Comparative Study of Free Radical Grafting and Alkaline Conjugation for Enhanced Resveratrol Incorporation and Whey Protein Functionalities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of WPI–Resveratrol Conjugates
2.3. Determination of Total Phenolic Content and % Grafting Efficiency
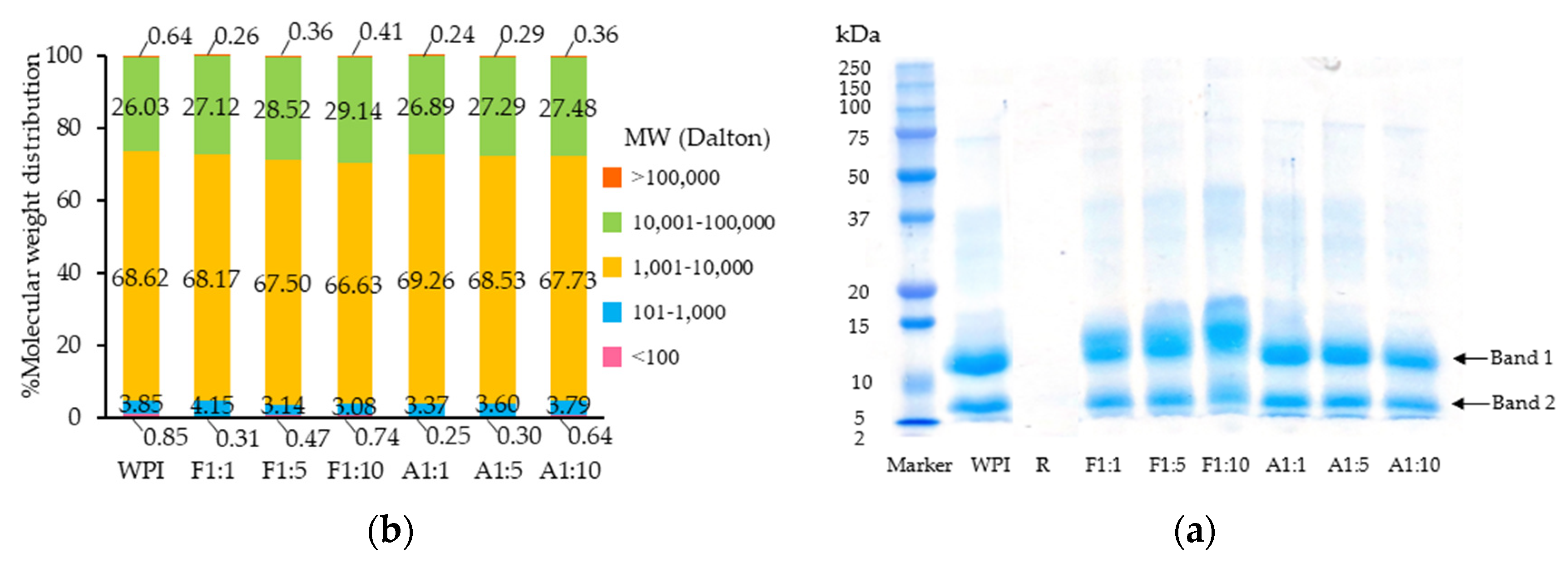
2.4. Determination of Molecular Weight (M.W.)
2.4.1. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.4.2. High-Performance Size Exclusion Chromatography (HPSEC)
2.5. Structural Analysis
2.5.1. UV Spectroscopy
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer (FTIR)
2.6. Determination of Solubility and Functional Properties
2.6.1. Water Solubility
2.6.2. Emulsifying Properties
2.6.3. Foaming Properties
2.7. Determination of Antioxidant Activities
2.7.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.7.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
2.7.3. FRAP Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characteristics
3.1.1. SDS-PAGE and M.W. Distribution
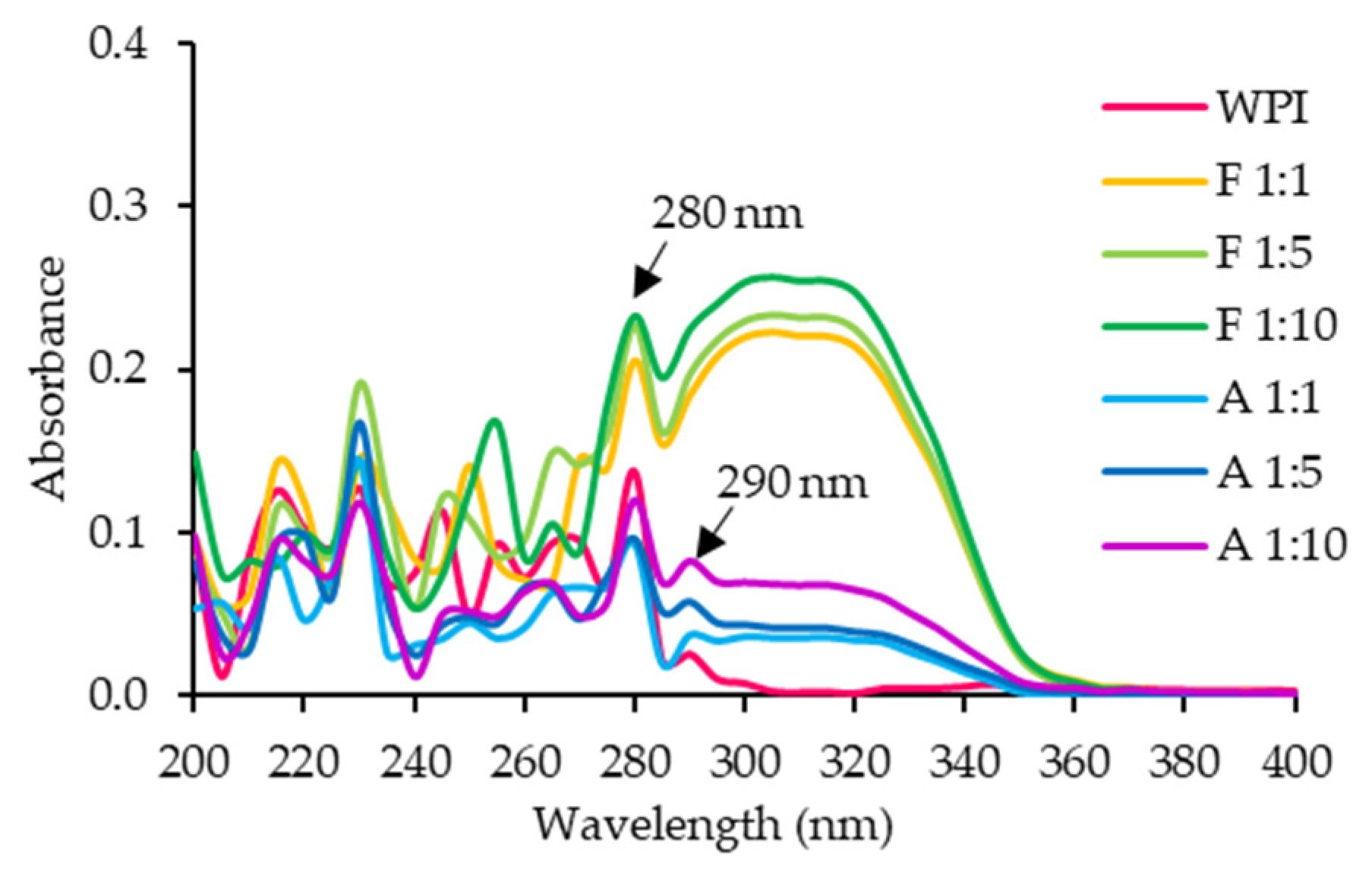
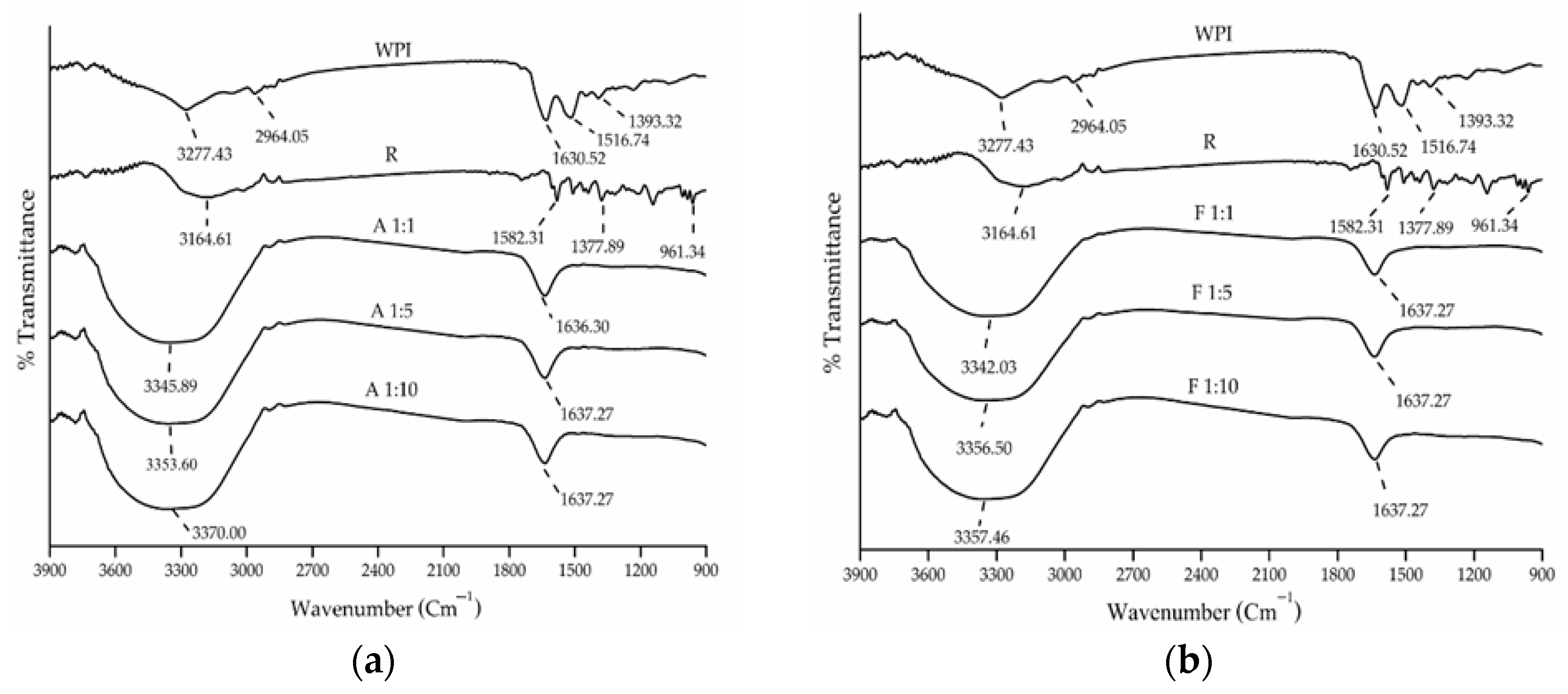
3.1.2. UV and FTIR Spectra
3.1.3. Total Phenolic Content and % Grafting Efficiency
3.2. Solubility and Functional Properties
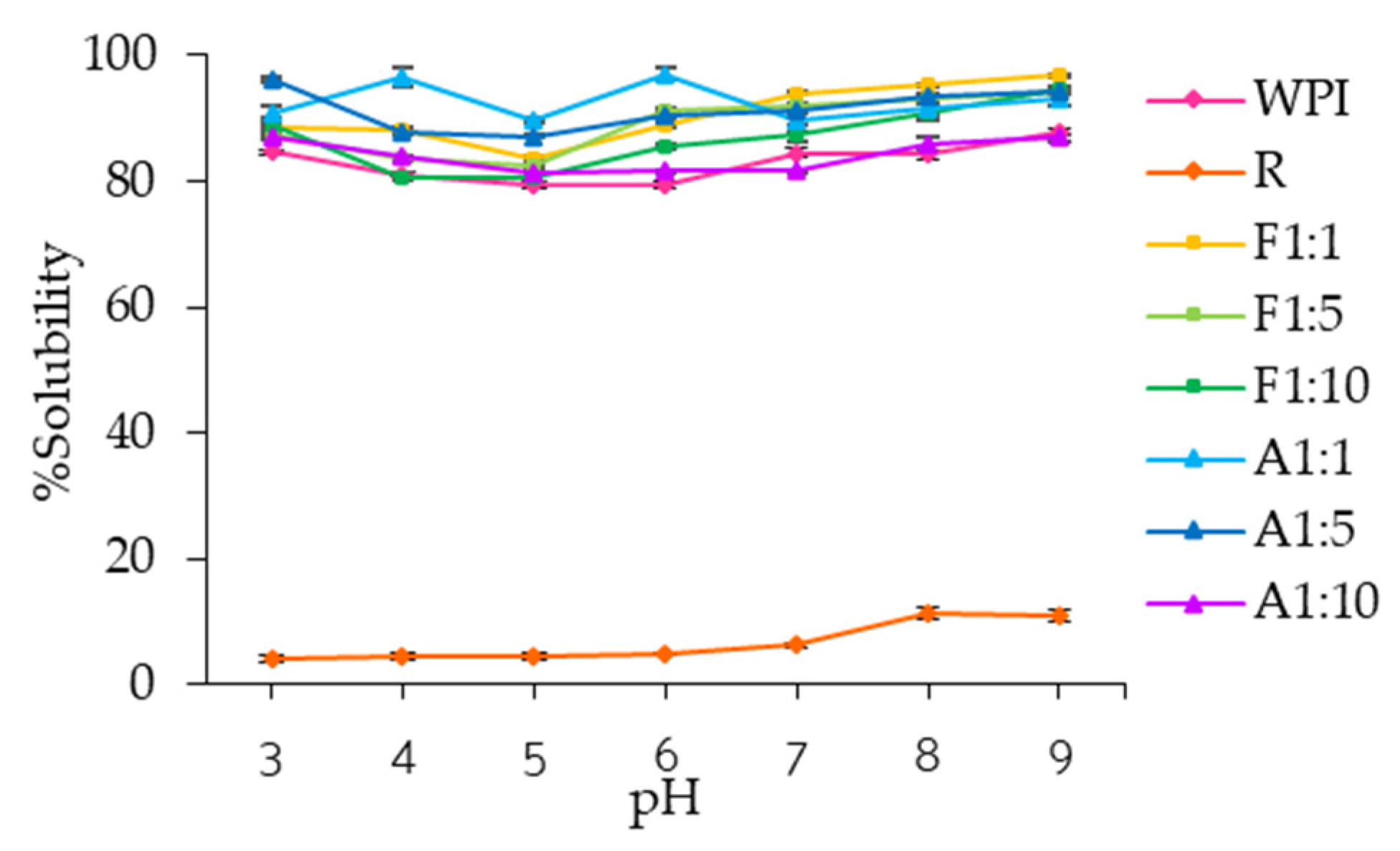
3.2.1. Water Solubility
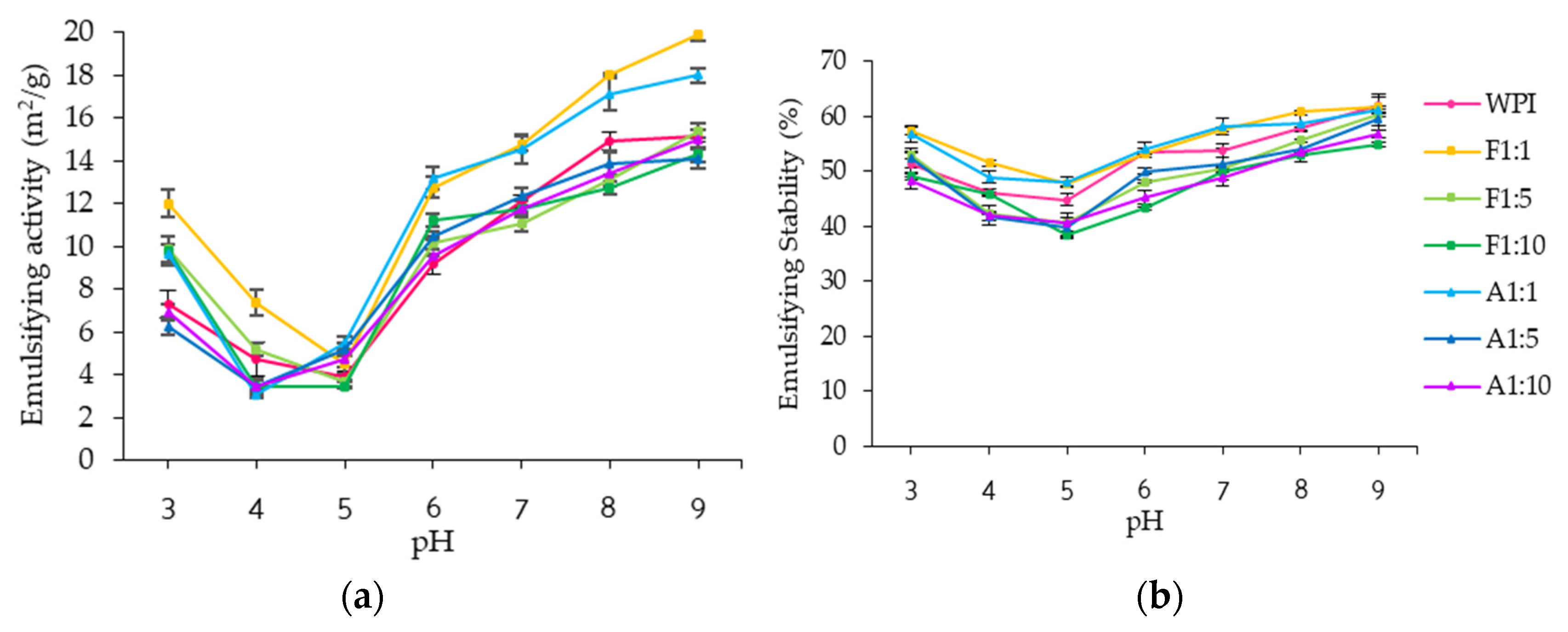
3.2.2. Emulsifying Properties
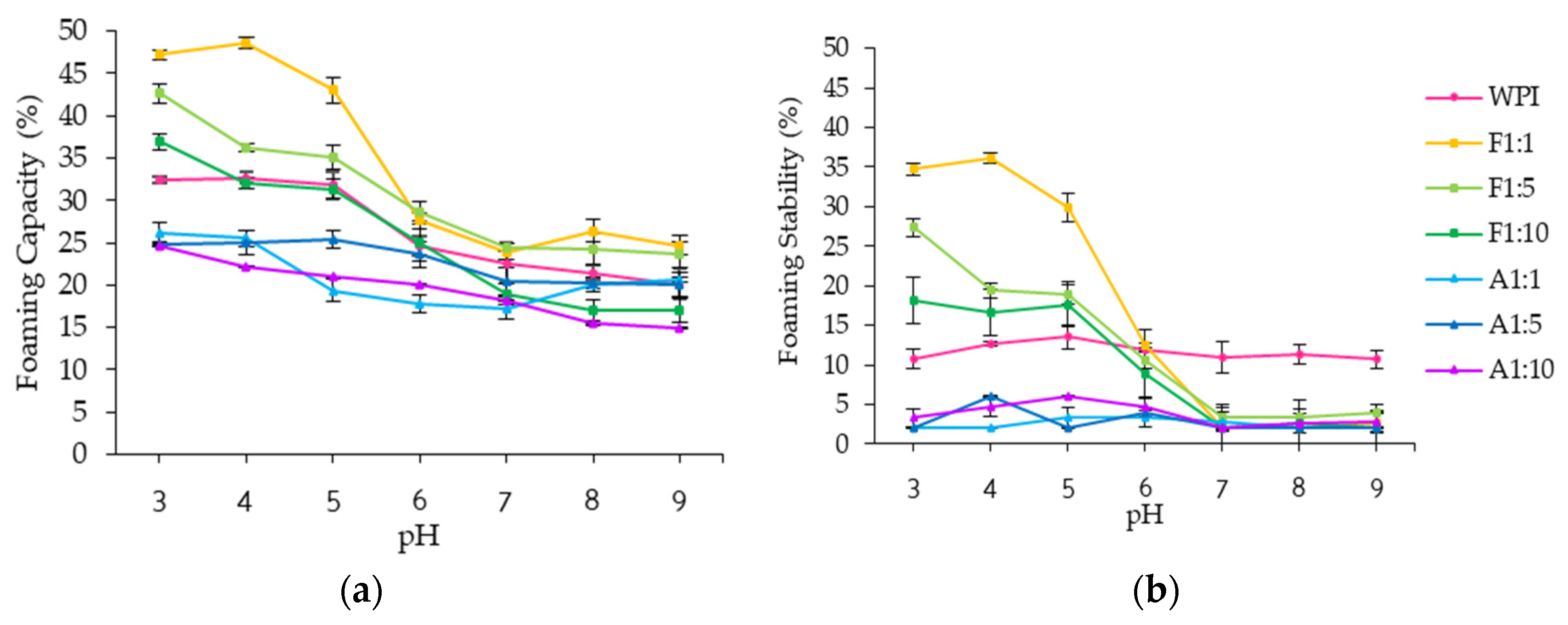
3.2.3. Foaming Properties
3.3. Antioxidant Activities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WPI | Whey protein isolate |
| R | Resveratrol |
| F | Free radical grafting method |
| A | Alkaline method |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| ABTS | 2,2′-Azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
References
