Liupao Tea Extract Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice by Regulating the Gut–Joint Axis Mediated via Fatty Acid Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of LPTE
2.3. Chemometric Analysis of LPTE
2.4. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analyses
2.5. Identification and Quantification of Potential Active Ingredients in LPTE
2.6. Animals and Management
2.7. Micro-CT Imaging
2.8. Histopathological Analysis
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Serum Metabolomic Analysis
2.11. Determination of Alterations in Gene Expression Levels via qPCR
2.12. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.13. Fecal SCFA Metabolomic Analysis
2.14. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
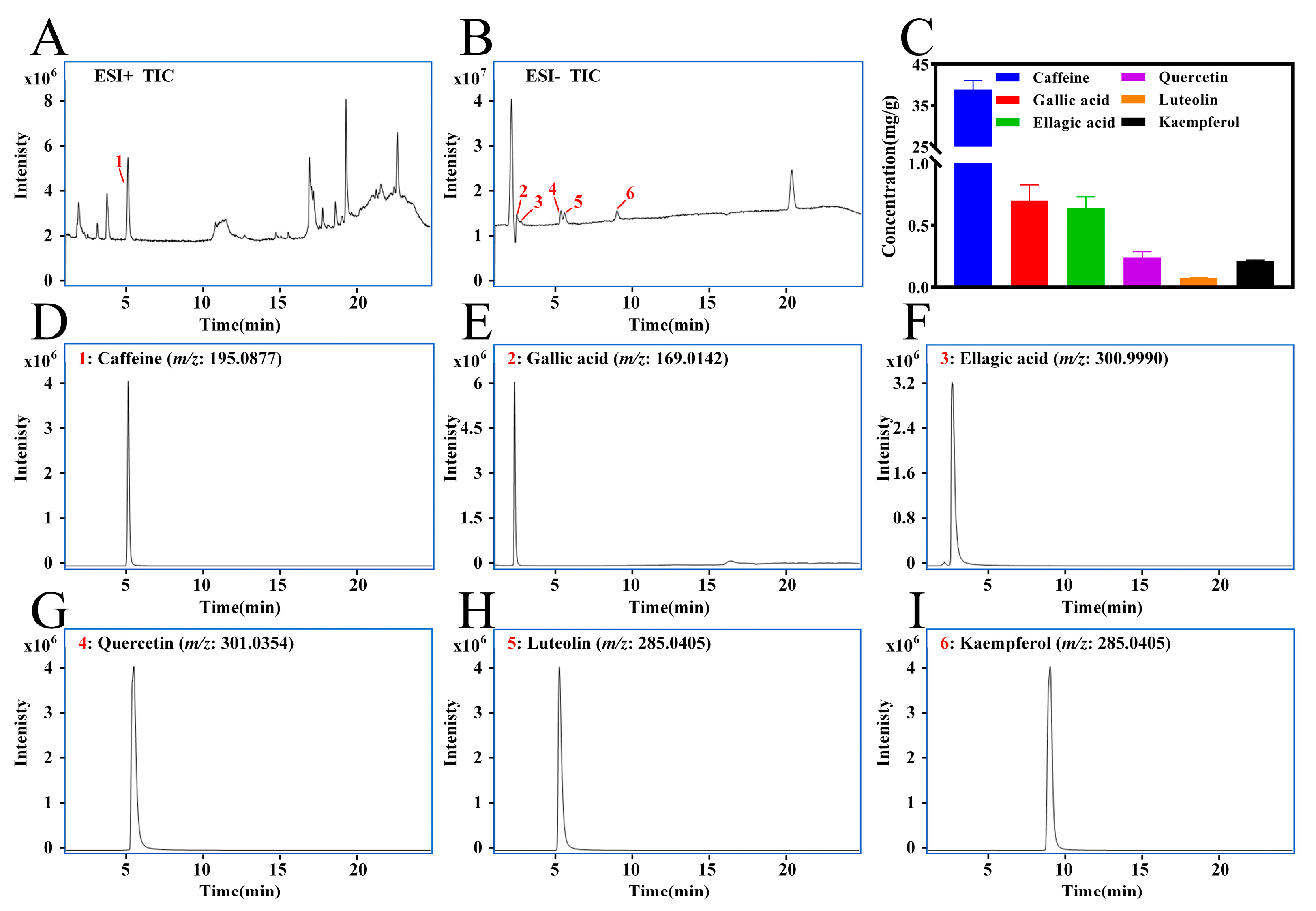
3.1. Phytochemical Profile and Main Components Analyses of LPTE
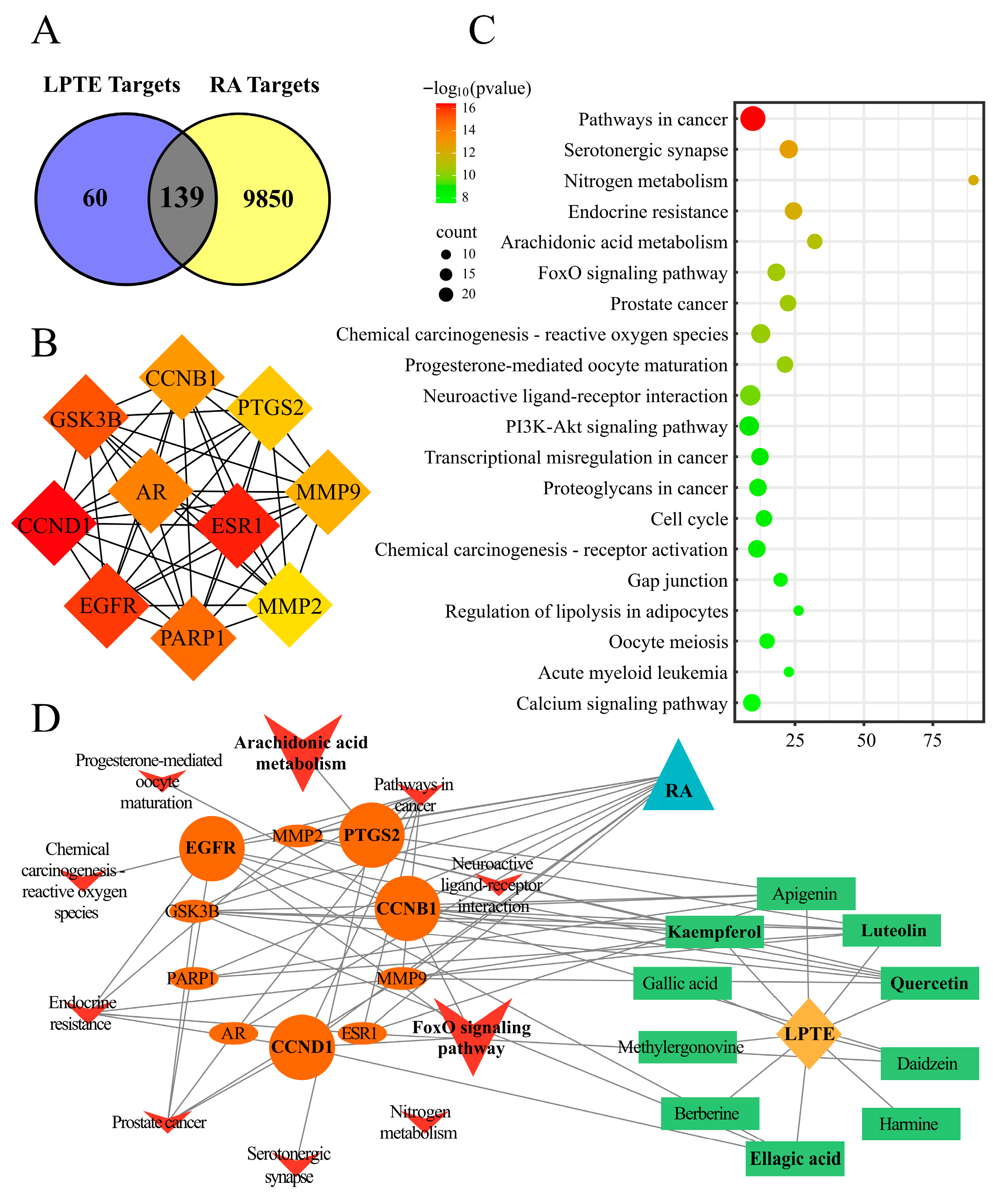
3.2. Network Pharmacology Analysis
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Key Characteristic Compounds in LPTE
3.4. Molecular Docking Analysis
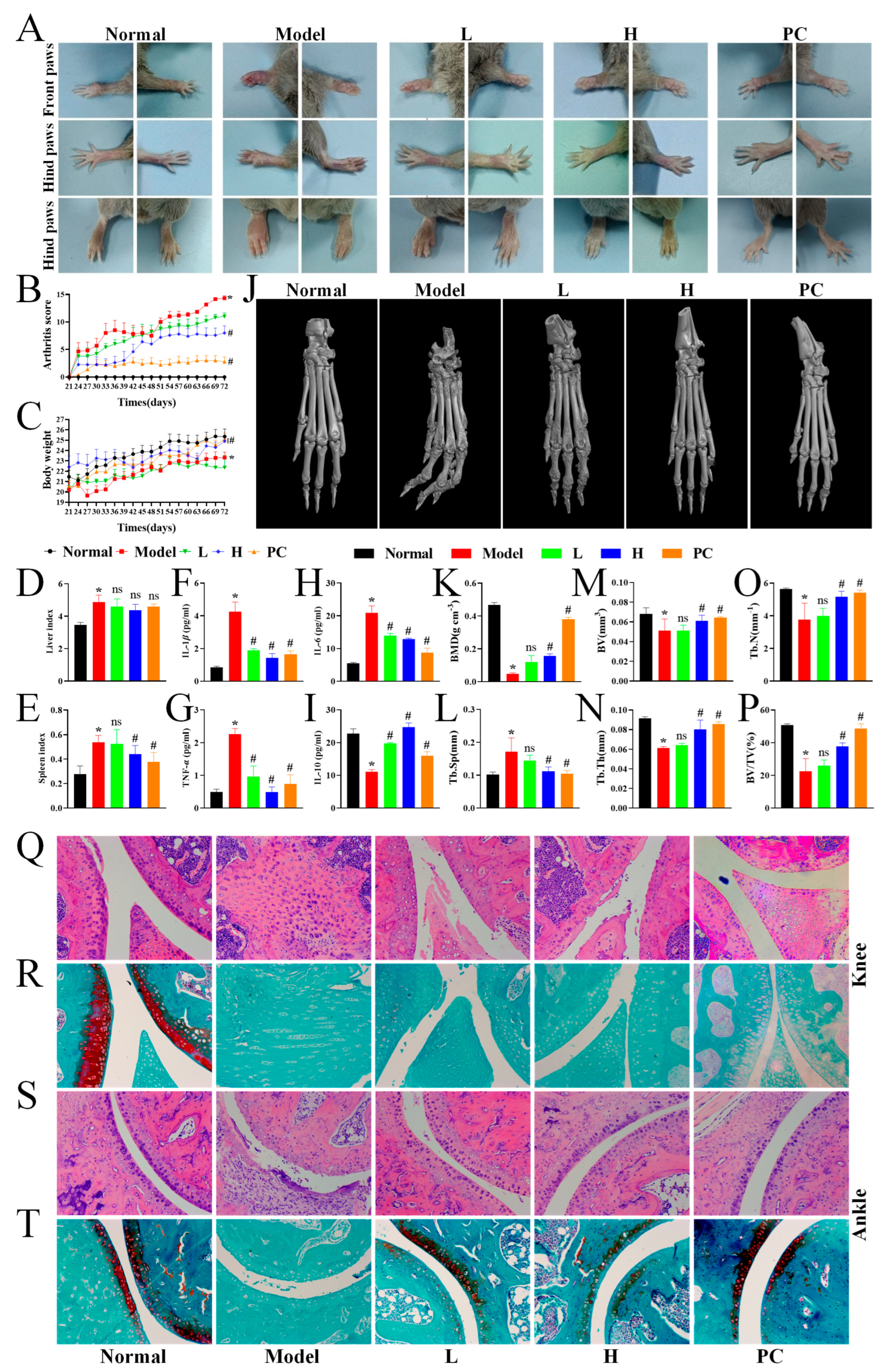
3.5. LPTE Attenuated the Severity of Arthritis and Bone Destruction in RA Mice
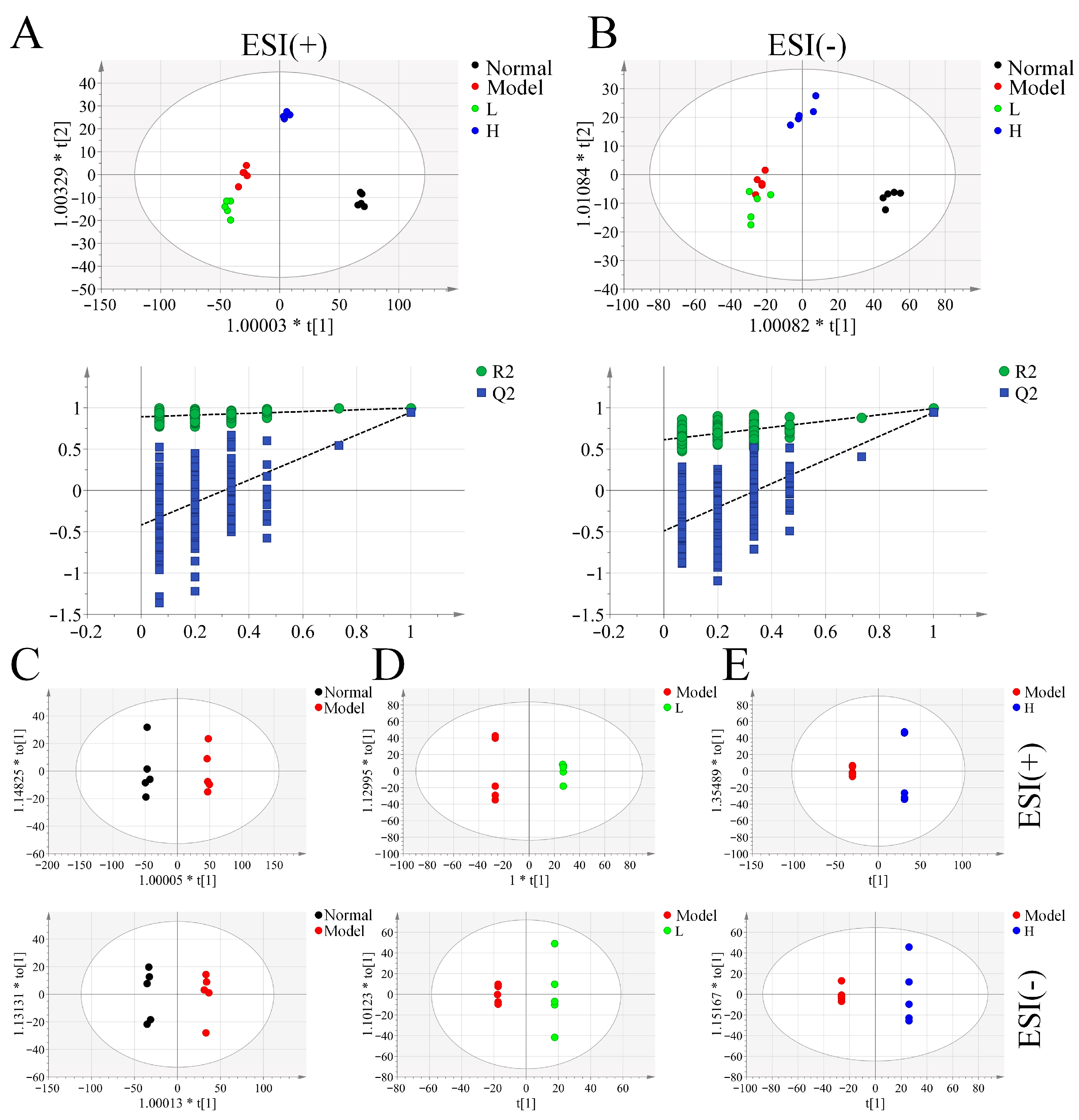
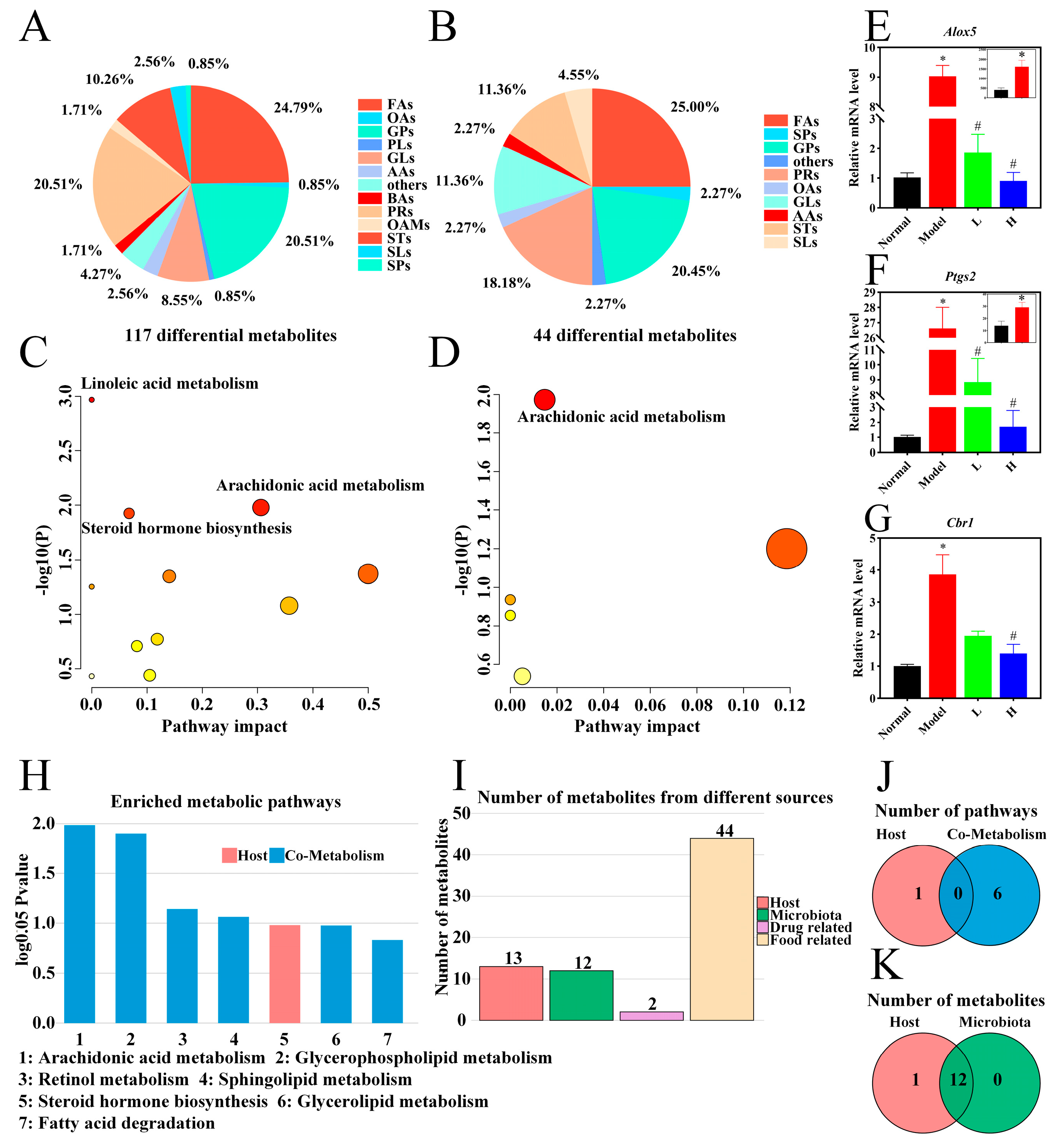
3.6. Serum Metabolomic Analysis of LPTE in RA Management
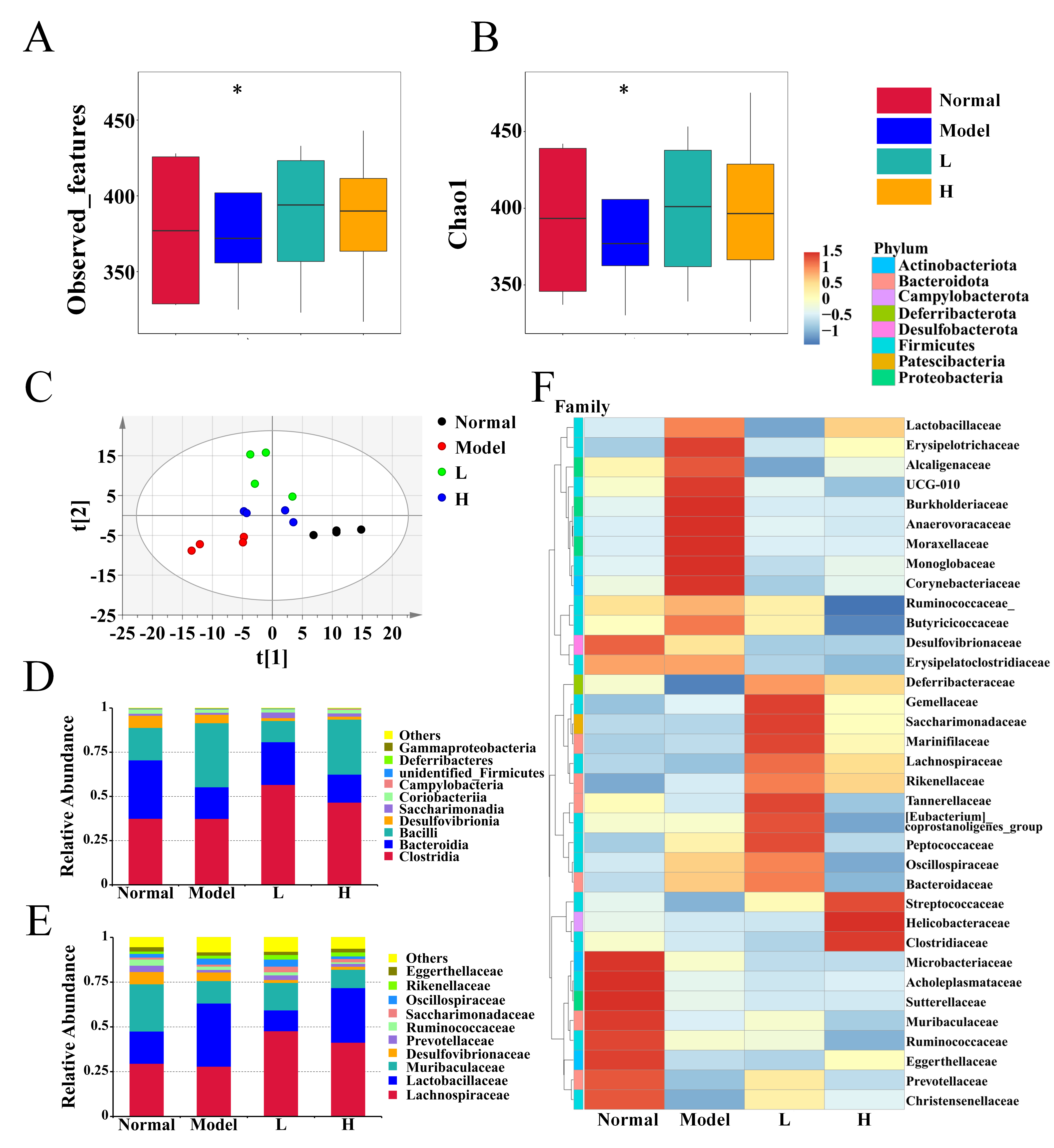
3.7. LPTE Reshaped the Gut Microbiota Profiles in RA Mice
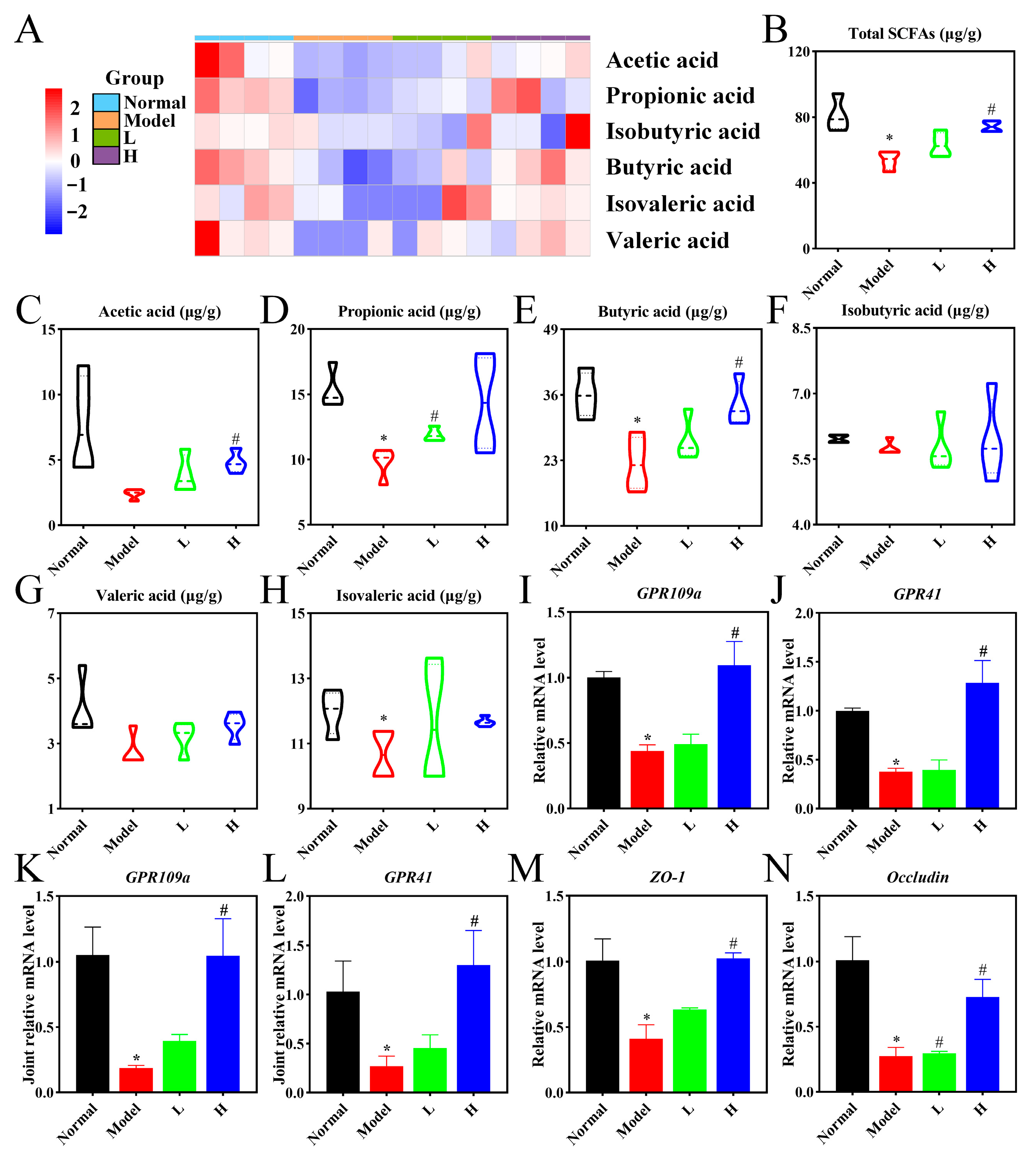
3.8. LPTE Enhanced Intestinal Barrier Function and Increased SCFAs Production
3.9. Integrated Correlation Analysis of Gut Microbiota, Differential Metabolites, SCFAs, and RA-Related Factors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, M.H.; Berman, J.R. What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? JAMA 2022, 327, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, A.; Bathon, J.M.; Emery, P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2023, 402, 2019–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Nie, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Jin, L.; Du, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, H.; Luobu, O. Traditional Tibetan Medicine Twenty-Five Wei’er Tea Pills Ameliorate Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Chemical Crosstalk Between Gut Microbiota and the Host. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 828920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Xing, J.; Chen, W.; Jia, J.; Li, Q. Fluorinated polyamidoamine dendrimer-mediated miR-23b delivery for the treatment of experimental rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, A.M.; Nieminen, P. Fatty Acids and Oxylipins in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis-a Complex Field with Significant Potential for Future Treatments. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshram, M.A.; Bhise, U.O.; Makhal, P.N.; Kaki, V.R. Synthetically-tailored and nature-derived dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitors: Structural aspects and SAR. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 225, 113804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, G.; Bai, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.; Tao, H.; Chen, H.; Wei, M.; Niu, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Punicalagin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by downregulating M1 macrophage and pyroptosis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Rheumatoid arthritis therapy reappraisal: Strategies, opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.Y.; Nie, Q.; Tai, H.C.; Song, X.L.; Tong, Y.F.; Zhang, L.J.; Wu, X.W.; Lin, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ye, D.Y.; et al. Tea and tea drinking: China’s outstanding contributions to the mankind. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Z.; Li, N.; Zhou, F.; Ouyang, J.; Lu, D.M.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.B.; et al. Microbial bioconversion of the chemical components in dark tea. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wei, Z.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Guan, X.; She, Z.; Liu, W.; Tong, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Integrated bioinformatics and multiomics reveal Liupao tea extract alleviating NAFLD via regulating hepatic lipid metabolism and gut microbiota. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-J.; Wei, X.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, D.-T.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Gandhi, G.R.; Hua-Bin, L.; Gan, R.-Y. State-of-the-art review of dark tea: From chemistry to health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Long, X.; Yi, R.; Zhao, X. Polyphenols in Liubao Tea Can Prevent CCl4-Induced Hepatic Damage in Mice through Its Antioxidant Capacities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, X.; Yi, R.; Sun, P.; Zou, M.; Long, X.; Zhao, X. Preventive Effect of Raw Liubao Tea Polyphenols on Mouse Gastric Injuries Induced by HCl/Ethanol via Anti-Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Bao, Z.; Ma, S.; Ou, C.; Hu, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Pan, Y.; Gong, S.; Fan, F.; et al. A local dark tea-Liubao tea-extract exhibits remarkable performance in oral tissue regeneration, inflammation relief and oral microbiota reconstruction. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 7400–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Shi, Y.; Xu, A.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P. Liubao tea extract ameliorates ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma by regulating gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10605–10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Yang, C.; Xiang, T.; Dou, C.; Sun, D.; Dai, Q.; Ling, Z.; Xu, J.; Luo, F.; Chen, Y. Gold nanoparticles exhibit anti-osteoarthritic effects via modulating interaction of the “Microbiota-gut-joint” axis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mules, T.C.; Inns, S.; Le Gros, G. Helminths’ therapeutic potential to treat intestinal barrier dysfunction. Allergy 2023, 78, 2892–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.M.; Mulle, J.G.; Pacifici, R. Osteomicrobiology: The influence of gut microbiota on bone in health and disease. Bone 2018, 115, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Lin, M.; Song, W.; Wu, J.; Cao, G.; Huang, P.; Su, Z.; Gu, W.; Deng, X.; Xu, P.; et al. The gut-joint axis mediates the TNF-induced RA process and PBMT therapeutic effects through the metabolites of gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2281382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, U.G.; Lalli, A.; Bandini, B.; de Sire, R.; Angeletti, S.; Lustig, S.; Ammendolia, A.; Budhiparama, N.C.; de Sire, A. Role of the Gut Microbiota in Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Spondylarthritis: An Update on the Gut–Joint Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Dai, M.; Wu, B.; Li, Y. The bridge of the gut-joint axis: Gut microbial metabolites in rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1007610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinolo, M.A.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Nachbar, R.T.; Curi, R. Regulation of inflammation by short chain fatty acids. Nutrients 2011, 3, 858–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.; Omata, Y.; Hofmann, J.; Böttcher, M.; Iljazovic, A.; Sarter, K.; Albrecht, O.; Schulz, O.; Krishnacoumar, B.; Krönke, G.; et al. Short-chain fatty acids regulate systemic bone mass and protect from pathological bone loss. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Xiong, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Chen, T. Rapid Selenoprotein Activation by Selenium Nanoparticles to Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis and Pathological Bone Loss. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2401620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, R.; Zhang, T.; Yu, L.; Dong, Y.; Ma, B. Liupao tea extract alleviates diabetes mellitus and modulates gut microbiota in rats induced by streptozotocin and high-fat, high-sugar diet. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; She, Z.; Huang, L.; Wei, H.; Yang, S.; Wei, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, B.; Hu, Z.; et al. Combining bioinformatics and multiomics strategies to investigate the key microbiota and active components of Liupao tea ameliorating hyperlipidemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 333, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Zhou, H.L.; She, Z.Y.; Lu, H.H.; Wen, M.S.; Wang, X.C.; Wei, Z.J.; Yang, S.Y.; Guan, X.; Tong, Y.; et al. Phytochemical and medicinal profiling of Russula vinosa Lindbl (RVL) using multiomics techniques. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 192, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Yu, J.; Lin, Y.N.; Lin, T.M. Recent advances in LC-MS-based metabolomics for clinical biomarker discovery. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2023, 42, 2349–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabke, K.; Hendrick, G.; Devkota, S. The gut microbiome and metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 4050–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Yuan, M.; Li, Z.; Lin, Q.; Zhen, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xia, F. Polyphenol-Rich Liupao Tea Extract Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced MAFLD by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 8313-2018; Determination of Total Polyphenols and Catechins Content in Tea. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- SN/T 4592-2016; Determination of Total Flavonoids in Export Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 8314–2013; Tea-Determination of Free Amino Acids Content. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- NY/T 1676-2008; Determination of Crude Mushroom Polysaccharides. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Zhou, B.; Ma, C.; Ren, X.; Xia, T.; Zheng, C.; Liu, X. Correlation analysis between filamentous fungi and chemical compositions in a pu-erh type tea after a long-term storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Mao, Q.; Xiong, R.; Zhou, D.; Huang, S.; Saimaiti, A.; Shang, A.; Luo, M.; Li, H.; Li, H.; et al. Preventive Effects of Different Black and Dark Teas on Obesity and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Modulate Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qin, Y.; Ma, S.; Ming, S.; Weng, Z.; Xuan, Y.; Gong, S.; Fan, F.; Chen, P.; Chu, Q.; et al. Liubao tea extract restrains obesity-related hyperlipidemia via regulation of AMPK/p38/NF-kappaB pathway and intestinal microbiota. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yin, Y.; Shi, G.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, S.; Wei, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L.; Zhang, T. A highly selective JAK3 inhibitor is developed for treating rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing γc cytokine-related JAK-STAT signal. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.J. A sensitive GC/MS detection method for analyzing microbial metabolites short chain fatty acids in fecal and serum samples. Talanta 2019, 196, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, H.X.; Luo, N.; Liang, X.Q.; Yang, P.C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.T.; Yang, Q.L.; Huang, S.X.; Lin, L. Association between flavonoid intake and rheumatoid arthritis among US adults. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 131, 109673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Mehta, K.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Ahmadi, A.; Arora, S.; Bungau, S. Exploring the role of polyphenols in rheumatoid arthritis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5372–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.Z.; Qin, D.Y.; Li, Q.M.; Zha, X.Q.; Pan, L.H.; Peng, D.Y.; Luo, J.P. Dendrobium huoshanense stem polysaccharide ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis in mice via inhibition of inflammatory signaling pathways. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 258, 117657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lin, W.; Deng, X.; Ba, X.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Tu, S. Potential Implications of Quercetin in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Gad, A.M.; Fikry, E.M.; Eid, A.H. Ellagic acid attenuates testicular disruption in rheumatoid arthritis via targeting inflammatory signals, oxidative perturbations and apoptosis. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Li, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, S.; Kwan, H.Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, M.; Xia, Q.; Liu, Z.; Su, T. Therapeutic effects of Siegesbeckia orientalis L. and its active compound luteolin in rheumatoid arthritis: Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 317, 116852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, T.; He, H.; Chen, L.; Han, K.