Anti-Diabetic Effect of Soy–Whey Dual-Protein on Mice with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Through INS/IRS1/PI3K Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Soy–Whey Dual-Protein Solution Sample Preparation
2.3. Cell Experiments
2.3.1. Cell Culture
2.3.2. Cytotoxicity
2.3.3. Glucose Uptake
2.3.4. In Vitro Fluorescence Staining
2.3.5. Western Blot
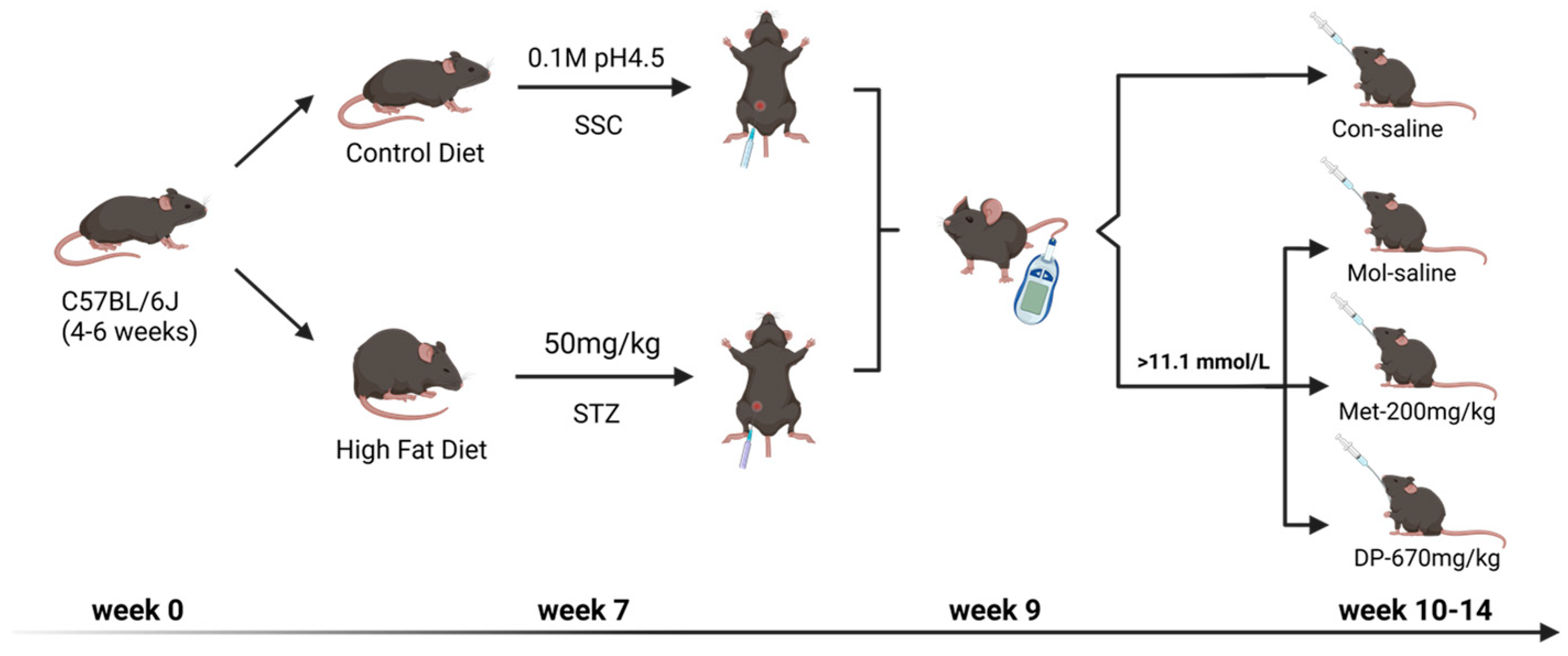
2.4. Animal Experiments
2.4.1. Body Weight, FBG, and Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
2.4.2. Analysis of Serum Biochemistry
2.4.3. Detection of Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
2.4.4. Detection of CD45 in Pancreas Slices by CLSM
2.4.5. Detection of CD45 T Cells in Pancreas by Flow Cytometry
2.4.6. 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
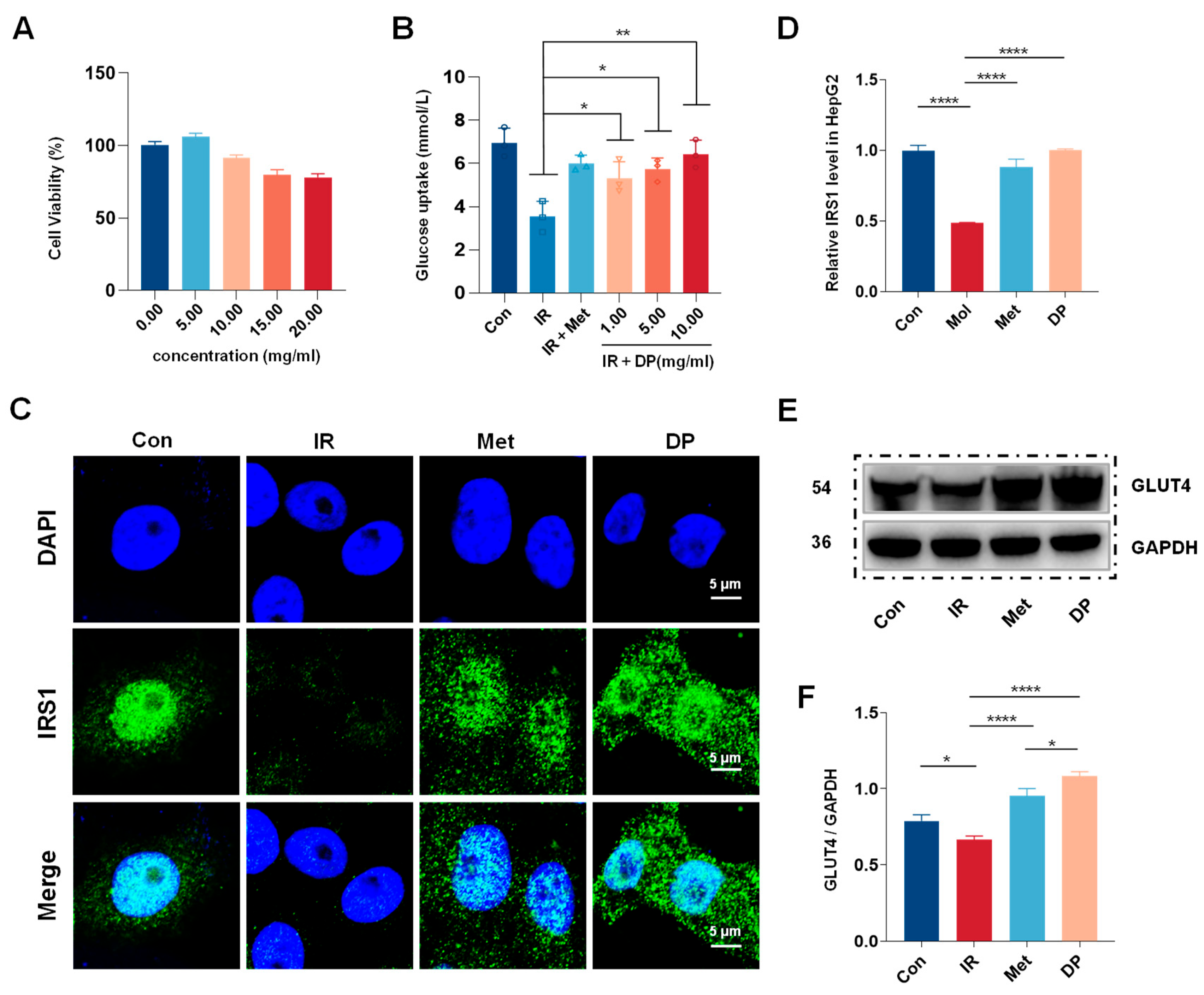
3.1. Effects of DP on the Insulin Resistance (IR)-HepG2 Cell Model
3.2. Effects of DP on Blood Glucose, Body Weight, and Food Intake in T2DM Mice
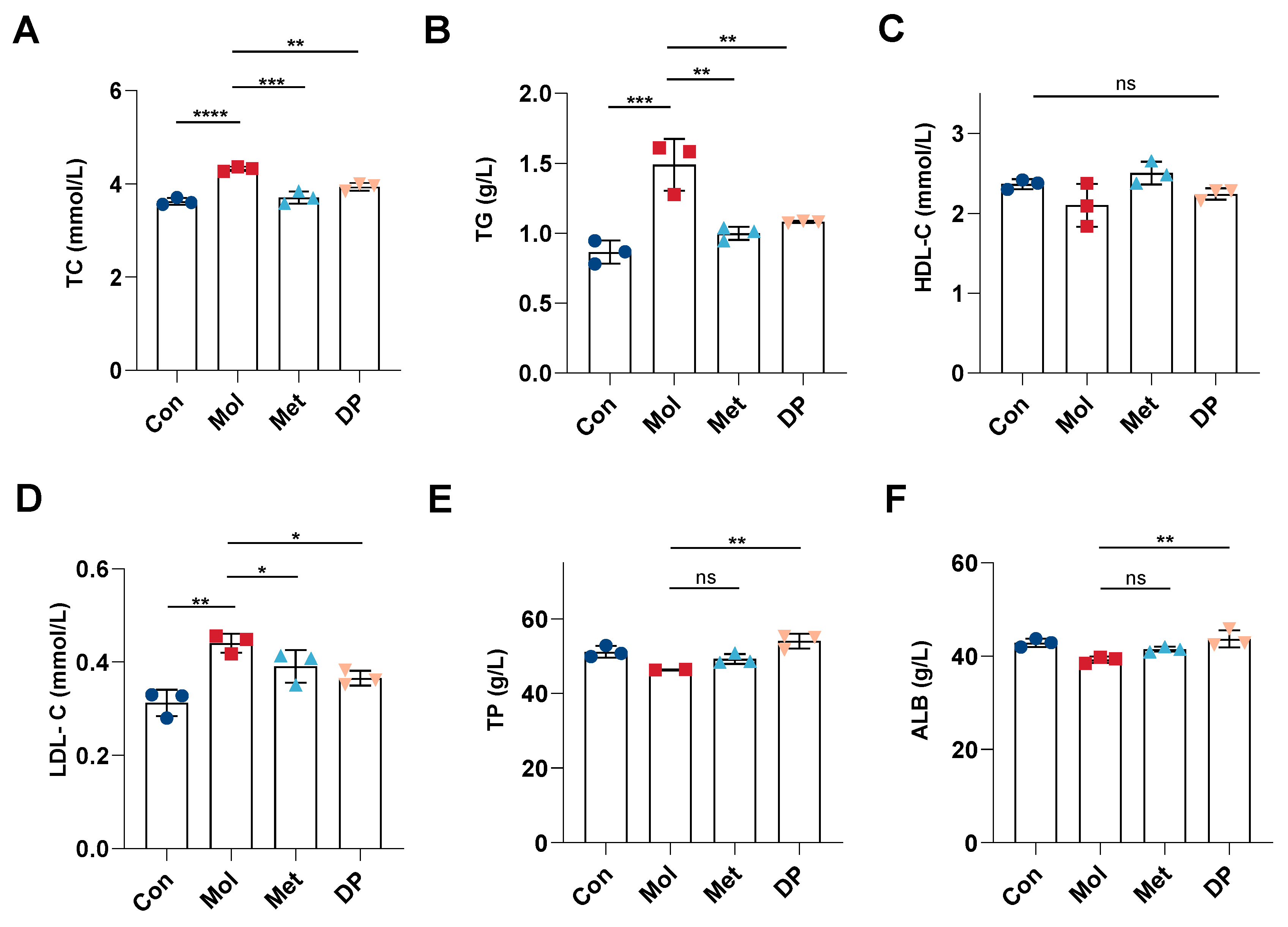
3.3. Effects of DP on Lipid and Protein Metabolism in Mice with T2DM
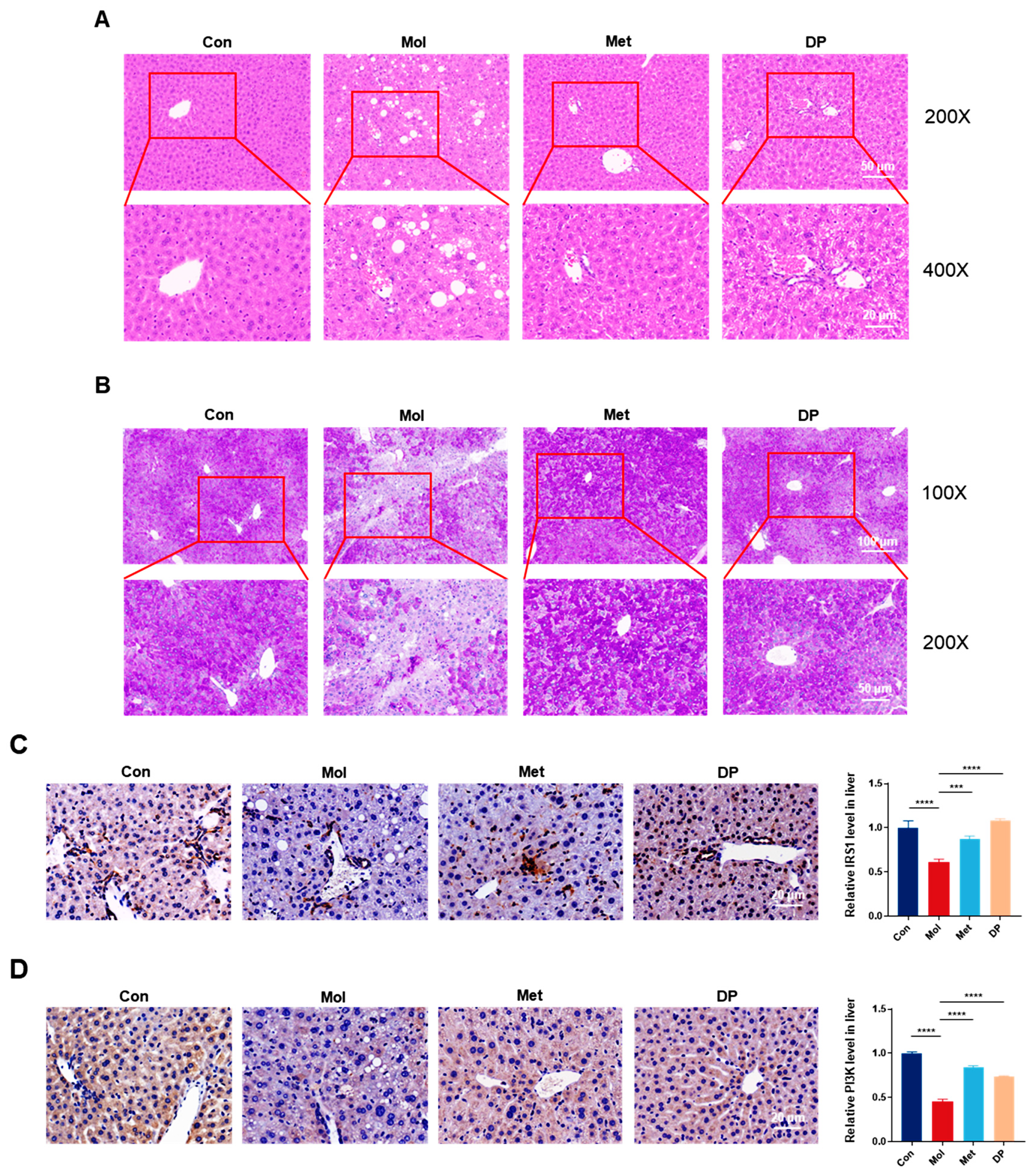
3.4. Effects of DP on Liver Injury in Mice with T2DM
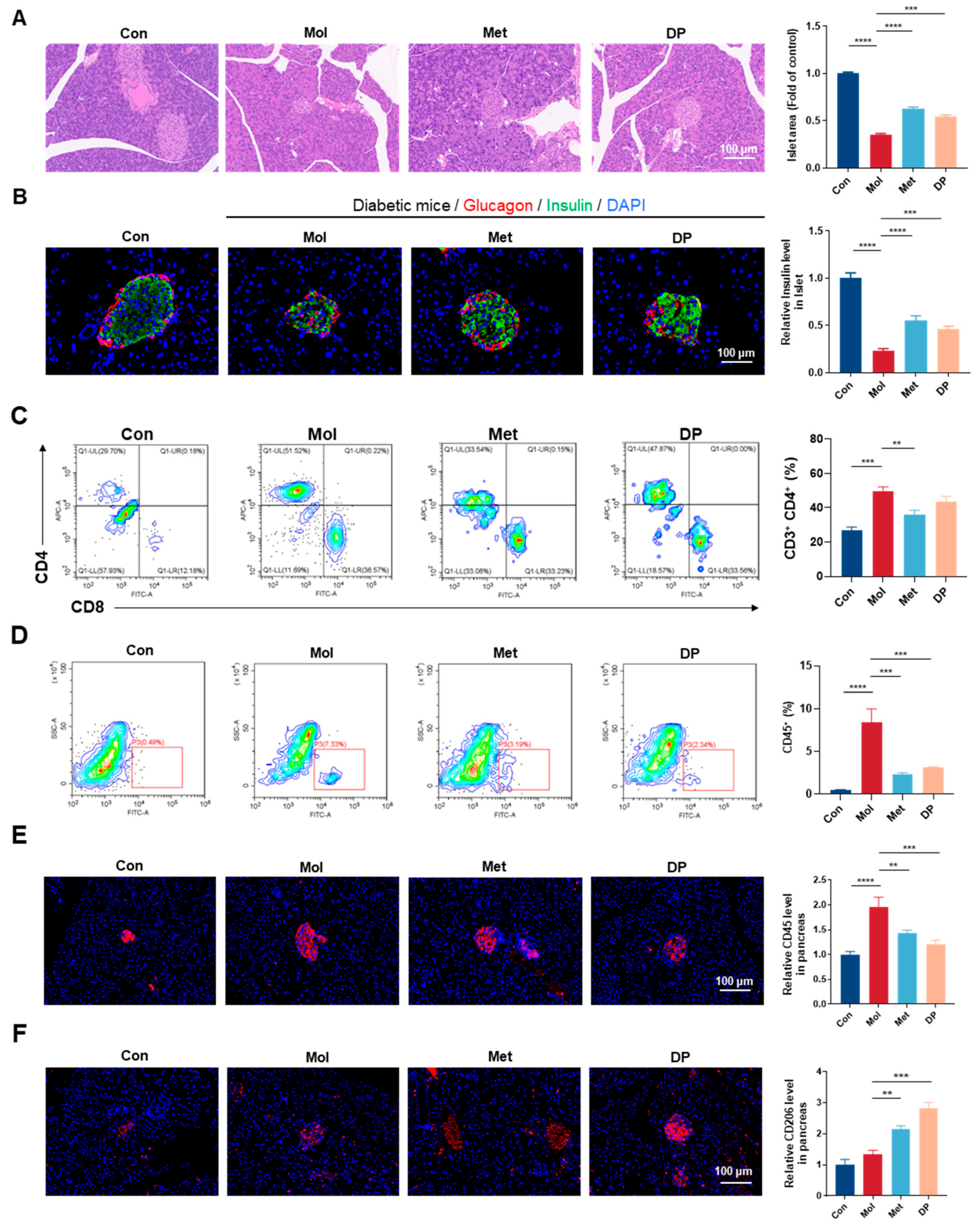
3.5. Effects of DP on Pancreatic Tissue in Mice with T2DM
3.6. Effects of DP on Islet Inflammation Regulation in Mice with T2DM
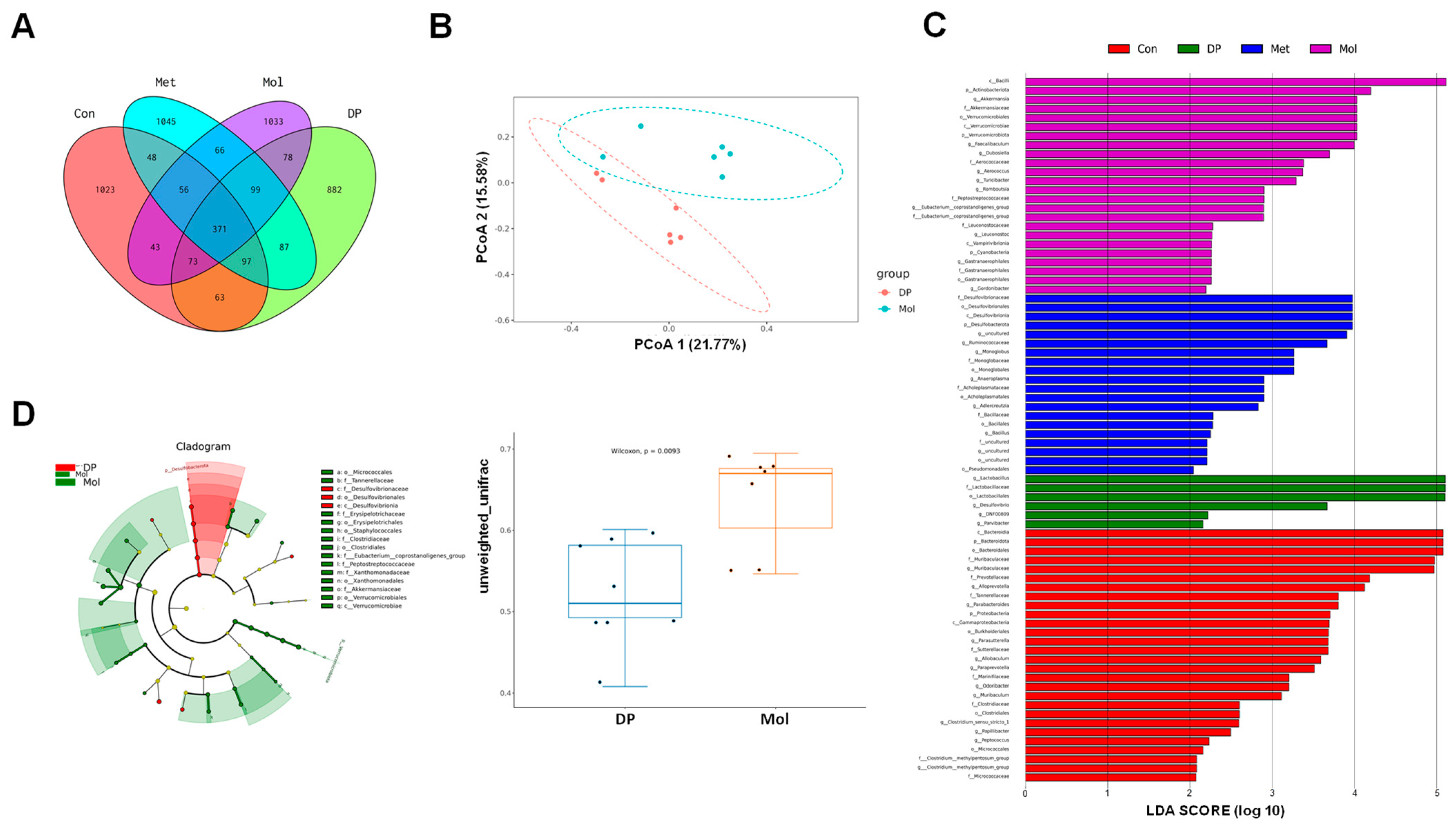
3.7. Effects of DP on Gut Microbiota in T2DM Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J. Metformin: Historical overview. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Nagasaki, H.; Fuchigami, M.; Furuta, S.; Seino, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Oiso, Y. The alpha-glucosidase inhibitor miglitol affects bile acid metabolism and ameliorates obesity and insulin resistance in diabetic