Study on the Effect of Ultrasonic and Cold Plasma Non-Thermal Pretreatment Combined with Hot Air on the Drying Characteristics and Quality of Yams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
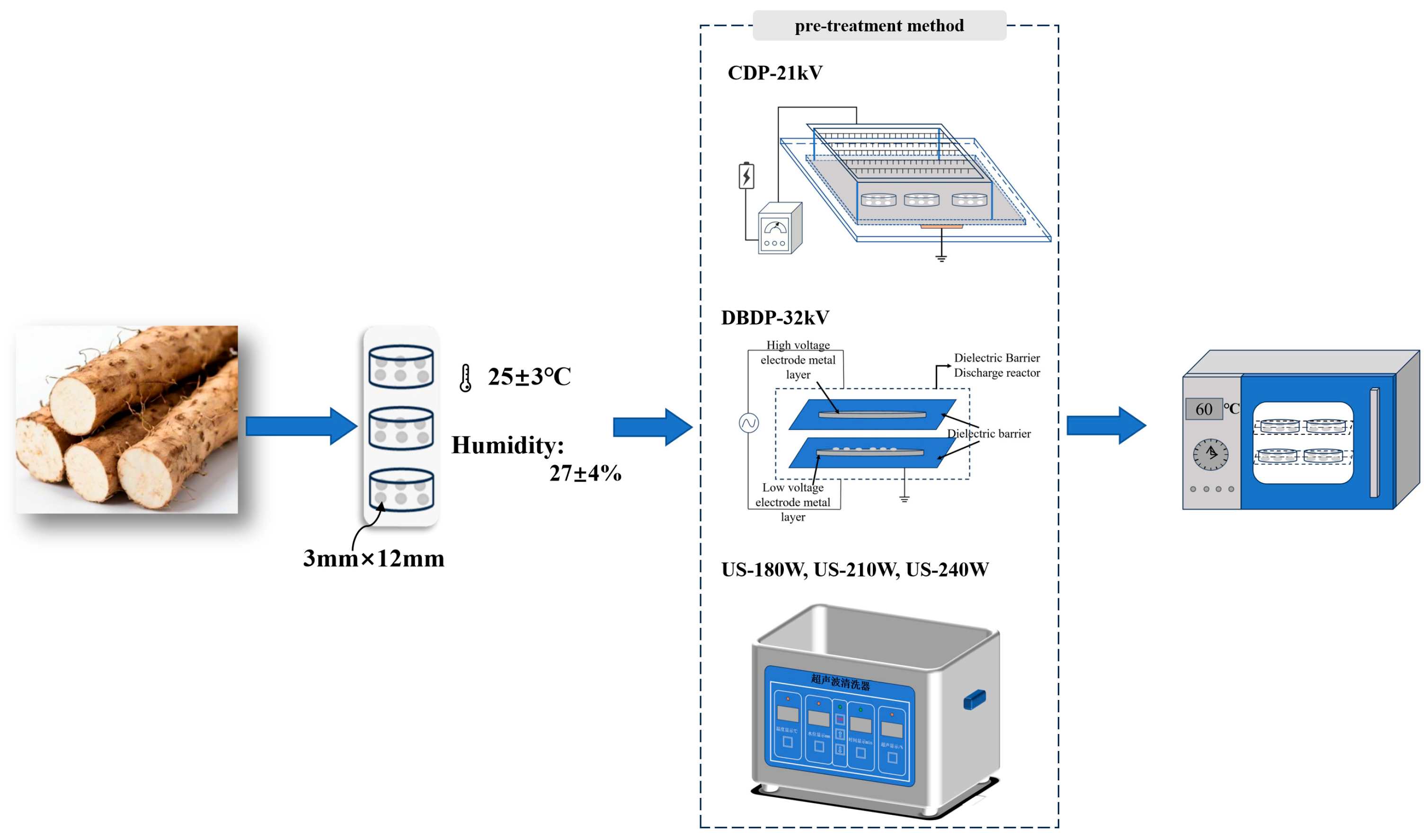
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Content and Methods
2.2.1. Pretreatment Experiments
2.2.2. Oven Drying
2.3. Drying Characteristics
2.3.1. Moisture Content
2.3.2. Average Drying Rate and Average Drying Time
2.3.3. Rehydration Rate
2.3.4. Effective Moisture Diffusivity
2.4. Color
2.5. Energy Consumption Analysis
2.6. Reducing Sugar Content
2.7. Total Phenol Content and Antioxidant Activity
2.8. Low-Field NMR and Imaging
2.9. Determination of Volatile Components (GC-MS)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
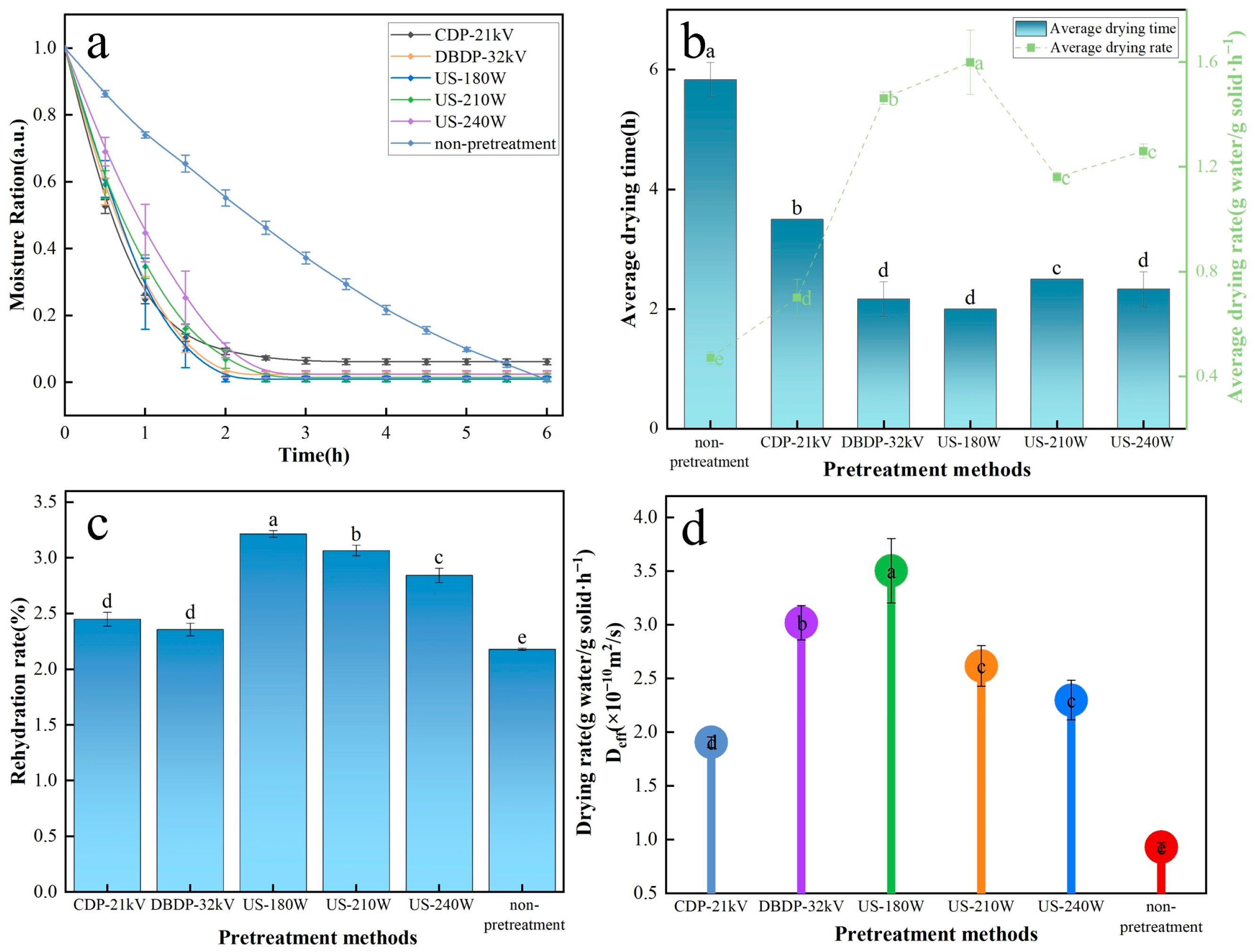
3.1. Analysis of Drying Characteristics
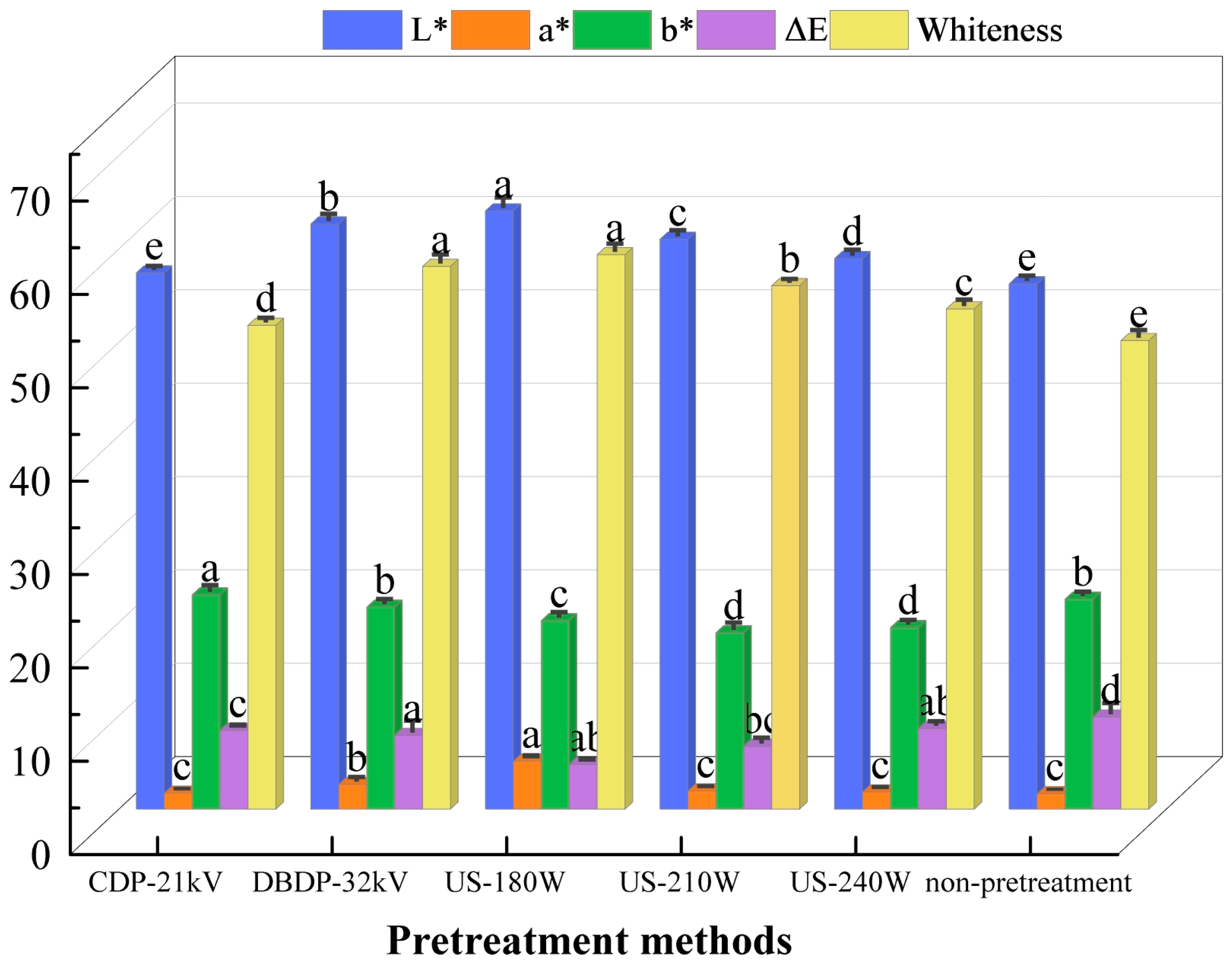
3.2. Analysis Color
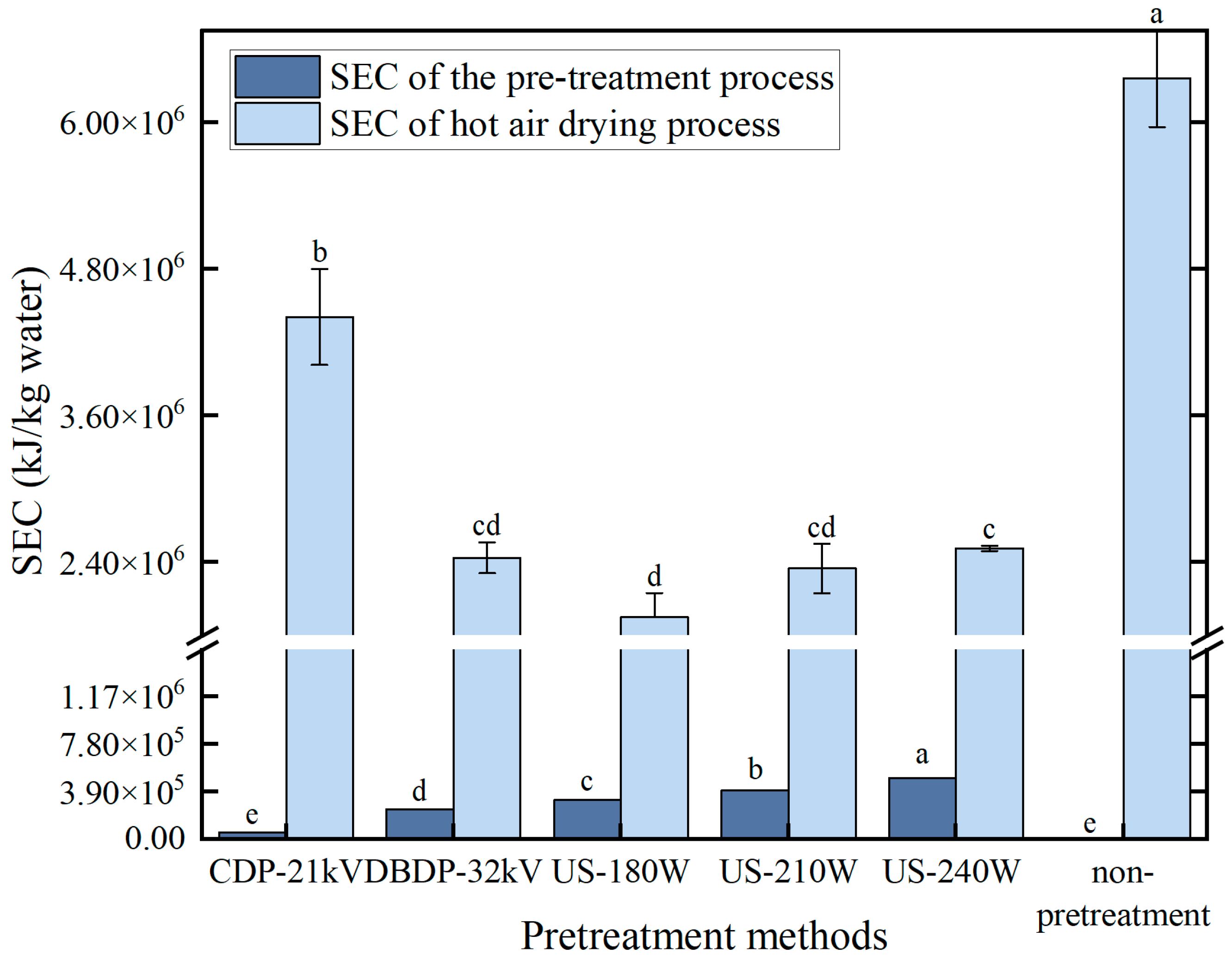
3.3. Drying Energy Consumption
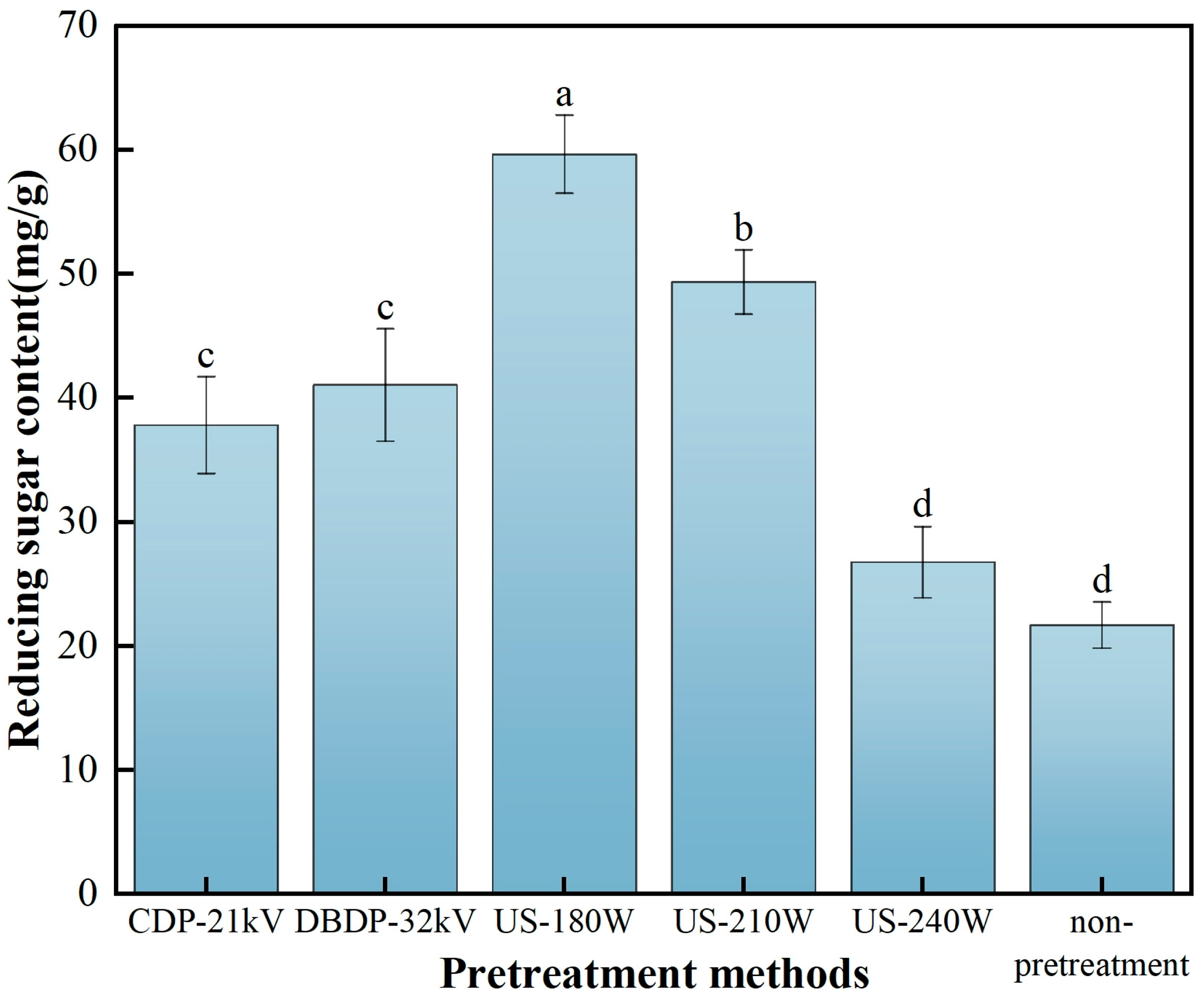
3.4. Analysis of Reducing Sugar Content
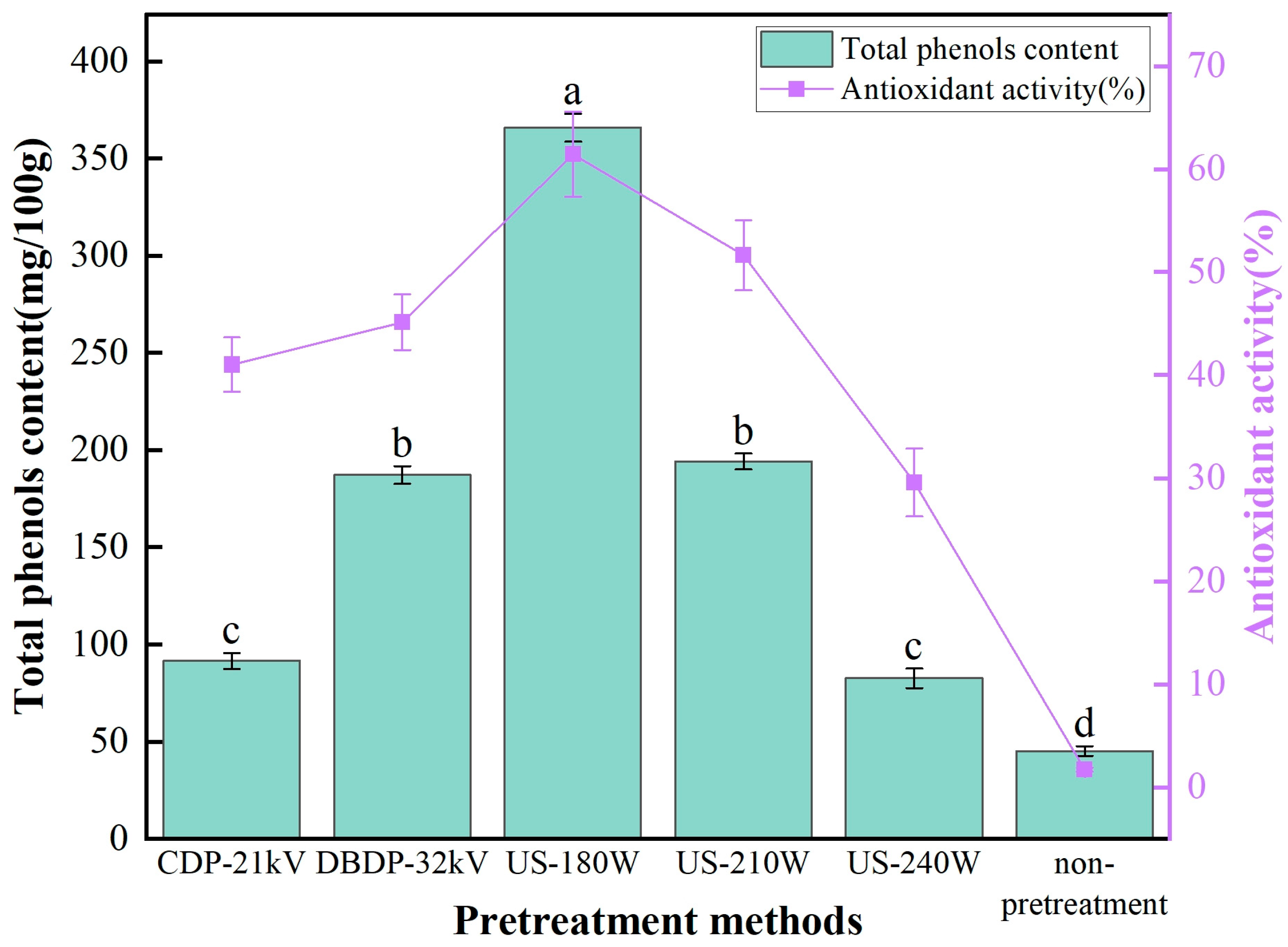
3.5. Analysis of Total Phenol Content and Antioxidant Activity
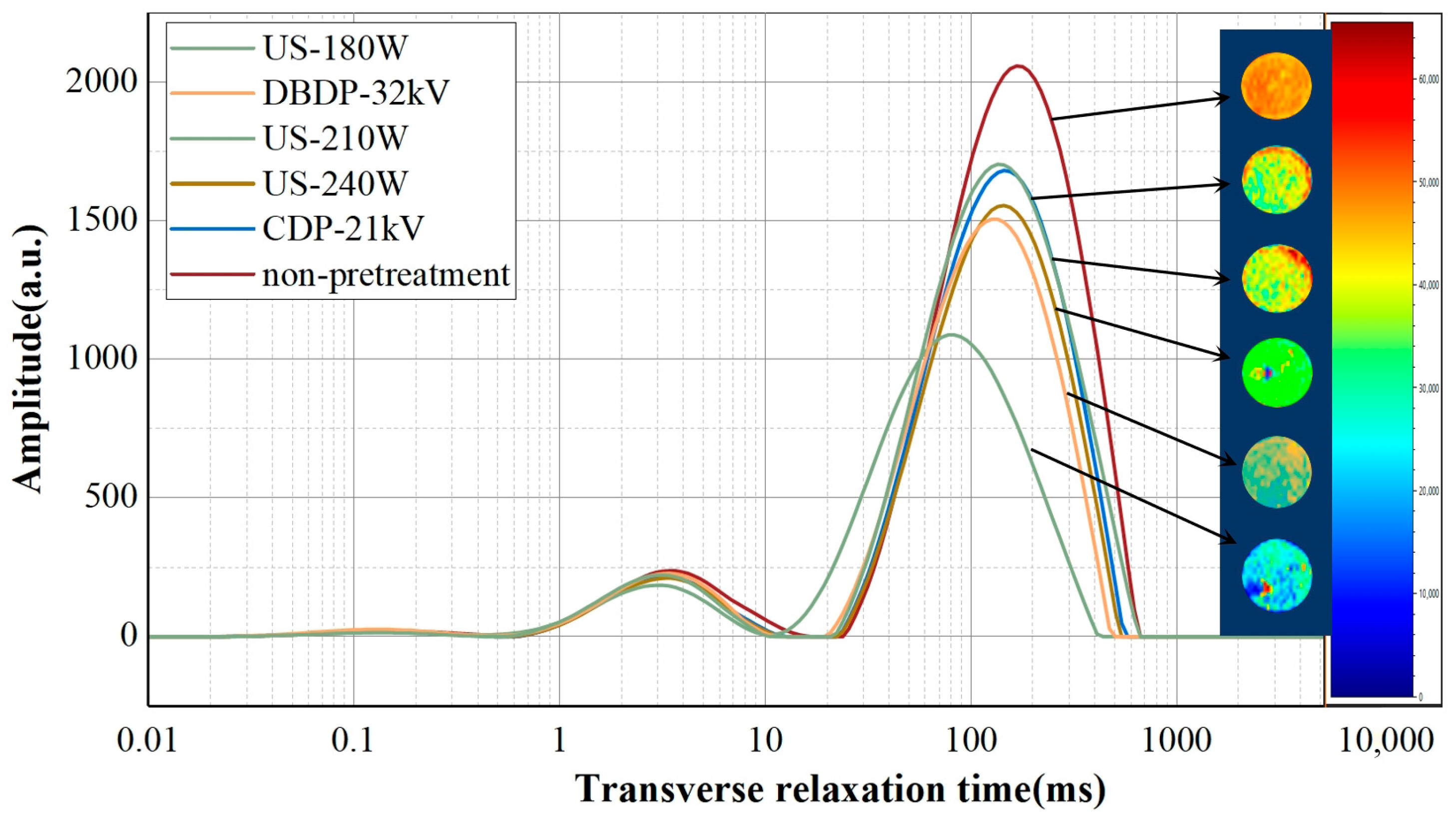
3.6. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
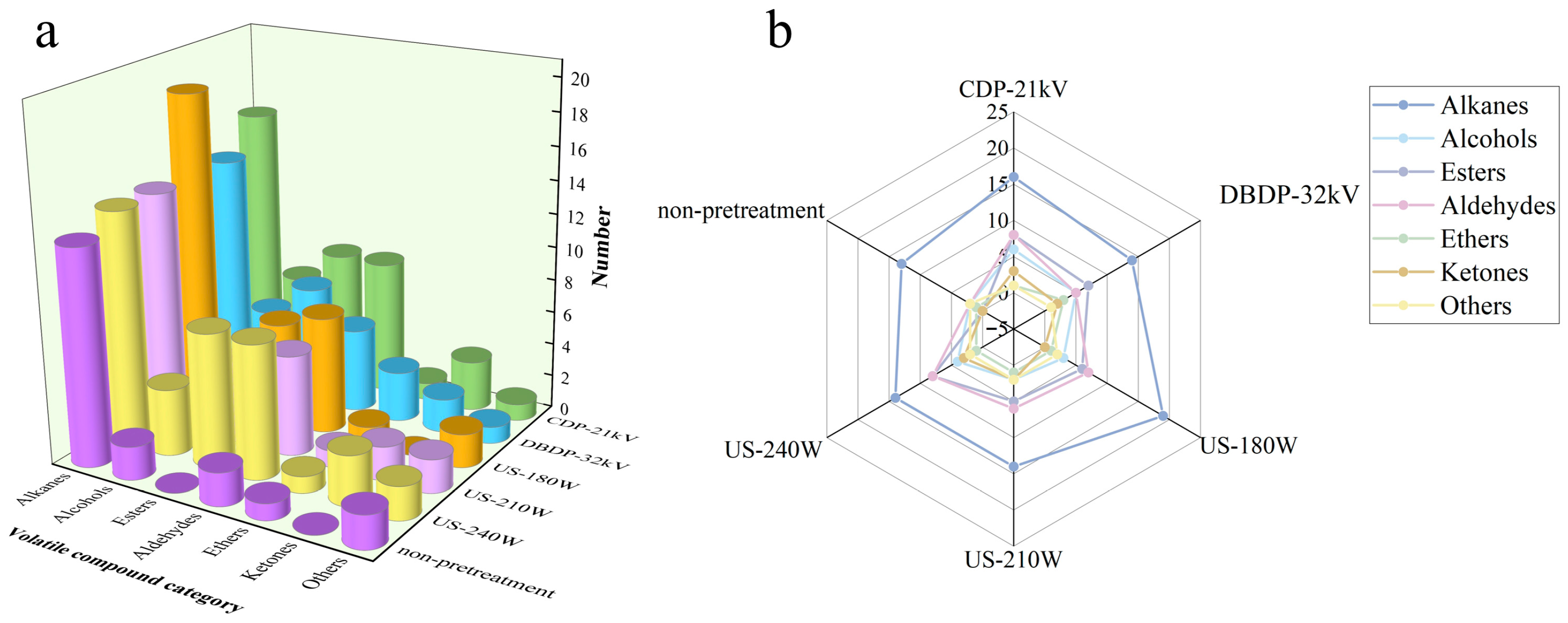
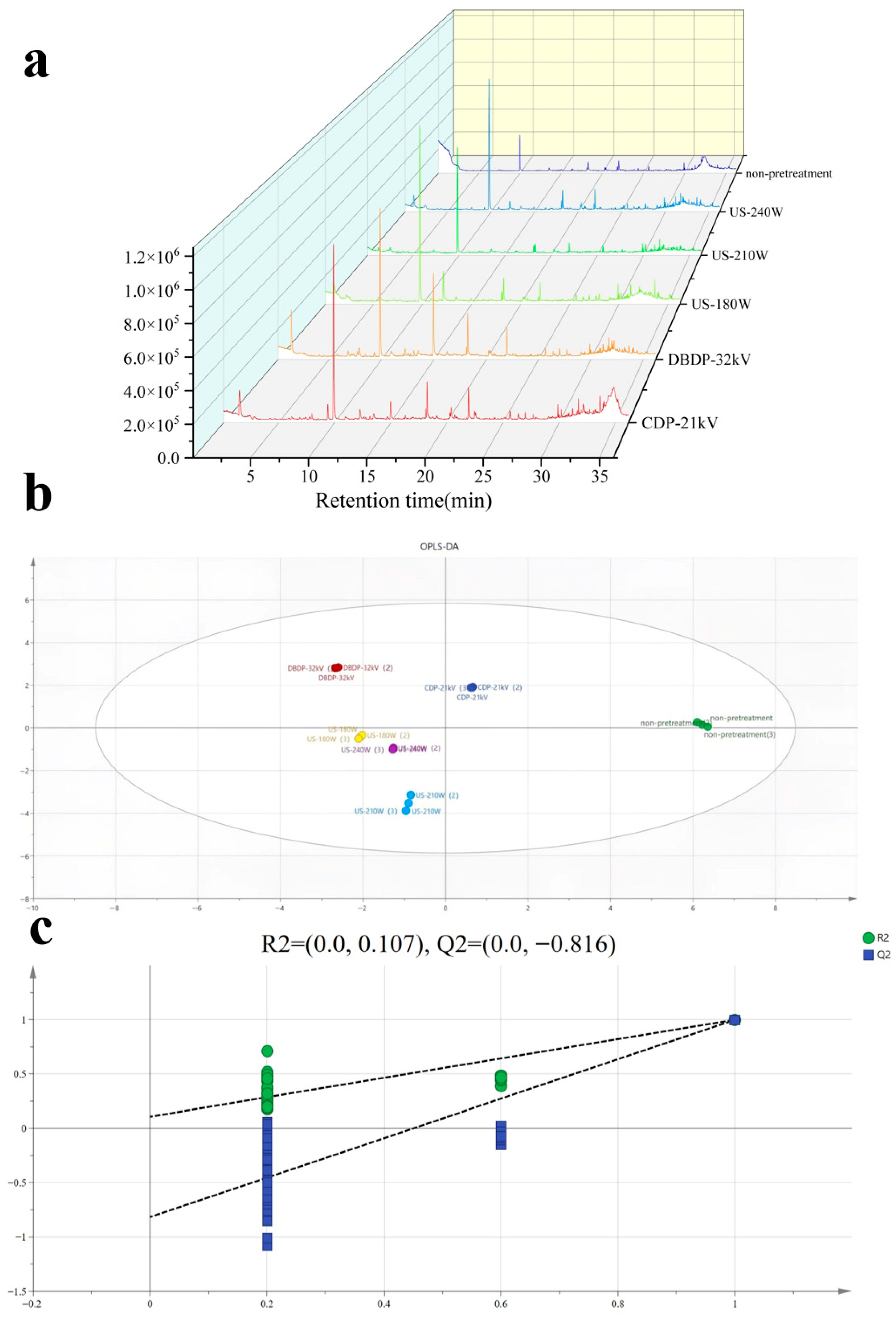
3.7. Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds
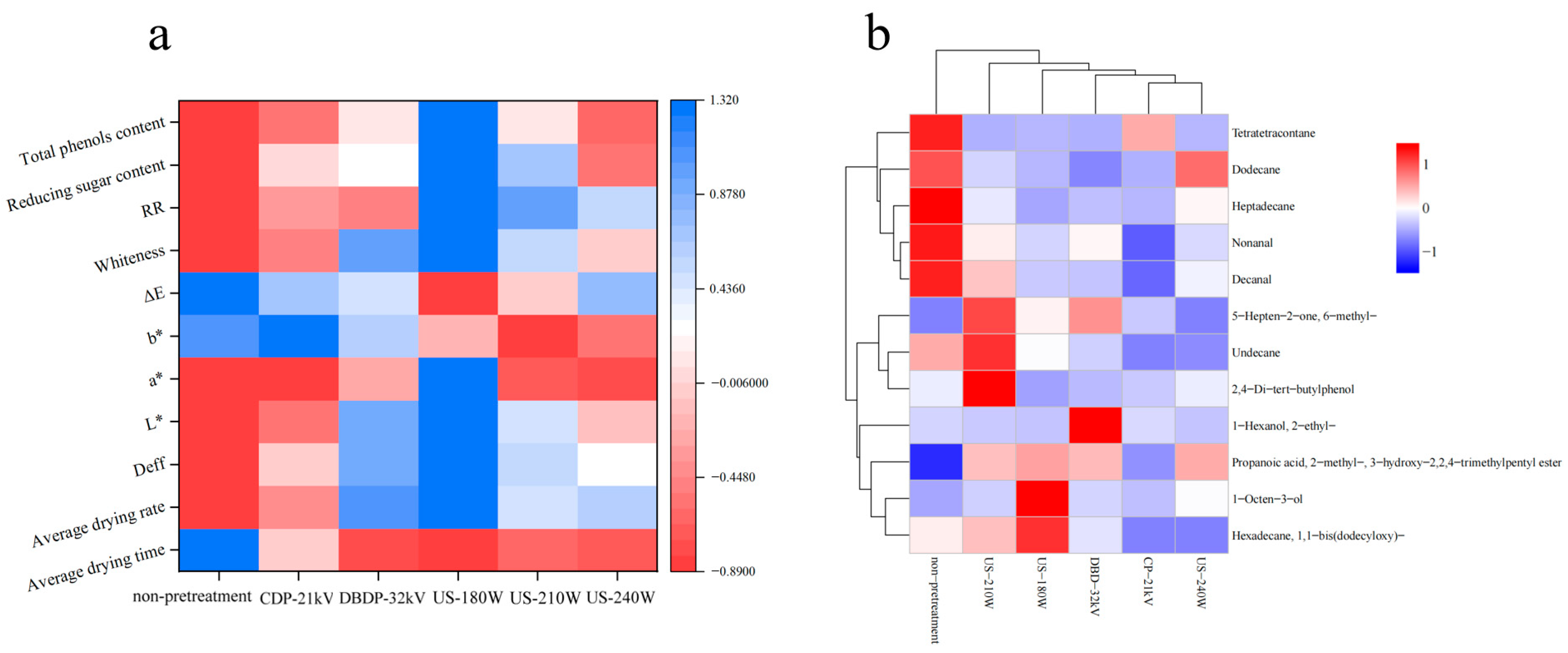
3.8. Correlation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDP | Corona discharge plasma |
| DBDP | Dielectric barrier discharge plasma |
| US | Ultrasonic waves |
| HAD | Hot-air drying |
| RR | Rehydration rate |
| LF-NMR | Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| TPC | Total phenol content |
References
- Edo, G.I.; Nwachukwu, S.C.; Akpoghelie, P.O.; Mafe, A.N.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A.; Yousif, E.; Zainulabdeen, K.; Jikah, A.N.; Owheruo, J.O.; et al. An overview of the nutritional composition, bioactivities and applications of Chinese yam (Dioscoreas oppositae). Ecol. Front. 2025, 45, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Xu, T.