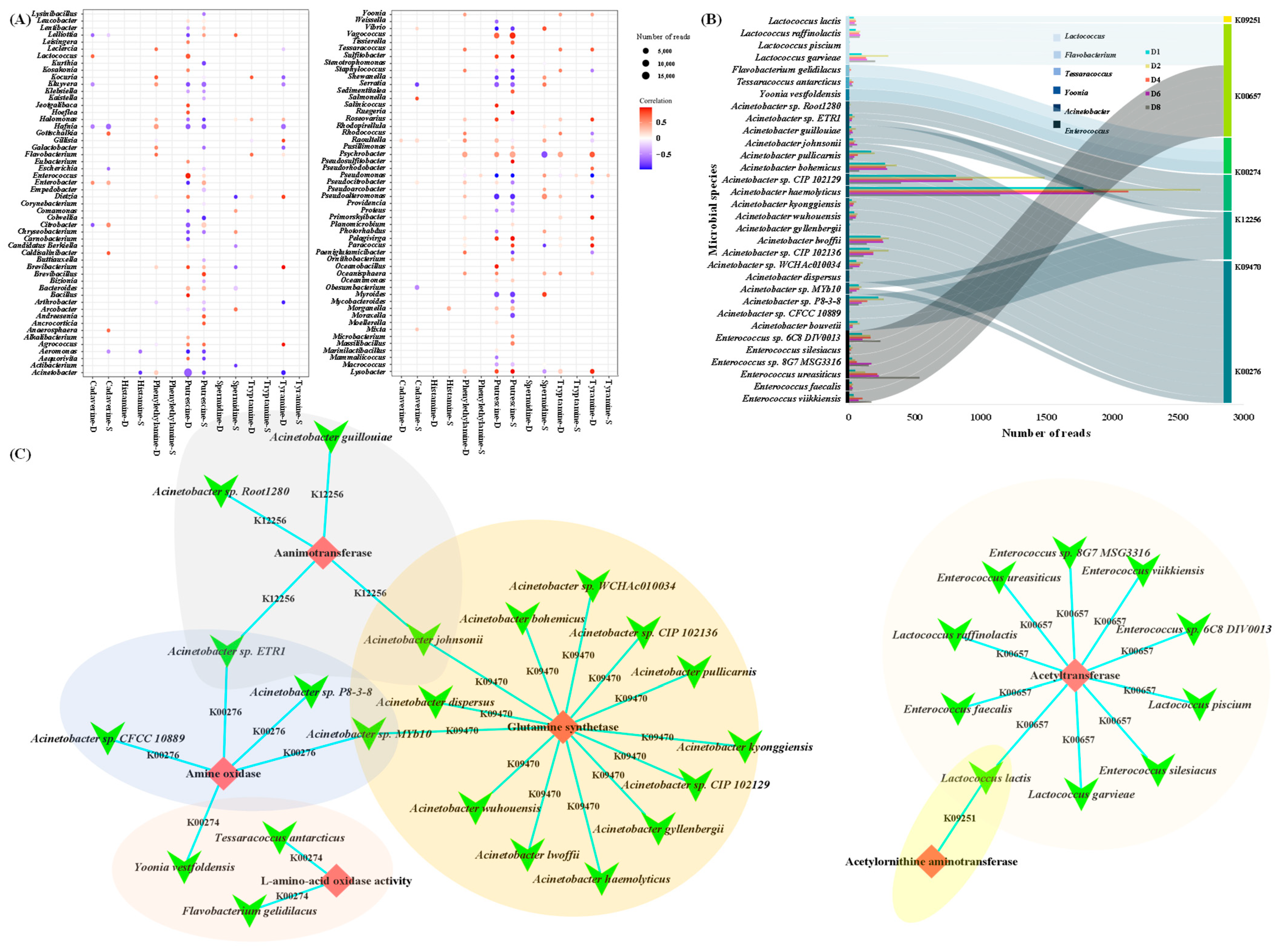
3.5. Relationship of Biogenic Amine and Metabolic Pathway in Chouguiyu
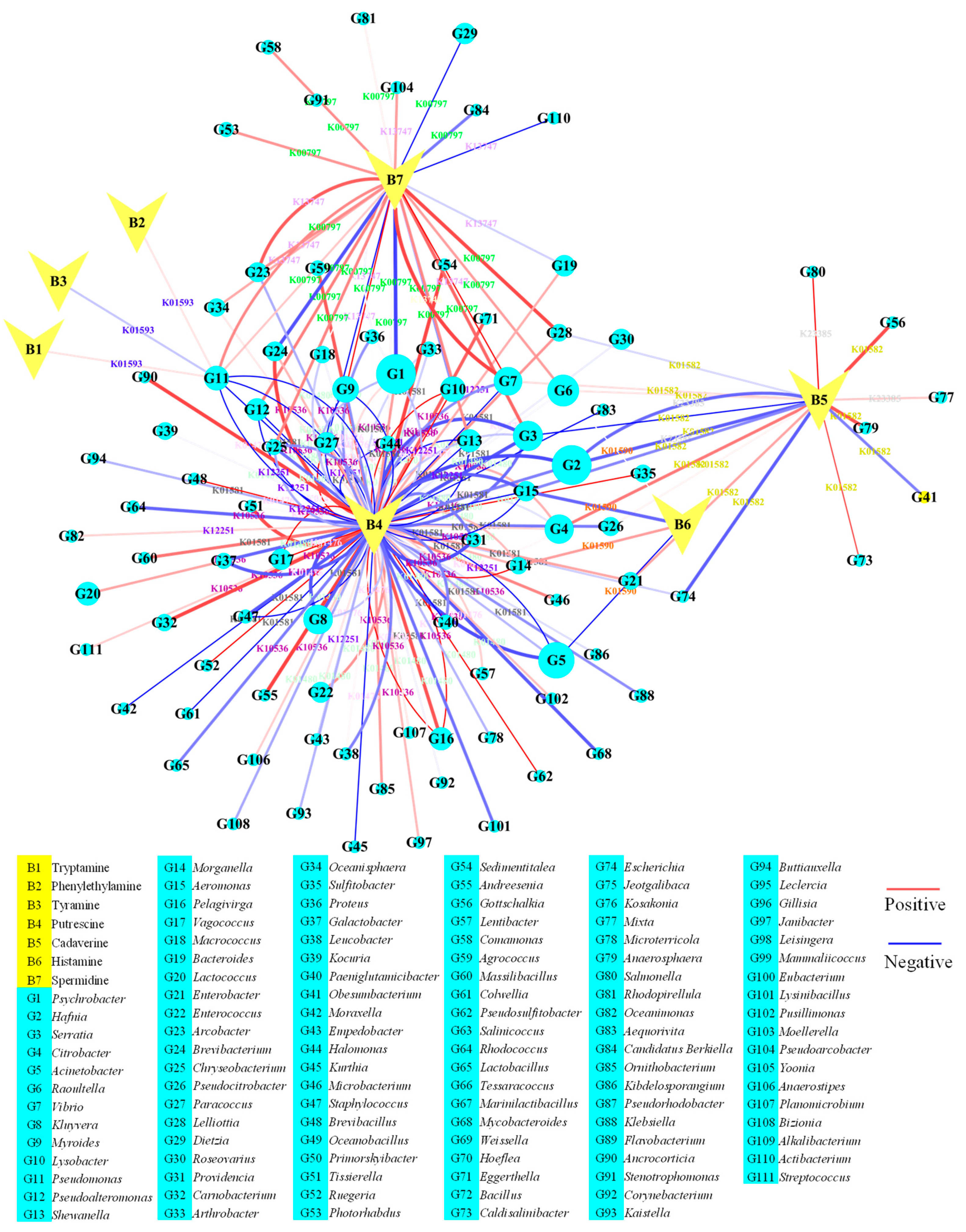
3.6. Identification of Core Microorganisms for Biogenic Amine Degradation in Chouguiyu
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dabade, D.S.; Jacxsens, L.; Miclotte, L.; Abatih, E.; Devlieghere, F.; De Meulenaer, B. Survey of multiple biogenic amines and correlation to microbiological quality and free amino acids in foods. Food Control 2021, 120, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turna, N.S.; Chung, R.; Mcintyre, L. A review of biogenic amines in fermented foods: Occurrence and health effects. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y. Novel insight into flavor and quality formation in naturally fermented low-salt fish sauce based on microbial metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, C.; Xu, B.; Dong, X.; Ma, N.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y. Halomonas shantousis sp. nov., a novel biogenic amines degrading bacterium isolated from Chinese fermented fish sauce. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.S.; Cho, S.K.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.; Cho, K.; Han, N.S. Isolation and characterization of biogenic amine-producing bacteria in fermented soybean pastes. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Cui, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Formation and improvement mechanism of physical property and volatile flavor of fermented tilapia surimi by newly isolated lactic acid bacteria based on two dimensional correlation networks. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. Novel insight into physicochemical and flavor formation in naturally fermented tilapia sausage based on microbial metabolic network. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, X.; Ma, X.; Hao, H.; Bi, J.; Zhang, G.; Hou, H. Evaluation of biogenic amines and microbial composition in the Chinese traditional fermented food grasshopper sub shrimp paste. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 134, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Lang, X.; Ji, Y.; Li, S.; Xin, N.; Meng, X.; Zhang, T.; Shen, X.; Zhao, C. The interaction between Lactobacillus plantarum SC-5 and its biogenic amine formation with different salt concentrations in Chinese Dongbei Suancai. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, M.; Cai, R.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xu, C. Metagenomic analysis reveals the linkages between bacteria and the functional enzymes responsible for potential ammonia and biogenic amine production in alfalfa silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 2594–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, D. Novel insight into the formation mechanism of umami peptides based on microbial metabolism in Chouguiyu, a traditional Chinese fermented fish. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Dong, J.; Tan, G.; Li, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, M. Metagenomic insights into the bacteria responsible for producing biogenic amines in sufu. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Lv, J.; Sun, Z.; Xu, W.; Ji, C.; Liang, H.; Li, S.; Yu, C.; Lin, X. Microbial succession and the changes of flavor and aroma in Chouguiyu, a traditional Chinese fermented fish. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S. Contribution of autochthonous microbiota succession to flavor formation during Chinese fermented mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Xiang, H. Taste mechanism of umami peptides from Chinese traditional fermented fish (Chouguiyu) based on molecular docking using umami receptor T1R1/T1R3. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Deng, J.; Yang, S. Formation and inhibition mechanism of novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Chouguiyu. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 851895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Du, F.; Han, X.; Li, J. Impacts of ε-polylysine hydrochloride with thymol on biogenic amines formation and biochemical changes of squid (Illexargentinus). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Cen, J.; Yang, S.; Yang, D. Novel insight into the formation mechanism of volatile flavor in Chinese fish sauce (Yu-lu) based on molecular sensory and metagenomics analyses. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Ladero, V.; Alvarez, M.A.; Lucas, P.M. Putrescine production via the ornithine decarboxylation pathway improves the acid stress survival of Lactobacillus brevis and is part of a horizontally transferred acid resistance locus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 175, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosma, I.; Badeka, A. Determination of six underivatized biogenic amines by LC-MS/MS and study of biogenic amine production during trout (Salmo trutta) storage in ice. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geornaras, I.; Dykes, G.A.; von Holy, A. Biogenic amine formation by poultry-associated spoilage and pathogenic bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1995, 21, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Zhongjun, C.; Cai, H.; Honggui, W.; Ouyang, P. Directed evolution and mutagenesis of lysine decarboxylase from Hafnia alvei AS1.1009 to improve its activity toward efficient cadaverine production. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2015, 20, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubelova, Z.; Bunka, F.; Tatakova, M.; Stajnochova, K.; Purevdorj, K.; Bunkova, L. Effects of temperature, pH and NaCl content on in vitro putrescine and cadaverine production through the growth of Serratia marcescens CCM 303. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2015, 50, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, G.; Greifova, M.; Karovicova, J. Effects of NaCl concentration and initial pH value on biogenic amine formation dynamics by Enterobacter spp. bacteria in model conditions. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2006, 45, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Xue, L.; Lu, S. Heterologous expression and application of multicopper oxidases from Enterococcus spp. for degradation of biogenic amines. Protein Pept. Lett. 2021, 28, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Du, X.; Feng, L.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y. The microbial community, biogenic amines content of soybean paste, and the degradation of biogenic amines by Lactobacillus plantarum HM24. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6458–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podeur, G.; Dalgaard, P.; Leroi, F.; Prévost, H.; Emborg, J.; Martinussen, J.; Hansen, L.H.; Pilet, M. Development of a real-time PCR method coupled with a selective pre-enrichment step for quantification of Morganella morganii and Morganella psychrotolerans in fish products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 203, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Kung, H.; Lin, C.; Tsai, H.; Tsai, Y. Histamine production by Raoultella ornithinolytica in mahi-mahi meat at various storage temperatures. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavizzari, T.; Breccia, M.; Bover-Cid, S.; Vidal-Carou, M.C.; Veciana-Nogues, M.T. Histamine, cadaverine, and putrescine produced in vitro by Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonadaceae isolated from spinach. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helinck, S.; Perello, M.; Deetae, P.; de Revel, G.; Spinnler, H. Debaryomyces hansenii, Proteus vulgaris, Psychrobacter sp. and Microbacterium foliorum are able to produce biogenic amines. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2013, 93, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Pennacchia, C.; Di Pasqua, R.; Fiore, A.; Fogliano, V.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Decarboxylase gene expression and cadaverine and putrescine production by Serratia proteamaculans in vitro and in beef. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 165, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Kong, C.; Luo, Y. Effect of cinnamon essential oil on bacterial diversity and shelf-life in vacuum-packaged common carp (Cyprinus carpio) during refrigerated storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kämpfer, P.; Jerzak, L.; Wilharm, G.; Golke, J.; Busse, H.; Glaeser, S.P. Psychrobacter ciconiae sp. nov., isolated from white storks (Ciconia ciconia). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65 Pt 3, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakanaka, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Nara, M.; Kitakata, A.; Kurihara, S. Functional analysis of arginine decarboxylase gene speA of Bacteroides dorei by markerless gene deletion. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves López, C.; De Angelis, M.; Martuscelli, M.; Serio, A.; Paparella, A.; Suzzi, G. Characterization of the Enterobacteriaceae isolated from an artisanal Italian ewe’s cheese (Pecorino Abruzzese). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, H.; Liu, L.; Jiang, X.; Wu, S.; Gao, H. Promiscuous enzymes cause biosynthesis of diverse siderophores in Shewanella oneidensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00030-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarcello, R.; De Angelis, M.; Settanni, L.; Formiglio, S.; Gaglio, R.; Minervini, F.; Moschetti, G.; Gobbetti, M. Selection of amine-oxidizing dairy lactic acid bacteria and identification of the enzyme and gene involved in the decrease of biogenic amines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6870–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y. Characterization of amine oxidases from Arthrobacter aurescens and application for determination of biogenic amines. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBeeR, J.; Bell, J.W.; Nolte, F.; Arcieri, J.; Correa, G. Histamine Limits by Country: A Survey and Review. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1610–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, 4th ed.; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2021.