mice. Metabolism 2013, 62, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.M.; Henley, W.E.; Weedon, M.N.; Lonergan, M.; Rodgers, L.R.; Jones, A.G.; Hamilton, W.T.; Sattar, N.; Janmohamed, S.; Holman, R.R.; et al. Sex and BMI Alter the Benefits and Risks of Sulfonylureas and Thiazolidinediones in Type 2 Diabetes: A Framework for Evaluating Stratification Using Routine Clinical and Individual Trial Data. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaeb, S.; Bakker, C.; Chow, L.S.; Bantle, A.E. High-Protein Diets for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, D.K.; Clifton, P.; Gannon, M.C.; Krauss, R.M.; Nuttall, F.Q. Protein in optimal health: Heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1571S–1575S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalvon-Demersay, T.; Azzout-Marniche, D.; Arfsten, J.; Egli, L.; Gaudichon, C.; Karagounis, L.G.; Tomé, D. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Plant Compared with Animal Protein Sources on Features of Metabolic Syndrome. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, E.J.; Allerton, D.M. The role of whey protein in postprandial glycaemic control. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Kabir, M.E.; Sarkar, S.; Wann, S.B.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Antidiabetic potential of soy protein/peptide: A therapeutic insight. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.W.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, Y.H.; Shin, D.H.; Shin, M.H.; Choi, B.Y. Sex-specific associations of habitual intake of soy protein and isoflavones with risk of type 2 diabetes. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, D.J.; Stote, K.S.; Paul, D.R.; Harris, G.K.; Rumpler, W.V.; Clevidence, B.A. Whey protein but not soy protein supplementation alters body weight and composition in free-living overweight and obese adults. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Shi, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, D. Whey protein and soy protein prevent obesity by upregulating uncoupling protein 1 to activate brown adipose tissue and promote white adipose tissue browning in high-fat diet-fed mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12836–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobert, C.P.; Pipe, E.A.; Capes, S.E.; Darlington, G.A.; Lampe, J.W.; Duncan, A.M. Soya protein does not affect glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambashivaiah, S.; Cope, M.; Mukherjea, R.; Selvam, S.; George, N.; Kuriyan, R.; Kurpad, A.V.; Sweazea, K.L. The Effect of Soy and Whey Protein Supplementation on Glucose Homeostasis in Healthy Normal Weight Asian Indians. J. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 2023, 2622057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piri Damaghi, M.; Mirzababaei, A.; Moradi, S.; Daneshzad, E.; Tavakoli, A.; Clark, C.C.T.; Mirzaei, K. Comparison of the effect of soya protein and whey protein on body composition: A meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomarc’h, F.; Arvisenet, G.; Bouhallab, S.; Canon, F.; Deutsch, S.M.; Drigon, V.; Dupont, D.; Famelart, M.-H.; Garric, G.; Guédon, E.; et al. Mixing milk, egg and plant resources to obtain safe and tasty foods with environmental and health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, T.; Ren, C.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Du, M. Advancement of food-derived mixed protein systems: Interactions, aggregations, and functional properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 627–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Q.; Liu, G.Y.; Zeng, H.B.; Chen, L.Y. Effects of high pressure homogenization on faba bean protein aggregation in relation to solubility and interfacial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; He, X.; Feng, D.; Li, H.; Han, D.; Li, Q.; Zhao, B.; Li, N.