Enhanced Protein Extraction from Auxenochlorella protothecoides Through Synergistic Mechanical Cell Disruption and Alkaline Solubilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Microalgae Cultivation
2.3. Protein Extraction from A. protothecoides
2.3.1. Preparation of Microalgae Biomass
2.3.2. Protein Extraction Using Alkaline Extraction Alone
2.3.3. Protein Extraction Using High-Pressure Homogenization Followed by Alkaline Treatment
2.3.4. Protein Extraction Using Bead Milling Followed by Alkaline Treatment
2.4. Determination of Soluble Protein Content
2.5. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Alkaline Solubilization of Protein
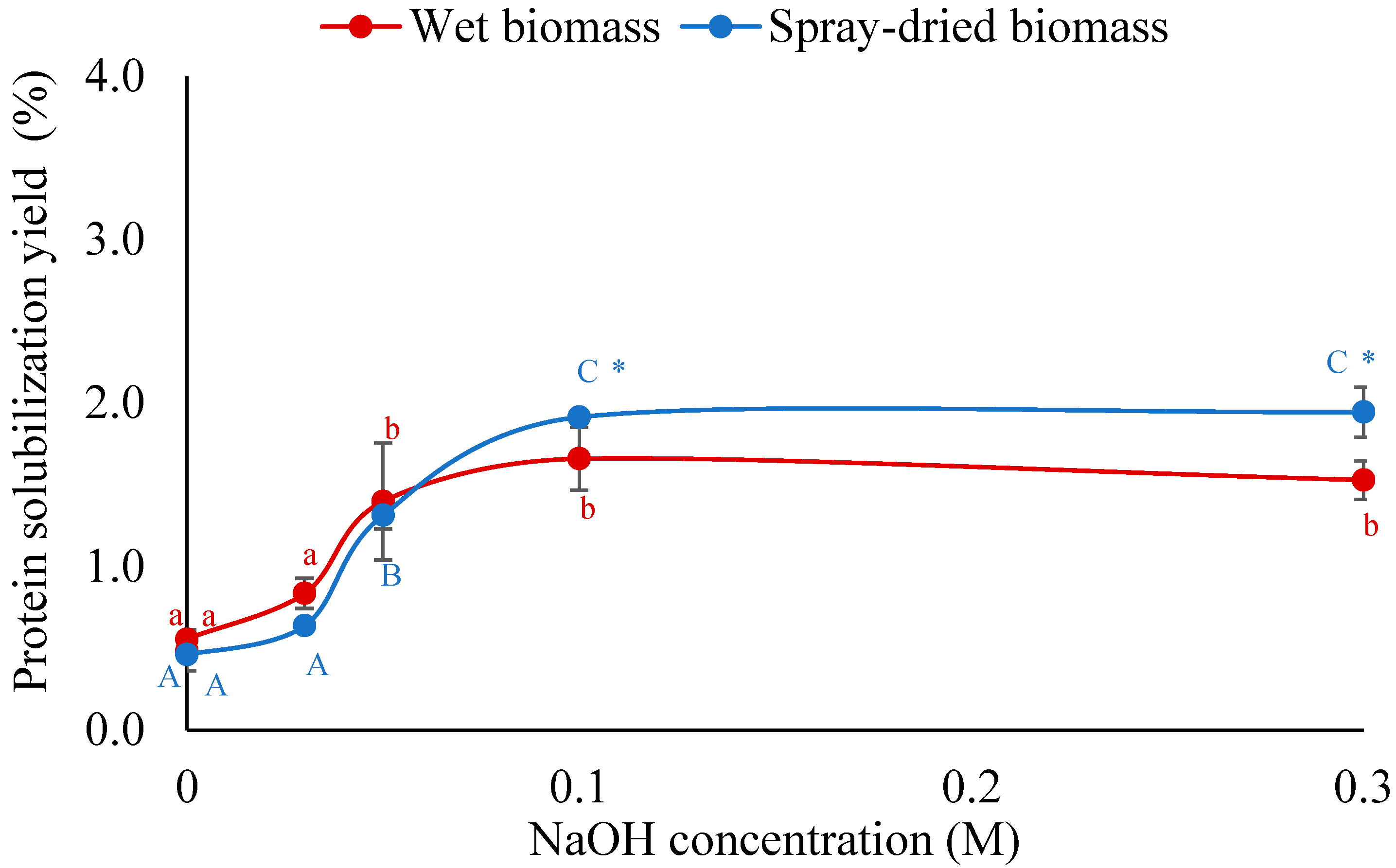
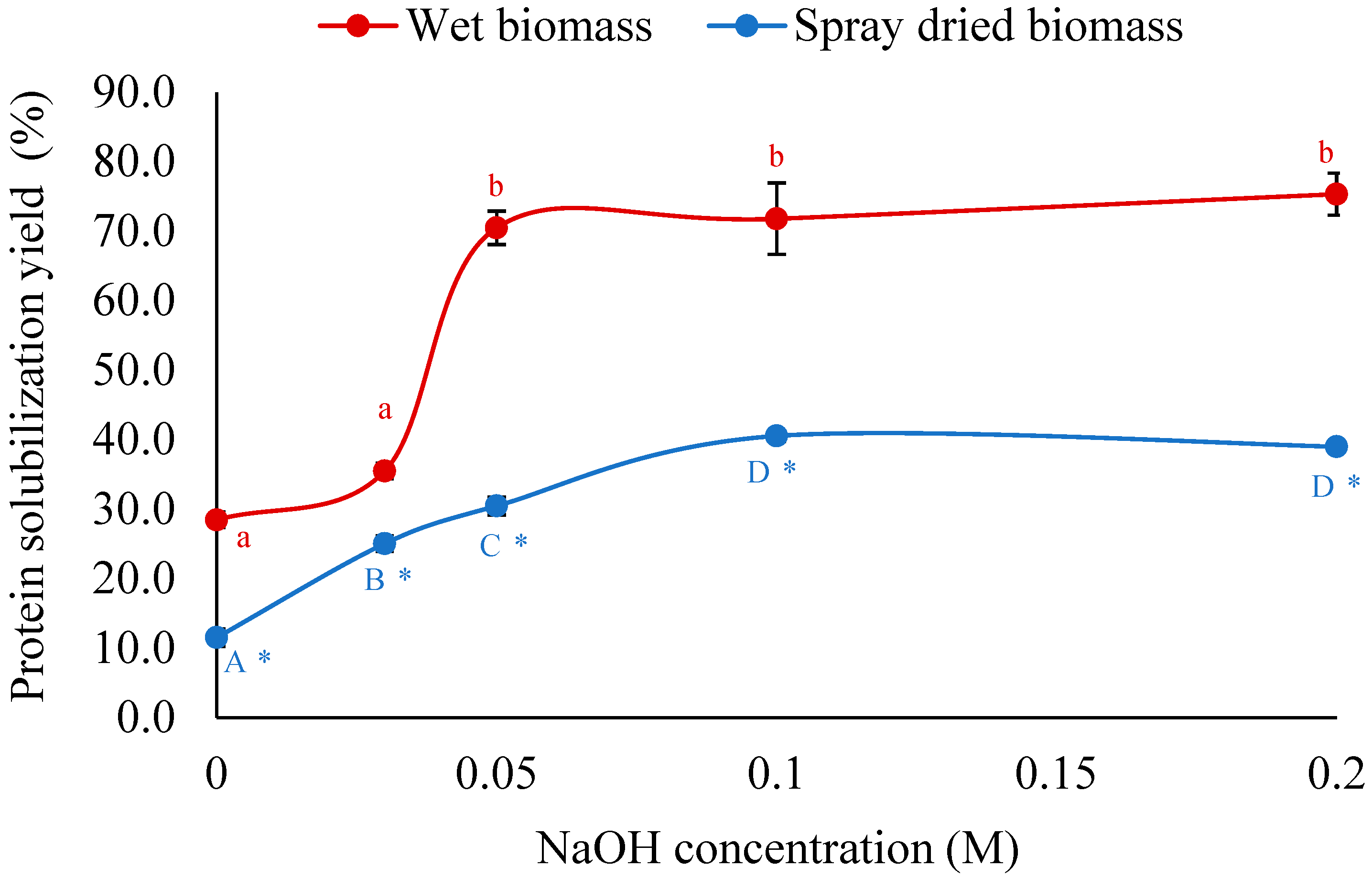
3.1.1. Effect of NaOH Concentration on Protein Solubilization Yield
3.1.2. Mixing Time for Protein Solubilization
3.2. High-Pressure Homogenization for Enhanced Solubilization of Protein
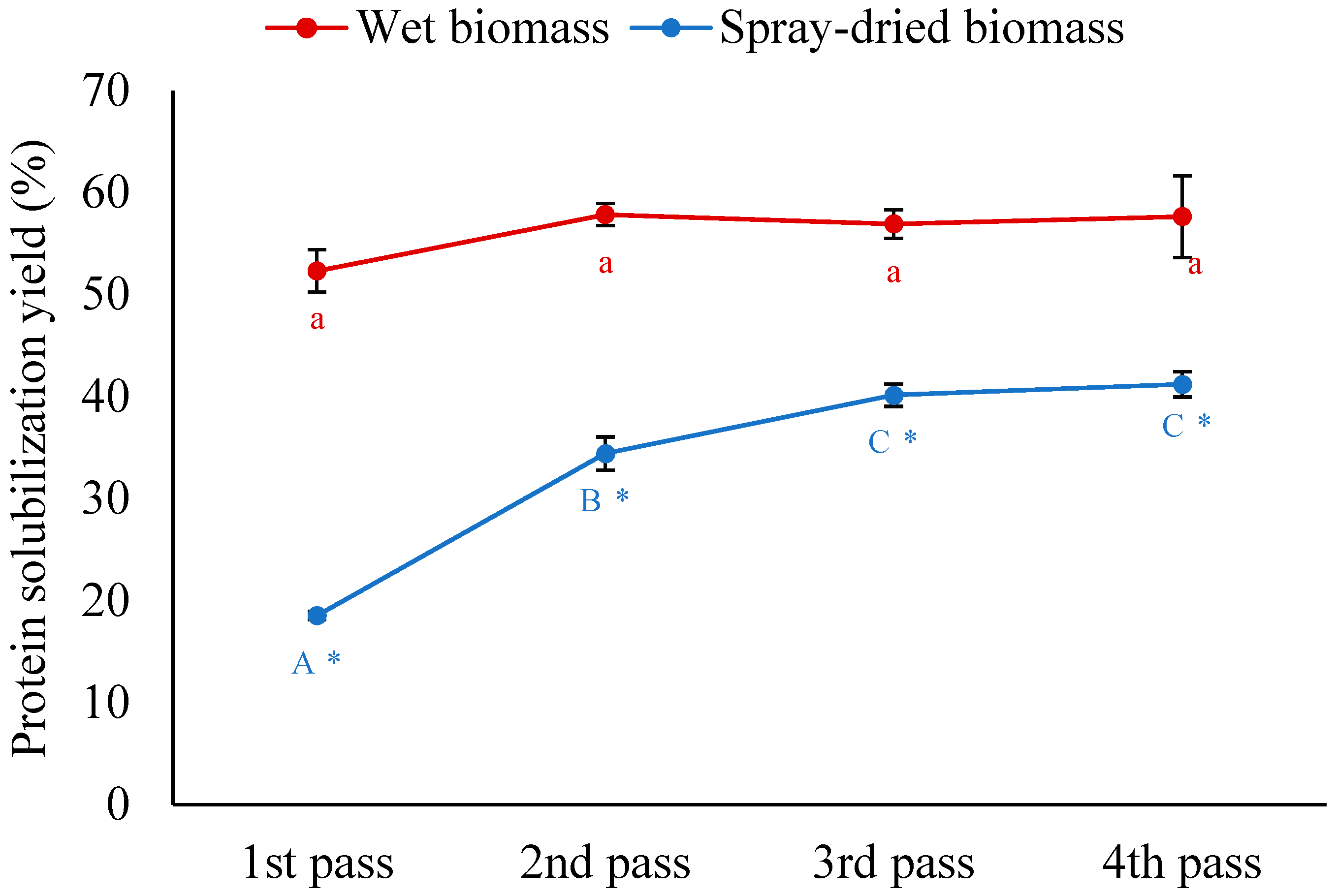
3.2.1. Effect of Number of HPH Passes
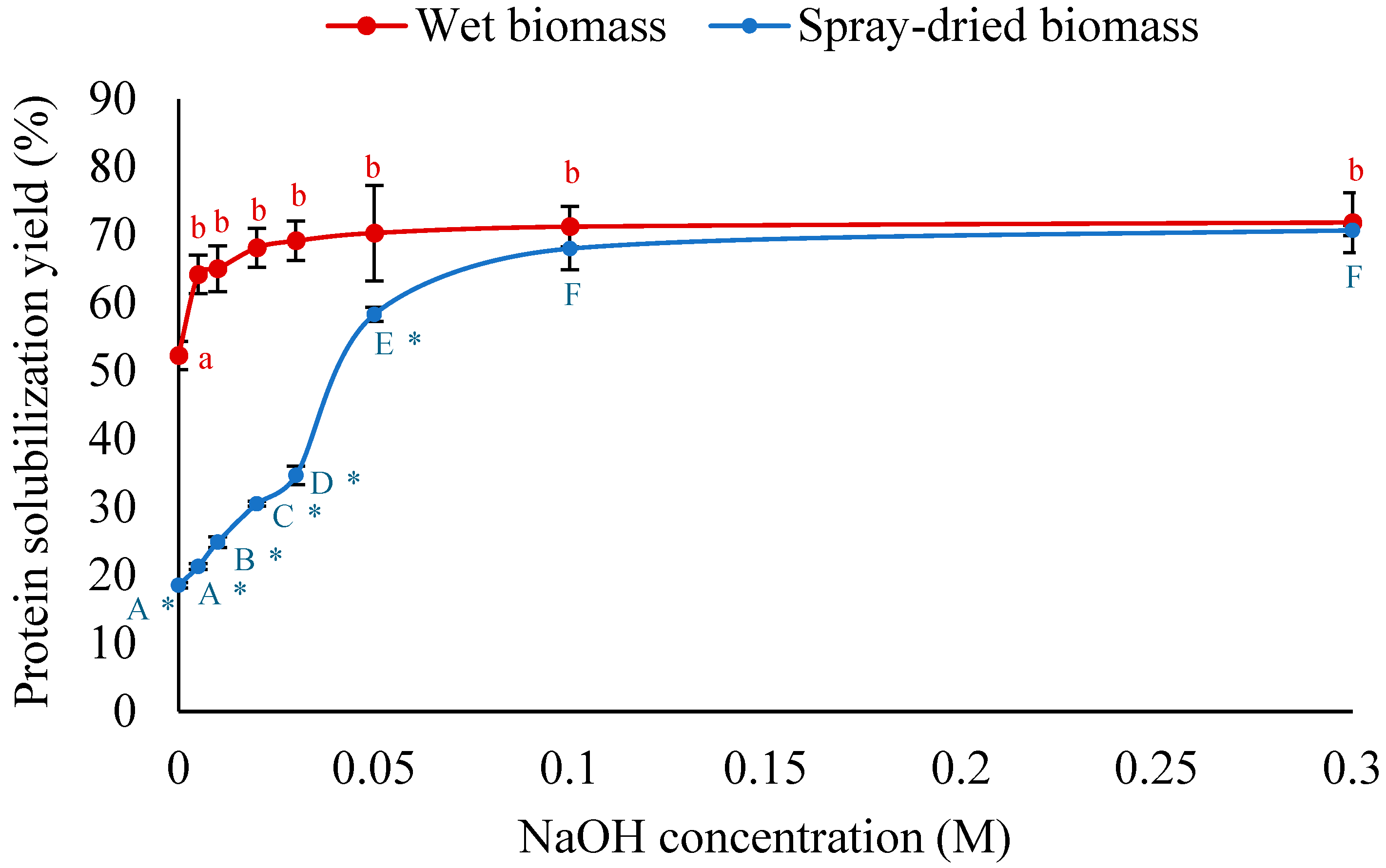