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Study of kaempferol in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis through modulation of the NLRP3/CASP1/GSDMD axis and T-cell activation: Based on network pharmacology, single-cell analysis, and experimental validation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Deng, H.C.; Zhang, Q.S.; Huang, L.; Xia, N.; Teng, J.W.; Zhu, P.C. Exploring the microbial community, physicochemical properties, metabolic characteristics, and pathways during tank fermentation of Liupao tea. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 204, 116449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ying, J.; Yan, F.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, S.; Chen, J.; Zhu, J. Novel antiosteoporotic peptides purified from protein hydrolysates of taihe black-boned silky fowl: By larval zebrafish model and molecular docking. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessis, N.; Decker, P.; Assier, E.; Semerano, L.; Boissier, M.-C. Arthritis models: Usefulness and interpretation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivernini, S.; Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity 2022, 55, 2255–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Chen, G.; Xiang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Pei, S.; Guo, S.; et al. Immunomodulatory roles of metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1285455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, X.; Huai, J.; Li, Y.; Cheng, C.; Bi, K.; Dai, R. Arachidonic acid metabonomics study for understanding therapeutic mechanism of Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan on rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 217, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Peng, Y.; Bi, K.; Dai, R. Targeted profiling of arachidonic acid and eicosanoids in rat tissue by UFLC-MS/MS: Application to identify potential markers for rheumatoid arthritis. Talanta 2017, 162, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, J.; Holinstat, M. Who is the real 12-HETrE? Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 132, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratz, C.; Anakwue, J.; Bhatia, H.; Pitz, S.; Fiebich, B.L. Anti-inflammatory effects of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists in interleukin-1beta stimulated primary human chondrocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kong, L.; Cao, D.; Zhan, X.; Gao, X.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Zhao, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Efficacy and mechanism of the Ermiao San series of formulas for rheumatoid arthritis based on Chinmedomics strategy. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Mahony, C.B.; Torres, A.; Murillo-Saich, J.; Kemble, S.; Cedeno, M.; John, P.; Bhatti, A.; Croft, A.P.; Guma, M. Dual inhibition of glycolysis and glutaminolysis for synergistic therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaiss, M.M.; Wu, H.J.J.; Mauro, D.; Schett, G.; Ciccia, F. The gut-joint axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Fachi, J.L.; Vieira, A.; Sato, F.T.; Vinolo, M.A. Regulation of immune cell function by short-chain fatty acids. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Marion, T.; Tong, Y.; Zaiss, M.M.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Resistant starch intake alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by modulating gut microbiota and promoting concomitant propionate production. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 116, 102564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Y. Microbiota metabolite short chain fatty acids, GPCR, and inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Luo, J.; Yu, Z.; Xu, B. A critical review on intestinal mucosal barrier protection effects of dietary polysaccharides. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuever, J. Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; The Family Desulfovibrionaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Deltaproteobacteria and Epsilonproteobacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 107–133. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Daza, M.C.; Roquim, M.; Dudonné, S.; Pilon, G.; Levy, E.; Marette, A.; Roy, D.; Desjardins, Y. Berry Polyphenols and Fibers Modulate Distinct Microbial Metabolic Functions and Gut Microbiota Enterotype-Like Clustering in Obese Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gámez-Macías, P.E.; Félix-Soriano, E.; Samblas, M.; Sáinz, N.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; González-Muniesa, P. Intestinal Permeability, Gut Inflammation, and Gut Immune System Response Are Linked to Aging-Related Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition: A Study in Female Mice. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2024, 79, glae045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgueno, J.F.; Abreu, M.T. Epithelial Toll-like receptors and their role in gut homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, M.; Lee, H.Y.; Bae, Y.S. Isovaleric acid ameliorates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclast differentiation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4287–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name (PDB ID) | Compound (Pubchem CID) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin (5280343) | Luteolin (5280445) | Ellagic Acid (5281855) | Kaempferol (5280863) | ||