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Xiao, J.; et al. Chinese yam (Dioscorea): Nutritional value, beneficial effects, and food and pharmaceutical applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.M.; Ali, M.R.; Shishir, M.R.I.; Mondal, S.C. Thin-layer drying kinetics of yam slices, physicochemical, and functional attributes of yam flour. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C. Chemical composition, physical properties, and antioxidant activities of yam flours as affected by different drying methods. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xia, L.; Wang, F.; Guo, S.; Zou, J.; Su, X.; Yu, P. Comparison of different drying methods on Chinese yam: Changes in physicochemical properties, bioactive components, antioxidant properties and microstructure. Int. J. Food Eng. 2020, 16, 20200009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondaruk, J.; Markowski, M.; Błaszczak, W. Effect of drying conditions on the quality of vacuum-microwave dried potato cubes. J. Food Eng. 2007, 81, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yin, Y.; Tang, J. Microwave Drying of Food and Agricultural Materials: Basics and Heat and Mass Transfer Modeling. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Yang, P.; Tang, X.; Luo, L.; Sunden, B. Application of infrared radiation in the drying of food products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiripour, M.; Habibi-Najafi, M.B.; Mohebbi, M.; Emadi, B. Optimization of osmo-vacuum drying of pear (Pyrus communis L.) using response surface methodology. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2015, 9, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, F.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W. Improving food drying performance by cold plasma pretreatment: A systematic review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 4402–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.P.; Law, C.L.; Hii, C.L. Effect of Pre-treatment and Drying Method on Colour Degradation Kinetics of Dried Salak Fruit During Storage. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; Liu, W.; Duan, X.; Ren, G.; Song, C. Effects of freeze–thaw pre-treatment with different freezing methods on the microwave freeze drying of carrots. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 7181–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiktor, A.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. Drying kinetics and quality of carrots subjected to microwave-assisted drying preceded by combined pulsed electric field and ultrasound treatment. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jin, T.Z.; Xiao, G. Effects of pulsed electric fields pretreatment and drying method on drying characteristics and nutritive quality of blueberries. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, S.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, W. Dielectric barrier discharge plasma pretreatment: A cleaner new way to improve energy efficiency and quality of wolfberry drying. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bußler, S.; Ehlbeck, J.; Schlüter, O.K. Pre-drying treatment of plant related tissues using plasma processed air: Impact on enzyme activity and quality attributes of cut apple and potato. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 40, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obajemihi, O.I.; Cheng, J.; Sun, D. Novel cold plasma functionalized water pretreatment for improving drying performance and physicochemical properties of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruits during infrared-accelerated pulsed vacuum drying. J. Food Eng. 2024, 379, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Bai, W.; Guan, P.; Song, Z.; Chen, H. Effect of electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying on active ingredients, textural properties and moisture distribution of yam (Dioscorea opposita). Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corzo, O.; Bracho, N.; Alvarez, C. Water effective diffusion coefficient of mango slices at different maturity stages during air drying. J. Food Eng. 2008, 87, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaee, F.; Fazeli, A.; Fatemian, H.; Tavakolipour, H. Mass transfer coefficient and the characteristics of coated apples in osmotic dehydrating. Food Bioprod. Process. 2011, 89, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, B.