Accurate Classification of Multi-Cultivar Watermelons via GAF-Enhanced Feature Fusion Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
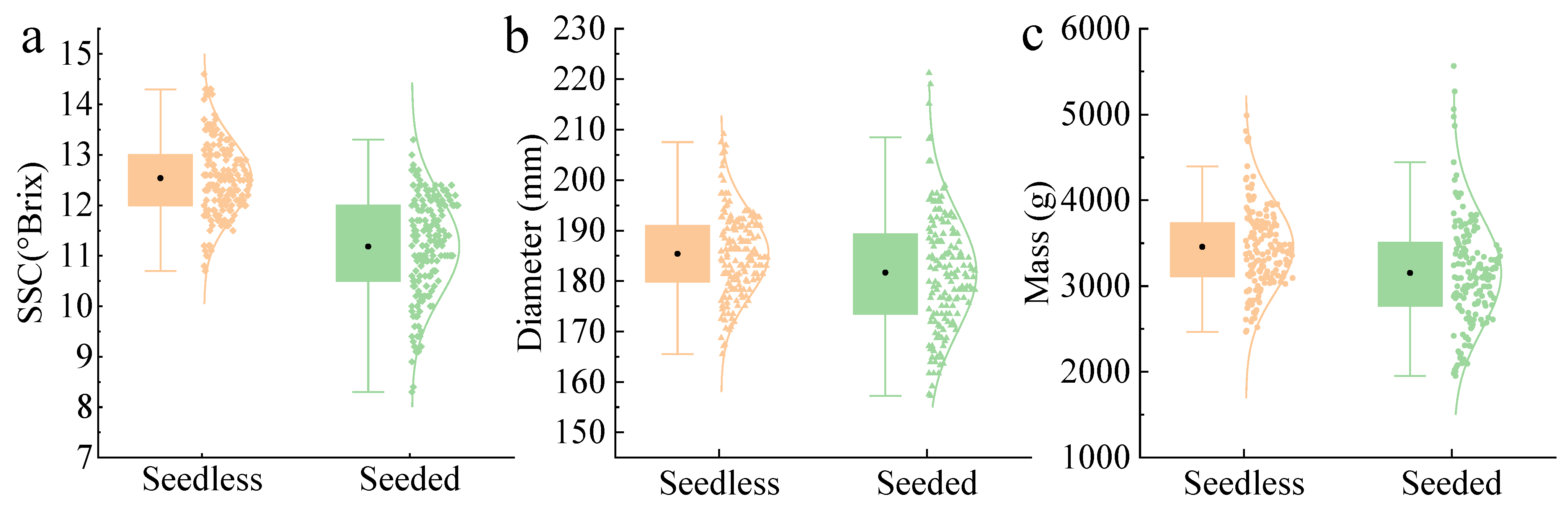
2.1. Watermelon Samples
2.2. Transmittance Spectrum Collection
2.3. Gramian Angular Field
2.4. Traditional Model Development
2.4.1. Dimensionality Reduction
2.4.2. Wavelength Selection
2.4.3. PLS-DA and SVM
2.5. Convolutional Neural Network
2.5.1. Single Image Input
2.5.2. Dual Image Input
2.5.3. Network Parameter Setting
2.5.4. CNN Visualization
2.6. Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
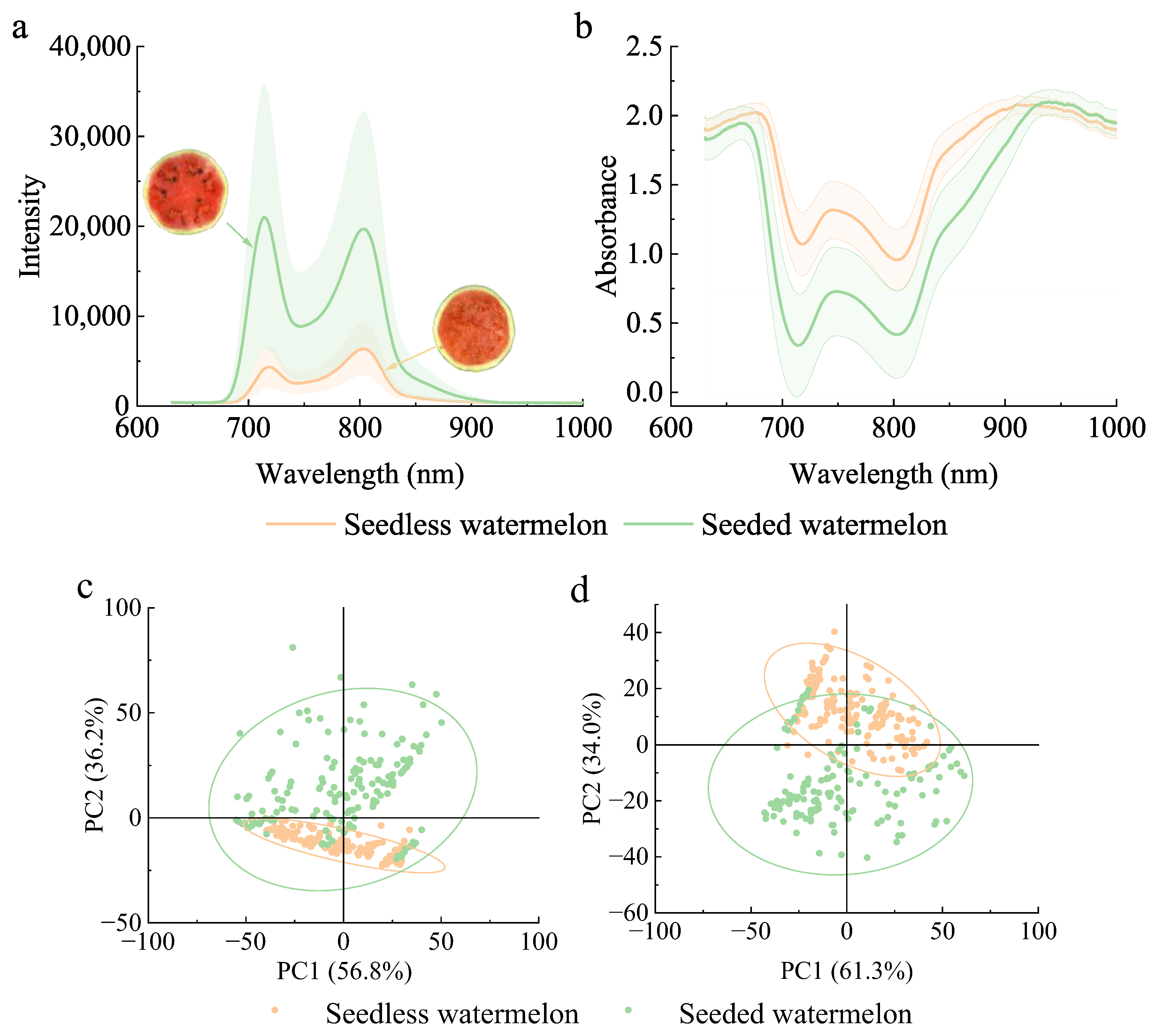
3.1. Analysis of Spectra
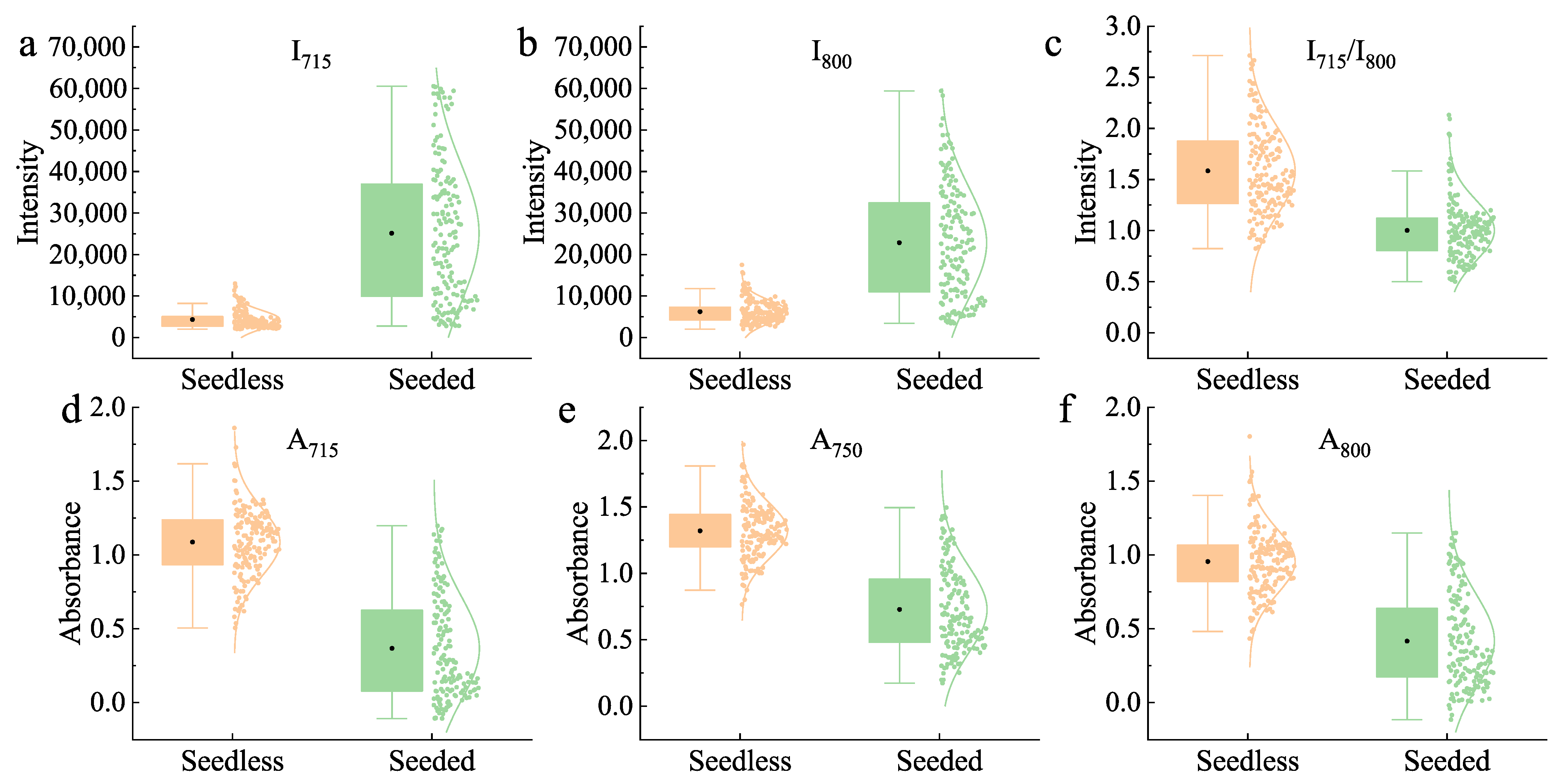
3.2. Classification Based on Intensity and Absorbance Value
3.3. Classification Result
3.3.1. Models Based on One-Dimensional Spectra
3.3.2. Models Based on Two-Dimensional Images
3.3.3. Model Visualization Analysis
3.3.4. CARS-GAF-CNN
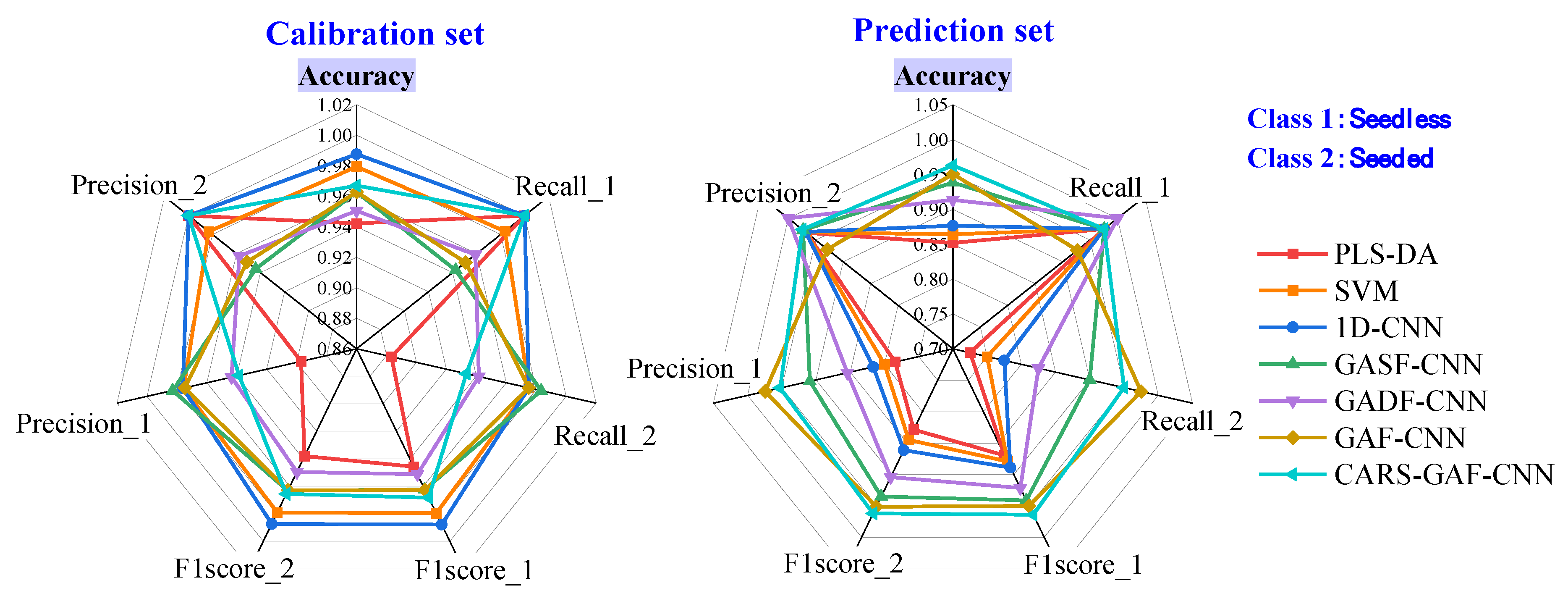
3.4. Model Comparison
3.5. Model Validation Using Different Samples
3.6. Discussion of the Developed CARS-GAF-CNN
3.6.1. Contribution and Interpretability of the Whole Wavelengths
3.6.2. Advantages of Image Construction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jie, D.; Wei, X. Review on the recent progress of non-destructive detection technology for internal quality of watermelon. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 151, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Ma, B.; Li, Y.; Dong, F. Quality detection of watermelons and muskmelons using innovative nondestructive techniques: A comprehensive review of novel trends and applications. Food Control 2024, 165, 110688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Ai, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Tian, S.; Yuan, L. A sexually and vegetatively reproducible diploid seedless watermelon inducer via ClHAP2 mutation. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trandel, M.A.; Johanningsmeier, S.; Schultheis, J.; Gunter, C.; Perkins-Veazie, P. Cell wall polysaccharide composition of grafted ‘Liberty’ watermelon with reduced incidence of hollow heart defect. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 623723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trandel, M.A.; Perkins-Veazie, P.; Schultheis, J. Predicting Hollow Heart Incidence in Triploid Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). HortScience 2020, 55, 1926–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; He, N.; Anees, M.; Yang, D.; Kong, W.