Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei E10 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Enhancing the Intestinal Barrier and Modulating Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
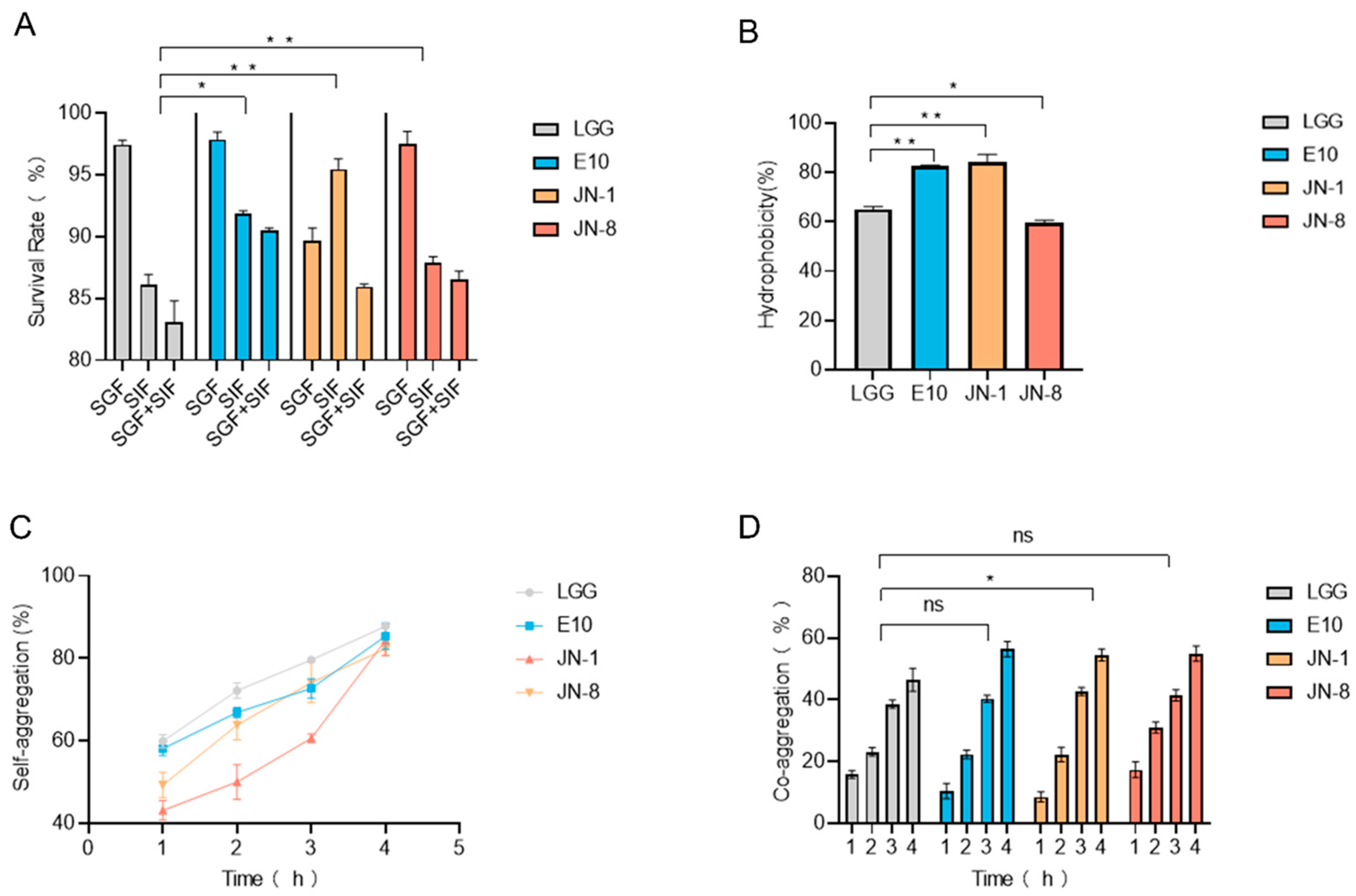
2.2. Gastrointestinal Transit Tolerance Assay
2.3. Hydrophobicity Assay
2.4. Evaluation of Bacterial Isolates for Self-Aggregation and Co-Aggregation
2.5. Animal Experimental Design
2.6. Disease Activity Index (DAI) and Colon Length Measurement
2.7. Measurement of Colon Length
2.8. Examination of Mouse Colon Histology
2.9. IHC/IF of Colon of Mice
2.10. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gastrointestinal Tolerance and Adhesion Properties of Lacticaseibacillus Strains
3.2. Effect of Lacticaseibacillus on Colitis
3.3. Protective Effects of E10 on Colitis
3.4. Gut Microbiota Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, L.A.; Dayimu, A.; Guan, X.; Duan, M.; Zeng, S.Y.; Wang, H.; Zong, J.H.; Sun, C.H.; Yang, X.R.; Yang, X.Y. Global evolving patterns and cross-country inequalities of inflammatory bowel disease burden from 1990 to 2019: A worldwide report. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 73, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; He, B.J.; Sun, Y.X.; Li, J.; Shen, P.; Hu, L.M.; Liu, G.Z.; Wang, J.X.; Duan, L.P.; Zhan, S.Y.; et al. Incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in urban China: A nationwide population-based study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Han, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.M.; Hu, J.C.; Shi, L.; Li, J.X. Long-term trends in the burden of inflammatory bowel disease in china over three decades: A joinpoint regression and age-period-cohort analysis based on gbd 2019. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 994619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, B.; Moraes, L.; Magnusson, M.K.; Öhman, L. Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and mechanisms of biological therapies. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, P.; Suez, J.; Derrien, M.; Elinav, E. Moving from probiotics to precision probiotics. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.B. Lactobacillus plantarum CAU1055 ameliorates inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced raw264.7 cells and a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis animal model. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6718–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levit, R.; de Giori, G.S.; de LeBlanc, A.D.; LeBlanc, J.G. Evaluation of the effect of soymilk fermented by a riboflavin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum strain in a murine model of colitis. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Pan, Q.Q.; Xue, Y.Z.; Yu, L.L.; Tian, F.W.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.X.; Chen, W. Identification of the key physiological characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum strains for ulcerative colitis alleviation. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Q.; Liu, Y.N.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Y.T.; Xia, Y.J.; Lai, P.F.H.; Ai, L.Z. The ameliorative effect of a Lactobacillus strain with good adhesion ability against dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yi, R.K.; Qian, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.N. Lactobacillus plantarum CQPC06 activity prevents dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by regulating the il-8 pathway. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2653–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, S.P.; Bi, D.R. The impact of Lactobacillus plantarum on the gut microbiota of mice with dss-induced colitis. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3921315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, R.; Gundamaraju, R.; Eri, R. Role of lactic acid probiotic bacteria in ibd. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 2352–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; O’Connell, R.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. Coordination of tolerogenic immune responses by the commensal microbiota. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, J220–J225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, M.; Seguella, L.; Del Re, A.; Lu, J.; Palenca, I.; Corpetti, C.; Rurgo, S.; Sanseverino, W.; Sarnelli, G.; Esposito, G. Next-generation probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausova, G.; Hyrslova, I.; Hynstova, I. In Vitro evaluation of adhesion capacity, hydrophobicity, and auto-aggregation of newly isolated potential probiotic strains. Fermentation 2019, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Veen, B.