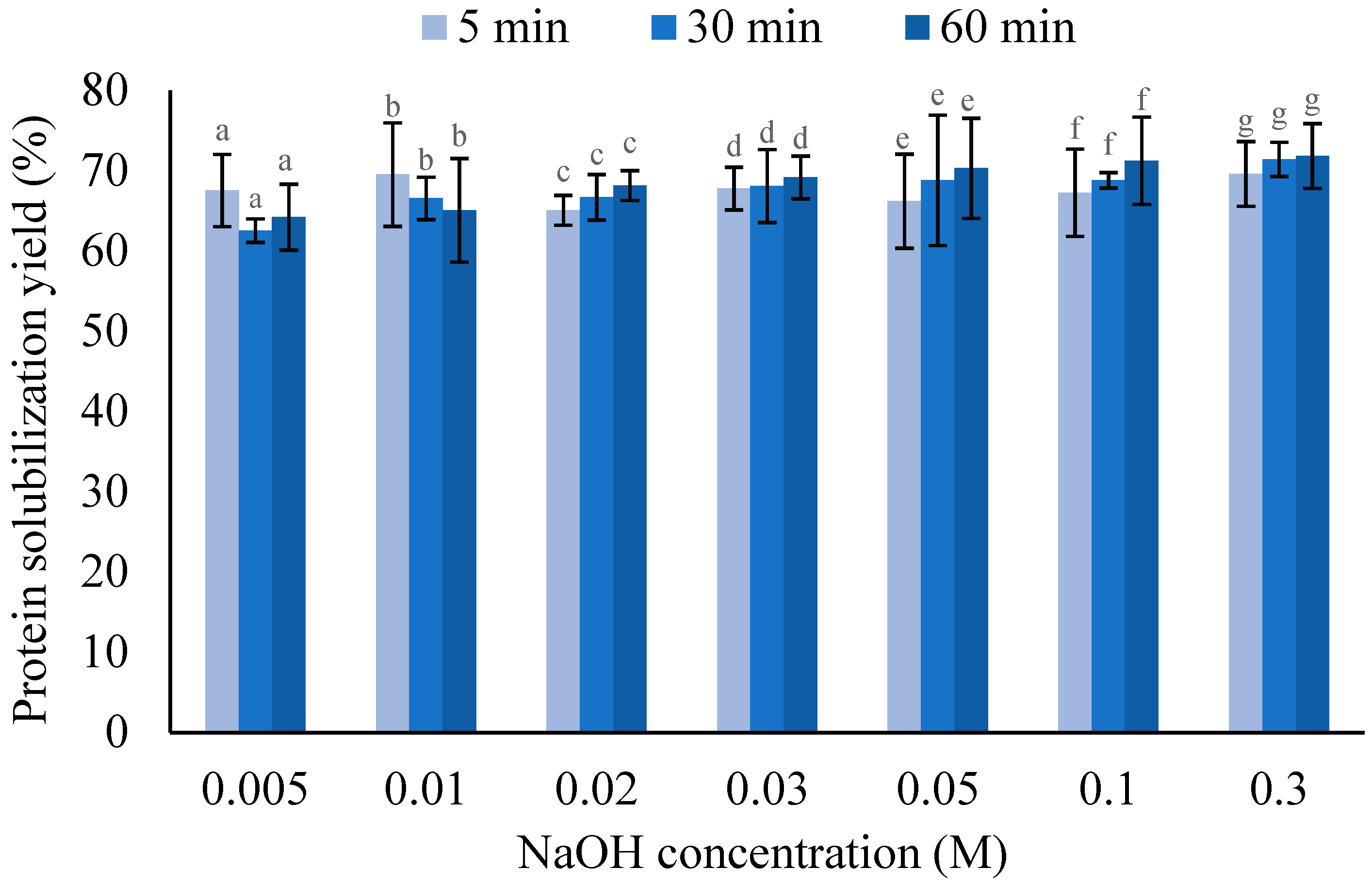
3.2.2. HPH Followed by Alkaline Treatment for Enhanced Protein Solubilization
3.3. Effect of Bead Milling on Protein Solubilization
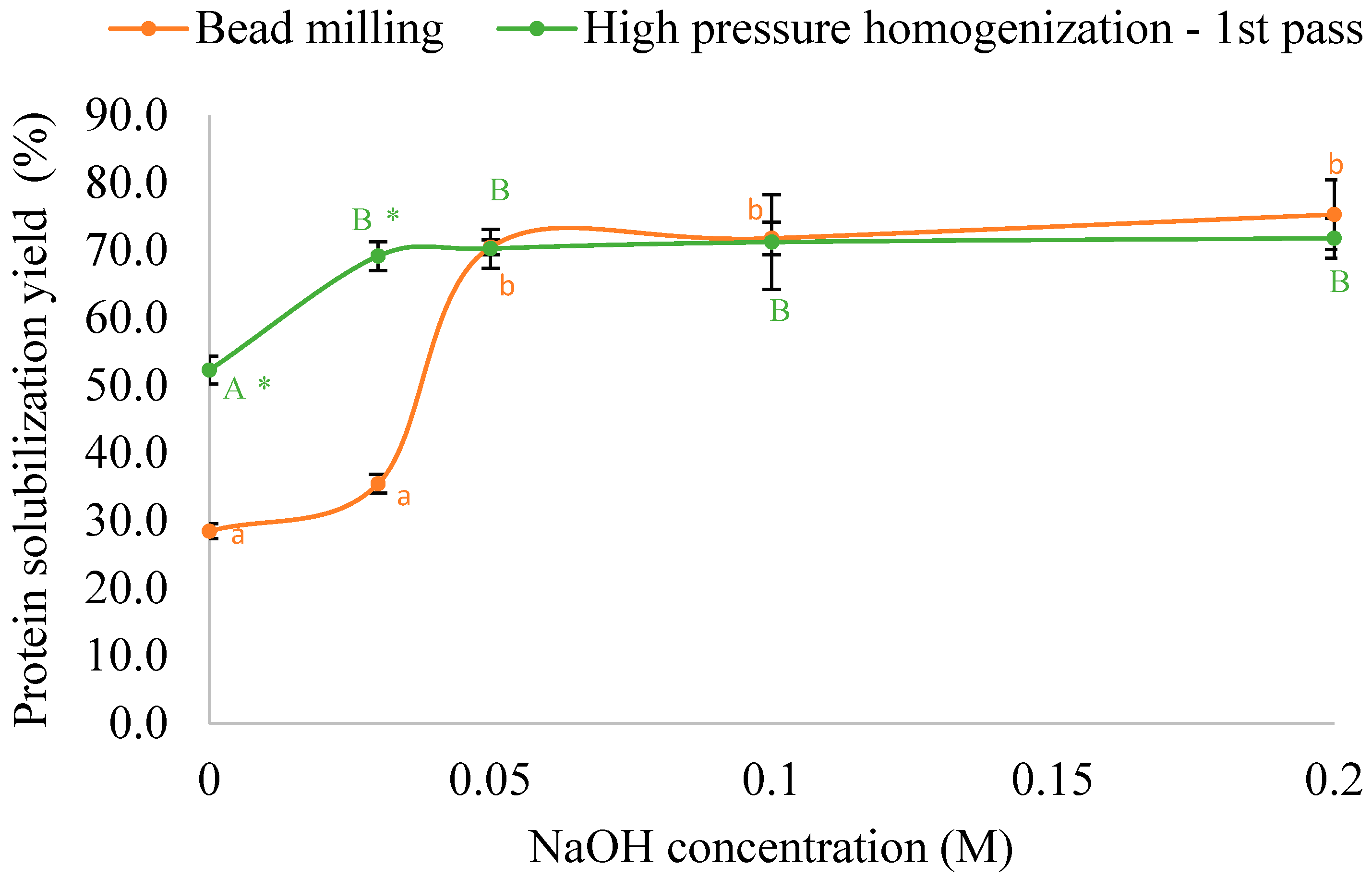
3.4. Comparison Between HPH and Bead Milling for Protein Solubilization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colla, L.M.; Oliveira Reinehr, C.; Reichert, C.; Costa, J.A.V. Production of Biomass and Nutraceutical Compounds by Spirulina platensis under Different Temperature and Nitrogen Regimes. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, H.J.; Almarales, A.; Carrillo, O.; Bermúdez, R.C. Utilisation of Chlorellavulgaris Cell Biomass for the Production of Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysates. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7723–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, E.W. Micro-Algae as a Source of Protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.W.; Teh, T.M.; Tan, C.F.; Bi, X.; Low, Z.E.; Rahman Talukder, M.M. Alkaline Solubilization of Microalgal Protein and Its Impact on the Functional Properties of Protein Extract. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, C.; Frances, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Laroche, C.; Pouzet, C.; Vaca-Garcia, C.; Pontalier, P.-Y. Understanding the Effect of Cell Disruption Methods on the Diffusion of Chlorella vulgaris Proteins and Pigments in the Aqueous Phase. Algal Res. 2015, 8, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, P.R.; Miron, T.L.; Olivieri, G.; Barbosa, M.J.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M. Mild Disintegration of the Green Microalgae Chlorella vulgaris Using Bead Milling. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubeau, S.; Marchal, L.; Pruvost, J.; Jaouen, P.; Legrand, J.; Fleurence, J. High Pressure Disruption: A Two-Step Treatment for Selective Extraction of Intracellular Components from the Microalga Porphyridium cruentum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 25, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, B.; Zermatten, C.; Haberkorn, I.; Mathys, A. Enhancing protein extraction from heterotrophic Auxenochlorella protothecoides microalgae through emerging cell disruption technologies combined with incubation. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 407, 131099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimichas, A.; Karveli, I.; Dimopoulos, G.; Giannakourou, M.; Taoukis, P. Kinetics of High Pressure Homogenization Assisted Protein Extraction from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 88, 103438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Chang, C.; Chen, J.; Cao, F.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, J. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Proteins Extracted from Three Microalgal Species. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.W.; Teh, T.M.; Weingarten, M.; Rahman Talukder, M.M. Integrating Bead Milling and Alkaline Solubilization for Enhanced Protein Recovery from Microalgae: A Comprehensive Approach. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.R.; Chew, K.W.; Zaid, H.F.M.; Chu, D.