Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer’s Spent Yeast Mannoproteins—Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Reagents
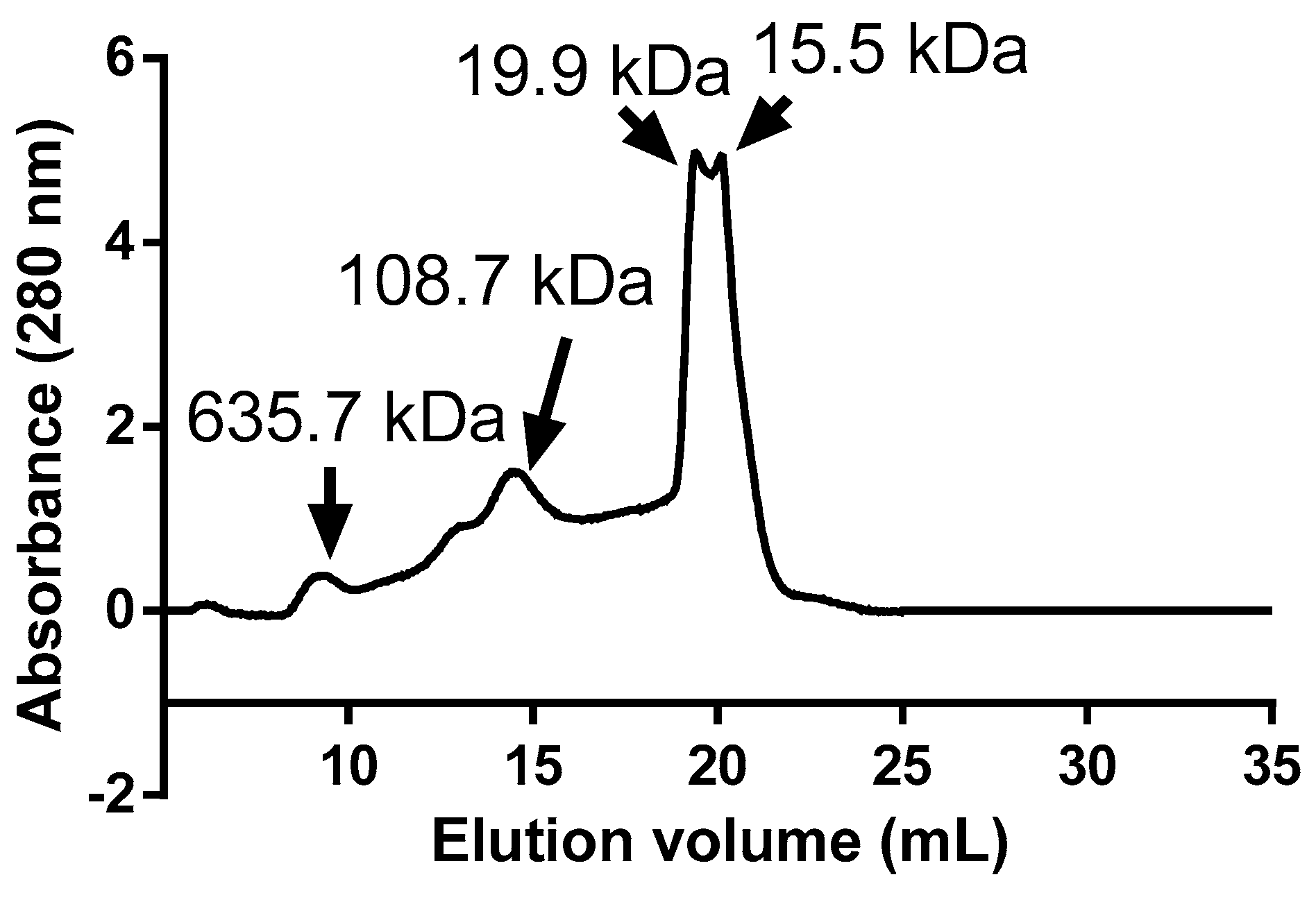
2.2. Extraction and Characterization of Mannoproteins
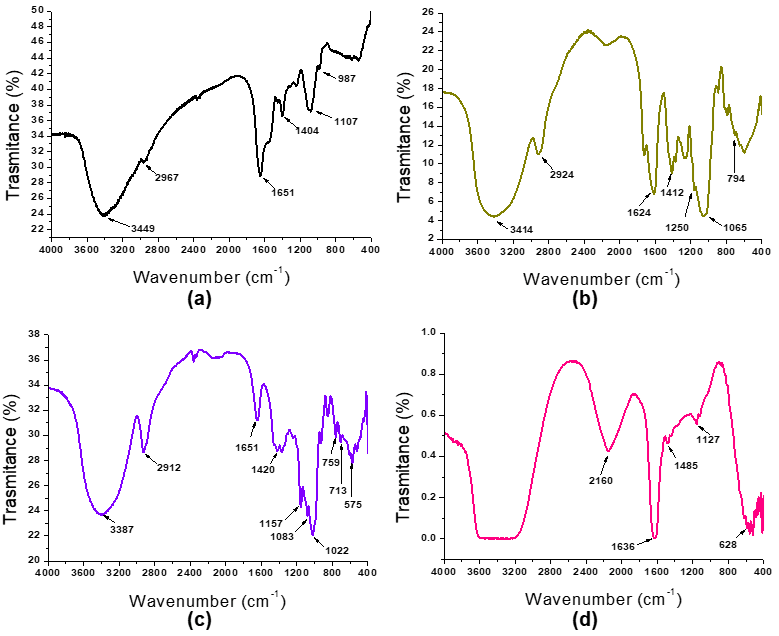
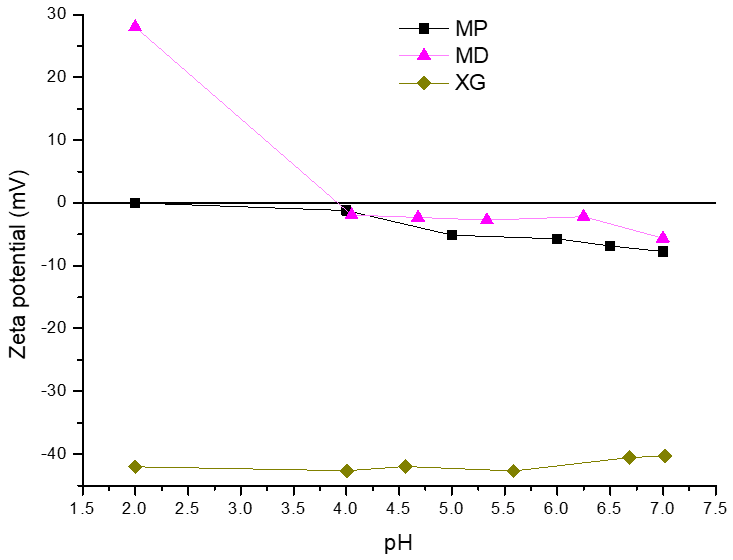
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of Encapsulating Material and Microcapsules
2.4. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion and In Vitro Colonic Fermentation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
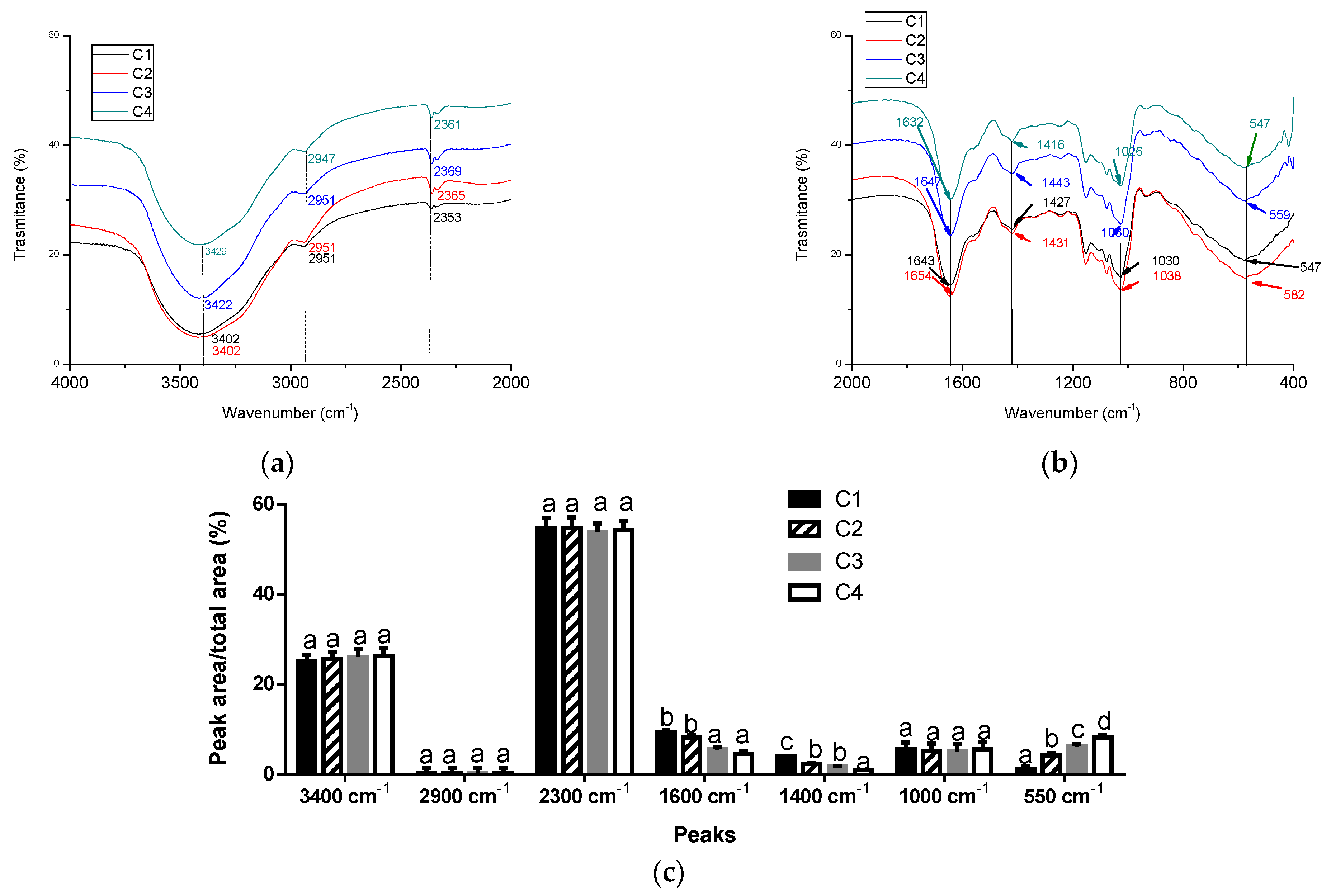
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Encapsulating Material
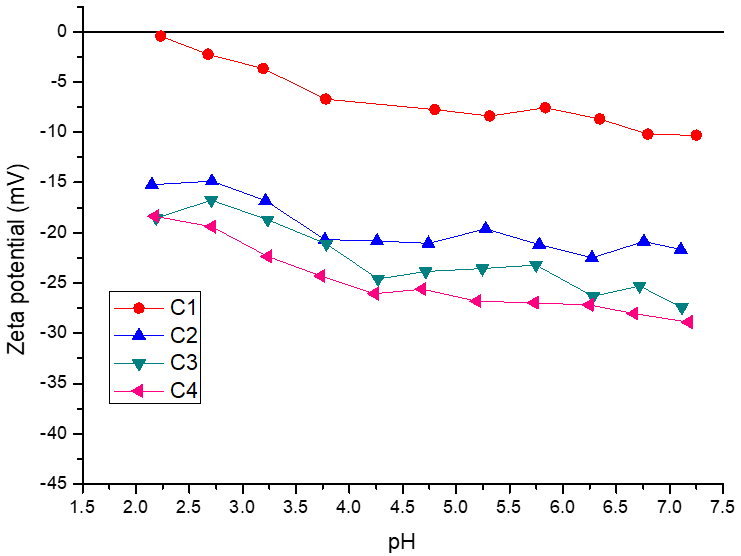
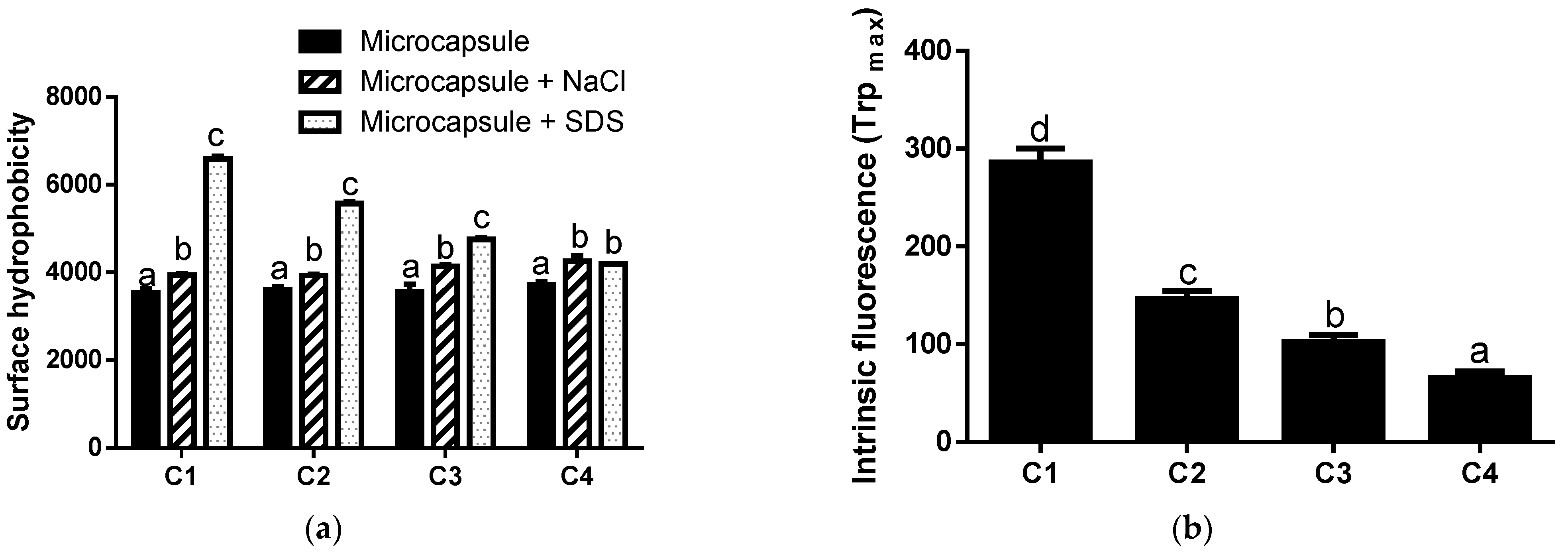
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Microcapsules
3.3. Calcium Bioaccessibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSY | Brewer’s spent yeast |
| CB | Colonic bioaccessibility |
| F0 | Peptides fraction with positive or neutral charge at pH 7.8 |
| F0.6 | Peptides fraction with negative charge at pH 7.8 |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| IB | Intestinal bioaccessibility |
| MD | Maltodextrin |
| MPs | Mannoproteins from brewer’s spent yeast |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TB | Total bioaccessibility |
| XG | Xanthan gum |
References
- Oliveira, A.S.; Ferreira, C.; Pereira, J.O.; Pintado, M.E.; Carvalho, A.P. Spent brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a potential source of bioactive peptides: An overview. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Karboune, S. A comparative study for the isolation and characterization of mannoproteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast cell wall. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Karboune, S.; Asehraou, A. Mannoproteins from inactivated whole cells of baker’s and brewer’s yeasts as functional food ingredients: Isolation and optimization. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Feng, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, H.; Chen, D.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J. The Inhibitory Effects of Hericium erinaceus β-glucan on in vitro Starch Digestion. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 621131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Araújo, V.B.; de Melo, A.N.F.; Costa, A.G.; Castro-Gomez, R.H.; Madruga, M.S.; de Souza, E.L.; Magnani, M. Followed extraction of β-glucan and mannoprotein from spent brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces uvarum) and application of the obtained mannoprotein as a stabilizer in mayonnaise. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 23, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R. Yeast proteins: The novel and sustainable alternative protein in food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marson, G.V.; de Castro, R.J.S.; Belleville, M.P.; Hubinger, M.D. Spent brewer’s yeast as a source of high added value molecules: A systematic review on its characteristics, processing and potential applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, M.E.; Drago, S.R.; Schierloh, L.P.; Cian, R.E. Identification of bioaccessible glycosylated neuroprotective peptides from brewer’s spent yeast mannoproteins by in vitro and in silico studies. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradello, G.; Tirelli, N. Yeast cells in microencapsulation. General features and controlling factors of the encapsulation process. Molecules 2021, 26, 3123. [Google Scholar]
- Heinen, G.D.; Garzón, A.G.; Cian, R.E.; Drago, S.R. Gastrointestinal and colonic bioaccessibility of calcium and ferulic acid from microcapsules made with brewer spent grain arabinoxylans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, C.; Hofmeyr, G.J.; Cormick, G.; Garcia-Casal, M.N.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Betrán, A.P. Current calcium fortification experiences: A review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1484, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Khashayar, P.; Tabari, M.; Sohrabvandi, S.; Fooladi Moghaddam, A. Water Fortified With Minerals (Ca, Mg, Fe, Zn). Int. J. Med. Res. Health Sci. 2016, 5, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Oneda, F.; Ré, M.I. The effect of formulation variables on the dissolution and physical properties of spray-dried microspheres containing organic salts. Powder Technol. 2003, 130, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Deng, H.; Li, L.; Jia, J.; Song, C.; Meng, X.; Xv, Q. Chitosan encapsulation soy peptide–calcium promotes calcium absorption and bone health of rats fed a low calcium diet. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 121, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, A.; Ghaitaranpour, A. Co-encapsulation of Vitamin D and Calcium for Food Fortification. J. Nutr. Fasting Health 2019, 7, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X. Fruit-Stalk Supplementing Calcium and Partition Regulation of Fruit Calcium for Prevention of Bitter Pit of Bagged Apple. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 3000–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arazo-Rusindo, M.; Reaño, G.; Pérez-Bravo, F.; Castillo-Valenzuela, O.; Benavides-Valenzuela, S.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Mariotti-Celis, M.S. Redesign of an instant legume soup for older adults with increased micronutrients bioaccessibility and adequate sensory attributes by using encapsulation. LWT 2023, 180, 114676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Lambré, C.; Leblanc, J.C.; et al. Re-evaluation of xanthan gum (E 415) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04909. [Google Scholar]
- Cian, R.E.; Campos-Soldini, A.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Drago, S.R.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Bioactive Phaseolus lunatus peptides release from maltodextrin/gum arabic microcapsules obtained by spray drying after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, A.G.; Cian, R.E.; Drago, S.R. Effects of agar-carrageenan wall materials and core-to-wall material ratio on physicochemical properties and in vitro bioaccessibility of microencapsulated bioactive peptides. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.A.; Sánchez, C.C.; Patino, J.M.R.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Santiago, L.G. Milk whey proteins and xanthan gum interactions in solution and at the air–water interface: A rheokinetic study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, T.; Kuang, W.; Xu, J.; Zhao, M. Influence of xanthan gum on physical characteristics of sodium caseinate solutions and emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanne-Cuménal, A.; Lainé, E.; Hoffart, V.; Verney, V.; Garrait, G.; Beyssac, E. Effect of Molecules’ Physicochemical Properties on Whey Protein/Alginate Hydrogel Rheology, Microstructure and Release Profile. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, L.; Randall, R. Proteins measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, P.; Halim, A.; Zauser, M.; Essig, A.; Joshi, H.J.; Zatorska, E.; Larsen, I.S.B.; Loibl, M.; Castells-Ballester, J.; Aebi, M.; et al. Mapping the O-Mannose glycoproteome in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2016, 15, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Salgado, P.R.; Mauri, A.N.; Drago, S.R. Pyropia columbina phycocolloids as microencapsulating material improve bioaccessibility of brewers’ spent grain peptides with ACE-I inhibitory activity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobaruela, E.d.C.; Santos, A.d.O.; de Almeida-Muradian, L.B.; Araujo, E.d.S.; Lajolo, F.M.; Menezes, E.W. Application of dietary fiber method AOAC 2011.25 in fruit and comparison with AOAC 991.43 method. Food Chem. 2018, 238, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.A.; Andermatten, R.B.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Santiago, L.G. β-Lactoglobulin heat-induced aggregates as carriers of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, H.; Tan, C.; Lin, S.; Kong, Y.; Tong, Y.; Meng, X. Extraction of mannoprotein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and analysis of its chemical composition and molecular structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 2252–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Z.; Liu, L.; Hui, H.; Wang, Q. Structural characterization and antineoplastic activity of saccharomyces cerevisiae mannoprotein. Int. J. Food. Prop. 2015, 18, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Application of xanthan gum as polysaccharide in tissue engineering: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.; Haq, B.; Al Shehri, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Muhammed, N.S.; Mahmoud, M. Modification of xanthan gum for a high-temperature and high-salinity reservoir. Polymers 2021, 13, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlicka, A.; Tavares, F.C.; Dörr, D.S.; Cholant, C.M.; Ely, F.; Santos, M.J.L.; Avellaneda, C.O. Dielectric behavior and FTIR studies of xanthan gum-based solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 305, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, I.; Selmin, F.; Pagani, S.; Minghetti, P.; Cilurzo, F. Nanofiller for the mechanical reinforcement of maltodextrins orodispersible films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.H.; Ahmad, M.; Siddiqui, N.A. A Novel Metal Halide based Natural Deep Eutectic solvent utilizing Calcium Chloride Dihydrate: Synthesis and characterization. Moroc. J. Chem. 2024, 12, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, J. Synthesis and Characterization of γ-irradiated PVA/PEG/CaCl2 Hydrogel for Wound Dressing. Am. J. Chem. 2012, 2, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosme, F.; Fernandes, C.; Ribeiro, T.; Filipe-Ribeiro, L.; Nunes, F.M. White wine protein instability: Mechanism, quality control and technological alternatives for wine stabilisation—An overview. Beverages 2020, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção Bicca, S. Structural Diversity of Yeast Mannoproteins and Its Impact on Their Functional Properties Towards Wine Polyphenols: Focus on the Role of Their Polysaccharide Part; Chemical Sciences; Institut Agro Montpelier: Montpelier, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Assunção Bicca, S.; Sieczkowski, N.; Schneider, R.; Mekoue, J.; Poncet-Legrand, C.; Doco, T. Exploring the dynamic between yeast mannoproteins structure and wine stability. Part 1: Polysaccharides part characteristics of S. cerevisiae and non-Saccharomyces mannoproteins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 363, 123770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengiyumva, E.M.; Alexandridis, P. Xanthan gum in aqueous solutions: Fundamentals and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churio, O.; Valenzuela, C. Development and characterization of maltodextrin microparticles to encapsulate heme and non-heme iron. LWT 2018, 96, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordón, M.G.; Paredes, A.J.; Camacho, N.M.; Penci, M.C.; González, A.; Palma, S.D.; Ribotta, P.D.; Martinez, M.L. Formulation, spray-drying and physicochemical characterization of functional powders loaded with chia seed oil and prepared by complex coacervation. Powder. Technol. 2021, 391, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iesa, N.B.; Chaipoot, S.