-V.; van Swam, I.; Wels, M.; Bron, P.A.; Kleerebezem, M. Congruent strain specific intestinal persistence of Lactobacillus plantarum in an intestine-mimicking In Vitro system and in human volunteers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.T.; Peng, F.; Liu, Z.G.; Peng, Z.; Guan, Q.Q.; Cai, P.; Xiong, S.J.; Yu, Q.; Xie, M.Y.; Xiong, T. Lactic acid bacteria with anti-hyperuricemia ability: Screening In Vitro and evaluating in mice. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Hsu, P.Y.; Pan, T.M. Therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei NTU 101 powder on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryaznova, M.; Dvoretskaya, Y.; Burakova, I.; Syromyatnikov, M.; Popov, E.; Kokina, A.; Mikhaylov, E.; Popov, V. Dynamics of changes in the gut microbiota of healthy mice fed with lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argañaraz-Martínez, E.; Babot, J.D.; Apella, M.C.; Chaia, A.P. Physiological and functional characteristics of Propionibacterium strains of the poultry microbiota and relevance for the development of probiotic products. Anaerobe 2013, 23, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremon, C.; Guglielmetti, S.; Gargari, G.; Taverniti, V.; Castellazzi, A.M.; Valsecchi, C.; Tagliacarne, C.; Fiore, W.; Bellini, M.; Bertani, L.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus paracasei cncm i-1572 on symptoms, gut microbiota, short chain fatty acids, and immune activation in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A pilot randomized clinical trial. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.F.; Tabashsum, Z.; Patel, P.; Bernhardt, C.; Biswas, D. Linoleic acids overproducing Lactobacillus casei limits growth, survival, and virulence of Salmonella typhimurium and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.A.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Metabolic activities and probiotic potential of bifidobacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 149, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Cheng, P.C.; Fan, C.K.; Pan, T.M. Time-dependent persistence of enhanced immune response by a potential probiotic strain Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei NTU 101. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 128, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Liu, F.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.S.; Xue, Y.; Xu, Z.H.; Geng, Y. Differences in the ability of lactic acid bacteria to prevent acute alcohol-induced liver injury via the gut microbiota-bile acid-liver axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 15265–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Adams, M.C. In Vitro assessment of the upper gastrointestinal tolerance of potential probiotic dairy propionibacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 91, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Miaris, C.; Kalantzopoulos, G.; Pot, B.; Tsakalidou, E. Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus strains isolated from dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrabi, S.T.; Bhat, B.; Gupta, M.; Bajaj, B.K. Phytase-producing potential and other functional attributes of lactic acid bacteria isolates for prospective probiotic applications. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2016, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escamilla-Montes, R.; Luna-González, A.; Flores-Miranda, M.D.; Alvarez-Ruiz, P.; Fierro-Coronado, J.A.; Sánchez-Ortiz, A.C.; Avila-Leal, J. Isolation and characterization of potential probiotic bacteria suitable for mollusk larvae cultures. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2015, 45, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bansal, P.; Singh, J.; Dhanda, S.; Bhardwaj, J.K. Aggregation, adhesion and efficacy studies of probiotic candidate pediococcus acidilactici NCDC 252: A strain of dairy origin. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 36, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Yang, B.; Zhang, H.