| PTGS2 (5F19) | S score | −6.7242 | −6.8201 | −6.6828 | −6.6104 |
| H-Bonds Type Amino acid | H-donor CYS 41 H-donor GLU 465 H-acceptor HIS 39 | H-donor HIS 39 H-acceptor TYR 130 | H-donor OAS 530 | H-donor HIS 39 H-acceptor TYR 130 | |
| π-Interactions Type Amino acid | pi-H CYS 47 | pi-H VAL 523 | |||
| pi-H ALA 527 | |||||
| CCNB1 (6GU2) | S score | −6.0425 | −6.0085 | −5.8914 | −5.8441 |
| H-Bonds Type Amino acid | H-donor ASP 146 H-donor ASP 128 | H-donor GLU 51 | H-acceptor LEU 83 | H-donor ASP 146 H-donor ASP 128 | |
| π-Interactions Type Amino acid | pi-H VAL 18 | ||||
| CCND1 (6P8E) | S score | −5.4586 | −5.5046 | −5.0949 | −5.4823 |
| H-Bonds Type Amino acid | H-donor GLY 228 H-acceptor ASN 276 | ||||
| π-Interactions Type Amino acid | pi-H LYS 152 pi-pi HIS 30 | pi-H LYS 152 pi-pi HIS 30 | |||
| EGFR (8FV3) | S score | −6.1760 | −5.6858 | −5.6894 | −5.7273 |
| H-Bonds Type Amino acid | H-donor ASN 842 H-donor SER 720 | H-donor ASN 842 H-donor ASP 855 | H-acceptor MET 793 | H-donor GLU 758 H-donor GLU 749 | |
| π-Interactions Type Amino acid | pi-H VAL 726 | pi-H VAL 726 | pi-H LEU 718 pi-H VAL 726 | pi-H LEU 861 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, Y.; She, Z.; Lin, X.; Luo, J.; Guan, X.; Wen, M.; Huang, L.; Yang, B.; Liang, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Liupao Tea Extract Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice by Regulating the Gut–Joint Axis Mediated via Fatty Acid Metabolism. Foods 2025, 14, 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162854
Tong Y, She Z, Lin X, Luo J, Guan X, Wen M, Huang L, Yang B, Liang X, Xu S, et al. Liupao Tea Extract Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice by Regulating the Gut–Joint Axis Mediated via Fatty Acid Metabolism. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162854
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Ying, Zhiyong She, Xueting Lin, Jichu Luo, Xuan Guan, Mingsen Wen, Li Huang, Bao Yang, Xiaoying Liang, Song Xu, and et al. 2025. "Liupao Tea Extract Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice by Regulating the Gut–Joint Axis Mediated via Fatty Acid Metabolism" Foods 14, no. 16: 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162854
APA StyleTong, Y., She, Z., Lin, X., Luo, J., Guan, X., Wen, M., Huang, L., Yang, B., Liang, X., Xu, S., Tan, Y., Zhu, P., Wei, Z., Liu, H., Liu, X., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Liupao Tea Extract Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice by Regulating the Gut–Joint Axis Mediated via Fatty Acid Metabolism. Foods, 14(16), 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162854






