Lipidomics Approach Reveals the Effects of Physical Refining Processes on the Characteristic Fatty Acids and Physicochemical Indexes of Safflower Seed Oil and Flaxseed Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Refining Process of SSO and FSO
2.2.1. Decolorization
2.2.2. Dewaxing
2.2.3. Deodorization
2.2.4. Deacidification
2.3. Physicochemical Index Analysis
2.4. Measurement of Fatty Acid Composition
2.5. Determination of Lipidomics
2.5.1. Metabolites Extraction
2.5.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
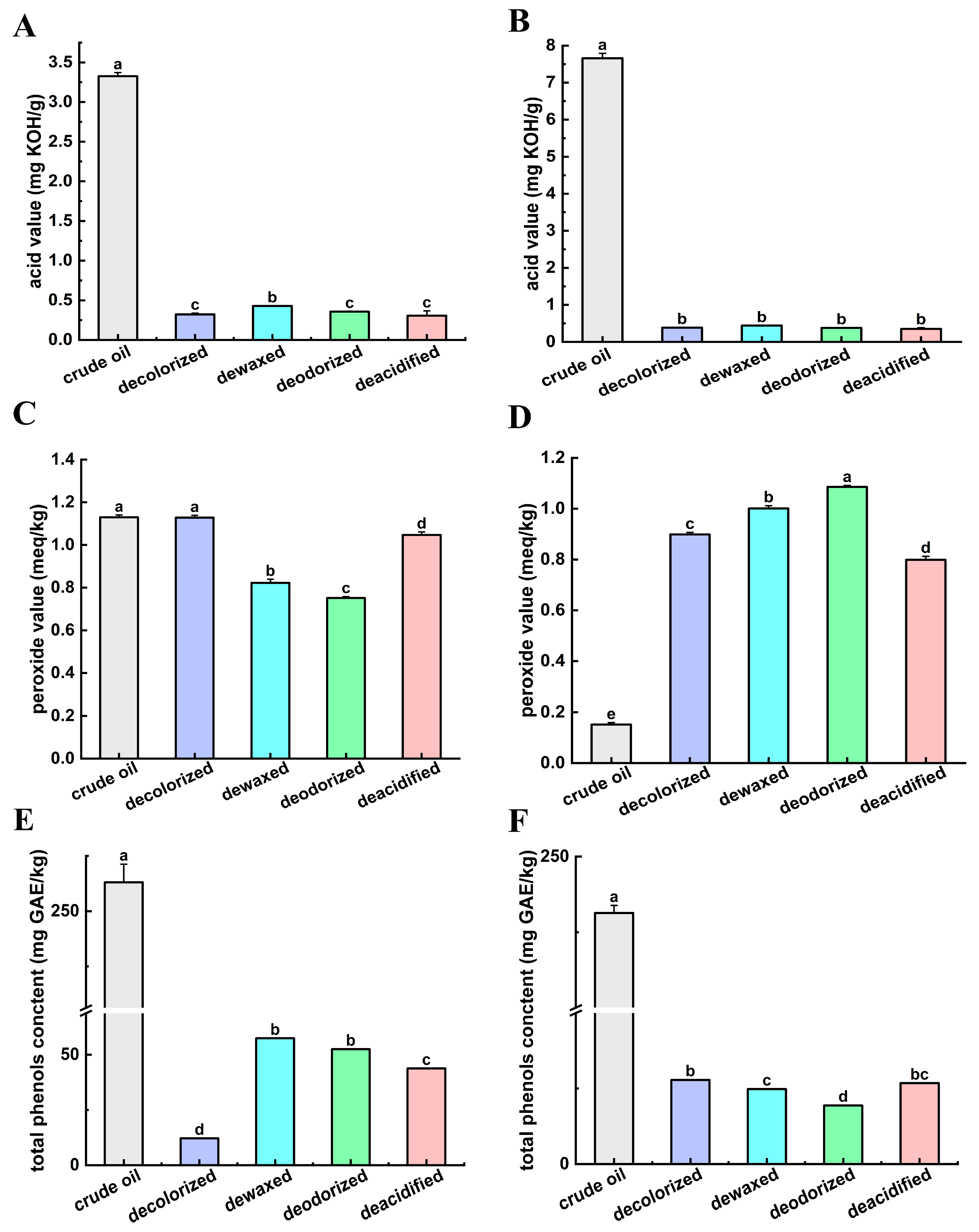
3.1. Assay for Effects of Refining Process on Physicochemical Index
3.1.1. Color
3.1.2. Acid Value
3.1.3. Peroxide Value
3.1.4. Total Phenolics Content
3.2. Assay for Effects of Refining Process on Fatty Acid Composition
3.3. Lipidomics Analysis of SSO and FSO
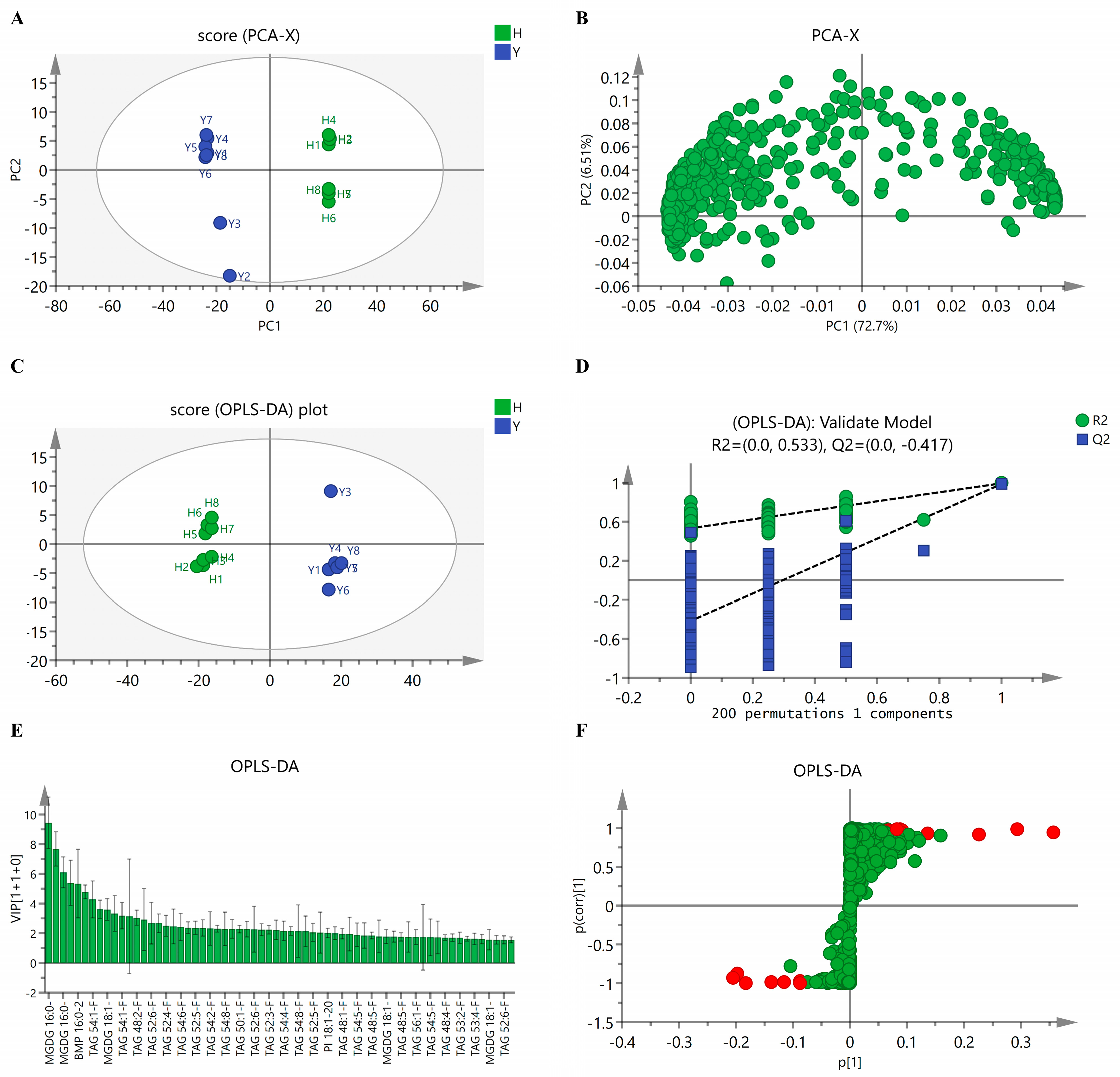
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis
3.3.2. Discrimination Analysis
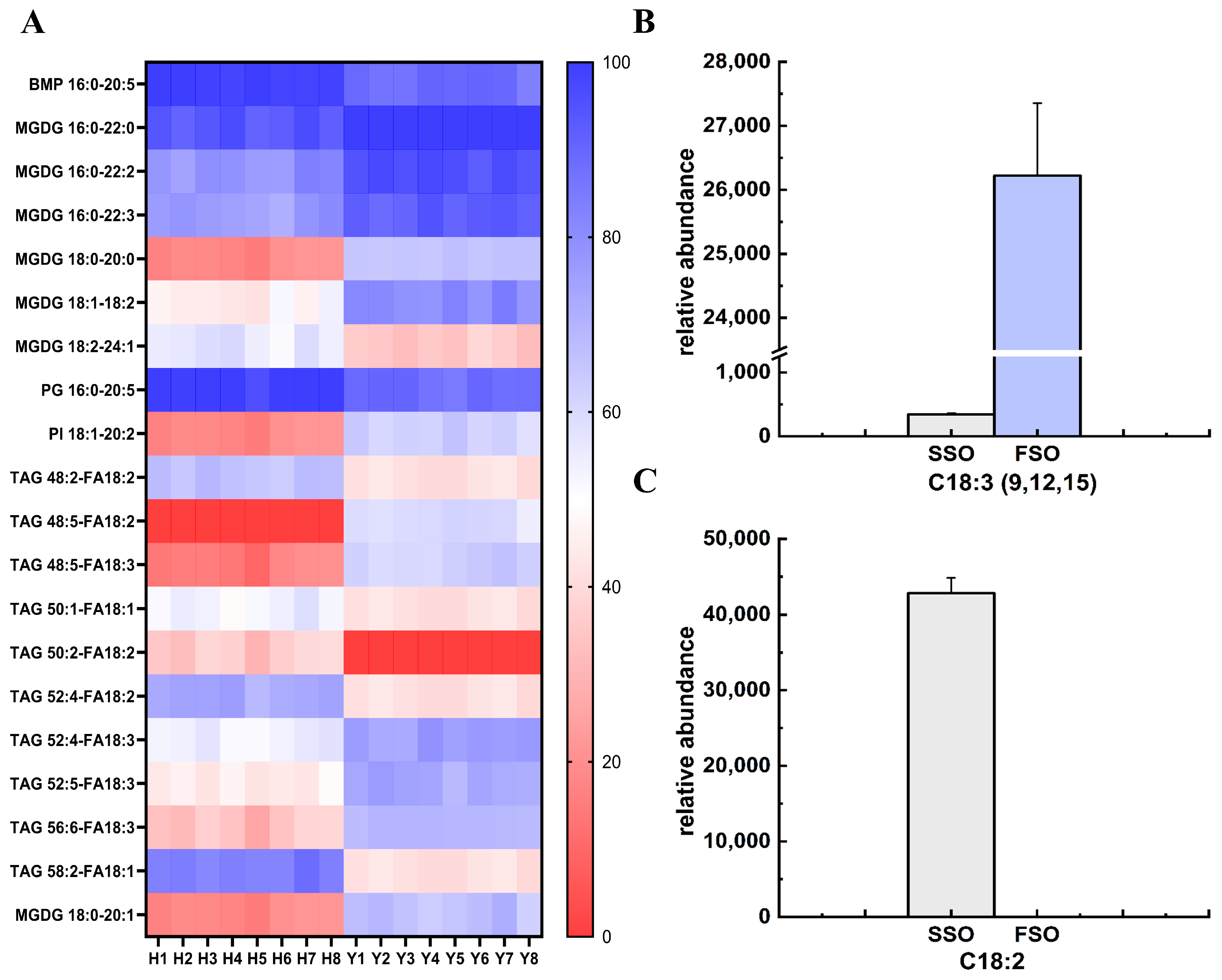
3.3.3. Analysis of the Notably Different Lipids
3.3.4. Characteristic Different Lipids Compounds in SSO and FSO
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, C.; Shen, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Liang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X. Edible Vegetable Oils from Oil Crops: Preparation, Refining, Authenticity Identification and Application. Process Biochem. 2023, 124, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostik, V.; Memeti, S.; Bauer, B. Fatty Acid Composition of Edible Oils and Fats. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2013, 4, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X. Lipidomics for Studying Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, S.-C.; Tan, C.-P.; Lai, O.-M.; Nyam, K.-L. Changes in 3-MCPD Esters, Glycidyl Esters, Bioactive Compounds and Oxidation Indexes during Kenaf Seed Oil Refining. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satriana; Maulida, A.; Qardhawi, R.; Syamsuddin, Y.; Supardan, M.D. Effect of Refining Process on Some Quality Attributes of Screw-Pressed Avocado Oil. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 50, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Farag, M.A.; Salah, M.; Liu, L.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, W. Impact of Refining on Phytochemicals and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Papaya (Carica papaya L.) Seed Oil in LPS-Stimulated THP-1 Cells. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Ye, Z.; Lv, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y. Composition Analysis and Health Risk Assessment of the Hazardous Compounds in Cooking Fumes Emitted from Heated Soybean Oils with Different Refining Levels. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, P.; Decker, E.A.; Maskan, M. Optimization of Neutralization Parameters in Minimal Refining Process of Sunflower Seed Oil. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 46, e16272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Chen, L.; Qiu, X.; Hu, W.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Bai, Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.; et al. Optimizing Refining Temperatures to Reduce the Loss of Essential Fatty Acids and Bioactive Compounds in Tea Seed Oil. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 94, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazani, S.M.; Boroujeni, Y.S.; Shaw, N.; Marangoni, A.G. Chapter 15—Scientific Issues and Challenges with Production and Refining Edible Oils and Fats. In Cellular Agriculture; Fraser, E.D.G., Kaplan, D.L., Newman, L., Yada, R.Y., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 215–232. ISBN 978-0-443-18767-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Xiao, T.; Ni, X.; Wei, T.; Liu, X.; Deng, Z.-Y.; Li, J. The Comparative Analysis of Different Oil Extraction Methods Based on the Quality of Flaxseed Oil. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, K.; Gong, T.; Ding, S.; Liu, H.; Shi, S.; Tu, J.; Zhu, L.; Song, L.; Song, L.; Zhang, X. Binding Mechanism and Bioavailability of a Novel Phosvitin Phosphopeptide (Glu-Asp-Asp-pSer-pSer) Calcium Complex. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becalski, A.; Feng, S.Y.; Lau, B.P.-Y.; Zhao, T. Glycidyl Fatty Acid Esters in Food by LC-MS/MS: Method Development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wei, F.; Xie, Y.; Lv, X.; Dong, X.; Chen, H. Research Advances Based on Mass Spectrometry for Profiling of Triacylglycerols in Oils and Fats and Their Applications. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincón, L.A.; Ramírez, J.C.; Orjuela, A. Assessment of Degumming and Bleaching Processes for Used Cooking Oils Upgrading into Oleochemical Feedstocks. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.229-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Acid Value in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.227-2023; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Peroxide Value in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Capannesi, C.; Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M.; Parenti, A. Electrochemical Sensor and Biosensor for Polyphenols Detection in Olive Oils. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoosh, R.; Niazmand, R.; Rezaei, M.; Sarabi, M. Kinetic Parameter Determination of Vegetable Oil Oxidation under Rancimat Test Conditions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.168-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Fatty Acids in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global Metabolic Profiling Procedures for Urine Using UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseke, T.; Opara, U.L.; Fawole, O.A. Novel Seeds Pretreatment Techniques: Effect on Oil Quality and Antioxidant Properties: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4451–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, Y.; Semwal, A.D. A Study on Monitoring of Frying Performance and Oxidative Stability of Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO) during Continuous/Prolonged Deep Fat Frying Process Using Chemical and FTIR Spectroscopy. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. CXS 19-1981, Rev 1987, 1999; Standard for Edible Fats and Oils Not Covered by Individual Standards. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, W.; Huang, L.; Zheng, T.; Zhong, R.; Pang, J.; Chen, L.; Cheng, W.; Liang, P. Quality Assessment of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Roe Oil before and after Refining. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14103–14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinzadeh, S.; Torbati, M.; Azadmard-Damirchi, S.; Savage, G.P. Effect of Refining on the Quality of Oils Extracted by Cold Press from Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) Seed and by Solvent from Its Cake. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 6475–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Du, Y.; Chen, X.; Cai, R.; Xie, J.; Shen, M. Investigation into the Effects of the Refining Steps before Deodorization on the Formation of Trans Fatty Acids in Linseed Oils. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurkul, M.M.; Cetinkaya, A.; Kaya, S.I.; Yayla, S.; Ozkan, S.A. Investigation of Health Effects of Major Phenolic Compounds in Foods: Extraction Processes, Analytical Approaches and Applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszowy, M. What Is Responsible for Antioxidant Properties of Polyphenolic Compounds from Plants? Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Ruiz-Méndez, M.V.; Romero, C.; Brenes, M. Effect of Refining on the Phenolic Composition of Crude Olive Oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Paul Raj, R. Selective Enrichment of n−3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids with C18–C20 Acyl Chain Length from Sardine Oil Using Pseudomonas Fluorescens MTCC 2421 Lipase. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.K.A.; Rial, R.C. Fatty Acid Profile, Nutritional and Therapeutic Properties of Vegetable Oils from the Brazilian Cerrado. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 137, 106819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, J. Microwave Resonator Can Help to Predict Oxidative Stability in C18-Based Vegetable Oils. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehdi, I.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Sbihi, H.M.; Tan, C.P.; Al-Resayes, S.I. Characterization of Ternary Blends of Vegetable Oils with Optimal ω-6/ω-3 Fatty Acid Ratios. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, D.; Wang, L. Effect of Deodorization Conditions on Fatty Acid Profile, Oxidation Products, and Lipid-Derived Free Radicals of Soybean Oil. Food Chem. 2024, 453, 139656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F. (Ed.) Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products; Industrial and nonedible products from oils and fats; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Chen, X.; Shi, P.; Wang, S.; Feng, F.; He, Y. Determination of α-Linolenic Acid and Linoleic Acid in Edible Oils Using near-Infrared Spectroscopy Improved by Wavelet Transform and Uninformative Variable Elimination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 634, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, W. Comparative Lipidomics Analysis of Seed Oils from Nine Tropical Fruits: Emphasizing the Fatty Acid and Lipid Molecule Profiles. Food Res. Int. 2024, 198, 115334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisia, I.; Young, J.W.; Yuan, Y.V.; Kitts, D.D. Association between Tocopherol Isoform Composition and Lipid Oxidation in Selected Multiple Edible Oils. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; De Souza, C.; Ramachandran, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, K. Lipidomics Insight on Differences between Human MFGM and Dietary-Derived Lipids. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullin-Matsuda, F.; Luquain-Costaz, C.; Bouvier, J.; Delton-Vandenbroucke, I. Bis (Monoacylglycero)Phosphate, a Peculiar Phospholipid to Control the Fate of Cholesterol: Implications in Pathology. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2009, 81, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Rossi, C.; Marcolongo, G.; Di Lena, A.; Venzo, A.; Berrie, C.P.; Corda, D. Selective in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Action of the Galactolipid Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 524, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockcroft, S. Expanding Functions of the Phosphatidylinositol/Phosphatidate Lipid Transporter, PITPNC1 in Physiology and in Pathology. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2025, 95, 101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losso, J.N.; Khachatryan, A.; Ogawa, M.; Godber, J.S.; Shih, F. Random Centroid Optimization of Phosphatidylglycerol Stabilized Lutein-Enriched Oil-in-Water Emulsions at Acidic pH. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerkamp, V.J.P.; Merkx, D.W.H.; Wang, J.; Vincken, J.-P.; Hennebelle, M.; van Duynhoven, J.P.M. Quantitative Assessment of Epoxide Formation in Oil and Mayonnaise by 1H-13C HSQC NMR Spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, L.R.; Gowda, S.G.B.; Roberts, T.H.; Gowda, D.; Khoddami, A.; Hui, S.-P. Nontargeted Lipidomics of Sorghum Grain Reveals Novel Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acids and Cultivar Differences in Lipid Profiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20690–20703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.K.; Prasad, P.; Sreedhar, R.V.; Akhilender Naidu, K.; Shang, X.; Keum, Y.-S. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs): Emerging Plant and Microbial Sources, Oxidative Stability, Bioavailability, and Health Benefits-A Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceló-Coblijn, G.; Murphy, E.J. Alpha-Linolenic Acid and Its Conversion to Longer Chain n-3 Fatty Acids: Benefits for Human Health and a Role in Maintaining Tissue n-3 Fatty Acid Levels. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Yang, D.; Mao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, L.; Yang, X.; Li, P. Accurate Quantification of TAGs to Identify Adulteration of Edible Oils by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole-Time of Flight-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, H.d.A.V.; Ferreira, G.A. Formulating Plant-Based Hexosomes for the Sustained Delivery of Food Proteins. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 244, 114169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compounds | VIP | S-Plot. p | S-Plot. p (corr) | Content in SSO (μg/mg) | Content in FSO (μg/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMP 16:0–20:5 | 5.3393 | −0.1986 | −0.8806 | 64.28 | 35.35 |
| MGDG 16:0–22:0 | 9.4371 | 0.3569 | 0.9500 | 41.66 | 129.81 |