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, L.; Luo, X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, W. A comparison of watermelon flesh texture across different ploidy levels using histology and cell wall measurements. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.; George, S.; Devassy, B.M.; George, S.N. Development of a unified framework of low-rank approximation and deep neural networks for predicting the spatial variability of SSC in ‘Spania’ watermelons using vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, D.; Zhou, W.; Wei, X. Nondestructive detection of maturity of watermelon by spectral characteristic using NIR diffuse transmittance technique. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Wang, D.; Feng, Z.; Li, W.; Cui, D. Integration of vibration and optical techniques for watermelon firmness assessment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Portillo, F.J.; Abellán-López, D.; Fabra-Rodriguez, M.; Peral-Orts, R.; Sánchez-Lozano, M. Detection of hollow heart disorder in watermelons using vibrational test and machine learning. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawgien, K.; Kiattisin, S. Machine learning techniques for classifying the sweetness of watermelon using acoustic signal and image processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 181, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Yu, Y.; Rao, X.; Wang, J. Firmness prediction and modeling by optimizing acoustic device for watermelons. J. Food Eng. 2016, 168, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, N.; Gan, Y.; Kong, L.Y. Emerging non-invasive microwave and millimeter-wave imaging technologies for food inspection. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 3302–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres-Hernandez, D.; Gutierrez, R.; Kung, K.; Rodriguez, J.; Lao, O.; Contreras, K.; Jo, K.-H.; Sanchez-Galan, J.E. Recent advances in automatic feature detection and classification of fruits including with a special emphasis on watermelon (Citrillus lanatus): A review. Neurocomputing 2023, 526, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Yu, Y.; Qu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, S.; Tao, K.; Xu, H. Transmittance spectra and acoustic properties of durians with different ripening: An exploration of application for complex-structured and large-sized fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 217, 113103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhai, L.; Zou, Y.; Sun, C.; Jayan, H.