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Chen, H.Q.; Chen, W. C9, t11, c15-clna and t9, t11, c15-clna from Lactobacillus plantarum ZS2058 ameliorate dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3758–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Ren, Y.; Xue, P.; Sheng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, T.; Geng, Y.; et al. Protective effect of the polyphenol ligustroside on colitis induced with dextran sulfate sodium in mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, X.L.; Li, Q.Q.; Sawaya, A.; Le Leu, R.K.; Conlon, M.A.; Wu, L.M.; Hu, F.L. Propolis from different geographic origins decreases intestinal inflammation and bacteroides spp. Populations in a model of dss-induced colitis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio: A relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Xie, X.Q.; Zhou, L.; Guan, Q.; Ren, Y.; Mao, Y.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H.; Geng, Y. Desulfovibrio fairfieldensis-derived outer membrane vesicles damage epithelial barrier and induce inflammation and pyroptosis in macrophages. Cells 2022, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchi, C. Towards a ‘cure’ for ibd. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, B.P.; Quigley, E.M.M. Probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2017, 46, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gionchetti, P.; Amadini, C.; Rizzello, F.; Venturi, A.; Palmonari, V.; Morselli, C.; Romagnoli, R.; Campieri, M. Probiotics—role in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2002, 34, S58–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, H. Probiotics and antibiotics in ibd. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Arreola, A.; Solis-Pacheco, J.R.; Lacroix, M.; Balcazar-López, E.; Navarro-Hernández, R.E.; Sandoval-García, F.; Gutiérrez-Padilla, J.A.; García-Morales, E.; Aguilar-Uscanga, B.R. In Vivo assessment and characterization of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic profile isolated from human milk powder. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano-Ayala, K.; Ascencio-Valle, F.J.; Gutiérrez-González, P.; Estrada-Girón, Y.; Torres-Vitela, M.R.; Macías-Rodríguez, M.E. Hydrophobic and adhesive patterns of lactic acid bacteria and their antagonism against foodborne pathogens on tomato surface (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 876–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, L.; Zheng, P.Y.; Xia, L.; Yong, Y.; Lu, G.F.; Tang, F.; Zhao, Z.G. Calycosin attenuates dextran sulfate sodium (dss)-induced experimental colitis. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Brenner, M.; Yang, W.L.; Wang, P. Recombinant human mfg-e8 ameliorates colon damage in dss- and tnbs-induced colitis in mice. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, W.; Alonzo, F.; Knight, K.L. Probiotic exopolysaccharide protects against systemic Staphylococcus aureus infection, inducing dual-functioning macrophages that restrict bacterial growth and limit inflammation. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00791-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengül, N.; Isik, S.; Aslim, B.; Uçar, G.; Demirbag, A.E. The effect of exopolysaccharide-producing probiotic strains on gut oxidative damage in experimental colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Gao, R.; Geng, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei E10 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Enhancing the Intestinal Barrier and Modulating Microbiota. Foods 2025, 14, 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142526
Dai Y, Lin Z, Zhang X, Wang Y, Sheng Y, Gao R, Geng Y, Xue Y, Ren Y. Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei E10 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Enhancing the Intestinal Barrier and Modulating Microbiota. Foods. 2025; 14(14):2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142526
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Yuanyuan, Ziming Lin, Xiaoyue Zhang, Yiting Wang, Yingyue Sheng, Ruonan Gao, Yan Geng, Yuzheng Xue, and Yilin Ren. 2025. "Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei E10 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Enhancing the Intestinal Barrier and Modulating Microbiota" Foods 14, no. 14: 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142526
APA StyleDai, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Sheng, Y., Gao, R., Geng, Y., Xue, Y., & Ren, Y. (2025). Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei E10 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Enhancing the Intestinal Barrier and Modulating Microbiota. Foods, 14(14), 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142526