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. The Effect of High-Pressure Homogenization on the Structure of Dual-Protein and Its Emulsion Functional Properties. Foods 2023, 12, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nell, S.; Suerbaum, S.; Josenhans, C. The impact of the microbiota on the pathogenesis of IBD: Lessons from mouse infection models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, N.; Yue, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Evivie, S.E.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Screening for Potential Novel Probiotics with Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV-Inhibiting Activity for Type 2 Diabetes Attenuation in vitro and in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Bhat, Z.F.; Gounder, R.S.; Mohamed Ahmed, I.A.; Al-Juhaimi, F.Y.; Ding, Y.; Bekhit, A.E. Effect of Dietary Protein and Processing on Gut Microbiota—A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Yi, S.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Protein blend ingestion before allogeneic stem cell transplantation improves protein-energy malnutrition in patients with leukemia. Nutr. Res. 2017, 46, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Han, D.; He, X.; Zeng, P.; Wang, J. Soy-whey dual-protein alleviates osteoporosis of ovariectomized rats via regulating bone fat metabolism through gut-liver-bone axis. Nutrition 2022, 103–104, 111723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ke, Y.; Feng, A.; Yuan, P.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, W. The Mechanism by Which Amentoflavone Improves Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Tian, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Qian, L. β-cell neogenesis: A rising star to rescue diabetes mellitus. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 62, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, R. Insulin resistance in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes is associated with C-reactive protein independent of abdominal obesity. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2010, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Horst, K.W.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Ackermans, M.T.; Soeters, M.R.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Romijn, J.A.; Serlie, M.J. Impaired insulin action in the liver, but not in adipose tissue or muscle, is a distinct metabolic feature of impaired fasting glucose in obese humans. Metabolism 2016, 65, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.E.; Stöckli, J.; Birnbaum, M.J. The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 751–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Islam, M.A.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S.H. Metabolic Control of Type 2 Diabetes by Targeting the GLUT4 Glucose Transporter: Intervention Approaches. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 3034–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, S.; Yokota, N.; Kawahara, H. BAG6 contributes to glucose uptake by supporting the cell surface translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Biol. Open 2020, 9, bio047324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, G.M.; Hamley, S.; Selathurai, A.; Kloehn, J.; De Souza, D.P.; O’callaghan, S.; Nijagal, B.; Tull, D.L.; McConville, M.J.; Bruce, C.R. Reversing diet-induced metabolic dysregulation by diet switching leads