- Singh, A.P.; Singh, R.; Verma, S.S.; Rai, V.; Kaschula, C.H.; Maiti, P.; Gupta, S.C. Health benefits of resveratrol: Evidence from clinical studies. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1851–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radeva, L.; Yoncheva, K. Resveratrol—A Promising Therapeutic Agent with Problematic Properties. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intagliata, S.; Modica, M.N.; Santagati, L.M.; Montenegro, L. Strategies to Improve Resveratrol Systemic and Topical Bioavailability: An Update. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieger, J.; Tatarczak-Michalewska, M.; Blicharska, E. Characterization of the cis/trans Isomerization of Resveratrol by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recharla, N.; Riaz, M.; Ko, S.; Park, S. Novel technologies to enhance solubility of food-derived bioactive compounds: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 39, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Encapsulation of resveratrol in zein/pectin core-shell nanoparticles: Stability, bioaccessibility, and antioxidant capacity after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidov-Pardo, G.; McClements, D.J. Resveratrol encapsulation: Designing delivery systems to overcome solubility, stability and bioavailability issues. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, R.; De Amicis, F.; Servidio, C.; Curcio, F.; Trombino, S. Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of resveratrol-loaded nanospheres potentially useful for human breast carcinoma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedovic, V.; Kalusevic, A.; Manojlovic, V.; Levic, S.; Bugarski, B. An overview of encapsulation technologies for food applications. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yong, H.; Yao, X.; Hu, H.; Yun, D.; Xiao, L. Recent advances in phenolic-protein conjugates: Synthesis, characterization, biological activities and potential applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35825–35840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.; Tchameni, Z.F.N.; Bhat, Z.F.