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Jiang, S.; Cai, J.; Zou, X. Comparative study of Vis/NIR reflectance and transmittance method for on-line detection of strawberry SSC. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.G.; Huang, W.Q.; Cai, Z.L.; Yan, Z.W.; Li, S.; Li, J.B. Online detection of sugar content in watermelon based on full-transmission visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2024, 44, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Tian, H.; Hu, D.; Yang, J.; Xie, L.; Xu, H.; Ying, Y. Integrating deep learning and data fusion for enhanced oranges soluble solids content prediction using machine vision and Vis/NIR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2024, 464, 141488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Early detection of freezing damage in oranges by online Vis/NIR transmission coupled with diameter correction method and deep 1D-CNN. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, R.; Li, X.; Li, J. Detection of early decayed oranges by using hyperspectral transmittance imaging and visual coding techniques coupled with an improved deep learning model. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 217, 113095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, M. Determination of watermelon soluble solids content based on visible/near infrared spectroscopy with convolutional neural network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 133, 104825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lan, W.; Wang, M.; Tu, K.; Zhu, L.; Pan, L. Exploring the impact of lenticels on the detection of soluble solids content in apples and pears using hyperspectral imaging and one-dimensional convolutional neural networks. Food Res. Int. 2025, 205, 115960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Mu, J.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y. Whale optimization algorithm-based multi-task convolutional neural network for predicting quality traits of multi-variety pears using near-infrared spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 215, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jayan, H.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Alzamora, S.M.; Gómez, P.L.; Zou, X. Detection model transfer of apple soluble solids content based on NIR spectroscopy and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Deng, J.; Zhu, C. Quantitative analysis of aflatoxin B1 in moldy peanuts based on near-infrared spectra with two-dimensional convolutional neural network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.; Taheri-Garavand, A.; Zhang, Y.