to altered hepatic de novo lipogenesis and glycerolipid synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Yi, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Ingestion of soy-whey blended protein augments sports performance and ameliorates exercise-induced fatigue in a rat exercise model. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahiru, E.; Hsiao, R.; Phillipson, D.; Watson, K.E. Mechanisms and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Diabetes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, R.; Jähnert, M.; Lazaratos, M.; Speckmann, T.; Schumacher, F.; Kleuser, B.; Ouni, M.; Jonas, W.; Schürmann, A. Altered liver lipidome markedly overlaps with human plasma lipids at diabetes risk and reveals adipose-liver interaction. J. Lipid Res. 2025, 66, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westcott, F.; Dearlove, D.J.; Hodson, L. Hepatic fatty acid and glucose handling in metabolic disease: Potential impact on cardiovascular disease risk. Atherosclerosis 2024, 394, 117237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Mazzucato, C.; Bonner-Weir, S. Pancreatic β Cell Regeneration as a Possible Therapy for Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiwara, M.; Ota, W.; Mizushige, T.; Kanamoto, R.; Ohinata, K. Enzymatic digest of whey protein and wheylin-1, a dipeptide released in the digest, increase insulin sensitivity in an Akt phosphorylation-dependent manner. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, M.Y.; Böni-Schnetzler, M.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Ehses, J.A. Islet inflammation impairs the pancreatic beta-cell in type 2 diabetes. Physiology 2009, 24, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarikonda, G.; Pettus, J.; Phatak, S.; Sachithanantham, S.; Miller, J.F.; Wesley, J.D.; Cadag, E.; Chae, J.; Ganesan, L.; Mallios, R.; et