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C. Role of drying techniques on physical, rehydration, flavor, bioactive compounds and antioxidant characteristics of garlic. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Guan, P.; Liu, J.; Lian, J.; Song, Z.; Chen, H.; Xing, R.; Lu, J.; Ding, C. Effects of ultrasound-assisted plasma-activated water pretreatment combined with electrohydrodynamics on drying characteristics, active ingredients and volatile components of yam (Dioscorea opposita). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 112, 107192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Wu, F.; Wang, P. Effects of different pretreatments on the drying and quality characteristics of Strobilanthes sarcorrhiza (C. Ling) by hot-air drying. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldo, D.; Sotin, H.; Pétro, D.; Le-Bail, G.; Guyot, S. Browning susceptibility of new hybrids of yam (Dioscorea alata) as related to their total phenolic content and their phenolic profile determined using LC-UV-MS. LWT 2022, 162, 113410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izli, N.; Izli, G.; Taskin, O. Drying kinetics, colour, total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity properties of kiwi dried by different methods. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Geng, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, L.; Wang, X. Convenient use of low field nuclear magnetic resonance to determine the drying kinetics and predict the quality properties of mulberries dried in hot-blast air. LWT 2021, 137, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellati, F.; Benvenuti, S.; Yoshizaki, F.; Bertelli, D.; Rossi, M.C. Headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of the volatile compounds of Evodia species fruits. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1087, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Ding, C.; Lu, J.; Bai, W.; Liu, J.; Lian, J.; Song, Z.; Chen, H.; Jia, Y. Influence of electrohydrodynamics on the drying characteristics, microstructure and volatile composition of apricot abalone mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii). Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 9, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricce, C.; Rojas, M.L.; Miano, A.C.; Siche, R.; Augusto, P.E.D. Ultrasound pre-treatment enhances the carrot drying and rehydration. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Bao, Y.; Han, B.; Zhu, J.; Duan, S.; Song, Z.; Chen, H. Effects of electrohydrodynamics on drying characteristics and volatile profiles of goji berry (Lycium barbarum L.). LWT 2024, 200, 116149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Mason, T.J.; Paniwnyk, L.; Lelas, V. Accelerated drying of button mushrooms, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower by applying power ultrasound and its rehydration properties. J. Food Eng. 2007, 81, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadali, G.; Apar, D.K.; Ozbek, B. Color Change Kinetics of Okra Undergoing Microwave Drying. Dry. Technol. 2007, 25, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Law, C.; Nema, P.K.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Deng, L.; Gao, Z.; Xiao, H. Pulsed vacuum drying enhances drying kinetics and quality of lemon slices. J. Food Eng. 2018, 224, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, M.; Kumar, V.; Naik, S.N. Convective drying of bitter yam slices (Dioscorea bulbifera): Mass transfer dynamics, color kinetics, and understanding the microscopic microstructure through MATLAB image processing. Food Phys. 2024, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Huang, D.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, S.; Gong, G. Ultrasound-assisted hot air drying characteristics of Phyllanthus emblica. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Fan, X. Effect of Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Moisture Migration and Quality of Cantharellus cibarius Following Hot Air Drying. Foods 2023, 12, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyüz, E.; Başkan, K.S.; Tütem, E.; Apak, R. High performance liquid chromatographic method with post-column detection for quantification of reducing sugars in foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1660, 462664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacka, M.; Wiktor, A.; Anuszewska, A.; Dadan, M.; Rybak, K.