-D. Image-based deep learning automated sorting of date fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 153, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Zhiguang, Q.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Ali, L.; Almaspoor, Z.; Monday, H.N. Recent advancements in fruit detection and classification using deep learning techniques. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9210947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, J.; Tian, S.; Tian, H.; Xu, H. Vis/NIR model development and robustness in prediction of potato dry matter content with influence of cultivar and season. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 197, 112202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.Q.; Yang, K.; Zhu, J.L.; Guo, W.C.; Lu, C.; Zhu, X.H. Qualitative identification of mature milk adulteration in bovine colostrum using noise-reduced dielectric spectra and linear model. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 7313–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Ying, X.; Lu, C.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Song, H. Utilization of deep learning models to predict calving time in dairy cattle from tail acceleration data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Cao, D. Key wavelengths screening using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method for multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 648, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, G.; Gao, C.; Shao, Y. Spectral and image analysis of hyperspectral data for internal and external quality assessment of peach fruit. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2022, 272, 121016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; He, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, D.; An, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.; Cheng, F. Array-optimized artificial olfactory sensor enabling cost-effective and non-destructive detection of mycotoxin-contaminated maize. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 139940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lu, R.; Pan, L.; Wang, X.; Tu, K. Assessment of the optical properties of peaches with fungal infection using spatially-resolved diffuse reflectance technique and their relationships with tissue structural and biochemical properties. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semyalo, D.; Kwon, O.; Wakholi, C.; Min, H.J.; Cho, B.-K. Nondestructive online measurement of pineapple maturity and soluble solids content using visible and near-infrared spectral analysis. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 209, 112706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Jin, H.; Yang, G. Series arc fault diagnosis method of photovoltaic arrays based on GASF and improved DCGAN. Adv. Eng. Inf. 2022, 54, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Yao, L.-F.; Tang, J.-W.; Ma, Z.-W.; Mou, J.-Y.; Wen, X.-R.; Usman, M.; Wu, X.; Wang, L. Rapid discrimination and ratio quantification of mixed antibiotics in aqueous solution through integrative analysis of SERS spectra via CNN combined with NN-EN model. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 69, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liang, Q.; Hancock, J.T.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Feature selection strategies: A comparative analysis of SHAP-value and importance-based methods. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Yu, P.; Liu, Z.; Guan, X.; Huang, J. Discriminating moisture content in Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr logs using fusion of 2D GADF spectral images and 1D NIR spectra. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y. Research on prediction of yellow flesh peach firmness using a novel acoustic real-time detection device and Vis/NIR technology. LWT 2024, 209, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeny, M.; Neshat, A.A.; Jahanbakhshi, A.; Mahmoudi, M.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Radeva, P. Grading and fraud detection of saffron via learning-to-augment incorporated Inception-v4 CNN. Food Control 2023, 147, 109554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Lan, W.; Tu, K.; Liu, J.; Pan, L. Discrimination of unsound soybeans using hyperspectral imaging: A deep learning method based on dual-channel feature fusion strategy and attention mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Hao, N.; Guo, X.; Miao, P.; Guan, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Bai, G.; Li, W. Rapid and accurate identification of Panax ginseng origins based on data fusion of near-infrared and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Food Res. Int. 2025, 204, 115925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; An, D.; Ning, X. Self-supervised learning-based multi-source spectral fusion for fruit quality evaluation: A case study in mango fruit ripeness prediction. Inf. Fusion 2025, 117, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Yang, T.