al. CD8 T-cell reactivity to islet antigens is unique to type 1 while CD4 T-cell reactivity exists in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 50, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Candia, P.; Prattichizzo, F.; Garavelli, S.; De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Di Rella, F.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Colamatteo, A.; Fusco, C.; Micillo, T.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes: How Much of an Autoimmune Disease? Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böni-Schnetzler, M.; Meier, D.T. Islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopidis, K.; Mazidi, M.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Tajik, B.; McArdle, A.; Isanejad, M. Effects of whey and soy protein supplementation on inflammatory cytokines in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; He, R.; Xue, E.; Deng, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, W.; Shi, Q. Inhibition of Notch activity suppresses hyperglycemia-augmented polarization of macrophages to the M1 phenotype and alleviates acute pancreatitis. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueddouri, D.; Caüzac, M.; Fauveau, V.; Benhamed, F.; Charifi, W.; Beaudoin, L.; Rouland, M.; Sicherre, F.; Lehuen, A.; Postic, C.; et al. Insulin resistance per se drives early and reversible dysbiosis-mediated gut barrier impairment and bactericidal dysfunction. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhou, N.; Zou, L.; Shi, Z.; Dun, B.; Ren, G.; Yao, Y. Soy Protein Alleviates Malnutrition in Weaning Rats by Regulating Gut Microbiota Composition and Serum Metabolites. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 774203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Si, Q.; Yang, S.; Jiao, T.; Zhu, H.; Tian, P.