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Wiriyacharee, P.; Lim, B.G.; Sringarm, K.; Burgett, M.; Chuttong, B. Effects of Maltodextrin and Gum Arabic Composition on the Physical and Antioxidant Activities of Dewaxed Stingless Bee Cerumen. Foods 2023, 12, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.M.; Lehtonen, M.; Räikkönen, H.; Kilpeläinen, P.O.; Mikkonen, K.S. Wood hemicelluloses as effective wall materials for spray-dried microcapsulation of polyunsaturated fatty acid-rich oils. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, H.C.F.; Tonon, R.V.; Grosso, C.R.F.; Hubinger, M.D. Encapsulation efficiency and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil microencapsulated by spray drying using different combinations of wall materials. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarbaglu, Z.; Mahdi Jafari, S.; Sarabandi, K.; Mohammadi, M.; Khakbaz Heshmati, M.; Pezeshki, A. Influence of spray drying encapsulation on the retention of antioxidant properties and microstructure of flaxseed protein hydrolysates. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Moretti, T.S.; Boschini, C.; Baliero, J.C.C.; Freitas, O.; Favaro-Trindade, C.S. Stability of microencapsulated B. lactis (BI 01) and L. acidophilus (LAC 4) by complex coacervation followed by spray drying. J. Microencapsul. 2007, 24, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xu, D. Encapsulation of calcium carbonate with a ternary mixture of sodium caseinate/gelatin/xanthan gum to enhance the dispersion stability of solid/oil/water emulsions. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1090827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yin, H.; Yan, J.; Qi, B.; Liu, J. Structural and physicochemical properties of soya bean protein isolate/maltodextrin mixture and glycosylation conjugates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, D. Stability mechanism of Monascus pigment–soy protein isolate–maltodextrin complex. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 7173–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Sun, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jafari, S.M.; Sun, B.; Wang, J. Stabilization of anthocyanins by simultaneous encapsulation-copigmentation via protein-polysaccharide polyelectrolyte complexes. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proaño, J.L.; Pérez, A.A.; Drago, S.R. Foaming properties are improved by interactions between brewer’s spent grain proteins and carrageenans in aqueous solution. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyomugasho, C.; Gwala, S.; Christiaens, S.; Jamsazzadeh Kermani, Z.; Van Loey, A.M.; Grauwet, T.; Hendrickx, M.E. Pectin nanostructure influences pectin-cation interactions and in vitro-bioaccessibility of Ca2+, Zn2+, Fe2+ and Mg2+-ions in model systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, A.G.; Pontoni, S.M.; Mamone, G.; Drago, S.R.; Cian, R.E. Xanthan gum and pectin as beverage stabilizers reduce the digestive enzyme hydrolysis of antioxidant and antihypertensive peptides obtained from a brewery byproduct. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.A.; Jesus, G.F.A.; Pereira, G.V.; Silva, B.C.; Sá, L.S.; Martins, M.L.; Mouriño, J.L.P. The Chelating Mineral on Organic Acid Salts Modulates the Dynamics and Richness of the Intestinal Microbiota of a Silver Catfish Rhamdia quelen. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.A.; Jesus, G.F.A.; Cardoso, L.; Silva, B.C.; Ferrarezi, J.V.S.; Fereira, T.H.; Sterzelecki, F.C.; Sugai, J.K.; Martins, M.L.; Mouriño, J.L.P. The intestinal health of silver catfish Rhamdia quelen can be changed by organic acid salts, independent of the chelating minerals. Aquaculture 2019, 505, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, M.E.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Drago, S.R.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Cian, R.E. Gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation of brewer’s spent yeast peptides modulate their antioxidant properties and effect on intestinal barrier. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, G.; Coronel, M.Z.; Pellegrini, G.; Mandalunis, P.; Rio, M.E.; de Portela, M.L.P.M.; Zeni, S.N. Effect of a combination GOS/FOS® prebiotic mixture and interaction with calcium intake on mineral absorption and bone parameters in growing rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
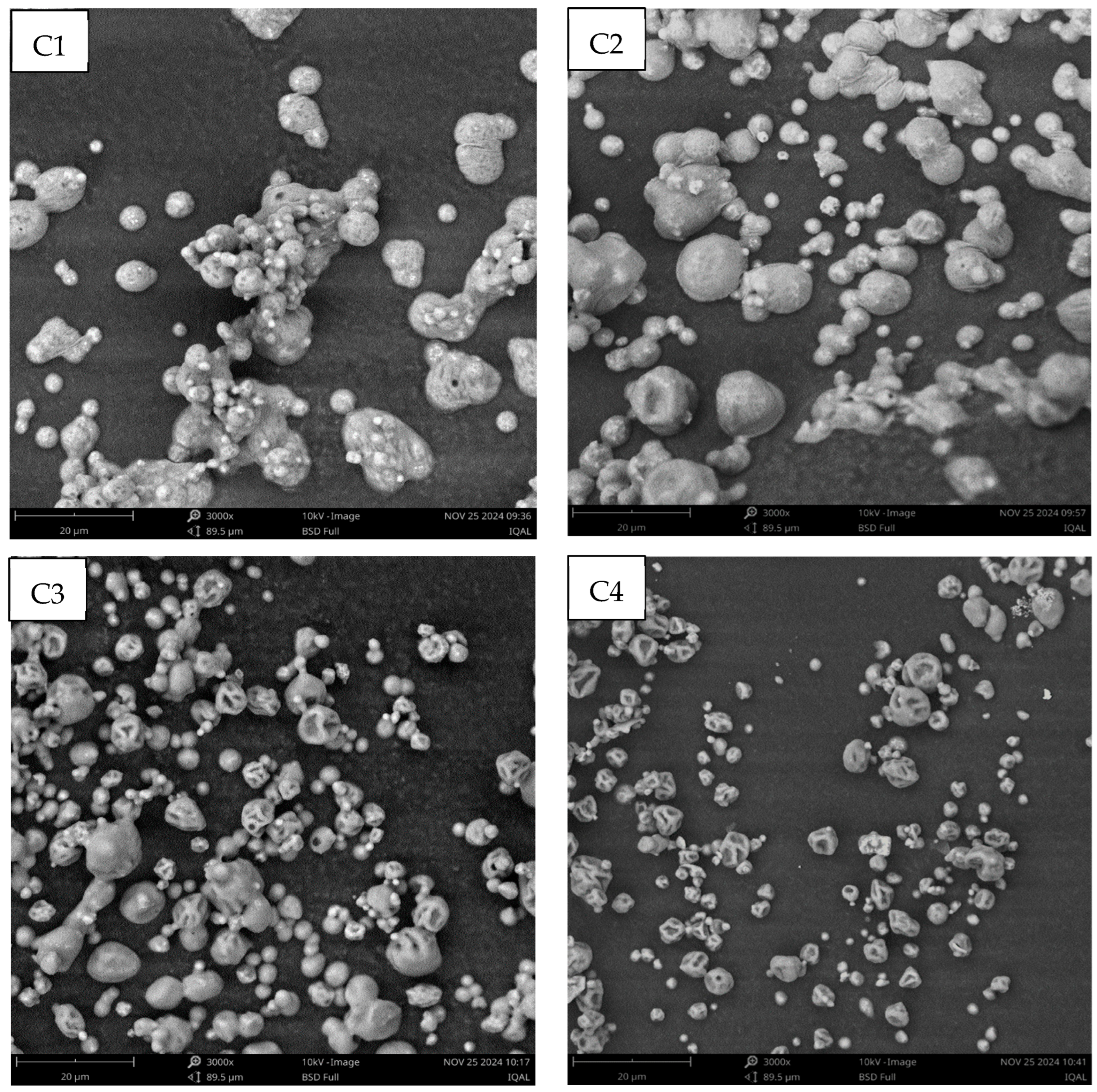
| Microcapsules | Moisture (g/100 g) | Ash (g/100 g d.b) | Carbohydrates (g/100 g d.b) | Protein (g/100 g d.b) | aw | Size (µm) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 16.3 ± 0.0 a | 30.9 ±3.1 a | 47.4 ± 0.9 a | 24.3 ± 0.0 a | 0.36 ± 0.00 d | 5.59 ± 0.02 d | 86.6 ± 0.8 a |