- Li, C.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B. Microbial community changes induced by a newly isolated salt-tolerant Tetragenococcus muriaticus improve the volatile flavor formation in low-salt fish sauce. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, C. Novel insight into the formation and improvement mechanism of physical property in fermented tilapia sausage by cooperative fermentation of newly isolated lactic acid bacteria based on microbial contribution. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; An, K.; Shi, Q.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Z. Evaluation of the relationship among biogenic amines, nitrite and microbial diversity in fermented mustard. Molecules 2021, 26, 6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, C.; Pan, C.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Antimicrobial activity and mechanism of action of oregano essential oil against Morganella psychrotolerans and potential application in tuna. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 165, 113758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.Y.; Kim, T.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Song, H.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Ahn, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, S.H. Role of jeotgal, a Korean traditional fermented fish sauce, in microbial dynamics and metabolite profiles during kimchi fermentation. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Li, C. Novel Insight into Metabolism Mechanism of Biogenic Amines During Fermentation of Chinese Traditional Fermented Mandarin Fish (Chouguiyu) Based on Metabolism Pathway and Correlation Network. Foods 2025, 14, 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162863
Li J, Yang D, Zhao Y, Wang D, Huang H, Li C. Novel Insight into Metabolism Mechanism of Biogenic Amines During Fermentation of Chinese Traditional Fermented Mandarin Fish (Chouguiyu) Based on Metabolism Pathway and Correlation Network. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162863
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jun, Daqiao Yang, Yongqiang Zhao, Di Wang, Hui Huang, and Chunsheng Li. 2025. "Novel Insight into Metabolism Mechanism of Biogenic Amines During Fermentation of Chinese Traditional Fermented Mandarin Fish (Chouguiyu) Based on Metabolism Pathway and Correlation Network" Foods 14, no. 16: 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162863
APA StyleLi, J., Yang, D., Zhao, Y., Wang, D., Huang, H., & Li, C. (2025). Novel Insight into Metabolism Mechanism of Biogenic Amines During Fermentation of Chinese Traditional Fermented Mandarin Fish (Chouguiyu) Based on Metabolism Pathway and Correlation Network. Foods, 14(16), 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162863