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. The application of unconventional technologies as pulsed electric field, ultrasound and microwave-vacuum drying in the production of dried cranberry snacks. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, J.; Bhandari, B.; Xiao, H.; Ding, C.; Peng, W.; Fang, X. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma on the drying kinetics, color, phenolic compounds, energy consumption and microstructure of lotus pollen. Dry. Technol. 2022, 40, 3100–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzimande, N.A.; Mianda, S.M.; Seke, F.; Sivakumar, D. Impact of different pre-treatments and drying methods on the physicochemical properties, bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of different tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) cultivars. LWT 2024, 207, 116641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.C.; Almeida, R.L.J.; Albuquerque, J.C.; de Andrade, E.W.V.; Gregório, M.G.; Santos, R.M.S.; Rodrigues, T.J.A.; Carvalho, R.D.O.; Gomes, M.M.D.A.; Moura, H.V.; et al. Optimization of ultrasound pre-treatment and the effect of different drying techniques on antioxidant capacity, bioaccessibility, structural and thermal properties of purple cabbage. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2024, 201, 109801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, C.D.S.; Mársico, E.T.; Ribeiro, R.D.O.R.; Conte-Júnior, C.A.; Mano, S.B.; Augusto, C.J.C.; Oliveira De Jesus, E.F. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF NMR 1H) to assess the mobility of water during storage of salted fish (Sardinella brasiliensis). J. Food Eng. 2016, 169, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, W.; Aziz, T.; Khojah, E.; Al-Asmari, F.; Alamri, A.S.; Alhomrani, M.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Drying kinetics and moisture migration mechanism of yam slices by cold plasma pretreatment combined with far-infrared drying. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 95, 103730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Jin, W.; Sun, S.; Hu, K.; Li, J. Effects of Drying Methods on the Physicochemical Aspects and Volatile Compounds of Lyophyllum decastes. Foods 2022, 11, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y. Fingerprint analysis of volatile flavor compounds in twenty varieties of Lentinula edodes based on GC-IMS. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 328, 112893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-jun, L.; Yang-yang, Q.; Bing, S.; Yang-yang, L.; Xing-hao, T.; Hong-jun, O.; Yahui, L.; Ge, T.; Zi-wei, Y.; Fei, C.; et al. Effects of four drying methods on Ganoderma lucidum volatile organic compounds analyzed via headspace solid-phase microextraction and comprehensive two-dimensional chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2021, 166, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Bi, Y.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Xiao, H.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, X. Non-thermal electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying improved the volatile organic compounds of lotus bee pollen via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 176, 114480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lin, W.; Sun, Y.; Pan, D.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, C.; He, J. Relationship between flavor characteristics and lipid oxidation in air-dried beef at different roasting stages. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024, 37, 100988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, D.; Dong, Y.; Ju, H.; Wu, C.; Lin, S. Characteristic volatiles fingerprints and changes of volatile compounds in fresh and dried Tricholoma matsutake Singer by HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1099, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Dong, K.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, G.; An, F.; Luo, Z.; Luo, P. Changes in volatile flavor of yak meat during oxidation based on multi-omics. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Ni, J.; Martynenko, A.; Chen, C.; Fang, X.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, H. Electrohydrodynamic drying of citrus (Citrus sinensis L.) peel: Comparative evaluation on the physiochemical quality and volatile profiles. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, T.; Aires, A.; Cosme, F.; Bacelar, E.; Morais, M.C.; Oliveira, I.; Ferreira-Cardoso, J.; Anjos, R.; Vilela, A.; Gonçalves, B. Bioactive (Poly)phenols, Volatile Compounds from Vegetables, Medicinal and Aromatic Plants. Foods 2021, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Fan, L.; Qin, G.; Wang, X. Effect of various drying pretreatments on the structural and functional properties of starch isolated from Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita Thumb.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelenein, D.; Caprioli, G.; Mustafa, A.M. Exploring the impacts of novel cold plasma technology on the volatile profile, flavor, and aroma properties of fruits and vegetables—A review. Food Saf. Health 2023, 1, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, I.M.; Mat Taher, Z.; Rahmat, Z.; Chua, L.S. A review of ultrasound-assisted extraction for plant bioactive compounds: Phenolics, flavonoids, thymols, saponins and proteins. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Ding, C. Study on the Effect of Ultrasonic and Cold Plasma Non-Thermal Pretreatment Combined with Hot Air on the Drying Characteristics and Quality of Yams. Foods 2025, 14, 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162831
Wang X, Song Z, Ding C. Study on the Effect of Ultrasonic and Cold Plasma Non-Thermal Pretreatment Combined with Hot Air on the Drying Characteristics and Quality of Yams. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162831
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xixuan, Zhiqing Song, and Changjiang Ding. 2025. "Study on the Effect of Ultrasonic and Cold Plasma Non-Thermal Pretreatment Combined with Hot Air on the Drying Characteristics and Quality of Yams" Foods 14, no. 16: 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162831
APA StyleWang, X., Song, Z., & Ding, C. (2025). Study on the Effect of Ultrasonic and Cold Plasma Non-Thermal Pretreatment Combined with Hot Air on the Drying Characteristics and Quality of Yams. Foods, 14(16), 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162831