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaglan, S. Recent Insights on the Conformational Changes, Functionality, and Physiological Properties of Plant-Based Protein–Polyphenol Conjugates. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 2131–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Salam, M.H.; El-Shibiny, S.; Salem, A. Factors Affecting the Functional Properties of Whey Protein Products: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2009, 25, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, V.; Lignou, S.; Methven, L. Influence of Age and Individual Differences on Mouthfeel Perception of Whey Protein-Fortified Products: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solak, B.B.; Akın, N. Health Benefits of Whey Protein: A Review. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2012, 2, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, G.T.D.; Lira, F.S.; Rosa, J.C.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Oyama, L.M.; Santos, R.V.; Pimentel, G.D. Dietary whey protein lessens several risk factors for metabolic diseases: A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keri Marshall, N. Therapeutic applications of whey protein. Altern. Med. Rev. 2004, 9, 136–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Shi, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.; Ni, F.; He, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Huang, M.; et al. The fabrication of novel zein and resveratrol covalent conjugates: Enhanced thermal stability, emulsifying and antioxidant properties. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, J. Oxidative stability and in vitro digestion of menhaden oil emulsions with whey protein: Effects of EGCG conjugation and interfacial cross-linking. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Qi, B.; Ju, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. Covalent conjugates of anthocyanins to soy protein: Unravelling their structure features and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion fate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. A comparative study of covalent and non-covalent interactions between zein and polyphenols in ethanol-water solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H. Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phongphisutthinant, R.; Wiriyacharee, P.; Boonyapranai, K.; Ounjaijean, S.; Taya, S.; Pitchakarn, P.; Pathomrungsiyounggul, P.; Utarat, P.; Wongwatcharayothin, W.; Somjai, C.; et al. Effect of conventional humid-dry heating through the Maillard reaction on chemical changes and enhancement of in vitro bioactivities from soy protein isolate hydrolysate-yeast cell extract conjugates. Foods 2024, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.; Pereira, C.G.; de Almeida Junior, J.C.; Viana, C.C.R.; de Oliveira Neves, L.N.; da Silva, P.H.F.; Bell, M.J.V.; de Carvalho dos Anjos, V. FTIR-ATR determination of protein content to evaluate whey protein concentrate adulteration. LWT 2019, 99, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Xie, M.; Hu, B.; Zhou, L.; Saeeduddin, M.; Zeng, X. Enhanced solubility and antioxidant activity of chlorogenic acid-chitosan conjugates due to the conjugation of chitosan with chlorogenic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 170, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Sun, H.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Functional and conformational changes to soy proteins accompanying anthocyanins: Focus on covalent and non-covalent interactions. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdani, A.M.; Wani, I.A.; Bhat, N.A.; Siddiqi, R.A. Effect of guar gum conjugation on functional, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of egg white lysozyme. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Granato, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J. Effects of different dietary polyphenols on conformational changes and functional properties of protein-polyphenol covalent complexes. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Fang, Z.; Wusigale; Bakry, A.M.; Chen, Y.; Liang, L. Complexation of trans- and cis-resveratrol with bovine serum albumin, β-lactoglobulin or α-lactalbumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wusigale; Cheng, H.; Van der Meeren, P.; Liang, L. The mechanism of resveratrol stabilization and degradation by synergistic interactions between constituent proteins of whey protein. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Xiao, N.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, L. Free radical grafting of whey protein isolate with tea polyphenol: Synthesis and changes in structural and functional properties. LWT 2022, 153, 112438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xi, T.; Zheng, J.; Cui, X. Chemical Properties of Whey Protein in Protein Powders and Its Impact on Muscle Growth in Athletes: A Review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2025, 20, 1934578X251326124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspirault, C.; Doyen, A.; Bazinet, L. Impact of Preheating Temperature on the Separation of Whey Proteins When Combined with Chemical or Bipolar Membrane Electrochemical Acidification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, W.N.; McClements, D.J.; Maqsood, S. Whey protein–polyphenol conjugates and complexes: Production, characterization, and applications. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, J. Conjugation of Ovotransferrin with Catechin Shows Improved Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2581–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, F.-X. Biological macromolecules: UV-visible spectrophotometry. Encycl. Life Sci. 2001, 99, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, N.; Ren, X.E.; Yang, F.; Huang, Y.; Wei, F.; Yang, L. The Effect of Hydrodynamic Cavitation on the Structural and Functional Properties of Soy Protein Isolate-Lignan/Stilbene Polyphenol Conjugates. Foods 2024, 13, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M. Modification approaches of walnut proteins to improve their structural and functional properties: A review. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Yanbo, W.; Fu, L. Dietary protein-phenolic interactions: Characterization, biochemical-physiological consequences, and potential food applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3589–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupančič, Š.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J. Stability and solubility of trans-resveratrol are strongly influenced by pH and temperature. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.H.; Benjakul, S.; Sae-leaw, T.; Balange, A.K.; Maqsood, S. Protein-polyphenol conjugates: Antioxidant property, functionalities and their applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M. Chemical, structural and functional properties of whey proteins covalently modified with phytochemical compounds. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2970–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E.; Altay, F. A review on protein–phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Wang, Y.; Selomulya, C. Emerging technologies to improve plant protein functionality with protein-polyphenol interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, A.; Kieserling, H.; Rohn, S.; Steinhäuser, U.; Drusch, S. Impact of Phenolic Acid Derivatives on β-Lactoglobulin Stabilized Oil-Water-Interfaces. Food Biophys. 