| MGDG 16:0–22:2 | 7.6786 | 0.2941 | 0.9786 | 16.75 | 74.68 |
| MGDG 16:0–22:3 | 6.1029 | 0.2255 | 0.9114 | 14.79 | 51.58 |
| MGDG 18:0–20:0 | 2.3003 | 0.0878 | 0.9830 | 0.00 | 5.16 |
| MGDG 18:1–18:2 | 3.5969 | 0.1371 | 0.9356 | 3.80 | 16.99 |
| MGDG 18:2–24:1 | 2.2701 | −0.0868 | −0.9709 | 5.76 | 0.64 |
| PI 18:1–20:2 | 2.0145 | 0.0769 | 0.9601 | 0.00 | 4.07 |
| PG 16:0–20:5 | 5.3846 | −0.1986 | −0.8806 | 65.41 | 35.72 |
| TAG 48:2-FA18:2 | 3.0391 | −0.1164 | −0.9882 | 9.04 | 0.00 |
| TAG 48:5-FA18:2 | 1.7521 | 0.0668 | 0.9697 | 0.28 | 3.33 |
| TAG 48:5-FA18:3 | 1.8425 | 0.0696 | 0.9576 | 0.85 | 4.16 |
| TAG 50:1-FA18:1 | 2.2708 | −0.0870 | −0.9926 | 5.02 | 0.00 |
| TAG 50:2-FA18:2 | 1.5509 | −0.0594 | −0.9843 | 2.40 | 0.02 |
| TAG 52:4-FA18:2 | 3.6126 | −0.1383 | −0.9886 | 12.75 | 0.00 |
| TAG 52:4-FA18:3 | 2.4975 | 0.0913 | 0.8663 | 5.23 | 11.54 |
| TAG 52:5-FA16:0 | 2.3542 | 0.0890 | 0.9453 | 2.78 | 8.32 |
| TAG 52:5-FA18:3 | 2.3483 | 0.0899 | 0.9488 | 3.51 | 9.20 |
| TAG 56:6-FA18:3 | 2.1467 | 0.0821 | 0.9808 | 2.19 | 6.71 |
| TAG 53:4-FA18:3 | 1.6159 | 0.0619 | 0.9408 | 1.94 | 4.64 |
| TAG 58:2-FA18:1 | 4.7773 | −0.1830 | −0.9935 | 22.25 | 0.00 |
| MGDG 18:0–20:1 | 2.3674 | 0.0907 | 0.9762 | 0.00 | 5.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Zhao, H.; Wu, F.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M. Lipidomics Approach Reveals the Effects of Physical Refining Processes on the Characteristic Fatty Acids and Physicochemical Indexes of Safflower Seed Oil and Flaxseed Oil. Foods 2025, 14, 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162845
Yang J, Zhao H, Wu F, Wang Z, Yuan L, Qiu Y, Wang L, Zhu M. Lipidomics Approach Reveals the Effects of Physical Refining Processes on the Characteristic Fatty Acids and Physicochemical Indexes of Safflower Seed Oil and Flaxseed Oil. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162845
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiayan, Haoan Zhao, Fanhua Wu, Zeyu Wang, Lin Yuan, Yu Qiu, Liang Wang, and Min Zhu. 2025. "Lipidomics Approach Reveals the Effects of Physical Refining Processes on the Characteristic Fatty Acids and Physicochemical Indexes of Safflower Seed Oil and Flaxseed Oil" Foods 14, no. 16: 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162845
APA StyleYang, J., Zhao, H., Wu, F., Wang, Z., Yuan, L., Qiu, Y., Wang, L., & Zhu, M. (2025). Lipidomics Approach Reveals the Effects of Physical Refining Processes on the Characteristic Fatty Acids and Physicochemical Indexes of Safflower Seed Oil and Flaxseed Oil. Foods, 14(16), 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162845