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Gong, L.; Zhao, J.; et al. Lactic acid bacteria reduce diabetes symptoms in mice by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis and inflammation in different manners. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5898–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Jin, H.; Liao, N.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; Shi, J. Vitamin A supplementation ameliorates ulcerative colitis in gut microbiota-dependent manner. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Li, H.; Feng, D.; Li, M.; Han, D.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Soy–Whey Dual-Protein on Mice with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Through INS/IRS1/PI3K Signaling Pathway. Foods 2025, 14, 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122115
Li N, Li H, Feng D, Li M, Han D, Liu T, Wang J. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Soy–Whey Dual-Protein on Mice with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Through INS/IRS1/PI3K Signaling Pathway. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122115
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Na, Hu Li, Duo Feng, Mengjie Li, Di Han, Tianxin Liu, and Jing Wang. 2025. "Anti-Diabetic Effect of Soy–Whey Dual-Protein on Mice with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Through INS/IRS1/PI3K Signaling Pathway" Foods 14, no. 12: 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122115
APA StyleLi, N., Li, H., Feng, D., Li, M., Han, D., Liu, T., & Wang, J. (2025). Anti-Diabetic Effect of Soy–Whey Dual-Protein on Mice with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Through INS/IRS1/PI3K Signaling Pathway. Foods, 14(12), 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122115