2022, 17, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S. Recent developments in food foams. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant Activity of Proteins and Peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranz, E.; Corrochano, A.R.; Shanahan, C.; Villalva, M.; Jaime, L.; Santoyo, S.; Callanan, M.J.; Murphy, E.; Giblin, L. Antioxidant activity and characterization of whey protein-based beverages: Effect of shelf life and gastrointestinal transit on bioactivity. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 57, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, F.; Xie, B.; Sun, Z.; McClements, D.J.; Deng, Q. Fabrication and characterization of whey protein isolates- lotus seedpod proanthocyanin conjugate: Its potential application in oxidizable emulsions. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn ns | Random Coil ns |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 15.73 ± 0.64 a | 58.00 ± 1.21 b | 23.05 ± 0.73 | 3.22 ± 1.10 |
| A 1:1 | 13.46 ± 0.86 b | 60.72 ± 1.18 a | 22.62 ± 1.76 | 3.20 ± 1.42 |
| A 1:5 | 13.82 ± 0.57 b | 60.46 ± 1.48 a | 21.97 ± 1.76 | 3.74 ± 0.81 |
| A 1:10 | 13.94 ± 0.64 b | 60.22 ± 1.54 a | 22.56 ± 2.01 | 3.28 ± 1.11 |
| F 1:1 | 13.46 ± 1.12 b | 60.62 ± 0.65 a | 22.39 ± 0.93 | 3.53 ± 1.07 |
| F 1:5 | 13.63 ± 0.69 b | 60.60 ± 1.09 a | 23.01 ± 1.79 | 2.76 ± 1.40 |
| F 1:10 | 13.89 ± 0.29 b | 60.03 ± 1.33 a | 22.51 ± 1.96 | 3.57 ± 1.07 |
| Sample | Total Phenolic Content | Grafting Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| A 1:1 | 10.26 ± 1.06 f | 9.52 ± 0.91 e |
| A 1:5 | 13.69 ± 0.94 e | 10.02 ± 0.63 de |
| A 1:10 | 15.91 ± 0.63 d | 10.65 ± 0.38 d |