| C2 | 15.3 ± 0.0 a | 32.1 ± 3.6 a | 47.6 ± 5.3 a | 23.9 ± 0.0 a | 0.34 ± 0.00 c | 4.92± 0.01 c | 88.7 ± 0.0 b |
| C3 | 14.6 ± 0.0 a | 30.8 ± 1.1 a | 45.2 ± 0.3 a | 23.8 ± 0.0 a | 0.32 ± 0.00 b | 4.11 ± 0.18 b | 90.8 ± 0.0 c |
| C4 | 15.4 ± 0.0 a | 27.9 ± 0.6 a | 48.9 ± 0.3 a | 24.9 ± 0.0 a | 0.30 ± 0.00 a | 3.29 ± 0.05 a | 95.6 ± 0.3 d |
| Microcapsules | IB (%) | CB (%) | TB (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 22.8 ± 0.2 c | 9.0 ± 0.1 a | 31.8 ± 0.1 d |
| C2 | 22.8 ± 0.0 c | 9.5 ± 0.4 a | 32.0 ± 0.4 d |
| C3 | 18.3 ± 0.2 b | 11.4 ± 0.2 b | 29.7 ± 0.2 c |
| C4 | 17.9 ± 0.0 b | 10.7 ± 0.1 b | 28.6 ± 0.1 b |
| Control (CaCl2) | 13.6 ± 0.1 a | 8.9 ± 0.1 a | 22.5 ± 0.1 a |
| Microcapsule | Acetic Acid (mg) | Propionic Acid (mg) | Butiric Acid (mg) | Total SCFAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 2.3 ± 0.0 b | 1.8 ± 0.0 b | N.D. | 4.1 ± 0.1 b |
| C2 | 2.3 ± 0.1 b | 2.0 ± 0.0 c | N.D. | 4.3 ± 0.1 b |
| C3 | 2.9 ± 0.2 c | 2.2 ± 0.0 d | N.D. | 5.1 ± 0.0 c |
| C4 | 2.9 ± 0.4 c | 2.1 ± 0.0 e | N.D. | 5.0 ± 0.1 c |
| Negative control (H2O) | 2.1 ± 0.0 a | 1.2 ± 0.0 a | N.D. | 3.3 ± 0.0 a |
| Positive control (D-Raffinose) | 4.8 ± 0.0 d | 2.9 ± 0.0 f | N.D. | 7.7 ± 0.0 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aquino, M.E.; Drago, S.R.; Cian, R.E. Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer’s Spent Yeast Mannoproteins—Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility. Foods 2025, 14, 2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152632
Aquino ME, Drago SR, Cian RE. Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer’s Spent Yeast Mannoproteins—Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152632
Chicago/Turabian StyleAquino, Marilin E., Silvina R. Drago, and Raúl E. Cian. 2025. "Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer’s Spent Yeast Mannoproteins—Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility" Foods 14, no. 15: 2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152632
APA StyleAquino, M. E., Drago, S. R., & Cian, R. E. (2025). Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer’s Spent Yeast Mannoproteins—Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility. Foods, 14(15), 2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152632