-T.; Tao, Y.; Show, P.L. Microalgal Protein Extraction from Chlorella vulgaris FSP-E Using Triphasic Partitioning Technique with Sonication. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi, B.; Trindade, L.M. Detailed Biochemical and Morphologic Characteristics of the Green Microalga Neochloris oleoabundans Cell Wall. Algal Res. 2018, 35, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhattab, M.; Kermanshahi-Pour, A.; Brooks, M.S.-L. Microalgae Disruption Techniques for Product Recovery: Influence of Cell Wall Composition. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 31, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.P. Microstructure of Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Microalgal Powders. Food Struct. 1985, 4, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tibbetts, S.M.; Berrue, F.; McGinn, P.J.; MacQuarrie, S.P.; Puttaswamy, A.; Patelakis, S.; Schmidt, D.; Melanson, R.; MacKenzie, S.E. A Rat Study to Evaluate the Protein Quality of Three Green Microalgal Species and the Impact of Mechanical Cell Wall Disruption. Foods 2020, 9, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, B.; Van Poucke, C.; De Witte, B.; Casciaro, V.; Moerdijk-Poortvliet, T.; Muylaert, K.; Robbens, J. The effect of drying, cell disruption and storage on the sensory properties of Nannochloropsis sp. Algal Res. 2023, 71, 103092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mixing Time (min) | Protein Solubilization Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Wet Biomass | Spray-Dried Biomass | |
| 5 | 0.454 ± 0.005 a | 1.078 ± 0.055 A * |
| 10 | 0.488 ± 0.035 a | 1.419 ± 0.152 B * |
| 20 | 0.835 ± 0.056 b | 1.621 ± 0.087 B * |
| 30 | 1.043 ± 0.039 c | 1.662 ± 0.129 C * |
| 40 | 1.534 ± 0.079 d | 1.857 ± 0.038 CD * |
| 50 | 1.600 ± 0.086 d | 1.872 ± 0.145 D * |
| 60 | 1.881 ± 0.144 e | 1.911 ± 0.041 D |
| 90 | 2.436 ± 0.060 f | 2.274 ± 0.021 E * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, J.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Teh, T.M.; Weingarten, M.; Talukder, M.M.R. Enhanced Protein Extraction from Auxenochlorella protothecoides Through Synergistic Mechanical Cell Disruption and Alkaline Solubilization. Foods 2025, 14, 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152597
Ng JW, Lee SY, Teh TM, Weingarten M, Talukder MMR. Enhanced Protein Extraction from Auxenochlorella protothecoides Through Synergistic Mechanical Cell Disruption and Alkaline Solubilization. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152597
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Jun Wei, Sze Ying Lee, Tong Mei Teh, Melanie Weingarten, and Md. Mahabubur Rahman Talukder. 2025. "Enhanced Protein Extraction from Auxenochlorella protothecoides Through Synergistic Mechanical Cell Disruption and Alkaline Solubilization" Foods 14, no. 15: 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152597
APA StyleNg, J. W., Lee, S. Y., Teh, T. M., Weingarten, M., & Talukder, M. M. R. (2025). Enhanced Protein Extraction from Auxenochlorella protothecoides Through Synergistic Mechanical Cell Disruption and Alkaline Solubilization. Foods, 14(15), 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152597