| F 1:1 | 32.23 ± 1.50 c | 15.89 ± 0.92 c |
| F 1:5 | 43.12 ± 1.01 b | 16.87 ± 0.31 b |
| F 1:10 | 57.50 ± 1.58 a | 17.61 ± 0.67 a |
| Sample | DPPH | ABTS | FRAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 49.23 ± 1.54 h | 84.79 ± 3.49 h | 28.35 ± 2.73 h |
| Resveratrol | 435.16 ± 1.29 a | 667.52 ± 2.17 a | 459.21 ± 4.98 a |
| A 1:1 | 86.37 ± 1.76 g | 87.93 ± 1.75 g | 91.59 ± 1.73 g |
| A 1:5 | 92.48 ± 1.83 f | 114.06 ± 1.69 f | 146.83 ± 1.58 f |
| A 1:10 | 144.32 ± 2.61 c | 122.63 ± 2.71 e | 173.42 ± 3.27 e |
| F 1:1 | 110.78 ± 3.13 e | 246.48 ± 3.67 d | 142.63 ± 2.30 d |
| F 1:5 | 139.12 ± 3.61 d | 285.30 ± 1.20 c | 190.62 ± 2.26 c |
| F 1:10 | 297.99 ± 2.04 b | 438.59 ± 2.77 b | 360.99 ± 1.31 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manochai, T.; Kamthai, S.; Siriwoharn, T. Comparative Study of Free Radical Grafting and Alkaline Conjugation for Enhanced Resveratrol Incorporation and Whey Protein Functionalities. Foods 2025, 14, 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152596
Manochai T, Kamthai S, Siriwoharn T. Comparative Study of Free Radical Grafting and Alkaline Conjugation for Enhanced Resveratrol Incorporation and Whey Protein Functionalities. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152596
Chicago/Turabian StyleManochai, Tanaporn, Suthaphat Kamthai, and Thanyaporn Siriwoharn. 2025. "Comparative Study of Free Radical Grafting and Alkaline Conjugation for Enhanced Resveratrol Incorporation and Whey Protein Functionalities" Foods 14, no. 15: 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152596
APA StyleManochai, T., Kamthai, S., & Siriwoharn, T. (2025). Comparative Study of Free Radical Grafting and Alkaline Conjugation for Enhanced Resveratrol Incorporation and Whey Protein Functionalities. Foods, 14(15), 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152596