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Comparison of metabolites and species classification of thirteen Zingiberaceae spices based on GC–MS and multi-spectral fusion technology. Foods 2023, 12, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample Set | Cultivar | Number | Origin | Time (Year 2024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration and prediction | Seedless | 163 | Jiangsu and Gansu Province | July to September |
| Seeded | 160 | Zhejiang and Hunan Province | July to September | |
| Validation | Seedless | 17 | Zhejiang Province | October |
| Seeded | 20 | Yunnan Province | December |
| Layer | Kernel Size | Stride | Out Channels | Activation | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | 300 300 3 | ||||
| Conv1, Conv2 | 3 3 | 1 | 8 | ReLU | |
| MaxPool1 | 2 2 | 2 | |||
| Conv3, Conv4 | 3 3 | 1 | 16 | ReLU | |
| MaxPool2 | 2 2 | 2 | |||
| Conv5, Conv6, Conv7 | 3 3 | 1 | 32 | ReLU | |
| MaxPool3 | 2 2 | 2 | |||
| fc1, fc2, fc3 | 100 | ReLU | |||
| drop | 0.1 | ||||
| fc4 | 2 | Softmax |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, C.; Qu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lv, X.; Yu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Rao, X.; Xu, H. Accurate Classification of Multi-Cultivar Watermelons via GAF-Enhanced Feature Fusion Convolutional Neural Networks. Foods 2025, 14, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162860
An C, Qu M, Zhao Y, Wu Z, Lv X, Yu Y, Wei Z, Rao X, Xu H. Accurate Classification of Multi-Cultivar Watermelons via GAF-Enhanced Feature Fusion Convolutional Neural Networks. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162860
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Changqing, Maozhen Qu, Yiran Zhao, Zihao Wu, Xiaopeng Lv, Yida Yu, Zichao Wei, Xiuqin Rao, and Huirong Xu. 2025. "Accurate Classification of Multi-Cultivar Watermelons via GAF-Enhanced Feature Fusion Convolutional Neural Networks" Foods 14, no. 16: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162860
APA StyleAn, C., Qu, M., Zhao, Y., Wu, Z., Lv, X., Yu, Y., Wei, Z., Rao, X., & Xu, H. (2025). Accurate Classification of Multi-Cultivar Watermelons via GAF-Enhanced Feature Fusion Convolutional Neural Networks. Foods, 14(16), 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162860






